-
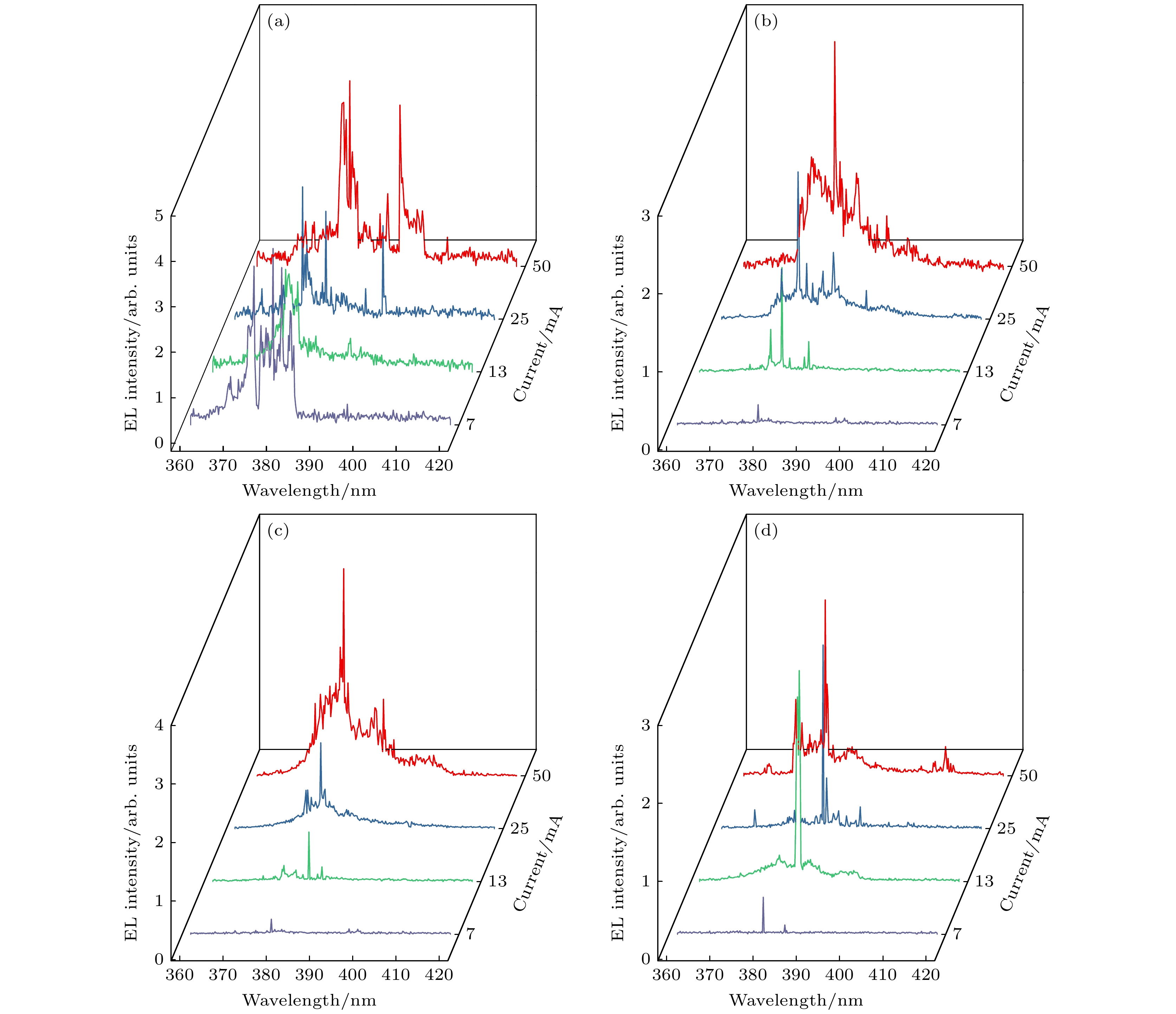
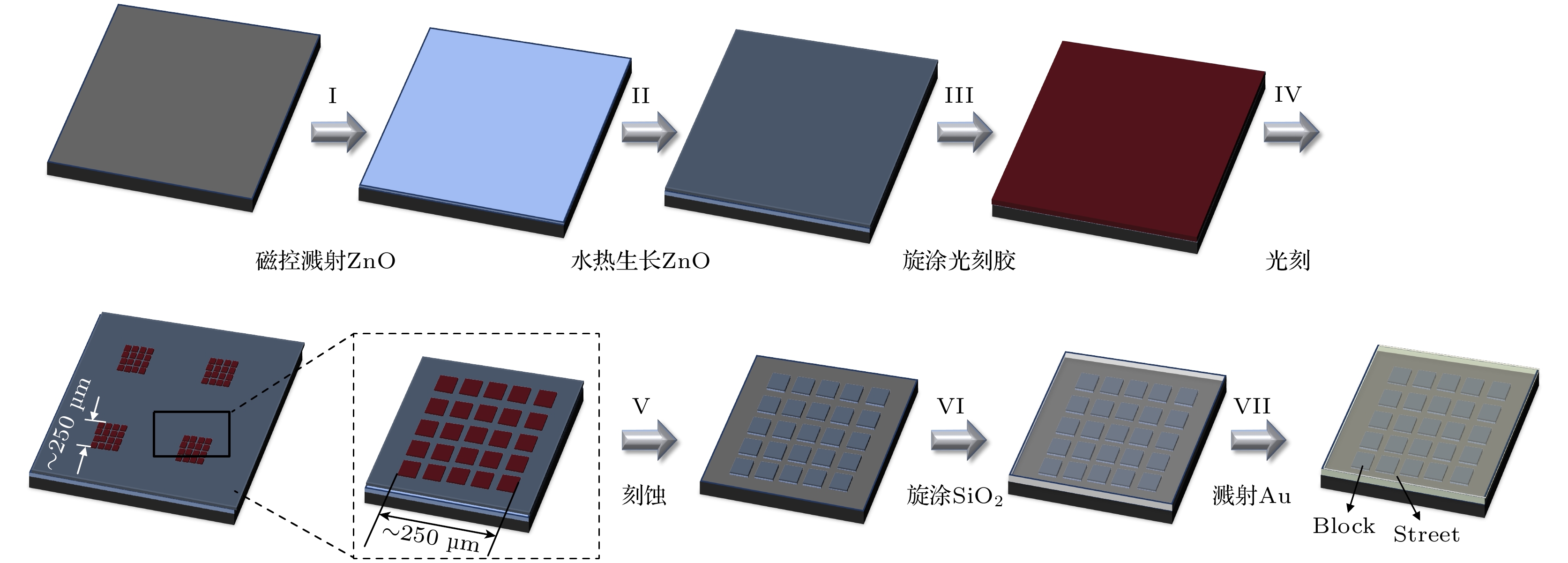
In this work, the randomness of electrically pumped random laser (RL) from ZnO-based metal-insulator-semiconductor (MIS) structured light-emitting device (LED) is significantly suppressed, by using appropriately patterned hydrothermal ZnO film with large crystal grains as the light-emitting layer. The hydrothermal ZnO film on silicon substrate, with the crystal grains sized over 500 nm, is first patterned into a number of square blocks separated by streets by using laser direct writing photolithography. Based on such a patterned ZnO film, the MIS (Au/SiO2/ZnO) structured LEDs are prepared on silicon substrates. Under the same injection current, the LED with the patterned ZnO film exhibits much fewer RL modes than that with the non-patterned ZnO film and, moreover, the former displays ever-fewer RL modes with the the decrease of block size. Besides, the wavelength of the strongest RL mode from the LED with the patterned ZnO film fluctuates in a much narrower range than that with the non-patterned ZnO film. It is worth mentioning that the LED with the patterned hydrothermal ZnO film can even be pumped into the single-mode RL under the desirable conditions such as low injection current and small patterned blocks. Moreover, the comparative investigation indicates that the LED with the large-grain hydrothermal ZnO film exhibits the smaller RL threshold current than that with the small-grain sputtered ZnO film, and the former has fewer RL modes and a higher output lasing power than the latter under the same injection current. As for the physical mechanism behind the aforementioned results, it is analyzed as follows. Regarding the LED with the patterned ZnO film, on the one hand, due to the limited numbers of crystal grains and grain boundaries within a single block, the multiple optical scattering is remarkably suppressed. Then, the paths through which the net optical gain and therefore the lasing action can be achieved via multiple optical scattering are much fewer than those in the case of the non-patterned ZnO film. On the other hand, due to optical gain competition among different RL modes occurring within the limited space of a single block, the RL modes with significant spatial overlap cannot lase simultaneously. For the two-fold reasons as mentioned above, the LED exhibits ever-fewer RL modes with the decrease of the size of blocks. Moreover, the inter-block optical coupling enables the optical gain competition among different RL modes to be more violent within a single block, leading to further reduction of RL modes.
-
Keywords:
- hydrothermal ZnO film /
- light-emitting device /
- random lasing /
- patterning /
- suppression of randomness
[1] Cao H, Zhao Y G, Ong H C, Ho S T, Dai J Y, Wu J Y, Chang R P H 1998 Appl. Phys. Lett. 73 3656
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yu S F, Leong E S P 2004 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 40 1186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Cao H, Zhao Y G, Ong H C, Chang R P H 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 15107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Thareja R K, Mitra A 2000 Appl. Phys. B: Lasers Opt. 71 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lau S P, Yang H Y, Yu S F, Li H D, Tanemura M, Okita T, Hatano H, Hng H H 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 013104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ursaki V V, Burlacu A, Rusu E V, Postolake V, Tiginyanu I M 2009 J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 11 075001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yu S F, Yuen C, Lau S P, Park W I, Yi G C 2004 Appl. Phys. Lett. 84 3241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ma X Y, Chen P L, Li D S, Zhang Y Y, Yang D R 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 251109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chu S, Olmedo M, Yang Z, Kong J Y, Liu J L 2008 Appl. Phys. Lett. 93 181106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Long H, Fang G J, Huang H H, Mo X M, Xia W, Dong B Z, Meng X Q, Zhao X Z 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 013509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhu H, Shan C X, Zhang J Y, Zhang Z Z, Li B H, Zhao D X, Yao B, Shen D Z, Fan X W, Tang Z K, Hou X H, Choy K L 2010 Adv. Mater. 22 1877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen P L, Ma X Y, Li D S, Zhang Y Y, Yang D R 2009 Opt. Express 17 4712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang C X, Jiang H T, Li Y P, Ma X Y, Yang D R 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 114 133105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang C X, Zhu C, Lü C Y, Li D S, Ma X Y, Yang D R 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 332 620
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jiang S M, Xia C T, Ji R, Pang H W, Li D S, Yang D R, Ma X Y 2024 Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 16 3719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ma X Y, Pan J W, Chen P L, Li D S, Zhang H, Yang Y, Yang D R 2009 Opt. Express 17 14426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ryglowski L, Cyprych K, Mysliwiec J 2022 Opt. Commun. 510 127939
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li Y P, Wang C X, Jin L, Ma X Y, Yang D R 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 161112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 徐韵, 李云鹏, 金璐, 马向阳, 杨德仁 2013 62 084207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu Y, Li Y P, Jin L, Ma X Y, Yang D R 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 084207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jiang X Y, Soukoulis C M 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 85 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Sebbah P, Vanneste C 2002 Phys. Rev. B 66 144202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 杜文博, 冷进勇, 朱家健, 周朴, 许晓军, 舒柏宏 2012 61 114203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du W B, Leng J Y, Zhu J J, Zhou P, Xu X J, Shu B H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 114203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhu G Y, Tian M F, Almokhtar M, Qin F F, Li B H, Zhou M Y, Gao F, Yang Y, Ji X, He S Q, Wang Y J 2022 Chin. Phys. Lett. 39 123401 (in Chinese)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Liu H, Li S J, You Y Q, Wang J W, Sun J, Zhang L, Xiong L L 2023 Optik 281 170853
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang Y Y, Xu C X, Jiang M M, Li J T, Dai J, Lu J F, Li P L 2016 Nanoscale 8 16631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 魏伟华, 李木天, 刘墨南 2018 67 064203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei W H, Li M T, Liu M N 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 064203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 马光辉, 张家斌, 张贺, 金亮, 王灌鑫, 徐英添 2019 中国光学 12 649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma G H, Zhang J B, Zhang H, Jin L, Wang G X, Xu Y T 2019 Chin. Opt. 12 649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
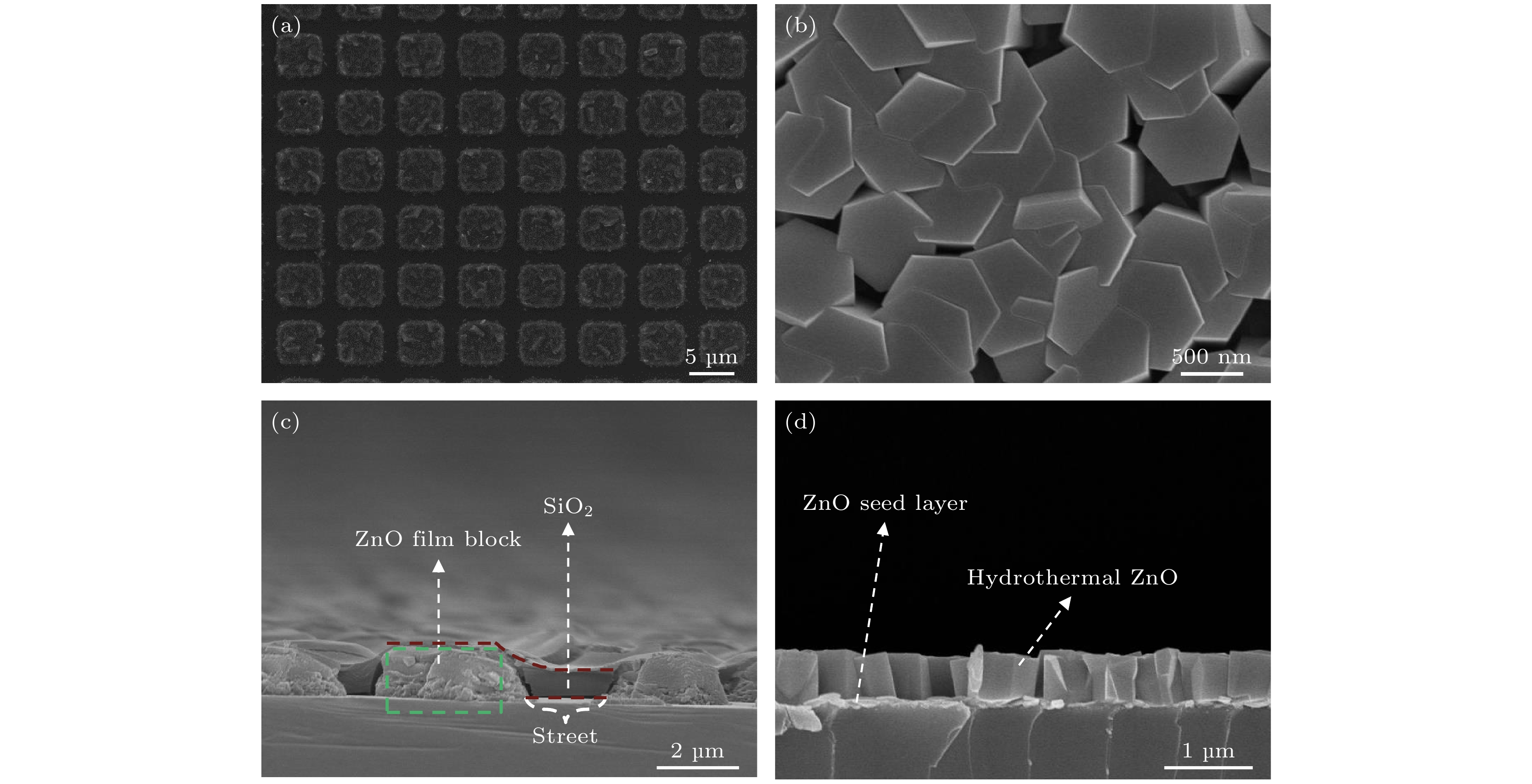
图 2 (a) 水热ZnO薄膜经图案化处理后的表面形貌SEM照片; (b) 单个Block内ZnO薄膜表面形貌的SEM照片; (c) Block和Street的截面SEM照片; (d) 单个Block的截面SEM照片
Figure 2. (a) SEM image for the surface morphology of the patterned hydrothermal ZnO film; (b) SEM image for the surface morphology of the ZnO film within a single block; (c) cross-sectional SEM image for the blocks and streets; (d) cross-sectional SEM image for the ZnO film within a single block.
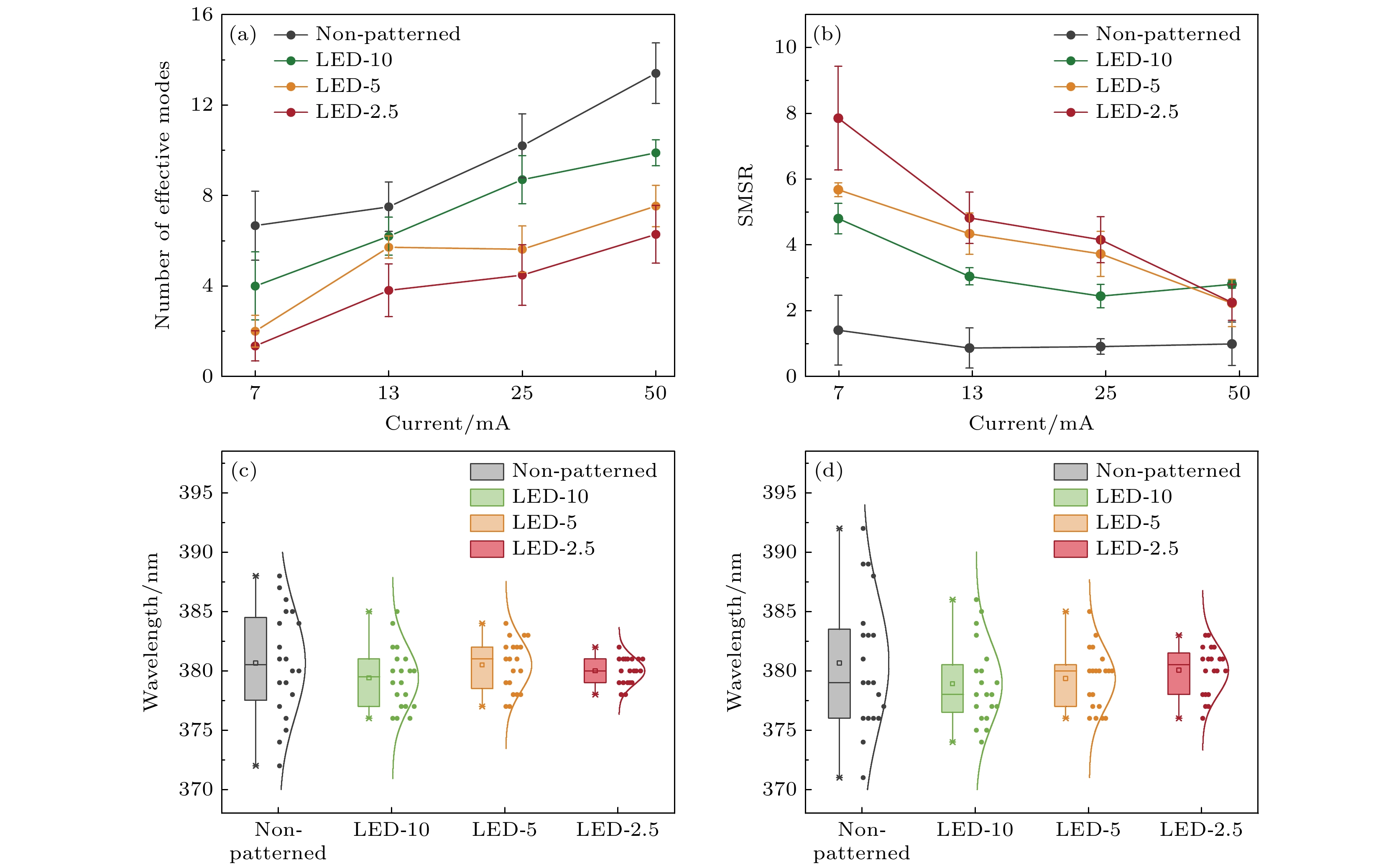
图 4 未经图案化处理的LED, LED-10, LED-5, LED-2.5的电抽运随机激射 (a), (b) 有效激射模式数和SMSR随注入电流的变化情况; (c), (d) 在注入电流分别为 7 mA和 25 mA时采集的20幅EL谱中最强激射峰的波长分布情况, 其中误差棒的最高点和最低点分别代表最大值和最小值, 方框的中间线代表中值、上边线和下边线分别代表第三四分位数和第一四分位数
Figure 4. Electrically pumped random lasing from non-patterned LED, LED-10, LED-5, and LED-2.5: (a), (b) Number of effective lasing modes and SMSR as a function of injected current; (c), (d) distributions of the wavelengths of the strongest lasing peaks in the 20 EL spectra acquired at the injection currents of 7 mA and 25 mA, respectively, the error bar represents the minimum and maximum values, and the middle line in the box represents the median value, the upper and lower lines of the box represent the third quartile (Q3) and first quartile (Q1), respectively.
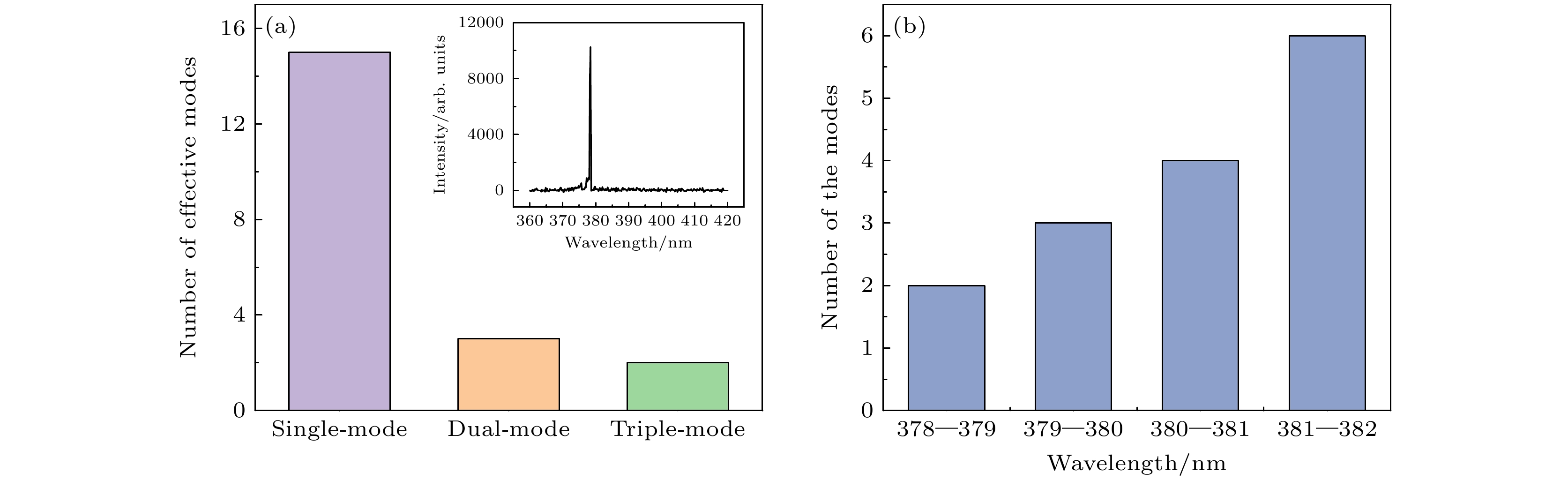
图 5 对于LED-2.5在注入电流为7 mA时采集的 20幅EL谱 (a) 出现单模、双模、三模激射的例数, 插图为出现单模激射的EL谱; (b) 单模激射的峰位分布情况
Figure 5. For the 20 EL spectra of LED-2.5 acquired at the injection current of 7 mA: (a) Number of cases exhibiting single-mode, dual-mode or triple-mode lasing, the inset shows the EL spectrum of single-mode random lasing; (b) distribution of wavelengths for the single-mode lasing actions.
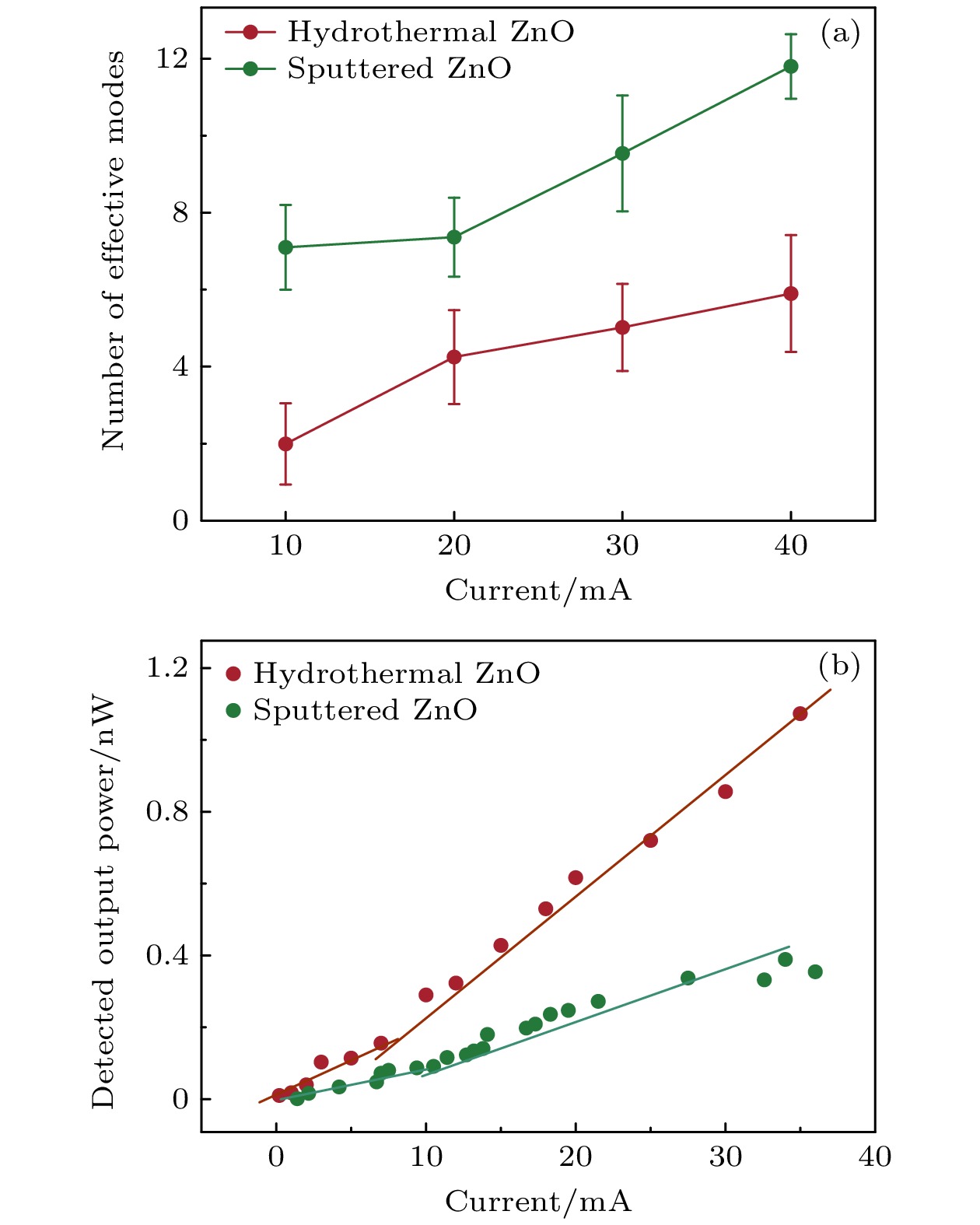
图 6 基于水热法和溅射法制备的ZnO薄膜的两种LED-2.5的电抽运随机激射 (a) 有效激射模式数随注入电流的变化情况; (b) 探测到的输出光功率随注入电流的变化关系曲线
Figure 6. Electrically pumped random lasing actions from the two LED-2.5 respectively based on the hydrothermal and sputtered ZnO film: (a) Number of effective lasing modes as a function of the injection current; (b) curves of the detected output optical power changing with the injection current.
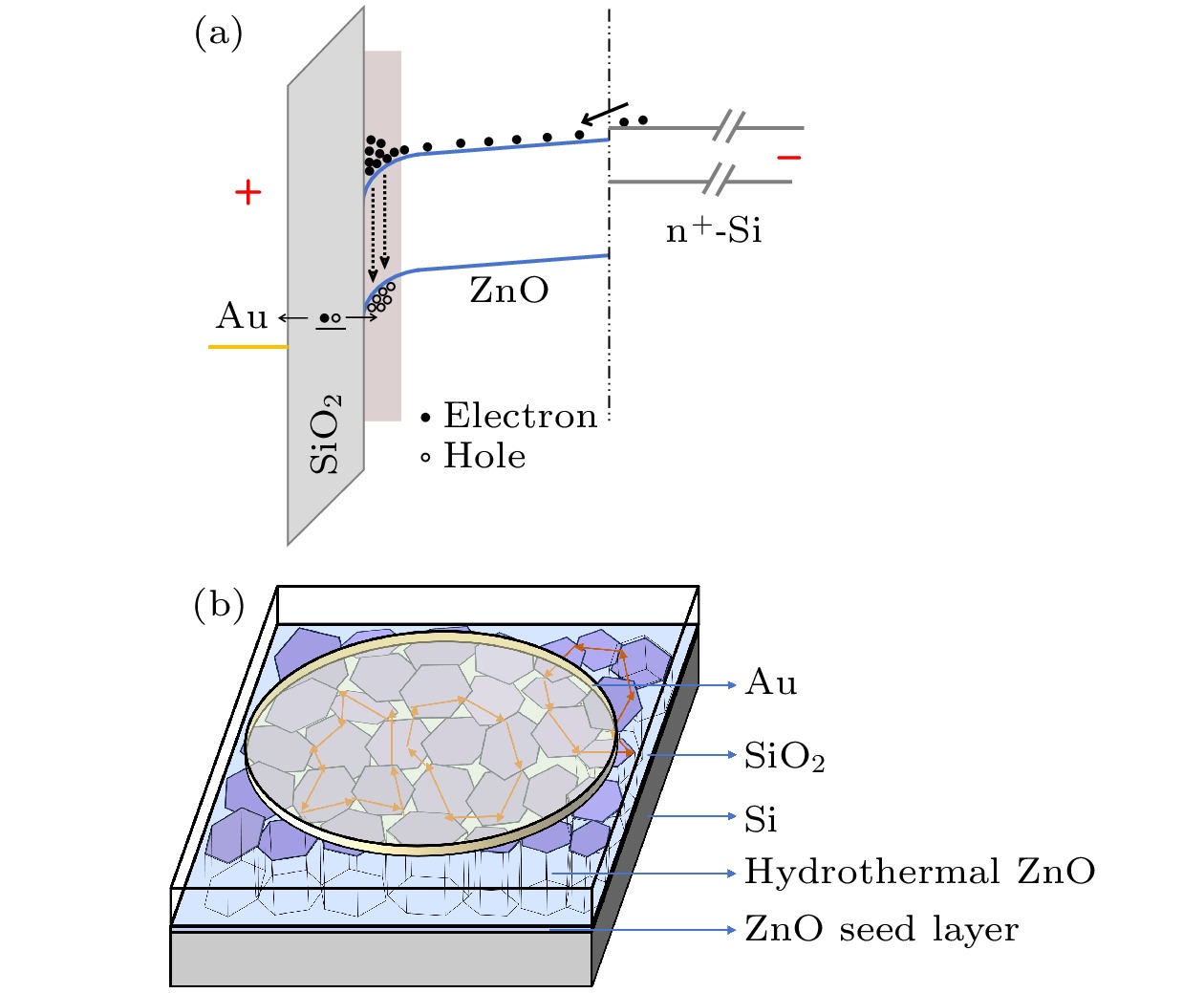
图 7 (a) 基于硅衬底上ZnO薄膜的MIS结构LED在足够高的正向偏压/注入电流下的能带结构示意图; (b) ZnO薄膜内光多重散射的示意图
Figure 7. (a) Schematic diagram of the energy band structure for the MIS-structured LED using ZnO film on silicon substrate under sufficiently high forward bias/injection current; (b) schematic diagram of multiple light scattering within the ZnO film.
-
[1] Cao H, Zhao Y G, Ong H C, Ho S T, Dai J Y, Wu J Y, Chang R P H 1998 Appl. Phys. Lett. 73 3656
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yu S F, Leong E S P 2004 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 40 1186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Cao H, Zhao Y G, Ong H C, Chang R P H 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 15107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Thareja R K, Mitra A 2000 Appl. Phys. B: Lasers Opt. 71 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lau S P, Yang H Y, Yu S F, Li H D, Tanemura M, Okita T, Hatano H, Hng H H 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 013104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ursaki V V, Burlacu A, Rusu E V, Postolake V, Tiginyanu I M 2009 J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 11 075001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yu S F, Yuen C, Lau S P, Park W I, Yi G C 2004 Appl. Phys. Lett. 84 3241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ma X Y, Chen P L, Li D S, Zhang Y Y, Yang D R 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 251109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chu S, Olmedo M, Yang Z, Kong J Y, Liu J L 2008 Appl. Phys. Lett. 93 181106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Long H, Fang G J, Huang H H, Mo X M, Xia W, Dong B Z, Meng X Q, Zhao X Z 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 013509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhu H, Shan C X, Zhang J Y, Zhang Z Z, Li B H, Zhao D X, Yao B, Shen D Z, Fan X W, Tang Z K, Hou X H, Choy K L 2010 Adv. Mater. 22 1877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen P L, Ma X Y, Li D S, Zhang Y Y, Yang D R 2009 Opt. Express 17 4712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang C X, Jiang H T, Li Y P, Ma X Y, Yang D R 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 114 133105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang C X, Zhu C, Lü C Y, Li D S, Ma X Y, Yang D R 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 332 620
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jiang S M, Xia C T, Ji R, Pang H W, Li D S, Yang D R, Ma X Y 2024 Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 16 3719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ma X Y, Pan J W, Chen P L, Li D S, Zhang H, Yang Y, Yang D R 2009 Opt. Express 17 14426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ryglowski L, Cyprych K, Mysliwiec J 2022 Opt. Commun. 510 127939
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li Y P, Wang C X, Jin L, Ma X Y, Yang D R 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 161112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 徐韵, 李云鹏, 金璐, 马向阳, 杨德仁 2013 62 084207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu Y, Li Y P, Jin L, Ma X Y, Yang D R 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 084207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jiang X Y, Soukoulis C M 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 85 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Sebbah P, Vanneste C 2002 Phys. Rev. B 66 144202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 杜文博, 冷进勇, 朱家健, 周朴, 许晓军, 舒柏宏 2012 61 114203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du W B, Leng J Y, Zhu J J, Zhou P, Xu X J, Shu B H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 114203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhu G Y, Tian M F, Almokhtar M, Qin F F, Li B H, Zhou M Y, Gao F, Yang Y, Ji X, He S Q, Wang Y J 2022 Chin. Phys. Lett. 39 123401 (in Chinese)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Liu H, Li S J, You Y Q, Wang J W, Sun J, Zhang L, Xiong L L 2023 Optik 281 170853
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang Y Y, Xu C X, Jiang M M, Li J T, Dai J, Lu J F, Li P L 2016 Nanoscale 8 16631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 魏伟华, 李木天, 刘墨南 2018 67 064203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei W H, Li M T, Liu M N 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 064203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 马光辉, 张家斌, 张贺, 金亮, 王灌鑫, 徐英添 2019 中国光学 12 649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma G H, Zhang J B, Zhang H, Jin L, Wang G X, Xu Y T 2019 Chin. Opt. 12 649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 531
- PDF Downloads: 12
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: