-
Ultrafast spectroscopy is a powerful method to generate and control topological phase transitions and spin-polarized electrical currents in topological quantum materials. These light-induced novel physical properties originate from the topologically nontrivial states of Dirac and Weyl fermions. The topological semimetal molybdenum phosphide (MoP) exhibits double and triple degenerate points in the momentum space. We present the preliminary results of spin-polarized electrical currents and optical response investigations of MoP. We design and construct an experimental setup to perform the photocurrent generation and control by circularly polarized light in topological insulator Bi2Se3. The results compare well with those reported, which confirms the validity and reliability of our experimental setup. Further, we conduct the photocurrent experiment on MoP by using 400 nm laser pulses for excitation and successfully detect the current signals at different sample positions. We attribute the observed currents to photo-induced thermal currents (not the photo current associated with the triple degenerate topological properties), which facilitates generating and controlling photocurrents in MoP in the future investigation. Our thermal current investigations are of essence for further exploring the photocurrents in various types of topological quantum materials.
-
Keywords:
- photocurrent /
- triple degenerate topological material /
- ultrafast spectroscopy /
- spin polarization
[1] Armitage N P, Mele E J, Vishwanath A 2018 Rev. Mod. Phys. 90 015001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wan X G, Turner A M, Vishwanath A, Savrasov S Y 2011 Phys. Rev. B 83 205101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Huang X C, Zhao L X, Long Y J, Wang P P, Chen D, Yang Z H, Liang H, Xue M Q, Weng H M, Fang Z, Dai X, Chen G F 2015 Phys. Rev. X 5 031023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bradlyn B, Cano J, Wang Z J, Vergniory M G, Felser C, Cava R J, Bernevig B A 2016 Science 353 6299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lü B Q, Feng Z L, Xu Q N, Gao X, Ma J Z, Kong L Y, Richard P, Huang Y B, Strocov V N, Fang C, Weng H M, Shi Y G, Qian T, Ding H 2017 Nature 546 627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Chi Z H, Chen X L, An C, et al. 2018 npj. Quantum. Materials 3 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhu Z M, Winkler G W, Wu Q S, Li J, Soluyanov A A 2016 Phys. Rev. X 6 031003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Tian Y C, Zhang W H, Li F S, Wu Y L, Wu Q, Sun F, Zhou G Y, Wang L L, Ma X C, Xue Q K, Zhao J M 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 107001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu Q, Zhou H X, Wu Y L, Hu L L, Ni S L, Tian Y C, Sun F, Zhou F, Dong X L, Zhao Z X, Zhao J M 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. (Express Letter) 37 097802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Toda Y, Kawanokami F, Kurosawa T, et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. B. 90 094513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 曹宁, 龙拥兵, 张治国, 高丽娟, 袁洁, 赵伯儒, 赵士平, 杨乾生, 赵继民, 傅盘铭 2008 57 2543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao N, Long Y B, Zhang Z G, Gao L J, Yuan J, Zhao B R, Zhao S P, Yang Q S, Zhao J M, Fu P M 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 2543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wu Y L, Yin X, Hasaien J, Ding Y, Zhao J M 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. (Express Letter) 37 047801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hu L L, Yang M, Wu Y L, Wu Q, Zhao H, Sun F, Wang W, He R, He S L, Zhang H, Huang R J, Li L F, Shi Y G, Zhao J M 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 094307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hsieh D, Mahmood F, Torchinsky D H, Cao G, Gedik N 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 035128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sun F, Yang M, Yang M W, Wu Q, Zhao H, Ye X, Shi Y G, Zhao J M 2018 Chin. Phys. Lett. 35 116301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Sun F, Wu Q, Wu Y L, Zhao H, Yi C J, Tian Y C, Liu H W, Shi Y G, Ding H, Dai X, Richard P, Zhao J M 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 235108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang M C, Qiao S, Jiang Z, Luo S N, Qi J 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 036601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Aku-Leh C, Zhao J M, Merlin R, Menéndez J, Cardona M 2005 Phys. Rev. B 71 205211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bragas A V, Aku-Leh C, Costantino S, Ingale A, Zhao J M, Merlin R 2004 Phys. Rev. B 69 205306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wu Y L, Wu Q, Sun F, Cheng C, Meng S, Zhao J M 2015 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112 11800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu R, Zhang Y L, Yan S C, Bian F, Wang W L, Bai X D, Lu X H, Zhao J M 2011 Nano Lett. 11 5159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hu L L, Sun F, Zhao H, Zhao J M 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 5214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wu Y L, Zhu L L, Wu Q, et al. 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 241110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang W H, Wu Y L, Wu Q, Hua J J, Zhao J M 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 107001
[25] Tian Y C, Tian H, Wu Y L, Zhu L L, Tao L Q, Zhang W, Shu Y, Xie D, Yang Y, Wei Z Y, Lu X H, Ren T L, Shih C K, Zhao J M 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 10582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhao J M, Bragas A V, Lockwood D J, Merlin R 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 107203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhao J M, Bragas A V, Merlin R, Lockwood D J 2006 Phys. Rev. B 73 184434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chan C K, Lindner N H, Refael G, Lee P A 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 041104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Morimoto T, Zhong S D, Orenstein J, Moore J E 2016 Phys. Rev. B 94 245121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Juan F D, Grushin A G, Morimoto T, Moore J E 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 15995
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Morimoto T, Nagaosa N 2016 Sci. Adv. 2 e1501524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Mclver J W, Hsieh D, Steinberg H, Herrero P J, Gedik N 2012 Nat. Nanotech. 7 96
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Ma Q, Xu S Y, Chan C K, Zhang C L, Chang G Q, Lin Y X, Xie W W, Palacios T, Lin H, Jia S, Lee P A, Herrero P J, Gedik N 2017 Nat. Phys. 13 842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Ma J C, Gu Q Q, Liu Y N, Lai J W, Yu P, Zhuo X, Liu Z, Chen J H, Feng J, Sun D 2019 Nat. Mater. 18 476
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Kumar N, Sun Y, Nicklas M, et al. 2019 Nat. Commum. 10 2475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
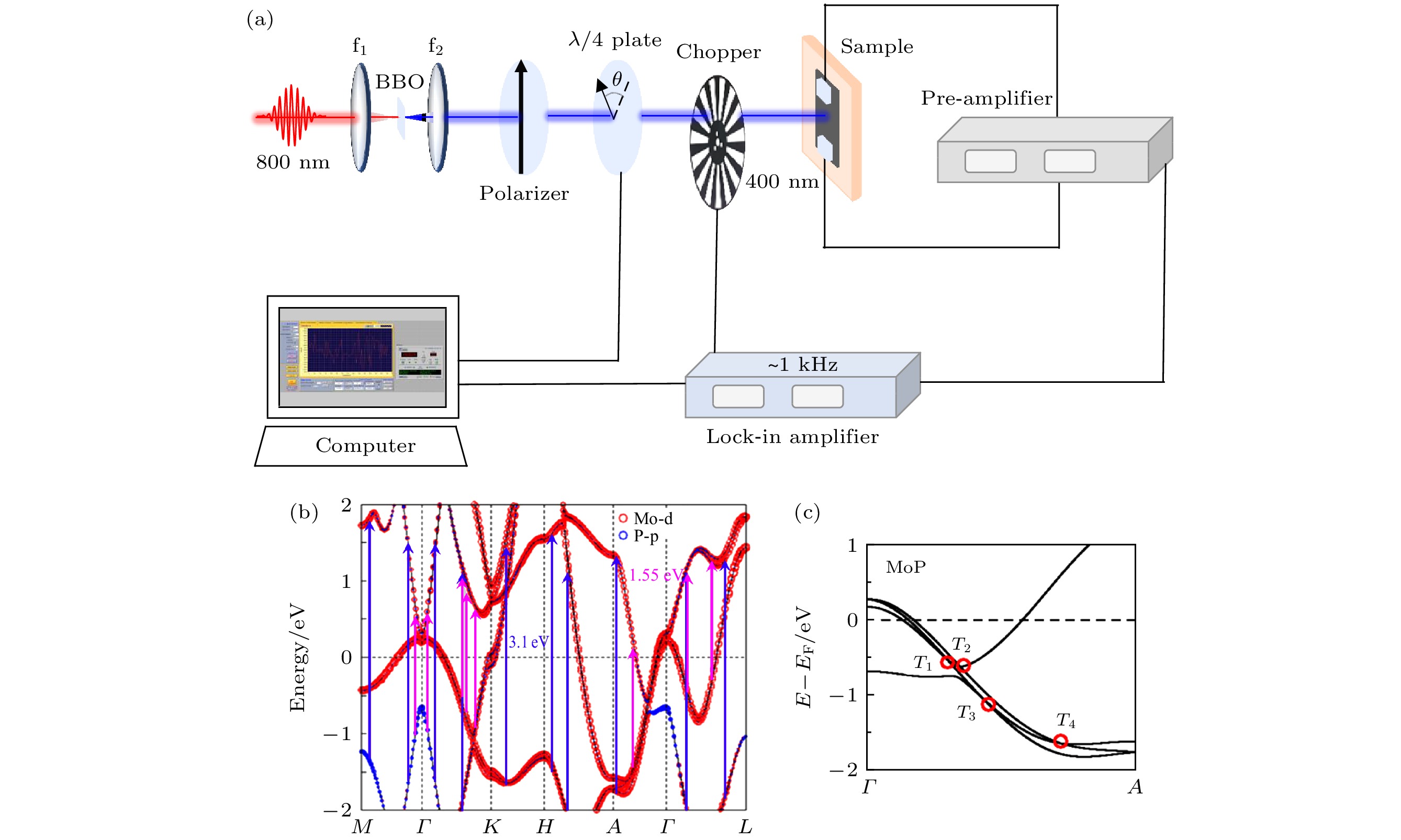
图 1 (a) 光电流产生和探测实验装置, f1和f2为透镜, BBO为倍频非线性晶体; (b) 800 nm (1.55 eV, 粉红色箭头) 和 400 nm (3.1 eV, 蓝紫色箭头) 脉冲激光可能激发的动量区域, 其中能带结构引自文献[35]计算结果; (c) MoP中的4个三重简并点局域放大(红色圆圈)[35]
Figure 1. (a) Schematic photocurrent experimental setup. f1 and f2 are focusing lenses. BBO is the doubling frequency nonlinear crystal; (b) the allowed excitation areas by 800 nm (1.55 eV, pink arrows) and 400 nm (3.1 eV, purple arrows) pulsed lasers, respectively. The band structure is adapted from Ref. [35]; (c) the four triple points are highlighted by the red circles[35].
图 2 MoP样品的表征 (a) 光电流实验所使用的MoP样品, 左图为SEM图像, 右图为加电极后粘到铜托上的样品实物图; (b) 常温下的Raman光谱, 红色箭头标出两个拉曼峰; (c) 0和7 T下的电输运测量; (d) 2 K温度下的电阻随磁场的变化; (e) 5 μm分辨率样品局部放大SEM图; (f) 20 μm分辨率样品局部放大SEM图
Figure 2. Characterizations of the MoP sample in the photocurrent experiment: (a) SEM image (left panel) and the sample after adding the electrodes (right panel); (b) Raman spectroscopy at room temperature, two red arrows mark the Raman peaks; (c) temperature dependence of the resistance at 0 and 7 T external magnetic field; (d) magnetic field dependence of resistance at 2 K; (e) SEM image with a resolution of 5 μm; (f) SEM image with a resolution of 20 μm.
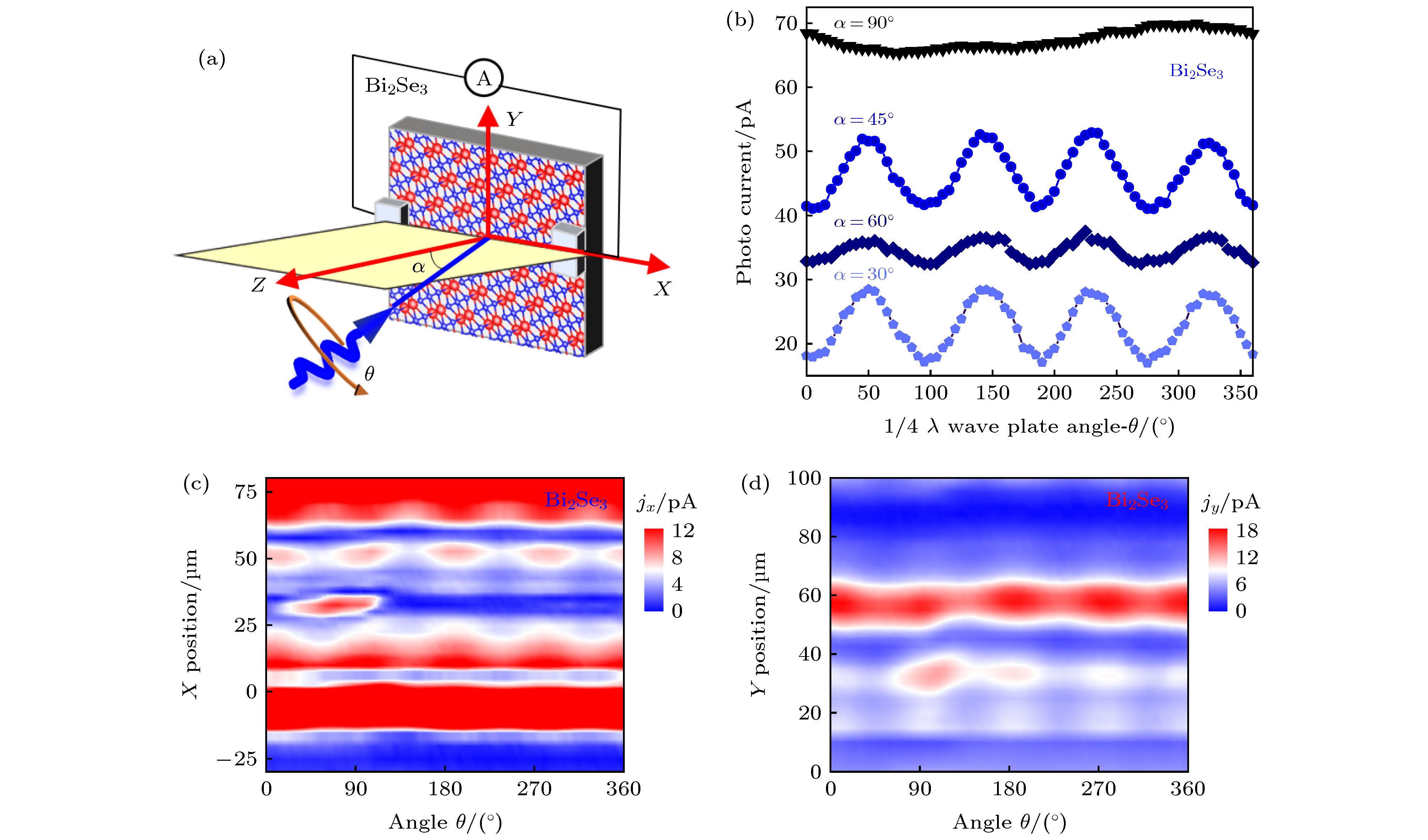
图 3 (a) 光电流实验示意图; (b) 不同入射角情形下Bi2Se3样品的光电流强度对激发光圆偏振度的依赖关系(有offset); (c) 光45°入射Bi2Se3样品情形下, 扫描X方向位置, 光电流强度对偏振的依赖关系图; (d) 光45°入射Bi2Se3样品情形下, 扫描Y方向位置, 光电流强度对偏振的依赖关系图
Figure 3. (a) Schematic of the experimental geometry; (b) photocurrent intensity depending on the polarization of the laser beam under different incident angles, which is offset for clarity; (c) photocurrent intensity depending on the sample position along the X axis, where the incident angle of ultrafast pulses is 45°; (d) photocurrent intensity depending on the sample position along the Y axis, with 45° incidence angle.
图 4 (a) MoP样品的晶格结构示意图; (b) 光激发样品的光斑位置示意图; (c) 400 nm超快激光照射MoP样品的P1和P2两个对称位置时, 分别测得的电流随偏振的依赖关系. 红色和蓝色代表P1和P2两个位置, 灰色为不加光照射时测得的电流
Figure 4. (a) Schematic lattice structure of MoP, purple and brown spheres represent P and Mo atoms, respectively; (b) schematic diagram of the experiment illustrating the two photoexcitation positions on the sample; (c) polarization dependence of the current intensity at P1 and P2 under 400 nm light excitation. Solid dots in red and blue are current intensity data obtained at P1 and P2, respectively. Gray dots donate the situation without any light excitation.
-
[1] Armitage N P, Mele E J, Vishwanath A 2018 Rev. Mod. Phys. 90 015001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wan X G, Turner A M, Vishwanath A, Savrasov S Y 2011 Phys. Rev. B 83 205101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Huang X C, Zhao L X, Long Y J, Wang P P, Chen D, Yang Z H, Liang H, Xue M Q, Weng H M, Fang Z, Dai X, Chen G F 2015 Phys. Rev. X 5 031023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bradlyn B, Cano J, Wang Z J, Vergniory M G, Felser C, Cava R J, Bernevig B A 2016 Science 353 6299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lü B Q, Feng Z L, Xu Q N, Gao X, Ma J Z, Kong L Y, Richard P, Huang Y B, Strocov V N, Fang C, Weng H M, Shi Y G, Qian T, Ding H 2017 Nature 546 627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Chi Z H, Chen X L, An C, et al. 2018 npj. Quantum. Materials 3 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhu Z M, Winkler G W, Wu Q S, Li J, Soluyanov A A 2016 Phys. Rev. X 6 031003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Tian Y C, Zhang W H, Li F S, Wu Y L, Wu Q, Sun F, Zhou G Y, Wang L L, Ma X C, Xue Q K, Zhao J M 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 107001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu Q, Zhou H X, Wu Y L, Hu L L, Ni S L, Tian Y C, Sun F, Zhou F, Dong X L, Zhao Z X, Zhao J M 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. (Express Letter) 37 097802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Toda Y, Kawanokami F, Kurosawa T, et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. B. 90 094513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 曹宁, 龙拥兵, 张治国, 高丽娟, 袁洁, 赵伯儒, 赵士平, 杨乾生, 赵继民, 傅盘铭 2008 57 2543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao N, Long Y B, Zhang Z G, Gao L J, Yuan J, Zhao B R, Zhao S P, Yang Q S, Zhao J M, Fu P M 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 2543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wu Y L, Yin X, Hasaien J, Ding Y, Zhao J M 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. (Express Letter) 37 047801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hu L L, Yang M, Wu Y L, Wu Q, Zhao H, Sun F, Wang W, He R, He S L, Zhang H, Huang R J, Li L F, Shi Y G, Zhao J M 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 094307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hsieh D, Mahmood F, Torchinsky D H, Cao G, Gedik N 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 035128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sun F, Yang M, Yang M W, Wu Q, Zhao H, Ye X, Shi Y G, Zhao J M 2018 Chin. Phys. Lett. 35 116301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Sun F, Wu Q, Wu Y L, Zhao H, Yi C J, Tian Y C, Liu H W, Shi Y G, Ding H, Dai X, Richard P, Zhao J M 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 235108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang M C, Qiao S, Jiang Z, Luo S N, Qi J 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 036601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Aku-Leh C, Zhao J M, Merlin R, Menéndez J, Cardona M 2005 Phys. Rev. B 71 205211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bragas A V, Aku-Leh C, Costantino S, Ingale A, Zhao J M, Merlin R 2004 Phys. Rev. B 69 205306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wu Y L, Wu Q, Sun F, Cheng C, Meng S, Zhao J M 2015 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112 11800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu R, Zhang Y L, Yan S C, Bian F, Wang W L, Bai X D, Lu X H, Zhao J M 2011 Nano Lett. 11 5159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hu L L, Sun F, Zhao H, Zhao J M 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 5214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wu Y L, Zhu L L, Wu Q, et al. 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 241110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang W H, Wu Y L, Wu Q, Hua J J, Zhao J M 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 107001
[25] Tian Y C, Tian H, Wu Y L, Zhu L L, Tao L Q, Zhang W, Shu Y, Xie D, Yang Y, Wei Z Y, Lu X H, Ren T L, Shih C K, Zhao J M 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 10582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhao J M, Bragas A V, Lockwood D J, Merlin R 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 107203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhao J M, Bragas A V, Merlin R, Lockwood D J 2006 Phys. Rev. B 73 184434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chan C K, Lindner N H, Refael G, Lee P A 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 041104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Morimoto T, Zhong S D, Orenstein J, Moore J E 2016 Phys. Rev. B 94 245121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Juan F D, Grushin A G, Morimoto T, Moore J E 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 15995
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Morimoto T, Nagaosa N 2016 Sci. Adv. 2 e1501524
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Mclver J W, Hsieh D, Steinberg H, Herrero P J, Gedik N 2012 Nat. Nanotech. 7 96
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Ma Q, Xu S Y, Chan C K, Zhang C L, Chang G Q, Lin Y X, Xie W W, Palacios T, Lin H, Jia S, Lee P A, Herrero P J, Gedik N 2017 Nat. Phys. 13 842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Ma J C, Gu Q Q, Liu Y N, Lai J W, Yu P, Zhuo X, Liu Z, Chen J H, Feng J, Sun D 2019 Nat. Mater. 18 476
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Kumar N, Sun Y, Nicklas M, et al. 2019 Nat. Commum. 10 2475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9428
- PDF Downloads: 196
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: