-
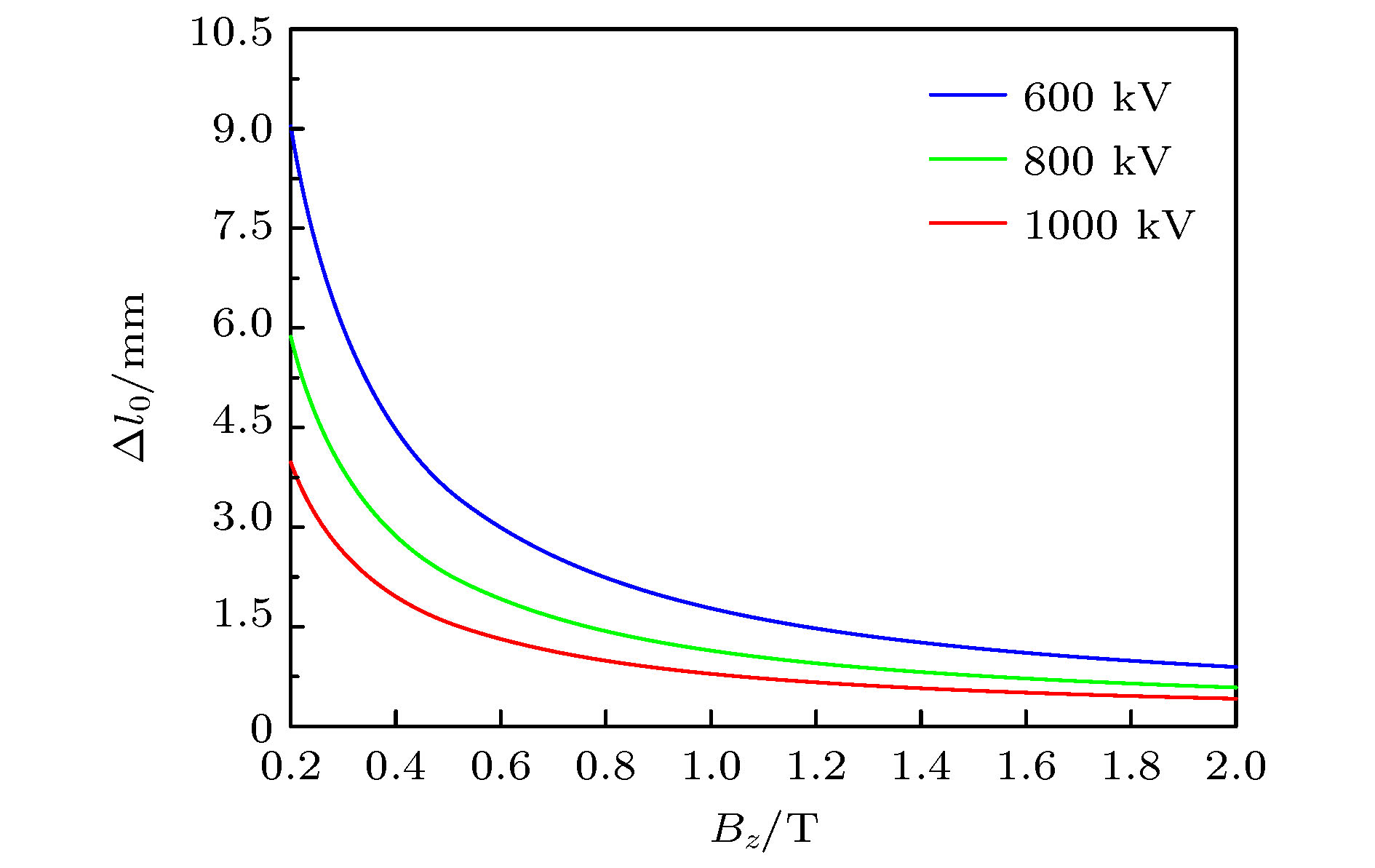
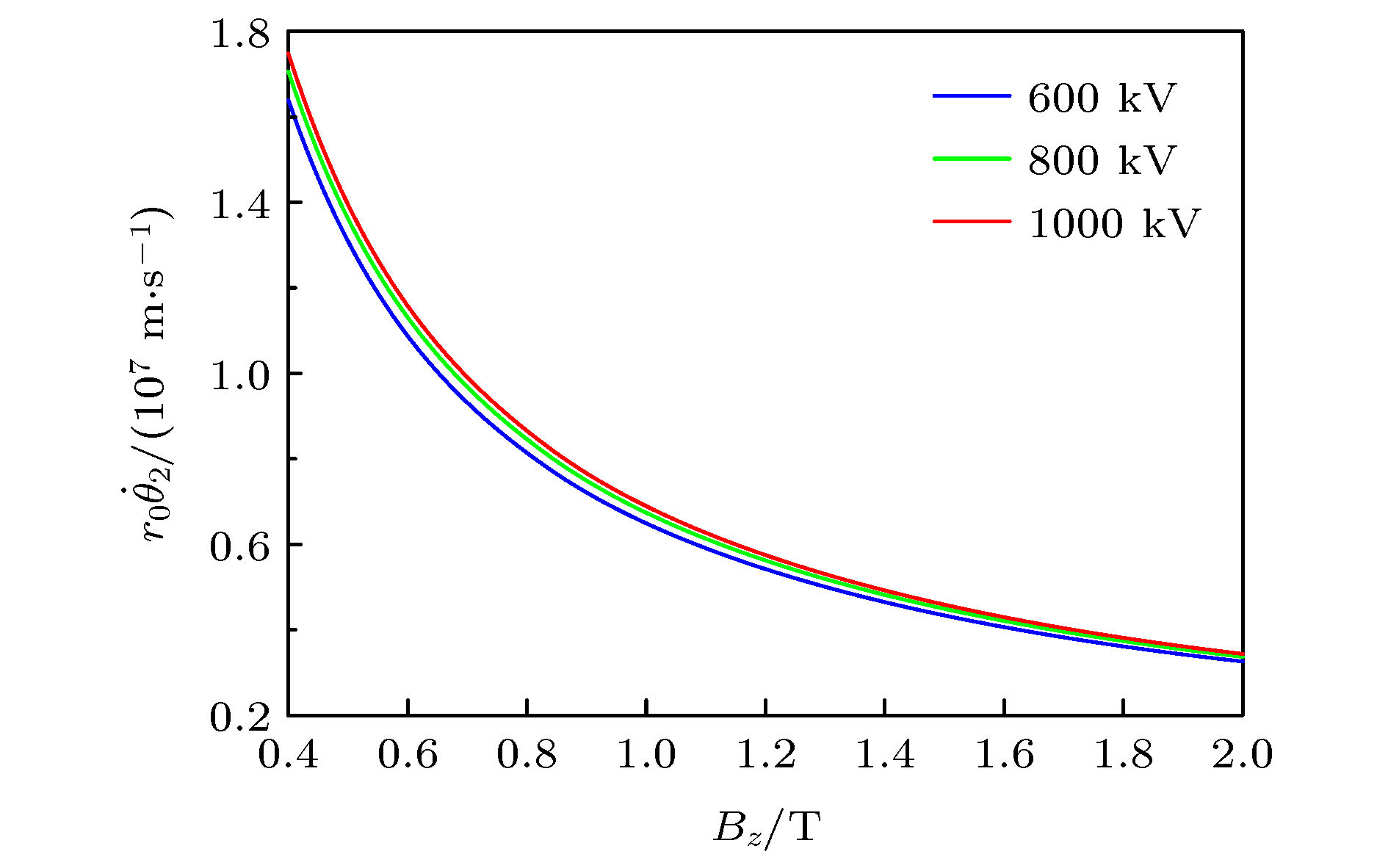
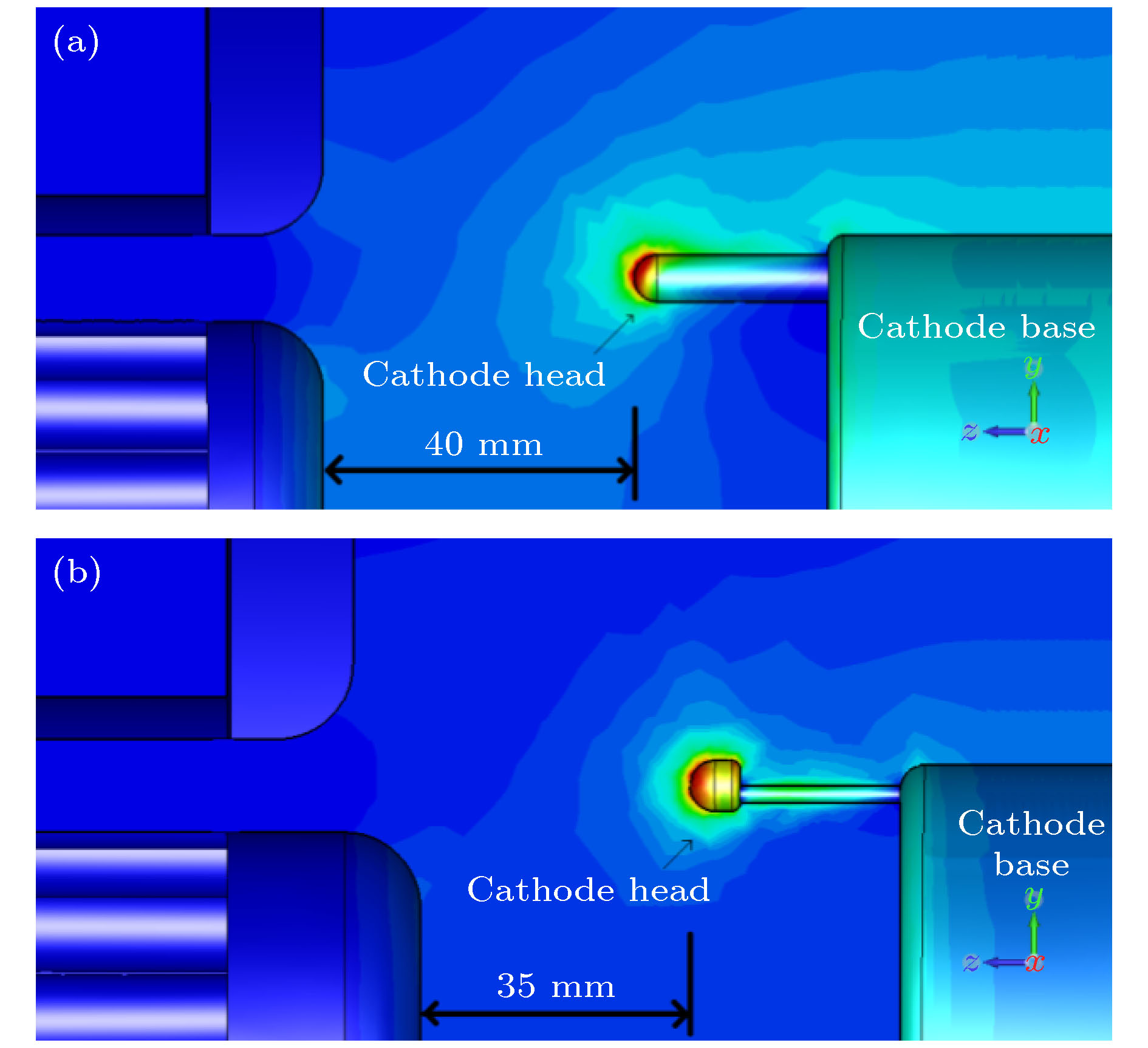
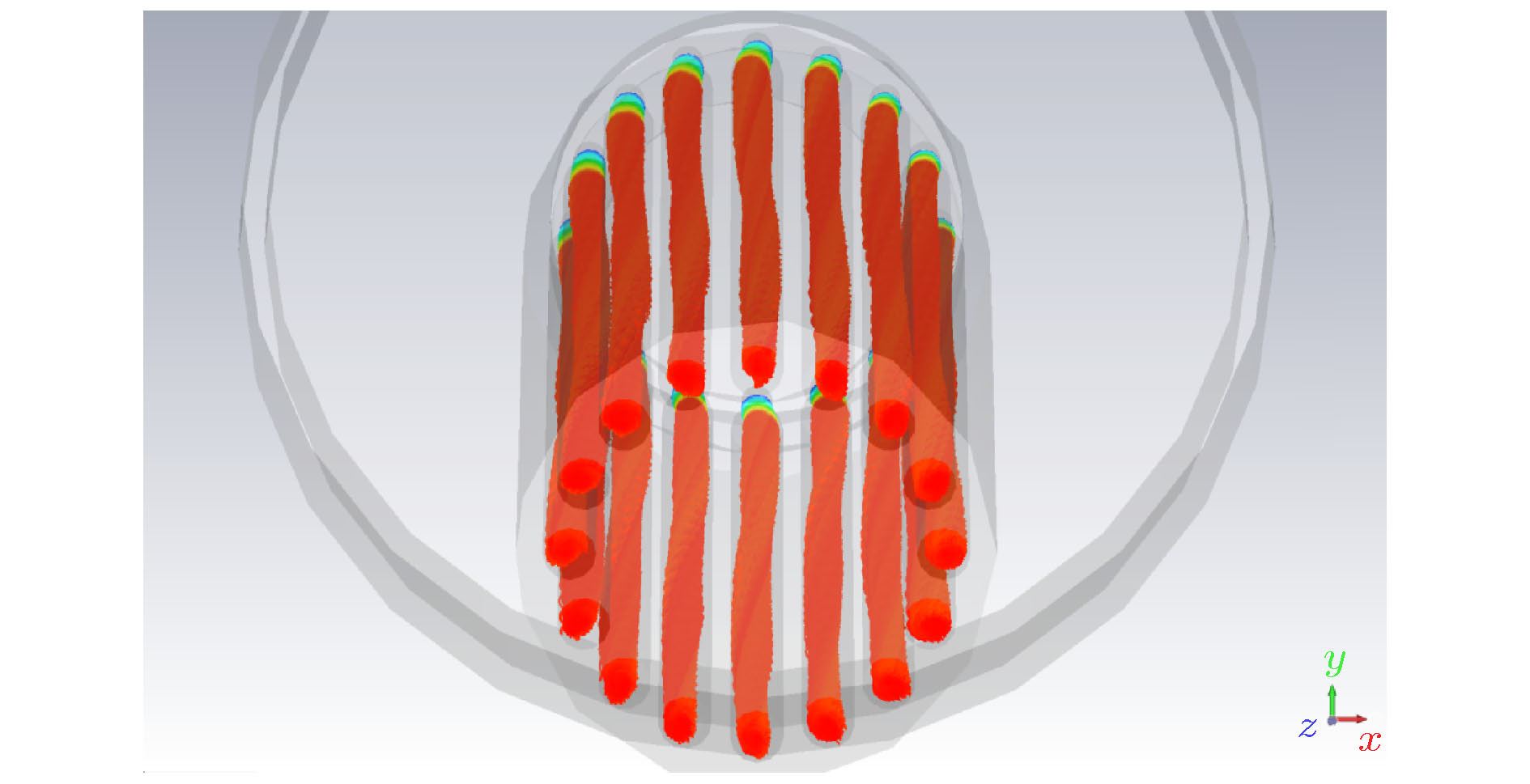
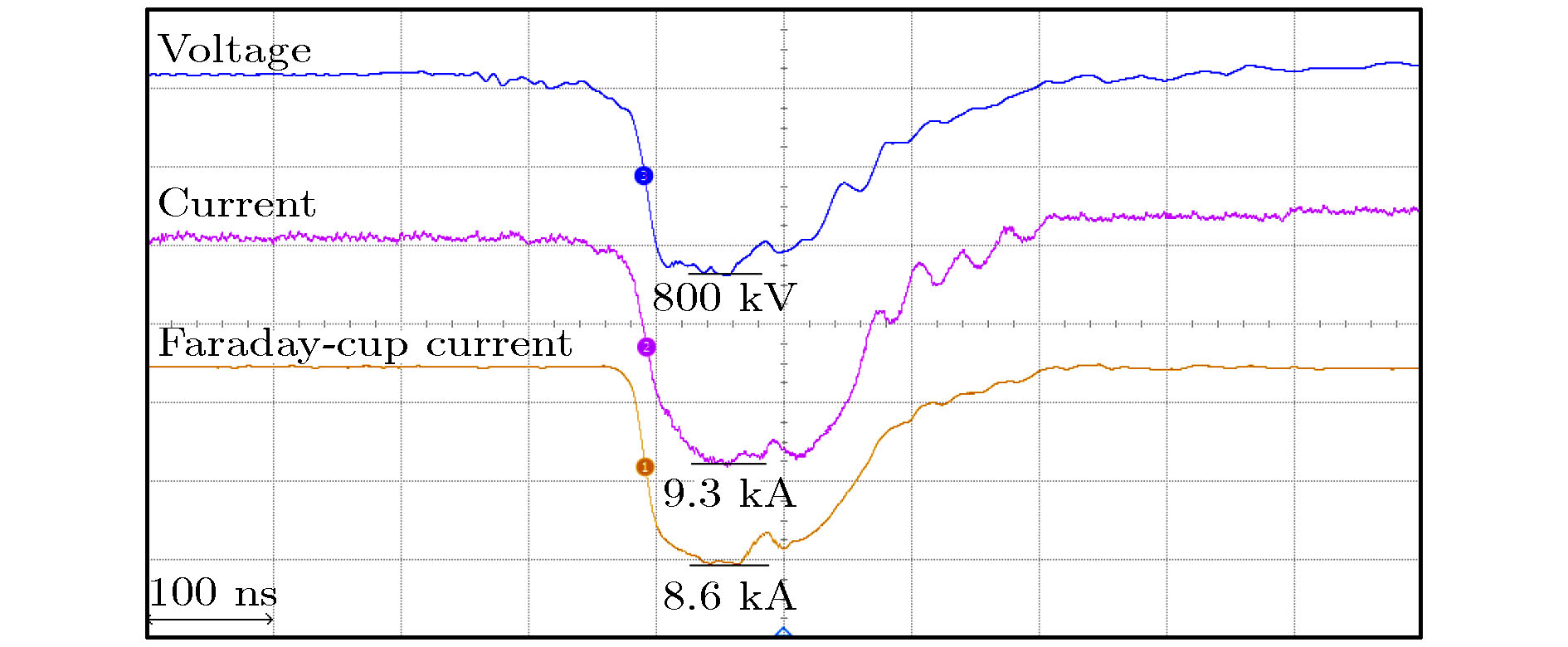
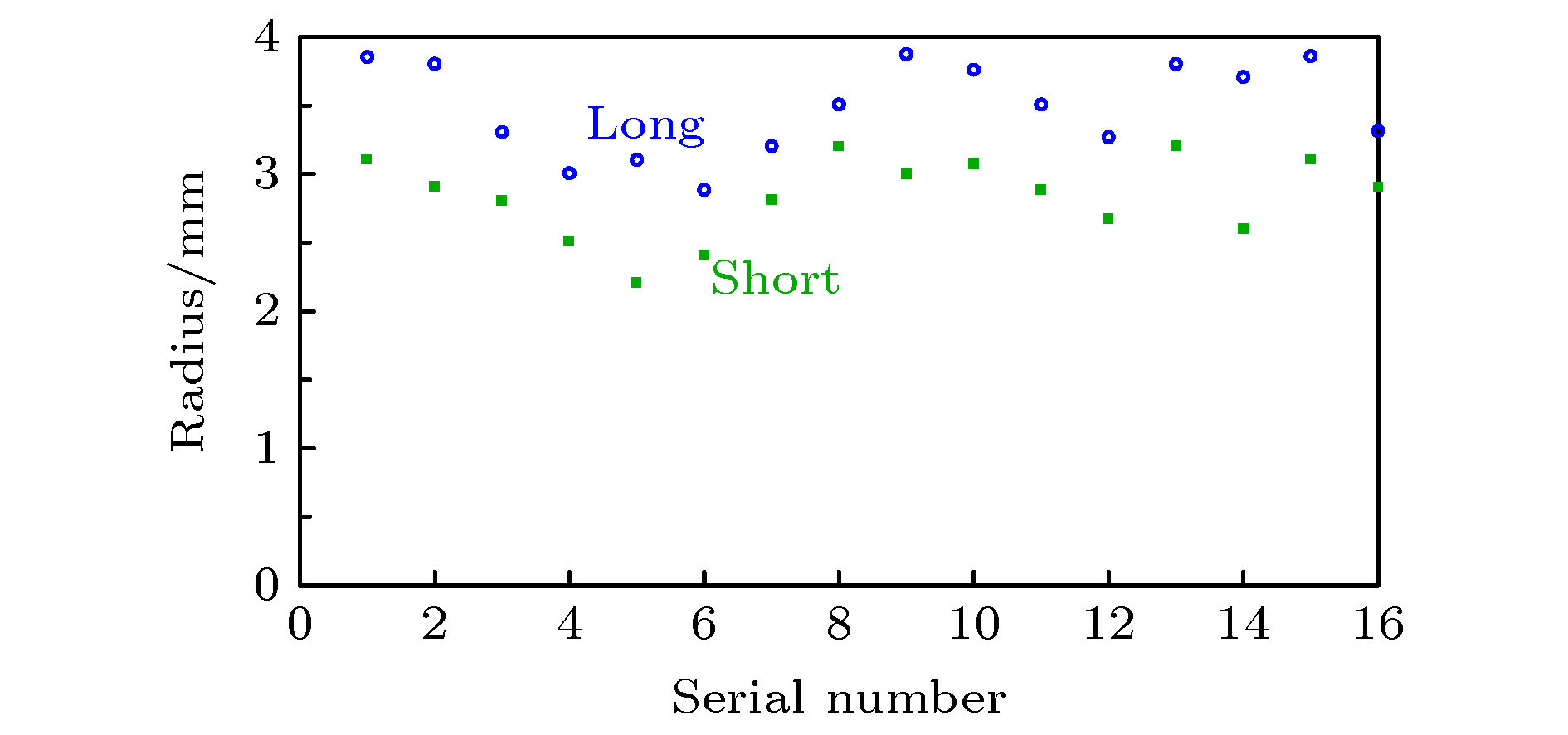
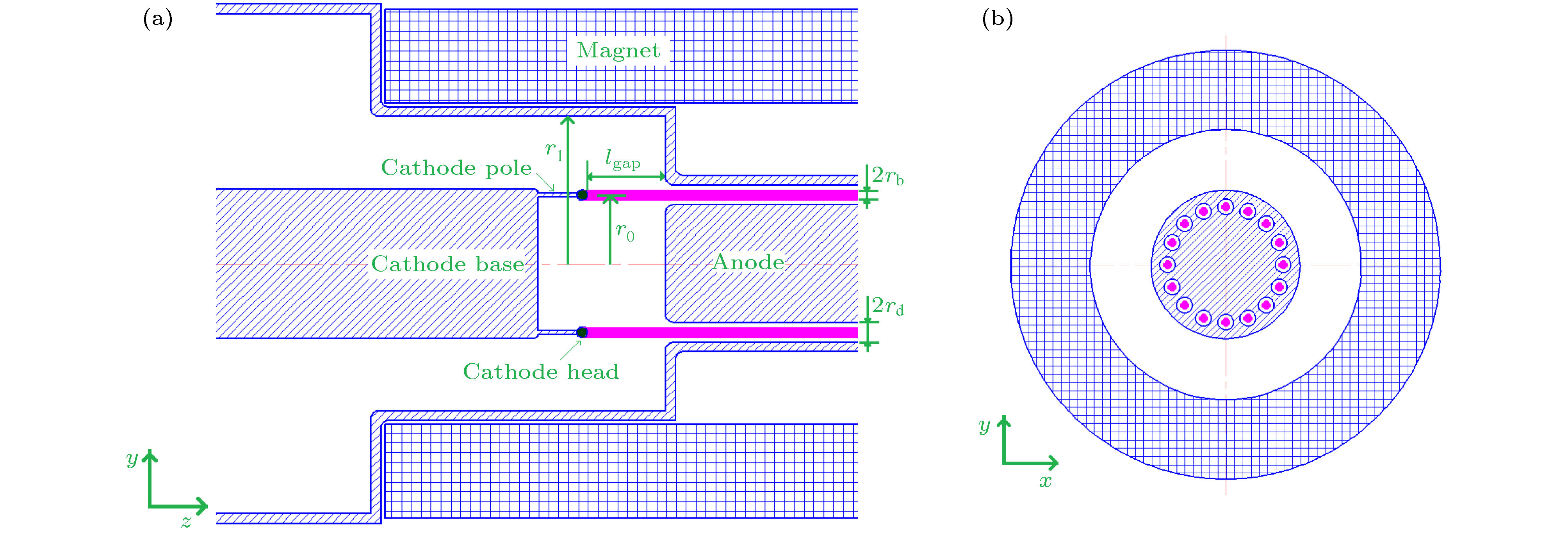
The relativistic klystron amplifier (RKA) is one of the most efficient sources to amplify a high-power microwave signal due to its intrinsic merit of high-power conversion efficiency, high gain and stable operating frequency. However, the transverse dimensions of the RKA dramatically decrease when the operating frequency increases to X band, and the power capacity of the RKA is limited by the transverse dimensions. An X-band multiple-beam relativistic klystron amplifier is proposed to overcome the radiation power limitation. Each electron beam propagates in separate drift tubes and shares the same coaxial interaction cavities in the multiple-beam relativistic klystron amplifier, and the transverse dimensions of the multiple-beam relativistic klystron amplifier are free from the operating frequency restriction and a microwave power of over 1 GW is generated in the experiment. For a high-power electron device, the transmission of electron beam is critical, and the power conversion efficiency of the device is affected. In this paper, we conduct an investigation into the transmission process of the intense relativistic multiple electron beams, and the number of the multiple electron beams is set to be 16. It is found that when the multiple electron beam is transmitted in the device, the electron beam rotates around the center of the whole device, causing the electron beam to deviate from the drift tube channel. At the same time, each electron beam rotates around itself, and the cross section of the electron beam is deformed and expanded. In the improper design of electron beam and drift tube parameters, two kinds of rotating motions cause beam to lose. A multiple-electron-beam diode structure is optimized by the particle-in-cell simulation to reduce beam loss, with the effects of the related factors taken into account. Each pole of the cathodes is made up of graphite and stainless steel. The cathode head is made up of graphite, for the graphite has a lower emission threshold. The cathode base and cathode pole are made up of stainless steel, for the stainless steel has a higher emission threshold. Also the shape and structure of cathode pole, cathode head and anode are optimized to reduce the electric field intensity on the cathode pole and enhance the electric field intensity on the end face of cathode head. At the same time, the electric field distribution of the cathode head is uniform to improve the electron beam emission uniformity. The simulation results demonstrate that the transmission efficiency of multiple electron beams can reach 99%. In the experiment, the transmission efficiency of multiple electron beams is 92% with a beam voltage and beam current of 801 kV and 9.3 kA, respectively.
-
Keywords:
- intense multiple electron beams /
- electron beams transmission /
- space charge effect /
- electron beams rotation
[1] Benford J, Swegle J A 著 (江伟华, 张弛 译) 2009 高功率微波 (第二版) (中译本) (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第3−5页
Benford J, Swegle J A (translated by Jiang W H, Zhang C) 2008 High Power Microwave (2nd Ed.) (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp3−5 (in Chinese)
[2] 丁耀根 2010 大功率速调管的制造和应用 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第7−13页
Ding Y G 2010 Design, Manufacture and Application of High Power Klystron (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp7−13 (in Chinese)
[3] Robert J B, Edl S 2005 高功率微波源与技术 (中译本) (北京: 清华大学出版社) 第282−289页
Robert J B, Edl S 2005 High Power Microwave Sources and Technologies (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) pp282−289 (in Chinese)
[4] 黄华, 吴洋, 刘振帮, 袁欢, 何琥, 李乐乐, 李正红, 金晓, 马弘舸 2018 67 088402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang H, Wu Y, Liu Z B, Yuan H, He H, Li L L, Li Z H, Jin X, Ma H G 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 088402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 吴洋, 许州, 周霖, 李文君, 唐传祥 2012 61 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y, Xu Z, Zhou L, Li W J, Tang C X 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Thomas H, Adam B, Rasheda B, Heinz B, Mark C, Edward E, Deepika G, Armand S, Brad S, Lou Z 2010 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38 1264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ding Y G, Shen B, Cao J, et al. 2009 IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 56 870
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li R J, Ruan C J, Zhang H F 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 033107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Friedman M, Pasour J, Smithe D 1997 Appl. Phys. Lett. 71 3724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 魏元璋, 李士锋, 王战亮, 黄华, 刘振帮, 何琥, 宫玉彬 2018 强激光与粒子束 30 063007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei Y Z, Li S F, Wang Z L, Huang H, Liu Z B, He H, Gong Y B 2018 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 30 063007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Edward B A, Andrew N D, Mikhail I F, et al. 2002 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 30 1041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang W, Ju J C, Zhang J, Zhou Y X, Zhong H H 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 053102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Qi Z M, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Zhong H H, Xu L R, Yang L 2016 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 37 782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 刘振帮, 金晓, 黄华, 陈怀璧 2012 61 128401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Jin X, Huang H, Chen H B 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 128401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 刘振帮, 黄华, 金晓, 袁欢, 戈弋, 何琥, 雷禄容 2015 64 018401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Huang H, Jin X, Yuan H, Ge Y, He H, Lei L R 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 018401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu Z B, Huang H, Jin X, Lei L R, Zhu L, Li L L, Li S F, Yan W K, He H 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 093110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 刘振帮, 金晓, 黄华, 陈怀璧, 王淦平 2012 61 248401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Jin X, Huang H, Chen H B, Wang G P 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 248401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 王淦平, 金晓, 黄华, 刘振帮 2017 66 044102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G P, Jin X, Huang H, Liu Z B 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 044102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 谢家麟, 赵永翔 1966 速调管群聚理论 (北京: 科学出版社) 第104—108, 208—209页
Xie J L, Zhao Y X 1966 Bunching Theory of Klystron (Beijing: Science Press) pp104–108, 208–209 (in Chinese)
[20] 王文祥 2009 微波工程技术 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第44, 45页
Wang W X 2009 Microwave Project and Technology (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp44, 45 (in Chinese)
-
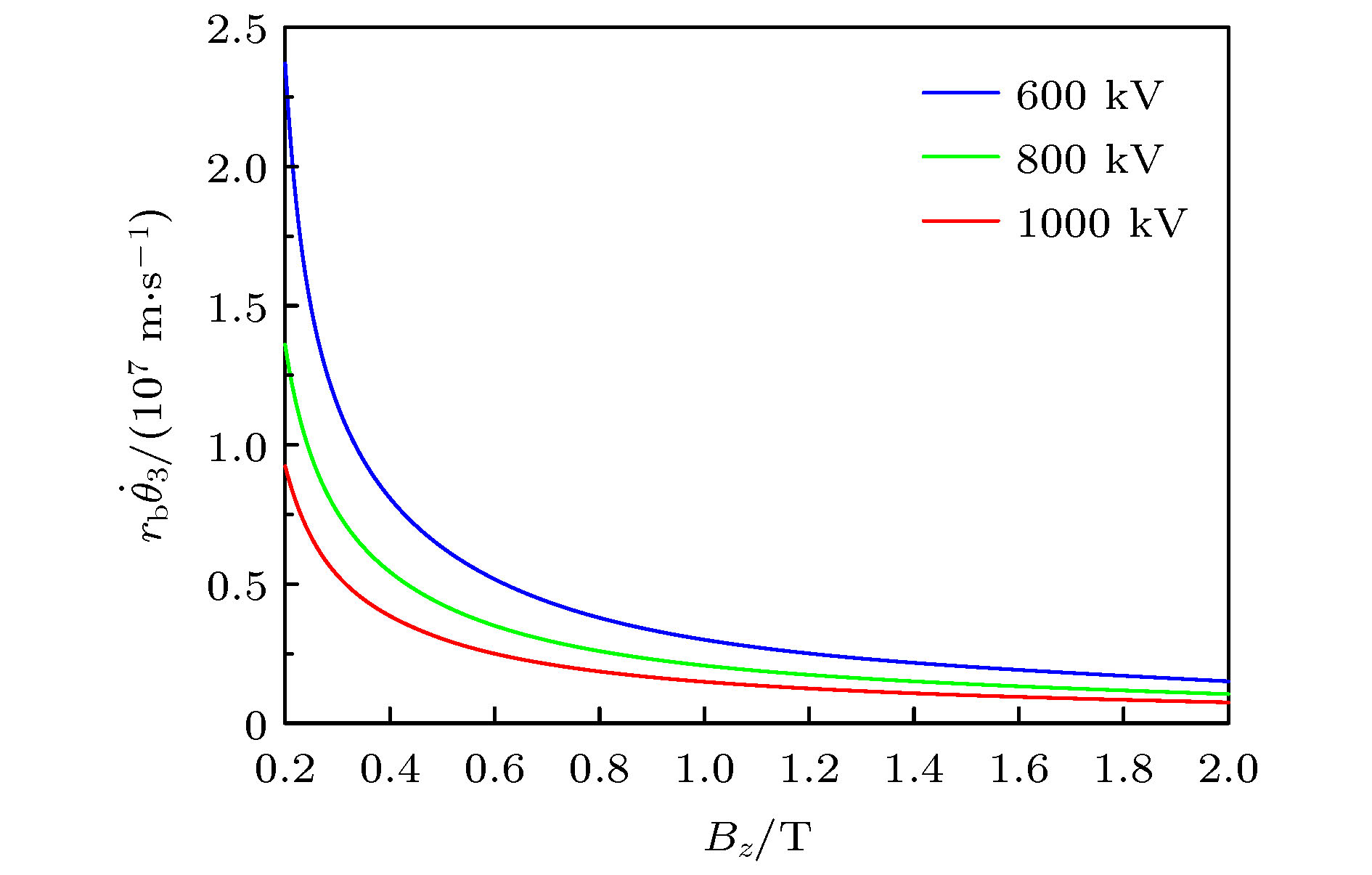
图 4 多注电子束绕束自身旋转角速度
${r_{\rm{b}}}{{\mathop \theta \limits^. }_3}$ 随引导磁场的变化Figure 4. Angular velocity of the multi-beams rotation around themselves
${r_{\rm{b}}}{{\mathop \theta \limits^. }_3}$ vs. Bz at different U0.${r_{\rm{b}}}{{\mathop \theta \limits^. }_3}$ represents the angular velocity of the multi-beams rotation around themselves.表 1 电子束电压、电流以及末端法拉第筒电流参数
Table 1. Electron beam voltage, current and terminal Faraday tube current parameters.
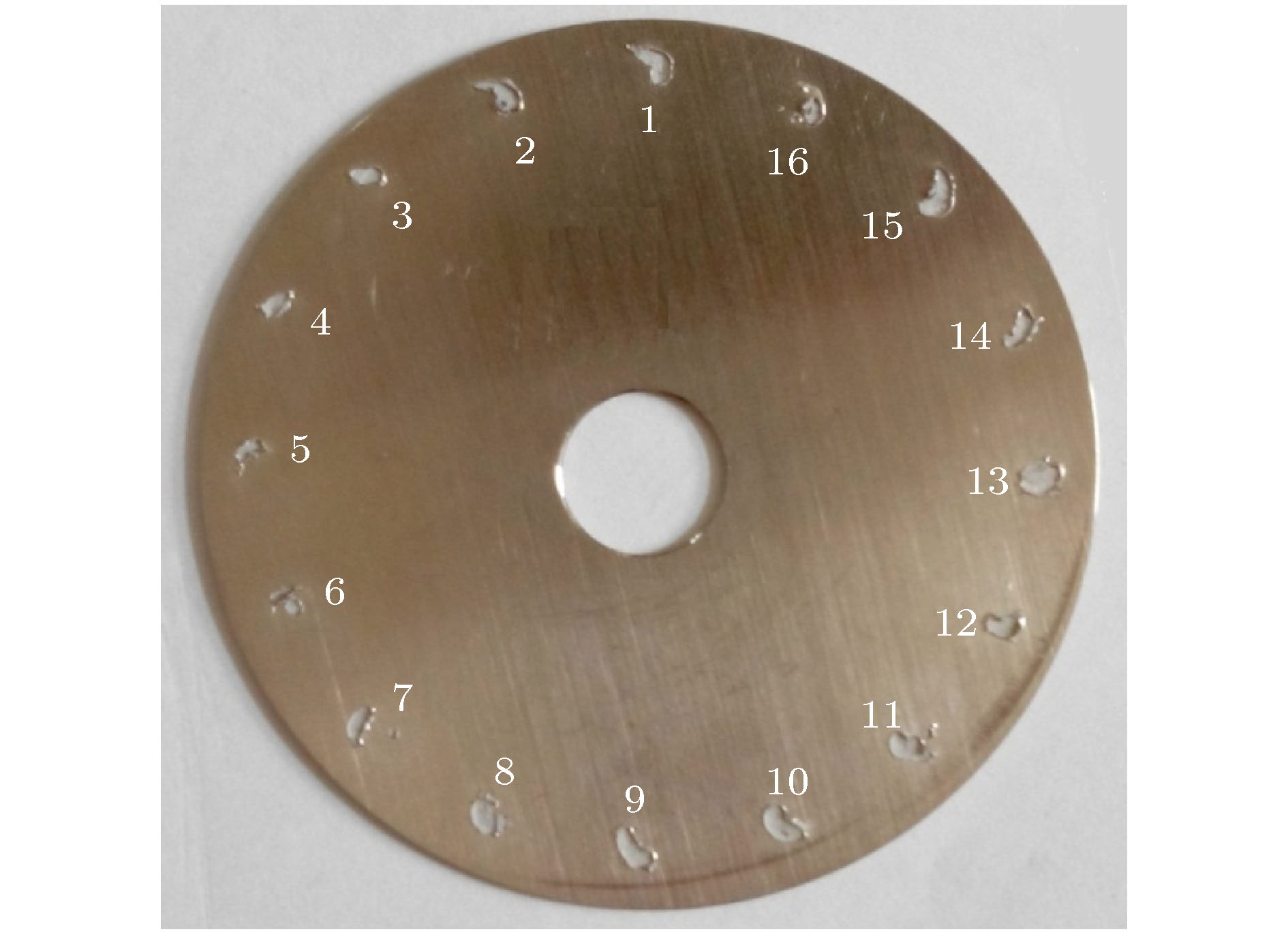
序号 电压/kV 电流/kA 末端电流/kA 通过率/% 1 800 9.3 8.6 92.4 2 805 9.3 8.6 92.4 3 799 9.2 8.5 92.4 平均 801 9.3 8.6 92.4 -
[1] Benford J, Swegle J A 著 (江伟华, 张弛 译) 2009 高功率微波 (第二版) (中译本) (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第3−5页
Benford J, Swegle J A (translated by Jiang W H, Zhang C) 2008 High Power Microwave (2nd Ed.) (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp3−5 (in Chinese)
[2] 丁耀根 2010 大功率速调管的制造和应用 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第7−13页
Ding Y G 2010 Design, Manufacture and Application of High Power Klystron (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp7−13 (in Chinese)
[3] Robert J B, Edl S 2005 高功率微波源与技术 (中译本) (北京: 清华大学出版社) 第282−289页
Robert J B, Edl S 2005 High Power Microwave Sources and Technologies (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) pp282−289 (in Chinese)
[4] 黄华, 吴洋, 刘振帮, 袁欢, 何琥, 李乐乐, 李正红, 金晓, 马弘舸 2018 67 088402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang H, Wu Y, Liu Z B, Yuan H, He H, Li L L, Li Z H, Jin X, Ma H G 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 088402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 吴洋, 许州, 周霖, 李文君, 唐传祥 2012 61 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y, Xu Z, Zhou L, Li W J, Tang C X 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Thomas H, Adam B, Rasheda B, Heinz B, Mark C, Edward E, Deepika G, Armand S, Brad S, Lou Z 2010 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38 1264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ding Y G, Shen B, Cao J, et al. 2009 IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 56 870
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li R J, Ruan C J, Zhang H F 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 033107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Friedman M, Pasour J, Smithe D 1997 Appl. Phys. Lett. 71 3724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 魏元璋, 李士锋, 王战亮, 黄华, 刘振帮, 何琥, 宫玉彬 2018 强激光与粒子束 30 063007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei Y Z, Li S F, Wang Z L, Huang H, Liu Z B, He H, Gong Y B 2018 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 30 063007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Edward B A, Andrew N D, Mikhail I F, et al. 2002 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 30 1041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang W, Ju J C, Zhang J, Zhou Y X, Zhong H H 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 053102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Qi Z M, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Zhong H H, Xu L R, Yang L 2016 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 37 782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 刘振帮, 金晓, 黄华, 陈怀璧 2012 61 128401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Jin X, Huang H, Chen H B 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 128401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 刘振帮, 黄华, 金晓, 袁欢, 戈弋, 何琥, 雷禄容 2015 64 018401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Huang H, Jin X, Yuan H, Ge Y, He H, Lei L R 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 018401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu Z B, Huang H, Jin X, Lei L R, Zhu L, Li L L, Li S F, Yan W K, He H 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 093110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 刘振帮, 金晓, 黄华, 陈怀璧, 王淦平 2012 61 248401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Jin X, Huang H, Chen H B, Wang G P 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 248401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 王淦平, 金晓, 黄华, 刘振帮 2017 66 044102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G P, Jin X, Huang H, Liu Z B 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 044102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 谢家麟, 赵永翔 1966 速调管群聚理论 (北京: 科学出版社) 第104—108, 208—209页
Xie J L, Zhao Y X 1966 Bunching Theory of Klystron (Beijing: Science Press) pp104–108, 208–209 (in Chinese)
[20] 王文祥 2009 微波工程技术 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第44, 45页
Wang W X 2009 Microwave Project and Technology (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp44, 45 (in Chinese)
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7083
- PDF Downloads: 70
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: