-
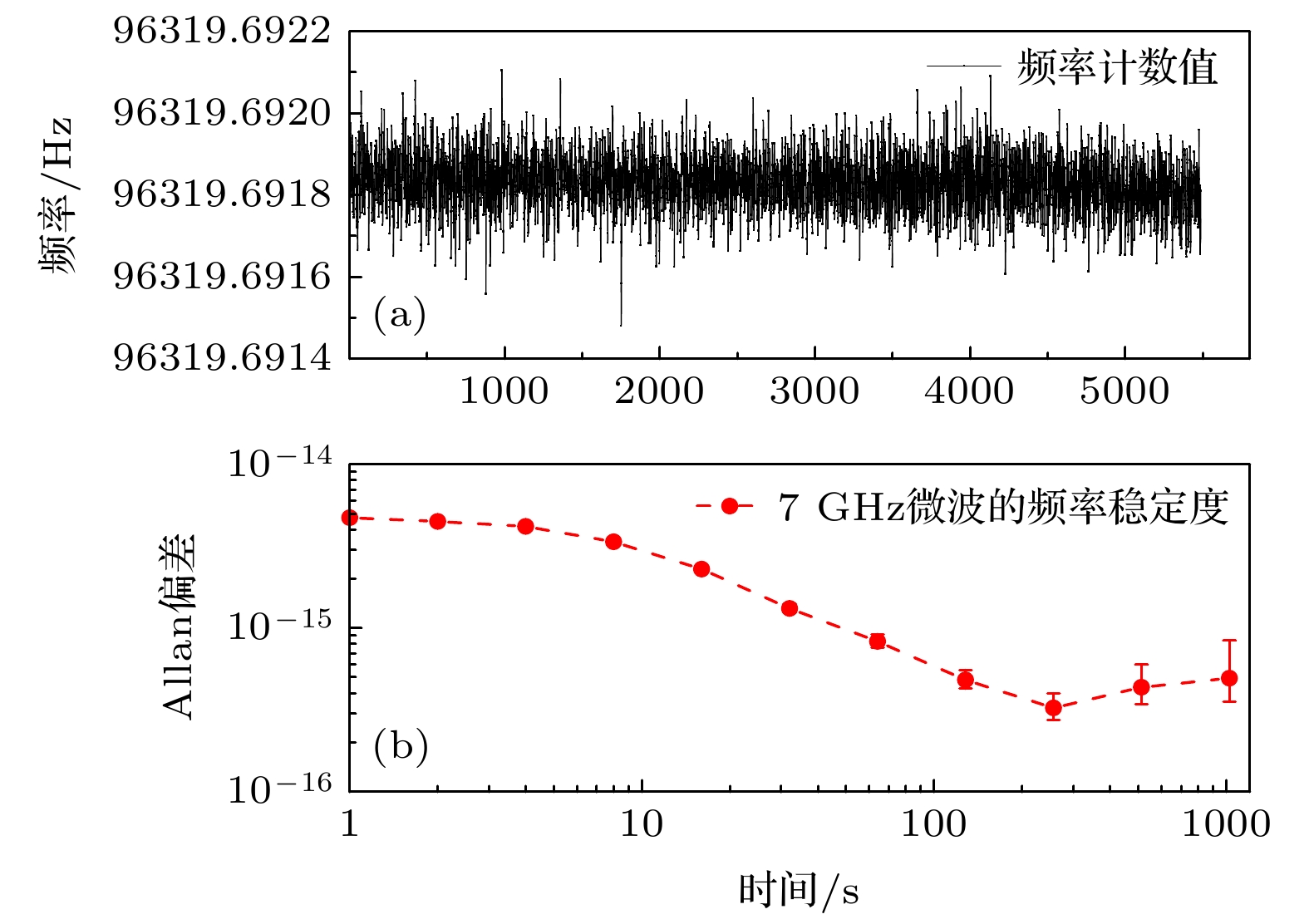
Low-noise microwave signals are of vital importance in fields such as cold atomic optical clocks, photon radars, and remote synchronization at large facilities. Here, we report a compact all-optical-fiber method to generate a low noise microwave signal, in which the fiber loop optical-microwave phase detector is used to coherently transfer the frequency stability of the ultra-stable laser to the microwave. Combining a narrow linewidth optical frequency comb and a fiber loop optical-microwave phase discriminator, a tight phase-lock between 7 GHz dielectric oscillator and optical frequency comb is achieved, the remaining phase noise of the synchronized optical pulse sequence and the microwave signal is –100 dBc/Hz@1 Hz, and the timing jitter is 8.6 fs (1 Hz—1.5 MHz); by building two sets of low-noise microwave generation systems, the measured residual phase noise of the 7 GHz microwave is –90 dBc/Hz@1 Hz, and the corresponding frequency stability is 4.8 × 10–15@1 s. These results provide a novel idea for generating the low-noise microwaves based on optical coherent frequency division.
-
Keywords:
- ultra-stable laser /
- optical frequency comb /
- low noise microwave signal /
- time synchronization
[1] Capmany J, Novak D 2007 Nat. Photon. 1 319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Millo J, Abgrall M, Lours M, English E M L, Jiang H, Guéna J, Clairon A, Tobar M E, Bize S, Le Coq Y, Santarelli G 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 141105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kim J, Cox J A, Chen J, Kärtner F X 2008 Nat. Photon. 2 733
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Doeleman S 2009 Frequency Standards and Metrology-Proceedings of the 7th Symposium (PacificGrove: World Scientific) p175
[5] Francois B, Calosso C E, Danet J M, Boudot R 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 094709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Grop S, Bourgeois P Y, Boudot R, Kersalé Y, Rubiola E, Giordano V 2010 Electron. Lett. 46 420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Maleki L 2011 Nat. Photon. 5 728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Giordano V, Grop S, Fluhr C, Dubois B, KersaléY, Rubiola E 2015 8th Symposium on Frequency Standards and Metrology (Potsdam: IOP Publishing Ltd), p012030
[9] Bartels A, Diddams S A, Oates C W, Wilpers G, Bergquist J C, Oskay W H, Hollberg L 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xie X, Bouchand R, Nicolodi D, Giunta M, Hänsel W, Lezius M, Joshi A, Datta S, Alexandre C, L Michel, Tremblin P, Santarelli G, Holzwarth R, Le Coq Y 2017 Nat. Photon. 11 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Didier A, Millo J, Grop S, Dubois B, Bigler E, Rubiola E, Lacroûte C, Kersalé Y 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 3682
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Ivanov E N, Diddams S A, Hollberg L 2003 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 9 1059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ivanov E N, Diddams S A, Hollberg L 2005 IEEE Trans. Sonics Ultrason. 52 1068
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wu K, Shum P P, Aditya S, Ouyang C, Wong J H, Lam H Q, Lee K E K 2011 J. Lightwave Technol. 29 3622
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Haboucha A, Zhang W, Li T, Lours M, Luiten A N, Le Coq Y, Santarelli G 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 3654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiang H, Taylor J, Quinlan F, Fortier T, Diddams S A 2011 IEEE Photonics J. 3 1004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Nakamura T, Davila-Rodriguez J, Leopardi H, Sherman J A, Fortier T M, Xie X, Campbell J C, McGrew W F, Zhang X, Hassan Y S, Nicolodi D, Beloy K, Ludlow A D, Diddams S A, Quinlan F 2020 Science 368 889
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Dai Y, Cen Q, Wang L, Zhou Y, Yin F, Dai J, Li J, Xu K 2015 Opt. Express 23 31936
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang L, Dai Y, Zhou Y, Yin F, Dai J, Li J, Xu K 2015 IEEE Avionics and Vehicle Fiber-Optics and Photonics Conference (Santa Barbara: IEEE) p40
[20] Chtioui M, Lelarge F, Enard A, Pommereau F, Carpentier D, Marceaux A, Dijk F, Achouche M 2011 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 24 318
[21] Li J, Xiong B, Sun C, Miao D, Luo Y 2015 Opt. Express 23 21615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jung K, Kim J. 2012 Opt. Lett. 37 2958
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Lessing M, Margolis H S, Brown C T A, Gill P, Marra G 2013 Opt. Express 21 27057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jung K, Shin J, Kang J, Hunziker S, Min C K, Kim J 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 1577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Lu X, Zhang S, Jeon C G, Kang C S, Kim J, Shi K 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 1447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lu X, Zhang S, Chen X, Kwon D, Jeon C G, Zhang Z, Kim J, Shi K 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 13305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Cao S, Lin B, Yuan X, Fang Z 2020 Opt. Commun. 478 126376
[28] 崔佳华, 林百科, 孟飞, 曹士英, 杨明哲, 林弋戈, 宋有建, 胡明列, 方占军 2020 红外与毫米波学报 39 25
Cui J, Lin B, Meng F, Cao S, Yang M, Lin Y, Song J, Hu M, Fang Z 2020 Infrared Millim. W. 39 25 (in Chinese)
[29] Zobel J W, Giunta M, Goers A J, Schmid L R, Reeves J, Holzwarth R, Adles E J 2019 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 31 1323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 FLOM-PD原理图. 其中, Circulator为保偏光纤环形器, PM EOM为保偏光纤电光调制器, QWP为1/4波片, FR为法拉第旋光镜, HWP为1/2波片, 3 dB coupler为2 × 2的3 dB保偏光纤耦合器, BPD为平衡光电探测器
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of FLOM-PD. Circulator represents polarization-maintaining fiber circulator; PM EOM represents polarization-maintainingelectro-optic modulator; QWP represents quarter-wave plates; FR represents faraday rotators; HWP represents half-wave plate; 3 dB coupler represents 2 × 2 3 dB polarization-maintaining fiber coupler; BPD represents balanced photodetector.
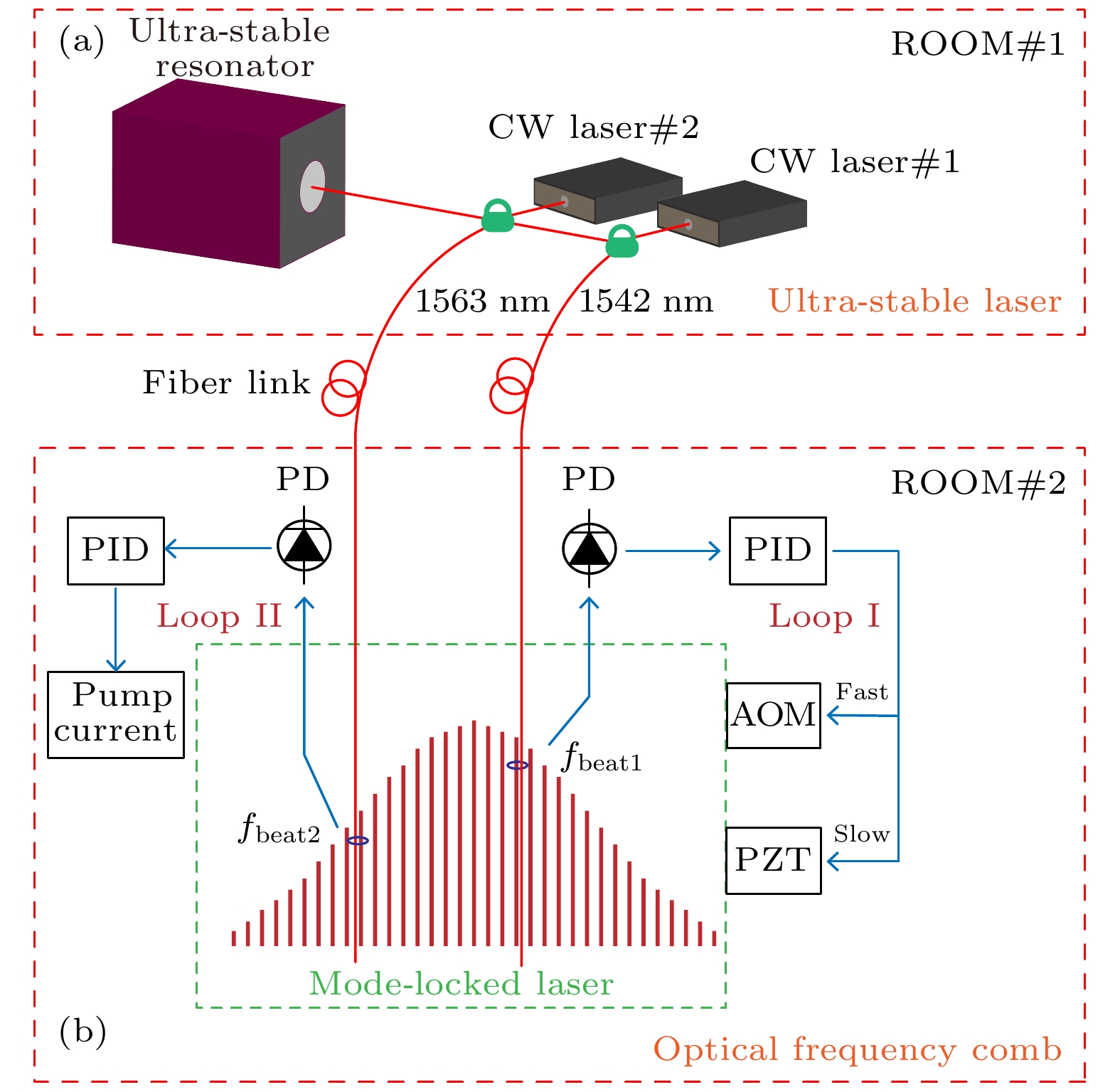
图 2 窄线宽光学频率梳原理图 (a)超稳激光系统; (b)飞秒光学频率梳. 其中, CW laser为连续激光, PID为比例-积分-微分控制器, PD为光电探测器, AOM为声光调制器, PZT为压电位移器
Figure 2. Schematic diagram ofnarrowlinewidth optical frequency comb: (a) Ultra-stable laser system; (b) optical frequency comb. CW laser represents continuous-wave laser, PID represents proportional-integral-differentialcontroller, PD represents photodetector, AOM represents acousto-optical modulator, PZT represents piezoelectric transducer.
图 3 基于FLOM-PD和光学频率梳的光学-微波同步方案 (a) 光学-微波同步装置; (b)环外相位噪声测量装置. 其中, EDFA为掺铒光纤放大器, PBS为偏振光束分束器, Coupler为保偏光纤耦合器, Circulator为保偏光纤环形器, VOA为可调光学衰减器, BPD为平衡光电探测器, PIC为比例积分控制器, DRO为介质振荡器, Power divider为微波功率分配器, FFT为快速傅里叶变换分析仪
Figure 3. Optical-microwave synchronization scheme based on FLOM-PD and optical frequency comb. (a) Optical-microwave synchronization setup; (b) out-of-loop phase noise measurement setup. EDFA represents erbium-doped fiber amplifiers, PBS represents polarization beam splitter, Coupler represents polarization-maintaining fiber coupler, Circulator represents polarization-maintainingfiber circulator, VOA represents variable optical attenuators, BPD represents balanced photodetector, PIC represents proportional-integral controller, DRO represents dielectric resonator oscillator, Power divider represents microwave power divider, FFT represents fast Fourier transform analyzer.
图 4 微波性能表征方案. 其中, CW Laser为连续激光, DRO为介质振荡器, PIC为比例积分控制器, LPF为低通滤波器, LNA为低噪声放大器.
Figure 4. Microwave performance characterization setup. CW laser represents continuous-wave laser, DRO represents dielectric resonator oscillator, PIC represents proportional-integral controller, LPF represents lowpass filter, LNA represents low noise amplifier.
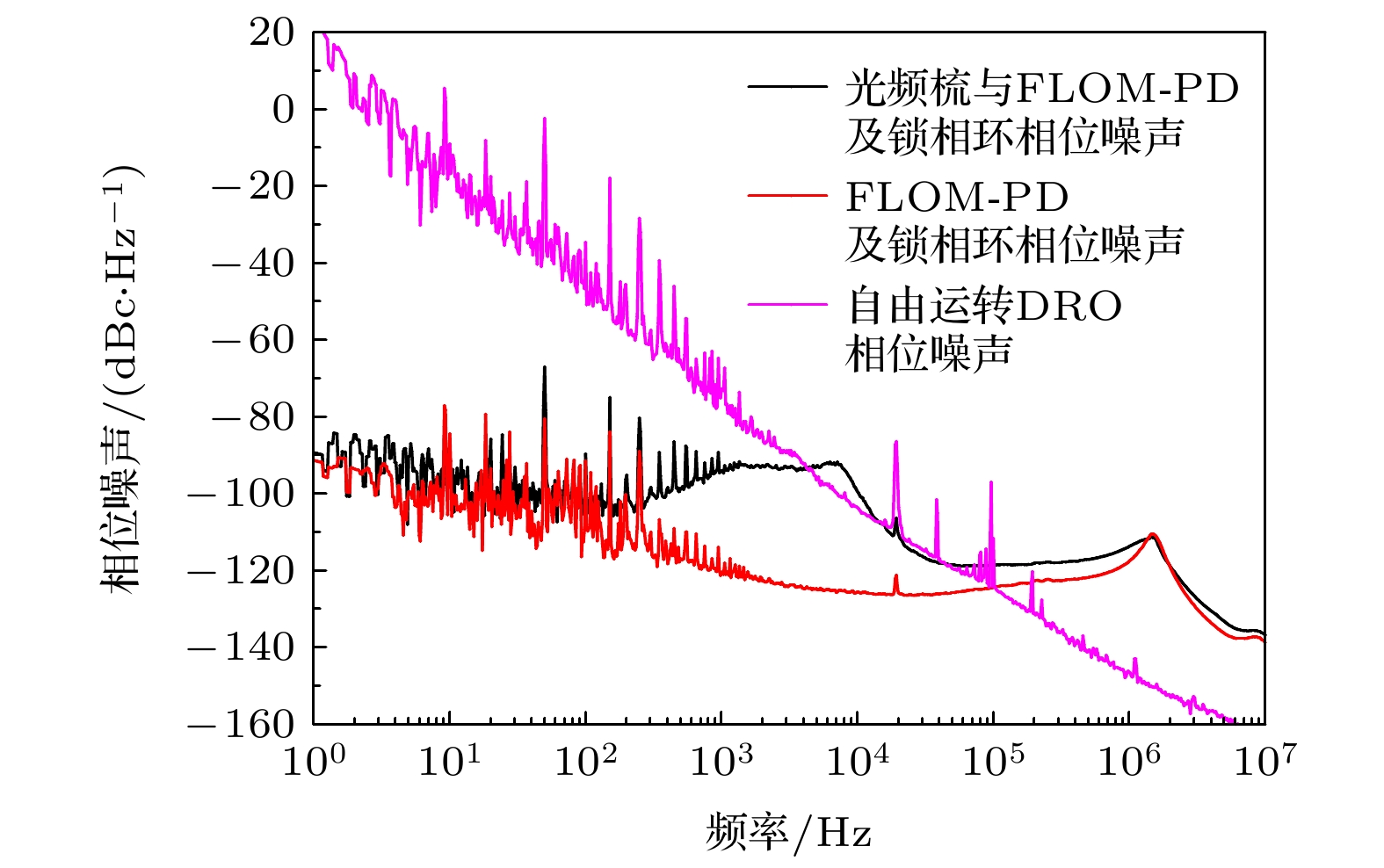
图 5 FLOM-PD及锁相系统的噪声测量方案.其中, CW Laser为连续激光, DRO为介质振荡器, PIC为比例积分控制器, LPF为低通滤波器, Phase shifter为微波相移器
Figure 5. Phase noise characterization setup of FLOM-PDandphase-lock system. CW laser represents continuous-wave laser, DRO represents dielectric resonator oscillator, PIC represents proportional-integral controller, LPF represents lowpass filter, Phase shifter represents microwave phase shifter.
-
[1] Capmany J, Novak D 2007 Nat. Photon. 1 319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Millo J, Abgrall M, Lours M, English E M L, Jiang H, Guéna J, Clairon A, Tobar M E, Bize S, Le Coq Y, Santarelli G 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 141105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kim J, Cox J A, Chen J, Kärtner F X 2008 Nat. Photon. 2 733
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Doeleman S 2009 Frequency Standards and Metrology-Proceedings of the 7th Symposium (PacificGrove: World Scientific) p175
[5] Francois B, Calosso C E, Danet J M, Boudot R 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 094709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Grop S, Bourgeois P Y, Boudot R, Kersalé Y, Rubiola E, Giordano V 2010 Electron. Lett. 46 420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Maleki L 2011 Nat. Photon. 5 728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Giordano V, Grop S, Fluhr C, Dubois B, KersaléY, Rubiola E 2015 8th Symposium on Frequency Standards and Metrology (Potsdam: IOP Publishing Ltd), p012030
[9] Bartels A, Diddams S A, Oates C W, Wilpers G, Bergquist J C, Oskay W H, Hollberg L 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xie X, Bouchand R, Nicolodi D, Giunta M, Hänsel W, Lezius M, Joshi A, Datta S, Alexandre C, L Michel, Tremblin P, Santarelli G, Holzwarth R, Le Coq Y 2017 Nat. Photon. 11 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Didier A, Millo J, Grop S, Dubois B, Bigler E, Rubiola E, Lacroûte C, Kersalé Y 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 3682
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Ivanov E N, Diddams S A, Hollberg L 2003 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 9 1059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ivanov E N, Diddams S A, Hollberg L 2005 IEEE Trans. Sonics Ultrason. 52 1068
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wu K, Shum P P, Aditya S, Ouyang C, Wong J H, Lam H Q, Lee K E K 2011 J. Lightwave Technol. 29 3622
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Haboucha A, Zhang W, Li T, Lours M, Luiten A N, Le Coq Y, Santarelli G 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 3654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiang H, Taylor J, Quinlan F, Fortier T, Diddams S A 2011 IEEE Photonics J. 3 1004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Nakamura T, Davila-Rodriguez J, Leopardi H, Sherman J A, Fortier T M, Xie X, Campbell J C, McGrew W F, Zhang X, Hassan Y S, Nicolodi D, Beloy K, Ludlow A D, Diddams S A, Quinlan F 2020 Science 368 889
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Dai Y, Cen Q, Wang L, Zhou Y, Yin F, Dai J, Li J, Xu K 2015 Opt. Express 23 31936
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang L, Dai Y, Zhou Y, Yin F, Dai J, Li J, Xu K 2015 IEEE Avionics and Vehicle Fiber-Optics and Photonics Conference (Santa Barbara: IEEE) p40
[20] Chtioui M, Lelarge F, Enard A, Pommereau F, Carpentier D, Marceaux A, Dijk F, Achouche M 2011 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 24 318
[21] Li J, Xiong B, Sun C, Miao D, Luo Y 2015 Opt. Express 23 21615
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jung K, Kim J. 2012 Opt. Lett. 37 2958
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Lessing M, Margolis H S, Brown C T A, Gill P, Marra G 2013 Opt. Express 21 27057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jung K, Shin J, Kang J, Hunziker S, Min C K, Kim J 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 1577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Lu X, Zhang S, Jeon C G, Kang C S, Kim J, Shi K 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 1447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lu X, Zhang S, Chen X, Kwon D, Jeon C G, Zhang Z, Kim J, Shi K 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 13305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Cao S, Lin B, Yuan X, Fang Z 2020 Opt. Commun. 478 126376
[28] 崔佳华, 林百科, 孟飞, 曹士英, 杨明哲, 林弋戈, 宋有建, 胡明列, 方占军 2020 红外与毫米波学报 39 25
Cui J, Lin B, Meng F, Cao S, Yang M, Lin Y, Song J, Hu M, Fang Z 2020 Infrared Millim. W. 39 25 (in Chinese)
[29] Zobel J W, Giunta M, Goers A J, Schmid L R, Reeves J, Holzwarth R, Adles E J 2019 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 31 1323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9451
- PDF Downloads: 226
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: