-
高灵敏色心量子自旋磁检测是弱磁、极弱磁检测及成像应用的关键. 本文通过搭建结合磁力线集聚结构(MFC)的系综金刚石氮空位(NV)色心的宽视场磁分布成像系统, 对系综金刚石NV色心磁检测增强进行了系统研究. 首先基于磁力线集聚效应仿真设计并制造了成对的T型薄片状MFC结构, 利用连续波光探测磁共振(ODMR)宽视场磁成像技术对MFC的磁增强效果进行验证. 实验测试的MFC间距的最小值为1.0 mm,此时磁增强倍数约为10.35, 通过进一步对比不同磁场强度以及不同间距条件下的MFC磁增强效果, 验证了MFC磁增强效果的有效性, 系统磁检测灵敏度由1.10 nT/Hz1/2提升至0.30 nT/Hz1/2. 通过进一步对比仿真与测量获得的磁增强倍数与间隙宽度的关系, 可对实验系统的磁增强及灵敏度进行有效估计. 在MFC间距为0.5 mm时, 对应的磁增强倍数可提升至约18.21, 磁灵敏度则可达0.25 nT/Hz1/2. 以上结果表明基于磁集聚效应可以实现系综金刚石氮空位色心磁检测灵敏度的有效提升, 为精密量子测量技术在弱磁、极弱磁检测应用方面提供了参考.
-
关键词:
- 磁力线集聚结构 /
- 系综金刚石氮空位色心 /
- 连续波光探测磁共振 /
- 磁灵敏度
The high-sensitivity magnetic sensor is the key to the weak magnetic and extremely weak magnetic detection imaging. In this paper, based on ensemble nitrogen-vacancy (NV) color center in diamond, a wide-field magnetic field distribution imaging system combined with the magnetic flux concentrator (MFC) is built for enhancing the magnetic detection. The paired T-shape chip MFC structures are designed and prepared based on the simulation of magnetic flux concentration effect, and the enhancement of magnetic field of MFC is verified by continuous wave optical detection magnetic resonance (CW-ODMR) imaging technology. When the gap width between the MFCs is 1.0 mm, the magnetic enhancement factor is about 10.35. To verify the effectiveness of the magnetic enhancement effect of the MFC, The magnetic enhancement effects are also measured under different magnetic field strengths and different gap widths. The magnetic sensitivity of the system increases from 1.10 nT/Hz1/2 to 0.30 nT/Hz1/2. By comparing the simulations with the measurements, the relationship between the measured magnetic enhancement multiple and the gap width can be obtained, and the better magnetic enhancement capability and sensitivity of the experimental system are also estimated. When the MFC’s gap width is 0.5 mm, the corresponding magnetic enhancement factor is increased to 18.21, and the corresponding magnetic sensitivity is 0.25 nT/Hz1/2. These results show that the magnetic detection sensitivity of the ensemble NV in diamond can be effectively improved based on magnetic flux concentration effect, which provides a reference for the applications of precision quantum measurement technology in weak magnetic and extremely weak magnetic detection.-
Keywords:
- magnetic flux concentrator /
- ensemble NV color center in diamond /
- continuous wave optical detection magnetic resonance /
- magnetic sensitivity
[1] Shenton M E, Hamoda H M, Schneiderman J S, Bouix S, Pasternak O, Rathi Y, Vu M A, Purohit M P, Helmer K, Koerte I, Lin A P, Westin C F, Kikinis R, Kubicki M, Stern R A, Zafonte R 2012 Brain Imaging Behav. 6 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lenz J, Edelstein A S 2006 IEEE Sens. J. 6 631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Xia H, Baranga A B A, Hoffman D, Romalis M V 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 211104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Anahory Y, Reiner J, Embon L, Halbertal D, Yakovenko A, Myasoedov Y, Rappaport M L, Huber M E, Zeldov E 2014 Nano Lett. 14 6481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Pannetier M, Fermon C, Le Goff G, Simola J, Kerr E 2004 Science 304 1648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yabukami S, Kato K, Ohtomo Y, Ozawa T, Arai K I 2009 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321 675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang Y, Gao J, Li M, Hasanyan D, Shen Y, Li J, Viehland D, Luo H 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 022903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang P F, Chen S Y, Guo M S, Peng S J, Wang M Q, Chen M, Ma W C, Zhang R, Su J H, Rong X, Shi F Z, Xu T, Du J F 2019 Sci. Adv. 5 eaau8038 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Maze J R, Stanwix P L, Hodges J S, Hong S, Taylor J M, Cappellaro P, Jiang L, Dutt M V G, Togan E, Zibrov A S, Yacoby A, Walsworth R L, Lukin M D 2008 Nature 455 644
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Barry J F, Schloss J M, Bauch E, Turner M J, Hart C A, Pham L M, Walsworth R L 2020 Rev. Mod. Phys. 92 015004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Davis H C, Ramesh P, Bhatnagar A, Lee-Gosselin A, Barry J F, Glenn D R, Walsworth R L, Shapiro M G 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 1319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Glenn D R, Fu R R, Kehayias P, Le Sage D, Lima E A, Weiss B P, Walsworth R L 2017 Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 18 3254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Jensen K, Leefer N, Jarmola A, Dumeige Y, Acosta V M, Kehayias P, Patton B, Budker D 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 160802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Fescenko I, Jarmola A, Savukov I, Kehayias P, Smits J, Damron J, Ristoff N, Mosavian N, Acosta V M 2020 Phys. Rev. Res. 2 023394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Griffith W C, Jimenez-Martinez R, Shah V, Knappe S, Kitching J 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 023502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Fan H, Li S, Nabaei V, Feng Q, Heidari H 2020 IEEE Sens. J. 20 9919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Szewczyk R, Ostaszewska-Lizewska A, Raback P 2020 Acta Phys. Pol. A 137 700
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hu J F, Ji M H, Qiu W C, Pan L, Li P S, Peng J P, Hu Y G, Liu H Y, Pan M C 2019 Sensors 19 4475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Feng Y L, Chen J Y, Wu K, Wang J P 2020 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 511 166728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Doherty M W, Dolde F, Fedder H, Jelezko F, Wrachtrup J, Manson N B, Hollenberg L C L 2012 Phys. Rev. B 85 205203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhao B B, Guo H, Zhao R, Du F F, Li Z H, Wang L, Wu D J, Chen Y L, Tang J, Liu J 2019 IEEE Magn. Lett. 10 8101104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Marinho Z, Cardoso S, Chaves R, Ferreira R, Melo L V, Freitas P P 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 109 07e521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang X M, Bi Y, Chen G B, Liu J, Li J, Feng K Q, Lv C, Wang W J 2018 AIP Adv. 8 125222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sun X, Jiang L J, Pong P W T 2013 Microelectron. Eng. 111 77
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Botsch L, Raatz N, Pezzagna S, Staacke R, John R, Abel B, Esquinazi P D, Meijer J, Diziain S 2020 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 91 125003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Schloss J M, Barry J F, Turner M J, Walsworth R L 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 034044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Barry J F, Turner M J, Schloss J M, Glenn D R, Song Y, Lukin M D, Park H, Walsworth R L 2016 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113 14133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Jensen K, Acosta V M, Jarmola A, Budker D 2013 Phys. Rev. B 87 014115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Leroy P, Coillot C, Roux A F, Chanteur G M 2006 IEEE Sens. J. 6 707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
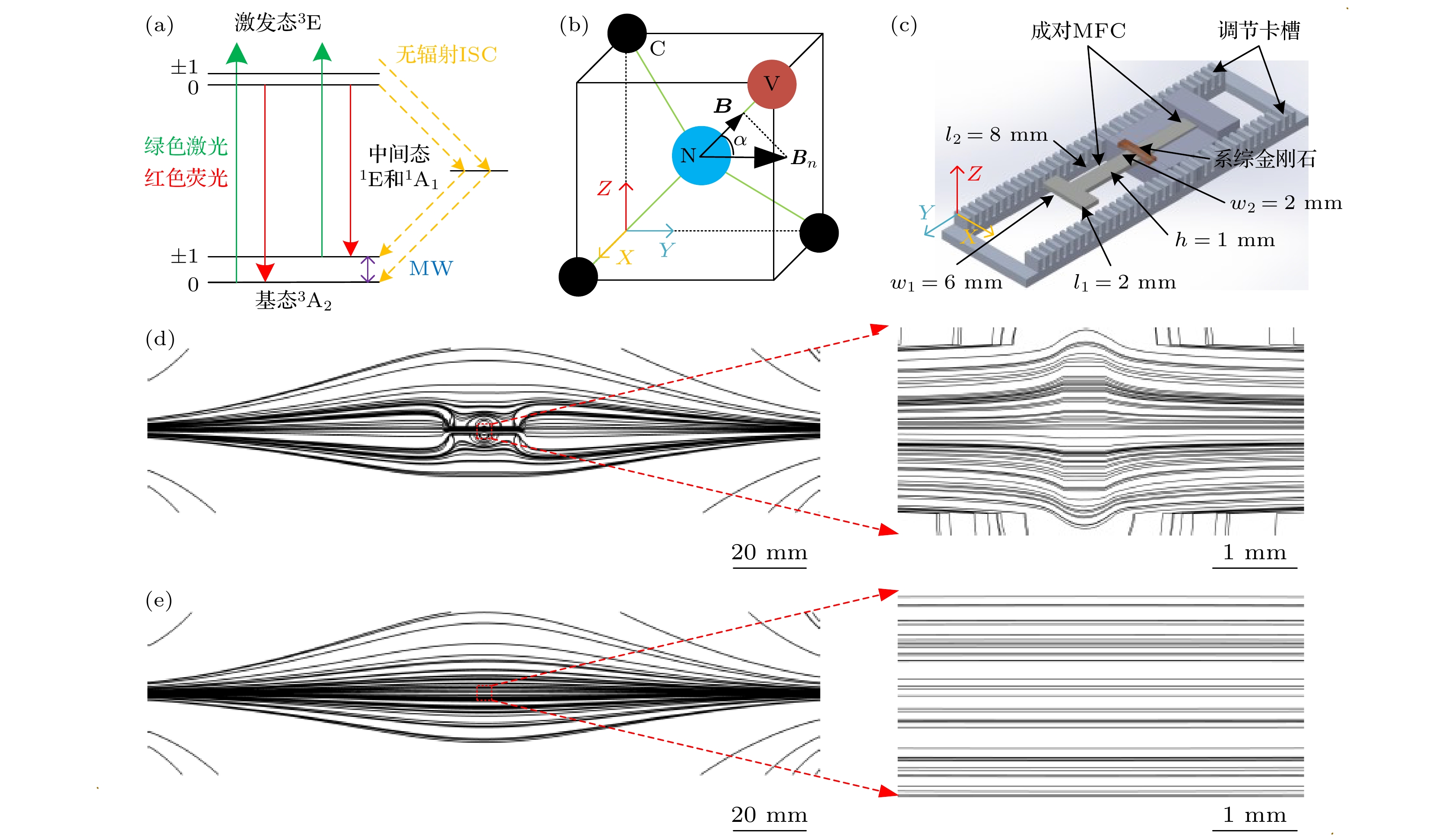
图 1 (a)金刚石NV色心能级跃迁示意图; (b)沿(100)面生长的金刚石晶胞中一种NV轴朝向与磁场方向夹角示意图; (c) T型薄片状MFC及调节装置示意图; (d) MFC间距为0.5 mm的两永磁体间磁场仿真流线图; (e)无MFC的两永磁体间磁场仿真流线图
Fig. 1. (a) Related energy levels of NV color center in diamond; (b) schematic diagram of the angle between the direction of the magnetic field and the direction of the NV axis in the diamond cell grown along the (100) plane; (c) schematic diagram of the T-shaped flake MFC and adjusting system; (d) simulation of magnetic field streamline diagram with MFC gap width of 0.5 mm between two permanent magnets; (e) simulation of magnetic field streamline diagram without MFC between two permanent magnets
图 2 (a) 实验装置示意图; (b) 用于仿真的几何结构俯视图, 红框为MFC间距0.5 mm时间隙部分放大示意图, 黑框为视场内的仿真磁场分布图
Fig. 2. (a) Schematic diagram of experimental setup; (b) top view of the geometric structure used in simulation, the red frame is the enlarged schematic diagram of the gap part when the MFC gap width is 0.5 mm, and the black frame is the simulated magnetic field distribution in the field of view.
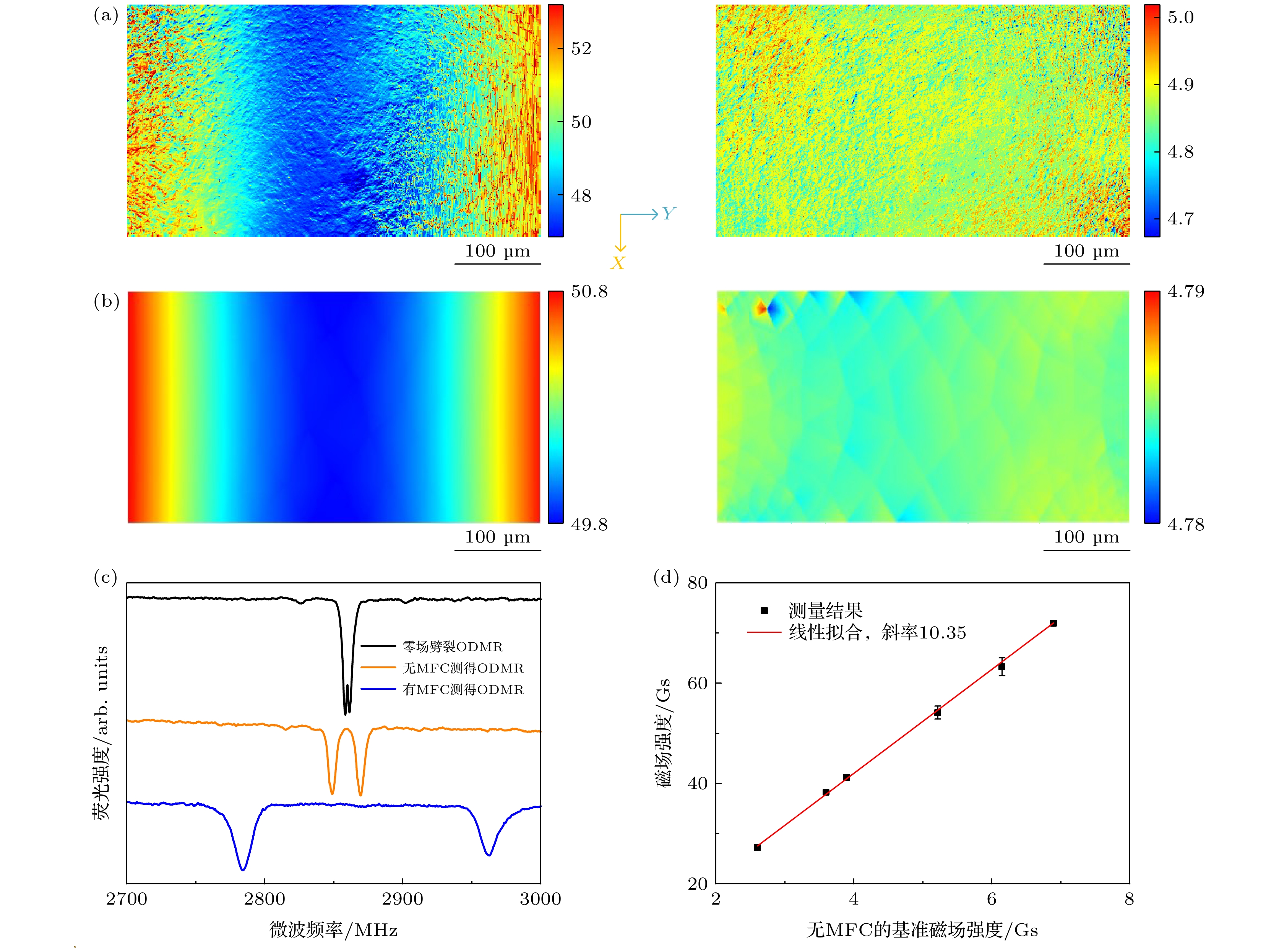
图 3 (a) 测量得到的1.0 mm间距MFC的测量位置磁场分布图(左)与同样位置处无MFC磁场分布图(右), 单位Gs; (b)仿真得到的图(a)的两个对应图; (c)三种状态的ODMR曲线, 只有背景磁场(黑线)、有待测磁场无MFC(橙线)、有间距1.0 mm 的MFC (蓝线); (d) MFC间距1.0 mm时改变待测磁场强度得到的增强磁场与基准磁场关系
Fig. 3. (a) Simulated magnetic field distribution diagram of the MFCs with a 1.0 mm gap (left) and without MFCs at the same position (right); (b) corresponding photos of panel (a) obtained by measurement; (c) ODMR curves under three conditions: only background magnetic field (black line), magnetic field without MFC (orange line), magnetic field with MFC of 1.0 mm gap (blue line); (d) relationship between the enhanced magnetic field and the reference magnetic field obtained by changing the intensity of the magnetic field to be measured when the MFCs gap is 1.0 mm.
图 4 (a) MFC不同间距下ODMR曲线; (b)仿真(红色圆圈)与测量(黑色方点)得到的不同间距MFC的磁场增强倍数曲线, 蓝线为拟合曲线.
Fig. 4. (a) ODMR curves of MFC with different gap widths; (b) magnetic field enhancement curve of MFC with different gap widths obtained by simulation (red circles) and measurement (black dots). The blue line is the fitting curve.
图 5 黑色方点为测量得到的不同间距下的磁灵敏度, 红线为无MFC状态下的磁灵敏度, 蓝线为拟合曲线, 蓝色星形为估计得到的间距为0.5 mm的磁灵敏度
Fig. 5. The black square points are the measured magnetic sensitivity at different intervals, the red line is the magnetic sensitivity without MFC, the blue line is the fitting curve, and the blue star is the estimated magnetic sensitivity with a pitch of 0.5 mm.
-
[1] Shenton M E, Hamoda H M, Schneiderman J S, Bouix S, Pasternak O, Rathi Y, Vu M A, Purohit M P, Helmer K, Koerte I, Lin A P, Westin C F, Kikinis R, Kubicki M, Stern R A, Zafonte R 2012 Brain Imaging Behav. 6 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lenz J, Edelstein A S 2006 IEEE Sens. J. 6 631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Xia H, Baranga A B A, Hoffman D, Romalis M V 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 211104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Anahory Y, Reiner J, Embon L, Halbertal D, Yakovenko A, Myasoedov Y, Rappaport M L, Huber M E, Zeldov E 2014 Nano Lett. 14 6481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Pannetier M, Fermon C, Le Goff G, Simola J, Kerr E 2004 Science 304 1648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yabukami S, Kato K, Ohtomo Y, Ozawa T, Arai K I 2009 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321 675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang Y, Gao J, Li M, Hasanyan D, Shen Y, Li J, Viehland D, Luo H 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 022903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang P F, Chen S Y, Guo M S, Peng S J, Wang M Q, Chen M, Ma W C, Zhang R, Su J H, Rong X, Shi F Z, Xu T, Du J F 2019 Sci. Adv. 5 eaau8038 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Maze J R, Stanwix P L, Hodges J S, Hong S, Taylor J M, Cappellaro P, Jiang L, Dutt M V G, Togan E, Zibrov A S, Yacoby A, Walsworth R L, Lukin M D 2008 Nature 455 644
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Barry J F, Schloss J M, Bauch E, Turner M J, Hart C A, Pham L M, Walsworth R L 2020 Rev. Mod. Phys. 92 015004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Davis H C, Ramesh P, Bhatnagar A, Lee-Gosselin A, Barry J F, Glenn D R, Walsworth R L, Shapiro M G 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 1319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Glenn D R, Fu R R, Kehayias P, Le Sage D, Lima E A, Weiss B P, Walsworth R L 2017 Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 18 3254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Jensen K, Leefer N, Jarmola A, Dumeige Y, Acosta V M, Kehayias P, Patton B, Budker D 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 160802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Fescenko I, Jarmola A, Savukov I, Kehayias P, Smits J, Damron J, Ristoff N, Mosavian N, Acosta V M 2020 Phys. Rev. Res. 2 023394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Griffith W C, Jimenez-Martinez R, Shah V, Knappe S, Kitching J 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 023502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Fan H, Li S, Nabaei V, Feng Q, Heidari H 2020 IEEE Sens. J. 20 9919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Szewczyk R, Ostaszewska-Lizewska A, Raback P 2020 Acta Phys. Pol. A 137 700
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hu J F, Ji M H, Qiu W C, Pan L, Li P S, Peng J P, Hu Y G, Liu H Y, Pan M C 2019 Sensors 19 4475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Feng Y L, Chen J Y, Wu K, Wang J P 2020 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 511 166728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Doherty M W, Dolde F, Fedder H, Jelezko F, Wrachtrup J, Manson N B, Hollenberg L C L 2012 Phys. Rev. B 85 205203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhao B B, Guo H, Zhao R, Du F F, Li Z H, Wang L, Wu D J, Chen Y L, Tang J, Liu J 2019 IEEE Magn. Lett. 10 8101104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Marinho Z, Cardoso S, Chaves R, Ferreira R, Melo L V, Freitas P P 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 109 07e521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang X M, Bi Y, Chen G B, Liu J, Li J, Feng K Q, Lv C, Wang W J 2018 AIP Adv. 8 125222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sun X, Jiang L J, Pong P W T 2013 Microelectron. Eng. 111 77
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Botsch L, Raatz N, Pezzagna S, Staacke R, John R, Abel B, Esquinazi P D, Meijer J, Diziain S 2020 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 91 125003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Schloss J M, Barry J F, Turner M J, Walsworth R L 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 034044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Barry J F, Turner M J, Schloss J M, Glenn D R, Song Y, Lukin M D, Park H, Walsworth R L 2016 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113 14133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Jensen K, Acosta V M, Jarmola A, Budker D 2013 Phys. Rev. B 87 014115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Leroy P, Coillot C, Roux A F, Chanteur G M 2006 IEEE Sens. J. 6 707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 10639
- PDF下载量: 308
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: