-
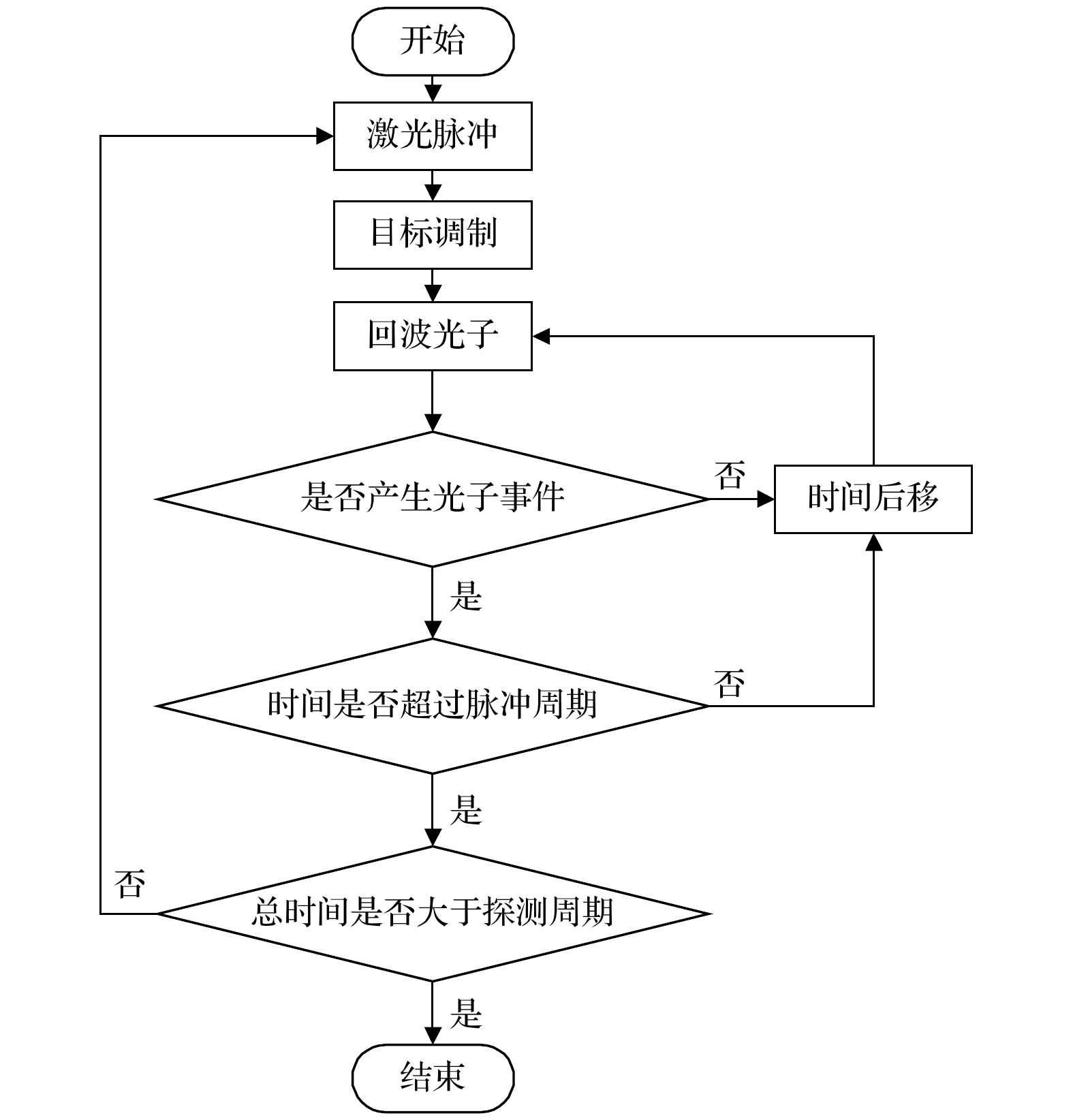
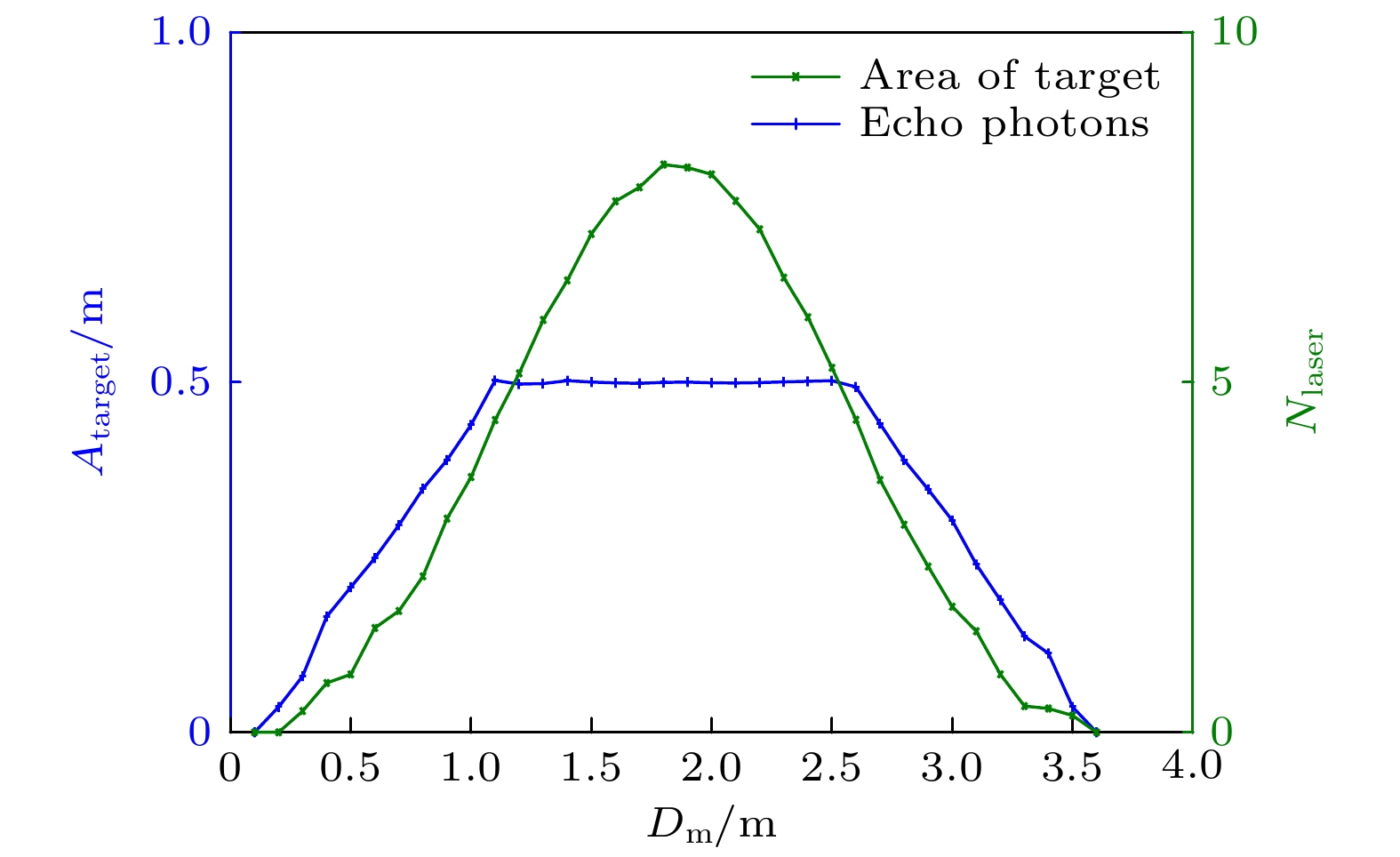
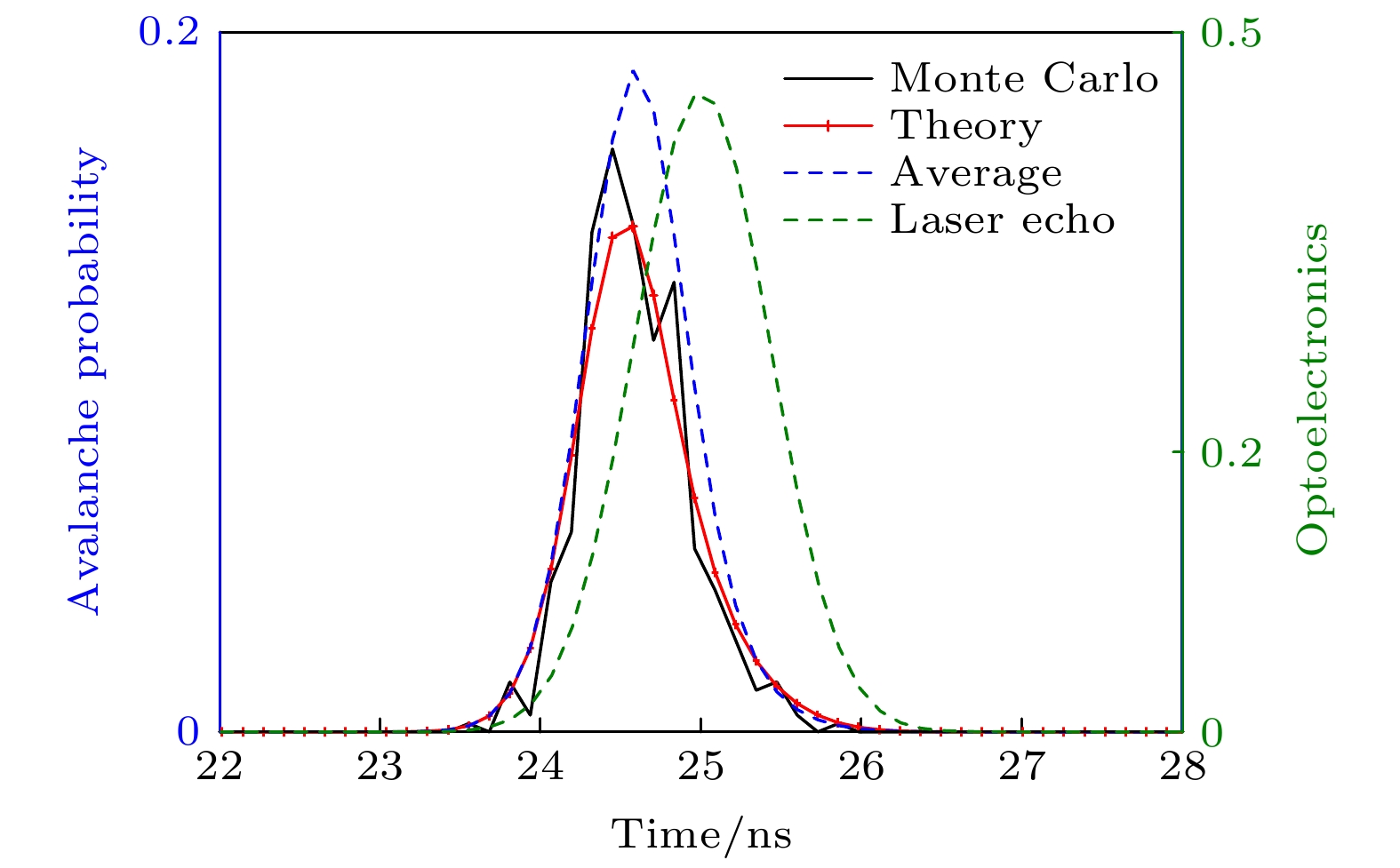
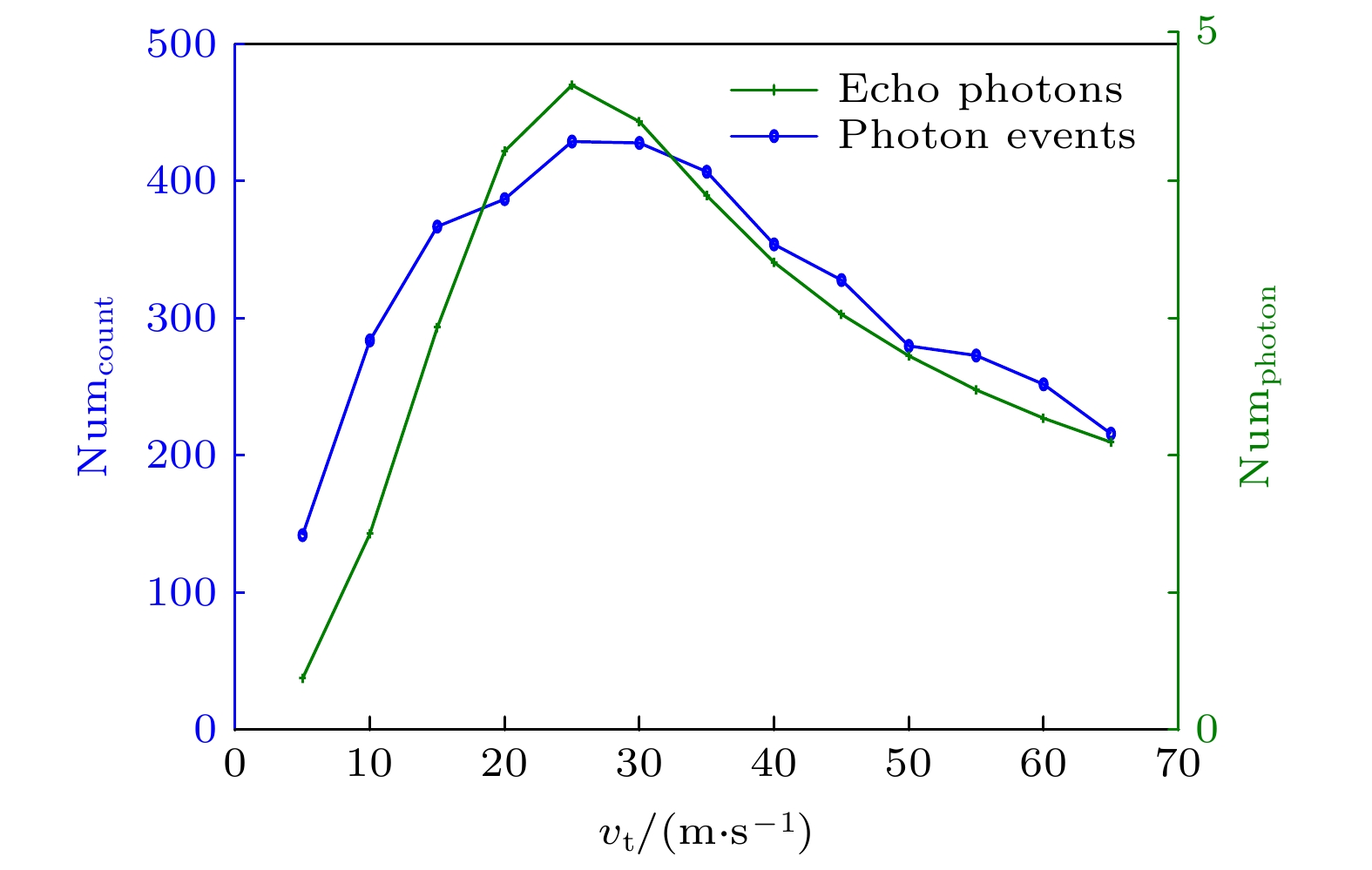
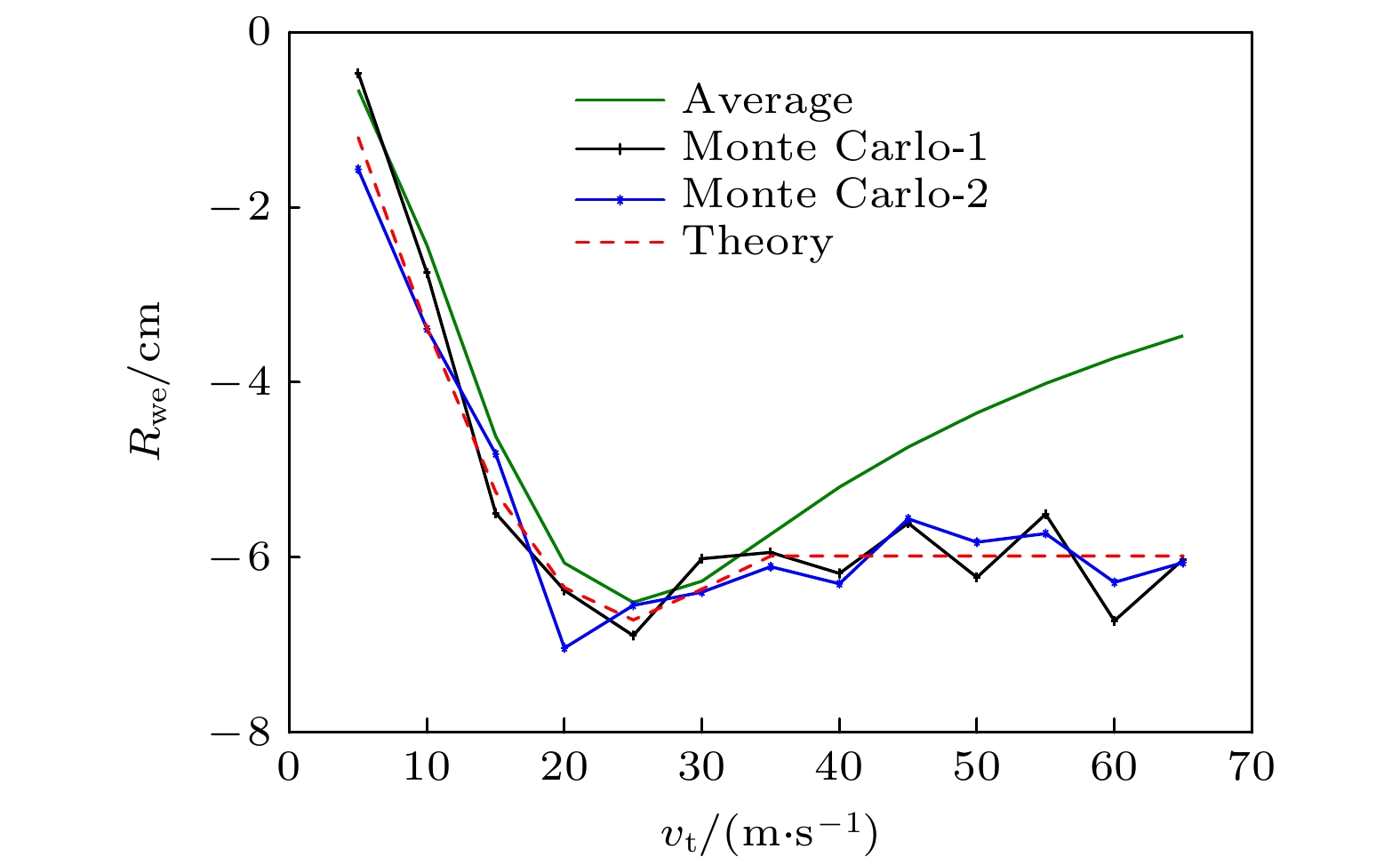
The photon counting Lidar enhances the signal-to-noise ratio of the echo signal and reduces the number of photons required for signal analysis, thereby improving the detection range and measurement accuracy. At present, the photon counting Lidar is mainly used to detect stationary targets, and the mechanism of the influence of long-distance target motion characteristics on the photon echo probability distribution is still unclear. Therefore, it is urgent to study the photon ranging performance of long-distance moving targets. In this paper, the probability distribution model of photon detection echo of moving targets is established, and a Monte Carlo model for photon detection of arbitrary targets is given. Through experimental comparison, the correctness of the Monte Carlo simulation model is verified. Furthermore, the probability distribution characteristics of the laser echo and photon echo of a small rectangular target in translation within a detection period are compared. And the variation law of the probability distribution of photon detection under different translational speeds is analyzed. In addition, the relationship between the photon ranging error and the translational speed of the target is discussed. The results show that the photon echo probability distribution of the translational target is more forward and the width is narrower than the laser pulse echo probability distribution. Compared with the extended target, the detection probability of the translational small target is significantly reduced, and the maximum average echo photon number is $ 1/10 $ times that of the extended target, as a result, the photon detection of the translational target requires higher laser pulse energy. When the length of target is 1m, the range walk error reaches a maximum value at a speed of$25\;{\text{m/s}}$ , i.e.$6.72\;{\text{ cm}}$ , which is$ 1/2 $ times that of the extended target. With the increase of the translational speed, the range walk error first increases and then turns stable with the light spot acting as the boundary.The method proposed in this paper can be further extended to photon detection and ranging of targets with other shapes, materials and attitudes. The research results provide a theoretical basis for the correction and performance improvement of the photon ranging of moving target. Furthermore, it lays the foundation for the detection of moving targets and accurate acquisition of information by photon counting Lidar. -
Keywords:
- photon ranging /
- moving target /
- range walk error /
- Monte Carlo
[1] 刘博, 于洋, 姜朔 2019 光电工程 46 190167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu B, Yu Y, Jiang S 2019 Opto-Electron. Eng. 46 190167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wulder M A, White J C, Nelson R F, Næsset E, Ørka H O, Coops N C, Hilker T, Bater C W, Gobakken T 2012 Remote Sens. Environ. 121 196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Johnson S, Gatt P, Nichols T 2003 Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 5086 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 侯利冰, 黄庚华, 况耀武, 陈凯, 舒嵘 2013 科学技术与工程 13 5186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou L B, Huang G H, Kuang Y W, Chen K, Shu R 2013 Sci. Tech. Eng. 13 5186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 罗远, 贺岩, 耿立明, 王明建, 雷琳君, 吴姚芳, 胡善江, 侯霞, 陈卫标 2016 中国激光 43 0514001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo Y, He Y, Geng L M, Wang M J, Lei L J, Wu Y F, Hu S J, Hou X, Chen W B 2016 Chin. J. Lasers 43 0514001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 邵禹, 王德江, 张迪, 陈成 2021 激光与光电子学进展 10 250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao Y, Wang D J, Zhang D, Chen C 2021 Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 10 250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Pawlikowska A M, Halimi A, Lamb R A, Buller G S 2017 Opt. Express 25 11919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Degnan J J 2002 J. Geodyn. 34 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Oh M S, Kong H J, Kim T H, Hong K H, Kim B W 2010 Opt. Commun. 283 304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Barton-Grimley R A, Thayer J P, Hayman M 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 1249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 黄科, 李松, 马跃, 田昕, 周辉, 张智宇 2018 67 064205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang K, Li S, Ma Y, Tian X, Zhou H, Zhang Z Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 064205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen Z D, Li X D, Li X H, Ye G C, Zhou Z G 2019 Opt. Commun. 434 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 寇添, 王海晏, 王芳, 陈闽, 徐强 2015 光学学报 35 0414001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kou T, Wang H Y, Wang F, Chen M, Xu Q 2015 Acta Opt. Sin. 35 0414001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 寇添, 王海晏, 王芳, 吴学铭, 王领, 徐强 2015 64 120601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kou T, Wang H Y, Wang F, Wu X M, Wang L, Xu Q 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 120601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 徐孝彬, 张合, 张祥金, 陈杉杉, 张伟 2016 65 210601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu X B, Zhang H, Zhang X J, Chen S S, Zhang W 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 210601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 谢庚承, 叶一东, 李建民, 袁学文 2018 中国激光 45 0610001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie B C, Ye Y D, Li J M, Yuan X W 2018 Chin. J. Lasers 45 0610001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xu X B, Zhang H, Luo M Z, Tan Z Y, Zhang M, Yang H, Li Z H 2019 Infrared Phys. Technol. 96 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 侯阿慧, 胡以华, 赵楠翔, 方佳节, 张鑫源 2021 中国激光 48 0401016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou A H, Hu Y H, Zhao N Y, Fang J J, Zhang X Y 2021 Chin. J. Lasers 48 0401016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 刘芳华, 贺岩, 罗远, 贾文武, 曹丽君, 李琳琳, 李凯鹏, 陈勇强, 郭守川, 陈卫标 2021 中国激光 48 1310001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu F H, He Y, Luo Y, Jia W W, Cao L J, Li L L, Li K P, Chen Y Q, Guo S C, Chen W B 2021 Chin. J. Lasers 48 1310001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Becker W 2005 Advanced Time-correlated Single Photon Counting Techniques (Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media) pp204–206
[21] Fouche D G. 2003 Appl. Opt. 42 5388
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] 刘博, 于洋, 姜朔 2019 光电工程 46 190167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu B, Yu Y, Jiang S 2019 Opto-Electron. Eng. 46 190167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wulder M A, White J C, Nelson R F, Næsset E, Ørka H O, Coops N C, Hilker T, Bater C W, Gobakken T 2012 Remote Sens. Environ. 121 196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Johnson S, Gatt P, Nichols T 2003 Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 5086 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 侯利冰, 黄庚华, 况耀武, 陈凯, 舒嵘 2013 科学技术与工程 13 5186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou L B, Huang G H, Kuang Y W, Chen K, Shu R 2013 Sci. Tech. Eng. 13 5186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 罗远, 贺岩, 耿立明, 王明建, 雷琳君, 吴姚芳, 胡善江, 侯霞, 陈卫标 2016 中国激光 43 0514001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo Y, He Y, Geng L M, Wang M J, Lei L J, Wu Y F, Hu S J, Hou X, Chen W B 2016 Chin. J. Lasers 43 0514001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 邵禹, 王德江, 张迪, 陈成 2021 激光与光电子学进展 10 250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao Y, Wang D J, Zhang D, Chen C 2021 Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 10 250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Pawlikowska A M, Halimi A, Lamb R A, Buller G S 2017 Opt. Express 25 11919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Degnan J J 2002 J. Geodyn. 34 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Oh M S, Kong H J, Kim T H, Hong K H, Kim B W 2010 Opt. Commun. 283 304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Barton-Grimley R A, Thayer J P, Hayman M 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 1249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 黄科, 李松, 马跃, 田昕, 周辉, 张智宇 2018 67 064205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang K, Li S, Ma Y, Tian X, Zhou H, Zhang Z Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 064205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen Z D, Li X D, Li X H, Ye G C, Zhou Z G 2019 Opt. Commun. 434 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 寇添, 王海晏, 王芳, 陈闽, 徐强 2015 光学学报 35 0414001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kou T, Wang H Y, Wang F, Chen M, Xu Q 2015 Acta Opt. Sin. 35 0414001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 寇添, 王海晏, 王芳, 吴学铭, 王领, 徐强 2015 64 120601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kou T, Wang H Y, Wang F, Wu X M, Wang L, Xu Q 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 120601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 徐孝彬, 张合, 张祥金, 陈杉杉, 张伟 2016 65 210601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu X B, Zhang H, Zhang X J, Chen S S, Zhang W 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 210601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 谢庚承, 叶一东, 李建民, 袁学文 2018 中国激光 45 0610001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie B C, Ye Y D, Li J M, Yuan X W 2018 Chin. J. Lasers 45 0610001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xu X B, Zhang H, Luo M Z, Tan Z Y, Zhang M, Yang H, Li Z H 2019 Infrared Phys. Technol. 96 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 侯阿慧, 胡以华, 赵楠翔, 方佳节, 张鑫源 2021 中国激光 48 0401016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou A H, Hu Y H, Zhao N Y, Fang J J, Zhang X Y 2021 Chin. J. Lasers 48 0401016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 刘芳华, 贺岩, 罗远, 贾文武, 曹丽君, 李琳琳, 李凯鹏, 陈勇强, 郭守川, 陈卫标 2021 中国激光 48 1310001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu F H, He Y, Luo Y, Jia W W, Cao L J, Li L L, Li K P, Chen Y Q, Guo S C, Chen W B 2021 Chin. J. Lasers 48 1310001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Becker W 2005 Advanced Time-correlated Single Photon Counting Techniques (Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media) pp204–206
[21] Fouche D G. 2003 Appl. Opt. 42 5388
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5564
- PDF Downloads: 83
- Cited By: 0



















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: