-
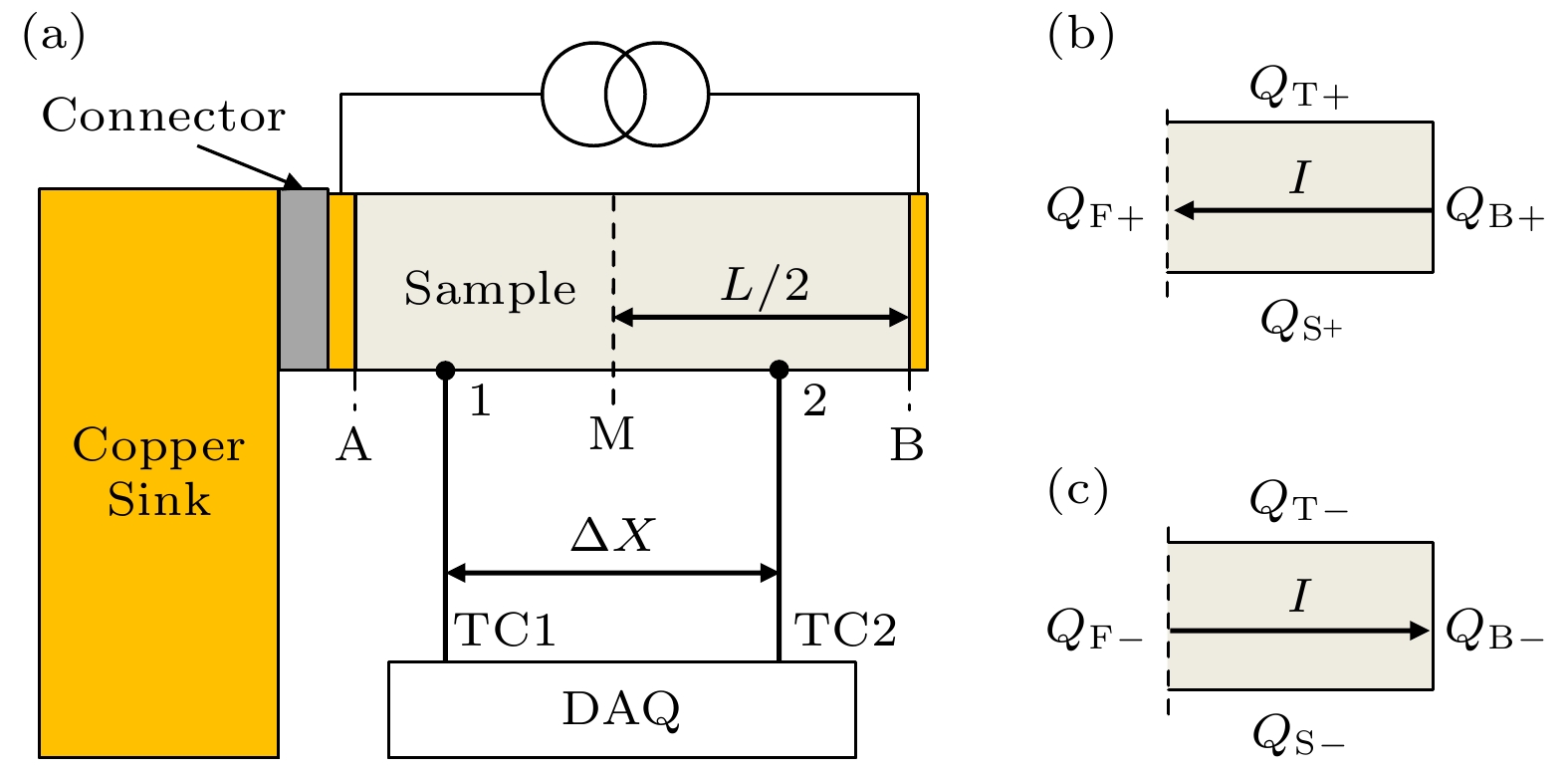
In the study of the physical effects of thermoelectric conversion, the Kelvin relationship is a bridge between the Seebeck coefficient and the Peltier coefficient, which brings the cooling and power generation performance of thermoelectric material into a unified evaluation system and dramatically simplifies the measurement process. However, some theoretical studies have shown that the Kelvin relationship is not satisfied under nonlinear conditions. Meanwhile, the measurement results of some experiments do not conform with this relationship. There have been few studies on accurately measuring the Peltier coefficient that is the basis of validating the Kelvin relation and studying the nonlinear thermoelectric effect. Based on this, a kind of Peltier coefficient measuring device with a cantilever beam structure is proposed in this work. We measure the difference between steady-state temperature and transient-state temperature on the sample surface and obtain the Peltier coefficients by the steady-state method and the transient-state method, respectively. By this measurement, we can obtain not only the Peltier coefficient of the material at low temperatures but also the interface resistance of the material. The Peltier coefficients measured by the steady-state method and the transient-state method are consistent with each other at various temperatures. Both of the variation trends with temperature are consistent with the temperature-dependent theoretical values calculated from the Kelvin relation. Our measured values are about 20% larger than the theoretical values.
[1] Mao J, Liu Z H, Zhou J W, Zhu H T, Zhang Q, Chen G, Ren Z F 2018 Adv. Phys. 67 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ambrosi R M, Kramer D P, Watkinson E J, Mesalam R, Barco A 2021 Nucl. Technol. 207 773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Siddique A R M, Mahmud S, Heyst B V 2017 Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 73 730
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Meng F, Chen L, Xie Z, Ge Y 2017 Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 4 106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cao Q, Luan W, Wang T 2018 Appl. Therm. Eng. 130 1472
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hao M R, Yang Y, Zhang S, Shen W Z, Schneider H, Liu H C 2014 Laser Photonics Rev. 8 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jaziri N, Boughamoura A, Muller J, Mezghani B, Tounsi F, Ismail M 2020 Energy Rep. 6 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Saber H H, AlShehri S A, Maref W 2019 Energy Convers. Manage. 191 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Choi H S, Yun S, Whang K I 2007 Appl. Therm. Eng. 27 2841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Thomson W 1857 Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinburgh 21 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Callen H B 1948 Phys. Rev. 73 1349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Onsager L 1931 Phys. Rev. 38 2265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ioffe A F 1957 Semiconductor Thermoelements and Thermoelectric Cooling (London: Infosearch Limited) pp18–21
[14] Heikes R R, Ure R W 1961 Thermoelectricity: Science and Engineering (New York-London: Interscience Publishers)
[15] Harman T C, Honig J M 1967 Thermoelectric and Thermomagnetic Effects and Applications (New York: MCGRAW-HILL)
[16] Rowe D M 2018 Thermoelectrics Handbook: Macro to Nano (Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press)
[17] Lee S, von Allmen P 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 88 022107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 杨振, 朱璨, 柯亚娇, 何雄, 罗丰, 王剑, 王嘉赋, 孙志刚 2021 70 108402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Z, Zhu C, Ke Y J, He X, Luo F, Jianl W, Wang J F, Sun Z G 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 108402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zebarjadi M, Esfarjani K, Shakouri A 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 122104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Sanchez D, Lopez R 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 026804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Kulik I O 1994 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 6 9737
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bogachek E N, Scherbakov A G, Landman U 1998 Solid State Commun. 108 851
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Garrido J, Casanovas A 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 115 123517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Straube H, Wagner J M, Breitenstein O 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 052107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Ma J, Sinha S 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 112 073719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Jin W L, Liu L Y, Yang T, Shen H G, Zhu J, Xu W, Li S Z, Li Q, Chi L F, Di C A, Zhu D D 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 3586
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Koyano M, Akashi N 2009 J. Electron. Mater. 38 1037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Caswell A E 1911 Phys. Rev. (Series I) 33 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Garrido J, Casanovas A 2012 J. Electron. Mater. 41 1990
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Weber L, Gmelin E 1991 Appl. Phys. A 53 136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Fukushima A, Kubota H, Yamamoto A, Suzuki Y, Yuasa S 2006 J. Appl. Phys. 99 08H706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Breitenstein O, Warta W, Langenkamp M 2010 Lock-in Thermography: Basics and Use for Evaluating Electronic Devices and Materials (Vol. 10) (Berlin: Springer)
[33] Verma R, Behera U, Kasthurirengan S, Shivaprakash N, Udgata S, Gangradey R 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 171 012098
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Thomson W 1857 Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. A 3 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Bhatt R, Bohra A K, Bhattacharya S, Basu R, Ahmad S, Singh A, Muthe K P, Gadkari S C 2017 AIP Conf Proc. 1832 060021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Borup K A, de Boor J, Wang H, Drymiotis F, Gascoin F, Shi X, Chen L D, Fedorov M I, Muller E, Iversena B B, Snyder G J 2015 Energy Environ. Sci. 8 423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Zhang C, de la Mata M, Li Z, et al. 2016 Nano Energy 30 630
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Yang Z, He B, He X, Luo F, Wang J, Zhu C, Liu H, Sun Z 2022 Energy Convers. Manage. 267 115871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Arisaka T, Otsuka M, Hasegawa Y 2019 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90 046104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
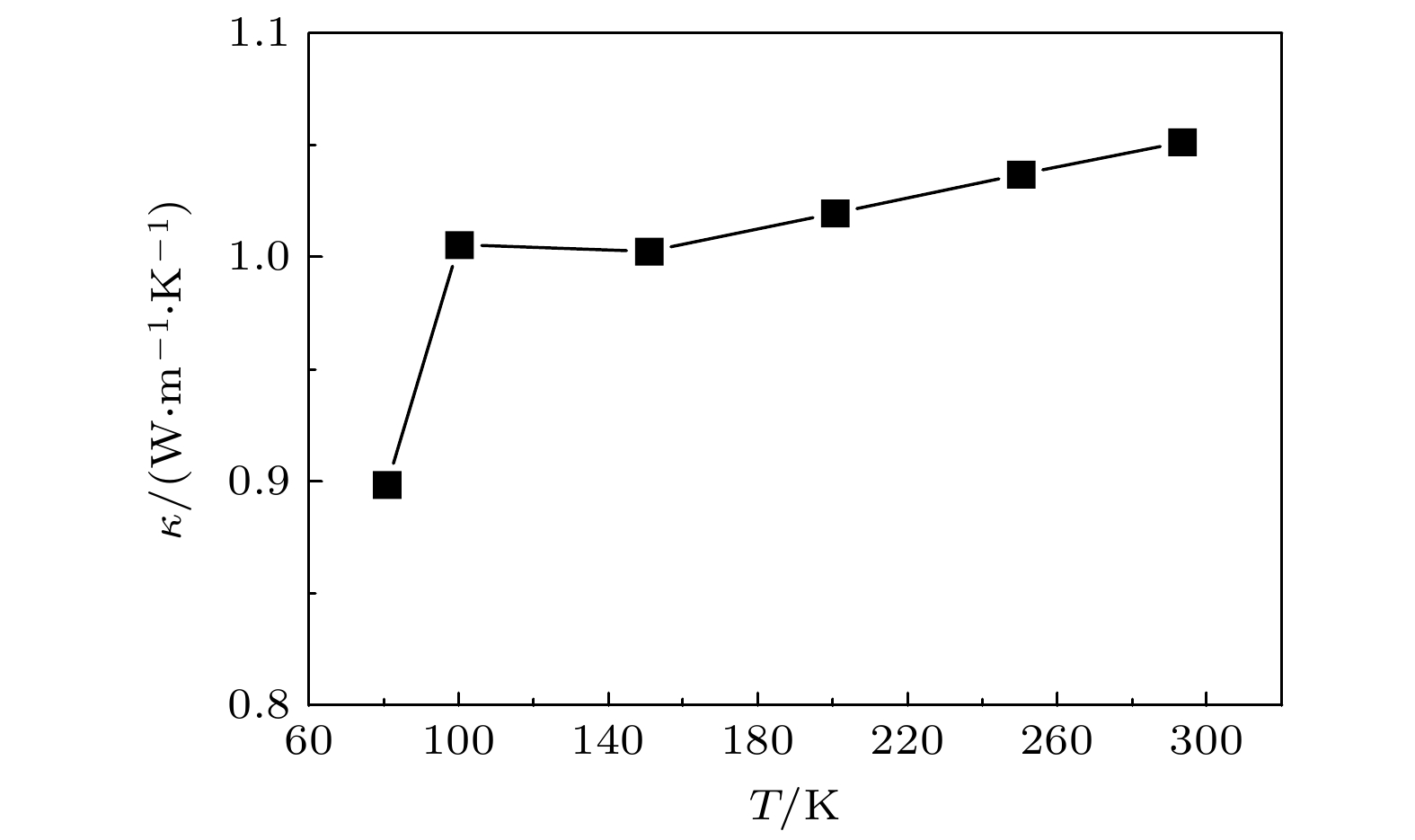
图 3 (a) 用于计算树脂厚度对温差影响的数模, 参数配置与正文中一致(图中温差ΔT为TC1点与TC2点的温度差, h为树脂层的厚度); (b)树脂层厚度对瞬态温差的影响
Figure 3. (a) Mathematical model for calculating the influence of resin thickness on temperature difference. The parameter configuration of the model is consistent with the body. ΔT is the temperature difference between TC1 and TC2, and h is the thickness of the resin layer. (b) The influence of resin layer thickness on transient temperature difference
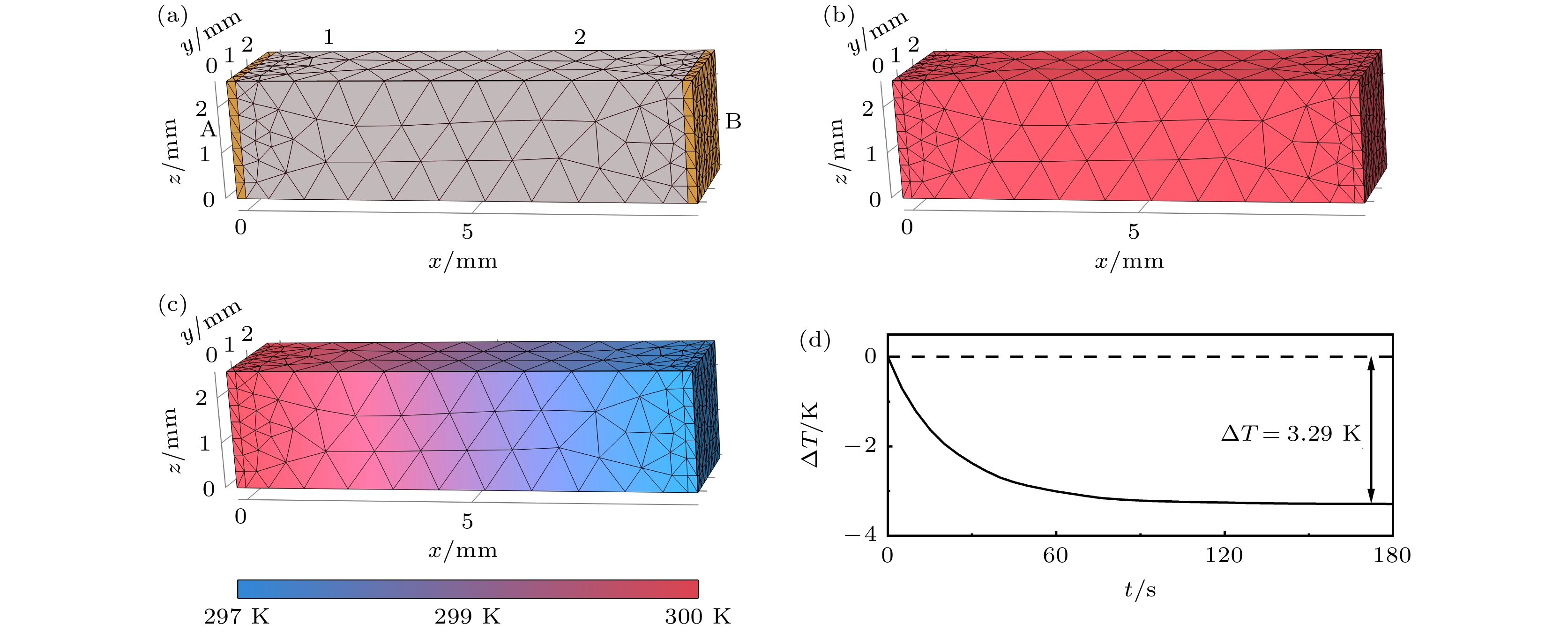
图 4 (a) 用于瞬态法计算的COMSOL数学模型; 通电(b) 0 和(c) 180 s时, 样品表面的温度分布; (d) 探针1, 2之间的温差随时间变化的曲线图
Figure 4. (a) COMSOL mathematical model for transient calculation. The temperature distribution on the surface of the sample at (b) 0 and (c) 180 s. (d) The curve of transient temperature difference between probe 1 and probe 2.
图 5 (a) 300 K时不同热源参数UB时的总体方差L; (b) +100 mA电流和最优UB值(–58.6 mV)下瞬态温差测量值(meas.)与模拟值(cal.)随时间的变化
Figure 5. (a) Plot of variance on the coefficient of the boundary heat source at 300 K; (b) the change curve of the transient temperature difference between measured value (meas.) and simulated value (cal.) with time under the condition of +100 mA current and optimum UB (–58.6 mV).
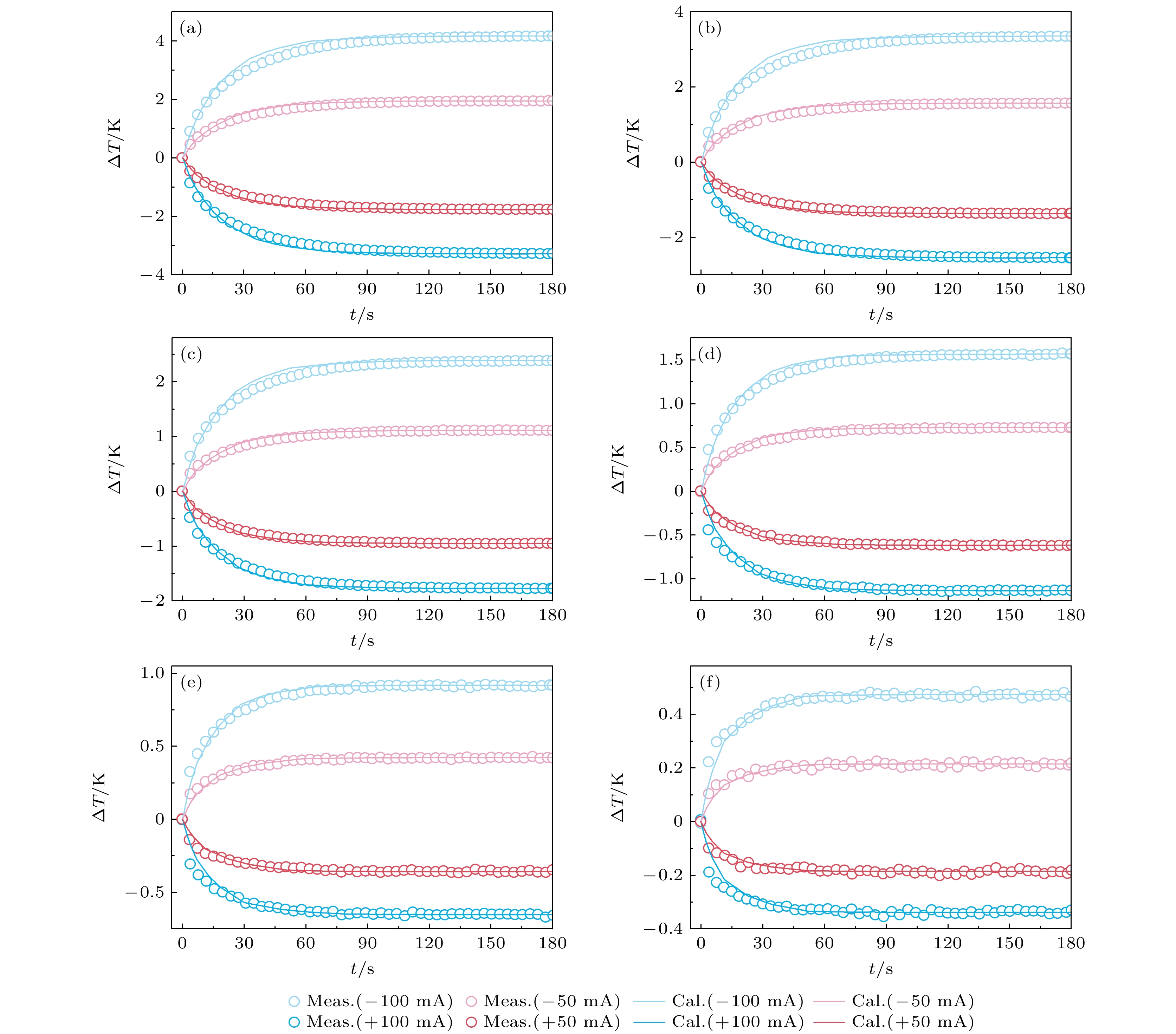
图 7 (a) 300, (b) 260, (c) 220, (d) 180, (e) 140和(f) 100 K时, 对样品分别通入±100 mA和±50 mA电流后, 瞬态温差的测量结果和相应的拟合结果, 其中meas.为测量的数据曲线, cal.为拟合的数据曲线
Figure 7. At (a) 300, (b) 260, (c) 220, (d) 180, (e) 140 and (f) 100 K, the measured transient temperature difference of the sample and its fitting results after ±100 mA and ±50 mA current are applied to the sample respectively. Where meas. is the measured curve, cal. is the fitted curve.
图 8 通入±100 mA和±50 mA电流时, 采用瞬态法(a)拟合的最优界面热源参数UB; (b)测量的Peltier系数Π与相对误差P, 对比了稳态法±100 mA 测量的Peltier系数Π和Peltier系数线性理论值; (c) 界面电阻RB与温度T的关系曲线; (d) 通入±100 mA电流时, B端面Joule热与发热量的比值QJ∕QB与温度T的关系曲线
Figure 8. (a) Optimal interfacial heat source coefficient UB fitted by the transient method when ±100 mA and ±50 mA currents are applied; (b) the measured Peltier coefficients Π and their errors P. The measured Peltier coefficients Π, and the linear theoretical values of Peltier coefficients for the steady-state method ±100 mA are also compared; (c) the relationship between the interface resistance RB and the temperature T; (d) plot of the ratio of Joule heat to heat generation QJ/QB at B-end versus temperature when ±100 mA current is applied.
表 1 Peltier系数测量方法及其结果
Table 1. Measurement methods of the Peltier coefficient and their results.
测量方法 研究对象 测量温度T/K Peltier系数 测量值Π/mV 线性理论值αT/mV 相对误差P 直接法 外部热源补偿 Cu/Bi[28] 291 16.1 16 0.6% 测量热流 碲化铋热电模组[29] 300 124.0±0.7 126 –1.6% 镍铝/镍铬[23] 310 27.2±1.3 12.6 115.8% 锁相热成像(LIT) N型多晶硅[24] 298 –72±10 –43[25] 67.4% P型多晶硅[24] 298 346±10 360[30] –3.9% 含镍有机薄膜[26] 298 –21.6 –23.5 –8.1% 间接法 测量电阻 金属薄膜界面[31] 295 27.0 — — 测量电压 (Bi, Sb)2Te3[27] 300 31 55 –43.6% 表 2 样品在不同温度下的Joule热与Fourier热(测量电流I = 100 mA)
Table 2. Sample’s Joule and Fourier heat at various temperatures with the measured current I = 100 mA.
测量温度
T/KJoule热
QJ/(10–4 W)Fourier热
QF/(10–3 W)QJ/QF
/%100 0.357 1.33 2.69 140 0.510 2.24 2.28 180 0.756 3.27 2.31 220 1.07 4.59 2.34 260 1.48 6.00 2.47 300 1.88 7.33 2.56 表 3 不同温度、不同电流下测得的稳态温差与相应的稳态法Peltier系数和界面电阻
Table 3. Measured steady-state temperature difference and its Peltier coefficient and interface resistance of steady-state method at different temperatures and currents.
测试温度T/K 不同测试电流I 时的稳态温差∆Tstd./K Peltier系数Πstd./mV 界面电阻RB/mΩ –100 mA +100 mA –50 mA +50 mA ±100 mA ±50 mA ±100 mA ±50 mA 100 0.47 –0.34 0.21 –0.19 –11.38 –11.23 16.49 13.78 140 0.92 –0.65 0.42 –0.36 –19.10 –19.02 28.71 27.24 180 1.56 –1.14 0.73 –0.62 –28.15 –28.10 38.83 39.78 220 2.39 –1.77 1.11 –0.96 –39.85 –39.66 49.89 51.37 260 3.35 –2.55 1.57 –1.38 –52.69 –52.63 58.79 56.42 300 4.17 –3.29 1.95 –1.77 –65.29 –65.22 61.03 46.41 表 4 不同温度、不同电流下测得的热源参数与相应的瞬态法Peltier系数和界面电阻
Table 4. Measured heat source parameters and its Peltier coefficient and interface resistance of transient method at different temperatures and currents.
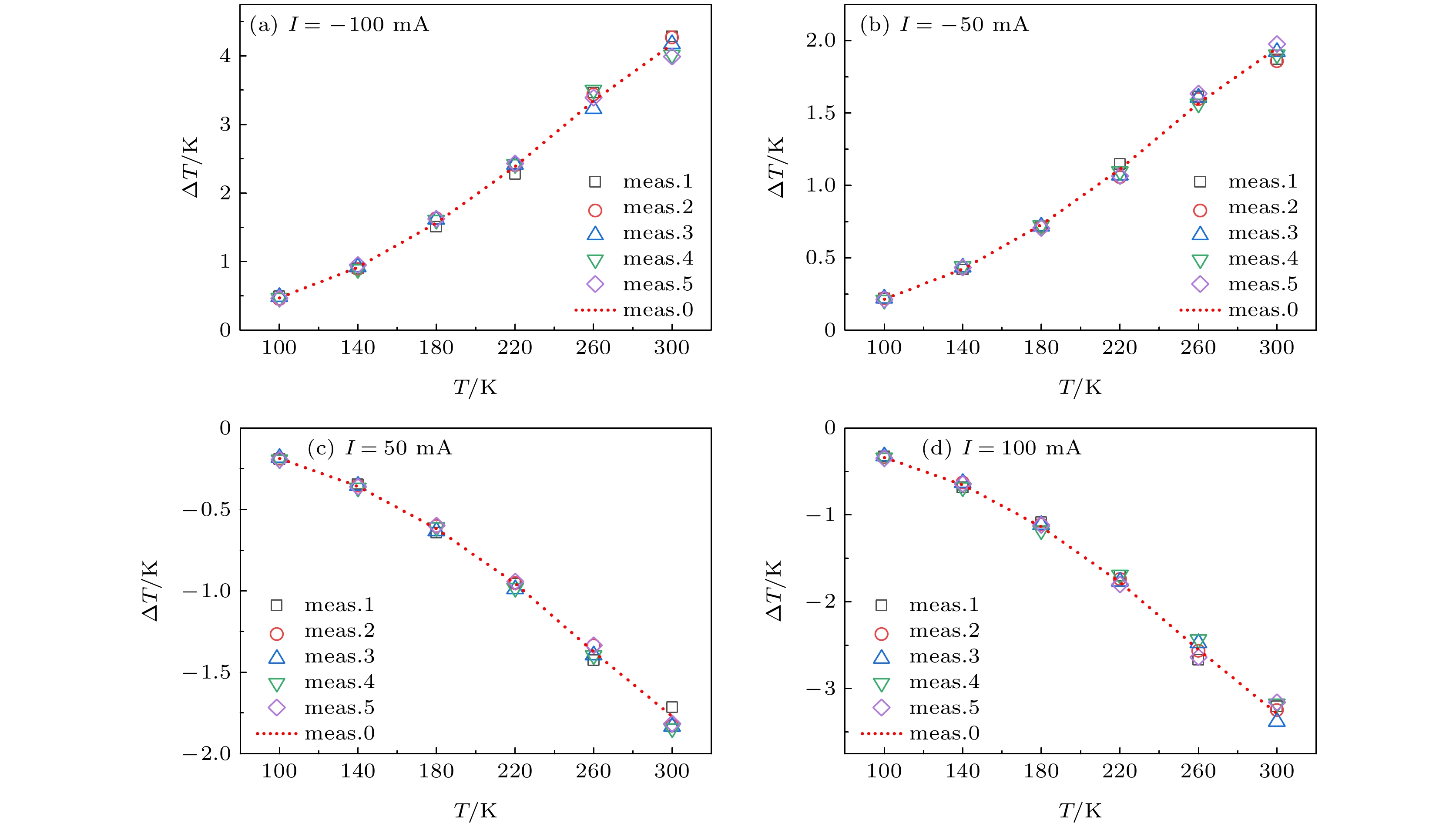
测试温度T/K 不同测试电流I 时的热源参数UB/mV Peltier系数Πtrans./mV 界面电阻RB/mΩ –100 mA +100 mA –50 mA +50 mA ±100 mA ±50 mA ±100 mA ±50 mA 100 –12.41 –9.29 –11.36 –10.06 –10.85 –10.71 15.60 13.00 140 –20.32 –15.09 –18.87 –16.39 –17.71 –17.63 26.15 24.80 180 –30.82 –23.45 –28.98 –25.19 –27.14 –27.09 36.85 37.90 220 –42.99 –33.52 –40.5 –35.63 –38.26 –38.07 47.35 48.70 260 –59.00 –47.11 –55.85 –50.1 –53.06 –52.98 59.45 57.50 300 –70.06 –58.61 –66.49 –62.18 –64.34 –64.34 57.25 43.10 表 5 稳态法Peltier系数的重复测量
Table 5. Repeated measurements of the Peltier coefficients measured by the steady-state method.
组别 稳态法Peltier系数Πstd./mV 100 K 140 K 180 K 220 K 260 K 300 K meas.0 (50 mA) –11.38 –19.10 –28.15 –39.85 –52.69 –65.29 meas.0 (100 mA) –11.23 –19.02 –28.10 –39.66 –52.63 –65.22 meas.1 (50 mA) –11.06 –17.49 –27.89 –39.21 –55.62 –62.88 meas.1 (100 mA) –11.15 –18.18 –26.51 –37.07 –56.12 –65.64 meas.2 (50 mA) –11.09 –17.96 –26.98 –37.49 –53.61 –64.66 meas.2 (100 mA) –10.69 –17.44 –28.07 –38.63 –54.89 –65.96 meas.3 (50 mA) –10.88 –18.11 –27.60 –38.35 –54.90 –65.92 meas.3 (100 mA) –10.93 –17.83 –27.88 –38.96 –52.15 –66.28 meas.4 (50 mA) –10.93 –18.55 –27.27 –38.75 –54.13 –65.75 meas.4 (100 mA) –10.99 –18.07 –28.45 –38.31 –54.30 –63.10 meas.5 (50 mA) –11.00 –18.17 –26.65 –37.45 –54.26 –66.52 meas.5 (100 mA) –11.00 –18.28 –27.99 –39.46 –55.16 –62.71 平均值/mV –10.96 –18.00 –27.53 –38.42 –54.41 –65.01 标准差/mV 0.12 0.31 0.59 0.73 1.04 1.36 平均相对误差/% 1.23 2.20 2.00 1.95 1.80 1.69 -
[1] Mao J, Liu Z H, Zhou J W, Zhu H T, Zhang Q, Chen G, Ren Z F 2018 Adv. Phys. 67 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ambrosi R M, Kramer D P, Watkinson E J, Mesalam R, Barco A 2021 Nucl. Technol. 207 773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Siddique A R M, Mahmud S, Heyst B V 2017 Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 73 730
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Meng F, Chen L, Xie Z, Ge Y 2017 Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 4 106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cao Q, Luan W, Wang T 2018 Appl. Therm. Eng. 130 1472
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hao M R, Yang Y, Zhang S, Shen W Z, Schneider H, Liu H C 2014 Laser Photonics Rev. 8 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jaziri N, Boughamoura A, Muller J, Mezghani B, Tounsi F, Ismail M 2020 Energy Rep. 6 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Saber H H, AlShehri S A, Maref W 2019 Energy Convers. Manage. 191 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Choi H S, Yun S, Whang K I 2007 Appl. Therm. Eng. 27 2841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Thomson W 1857 Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinburgh 21 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Callen H B 1948 Phys. Rev. 73 1349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Onsager L 1931 Phys. Rev. 38 2265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ioffe A F 1957 Semiconductor Thermoelements and Thermoelectric Cooling (London: Infosearch Limited) pp18–21
[14] Heikes R R, Ure R W 1961 Thermoelectricity: Science and Engineering (New York-London: Interscience Publishers)
[15] Harman T C, Honig J M 1967 Thermoelectric and Thermomagnetic Effects and Applications (New York: MCGRAW-HILL)
[16] Rowe D M 2018 Thermoelectrics Handbook: Macro to Nano (Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press)
[17] Lee S, von Allmen P 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 88 022107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 杨振, 朱璨, 柯亚娇, 何雄, 罗丰, 王剑, 王嘉赋, 孙志刚 2021 70 108402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Z, Zhu C, Ke Y J, He X, Luo F, Jianl W, Wang J F, Sun Z G 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 108402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zebarjadi M, Esfarjani K, Shakouri A 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 122104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Sanchez D, Lopez R 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 026804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Kulik I O 1994 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 6 9737
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bogachek E N, Scherbakov A G, Landman U 1998 Solid State Commun. 108 851
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Garrido J, Casanovas A 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 115 123517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Straube H, Wagner J M, Breitenstein O 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 052107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Ma J, Sinha S 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 112 073719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Jin W L, Liu L Y, Yang T, Shen H G, Zhu J, Xu W, Li S Z, Li Q, Chi L F, Di C A, Zhu D D 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 3586
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Koyano M, Akashi N 2009 J. Electron. Mater. 38 1037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Caswell A E 1911 Phys. Rev. (Series I) 33 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Garrido J, Casanovas A 2012 J. Electron. Mater. 41 1990
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Weber L, Gmelin E 1991 Appl. Phys. A 53 136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Fukushima A, Kubota H, Yamamoto A, Suzuki Y, Yuasa S 2006 J. Appl. Phys. 99 08H706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Breitenstein O, Warta W, Langenkamp M 2010 Lock-in Thermography: Basics and Use for Evaluating Electronic Devices and Materials (Vol. 10) (Berlin: Springer)
[33] Verma R, Behera U, Kasthurirengan S, Shivaprakash N, Udgata S, Gangradey R 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 171 012098
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Thomson W 1857 Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. A 3 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Bhatt R, Bohra A K, Bhattacharya S, Basu R, Ahmad S, Singh A, Muthe K P, Gadkari S C 2017 AIP Conf Proc. 1832 060021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Borup K A, de Boor J, Wang H, Drymiotis F, Gascoin F, Shi X, Chen L D, Fedorov M I, Muller E, Iversena B B, Snyder G J 2015 Energy Environ. Sci. 8 423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Zhang C, de la Mata M, Li Z, et al. 2016 Nano Energy 30 630
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Yang Z, He B, He X, Luo F, Wang J, Zhu C, Liu H, Sun Z 2022 Energy Convers. Manage. 267 115871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Arisaka T, Otsuka M, Hasegawa Y 2019 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90 046104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8488
- PDF Downloads: 90
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: