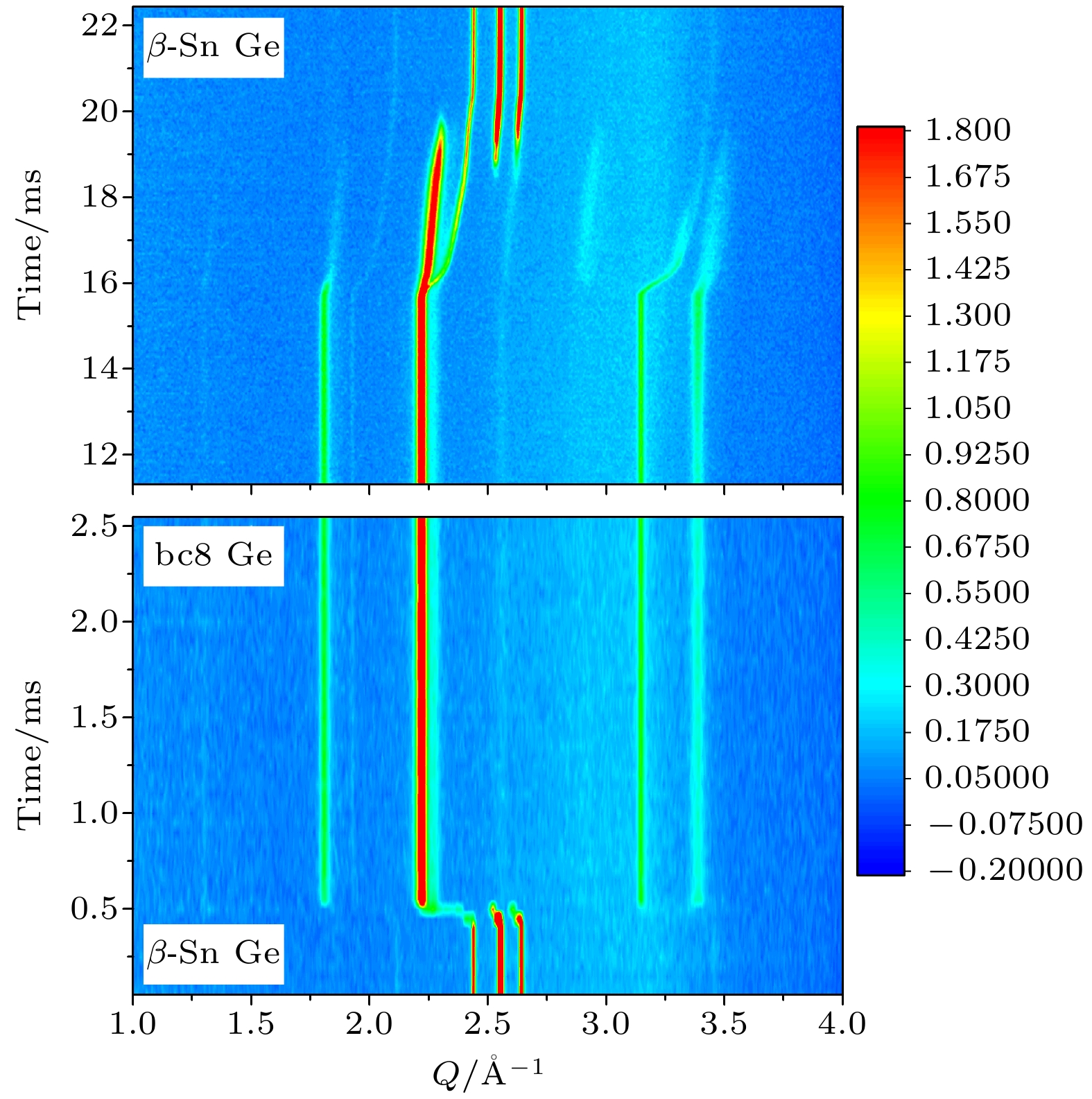
-
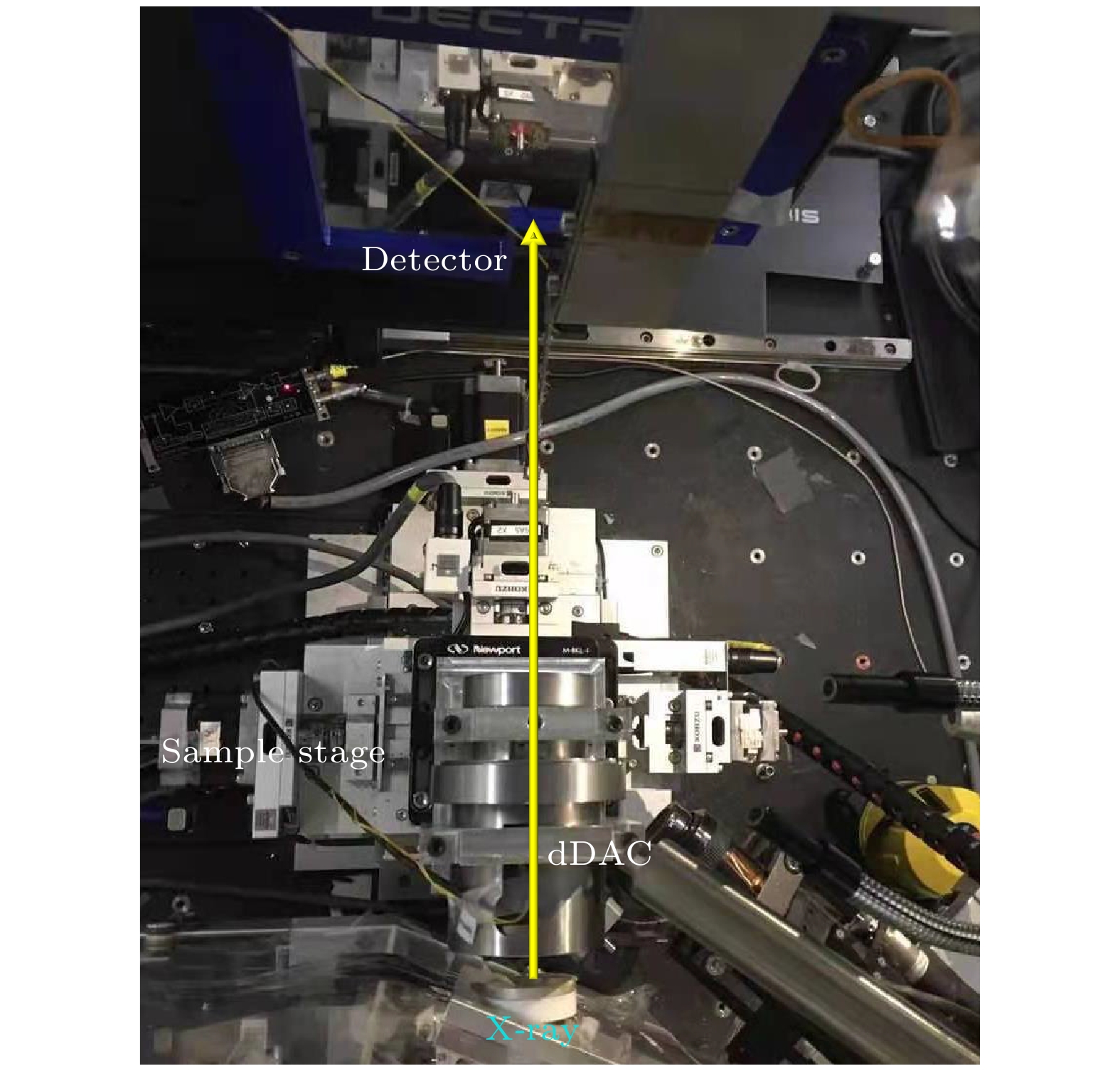
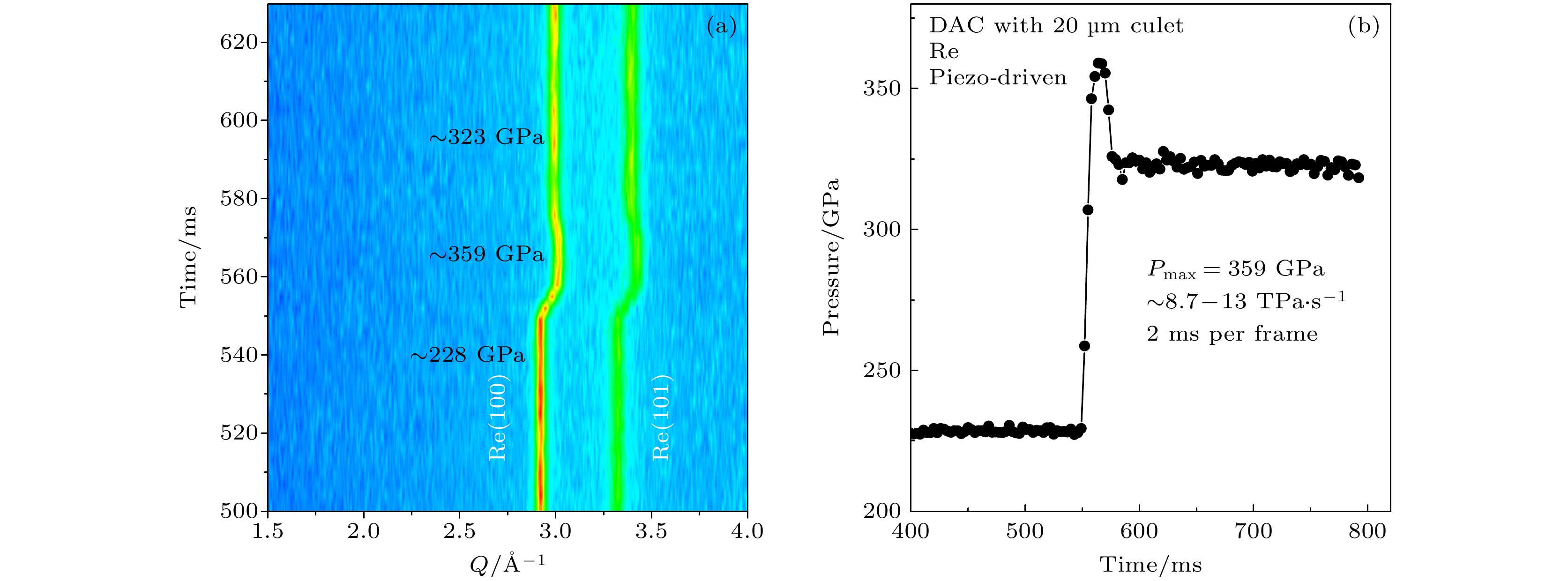
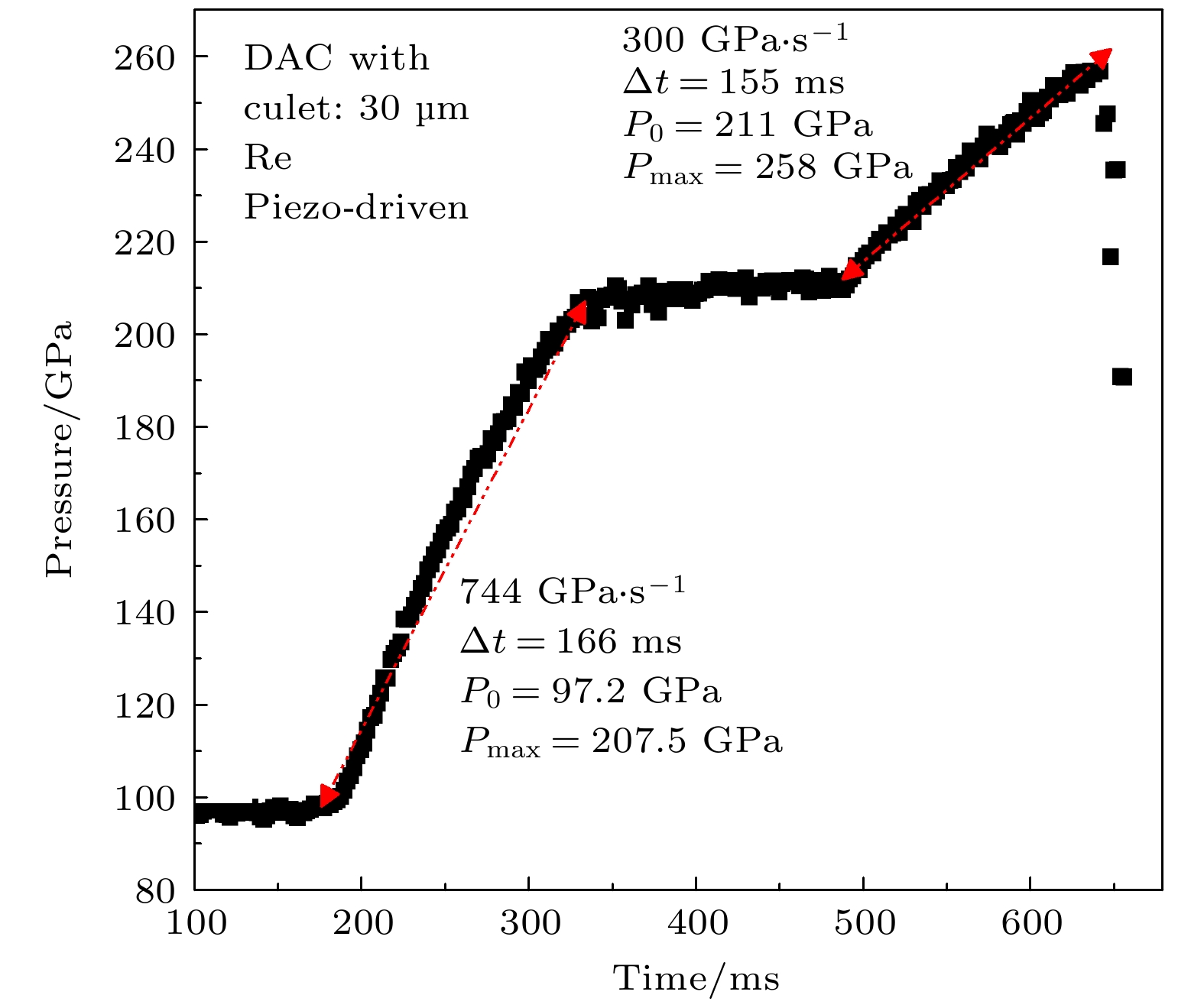
Non-equilibrium transition dynamics under high pressure depends on temperature, pressure and (de)compression rate. The studies require combination of time-resolved probe and rapid compression device on different time scales. Here we report the time-resolved X-ray diffraction (XRD) and dynamic diamond anvil cell (dDAC) system, which were recently developed at the BL15U1 beamline of Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF). There are two rapid loading methods for dDAC. One uses membrane control and the other is piezoelectric actuator driven dDAC. Both methods can dynamically compress the DAC sample chamber up to 300 GPa on millisecond scale (20 μm culet is used), and the time-resolved XRD data are obtained correspondingly. A new type of piezoelectric ceramic dDAC is designed with single-side drive or double-side drive, which allows us to realize extremely high pressure (above 300 GPa) with a fast compression rate of 13 TPa/s. During the rapid compression process, the X-ray diffraction spectra are collected continuously and simultaneously. The XRD detector is Pilatus 3X 900K, which has 2-ms resolution with 500 kHz frame rate. The millisecond time-resolved XRD and high pressure rapid compression system developed at BL15U1 of SSRF enrich the high-pressure experimental methods and enable the beamline to carry out ultra-high pressure experiments, non-equilibrium phase transition and relevant scientific researches.
-
Keywords:
- high pressure /
- dynamic diamond anvil cell /
- time-resolved XRD /
- structural phase transition
[1] 丁迎春, 徐明, 潘洪哲, 沈益斌, 祝文军, 贺红亮 2007 56 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding Y C, Xu M, Pang H Z, Shen Y B, Zhu W J, He H L 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yamanaka T, Fukuda T, Mimaki J 2002 Phys. Chem. Miner. 29 633
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Sui Y, Xu D, Zheng F, Su W 1996 J. Appl. Phys. 80 719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yue S, Cheng L, Liao B, Hu M 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 27125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] John S T, Li Z, Uehara K, Ma Y, Ahuja R 2004 Phys. Rev. B 69 132101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Nakashima M, Tabata K, Thamizhavel A, Kobayashi T C, Hedo M, Uwatoko Y, Shimizu K, Settai R, Ōnuki Y 2004 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16 L255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Levien L, Prewitt C T 1981 Am. Min. 66 324
[8] Abd-Elmeguid M M, Ni B, Khomskii D I, Pocha R, Johrendt D, Wang X, Syassen K 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 126403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Brazhkin V V, Lyapin A G, Stalgorova O V, Gromnitskaya E L, Popova S V, Tsiok O B 1997 J. Non. Crys. Solids 212 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ozoliņš V, Zunger A 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 82 767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sterer E, Silvera I F 2006 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77 115105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Schiferl D, Katz A I, Mills R L, Schmidt L C, Vanderborgh C, Skelton E F, Elam W T, Webb A W, QadriM S B, Schaefer M 1986 Physica B + C 139 897
[13] Shu H, Zhang Y, Wang B, Yang W, Dong H, Tobase T, Ye J, Huang X, Fu S, Zhou Q, Sekine T 2020 Phys. Plasmas 27 030701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Smith J S, Sinogeikin S V, Lin C, Rod E, Bai L, Shen G 2015 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86 072208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sinogeikin S V, Smith J S, Rod E, Lin C, Kenney-Benson C, Shen G 2015 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86 072209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Evans W J, Yoo C S, Lee G W, Cynn H, Lipp M J, Visbeck K 2007 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 78 073904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Jenei Z, Liermann H P, Husband R, Méndez A S J, Pennicard D, Marquardt H, O'Bannon1 E F, Pakhomova A, Konopkova Z, Glazyrin K, Wendt M, Wenz S, McBride E E, Morgenroth W, Winkler B, Rothkirch A, Hanfland M, Evans W J 2019 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90 065114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lin C, Liu X, Yong X, John S T, Smith J S, English N J, Wang B, Li M, Yang W, Mao H K 2020 P. Nation. Acad. Sci. 117 15437
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lin C, Liu X, Yang D, Li X, Smith J S, Wang B, Dong H, Li S, Yang W, John, S T 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 155702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lin C, Tse J S 2021 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12 8024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liermann H P, Damker H, Konôpková Z, Appel K, Schropp A, McWiliams S, Alexander G, Baehtz C 2016 Conceptual Design Report for Diamond Anvil Cell Setup (DAC) at the HED instrument of the European XFEL
[22] Zhang L L, Yan S, Jiang S 2015 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 26 060101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Biwer C M, Quan A, Huston L Q, Sturtevant B T, Sweeney C M 2021 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 92 103901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kumar M 1995 Phys. Condens. Matter 212 391
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Anzellini S, Dewaele A, Occelli F, Loubeyre P, Mezouar M 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 115 043511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
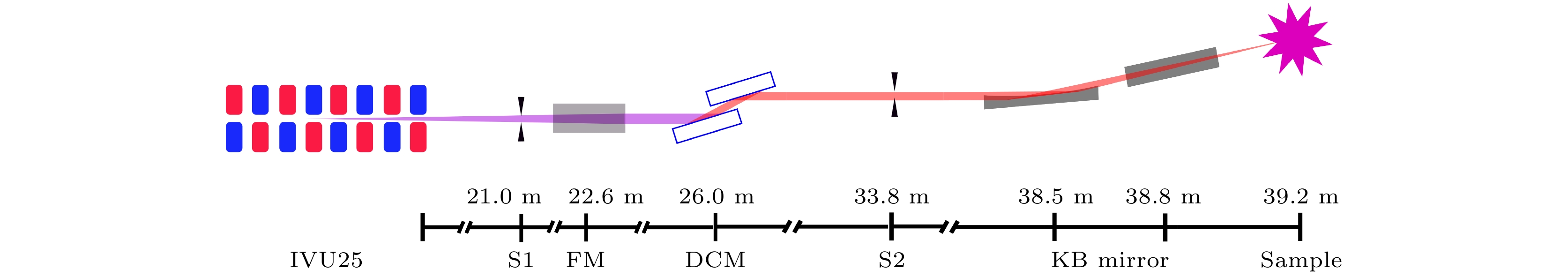
图 1 BL15U1线站束线布局图. 其中IVU25为磁极周期长度25 mm真空波荡器; S1为白光狭缝; FM为聚焦/准直镜; DCM为双晶单色器; S2为水平次级狭缝; KB为KB聚焦镜; Sample为样品点
Figure 1. Beam path layout of BL15U1. Where IVU25 is vacuum undulator with 25 mm period length; S1 is white beam slits; FM is toroidal focusing mirror; DCM is double crystal monochromator; S2 is horizontal secondary beam slits; KB is Kirkpatrick-Baez mirror; Sample is sample point.
图 2 单、双气膜控制dDAC实验装置 (a)双气膜控制dDAC原理图, 标记1为气膜; 标记2为气膜连接管, 标记3为大垫片, 标记4为卸压顶针, 标记5为样品腔, 标记6为组装罐; (b)单气膜控制dDAC实物图, 左边为气膜, 右边为单气膜控制dDAC实物图, 标记1为气膜, 标记2为气膜连接管, 标记6为组装罐
Figure 2. Single or double membrane controlled dDAC experimental device: (a) Schematic diagram of dual membrane controlled dDAC, mark 1 is gas membrane, mark 2 is gas membrane connecting pipe, mark 3 is large gasket, mark 4 is ejector pin, mark 5 is sample chamber, mark 6 is the assembly can; (b) the photo of single gas membrane control dDAC, the left is the gas membrane, and on the right is the photo of single gas membrane control dDAC, mark 1 is gas membrane, mark 2 is gas membrane connecting pipe, mark 6 is the assembly can.
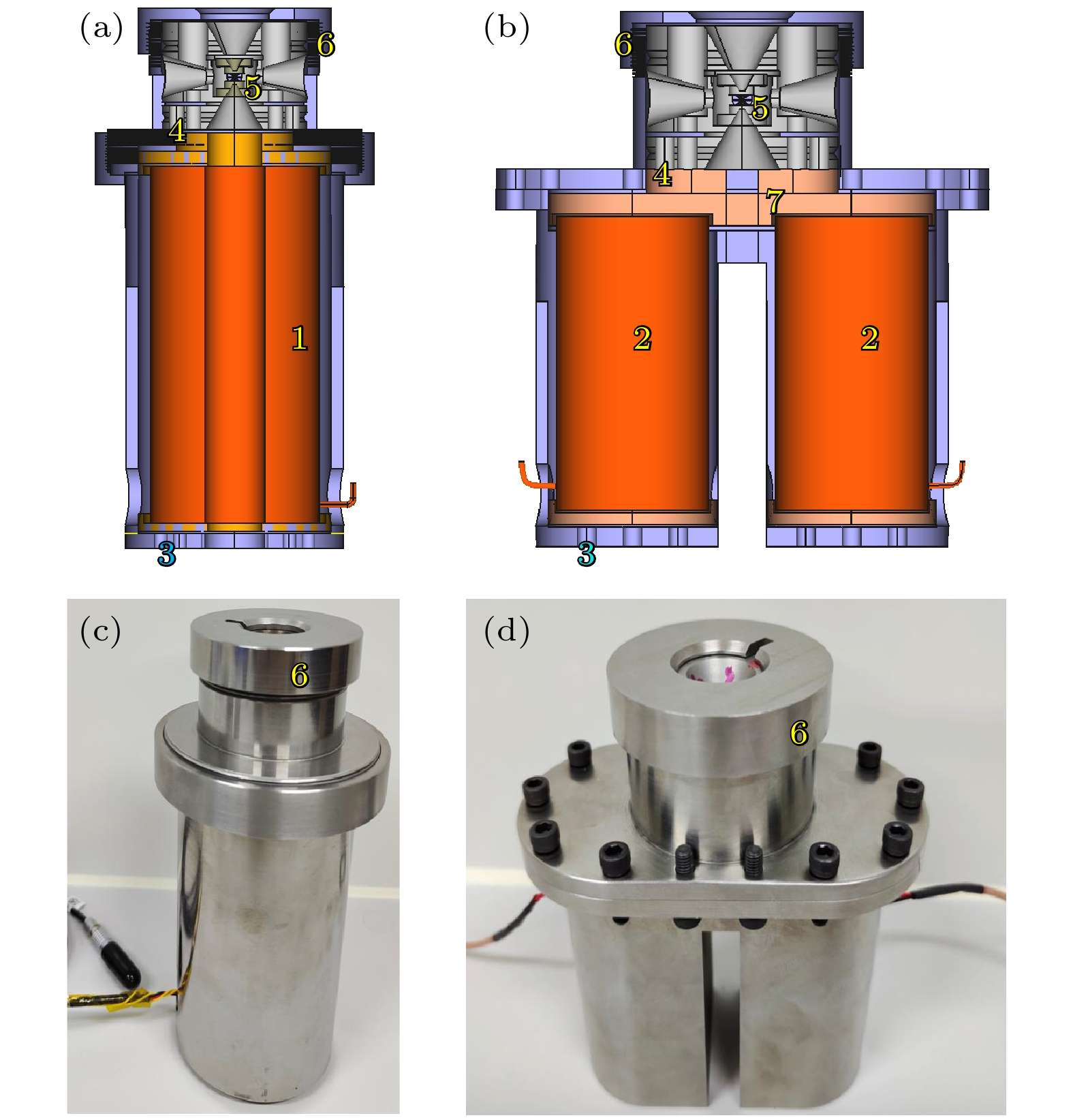
图 3 单、双压电陶瓷控制dDAC实验装置 (a)单压电陶瓷控制dDAC原理图, 标记1为实心圆柱压电陶瓷, 标记3为压电陶瓷顶丝, 标记4为卸压顶针, 标记5为样品腔, 标记6为组装罐; (b)双压电陶瓷控制dDAC原理图, 标记2为圆环压电陶瓷堆片, 标记7为连接钢板; (c)单压电陶瓷控制dDAC实物图; (d)双压电陶瓷控制dDAC实物图
Figure 3. Single and double piezoelectric ceramic control dDAC experimental device: (a) Schematic diagram of single cylinder piezoelectric ceramic control dDAC, mark 1 is solid cylindrical piezoelectric ceramics, mark 3 is piezoelectric ceramic top wire, mark 4 is ejector pin, mark 5 is sample chamber, mark 6 is the assembly can; (b) Schematic diagram of double barrel piezoelectric ceramic control dDAC, mark 2 is ring piezoelectric ceramic stack; mark 7 is perfobond ribs; (c) the photo of single cylinder piezoelectric ceramic control dDAC; (d) the photo of double barrel piezoelectric ceramic control dDAC.
图 4 气膜和压电陶瓷联合控制dDAC实验装置 (a)单气膜和单压电陶瓷联合控制dDAC实验装置实物图; (b)单气膜和双压电陶瓷联合控制dDAC实验装置实物图. 标记2为气膜连接管, 标记6为组装罐
Figure 4. Experimental device for joint control of gas membrane and piezoelectric ceramics for dDAC: (a) The photo of the dDAC experimental device for combined control of single gas membrane and single tube piezoelectric ceramics; (b) the photo of the dDAC experimental device for combined control of single gas membrane and double piezoelectric ceramics. Mark 2 is gas membrane connecting pipe, mark 6 is the assembly can.
-
[1] 丁迎春, 徐明, 潘洪哲, 沈益斌, 祝文军, 贺红亮 2007 56 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding Y C, Xu M, Pang H Z, Shen Y B, Zhu W J, He H L 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yamanaka T, Fukuda T, Mimaki J 2002 Phys. Chem. Miner. 29 633
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Sui Y, Xu D, Zheng F, Su W 1996 J. Appl. Phys. 80 719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yue S, Cheng L, Liao B, Hu M 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 27125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] John S T, Li Z, Uehara K, Ma Y, Ahuja R 2004 Phys. Rev. B 69 132101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Nakashima M, Tabata K, Thamizhavel A, Kobayashi T C, Hedo M, Uwatoko Y, Shimizu K, Settai R, Ōnuki Y 2004 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16 L255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Levien L, Prewitt C T 1981 Am. Min. 66 324
[8] Abd-Elmeguid M M, Ni B, Khomskii D I, Pocha R, Johrendt D, Wang X, Syassen K 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 126403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Brazhkin V V, Lyapin A G, Stalgorova O V, Gromnitskaya E L, Popova S V, Tsiok O B 1997 J. Non. Crys. Solids 212 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ozoliņš V, Zunger A 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 82 767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sterer E, Silvera I F 2006 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77 115105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Schiferl D, Katz A I, Mills R L, Schmidt L C, Vanderborgh C, Skelton E F, Elam W T, Webb A W, QadriM S B, Schaefer M 1986 Physica B + C 139 897
[13] Shu H, Zhang Y, Wang B, Yang W, Dong H, Tobase T, Ye J, Huang X, Fu S, Zhou Q, Sekine T 2020 Phys. Plasmas 27 030701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Smith J S, Sinogeikin S V, Lin C, Rod E, Bai L, Shen G 2015 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86 072208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sinogeikin S V, Smith J S, Rod E, Lin C, Kenney-Benson C, Shen G 2015 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86 072209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Evans W J, Yoo C S, Lee G W, Cynn H, Lipp M J, Visbeck K 2007 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 78 073904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Jenei Z, Liermann H P, Husband R, Méndez A S J, Pennicard D, Marquardt H, O'Bannon1 E F, Pakhomova A, Konopkova Z, Glazyrin K, Wendt M, Wenz S, McBride E E, Morgenroth W, Winkler B, Rothkirch A, Hanfland M, Evans W J 2019 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90 065114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lin C, Liu X, Yong X, John S T, Smith J S, English N J, Wang B, Li M, Yang W, Mao H K 2020 P. Nation. Acad. Sci. 117 15437
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lin C, Liu X, Yang D, Li X, Smith J S, Wang B, Dong H, Li S, Yang W, John, S T 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 155702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lin C, Tse J S 2021 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12 8024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liermann H P, Damker H, Konôpková Z, Appel K, Schropp A, McWiliams S, Alexander G, Baehtz C 2016 Conceptual Design Report for Diamond Anvil Cell Setup (DAC) at the HED instrument of the European XFEL
[22] Zhang L L, Yan S, Jiang S 2015 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 26 060101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Biwer C M, Quan A, Huston L Q, Sturtevant B T, Sweeney C M 2021 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 92 103901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kumar M 1995 Phys. Condens. Matter 212 391
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Anzellini S, Dewaele A, Occelli F, Loubeyre P, Mezouar M 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 115 043511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8119
- PDF Downloads: 297
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: