-
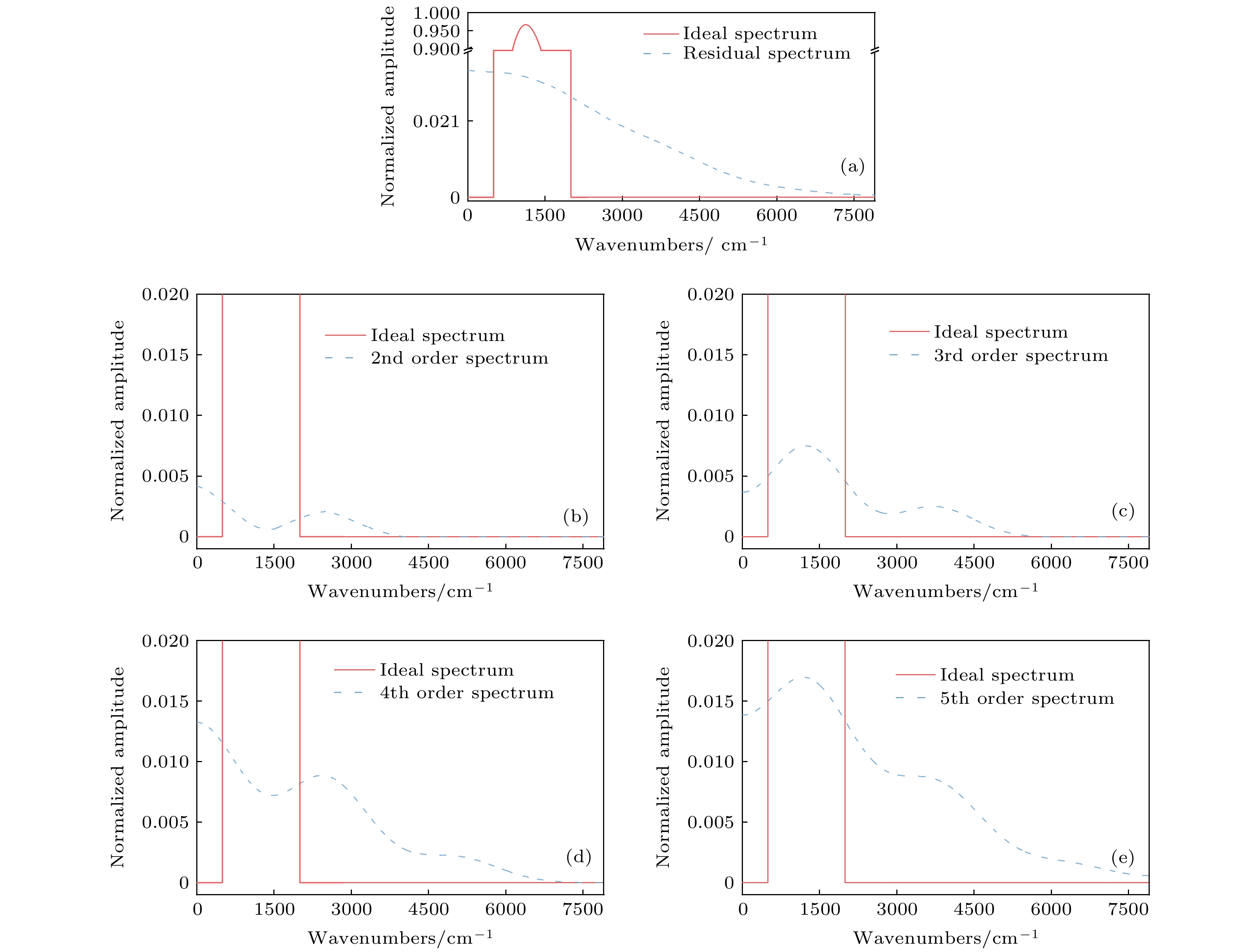
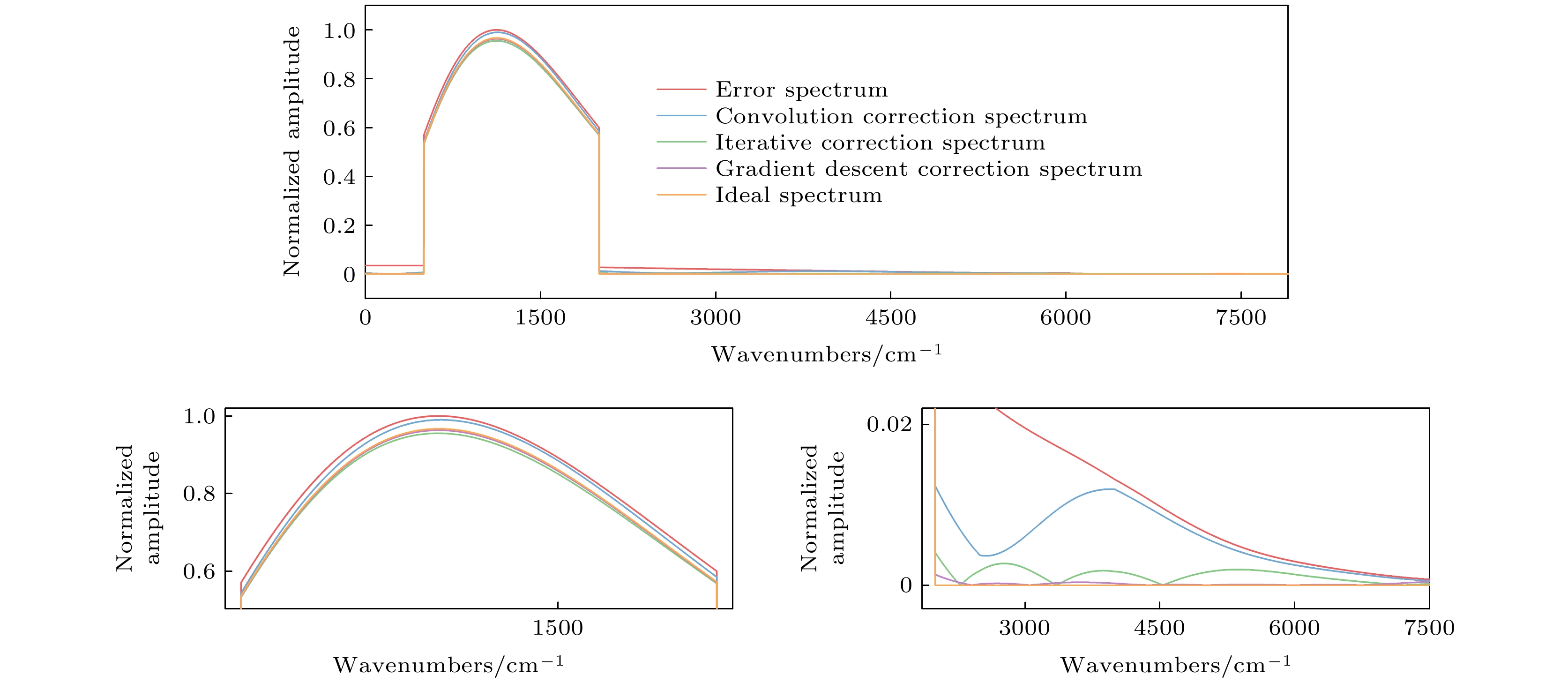
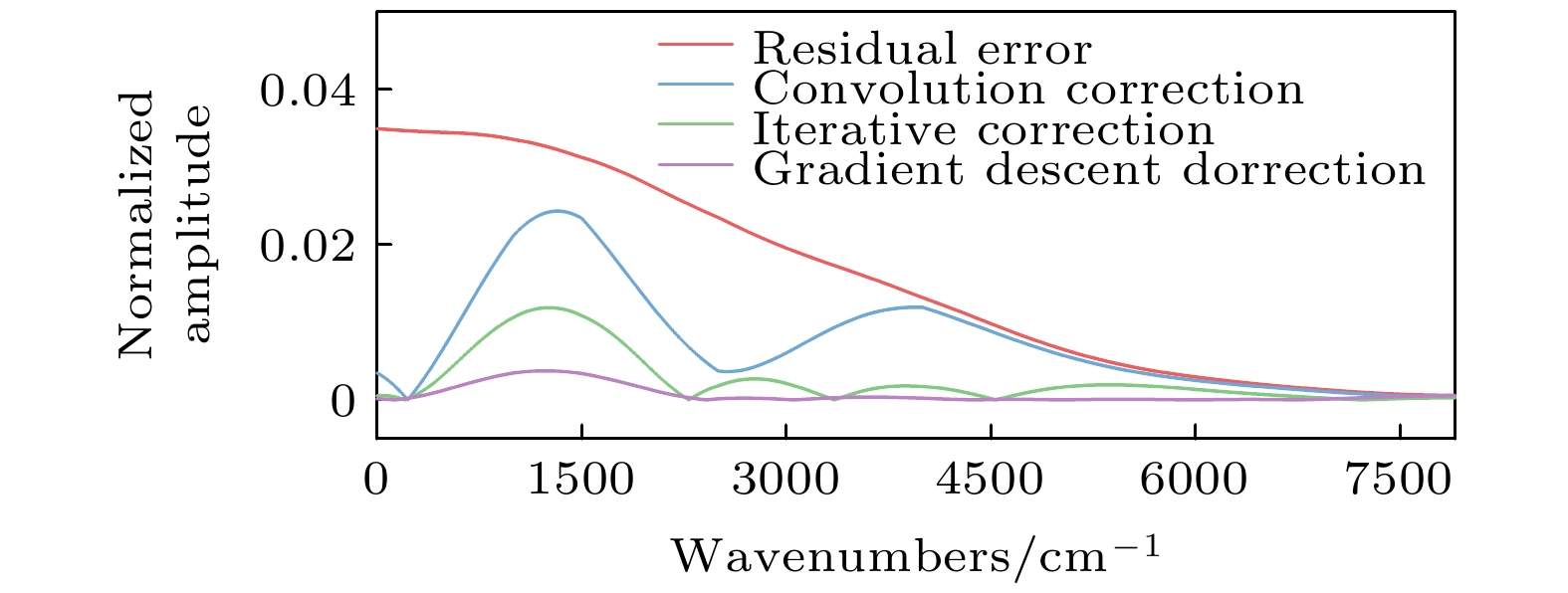
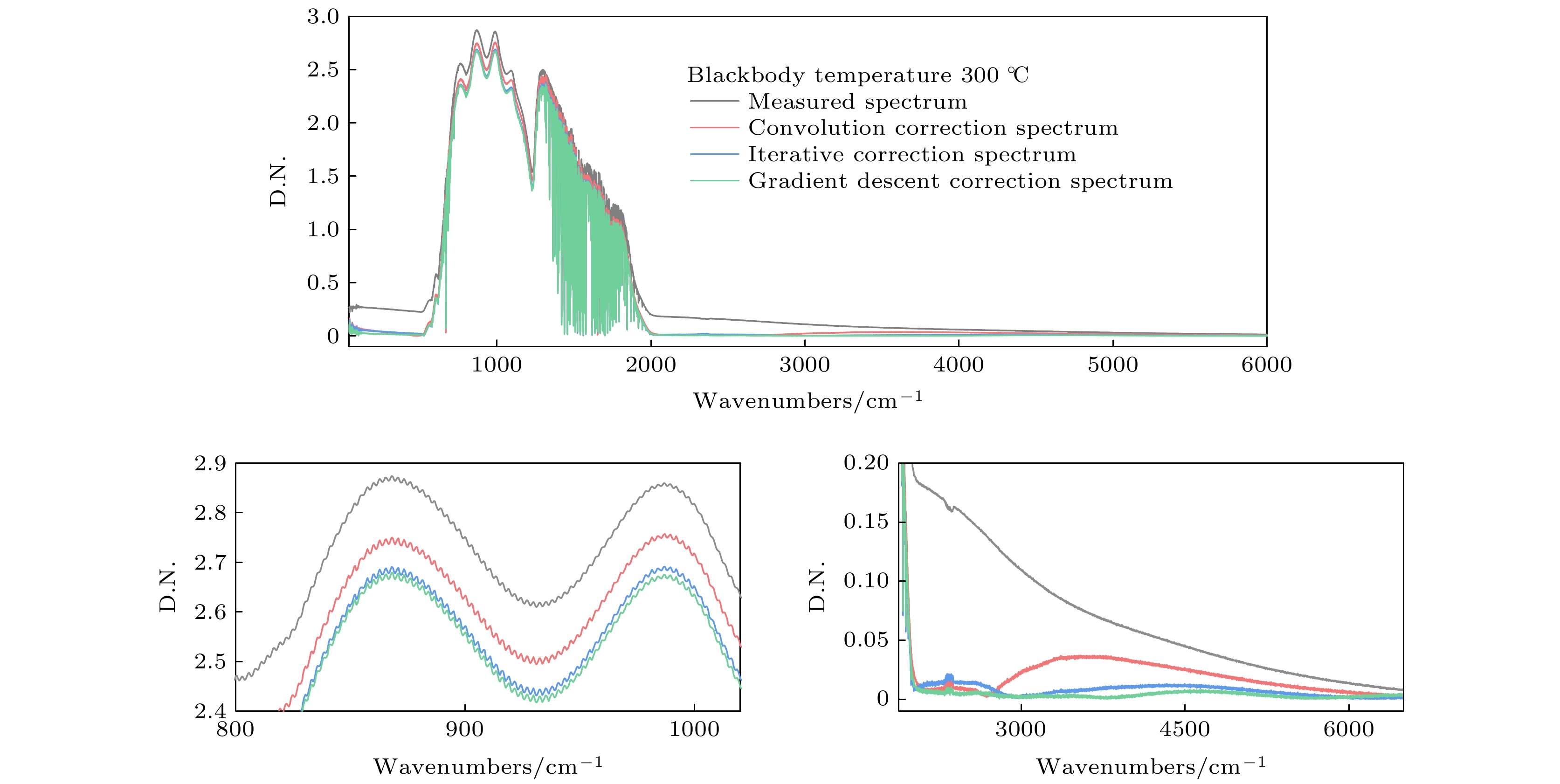
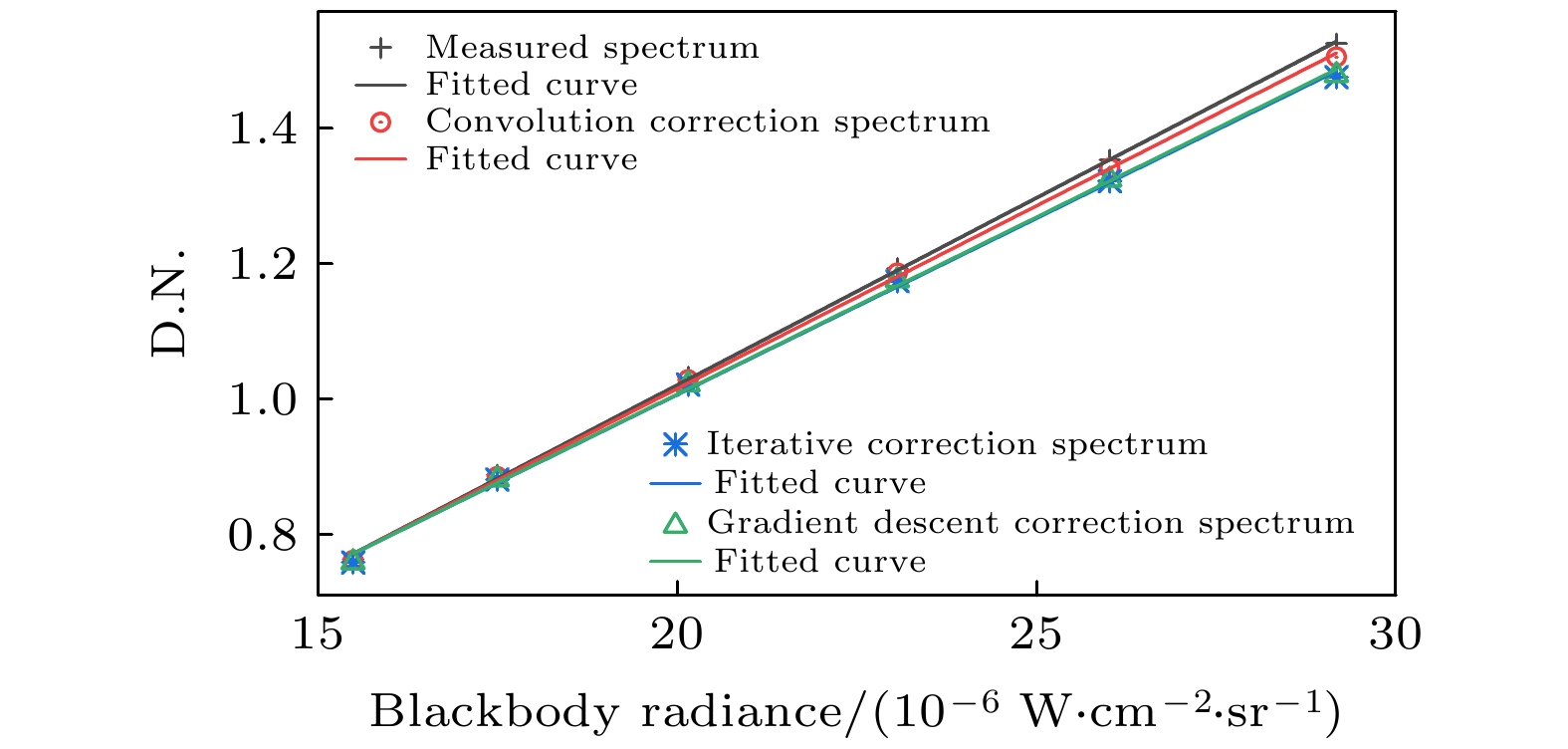
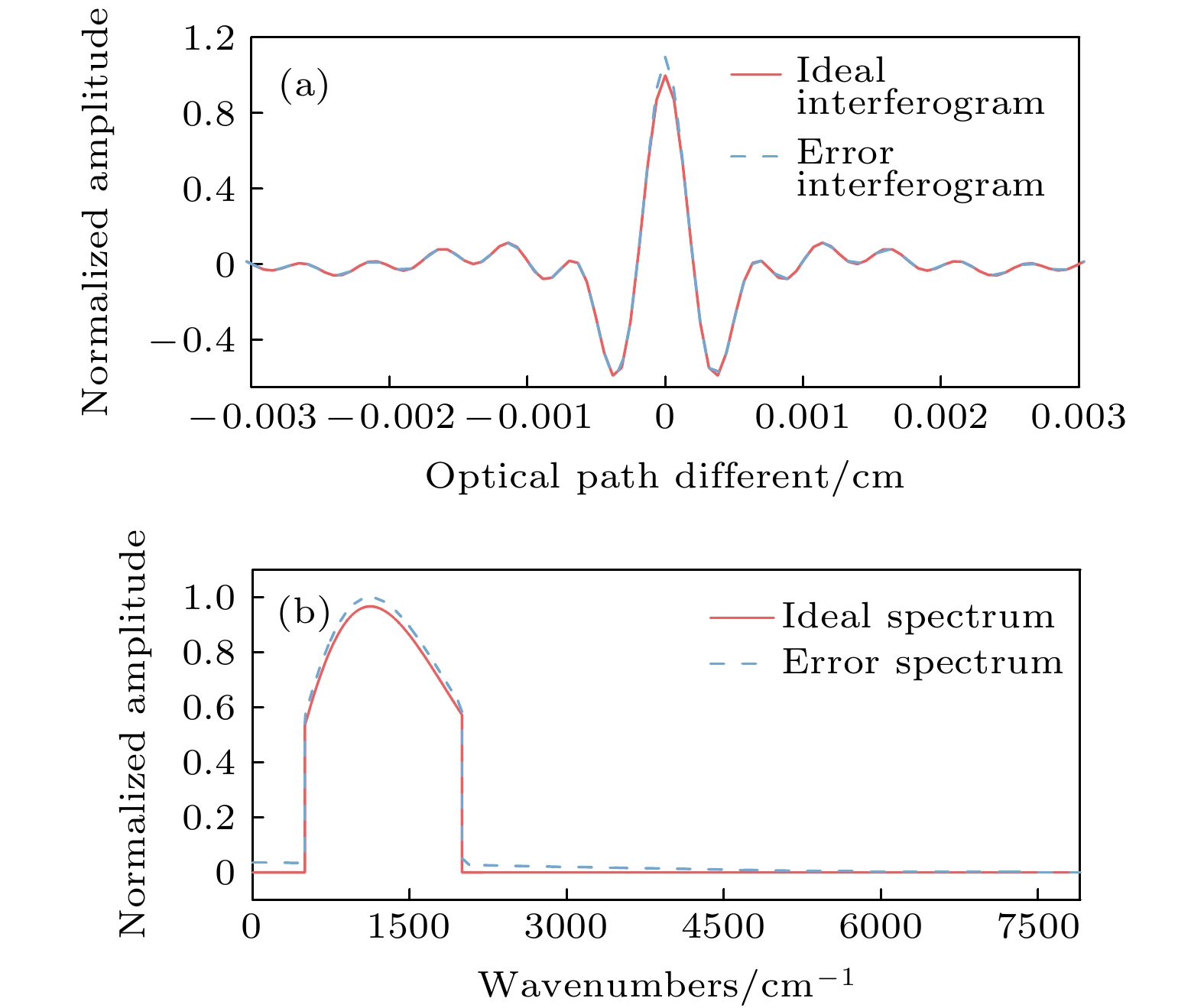
The infrared detector can generate nonlinear response error when the Fourier transform infrared spectrometer is used for implementing the radiometric calibration or observing the high temperature targets. Based on the relationship between the incident radiation intensity and the electron concentration in the optical conduction band, the mechanism of the nonlinear response error caused by the high incident photon flow is analyzed. According to Planck radiation law and interference principle, the effect of nonlinear error on spectrum is studied by simulating blackbody radiation data with nonlinear error. It is found that the nonlinear response with a different order has a different influence region, and the higher-order nonlinear response has a wider influence range and generates a larger nonlinear response error. By the general nonlinear response correction method the nonlinear response coefficient is obtained through constructing the nonlinear response model of the interference data and then the spectral distortion produced by the detector is corrected. According to the convolution iteration method, the polar orbit meteorological satellite CrIS constructs the convolution equation to correct the second-order nonlinear response by taking the low-wave number band of 50-500 cm–1 as the characteristic region. The European Meteorological Agency’s Airborne Infrared Interferometer Evaluation System (ARIES) selected two feature areas, 50-500 cm–1 and 2000-2500 cm–1, and iteratively corrected the second-order and third-order nonlinear response. The gradient descent method is often used to solve the optimization problems of unconstrained multivariate functions. Based on the gradient descent algorithm, an iterative method suitable for correcting the high-order nonlinear response errors is proposed in this paper. In this method, the information about the iteration point is obtained by constructing the nonlinear response function of the high-order detector and setting the appropriate iteration initialization. According to the initial value of the iteration and the information about the known iteration point, the gradient of the iteration variable is calculated to determine the iteration value of the next unknown variable, thus quickly searching for the global minimum point and determining the nonlinear response coefficient. We use Fourier transform infrared spectrometer to carry out radiometric calibration experiment and compare the effects of three correction methods: convolution, cross iteration and gradient descent method. The results show that the three correction methods can effectively reduce the nonlinear error, and improve the fitting extent by 0.15%, 0.29% and 0.39% respectively. The spectral data corrected by gradient descent method are more accurate.
-
Keywords:
- remote sensing /
- infrared spectrometer /
- high-order nonlinearity response /
- gradient descent method
[1] 刘文清, 陈臻懿, 刘建国, 谢品华, 张天舒, 阚瑞峰, 徐亮 2018 中国环境监测 34 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu W Q, Chen Z R, Liu J G, Xie P H, Zhang T S, Kan R F, Xu L 2018 Envir. Monitor. China 34 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 冯明春, 徐亮, 高闽光, 焦洋, 李相贤, 金岭, 程巳阳, 童晶晶, 魏秀丽, 李胜 2012 红外技术 34 366
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng M C, Xu L, Gao M G, Jiao Y, Li X X, Jin L, Cheng S Y, Dong J J, Wei X L, Li S 2012 IR. Tech. 34 366
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shen X C, Ye S B, Xu L, Hu R, Jin L, Xu H Y, Liu J G, Liu W Q 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 5794
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 焦洋, 徐亮, 高闽光, 冯明春, 金岭, 童晶晶, 李胜 2012 光谱学与光谱分析 32 1754
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiao Y, Xu L, Gao M G, Feng M C, Jin L, Dong J J, Li S 2012 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 32 1754
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 冯明春, 徐亮, 刘文清, 刘建国, 高闽光, 魏秀丽 2016 65 014210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng M C, Xu L, Liu W Q, Liu J G, Gao M G, Wei X L 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 014210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shao L, Griffiths P R 2008 Anal. Chem. 80 5219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 金岭, 徐亮, 高闽光, 童晶晶, 程巳阳, 李相贤 2013 大气与环境光学学报 8 416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jin L, Xu L, Gao M G, Dong J J, Cheng S Y, Li X X 2013 J. Atmosph. Environ. Opt. 8 416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Clare J F 2002 Meas. Sci. Technol. 13 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Carter R O, Lindsay N E, Beduhn D 1990 Appl. Spectrosc. 44 1147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Han Y, Revercomb H, Cromp M, Gu D, Johnson D, Mooney D, Scott D, Strow L, Bingham G, Borg L, Chen Y, DeSlover D, Esplin M, Hagan D, Jin X, Knuteson R, Motteler H, Predina J, Suwinski L, Taylor J, Tobin D, Tremblay D, Wang C, Wang L, Wang L, Zavyalov V 2013 J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 118 12734
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 杨敏珠, 邹曜璞, 张磊, 韩昌佩 2017 红外与激光工程 44 272
Yang M Z, Zou Y F, Zhang L, Han C P 2017 Infrared Laser Eng. 44 272
[12] Fiedler L, Newman S, Bakan S 2005 Appl. Opt. 44 5332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Felix P, Moulin M, Munier B, Portmann J, Reboul J P 1980 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 27 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bartoli F 1974 J. Appl. Phys. 45 2150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Bose 1924 Z. Phys. 26 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Griffiths P R 2007 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry (2 nd Ed.) (New York: Wiley-Interscience) p88−116
[17] Vorontsov M A, Carhart G W, Ricklin J C 1997 Opt. Lett. 22 907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 徐亮, 王君, 刘建国, 高闽光, 陆亦怀, 刘文清, 魏秀丽, 张天舒, 陈华, 刘志明 2007 大气与环境光学学报 2 218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu L, Wang J, Liu J G, Gao M G, Lu Y H, Liu W Q, Wei X L, Zhang T S, Chen H, Liu Z M 2007 J. Atmosph. Environ. Opt. 2 218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Revercomb H E, Buijs H, Howell H B, Laporte D D, Smith W L, Sromovsky L A 1988 Appl. Opt. 27 3210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 徐亮, 陈华, 刘建国, 高闽光, 陆亦怀, 刘文清, 张天舒, 魏秀丽, 赵雪松, 朱军 2007 大气与环境光学学报 2 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu L, Chen H, Liu J G, Gao M G, Lu Y H, Liu W Q, Zhang T S, Wei X L, Zhao X S, Zhu J 2007 J. Atmosph. Environ. Opt. 2 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 无大气吸收波段三种校正方法拟合优度对比
Table 1. Comparison of R2 of three methods at band without atmospheric absorption.
Wavenu-mber
/cm–1R2 Measured
spectrumConvolution
correction
spectrumIterative
correction
spectrumGradient
correction
spectrum610—
6200.99403 0.99483 0.99829 0.99997 770—
7800.99401 0.99478 0.99826 0.99992 820—
8300.99263 0.99334 0.99671 0.99912 870—
8800.99335 0.99393 0.99672 0.99974 910—
9200.99374 0.99429 0.99782 0.99946 -
[1] 刘文清, 陈臻懿, 刘建国, 谢品华, 张天舒, 阚瑞峰, 徐亮 2018 中国环境监测 34 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu W Q, Chen Z R, Liu J G, Xie P H, Zhang T S, Kan R F, Xu L 2018 Envir. Monitor. China 34 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 冯明春, 徐亮, 高闽光, 焦洋, 李相贤, 金岭, 程巳阳, 童晶晶, 魏秀丽, 李胜 2012 红外技术 34 366
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng M C, Xu L, Gao M G, Jiao Y, Li X X, Jin L, Cheng S Y, Dong J J, Wei X L, Li S 2012 IR. Tech. 34 366
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shen X C, Ye S B, Xu L, Hu R, Jin L, Xu H Y, Liu J G, Liu W Q 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 5794
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 焦洋, 徐亮, 高闽光, 冯明春, 金岭, 童晶晶, 李胜 2012 光谱学与光谱分析 32 1754
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiao Y, Xu L, Gao M G, Feng M C, Jin L, Dong J J, Li S 2012 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 32 1754
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 冯明春, 徐亮, 刘文清, 刘建国, 高闽光, 魏秀丽 2016 65 014210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng M C, Xu L, Liu W Q, Liu J G, Gao M G, Wei X L 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 014210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shao L, Griffiths P R 2008 Anal. Chem. 80 5219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 金岭, 徐亮, 高闽光, 童晶晶, 程巳阳, 李相贤 2013 大气与环境光学学报 8 416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jin L, Xu L, Gao M G, Dong J J, Cheng S Y, Li X X 2013 J. Atmosph. Environ. Opt. 8 416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Clare J F 2002 Meas. Sci. Technol. 13 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Carter R O, Lindsay N E, Beduhn D 1990 Appl. Spectrosc. 44 1147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Han Y, Revercomb H, Cromp M, Gu D, Johnson D, Mooney D, Scott D, Strow L, Bingham G, Borg L, Chen Y, DeSlover D, Esplin M, Hagan D, Jin X, Knuteson R, Motteler H, Predina J, Suwinski L, Taylor J, Tobin D, Tremblay D, Wang C, Wang L, Wang L, Zavyalov V 2013 J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 118 12734
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 杨敏珠, 邹曜璞, 张磊, 韩昌佩 2017 红外与激光工程 44 272
Yang M Z, Zou Y F, Zhang L, Han C P 2017 Infrared Laser Eng. 44 272
[12] Fiedler L, Newman S, Bakan S 2005 Appl. Opt. 44 5332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Felix P, Moulin M, Munier B, Portmann J, Reboul J P 1980 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 27 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bartoli F 1974 J. Appl. Phys. 45 2150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Bose 1924 Z. Phys. 26 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Griffiths P R 2007 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry (2 nd Ed.) (New York: Wiley-Interscience) p88−116
[17] Vorontsov M A, Carhart G W, Ricklin J C 1997 Opt. Lett. 22 907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 徐亮, 王君, 刘建国, 高闽光, 陆亦怀, 刘文清, 魏秀丽, 张天舒, 陈华, 刘志明 2007 大气与环境光学学报 2 218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu L, Wang J, Liu J G, Gao M G, Lu Y H, Liu W Q, Wei X L, Zhang T S, Chen H, Liu Z M 2007 J. Atmosph. Environ. Opt. 2 218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Revercomb H E, Buijs H, Howell H B, Laporte D D, Smith W L, Sromovsky L A 1988 Appl. Opt. 27 3210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 徐亮, 陈华, 刘建国, 高闽光, 陆亦怀, 刘文清, 张天舒, 魏秀丽, 赵雪松, 朱军 2007 大气与环境光学学报 2 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu L, Chen H, Liu J G, Gao M G, Lu Y H, Liu W Q, Zhang T S, Wei X L, Zhao X S, Zhu J 2007 J. Atmosph. Environ. Opt. 2 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7200
- PDF Downloads: 90
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: