-
The perfectly matched layer plays a key role in electromagnetic simulations, and it makes the infinite space look like a finite space, so that the electromagnetic waves propagating to the boundary seem like their propagations to the infinity. The inner perfectly matched layer has a similar concept, usually in the form of a cylinder or sphere placed inside the physical field. It makes the electromagnetic field matched at the boundary, so that the electromagnetic waves propagate on its convex surface as if they were propagating to an infinite distance, without any scattering. In addition to the perfectly matched layer, planar absorbers can be realized in a variety of ways, such as spatial Kramers-Kronig relations, photonic crystals, metamaterials, etc. On the other hand, the inner cylindrical or spherical absorbers are generally perfect absorbers, electromagnetic “black hole”, etc. Transformation optics always arouse great research interests. For its property of controlling propagation of electromagnetic waves arbitrarily under coordinate mappings, transformation optics has a wide range of applications and has also been used as a theoretical tool for designing absorbers. However, to the authors’ knowledge, there is no effective method to achieve perfect absorption of inner absorbers with no reflections and independence of incident angle or wave frequency. In this paper, transformation optics theory is used to design an inner perfectly matched layer whose material parameters are obtained by a radial coordinate transformation of the complex plane. Through investigating the electromagnetic wave patterns and the two-dimensional far-field diagrams, we intuitively compare and analyse one by one the absorption characteristics of the matched and mismatched perfect absorber, electromagnetic “black hole” and the inner perfectly matched layer. It is found that the matched perfect absorber has better absorption property than mismatched one and electromagnetic “black hole”. In the electromagnetic “black hole” there appear a lot of scatterings. While our inner perfectly matched layer demonstrates the best effectiveness of absorption with no back scattering. It can be used as an absorbing kernel in electromagnetic simulations and relevant experiments.
-
Keywords:
- inner perfectly matched layer /
- transformation optics theory /
- electromagnetic “black hole” /
- absorption characteristics
[1] Berenger J P 1994 J. Comput. Phys. 114 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chew W C, Weedon W H 1994 Microwave Opt. Technol. Lett. 7 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Horsley S A R, Artoni M, La Rocca G C 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ye D X, Cao C, Zhou T Y, Huangfu J T, Zheng G A, Ran L X 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jiang W, Ma Y G, Yuan J, Yin G, Wu W H, He S L 2016 Laser Photonics Rev. 11 1600253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Luo J, Lai Y 2019 Opt. Express 27 015800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Landy N L, Sajuyigbe S, Mock J J, Smith D R, Padilla W J 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 207402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu X L, Starr T, Starr A F, Padilla W J 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 207403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Leonhardt U, Philbin T G 2006 New J. Phys. 8 247
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Narimanov E E, Kildishev A V 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 041106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Cheng Q, Cui T J, Jiang W X, Cai B G 2010 New J. Phys. 12 063006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Argyropoulos C, Kallos E, Hao Y 2010 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27 2020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sheng C, Liu H, Wang Y, Zhu S N, Genov D A 2013 Nat. Photonics 7 902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen H Y, Miao R X, Li M 2010 Opt. Express 18 15183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pendry J B, Schurig D, Smith D R 2006 Science 312 1780
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Schurig D, Mock J J, Justice B J, Cummer S A, Pendry J B, Starr A F, Smith D R 2006 Science 314 977
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Leonhardt U 2006 Science 312 1777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xu L, Chen H Y 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Odabasi H, Teixeira F L, Chew W C 2011 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 28 1317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Popa B I, Cummer S A 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 063837
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Sainath K, Teixeira F L 2015 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 32 1645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 周梦颖, 陶思岑, 杨福宝, 陈焕阳 2019 厦门大学学报 (自然科学版) 58 783
Zhou M Y, Tao S C, Yang F B, Chen H Y 2019 J. Xiamen Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 58 783
-
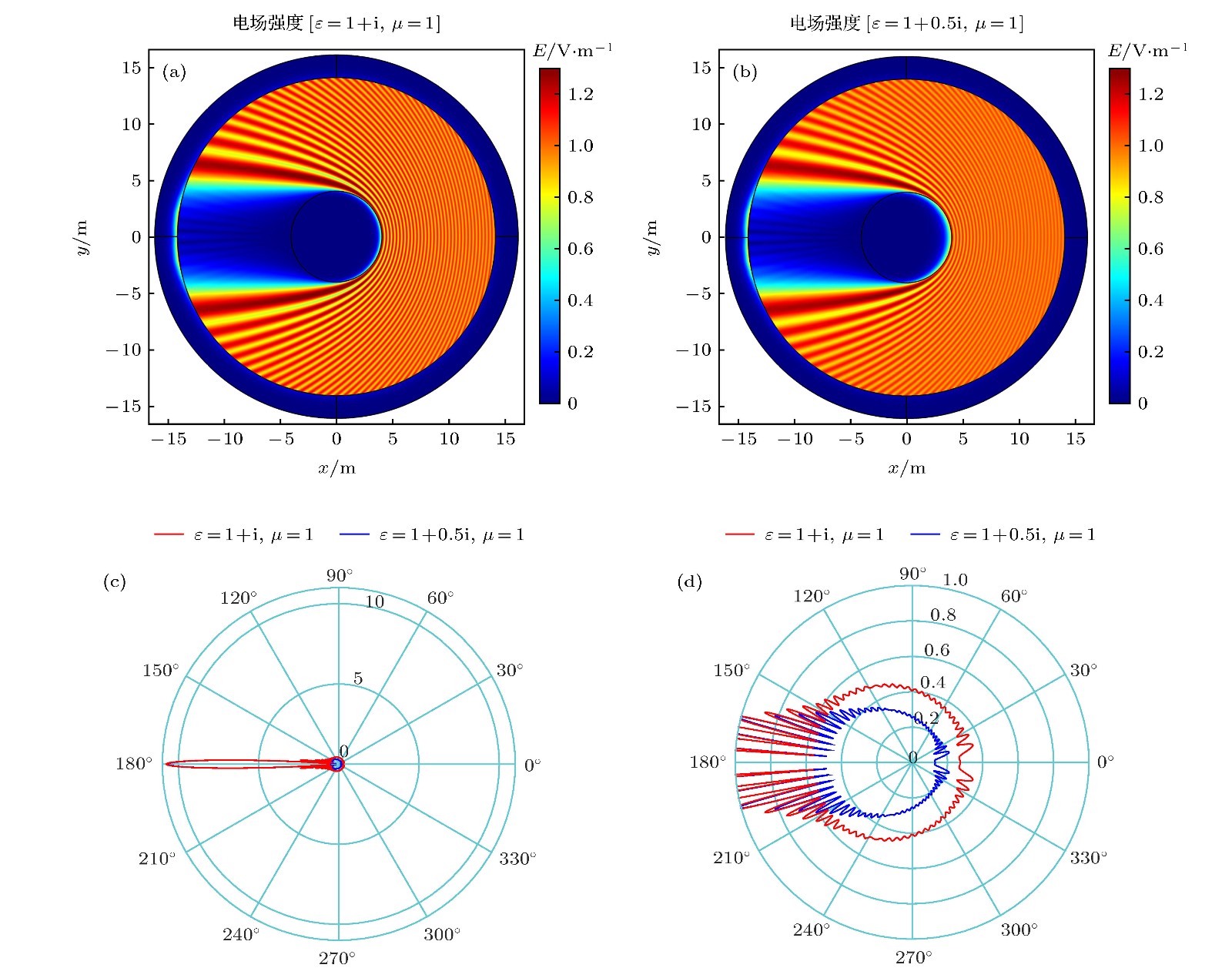
图 1 两个完美吸收体的吸收及散射特性对比图 (a) 吸收体 (
$\varepsilon=1+{\rm i}, \mu=1$ ) 的电场强度图; (b) 吸收体 ($ \varepsilon=1+0.5 {\rm i}, \mu=1$ ) 的电场强度图; (c) 两个吸收体的远场分布对比图; (d) 两个吸收体的远场分布对比放大图Figure 1. Comparison diagram of absorption and scattering characteristics of two perfect absorbers: (a) The electric field intensity diagram of absorber (
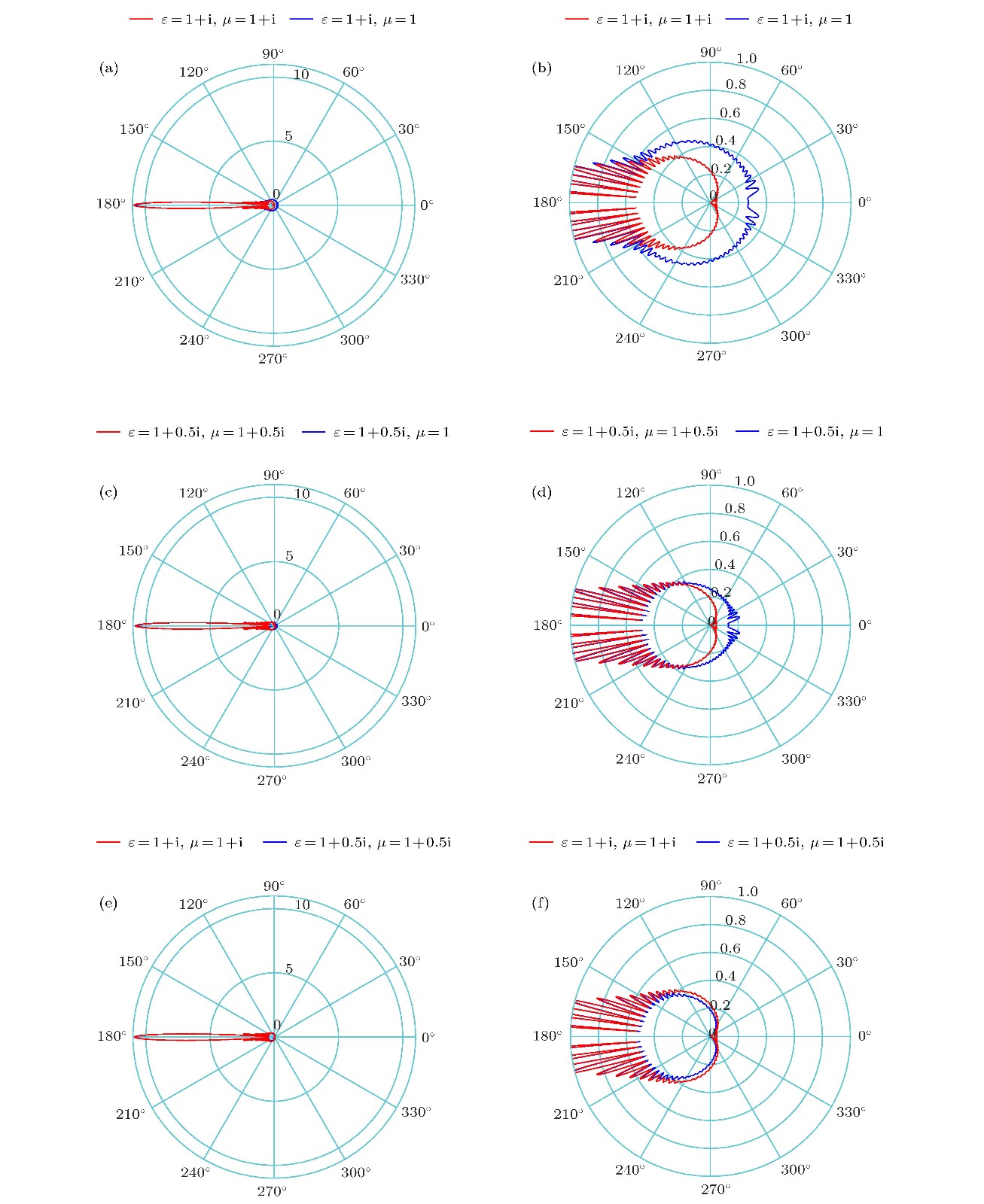
$ \varepsilon=1+{\rm i}, \mu=1$ ); (b) the electric field intensity diagram of absorber ($ \varepsilon=1+0.5 {\rm i}, \mu=1$ ); (c) the comparison diagram of the far field distribution of the two absorbers; (d) the comparison diagram of the enlarged far field distribution of the two absorbers图 2 不同完美吸收体的吸收特性对比 (a), (b) 1组吸收体阻抗匹配与不匹配的远场对比图和远场对比放大图; (c), (d) 2 组吸收体阻抗匹配与不匹配的远场对比图和远场对比放大图; (e), (f)两组阻抗匹配的吸收体的远场对比图和远场对比放大图
Figure 2. Absorption characteristics comparison of different perfect absorbers: (a) The far field comparison diagram and (b) far field comparison enlarged diagram of impedance-matched and impedance-mismatched absorbers of the first set; (c) the far field comparison diagram and (d) far field comparison enlarged diagram of impedance-matched and impedance-mismatched absorbers of the second set; (e) the far field comparison diagram and (f) far field comparison enlarged diagram of impedance-matched absorbers of the above two sets
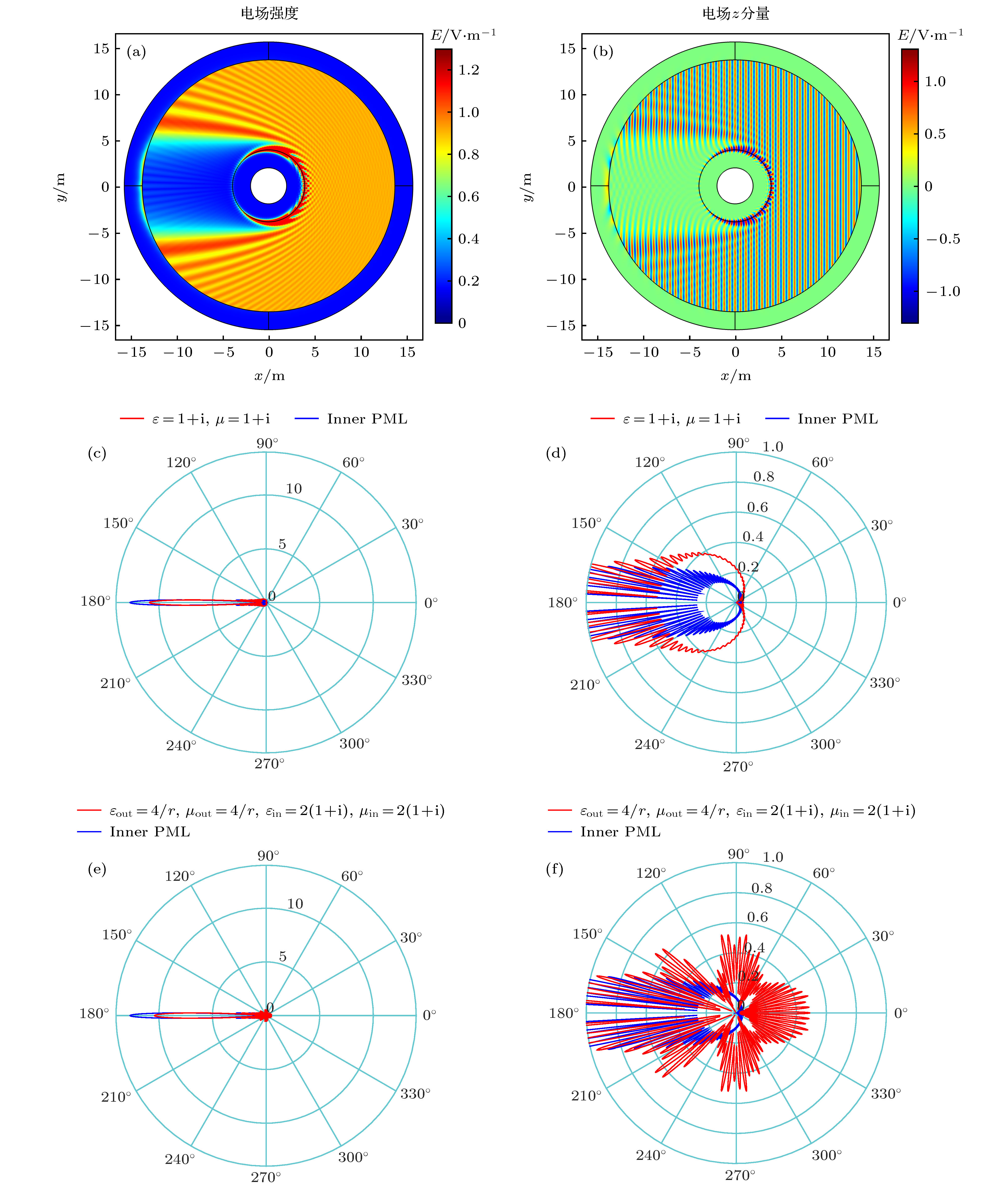
图 3 电磁“黑洞”吸收特性分析 (a) 阻抗不匹配和(b) 阻抗匹配的电磁“黑洞”电场强度图; (c) 阻抗不匹配和(d) 阻抗匹配的电磁“黑洞”电场z分量图; 阻抗不匹配和阻抗匹配的电磁“黑洞”的(e) 远场对比图和(f) 远场对比放大图
Figure 3. Analysis of absorption characteristics of electromagnetic “black hole”: The electric field intensity diagram of (a) impedance-mismatched and (b) impedance-matched electromagnetic “black hole”; the electric field z component diagram of (c) impedance-mismatched and (d) impedance-matched electromagnetic “black hole”; (e) the far field comparison diagram and (f) far field comparison enlarged diagram of impedance-mismatched and impedance-matched electromagnetic “black hole”
图 4 完美吸收体与电磁“黑洞”吸收特性对比 (a), (b)阻抗不匹配的完美吸收体和电磁“黑洞”的远场对比图和远场对比放大图; (c), (d)阻抗匹配的完美吸收体和电磁“黑洞”的远场对比图和远场对比放大图
Figure 4. Absorption characteristics comparison of perfect absorber and electromagnetic “black hole”: (a) The far field comparison diagram and (b) far field comparison enlarged diagram of impedance-mismatched perfect absorber and electromagnetic “black hole”; (c) the far field comparison diagram and (d) far field comparison enlarged diagram of impedance-matched perfect absorber and electromagnetic “black hole”
图 6 完美吸收体、电磁“黑洞”与内置完美匹配层(inner PML)的吸收特性对比 (a), (b)内置完美匹配层的电场强度图和电场z分量图; (c), (d)阻抗匹配的完美吸收体和内置完美匹配层的远场对比图和远场对比放大图; (e), (f)阻抗匹配的电磁“黑洞”和内置完美匹配层的远场对比图和远场对比放大图
Figure 6. Absorption characteristics comparison of perfect absorber, electromagnetic “black hole” and inner PML: (a) Electric field intensity diagram and (b) electric field z component diagram of inner PML; (c) far field comparison diagram and (d) far field comparison enlarged diagram of impedance-matched perfect absorber and inner PML; (e) far field comparison diagram and (f) far field comparison enlarged diagram of impedance-matched electromagnetic “black hole” and inner PML
-
[1] Berenger J P 1994 J. Comput. Phys. 114 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chew W C, Weedon W H 1994 Microwave Opt. Technol. Lett. 7 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Horsley S A R, Artoni M, La Rocca G C 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ye D X, Cao C, Zhou T Y, Huangfu J T, Zheng G A, Ran L X 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jiang W, Ma Y G, Yuan J, Yin G, Wu W H, He S L 2016 Laser Photonics Rev. 11 1600253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Luo J, Lai Y 2019 Opt. Express 27 015800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Landy N L, Sajuyigbe S, Mock J J, Smith D R, Padilla W J 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 207402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu X L, Starr T, Starr A F, Padilla W J 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 207403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Leonhardt U, Philbin T G 2006 New J. Phys. 8 247
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Narimanov E E, Kildishev A V 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 041106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Cheng Q, Cui T J, Jiang W X, Cai B G 2010 New J. Phys. 12 063006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Argyropoulos C, Kallos E, Hao Y 2010 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27 2020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sheng C, Liu H, Wang Y, Zhu S N, Genov D A 2013 Nat. Photonics 7 902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen H Y, Miao R X, Li M 2010 Opt. Express 18 15183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pendry J B, Schurig D, Smith D R 2006 Science 312 1780
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Schurig D, Mock J J, Justice B J, Cummer S A, Pendry J B, Starr A F, Smith D R 2006 Science 314 977
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Leonhardt U 2006 Science 312 1777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xu L, Chen H Y 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Odabasi H, Teixeira F L, Chew W C 2011 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 28 1317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Popa B I, Cummer S A 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 063837
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Sainath K, Teixeira F L 2015 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 32 1645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 周梦颖, 陶思岑, 杨福宝, 陈焕阳 2019 厦门大学学报 (自然科学版) 58 783
Zhou M Y, Tao S C, Yang F B, Chen H Y 2019 J. Xiamen Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 58 783
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 15211
- PDF Downloads: 396
- Cited By: 0


















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: