-
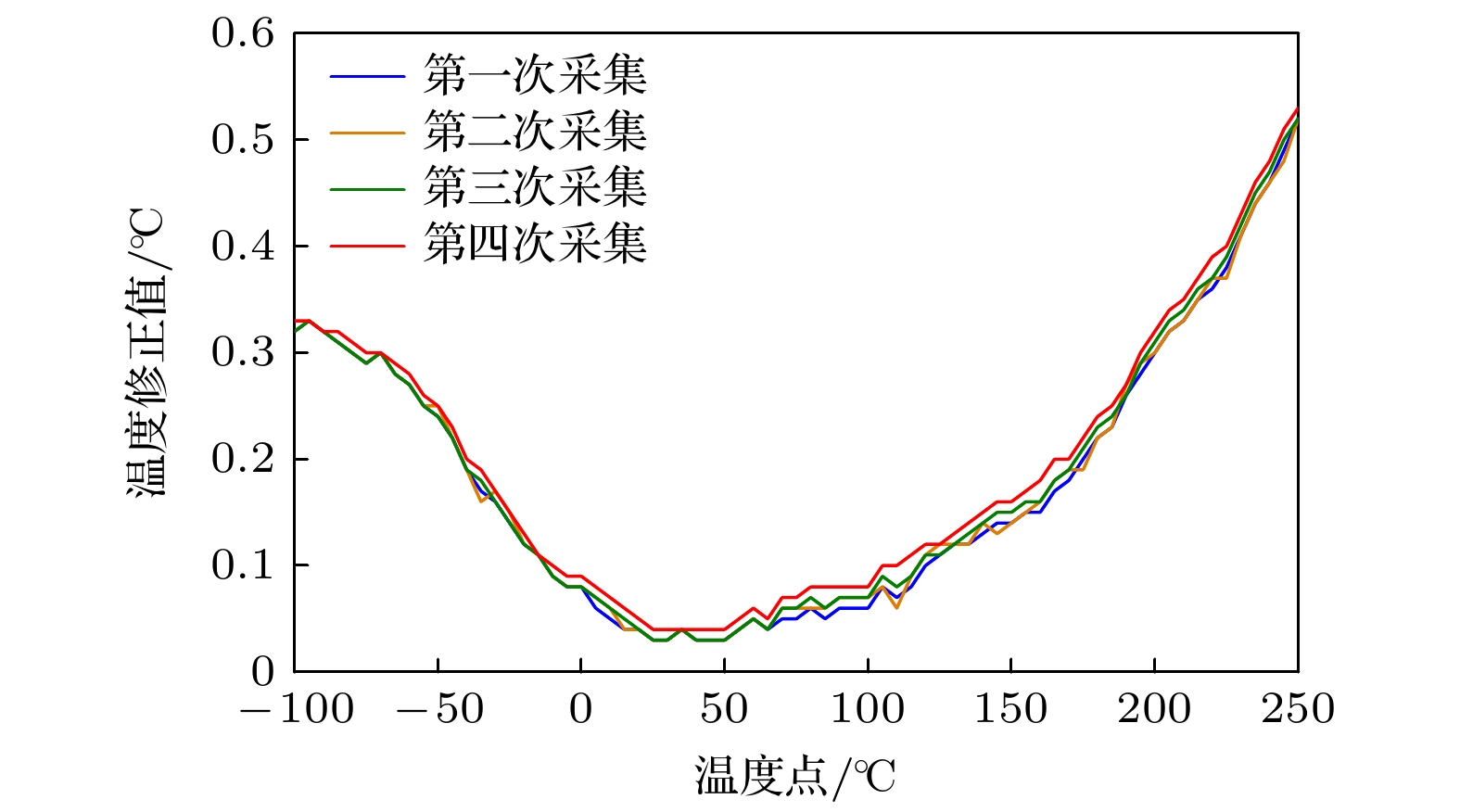
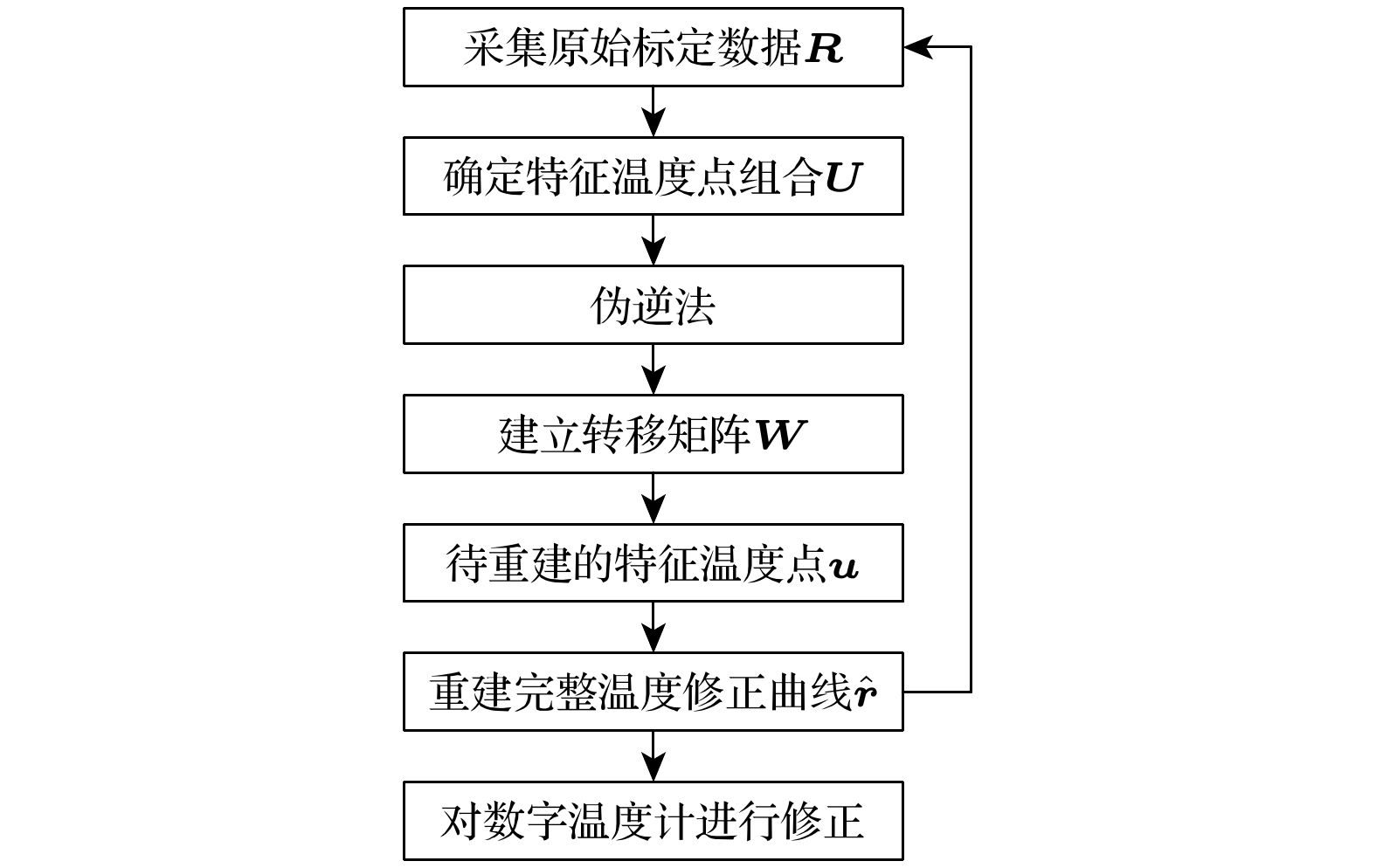
At present, high-precision digital thermometers based on industrial platinum resistance have become a popular research direction and are widely used in environmental monitoring, medical health, industrial automation and other fields. However, due to the influence of materials and manufacturing processes, the measurement accuracy is average. With the increase of service life, it is inevitable that the temperature measurement deviation will be caused by the drift of the resistance value. The algorithm of correcting temperature is an effective method to improve the measurement accuracy of digital thermometers. Traditional compensation function correction algorithms such as polynomial fitting and B-spline fitting have good correction effect, but the problems of resistance drift cannot be solved. The segmented linear correction algorithm is simple and easy to implemente, but it requires multi-point temperature measurements. Because of the nonlinear changes of the temperature correction curve, the correction effect is average, which limits its correction accuracy and universality. Therefore, we propose n algorithm of reconstructing temperature correction curve based on the pseudo inverse method. Firstly, the reconstruction matrix is built by using the original data and multiple characteristic temperature points. Then, the complete temperature correction curve is reconstructed by the characteristic temperature points to be reconstructed and the reconstruction matrix. Finally, the reconstructed temperature correction curve is automatically included in the sample database, which improves the diversity of samples and the correction accuracy of the algorithm. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has a better correction effect on nonlinear changes and drifts of the temperature correction curve. And the proposed algorithm is less affected by the number of characteristic temperature points and the selection combination. The complete temperature correction curve is well reconstructed by collecting only 4 characteristic temperature points. Therefore, the proposed algorithm can provide the effective support for improving the measurement accuracy of digital thermometer.
-
Keywords:
- pseudo inverse /
- reconstruction algorithm /
- temperature correction curve reconstruction /
- digital thermometer
[1] Preston-Thomas H 1990 Metrologia 27 186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Coakley K J, Clark A V, Hehman C S 2003 Meas. Sci. Technol. 14 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 方院生, 王琦, 丁诚, 王文龙, 唐曦凌, 马勇 2015 测控技术 11 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang Y S, Wang Q, Ding C, Wang W L, Tang X L, Ma Y 2015 Meas. Con. Technol. 11 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 方院生, 姚丽娟, 肖勇, 王琦 2014 测控技术 33 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang Y S, Yao L J, Xiao Y, Wang Q 2014 Meas. Con. Technol. 33 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 胡静静, 沈媛媛 2024 流体测量与控制 5 23
Hu J J, Shen Y Y 2024 Fluid Measurem. Contr. 5 23
[6] 任建平, 孙建平, 李婷, 何佳融, 曾佳旭 2021 计量学报 42 589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren J P, Sun J P, Li T, He J R, Zeng J X 2021 Acta Metrol. Sin. 42 589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Pearce J V, Rusby R L, Harris P M 2013 Metrologia 50 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Babita P U, Meena H, Gupta G 2022 Measurement 203 111994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 冯邻江, 卢明肖, 周寻, 严俐, 蔡翱, 谢雨辰 2024 自动化技术与应用 43 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fen L J, Lu M X, Zhou X, Yan L, Cai A, Xie Y C 2024 Techn. Automat. Appl. 43 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 何慎之 2024 中国仪器仪表 6 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He S Z 2024 China Instrum. 6 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 魏永超, 刘倩倩, 朱泓超, 朱姿翰, 李锦 2024 红外技术 46 843
We Y C, Liu Q Q, Zhu H C, Zhu Z H, Li J 2024 Infrared Technol. 46 843
[12] 吴志祥, 周祥才, 黄亮, 陈功 2014 自动化与仪表 2 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Z X, Zhou X C, Huang L, Chen G 2014 Automat. Instrumentation 2 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王昕, 康哲铭, 刘龙, 范贤光 2020 69 200701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X, Kang Z M, Liu L, Fan X G 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 200701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王昕, 康哲铭, 刘龙, 范贤光 2020 光子学报 49 0330001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X, Kang Z M, Liu L, Fan X G 2020 Acta Photonica Sin. 49 0330001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cadusch P J, Hlaing M M, Wade S A 2013 J. Raman. Spectrosc. 44 1587
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Martin T, Cohen E, Kirby R M 2009 Comput. Aided Geom. D. 26 648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang W, Pottmann H, Liu Y 2006 ACM T. Graphic. 25 214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 魏国, 王昕, 雷苗, 孙圣和 2008 传感器与微系统 27 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei G, Wang X, Lei M, Sun S H 2008 TMT 27 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 刘龙 2021 博士学位论文(厦门: 厦门大学)
Liu L 2021 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xiamen: Xiamen University
[20] Chen S, Ong Y H, Liu Q 2012 J. Raman. Spectrosc. 44 875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
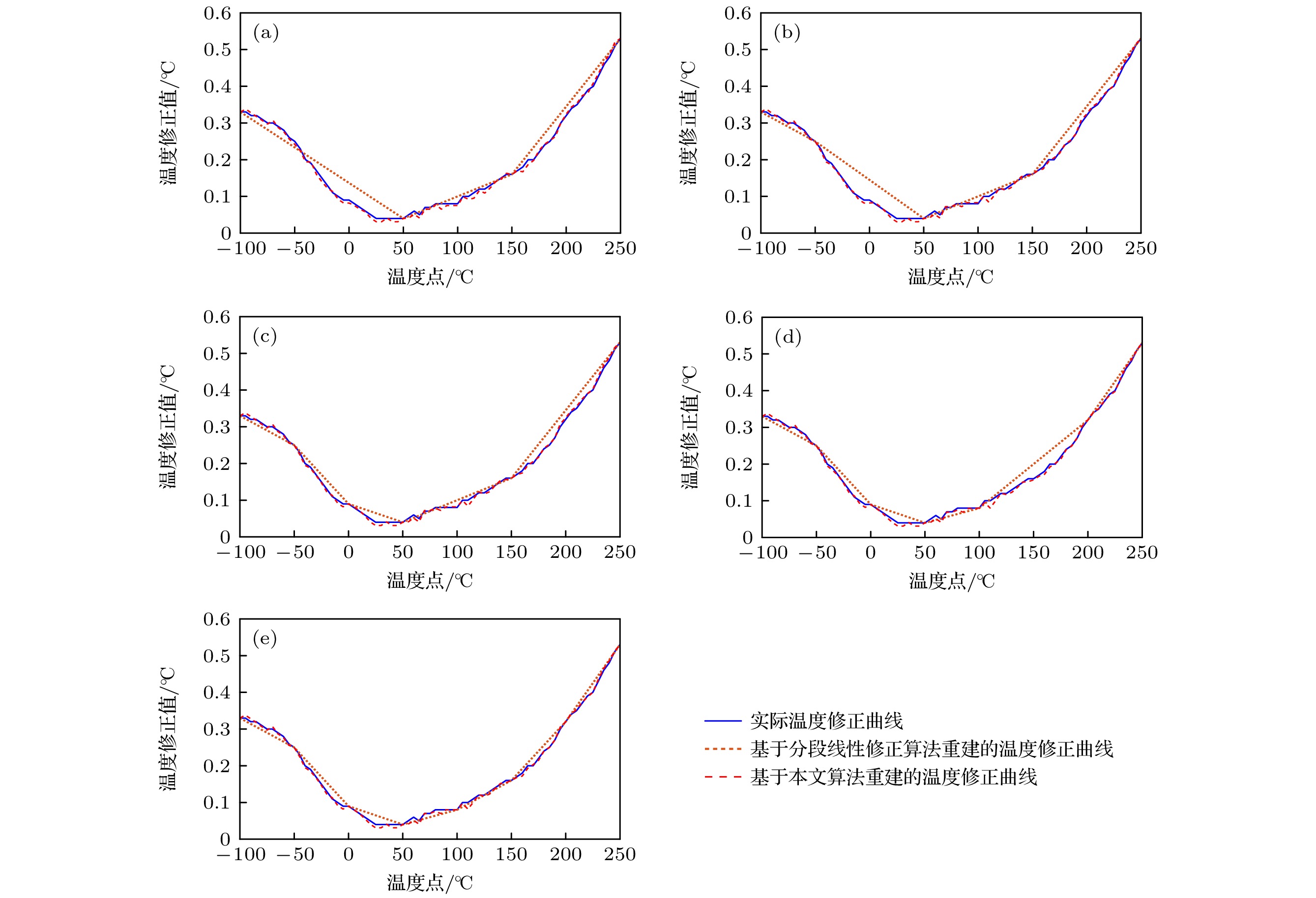
图 3 不同特征温度点个数情况下, 基于分段线性修正算法和本文算法重建的温度修正曲线 (a) 特征温度点个数为4; (b) 特征温度点个数为5; (c) 特征温度点个数为6; (d) 特征温度点个数为7; (e) 特征温度点个数为8
Figure 3. Reconstructed temperature correction curve based on the piecewise linear correction algorithm and the proposed algorithm by different number of characteristic temperature points: (a) Number of characteristic temperature points is 4; (b) number of characteristic temperature points is 5; (c) number of characteristic temperature points is 6; (d) number of characteristic temperature points is 7; (e) number of characteristic temperature points is 8.
表 1 不同特征温度点个数情况下的特征温度点组合
Table 1. Combination of characteristic temperature points by different number of characteristic temperature points.
特征温度点数量/个 4 5 6 7 8 特征温度点1/℃ –100 –100 –100 –100 –100 特征温度点2/℃ 50 –50 –50 –50 –50 特征温度点3/℃ 150 50 0 0 0 特征温度点4/℃ 250 150 50 50 50 特征温度点5/℃ — 250 150 100 100 特征温度点6/℃ — — 250 200 150 特征温度点7/℃ — — — 250 200 特征温度点8/℃ — — — — 250 表 2 基于分段线性修正算法和本文算法重建的温度修正曲线的RMSE值
Table 2. RMSEs of the reconstructed temperature correction curve based on the piecewise linear correction algorithm and the proposed algorithm.
特征温度点数量/个 4 5 6 7 8 多段线性修正算法
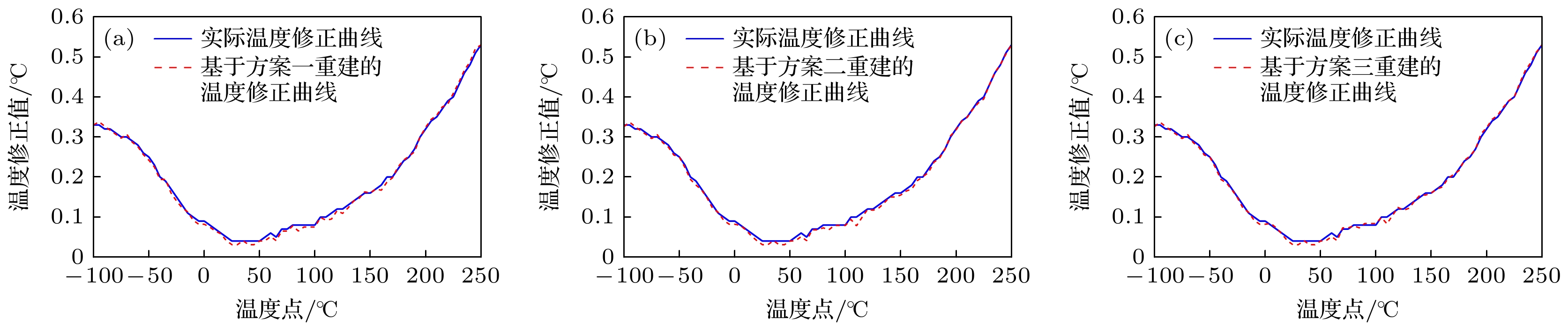
/RMSE值0.0264 0.0288 0.0176 0.0190 0.0129 本文算法/RMSE值 0.0065 0.0055 0.0054 0.0057 0.0054 表 3 不同特征温度点组合方案
Table 3. Combination schemes by different characteristic temperature points.
特征温度
点1/℃特征温度
点2/℃特征温度
点3/℃特征温度
点4/℃方案一 –100 50 150 250 方案二 –100 0 100 200 方案三 –50 50 150 250 -
[1] Preston-Thomas H 1990 Metrologia 27 186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Coakley K J, Clark A V, Hehman C S 2003 Meas. Sci. Technol. 14 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 方院生, 王琦, 丁诚, 王文龙, 唐曦凌, 马勇 2015 测控技术 11 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang Y S, Wang Q, Ding C, Wang W L, Tang X L, Ma Y 2015 Meas. Con. Technol. 11 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 方院生, 姚丽娟, 肖勇, 王琦 2014 测控技术 33 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang Y S, Yao L J, Xiao Y, Wang Q 2014 Meas. Con. Technol. 33 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 胡静静, 沈媛媛 2024 流体测量与控制 5 23
Hu J J, Shen Y Y 2024 Fluid Measurem. Contr. 5 23
[6] 任建平, 孙建平, 李婷, 何佳融, 曾佳旭 2021 计量学报 42 589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren J P, Sun J P, Li T, He J R, Zeng J X 2021 Acta Metrol. Sin. 42 589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Pearce J V, Rusby R L, Harris P M 2013 Metrologia 50 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Babita P U, Meena H, Gupta G 2022 Measurement 203 111994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 冯邻江, 卢明肖, 周寻, 严俐, 蔡翱, 谢雨辰 2024 自动化技术与应用 43 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fen L J, Lu M X, Zhou X, Yan L, Cai A, Xie Y C 2024 Techn. Automat. Appl. 43 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 何慎之 2024 中国仪器仪表 6 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He S Z 2024 China Instrum. 6 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 魏永超, 刘倩倩, 朱泓超, 朱姿翰, 李锦 2024 红外技术 46 843
We Y C, Liu Q Q, Zhu H C, Zhu Z H, Li J 2024 Infrared Technol. 46 843
[12] 吴志祥, 周祥才, 黄亮, 陈功 2014 自动化与仪表 2 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Z X, Zhou X C, Huang L, Chen G 2014 Automat. Instrumentation 2 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王昕, 康哲铭, 刘龙, 范贤光 2020 69 200701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X, Kang Z M, Liu L, Fan X G 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 200701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王昕, 康哲铭, 刘龙, 范贤光 2020 光子学报 49 0330001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X, Kang Z M, Liu L, Fan X G 2020 Acta Photonica Sin. 49 0330001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cadusch P J, Hlaing M M, Wade S A 2013 J. Raman. Spectrosc. 44 1587
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Martin T, Cohen E, Kirby R M 2009 Comput. Aided Geom. D. 26 648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang W, Pottmann H, Liu Y 2006 ACM T. Graphic. 25 214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 魏国, 王昕, 雷苗, 孙圣和 2008 传感器与微系统 27 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei G, Wang X, Lei M, Sun S H 2008 TMT 27 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 刘龙 2021 博士学位论文(厦门: 厦门大学)
Liu L 2021 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xiamen: Xiamen University
[20] Chen S, Ong Y H, Liu Q 2012 J. Raman. Spectrosc. 44 875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3739
- PDF Downloads: 40
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: