-
In the study of complex networks, researchers have long focused on the identification of influencing nodes. Based on topological information, several quantitative methods of determining the importance of nodes are proposed. K-shell is an efficient way to find potentially affected nodes. However, the K-shell overemphasizes the influence of the location of the central nodebut ignores the effect of the force of the nodes located at the periphery of the network. Furthermore, the topology of real networks is complex, which makes the computation of the K-shell problem for large scale-free networks extremely difficult. In order to avoid ignoring the contribution of any node in the network to the propagation, this work proposes an improved method based on the iteration factor and information entropy to estimate the propagation capability of each layer of nodes. This method not only achieves the accuracy of node ordering, but also effectively avoids the phenomenon of rich clubs. To evaluate the performance of this method, the SIR model is used to simulate the propagation efficiency of each node, and the algorithm is compared with other algorithms. Experimental results show that this method has better performance than other methods and is suitable for large-scale networks.
-
Keywords:
- influential nodes /
- iteration factor /
- information entropy /
- complex networks
[1] Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A 2002 Phys. Rev. E 65 036104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Leskovec J, Adamic L A, Huberman B A 2007 Acm Trans. Web 1 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Freeman L C 1978 Soc. Networks 1 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Freeman L C 1977 Sociometry 40 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Sabidussi G 1966 Psychometrika 31 581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lü L Y, Zhou T, Zhang Q M, Stanley H E 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 10168
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lü L Y, Chen D B, Ren X L, Zhang Q M, Zhang Y C, Zhou T 2016 Phys. Rep. 650 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Brin S, Page L 1998 Comput. Netw. ISDN Syst. 30 107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lü L Y, Zhang Y C, Yeung C H, Zhou T 2011 PloS One 6 21202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kitsak M, Gallos L K, Havlin S, Liljeros F, Muchnik L, Stanley H E, Makse H A 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Pei S, Muchnik L, Andrade J S, Zheng Z M, Makse H A 2014 Sci. Rep. 4 5547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Montresor A, De Pellegrini F, Miorandi D 2011 Proceedings of the 30th Annual ACM SIGACT-SIGOPS Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing San Jose, CA, June 6–8, 2011 p207
[13] Basaras P, Katsaros D, Tassiulas L 2013 Computer 46 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang Z X, Zhao Y, Xi J K, Du C J 2016 Physica A 461 171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhou S, Mondragon R J 2004 IEEE Commun. Lett. 8 180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang M, Li W C, Guo Y N, Peng X Y, Li Y X 2020 Physica A 554 124229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zareie A, Sheikhahmadi A, Jalili M, Fasaei M S K 2020 Knowledge-Based Syst. 194 105580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 3200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hethcote H W 2000 SIAM Rev. 42 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ma L I, Ma C, Zhang H F, Wang B H 2016 Physica A 451 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li Z, Ren T, Ma X Q, Liu S M, Zhang Y X, Zhou T 2019 Sci. Rep. 9 8387
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bae J, Kim S 2014 Physica A 395 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Bhat N, Aggarwal N, Kumar S 2020 Procedia Comput Sci. 171 662
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 阮逸润, 老松杨, 汤俊, 白亮 2020 71 176401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ruan Y R, Lao S Y, Tang J, Bai L, Guo Y M 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 176401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Colizza V, Flammini A, Serrano M A, Vespignani A 2006 Nat. Phys. 2 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Rui X B, Meng F R, Wang Z X, Yuan G 2019 Appl. Intell. 49 2684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu D, Jing Y, Zhao J, Wang W J, Song G J 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 43330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Namtirtha A, Dutta A, Dutta B 2018 Physica A 499 310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kim H, Anderson R 2012 Phys. Rev. E 85 026107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Takaguchi T, Sato N, Yano K, Masuda N 2012 New J. Phys. 14 093003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Qu C Q, Zhan X X, Wang G H, Wu J L, Zhang Z K 2019 Chaos 29 033116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 胡钢, 许丽鹏, 徐翔 2021 70 108901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu G, Xu L P, Xu X 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 108901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Newman M E J 2006 Phys. Rev. E 74 036104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Yin H, Benson A R, Leskovec J, Gleich D F 2017 Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (Halifax, Candana) August 13–17, 2017 p555
[35] Adamic L A 2005 Glance N Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Link Discovery (New York, USA) 2005 p36
[36] Mcauley J, Leskovec J 2012 Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (Lake Tahoe, Nevada) 2012 p539
[37] Leskovec J, Huttenlocher D, Kleinberg J 2010 Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on World Wide Web (New York, USA) 2010 p65
[38] Rozemberczki B, Davies R, Sarkar R, Sutton C 2019 Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining New York, USA, 2019 p65
[39] Rocha L, Liljeros F, Holme P 2011 PLoS Comput. Biol. 7 1001109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Leskovec J, Kleinberg J, Faloutsos C 2007 ACM Trans. Knowl. Discovery Data 1 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Moreno Y, Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A 2002 Eur. Phys. J. B 26 521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Kenall M G 1938 Biometrika 30 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Zhang J X, Chen D B, Dong Q, Zhao Z D 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 27823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Morone F, Makse H 2015 Nature 524 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Goyal A, Lu W, Lakshmanan L 2011 Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on World Wide Web Hyderabad, India, 2011 p47
[46] Jung K, Heo W, Chen W 2012 IEEE 12th International Conference on Data Mining Brussels, Belgium, December 10–13, 2012 p918
-
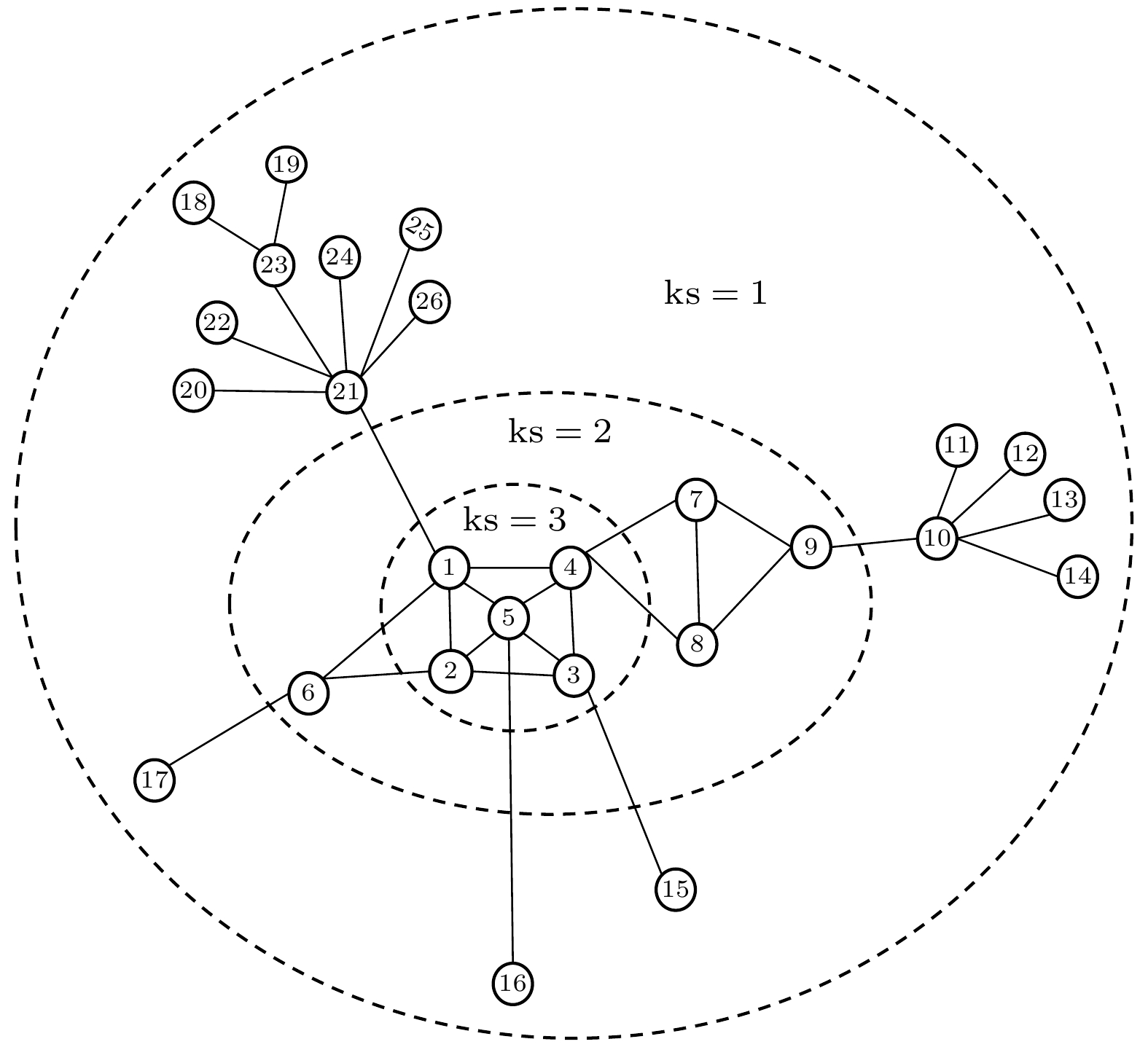
表 1 节点在每个shell中的信息熵
Table 1. Information entropy of each node.
ks Node E 3 1 0.9571 4 0.8565 5 0.8099 2 0.7151 3 0.6366 2 7/8/9 0.4861 6 0.4374 1 21 0.6675 10 0.4034 23 0.3720 20/22/24/25/26 0.2420 11/12/13/14/16 0.1992 15 0.1733 17/18/19 0.1435 表 2 节点在每个迭代层中的信息熵
Table 2. Information entropy of each node.
Iteration Node E+ 7 5 1.3728 6 1 1.4579 4 1.4378 2 1.2159 3 1.0589 5 7/8 0.7839 4 6 0.7189 9 0.6430 3 21 0.8084 2 10 0.4818 23 0.3720 1 16 0.3400 15 0.3139 20/22/24/25/26 0.2420 17 0.2219 11/12/13/14 0.1992 18/19 0.1435 IE+算法伪代码 输入: 网络结构G =(V, E) 输出: 网络中节点的排序索引Rank 1: 通过G = (V, E)得出邻接矩阵A 2: 通过K-shell算法得出每个节点的ks值 3: IT ← 1 4: while |V| do 5: Vtemp ←{ } 6: Vi.k ← $\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{j = 1}^N { {a_{ij} } }$ 7: mindegree ← min(V.k) 8: Vtemp ← find (V. k == mindegree) 9: while Vtemp do 10: Vtemp. IT←IT 11: Vtemp.e+←$ -{\sum }_{j\in \varGamma \left(i\right)}{I}_{j}\cdot {\rm{ln}}{I}_{j}\cdot {\rm{k}}{{\rm{s}}}_{j} $ 12: endwhile 13: delete(Vtemp) 14: IT←IT+1 15: V←V-Vtemp 16: endwhile 17: ITMax ← IT 18: while length(Rank) < N do 19: for IT←ITMax to 1 do 20: Vtemp = find(max(V.IT.e+)) 21: if length (Vtemp) > 1 22: 按节点序号从大到小排序 23: end if 24: Rank ← { Vtemp, Rank} 25: end for 26: end while 27: return Rank 表 3 由不同方法得出的排名: DC, CC, ks, Cnc, Cnc+, IKS, IE+
Table 3. The ranking lists determined by different methonds: DC, CC, ks, Cnc, Cnc+, IKS, IE+.
Rank DC CC ks Cnc Cnc+ IKS IE+ 1 21 1 1—5 4, 5 1 1 5 2 1, 4, 5, 10 4 6—9 1 4, 5 7 1 3 2, 3 5 10—26 2 2 21 8 4 6—9, 23 21 3 3 4 7 5 11—20 7, 8 21 6—8 9 6 6 22, 24—26 6 6—8 9, 21 10 21 7 9 10 16 5 10 8 23 9 23 8 16 9 16, 20, 22, 24—26 15, 16, 23 15 23 4 10 17 10, 20, 22, 24—26 2 9 11 others 6 23 12 26 15 13 3 2 14 20, 22, 24, 25 20, 22, 24—262 15 11—13, 14, 16 3 16 15 17 17 17—19 11—14 18 18, 19 表 4 八个常见网络的基本拓扑特征, N和|E|是节点和边的数量,
$ \langle d \rangle $ 和$ \langle k \rangle $ 是平均距离和平均度, c是聚类系数, βth和βc是流行阈值和传播值Table 4. The basic topological features of the eight real neworks, N and |E|, |E| are the number of nodes and edges,
$ \langle d \rangle $ and$ \langle k \rangle $ are the average distance and the average degree, c is the clustering coefficient, βth and βc are the epidemic threshold and the spread value.Network N |E| $\langle d \rangle$ c $ \langle k \rangle $ βth βc NS 379 914 6.0419 0.7981 4.8232 0.1247 0.2494 EEC 986 16064 2.5869 0.4505 32.5842 0.0134 0.0268 PB 1222 16714 2.7375 0.3600 27.3552 0.0123 0.0246 Fecebook 4039 88234 3.6925 0.6170 43.6910 0.0094 0.0188 WV 7066 100736 3.2475 0.2090 28.5129 0.0069 0.0138 Sport 13866 86858 4.2748 0.2761 12.5281 0.0260 0.0520 Sex 15810 38540 7.4630 0 4.8754 0.0365 0.0730 CondMat 23122 93497 5.3523 0.6334 8.0835 0.0450 0.0900 表 5 SIR模型中节点影响指数R与五个中心性指数之间的Kendall Tau
Table 5. The Kendall Tau between the node influence index R of SIR model and five centrality indices.
Network DC CC Cnc Cnc+ ks IKS IE+ NS 0.4593 0.3829 0.5604 0.7074 0.4643 0.7301 0.8958 EEC 0.8584 0.8238 0.8999 0.8771 0.8754 0.8963 0.9017 PB 0.8443 0.7956 0.8771 0.8667 0.8653 0.8859 0.9465 Facebook 0.6255 0.4948 0.7416 0.8614 0.6773 0.8926 0.9364 WV 0.8022 0.8583 0.8992 0.8939 0.9171 0.8981 0.9661 Sport 0.6909 0.6891 0.7875 0.8025 0.7437 0.8583 0.9197 Sex 0.4119 0.7329 0.7623 0.8283 0.5151 0.8065 0.8174 CondMat 0.5912 0.7268 0.7303 0.8114 0.6464 0.8565 0.9254 表 6 不同排序方法的单调性 M
Table 6. The monotonicity M of different ranking methods.
Network M(DC) M(CC) M(Cnc) M(Cnc+) M(ks) M(IKS) M(IE+) NS 0.7642 0.9927 0.9302 0.9593 0.6428 0.8286 0.9221 EEC 0.9571 0.9828 0.9748 0.9998 0.9216 0.9328 0.9881 PB 0.9328 0.9301 0.9433 0.9586 0.9063 0.9266 0.9721 Facebook 0.9398 0.9667 0.9355 0.9646 0.9419 0.9457 0.9898 Sport 0.9032 0.9534 0.9292 0.9377 0.8606 0.9137 0.9818 Sex 0.6001 0.9122 0.9332 0.9581 0.5287 0.9248 0.9989 CondMat 0.8615 0.9544 0.9871 0.9864 0.8032 0.9069 0.9996 -
[1] Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A 2002 Phys. Rev. E 65 036104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Leskovec J, Adamic L A, Huberman B A 2007 Acm Trans. Web 1 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Freeman L C 1978 Soc. Networks 1 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Freeman L C 1977 Sociometry 40 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Sabidussi G 1966 Psychometrika 31 581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lü L Y, Zhou T, Zhang Q M, Stanley H E 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 10168
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lü L Y, Chen D B, Ren X L, Zhang Q M, Zhang Y C, Zhou T 2016 Phys. Rep. 650 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Brin S, Page L 1998 Comput. Netw. ISDN Syst. 30 107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lü L Y, Zhang Y C, Yeung C H, Zhou T 2011 PloS One 6 21202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kitsak M, Gallos L K, Havlin S, Liljeros F, Muchnik L, Stanley H E, Makse H A 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Pei S, Muchnik L, Andrade J S, Zheng Z M, Makse H A 2014 Sci. Rep. 4 5547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Montresor A, De Pellegrini F, Miorandi D 2011 Proceedings of the 30th Annual ACM SIGACT-SIGOPS Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing San Jose, CA, June 6–8, 2011 p207
[13] Basaras P, Katsaros D, Tassiulas L 2013 Computer 46 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang Z X, Zhao Y, Xi J K, Du C J 2016 Physica A 461 171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhou S, Mondragon R J 2004 IEEE Commun. Lett. 8 180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang M, Li W C, Guo Y N, Peng X Y, Li Y X 2020 Physica A 554 124229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zareie A, Sheikhahmadi A, Jalili M, Fasaei M S K 2020 Knowledge-Based Syst. 194 105580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 3200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hethcote H W 2000 SIAM Rev. 42 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ma L I, Ma C, Zhang H F, Wang B H 2016 Physica A 451 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li Z, Ren T, Ma X Q, Liu S M, Zhang Y X, Zhou T 2019 Sci. Rep. 9 8387
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bae J, Kim S 2014 Physica A 395 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Bhat N, Aggarwal N, Kumar S 2020 Procedia Comput Sci. 171 662
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 阮逸润, 老松杨, 汤俊, 白亮 2020 71 176401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ruan Y R, Lao S Y, Tang J, Bai L, Guo Y M 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 176401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Colizza V, Flammini A, Serrano M A, Vespignani A 2006 Nat. Phys. 2 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Rui X B, Meng F R, Wang Z X, Yuan G 2019 Appl. Intell. 49 2684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu D, Jing Y, Zhao J, Wang W J, Song G J 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 43330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Namtirtha A, Dutta A, Dutta B 2018 Physica A 499 310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kim H, Anderson R 2012 Phys. Rev. E 85 026107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Takaguchi T, Sato N, Yano K, Masuda N 2012 New J. Phys. 14 093003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Qu C Q, Zhan X X, Wang G H, Wu J L, Zhang Z K 2019 Chaos 29 033116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 胡钢, 许丽鹏, 徐翔 2021 70 108901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu G, Xu L P, Xu X 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 108901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Newman M E J 2006 Phys. Rev. E 74 036104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Yin H, Benson A R, Leskovec J, Gleich D F 2017 Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (Halifax, Candana) August 13–17, 2017 p555
[35] Adamic L A 2005 Glance N Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Link Discovery (New York, USA) 2005 p36
[36] Mcauley J, Leskovec J 2012 Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (Lake Tahoe, Nevada) 2012 p539
[37] Leskovec J, Huttenlocher D, Kleinberg J 2010 Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on World Wide Web (New York, USA) 2010 p65
[38] Rozemberczki B, Davies R, Sarkar R, Sutton C 2019 Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining New York, USA, 2019 p65
[39] Rocha L, Liljeros F, Holme P 2011 PLoS Comput. Biol. 7 1001109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Leskovec J, Kleinberg J, Faloutsos C 2007 ACM Trans. Knowl. Discovery Data 1 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Moreno Y, Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A 2002 Eur. Phys. J. B 26 521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Kenall M G 1938 Biometrika 30 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Zhang J X, Chen D B, Dong Q, Zhao Z D 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 27823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Morone F, Makse H 2015 Nature 524 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Goyal A, Lu W, Lakshmanan L 2011 Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on World Wide Web Hyderabad, India, 2011 p47
[46] Jung K, Heo W, Chen W 2012 IEEE 12th International Conference on Data Mining Brussels, Belgium, December 10–13, 2012 p918
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6691
- PDF Downloads: 220
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad:







