-
Magnetized laser plasma has attracted a lot of attention in recent years especially in magnetized inertial confinement fusion, laboratory astrophysics, and industrial application. Pulsed intense magnetic field device is the core equipment of magnetized laser plasma experiment. Here in this work, an inductively coupled coil is developed to optimize the pulsed intense magnetic field device. The primary coil of a multi-turn solenoid is used instead of a single-turn coil. Then the energy of the solenoid is delivered to the secondary coil via inductively coupled transformer, which increases the current density markedly. The current generates a stronger magnetic field in the single-turn magnetic field coil. The influence of the diameter and the number of turns of the primary solenoid of the inductively coupled coil on the magnetic field are explored in experiment and simulation. It is found that for a discharge system of 2.4 μF capacitance, the optimized parameters of the primary solenoid are 35 turns and 35 mm diameter. The optimized magnetic field is 3.6 times stronger than that of the conventional directly connected single-turn coil. At a charging voltage of 20 kV, the peak magnetic field reaches 19 T in a magnetic field coil of 5 mm inner diameter. The inductively coupled coil made of CuBe solves the problem of coil expansion in intense magnetic field, and a peak magnetic field of 33 T is obtained at a charging voltage of 35 kV. The present approach creates stronger magnetic field environments. At the same time, the inductively coupled coil reduces the requirements for system inductance, so that components such as energy storage capacitors and switch can be placed far from the coil, which improves the flexibility of the experiment setup.
-
Keywords:
- laser plasma /
- magnetized plasma /
- pulsed intense magnetic field device /
- inductively coupled coil
[1] Gotchev O V, Chang P Y, Knauer J P, Meyerhofer D D, Polomarov O, Frenje J, Li C K, Manuel M J E, Petrasso R D, Rygg J R, Séguin F H, Betti R 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 215004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chang P Y, Fiksel G, Hohenberger M, Knauer J P, Betti R, Marshall F J, Meyerhofer D D, Séguin F H, Petrasso R D 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 035006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hohenberger M, Chang P Y, Fiksel G, Knauer J P, Betti R, Marshall F J, Meyerhofer D D, Séguin F H, Petrasso R D 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 056306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bailly-Grandvaux M, Santos J J, Bellei C, et al. 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 孙可煦, 黄天晅, 丁永坤, 易荣清, 江少恩, 崔延莉, 汤晓青, 陈久森, 张保汉, 郑志坚 2002 51 1750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun K X, Huang T X, Ding Y K, Yi R Q, Jiang S E, Cui Y L, Tang X Q, Chen J S, Zhang B H, Zheng Z J 2002 Acta Phys. Sin. 51 1750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Tang H B, Hu G Y, Liang Y H, Tao T, Wang Y L, Hu P, Zhao B, Zheng J 2018 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 60 5
[7] 裴晓星, 仲佳勇, 张凯, 郑无敌, 梁贵云, 王菲鹿, 李玉同 2014 63 145201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pei X X, Zhong J Y, Zhang K, Zheng W D, Liang G Y, Wang F L, Li Y T, Zhao G 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 145201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 张凯, 仲佳勇, 裴晓星, 李玉同, 阪和洋一, 魏会冈, 袁大伟, 李芳, 韩波, 王琛, 贺昊, 尹传磊, 廖国前, 方远, 杨骕, 远晓辉, 梁贵云, 王菲鹿, 朱健强, 丁永坤, 张杰, 赵刚 2015 64 165201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang K, Zhong J Y, Pei X X, Li Y T, Sakawa Y, Wei H G, Yuan D W, Li F, Han B, Wang C, He H, Yin C L, Liao G Q, Fang Y, Yang S, Yuan X H, Liang G Y, Wang F L, Zhu J Q, Zhang J, Zhao G 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 165201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Creel J R, Donnelly T, Lunney J G 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 071104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Law K F F, Bailly-Grandvaux M, Morace A, Sakata S, Matsuo K, Kojima S, Lee S, Vaisseau X, Arikawa Y, Yogo A, Kondo K, Zhang Z, Bellei C, Santos J J, Fujioka S, Azechi H 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 091104
[11] Pollock B B, Froula D H, Davis P F, Ross J S, Fulkerson S, Bower J, Satariano J, Price D, Krushelnick K, Glenzer S H 2006 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77 114703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Albertazzi B, BéArd J, Ciardi A, et al. 2013 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 84 043505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Pollock B B, Froula D H, Tynan G R, Divol L, Price D, Costa R, Yepiz F, Fulkerson S, Mangini F, Glenzer Het 2008 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79 10F550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Gotchev O V, Knauer J P, Chang P Y, Jang N W, Shoup III M J, Meyerhofer D D, Betti R 2009 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80 043504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li C X, Jin X, Wang G P, Zhang B Z, Gong H T, Gan Y Q, Li F, Song F L 2021 Laser Part. Beams 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Barnak D H, Davies J R, Fiksel G, Chang P Y, Zabir E, Betti R 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 033501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhu J Q 2018 High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 6 e55
[18] Fiksel G, Agliata A, Barnak D, Brent G, Chang P Y, Folnsbee L, Gates G, Hasset D, Lonobile D, Magoon J, Mastrosimone D, Shoup III M J, Betti R 2015 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86 016105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang Y L, Hu G Y, Hu P, Tang H B, Yuan P, Zheng J 2019 J. Instrum. 14 P09024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang Y L, Hu G Y, Hu P, Liang Y H, Yuan P, Zheng J 2019 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90 75108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Hu P, Hu G Y, Wang Y L, Tang H B, Zheng J 2020 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 91 014703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hu G Y, Liang Y H, Song F L, Yuan P, Wang Y L, Zhao B, Zheng J 2015 Plasma Sci. Technol. 17 134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Fiksel G, Backhus R, Barnak D H, Chang P Y, Davies J R, Jacobs-Perkins D, McNally P, Spielman R B, Viges E, Betti R 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 084703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 李瀚荪 2006 电路分析基础 (第4版) (北京: 高等教育出版社) 第12页
Li H S 2006 Circuit Analysis (Vol. 4) (Beijing: Higher Education Press) p12 (in Chinese)
[25] 布卢姆H 著 (江伟华, 张驰译) 2008 脉冲功率系统的原理与应用 (北京: 清华大学出版社) 第188页
Bluhm H(translated by Jiang W H, Zhang C)2008 Pulsed Power Systems: Principles and Applications (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) p188 (in Chinese)
[26] 张丝雨 2005 最新金属材料牌号、性能、用途及中外牌号对照速用速查实用手册(香港: 中国科技文化出版社)第709页、第1122页
Zhang S Y 2005 The Latest Metal Material Grades, Properties, Uses and Comparison of Chinese and Foreign Grades, Quick-use Quick Reference Practical Manual (Hong Kong: China Science and Culture Publishing Press) p709, p1122 (in Chinese)
-
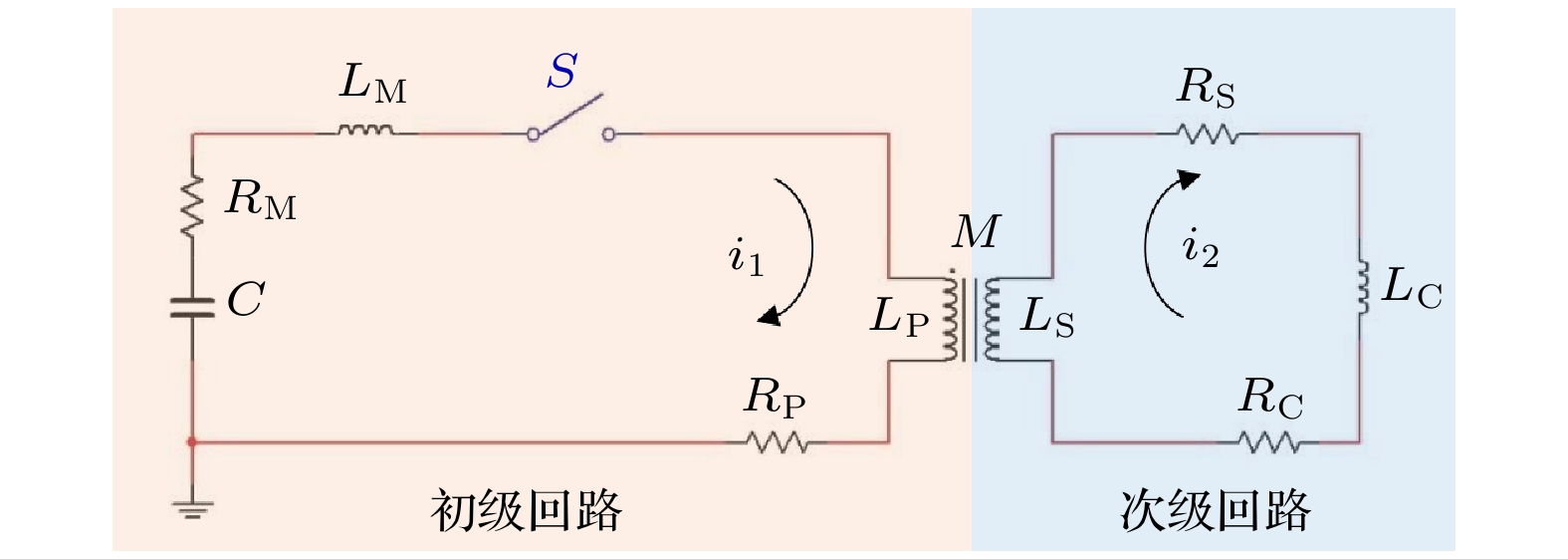
图 1 脉冲强磁场设备的电路图. 橘色框内是初级回路, 蓝色框内是次级回路.
$ {L}_{\mathrm{M}} $ 和$ {R}_{\mathrm{M}} $ 分别为初级回路除螺线管之外的电感和电阻;$ {L}_{\mathrm{P}} $ 和$ {R}_{\mathrm{P}} $ 分别为变压器初级螺线管的电感和电阻;$ {L}_{\mathrm{S}} $ 和$ {R}_{\mathrm{S}} $ 分别为变压器次级线圈的电感和电阻;$ {L}_{\mathrm{C}} $ 和$ {R}_{\mathrm{C}} $ 分别为次级回路中除变压器次级线圈以外的电感和电阻;$ C $ 是电容器的电容Figure 1. Circuit diagram of a pulsed intense magnetic field device. The left orange box is the primary circuit, and the right blue box is the secondary circuit.
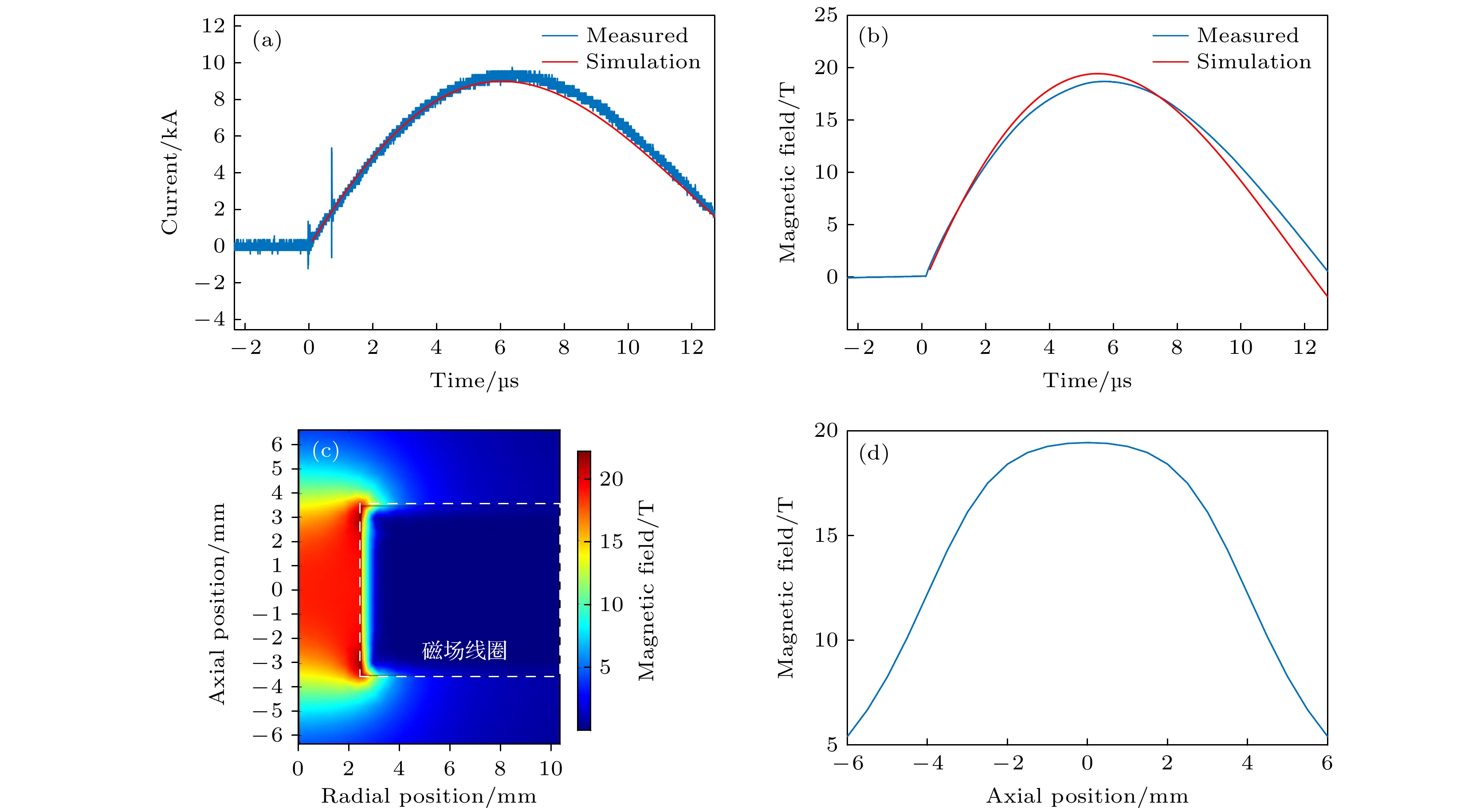
$ {L}_{\mathrm{M}} $ and$ {R}_{\mathrm{M}} $ are the inductance and resistance of the primary circuit except the solenoid;$ {L}_{\mathrm{P}} $ and$ {R}_{\mathrm{P}} $ are the inductance and resistance of the transformer primary solenoid;$ {L}_{\mathrm{S}} $ and$ {R}_{\mathrm{S}} $ are the inductance and resistance of the transformer secondary coil;$ {L}_{\mathrm{C}} $ and$ {R}_{\mathrm{C}} $ are the inductance and resistance of the secondary circuit except the secondary coil of the transformer; C is the capacitance of the capacitor.图 5 使用35匝、直径35 mm初级螺线管的电感耦合线圈在20 kV时的放电测试结果和模拟结果 (a)初级回路电流波形; (b)磁场线圈的磁场波形; (c)磁场峰值时磁场强度的二维轴对称分布; (d)线圈轴向上的峰值磁场分布
Figure 5. Experimental and simulation results of the pulsed magnetic field at 20 kV discharge voltage using an inductively coupled coil with primary solenoid of 35-turns and 35-mm diameter: (a) Current pulse of the primary solenoid; (b) magnetic field pulse at the center of the magnetic field coil; (c) two dimensional axisymmetric distribution of the peak magnetic field; (d) the peak magnetic field distribution along the axis of the magnetic field coil.
图 6 磁场线圈产生的峰值磁场强度随放电电压的变化. 虚线为模拟结果, 点为实验结果. 电感耦合线圈材料分别是Cu, CuBe和马氏体时效钢, 屈服强度分别为[25]: 黄铜200 Mpa, 铍铜1 GPa, 马氏体时效钢2 GPa
Figure 6. The peak magnetic field produced by magnetic field coil varies with the discharge voltage. The dotted line is the simulation result, and the dot is the experimental result. These inductively coupled coils are made of Cu, CuBe or Maraging steel with yield strength of: Cu ~200 MPa, CuBe ~1 GPa, Maraging steele ~2 GPa.
表 1 最高磁场强度时脉冲强磁场设备的电感和电阻分布
Table 1. The distribution of inductance and resistance of pulsed magnetic field device.
参数 放电系统 初级螺线管 次级线圈 次级回路(不包
括次级线圈)电感 450 $ \mathrm{n}\mathrm{H} $ 16.6 $\text{μ}\mathrm{H}$ 15 $ \mathrm{n}\mathrm{H} $ 3 nH 电阻 0.1 Ω 32 mΩ 0.2 mΩ 0.9 mΩ -
[1] Gotchev O V, Chang P Y, Knauer J P, Meyerhofer D D, Polomarov O, Frenje J, Li C K, Manuel M J E, Petrasso R D, Rygg J R, Séguin F H, Betti R 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 215004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chang P Y, Fiksel G, Hohenberger M, Knauer J P, Betti R, Marshall F J, Meyerhofer D D, Séguin F H, Petrasso R D 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 035006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hohenberger M, Chang P Y, Fiksel G, Knauer J P, Betti R, Marshall F J, Meyerhofer D D, Séguin F H, Petrasso R D 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 056306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bailly-Grandvaux M, Santos J J, Bellei C, et al. 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 孙可煦, 黄天晅, 丁永坤, 易荣清, 江少恩, 崔延莉, 汤晓青, 陈久森, 张保汉, 郑志坚 2002 51 1750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun K X, Huang T X, Ding Y K, Yi R Q, Jiang S E, Cui Y L, Tang X Q, Chen J S, Zhang B H, Zheng Z J 2002 Acta Phys. Sin. 51 1750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Tang H B, Hu G Y, Liang Y H, Tao T, Wang Y L, Hu P, Zhao B, Zheng J 2018 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 60 5
[7] 裴晓星, 仲佳勇, 张凯, 郑无敌, 梁贵云, 王菲鹿, 李玉同 2014 63 145201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pei X X, Zhong J Y, Zhang K, Zheng W D, Liang G Y, Wang F L, Li Y T, Zhao G 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 145201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 张凯, 仲佳勇, 裴晓星, 李玉同, 阪和洋一, 魏会冈, 袁大伟, 李芳, 韩波, 王琛, 贺昊, 尹传磊, 廖国前, 方远, 杨骕, 远晓辉, 梁贵云, 王菲鹿, 朱健强, 丁永坤, 张杰, 赵刚 2015 64 165201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang K, Zhong J Y, Pei X X, Li Y T, Sakawa Y, Wei H G, Yuan D W, Li F, Han B, Wang C, He H, Yin C L, Liao G Q, Fang Y, Yang S, Yuan X H, Liang G Y, Wang F L, Zhu J Q, Zhang J, Zhao G 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 165201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Creel J R, Donnelly T, Lunney J G 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 071104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Law K F F, Bailly-Grandvaux M, Morace A, Sakata S, Matsuo K, Kojima S, Lee S, Vaisseau X, Arikawa Y, Yogo A, Kondo K, Zhang Z, Bellei C, Santos J J, Fujioka S, Azechi H 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 091104
[11] Pollock B B, Froula D H, Davis P F, Ross J S, Fulkerson S, Bower J, Satariano J, Price D, Krushelnick K, Glenzer S H 2006 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77 114703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Albertazzi B, BéArd J, Ciardi A, et al. 2013 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 84 043505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Pollock B B, Froula D H, Tynan G R, Divol L, Price D, Costa R, Yepiz F, Fulkerson S, Mangini F, Glenzer Het 2008 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79 10F550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Gotchev O V, Knauer J P, Chang P Y, Jang N W, Shoup III M J, Meyerhofer D D, Betti R 2009 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80 043504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li C X, Jin X, Wang G P, Zhang B Z, Gong H T, Gan Y Q, Li F, Song F L 2021 Laser Part. Beams 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Barnak D H, Davies J R, Fiksel G, Chang P Y, Zabir E, Betti R 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 033501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhu J Q 2018 High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 6 e55
[18] Fiksel G, Agliata A, Barnak D, Brent G, Chang P Y, Folnsbee L, Gates G, Hasset D, Lonobile D, Magoon J, Mastrosimone D, Shoup III M J, Betti R 2015 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86 016105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang Y L, Hu G Y, Hu P, Tang H B, Yuan P, Zheng J 2019 J. Instrum. 14 P09024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang Y L, Hu G Y, Hu P, Liang Y H, Yuan P, Zheng J 2019 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90 75108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Hu P, Hu G Y, Wang Y L, Tang H B, Zheng J 2020 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 91 014703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hu G Y, Liang Y H, Song F L, Yuan P, Wang Y L, Zhao B, Zheng J 2015 Plasma Sci. Technol. 17 134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Fiksel G, Backhus R, Barnak D H, Chang P Y, Davies J R, Jacobs-Perkins D, McNally P, Spielman R B, Viges E, Betti R 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 084703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 李瀚荪 2006 电路分析基础 (第4版) (北京: 高等教育出版社) 第12页
Li H S 2006 Circuit Analysis (Vol. 4) (Beijing: Higher Education Press) p12 (in Chinese)
[25] 布卢姆H 著 (江伟华, 张驰译) 2008 脉冲功率系统的原理与应用 (北京: 清华大学出版社) 第188页
Bluhm H(translated by Jiang W H, Zhang C)2008 Pulsed Power Systems: Principles and Applications (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) p188 (in Chinese)
[26] 张丝雨 2005 最新金属材料牌号、性能、用途及中外牌号对照速用速查实用手册(香港: 中国科技文化出版社)第709页、第1122页
Zhang S Y 2005 The Latest Metal Material Grades, Properties, Uses and Comparison of Chinese and Foreign Grades, Quick-use Quick Reference Practical Manual (Hong Kong: China Science and Culture Publishing Press) p709, p1122 (in Chinese)
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7986
- PDF Downloads: 95
- Cited By: 0































 DownLoad:
DownLoad: