-
识别复杂网络中的传播关键节点在加速信息扩散、抑制病毒或谣言的传播等应用中至关重要. 现有识别网络传播中关键节点的方法各有局限: 复杂网络中心性方法仅从局域或者全局拓扑结构预测节点影响力; 传统机器学习和深度学习方法不适用于图结构数据; 已有基于图神经网络的方法忽视了传播过程自身的动力学特性. 鉴于此, 本文提出一种融合传播过程动力学特征与节点局域结构的传播动态图神经网络(propagation dynamics graph neural network, PDGNN), 用于识别复杂网络传播中的关键节点. 通过结合易感-感染-恢复传播模型, 提取节点传播过程中的动态感染特征, 构建高维特征向量并设计优化的损失函数, 以实现对复杂网络传播关键节点的准确识别. 在2个合成网络和7个真实网络上的实验结果表明, PDGNN在复杂网络传播关键节点识别准确性上优于经典的中心性方法、基于传统机器学习和深度学习的方法以及现有的基于图神经网络的方法.Identifying the most influential nodes in the spreading process in complex networks is crucial in many applications, such as accelerating the diffusion of information and suppressing the spread of viruses or rumors. Existing methods of identifying influential spreaders have their limitations. Specifically speaking, classical network centrality methods rely solely on local or global topology to predict node influence; traditional machine learning and deep learning methods are not suitable for graph-structured data; existing graph neural network-based methods neglect the dynamic characteristics of the propagation process itself. Researchers have pointed out that the spreading influence of nodes not only depends on their structural location, but is also significantly influenced by the dynamics of the spreading process itself. In this work, we propose a propagation dynamics graph neural network (PDGNN) that integrates the dynamic features of the propagation process and the structural features of nodes to identify influential nodes. Specifically speaking, based on the susceptible-infected-recovered (SIR) propagation model, the dynamic infection features and potential infection capacity of nodes are extracted from the epidemic spreading process. Then a high-dimensional feature vector of each node consisting of the embedding and degree of its local transmission tree, as well as its dynamics-sensitive centrality is constructed and used as the input to the graph neural network. To deal with the problem of imbalanced numbers between critical nodes and non-critical nodes in training the model and optimizing the output, an optimized loss function is designed, which combines focal loss with mean squared error. Experimental results in two synthetic networks and seven real-world networks show that the PDGNN outperforms classical centrality methods, traditional machine learning and deep learning-based methods, and existing graph neural network-based methods in identifying influential nodes in the spreading process in complex networks. The performance of PDGNN is robust when the infection rate and the size of the training set change. In a wide range of infection rates, the proposed PDGNN can accurately identify influential spreaders. Despite the fact that the training set accounts for 30% of the total dataset, the PDGNN has the smallest inaccuracy in all nine studied networks.
-
Keywords:
- complex networks /
- influential nodes /
- graph neural network /
- local transmission tree
[1] 汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣 2012 网络科学导论 (北京: 高等教育出版社)第7—14页
Wang X F, Li X, Chen G R 2012 Network Science: An Introduction (Beijing: Higher Education Press) pp7–14
[2] Nielsen B F, Simonsen L, Sneppen K 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 118301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Song K, Park H, Lee J, Kim A, Jung J 2023 Sci. Rep. 13 11469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kitsak M, Gallos L K, Havlin S, Liljeros F, Muchnik L, Stanley H E, Makse H A 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kim S, Jiang J Y, Han J, Wang W 2023 Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media Limassol, Cyprus, June 5–8 2023, pp482–493
[6] Lü L, Chen D, Ren X L, Zhang Q M, Zhang Y C, Zhou T 2016 Phys. Rep. 650 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Pei S, Morone F, Makse H A 2018 Complex Spreading Phenomena in Social Systems: Influence and Contagion in Real-World Social Networks (Berlin: Springer) pp125–148
[8] Liu J, Li X, Dong J 2021 Sci. China Tech. Sci. 64 451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Fan T, Lü L, Shi D, Zhou T 2021 Commun. Phys. 4 272
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liu Y, Zeng Q, Pan L, Tang M 2023 IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 10 2201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhao G, Jia P, Huang C, Zhou A, Fang Y 2020 IEEE Access 8 65462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Asgharian Rezaei A, Munoz J, Jalili M, Khayyam H 2023 Expert Syst. Appl. 214 119086
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yu E Y, Wang Y P, Fu Y, Chen D B, Xie M 2020 Knowledge-Based Syst. 198 105893
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ou Y, Guo Q, Xing J L, Liu J G 2022 Expert. Syst. Appl. 203 117515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ahmad W, Wang B, Chen S 2024 Appl. Intell. 54 3260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhao G, Jia P, Zhou A, Zhang B 2020 Neurocomputing 414 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Rashid Y, Bhat J I 2024 Knowledge-Based Syst. 283 111163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xiong Y, Hu Z, Su C, Cai S M, Zhou T 2024 Appl. Soft Comput. 163 111895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Munikoti S, Das L, Natarajan B 2021 In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Melbourne, Australia, October 17–20 2021, pp3245–3251
[20] Xhonneux L P, Qu M, Tang J 2020 Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning Virtual Event, July 13–18 2020, pp10432–10441
[21] Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 3200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wang W, Tang M, Zhang H F, Gao H, Do Y, Liu Z H 2014 Phys. Rev. E 90 042803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 李江, 刘影, 王伟, 周涛 2024 73 048901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J, Liu Y, Wang W, Zhou T 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 048901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Šikić M, Lančić A, Antulov-Fantulin N, Štefančić H 2013 Eur. Phys. J. B 86 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Lawyer G 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 8665
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Liu Y, Tang M, Zhou T, Do Y 2016 Phys. A 452 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Narayanan A, Chandramohan M, Venkatesan R, Chen L H, Liu Y, Jaiswal S 2017 arXiv: 1707.05005 [cs.LG]
[28] Liu J G, Lin J H, Guo Q, Zhou T 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 21380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wu Y, Hu Y, Yin S, Cai B, Tang X, Li X 2024 Knowledge-Based Syst. 301 112235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K, Dollár P 2017 Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Venice, Italy, October 22–29 2017, pp2980–2988
[31] Rozemberczki B, Allen C, Sarkar R 2021 J. Complex Netw. 9 cnab014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Spring N, Mahajan R, Wetherall D, Anderson T 2004 IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 12 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Adamic L A, Glance N 2005 Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Link Discovery Chicago Illinois, USA, August 21–25 2005, pp36–43
[34] Gleiser P M, Danon L 2003 Adv. Complex. Syst. 6 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Watts D J, Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Rossi R, Ahmed N 2015 Proceedings of the 29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence Austin, Texas, USA, January 25–30 2015, pp4292–4293
[37] Panzarasa P, Opsahl T, Carley K M 2009 J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 60 911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Castellano C, Pastor-Satorras R 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 218701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] 李睿琪, 王伟, 舒盼盼, 杨慧, 潘黎明, 崔爱香, 唐明 2016 复杂系统与复杂性科学 13 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li R Q, Wang W, Shu P P, Yang H, Pan L M, Cui A X, Tang M 2016 Complex Syst. Complex Sci. 13 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Morone F, Makse H A 2015 Nature 524 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
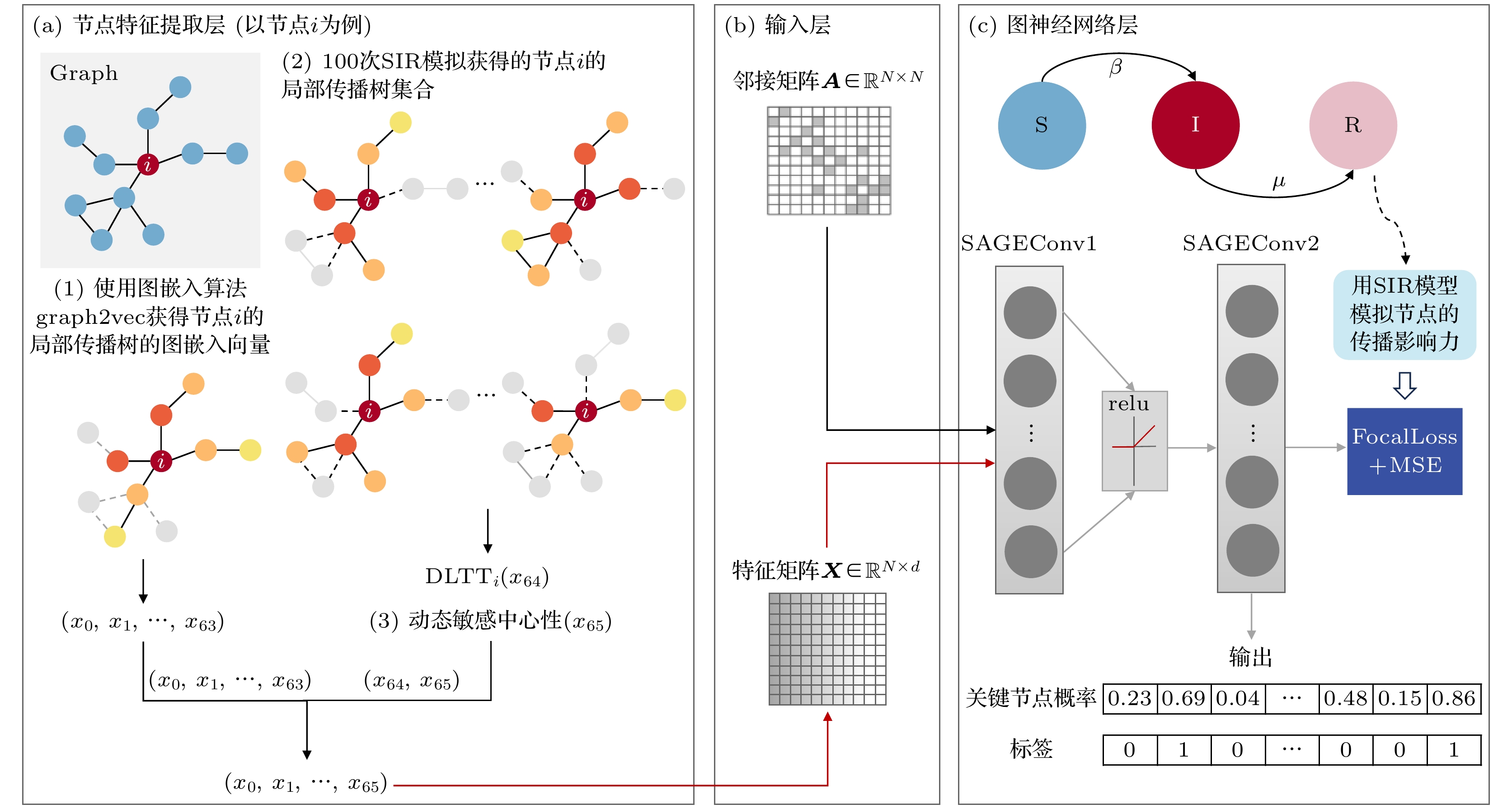
图 1 PDGNN框架, 以11个节点和11条边组成的网络G作为示例 (a)计算图G中每个节点的三个特征, 作为每个节点的特征向量, 进而得到G的特征矩阵X; (b)将特征矩阵X和图的邻接矩阵A作为模型的输入; (c)使用包含两层SAGEConv的图神经网络模型进行训练, 计算损失函数, 根据损失函数值对模型参数进行优化, 使用训练好的模型进行分类, 输出测试集中每个节点的分类概率和预测类别
Fig. 1. Framework of PDGNN. A network G consisting of 11 nodes and 11 edges is used as an example: (a) Three features of each node in graph G are calculated and uesd as the feature vectors of each node, which form feature matrix X of graph G; (b) the feature matrix X and adjacency matrix A of the graph are used as the inputs of the model; (c) the graph neural network model with two layers of SAGEConv is trained and the loss function is calculated. Based on the loss function, the model’s parameters are optimized. By using the trained model, the classification probabilities and predicted class of each node in the test set are output.
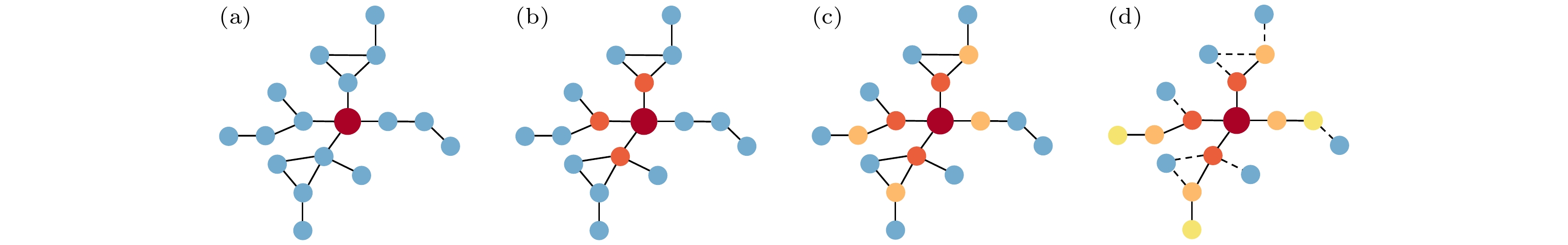
图 2 感染节点的局部传播树 (a)网络的局域结构, 红色节点为初始I态节点, 蓝色节点为S态节点. (b)—(d)三步SIR传播中, 局部传播树的生成过程. 图中深橙、浅橙和黄色节点分别表示第一步、第二步、第三步传播被感染的节点. 最终生成的局部传播树由图(d)中红、深橙、浅橙和黄色节点及它们之间的连边共同构成. 虚线表示局部传播树与其余节点之间的连接, 连接的数目定义为局部传播树的度
Fig. 2. Local transmission tree for the infected node: (a) Local structure of the network. The red node is in I state and blue nodes are in S state initially. (b)–(d) The generation of local transmission tree in a three-step SIR propagation. The dark orange, light orange and yellow nodes in the graph are nodes infected in the first, second and third steps of transmission respectively. The generated local transmission tree in panel (d) consists of the red, dark orange, light orange and yellow nodes and the connecting edges between them. The dashed lines indicate the connections between the local transmission tree and the remaining nodes, and the number of connections is defined as the degree of the local transmission tree.
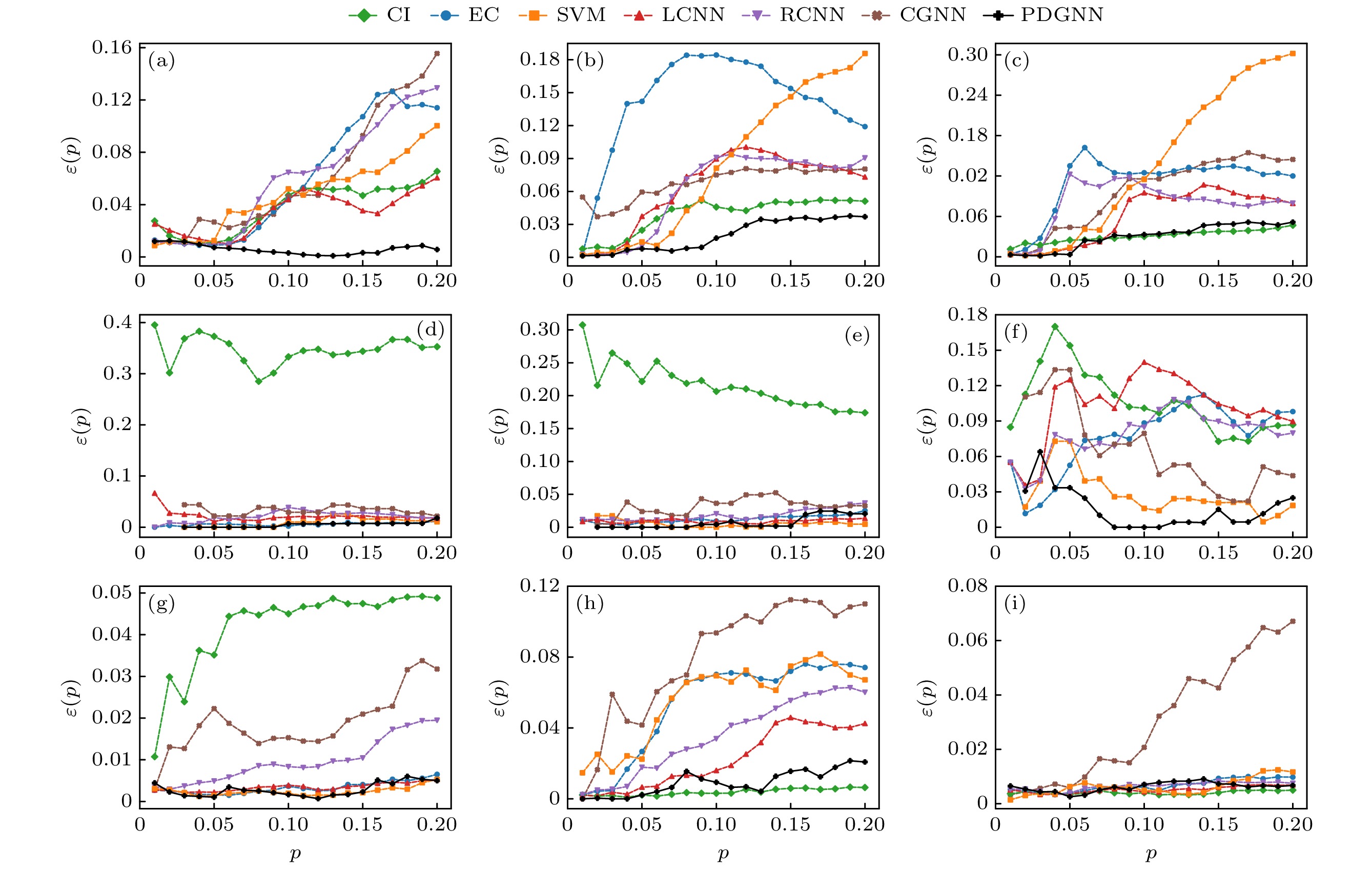
图 3 7个方法在9个网络上的不精确函数曲线 (a) Musae_chameleon; (b) Router; (c) Blogs; (d) Jazz; (e) Celegans; (f) Ca-netscience; (g) CollegeMsg; (h) SCF1; (i) SCF2
Fig. 3. The imprecision function curves for seven methods in nine networks: (a) Musae_chameleon; (b) Router; (c) Blogs; (d) Jazz; (e) Celegans; (f) Ca-netscience; (g) CollegeMsg; (h) SCF1; (i) SCF2.
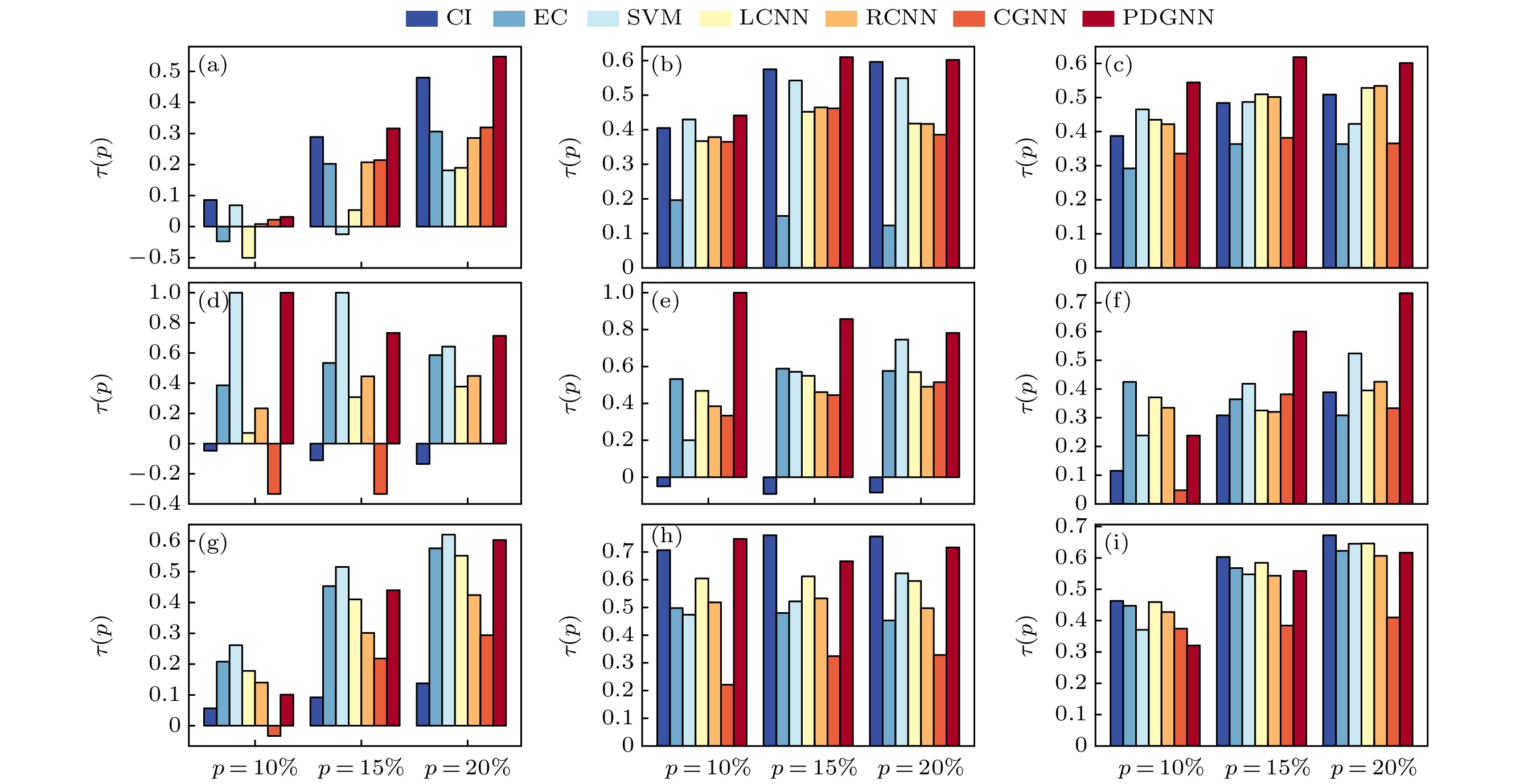
图 4 7个方法在9个网络上得到的节点重要性排序与真实传播影响力排序之间的肯德尔相关系数. 实际传播能力排序在前p 的节点被用于计算 (a) Musae_chameleon; (b) Router; (c) Blogs; (d) Jazz; (e) Celegans; (f) Ca-netscience; (g) CollegeMsg; (h) SCF1; (i) SCF2
Fig. 4. Kendall’s τ correlation between nodes’ importance and their real spreading influence under seven methods in nine networks. The top ranked p nodes with the highest spreading influence are taken into calculation: (a) Musae_chameleon; (b) Router; (c) Blogs; (d) Jazz; (e) Celegans; (f) Ca-netscience; (g) CollegeMsg; (h) SCF1; (i) SCF2.
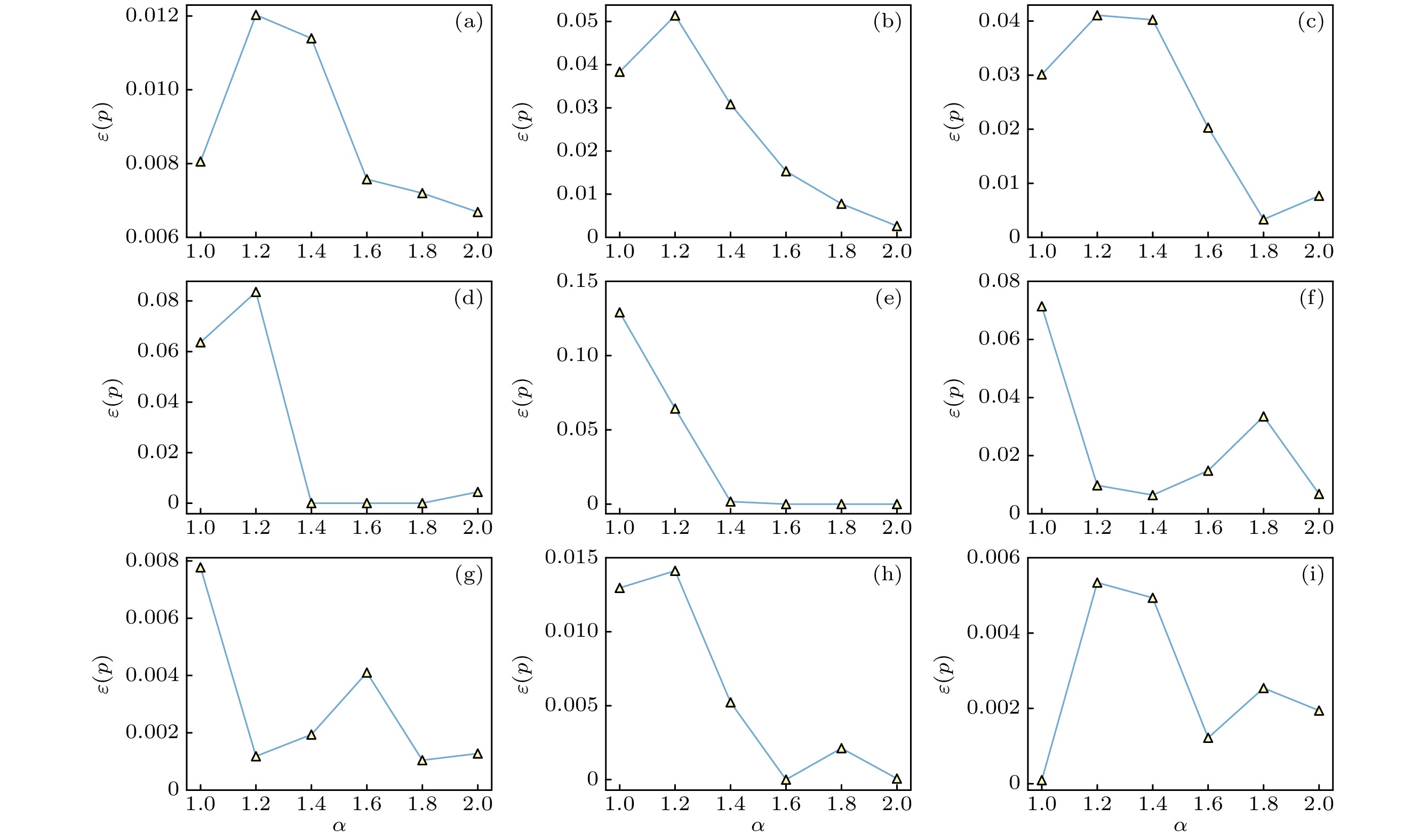
图 5 不同感染速率下PDGNN模型的不精确函数值. α表示传播阈值$ \beta_{\mathrm{c}} $的倍数, $ p=5{\text{%}} $, 训练集比例$ r=60{\text{%}} $ (a) Musae_chameleon; (b) Router; (c) Blogs; (d) Jazz; (e) Celegans; (f) Ca-netscience; (g) CollegeMsg; (h) SCF1; (i) SCF2
Fig. 5. Imprecisions of PDGNN under different infection rates $ \beta=\alpha\beta_{\mathrm{c}} $. Other parameters are set as $ p=5{\text{%}} $, the training set fraction $ r=60{\text{%}} $ and recovery rate $ \mu=1 $: (a) Musae_chameleon; (b) Router; (c) Blogs; (d) Jazz; (e) Celegans; (f) Ca-netscience; (g) CollegeMsg; (h) SCF1; (i) SCF2.
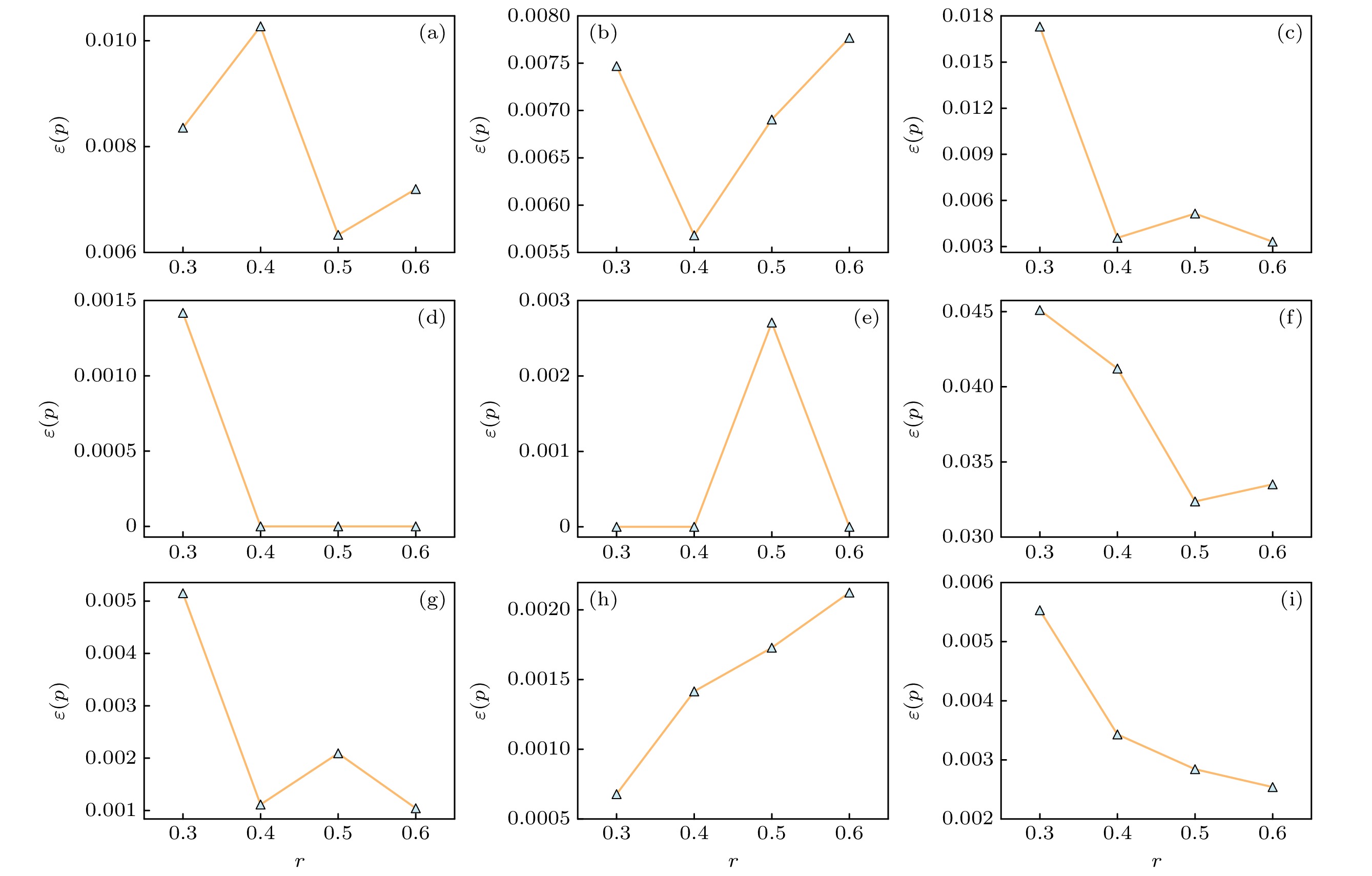
图 6 不同训练集比例下PDGNN模型的不精确函数值. 其中$ p=5{\text{%}} $, 感染速率$ \beta=1. 8\beta_{\mathrm{c }}$ (a) Musae_chameleon; (b) Router; (c) Blogs; (d) Jazz; (e) Celegans; (f) Ca-netscience; (g) CollegeMsg; (h) SCF1; (i) SCF2
Fig. 6. Imprecision of the PDGNN model under different training fractions. Other parameters are set as $ p=5{\text{%}} $, infection rate $ \beta=1. 8\beta_{\mathrm{c}} $ and recovery rate $ \mu=1 $: (a) Musae_chameleon; (b) Router; (c) Blogs; (d) Jazz; (e) Celegans; (f) Ca-netscience; (g) CollegeMsg; (h) SCF1; (i) SCF2.
表 1 9个网络的统计特性. $ \left|N\right| $为网络中节点数, $ \left|E\right| $为网络中边数, $ \langle k \rangle $为网络的平均度, $ k_{{\mathrm{max}}} $为网络的最大度, c为网络的平均聚类系数, $ \beta_{\mathrm{c}} $为SIR传播过程的爆发阈值
Table 1. Statistical features of nine networks. $ \left|N\right| $ and $ \left|E\right| $ are the number of nodes and edges in the network respectively, $ \langle k \rangle $ is the average degree, $ k_{{\mathrm{max}}} $ is the maximum degree, c is the average clustering coefficient, and $ \beta_{\mathrm{c}} $ is the epidemic threshold in SIR spreading.
网络 $ \left|N\right| $ $ \left|E\right| $ $ \langle k \rangle $ $ k_{{\mathrm{max}}} $ c $ \beta_{\mathrm{c}} $ Musae_chameleon 2277 31371 27. 555 732 0. 481 0. 036 Router 5022 6258 2. 492 106 0. 012 0. 401 Blogs 3982 6803 3. 417 189 0. 284 0. 293 Jazz 198 2742 27. 69 78 0. 242 0. 036 Celegans 295 2244 15. 214 116 0. 189 0. 066 Ca-netscience 379 914 4. 823 34 0. 741 0. 207 CollegeMsg 1893 13835 14. 62 255 0. 109 0. 068 SCF1 1000 2991 5. 982 99 0. 032 0. 167 SCF2 2000 8997 8. 997 43 0. 009 0. 111 表 2 4个方法在9个网络上的分类性能. 在所有的结果中, 粗体表示最好的结果
Table 2. Classification performance of the four methods in nine networks. Among all the results, we emphasize the best one in bold.
Networks SVM CGNN RF PDGNN Recall PR_AUC Recall PR_AUC Recall PR_AUC Recall PR_AUC Musae_chameleon 0 3603 0.3603 0 0.378 0 0.2667 0.9524 0.3991 Router 0.4048 0.7776 0.3864 0.603 0.4762 0.7714 1 0.8761 Blogs 0.5897 0.8095 0.4651 0.6582 0.3333 0.7134 1 0.9089 Jazz 0 1 0 0.1843 0.5 1 1 1 Celegans 0.6 0.75 0 0 0.2 0.3333 1 0.8889 Ca-netscience 0.1667 0.7452 0 0.1607 0 0.6389 1 1 CollegeMsg 0.1579 0.5673 0.125 0.2968 0.0526 0.6965 1 0.6431 SCF1 0.2 0.5741 0.6 0.7783 0.2 0.4792 1 0.9709 SCF2 0.4091 0.8158 0.2268 0.7653 0.1818 0.8002 1 0.8837 -
[1] 汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣 2012 网络科学导论 (北京: 高等教育出版社)第7—14页
Wang X F, Li X, Chen G R 2012 Network Science: An Introduction (Beijing: Higher Education Press) pp7–14
[2] Nielsen B F, Simonsen L, Sneppen K 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 118301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Song K, Park H, Lee J, Kim A, Jung J 2023 Sci. Rep. 13 11469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kitsak M, Gallos L K, Havlin S, Liljeros F, Muchnik L, Stanley H E, Makse H A 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kim S, Jiang J Y, Han J, Wang W 2023 Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media Limassol, Cyprus, June 5–8 2023, pp482–493
[6] Lü L, Chen D, Ren X L, Zhang Q M, Zhang Y C, Zhou T 2016 Phys. Rep. 650 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Pei S, Morone F, Makse H A 2018 Complex Spreading Phenomena in Social Systems: Influence and Contagion in Real-World Social Networks (Berlin: Springer) pp125–148
[8] Liu J, Li X, Dong J 2021 Sci. China Tech. Sci. 64 451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Fan T, Lü L, Shi D, Zhou T 2021 Commun. Phys. 4 272
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liu Y, Zeng Q, Pan L, Tang M 2023 IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 10 2201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhao G, Jia P, Huang C, Zhou A, Fang Y 2020 IEEE Access 8 65462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Asgharian Rezaei A, Munoz J, Jalili M, Khayyam H 2023 Expert Syst. Appl. 214 119086
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yu E Y, Wang Y P, Fu Y, Chen D B, Xie M 2020 Knowledge-Based Syst. 198 105893
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ou Y, Guo Q, Xing J L, Liu J G 2022 Expert. Syst. Appl. 203 117515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ahmad W, Wang B, Chen S 2024 Appl. Intell. 54 3260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhao G, Jia P, Zhou A, Zhang B 2020 Neurocomputing 414 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Rashid Y, Bhat J I 2024 Knowledge-Based Syst. 283 111163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xiong Y, Hu Z, Su C, Cai S M, Zhou T 2024 Appl. Soft Comput. 163 111895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Munikoti S, Das L, Natarajan B 2021 In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Melbourne, Australia, October 17–20 2021, pp3245–3251
[20] Xhonneux L P, Qu M, Tang J 2020 Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning Virtual Event, July 13–18 2020, pp10432–10441
[21] Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 3200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wang W, Tang M, Zhang H F, Gao H, Do Y, Liu Z H 2014 Phys. Rev. E 90 042803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 李江, 刘影, 王伟, 周涛 2024 73 048901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J, Liu Y, Wang W, Zhou T 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 048901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Šikić M, Lančić A, Antulov-Fantulin N, Štefančić H 2013 Eur. Phys. J. B 86 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Lawyer G 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 8665
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Liu Y, Tang M, Zhou T, Do Y 2016 Phys. A 452 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Narayanan A, Chandramohan M, Venkatesan R, Chen L H, Liu Y, Jaiswal S 2017 arXiv: 1707.05005 [cs.LG]
[28] Liu J G, Lin J H, Guo Q, Zhou T 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 21380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wu Y, Hu Y, Yin S, Cai B, Tang X, Li X 2024 Knowledge-Based Syst. 301 112235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K, Dollár P 2017 Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Venice, Italy, October 22–29 2017, pp2980–2988
[31] Rozemberczki B, Allen C, Sarkar R 2021 J. Complex Netw. 9 cnab014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Spring N, Mahajan R, Wetherall D, Anderson T 2004 IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 12 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Adamic L A, Glance N 2005 Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Link Discovery Chicago Illinois, USA, August 21–25 2005, pp36–43
[34] Gleiser P M, Danon L 2003 Adv. Complex. Syst. 6 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Watts D J, Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Rossi R, Ahmed N 2015 Proceedings of the 29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence Austin, Texas, USA, January 25–30 2015, pp4292–4293
[37] Panzarasa P, Opsahl T, Carley K M 2009 J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 60 911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Castellano C, Pastor-Satorras R 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 218701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] 李睿琪, 王伟, 舒盼盼, 杨慧, 潘黎明, 崔爱香, 唐明 2016 复杂系统与复杂性科学 13 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li R Q, Wang W, Shu P P, Yang H, Pan L M, Cui A X, Tang M 2016 Complex Syst. Complex Sci. 13 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Morone F, Makse H A 2015 Nature 524 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 2630
- PDF下载量: 78
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: