-
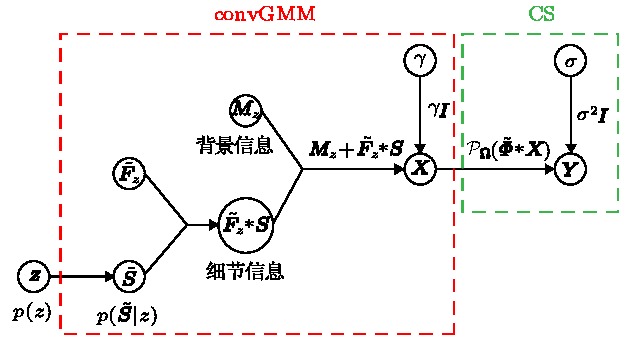
Statistical compressive sensing needs to use the statistical description of source signal. By decomposing a whole image into a set of non-overlapping or overlapping patches, the Gaussian mixture model (GMM) has been used to statistically represent patches in an image. Compressive sensing, however, always imposes compression on the whole image. It is obvious that the entire image contains much richer information than the small patches. Extending from the small divided patches to an entire image, we propose a convolutional Gaussian mixture model (convGMM) to depict the statistics of an entire image and apply it to compressive sensing. We present the algorithm details by learning a convGMM from training images based on maximizing the marginal log-likelihood estimation. The learned convGMM is used to perform the model-based compressive sensing by using the convGMM as a model of the underlying image. In addition, aiming at the problem of high-dimensional image that makes learning, estimation and optimization suffer high computational complexity, all of the training and reconstruction process in our method can be fast and efficiently calculated in the frequency-domain by two-dimensional fast Fourier transforms. The performance of the convGMM on compressive sensing is demonstrated on several image sets.
-
Keywords:
- convolutional Gaussian mixture models /
- statistical compressive sensing /
- expectation maximization /
- convolutional sparse coding
[1] Donoho D L 2006 IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 52 1289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Candès E J, Romberg J, Tao T 2006 IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 52 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ji S, Xue Y, Carin L 2008 IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 56 2346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chen M, Silva J, Paisley J, Wang C, Dunson D, Carin L 2010 IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 58 6140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yu G, Sapiro G 2011 IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 59 5842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yang J, Liao X, Yuan X, Llull P, Brady D J, Sapiro G, Carin L 2015 IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 24 106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yu G, Sapiro G, Mallat S 2012 IEEE Tran. Image Process. 21 2481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang C, Liu X F, Yu W K, Yao X R, Zheng F, Dong Q, Lan R M, Sun Z B, Zhai G J, Zhao Q 2017 Chin. Phys. Lett. 34 104203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang Y Y, Ren Y C, Chen L Y, Song C, Li C Z, Zhang C, Xu D G, Yao J Q 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 114204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xiao D, Cai H K, Zheng H Y 2015 Chin. Phys. B 24 060505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 宁方立, 何碧静, 韦娟 2013 62 174212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ning F L, He B J, Wei J 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 174212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 李少东, 陈永彬, 刘润华, 马晓岩 2017 66 038401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S D, Chen Y B, Liu R H, Ma X Y 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 038401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Duarte M F, Davenport M A, Takhar D, Laska J N, Sun T, Kelly K F, Baraniuk R G 2008 IEEE Sig. Process. Mag. 25 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zeiler M D, Krishnan D, Taylor G W, Fergus R 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) San Francisco, June 13−18, 2010 p2528
[15] Grosse R, Raina R, Kwong H, Ng A Y 2007 Proceedings of the Twenty-Third Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence Vancouver, July 19−22, 2007 p149
[16] Yang J, Yu K, Huang T 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) San Francisco, June 13−18, 2010 p3517
[17] Wohlberg B 2016 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Davis P J 2012 Circulant Matrices (Providence, Rhode Island: American Mathematical Society)
[19] Dempster A, Laird N, Rubin D 1977 J. R. Stat. Soc. 39 1
[20] Renna F, Calderbank R, Carin L, Rodrigues M R D 2014 IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 62 2265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tropp J A, Gilbert A C 2007 IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 53 4655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yang J, Zhang Y 2011 SIAM J Sci. Comput. 33 250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liao X, Li H, Carin L 2014 SIAM Imaging Sci. 7 797
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Xu Y, Yin W, Osher S 2014 Inverse Probl. Imag. 8 901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Krizhevsky A, Hinton G 2009 Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images (Toronto: University of Toronto) Technical Report Vol. 1, No. 4, p7
[26] Li F F, Rob F, Pietro P 2007 Comput. Vis. Image Und. 106 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu Z W, Luo P, Wang X G, Tang X O 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Santiago, December 7−13, 2015 p3730
-
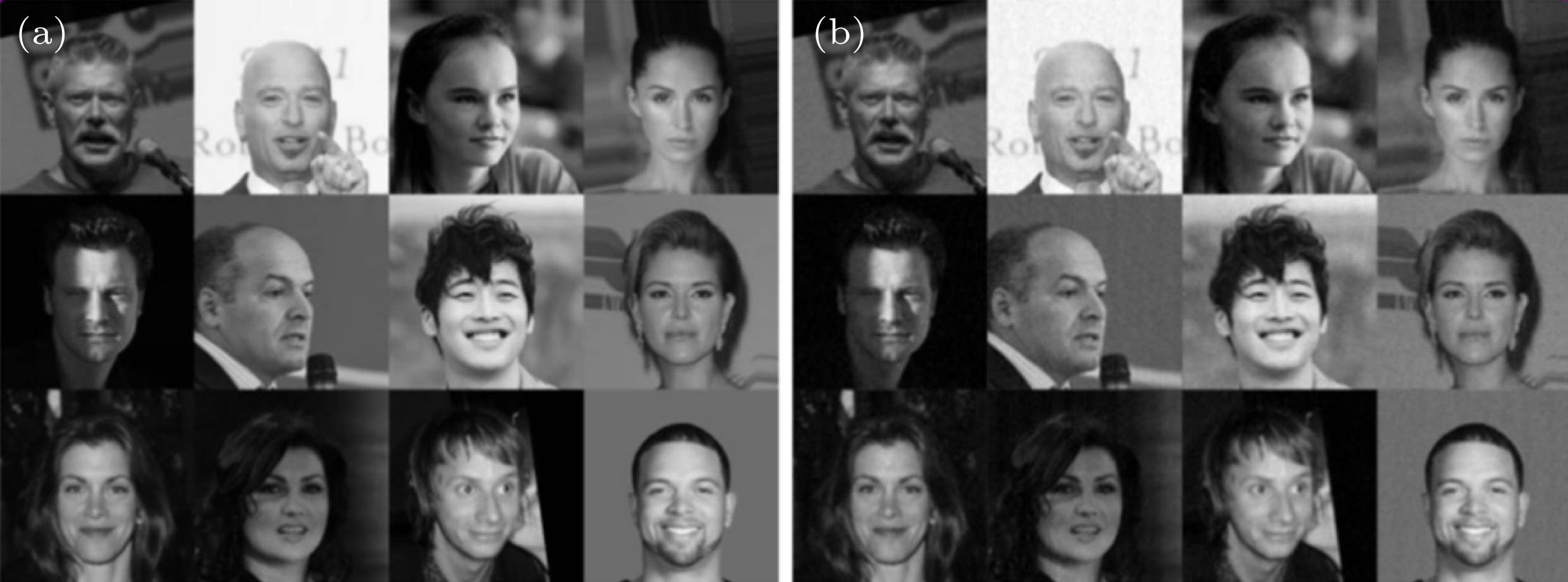
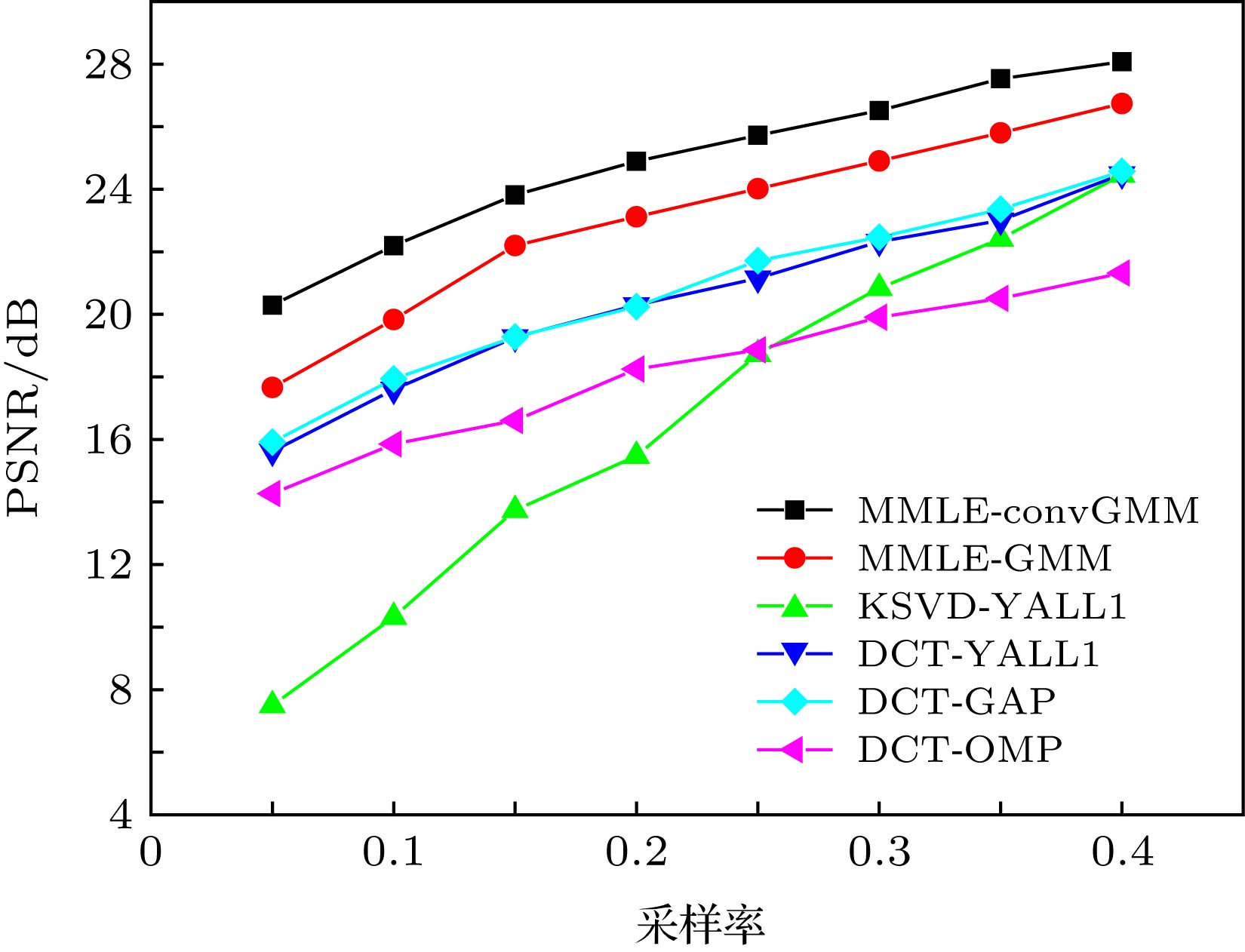
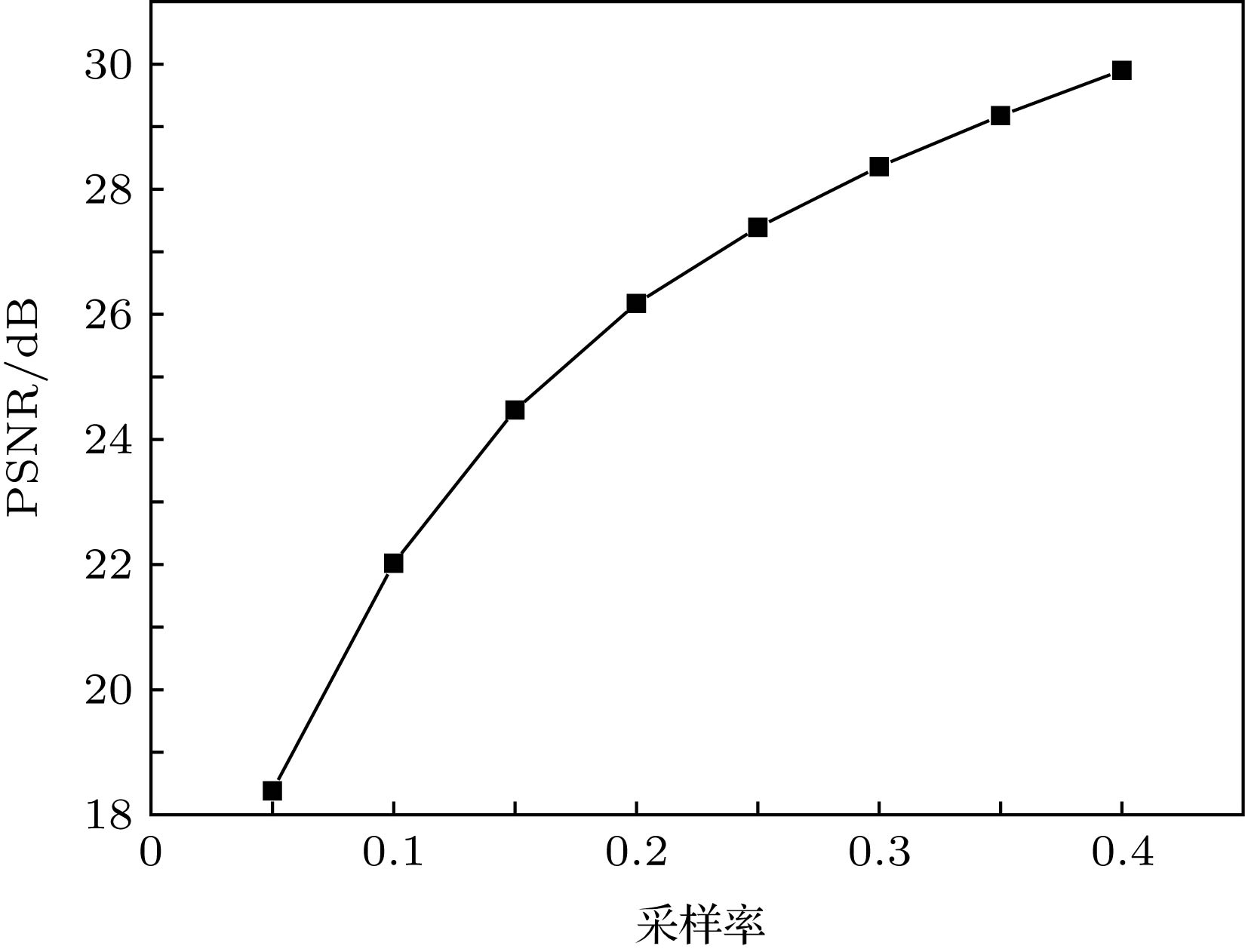
图 4 采样率为0.4时, 12张Caltech 101“飞机”图像在不同算法下的恢复情况 (a)原图像; (b) MMLE-convGMM下的恢复图像; (c) MMLE-GMM下的恢复图像; (d) KSVD-YALL1下的恢复图像; (e) DCT-YALL1下的恢复图像; (f) DCT-GAP下的恢复图像; (g) DCT-OMP下的恢复图像
Figure 4. Reconstructed performance comparison of 12 randomly selected “airplane” images from Caltech 101: (a) Original images; (b) images reconstructed by MMLE-convGMM; (c) images reconstructed by MLE-GMM; (d) images reconstructed by KSVD-YALL1; (e) images reconstructed by DCT-YALL1; (f) images reconstructed by DCT-GAP; (g) images reconstructed by DCT-OMP. All of the sampling rates are 0.4.
-
[1] Donoho D L 2006 IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 52 1289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Candès E J, Romberg J, Tao T 2006 IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 52 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ji S, Xue Y, Carin L 2008 IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 56 2346
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chen M, Silva J, Paisley J, Wang C, Dunson D, Carin L 2010 IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 58 6140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yu G, Sapiro G 2011 IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 59 5842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yang J, Liao X, Yuan X, Llull P, Brady D J, Sapiro G, Carin L 2015 IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 24 106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yu G, Sapiro G, Mallat S 2012 IEEE Tran. Image Process. 21 2481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang C, Liu X F, Yu W K, Yao X R, Zheng F, Dong Q, Lan R M, Sun Z B, Zhai G J, Zhao Q 2017 Chin. Phys. Lett. 34 104203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang Y Y, Ren Y C, Chen L Y, Song C, Li C Z, Zhang C, Xu D G, Yao J Q 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 114204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xiao D, Cai H K, Zheng H Y 2015 Chin. Phys. B 24 060505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 宁方立, 何碧静, 韦娟 2013 62 174212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ning F L, He B J, Wei J 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 174212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 李少东, 陈永彬, 刘润华, 马晓岩 2017 66 038401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S D, Chen Y B, Liu R H, Ma X Y 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 038401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Duarte M F, Davenport M A, Takhar D, Laska J N, Sun T, Kelly K F, Baraniuk R G 2008 IEEE Sig. Process. Mag. 25 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zeiler M D, Krishnan D, Taylor G W, Fergus R 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) San Francisco, June 13−18, 2010 p2528
[15] Grosse R, Raina R, Kwong H, Ng A Y 2007 Proceedings of the Twenty-Third Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence Vancouver, July 19−22, 2007 p149
[16] Yang J, Yu K, Huang T 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) San Francisco, June 13−18, 2010 p3517
[17] Wohlberg B 2016 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Davis P J 2012 Circulant Matrices (Providence, Rhode Island: American Mathematical Society)
[19] Dempster A, Laird N, Rubin D 1977 J. R. Stat. Soc. 39 1
[20] Renna F, Calderbank R, Carin L, Rodrigues M R D 2014 IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 62 2265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tropp J A, Gilbert A C 2007 IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 53 4655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yang J, Zhang Y 2011 SIAM J Sci. Comput. 33 250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liao X, Li H, Carin L 2014 SIAM Imaging Sci. 7 797
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Xu Y, Yin W, Osher S 2014 Inverse Probl. Imag. 8 901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Krizhevsky A, Hinton G 2009 Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images (Toronto: University of Toronto) Technical Report Vol. 1, No. 4, p7
[26] Li F F, Rob F, Pietro P 2007 Comput. Vis. Image Und. 106 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu Z W, Luo P, Wang X G, Tang X O 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Santiago, December 7−13, 2015 p3730
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9242
- PDF Downloads: 65
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: