-
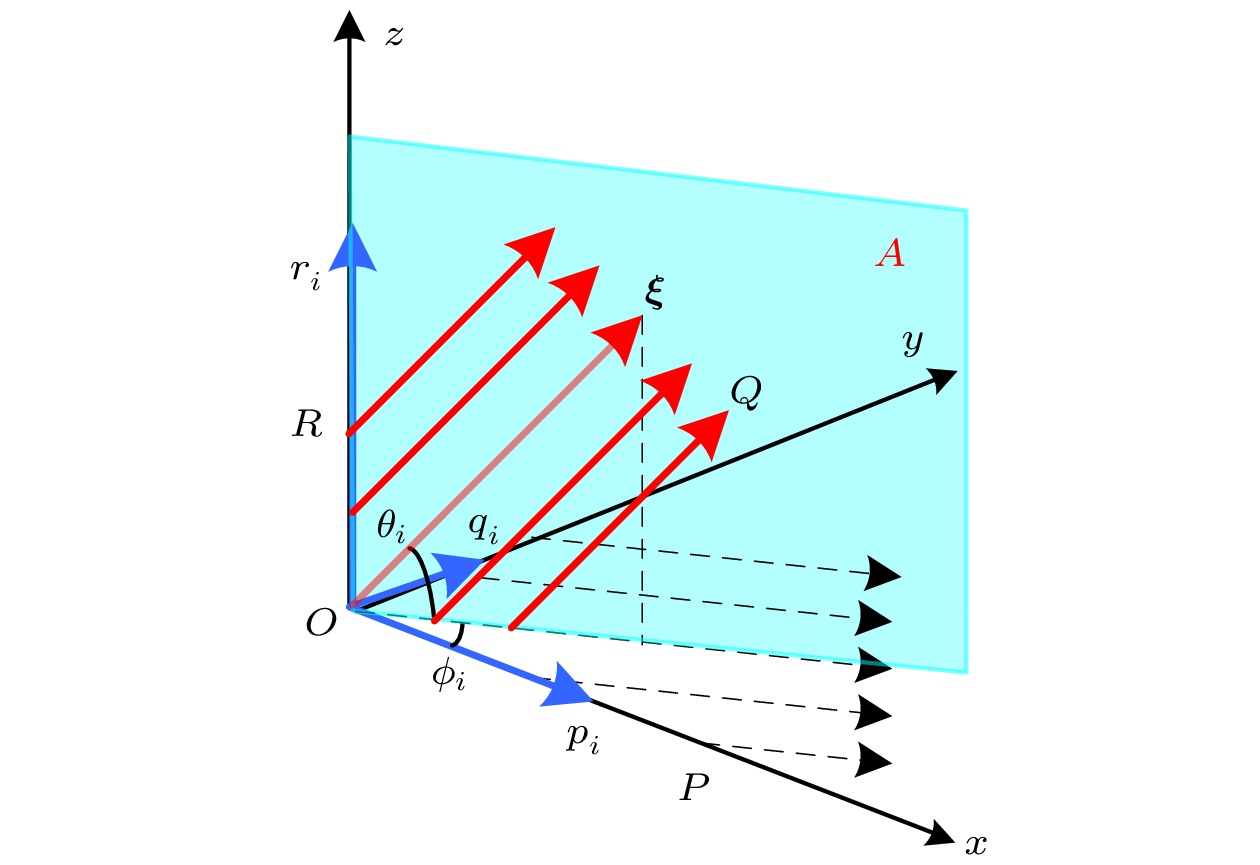
Computed tomography (CT) is an effective tool for three-dimensional (3D) imaging by using optical detectors to capture the two-dimensional (2D) projections of tested parameters from multiple views and realizing 3D reconstruction through various algorithms. However, for practical applications, typically only a few detectors can be applied due to their high expense and the limited optical access of the test environment. The realization of high precision reconstruction with a few projections is of great significance for promoting the development and application of CT technology. The spatial arrangement of the detectors determines the amount of useful information collected by the system, which greatly affects the quality of CT reconstruction. Therefore, in this work we study the optimization method of projection arrangement based on the 3D Mojette transform theory. Mojette transform is a special discrete form of Radon transform, which can realize projection sampling with minimum redundancy and accurate tomographic reconstruction from less projection angles. It provides a new way to realize the CT technology with fewer projections. However, the existing researches mainly focus on the reconstruction theories of 2D Mojette transform, which is used for realizing the 2D slice tomography. In order to realize the real 3D tomographic reconstruction, in this work we establish a mathematical model of 3D Mojette transform, and study its accurate reconstruction condition. The results show that the 3D Mojette transform is a combination of twice 2D Mojette transform in two directions. The accurate reconstruction condition of 3D Mojette transform is that the sum of the absolute values of projection vectors’ components in x, y, and z directions is greater than the number of discrete grids in each direction. The correctness of the mathematical model and the accurate reconstruction condition are verified by numerical simulations. Considering the limitation of the pixels in the practical detectors, the method to determine the optimal arrangement of projection angles is proposed. The results indicate that the optimal arrangement is that all detectors are located in the same horizontal plane around the tested object, where the projection model is reduced to 2D Mojette transform. In this case, the minimum projection angles and pixels are required and the projection angles can be positioned in a smaller spatial range. If the condition cannot be satisfied in practice, projection vectors with smaller |pi| and |qi| should be chosen. This research provides the theoretical basis for establishing the actual CT system. -
Keywords:
- computed tomography /
- three-dimensional Mojette transform /
- accurate reconstruction condition /
- projection angle
[1] 王少宏, 张希成, 张存林 2003 52 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S H, Zhang X C, Zhang C L 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 杨乐, 李凯, 戴宏毅, 张明 2019 68 140301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang L, Li K, Dai H Y, Zhang M 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 140301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 马振鹤, 窦世丹, 马毓姝, 刘健, 赵玉倩, 刘江红, 吕江涛, 王毅 2016 65 235202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma Z H, Dou S D, Ma Y S, Liu J, Zhao Y Q, Liu J H, Lü J T, Wang Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 235202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 张兰强, 顾乃庭, 饶长辉 2013 62 169501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang L Q, Gu N T, Rao C H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 169501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen Y, Gu F, Cao Z, Lia J, Zhang Y 2018 Opt. Laser Technol. 106 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 杨亚良, 丁志华, 王凯, 吴凌, 吴兰 2009 58 1773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Y L, Ding Z H, Wang K, Wu L, Wu L 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 1773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 吴彤, 孙帅帅, 王绪晖, 王吉明, 赫崇君, 顾晓蓉, 刘友文 2018 67 104208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu T, Sun S S, Wang X H, Wang J M, He C J, Gu X R, Liu Y W 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 104208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu H, Yu T, Zhang M, Cai W 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 7107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 计文平, 沈兰荪 2007 测控技术 26 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ji W P, Shen L S 2007 Meas. & Control Tech. 26 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jean R V 1980 Mathematical Biosciences 49 155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] [12] Recur B, Sarkissian H, Servieres M 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing Melbourne, Australia, September 15−18, 2013 p1041
[13] 李梦婕 2015 硕士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Li M J 2015 M. S. Thesis (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[14] 蒋敏, 曲芝萍, 孙怡 2019 光学学报 39 0711001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang M, Qu Z P, Sun Y 2019 Acta Opt. Sin. 39 0711001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Recur B, Desbarats P, Domenger J 2008 International Conferences in Central Europe on Computer Graphics Visualization and Computer Vision Plzen, Czech Republic, February 4−7, 2008 p191
[16] Fayad H, Guedon J P, Svalbe I, Bizais Y, Normand H 2008 Proc. SPIE, Medical Imaging San Diego, USA, March 25, 2008 p69132S
[17] Wang J, Guo Z, Nie L, Wu S 2019 Opt. Express 27 21050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Floyd J, Kempf A M 2011 Proc. Combust. Inst. 33 751
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang J, Song Y, Li Z H, Kempf A, He A Z 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 1231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Hou W, Zhang C 2013 J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 5 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Dai X B, Shu H Z, Luo L M, Han G N, Coatrieux J L 2010 Pattern Recognit. 43 1152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cai W, Li X, Li F, Ma L 2013 Opt. Express 21 7050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 模拟仿真中采用的不同投影矢量
Table 1. Projection vectors used in simulation.
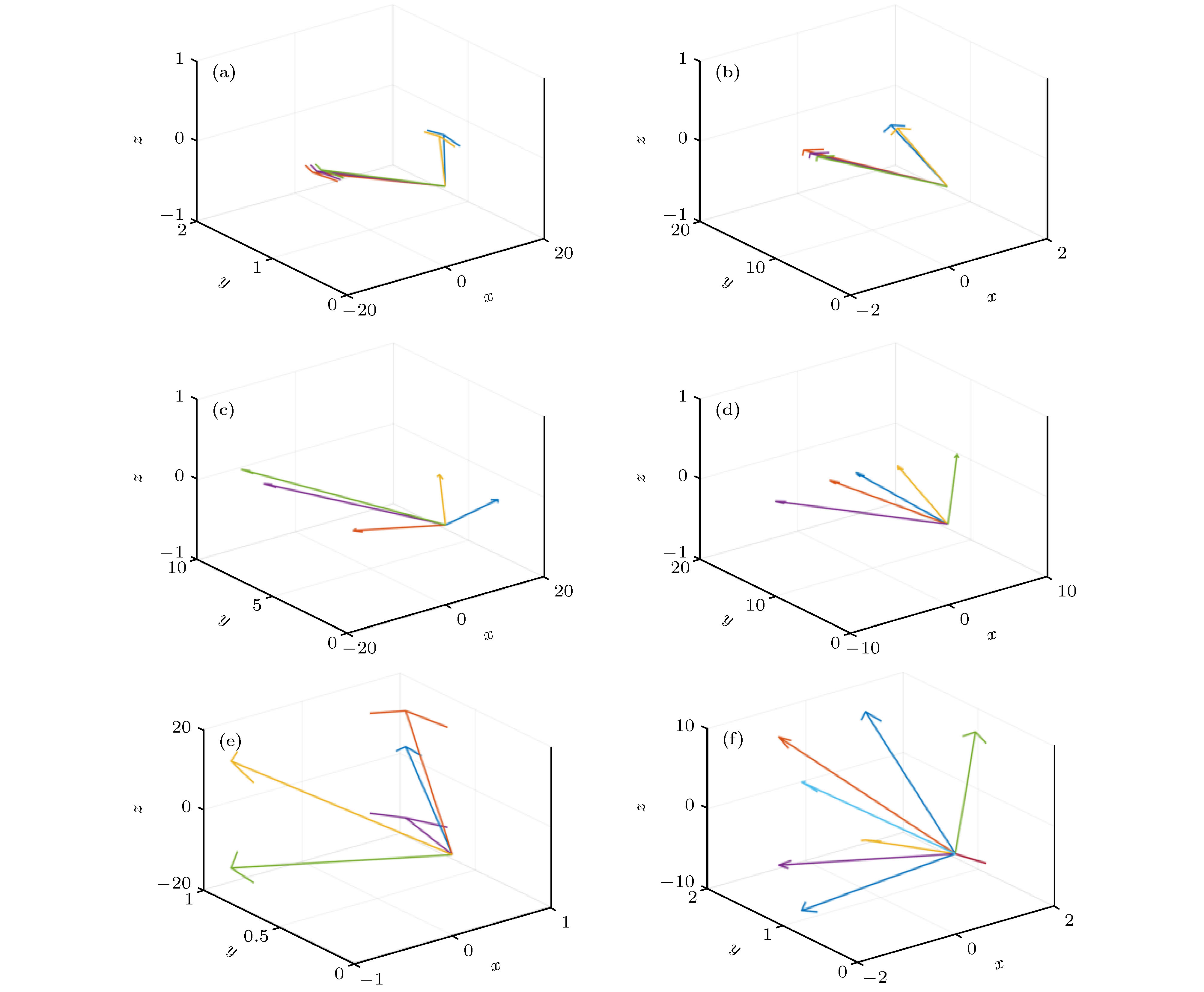
条件 投影矢量 (7)式是否满足 是否能精确重建 Case 1 (15, 1, 1), (13, 1, 1), (9, 1, 1), (7, 1, 1), (4, 1, 1) √ 是 Case 2 (15, 1, 1), (13, 1, 1), (9, 1, 1), (7, 1, 1), (3, 1, 1) × 否 Case 3 (1, 15, 1), (1, 13, 1), (1, 9, 1), (1, 7, 1), (1, 4, 1) √ 是 Case 4 (1, 15, 1), (1, 13, 1), (1, 9, 1), (1, 7, 1), (1, 4, 1) × 否 Case 5 (1, 1, 15), (1, 1, 13), (1, 1, 9), (1, 1, 7), (1, 1, 5) √ 是 Case 6 (1, 1, 15), (1, 1, 13), (1, 1, 9), (1, 1, 7), (1, 1, 3) × 否 -
[1] 王少宏, 张希成, 张存林 2003 52 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S H, Zhang X C, Zhang C L 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 杨乐, 李凯, 戴宏毅, 张明 2019 68 140301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang L, Li K, Dai H Y, Zhang M 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 140301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 马振鹤, 窦世丹, 马毓姝, 刘健, 赵玉倩, 刘江红, 吕江涛, 王毅 2016 65 235202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma Z H, Dou S D, Ma Y S, Liu J, Zhao Y Q, Liu J H, Lü J T, Wang Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 235202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 张兰强, 顾乃庭, 饶长辉 2013 62 169501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang L Q, Gu N T, Rao C H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 169501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen Y, Gu F, Cao Z, Lia J, Zhang Y 2018 Opt. Laser Technol. 106 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 杨亚良, 丁志华, 王凯, 吴凌, 吴兰 2009 58 1773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Y L, Ding Z H, Wang K, Wu L, Wu L 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 1773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 吴彤, 孙帅帅, 王绪晖, 王吉明, 赫崇君, 顾晓蓉, 刘友文 2018 67 104208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu T, Sun S S, Wang X H, Wang J M, He C J, Gu X R, Liu Y W 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 104208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu H, Yu T, Zhang M, Cai W 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 7107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 计文平, 沈兰荪 2007 测控技术 26 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ji W P, Shen L S 2007 Meas. & Control Tech. 26 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jean R V 1980 Mathematical Biosciences 49 155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] [12] Recur B, Sarkissian H, Servieres M 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing Melbourne, Australia, September 15−18, 2013 p1041
[13] 李梦婕 2015 硕士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Li M J 2015 M. S. Thesis (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[14] 蒋敏, 曲芝萍, 孙怡 2019 光学学报 39 0711001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang M, Qu Z P, Sun Y 2019 Acta Opt. Sin. 39 0711001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Recur B, Desbarats P, Domenger J 2008 International Conferences in Central Europe on Computer Graphics Visualization and Computer Vision Plzen, Czech Republic, February 4−7, 2008 p191
[16] Fayad H, Guedon J P, Svalbe I, Bizais Y, Normand H 2008 Proc. SPIE, Medical Imaging San Diego, USA, March 25, 2008 p69132S
[17] Wang J, Guo Z, Nie L, Wu S 2019 Opt. Express 27 21050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Floyd J, Kempf A M 2011 Proc. Combust. Inst. 33 751
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang J, Song Y, Li Z H, Kempf A, He A Z 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 1231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Hou W, Zhang C 2013 J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 5 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Dai X B, Shu H Z, Luo L M, Han G N, Coatrieux J L 2010 Pattern Recognit. 43 1152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cai W, Li X, Li F, Ma L 2013 Opt. Express 21 7050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7229
- PDF Downloads: 77
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: