-
回音壁模式微腔的色散调控是克尔光频梳生成的关键. 然而回音壁模式微腔色散设计主要是通过改变微腔结构调控模场分布, 方式较为单一. 本文将径向分布的梯度折射率$n(r)$引入回音壁模式微腔, 提出使用改变折射率分布调控梯度折射率微腔色散. 通过数值计算和有限元仿真结果表明, 折射率梯度的约束使微腔模场的位置远离微腔边缘, 梯度折射率微腔具有零几何色散特性. 基于设计不同折射率分布提出两种色散调控方式—修饰微腔边缘几何外形和构建双势阱. 并且研究了微腔半径、楔角大小、离子扩散和塑形工艺顺序、双势阱宽度和间距对色散的影响. 仿真结果表明两种方式均可以得到通信波段较大范围的反常色散, 梯度折射率微腔色散调控方式十分灵活, 在非线性光学应用领域具有极大潜力.
Kerr optical frequency combs based on whispering-gallery mode (WGM) microresonators have great potential for applications in various fields, such as precision measurement, spectral analysis, optical communication, and quantum technology. The interaction between dispersion and nonlinearity is crucial for determining the stability and bandwidth performance of optical frequency combs. In particular, the Kerr bright soliton optical frequency comb requires a suitable anomalous group velocity dispersion (GVD) to maintain the dissipative system. Therefore, designing the dispersion of the WGM microresonator is essential for generating the Kerr optical frequency comb. However, WGM microresonators typically have normal and fixed material dispersion, and their dispersion design is mainly based on modulating the mode field distribution by changing the microresonator structure to achieve anomalous dispersion, which limits their flexibility. In this paper, we introduce a radially distributed gradient refractive index n(r) into WGM microresonators and propose to use the refractive index profile for controlling the dispersion of gradient-index (GRIN) microresonators. Numerical simulations and finite element analysis demonstrate that the refractive index gradient constrains the mode field and pushes it away from the cavity edge, resulting in near-zero geometric dispersion in the GRIN microresonator. Two dispersion modulation methods are explored: modifying the microresonator’s geometric shape and constructing a dual potential well. The effects of microresonator radius, wedge angle, ion diffusion sequence, and potential well width and spacing on dispersion are systematically investigated. Simulation results show that both methods can achieve a wide range of anomalous dispersion within the communication band. In the first method, mode field leakage in the bilateral wedge-shaped GRIN microresonator produces anomalous dispersion, while no leakage results in normal dispersion. When the mode field is pushed away from the edge, near-zero dispersion is achieved. In the second method, energy coupling between the inner mode and the outer mode in the dual potential well structure leads to anomalous dispersion in the inner mode and normal dispersion in the outer mode. Our findings highlight the flexibility of GRIN microresonator dispersion control and indicate great potential for nonlinear optical applications. [1] Vahala K 2003 Nature 424 839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 孟令俊, 王梦宇, 沈远, 杨煜, 徐文斌, 张磊, 王克逸 2020 69 014203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Meng L J, Wang M Y, Shen Y, Yang Y, Xu W B, Zhang L, Wang K Y 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 014203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu W, Li W, Wang R, Xing E, Jing N, Zhou Y, Tang J, Liu J 2021 Opt. Commun. 497 127148
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wan H, Liu L, Ding Z, Wang J, Xiao Y, Zhang Z 2018 Opt. Laser Technol. 102 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jiang S, Guo C, Fu H, Che K, Xu H, Cai Z 2020 Opt. Express 28 38304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Strekalov D V, Marquardt C, Matsko A B, Schwefel H G L, Leuchs G 2016 J. Opt. 18 123002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wu X Y, Wang K, Wang H, Lu B, Gao Y P, Wang C 2023 EPL 141 25001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Fuerst J U, Strekalov D V, Elser D, Aiello A, Andersen U L, Marquardt C, Leuchs G 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 263904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cheng S, Zhang X, Shang M, Liu X, Jia K, Xie Z, Zhu S 2024 Phys. Rev. A 109 L011502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Del’Haye P, Schliesser A, Arcizet O, Wilken T, Holzwarth R, Kippenberg T J 2007 Nature 450 1214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nakagawa Y, Mizumoto Y, Kato T, Kobatake T, Itobe H, Kakinuma Y, Tanabe T 2016 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 33 1913
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Xu L, Xie C, Wang M, Guo Z, Wei B, Zhang H, Zhang L, He X 2023 Opt. Express 31 38365
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sturman B, Breunig I 2015 New J. Phys. 17 125006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tian J, Lin G 2024 J. Lightwave Technol. 42 2118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kippenberg T J, Gaeta A L, Lipson M, Gorodetsky M L 2018 Science 361 eaan8083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Fujii S, Tanabe T 2020 Nanophotonics 9 1087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Grudinin I S, Yu N 2015 Optica 2 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhou C, Du J, He Z 2017 IEEE Photon. J. 9 7908008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jin X, Wang J, Wang M, Dong Y, Li F, Wang K 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 8023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ke C, Ma J, Huang Y, Zeng Z, Xu C, Qin J 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 1522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ilchenko V, Savchenkov A, Matsko A, Maleki L 2003 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 20 157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhu D, Zhou Y, Yu X, Shum P, Luan F 2012 Opt. Express 20 26285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen T, Kang Z, Yang Y, Zhao S, Zhang J, Zhang L, Wang K 2023 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 40 1208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chen T, Kang Z, Zhang J, Huang Z, Tang D, Yang B, Yang Y, Wang K 2024 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 41 486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Ba Q, Zhou Y, Li J, Xiao W, Ye L, Liu Y, Chen J H, Chen H 2022 eLight 2 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Dadashi K, Kurt H, Ustun K, Esen R 2014 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 31 2239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 王克逸, 汪景昌 1989 38 1334
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang K Y, Wang J C 1989 Acta Phys. Sin. 38 1334
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Sellmeier W 1872 Annalen der Physik 223 386
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Nie M, Jia K, Xie Y, Zhu S, Xie Z, Huang S W 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 6395
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
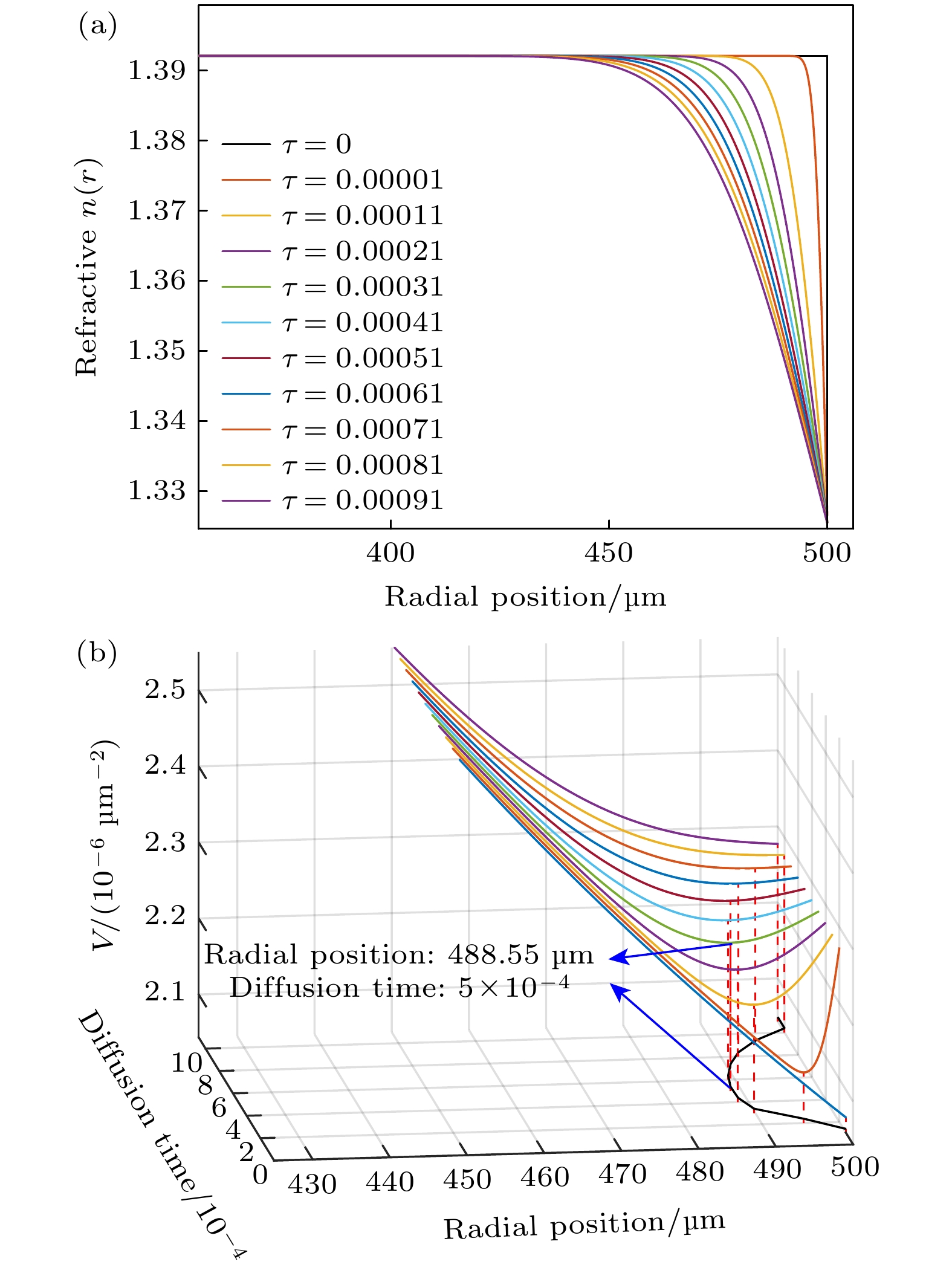
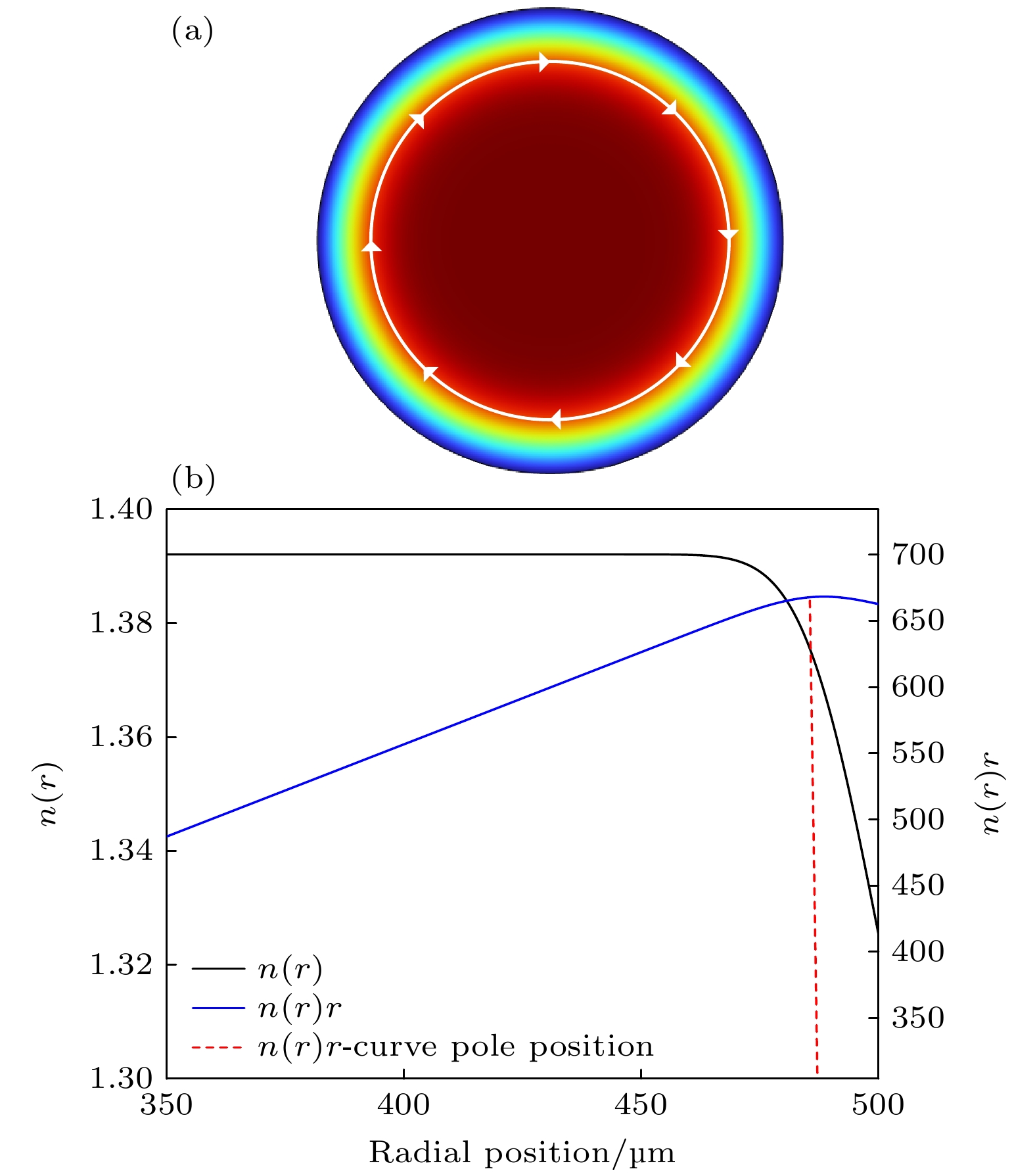
图 1 (a) GRIN微腔的折射率分布, 从边缘到内部折射率由低变高, 模场远离微腔表面; (b) GRIN微腔沿径向折射率分布曲线n(r), 其中n(r)r曲线极点为基模位置
Fig. 1. (a) Refractive index distribution of the GRIN microresonator, with low to high refractive indices from the edges to the interior, with the mode field away from the microresonator surface; (b) GRIN microresonator refractive index distribution curve n(r) along the radial direction, where n(r)r curve pole is the fundamental mode position.
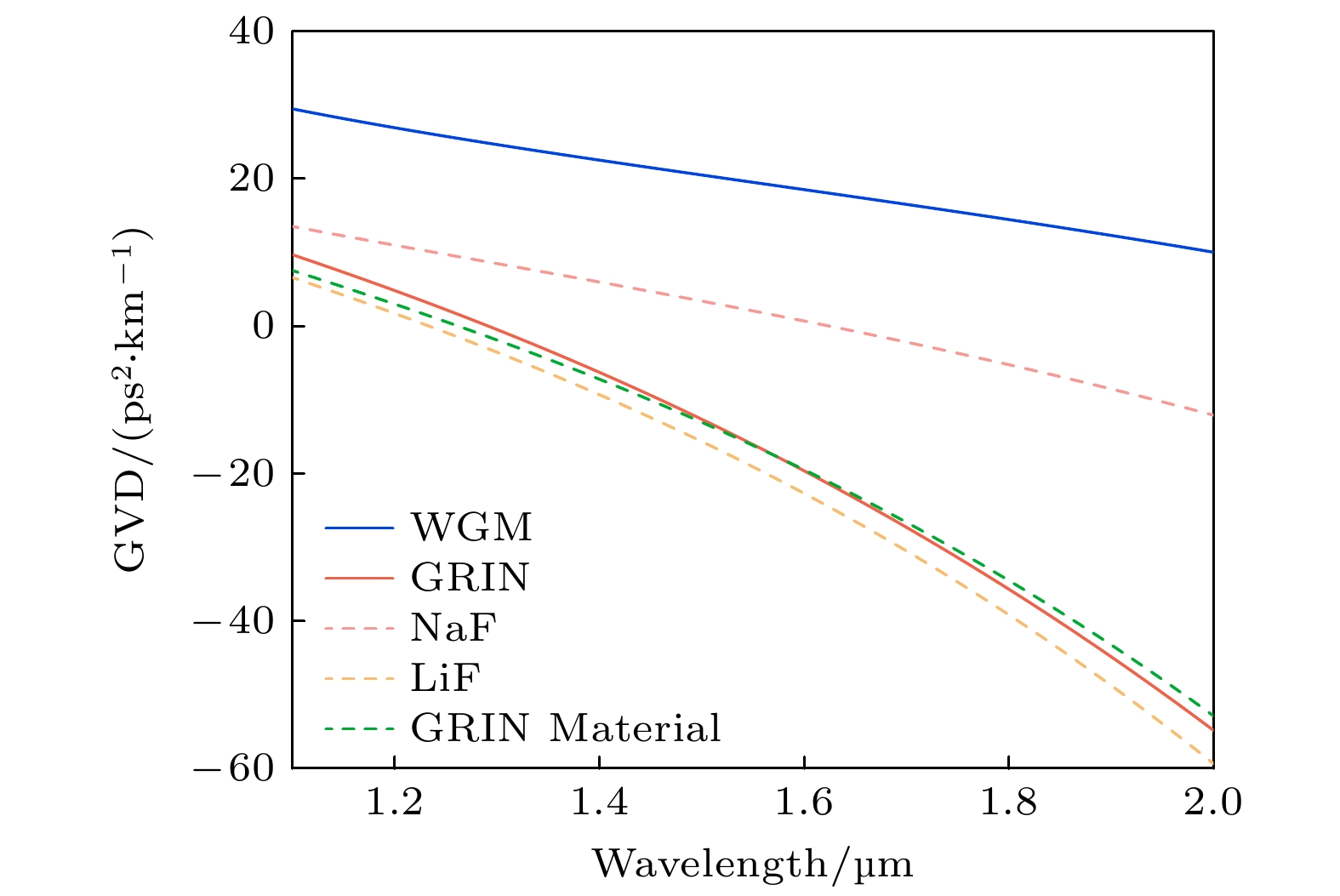
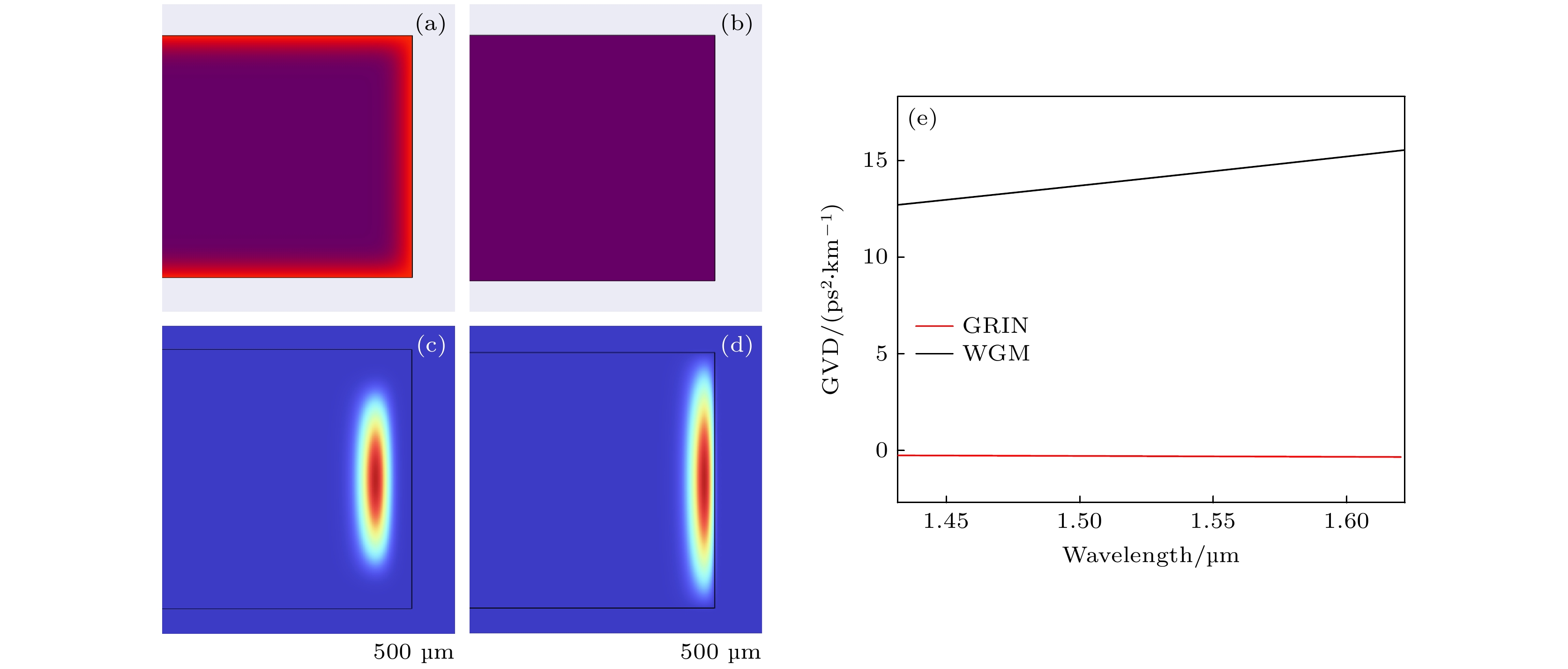
图 4 (a) GRIN微腔的折射率分布; (b) GRIN微腔的基模模场; (c) WGM微腔的折射率分布; (d) WGM微腔的基模模场; (e) GRIN, WGM微腔几何色散
Fig. 4. (a) Refractive index distribution of GRIN microresonator; (b) fundamental mode field of GRIN microresonator; (c) refractive index distribution of WGM microresonator; (d) fundamental mode field of WGM microresonator; (e) geometric dispersion of GRIN, WGM microresonator
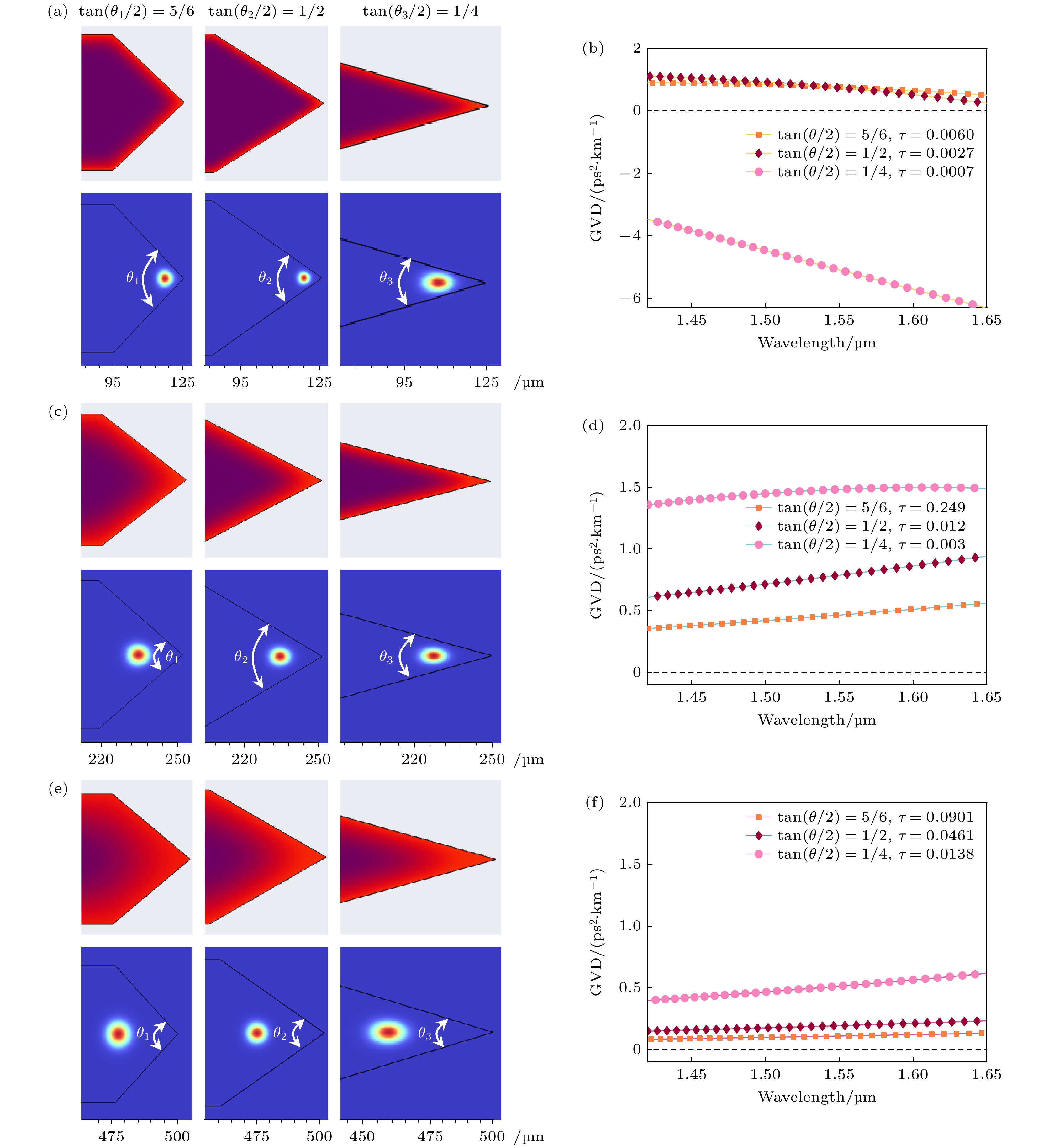
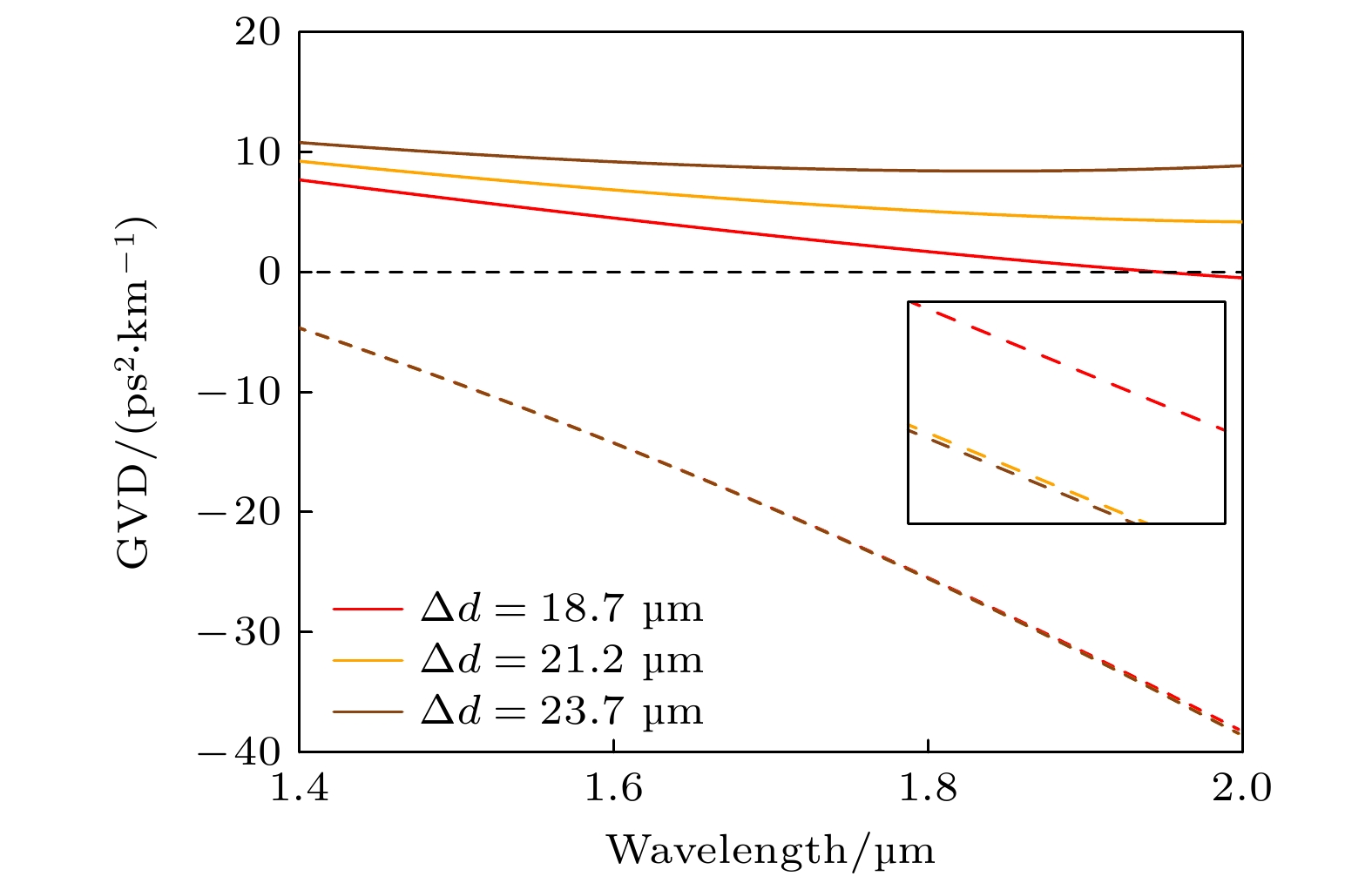
图 5 不同半径和楔角大小的后扩散双边楔形GRIN微腔及其GVD (a), (c), (e) GRIN 微腔折射率分布和基模模场; (b), (d), (f)对应的GRIN 微腔的 GVD
Fig. 5. Diffusion-after bilateral wedge-shaped GRIN microresonator and their GVD with different radius and wedge angle sizes: (a), (c), (e) Refractive index distributions and fundamental mode fields of GRIN microresonators; (b), (d), (f) GVD of the corresponding GRIN microresonators
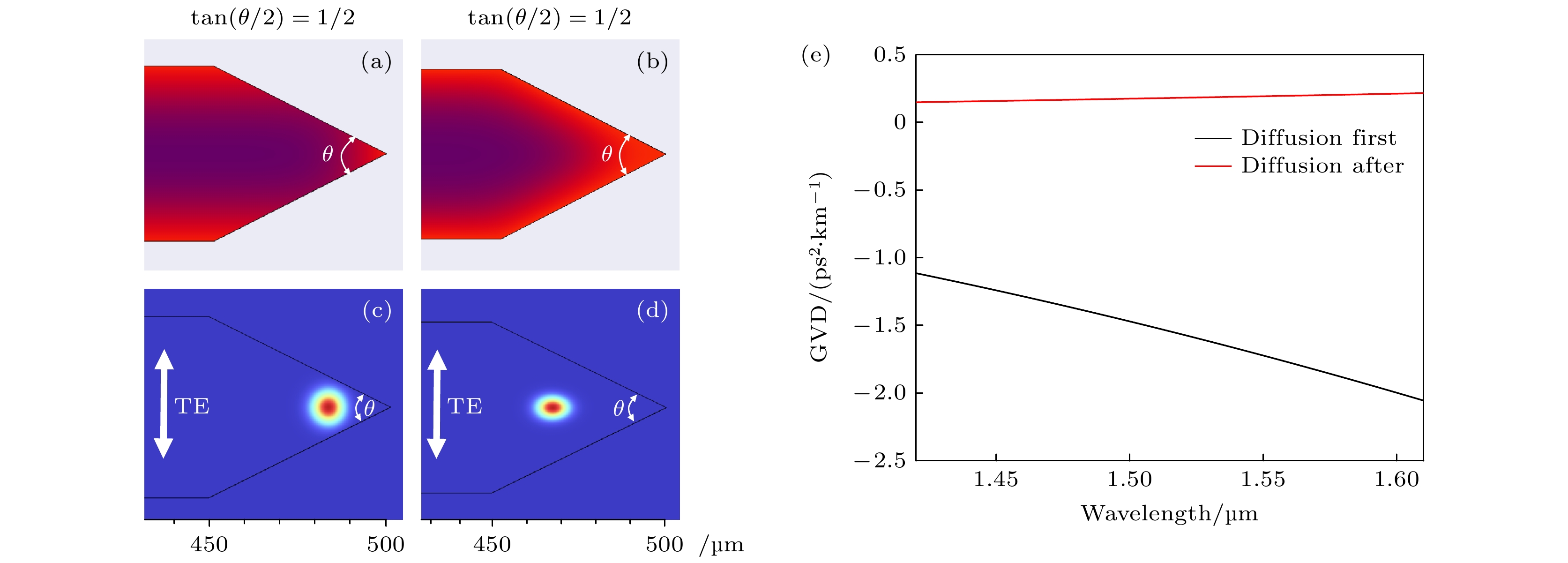
图 6 (a) 500 µm, 楔角半角正切1/2的先扩散微腔的折射率分布; (b) 500 µm, 楔角半角正切1/2的后扩散微腔的折射率分布; (c) 对应的先扩散微腔的基模模场; (d) 对应的后扩散微腔的基模模场; (e) 两种 GRIN 微腔的 GVD
Fig. 6. (a) Refractive index distribution of a 500 µm, wedge-angle half-angle tangent 1/2 of the diffusion-first microresonator; (b) refractive index distribution of a 500 µm, wedge-angle half-angle tangent 1/2 of the diffusion-after microresonator; (c) corresponding fundamental mode fields of the first diffusion microresonator; (d) corresponding fundamental mode fields of the after-diffusion microresonator; (e) GVD of the two GRIN microresonators.
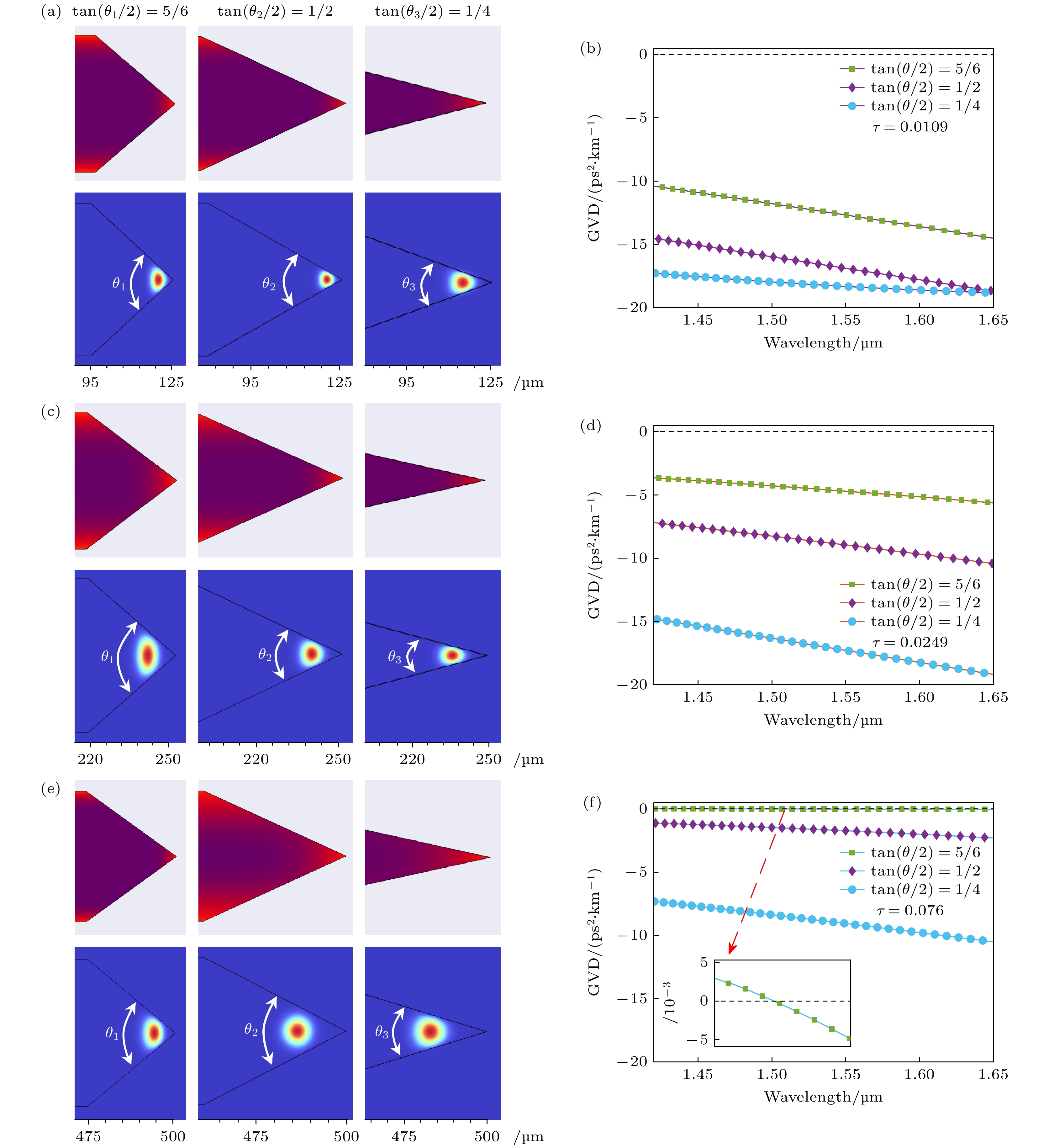
图 7 不同半径和楔角大小的先扩散双边楔形 GRIN 微腔及其GVD (a), (c), (e) GRIN 微腔折射率分布和基模模场; (b), (d), (f)对应的GRIN 微腔的 GVD
Fig. 7. Diffusion-first bilateral wedge-shaped GRIN microresonator and their GVD with different radius and wedge angle sizes: (a), (c), (e) Refractive index distributions and fundamental mode fields of GRIN microresonators; (b), (d), (f) GVD of corresponding GRIN microresonators.
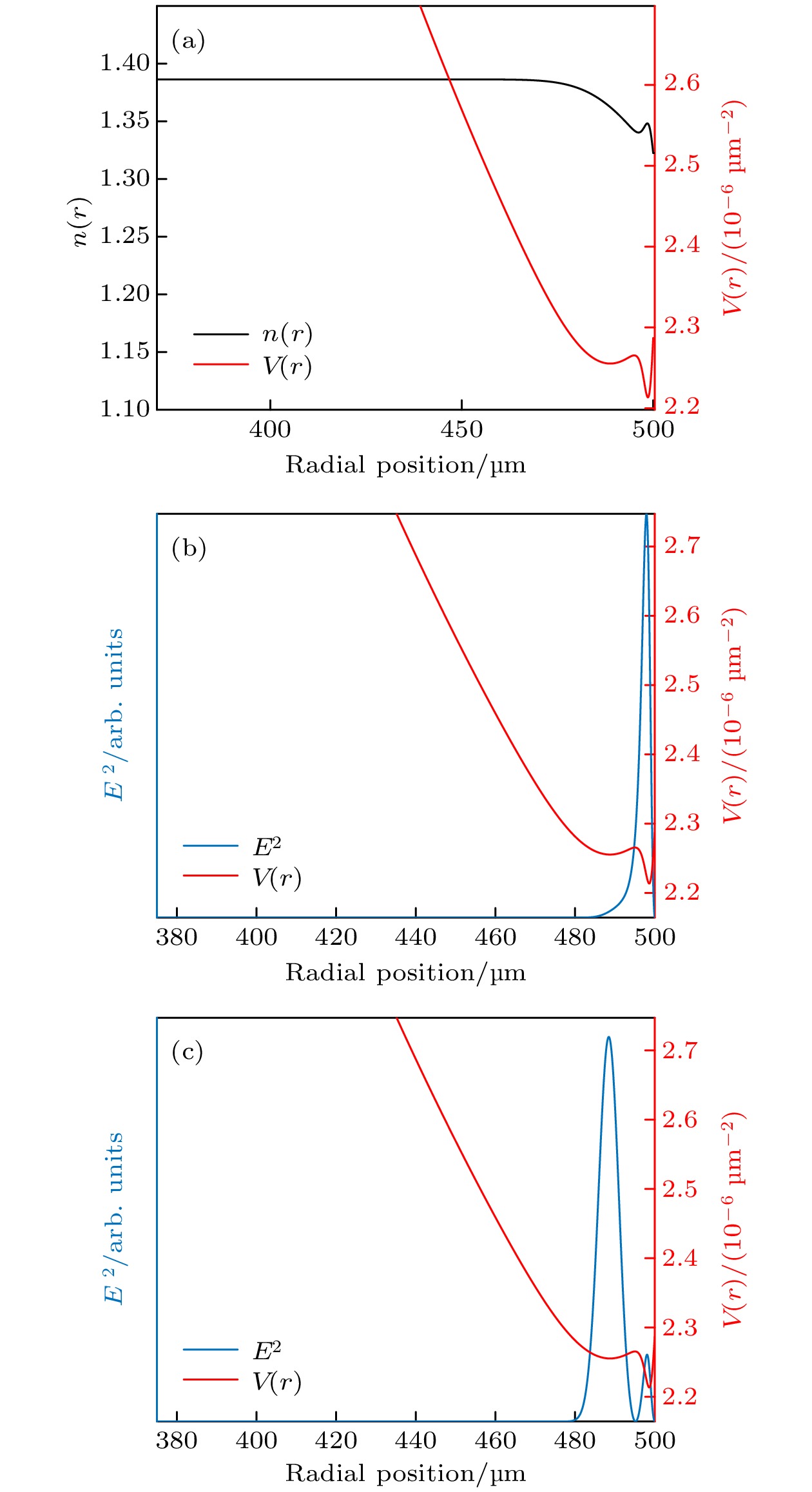
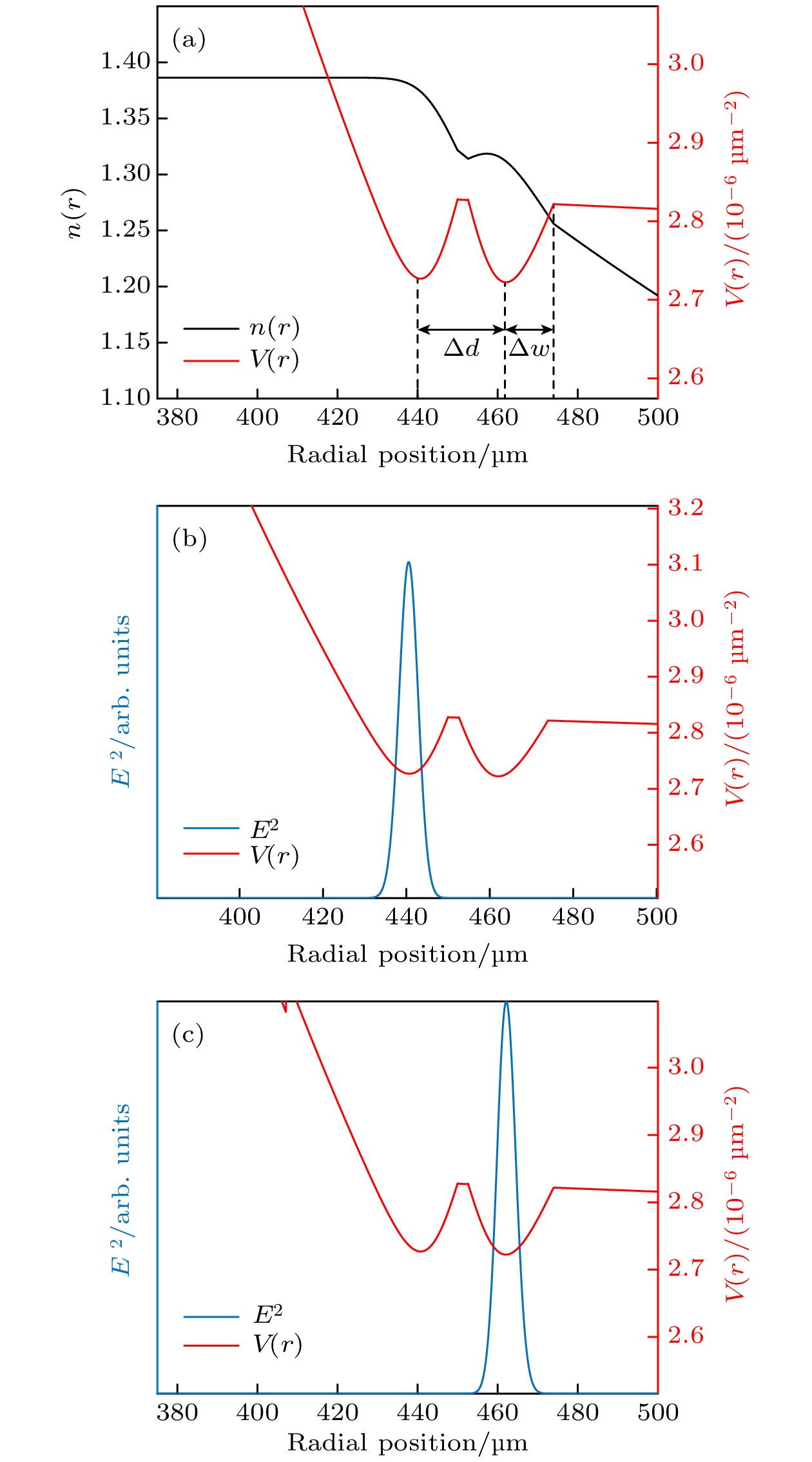
图 8 (a)双势阱GRIN微腔的折射率分布$ n(r) $和势函数$ V(r) $; (b)内层基模径向模场; (c)外层基模径向模场
Fig. 8. (a) Refractive index distribution $ n(r) $ and potential function $ V(r) $ of the GRIN microresonator with double-potential well; (b) radial mode field of the fundamental mode of the inner layer; (c) radial mode field of the fundamental mode of the outer layer.
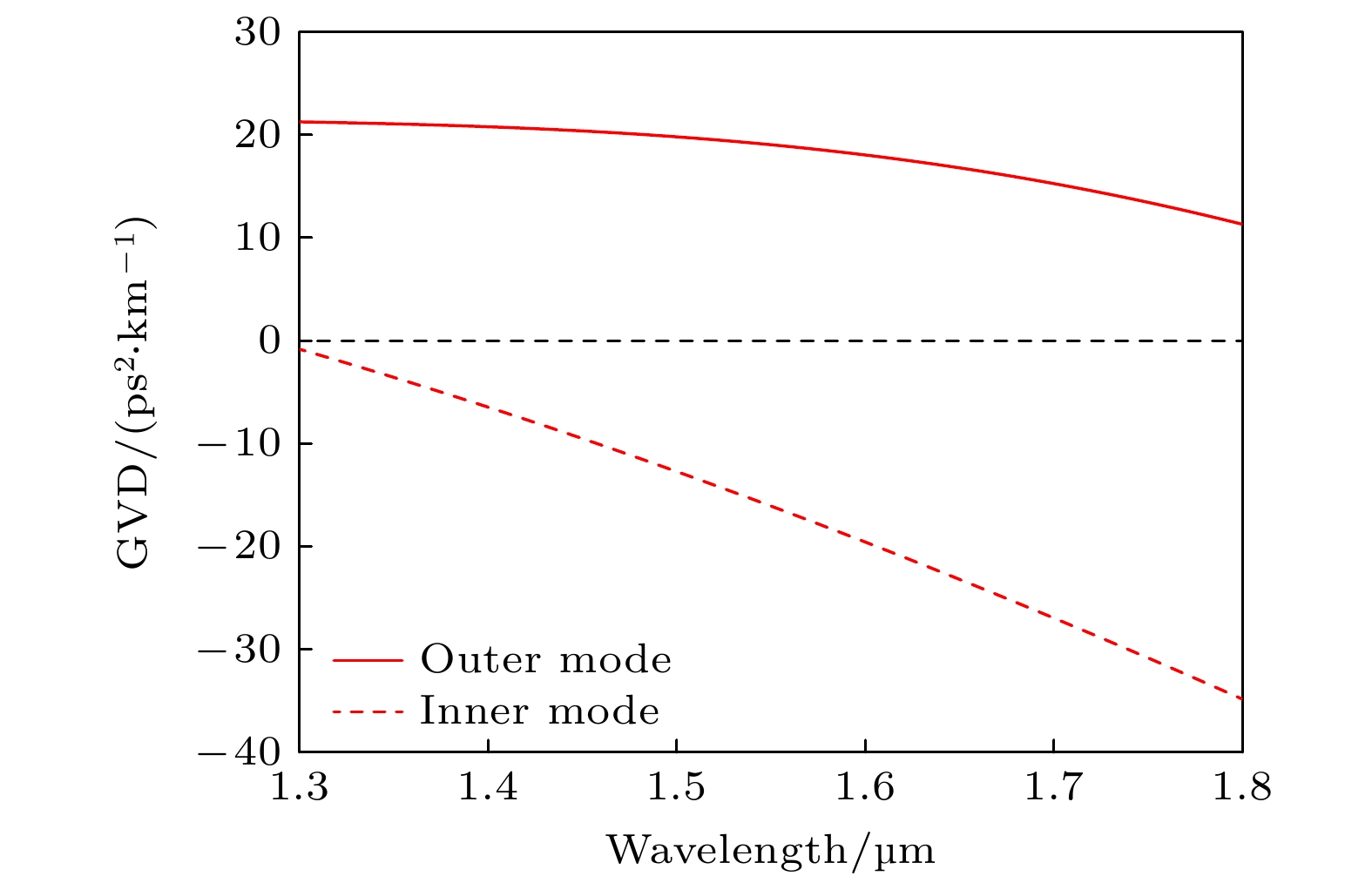
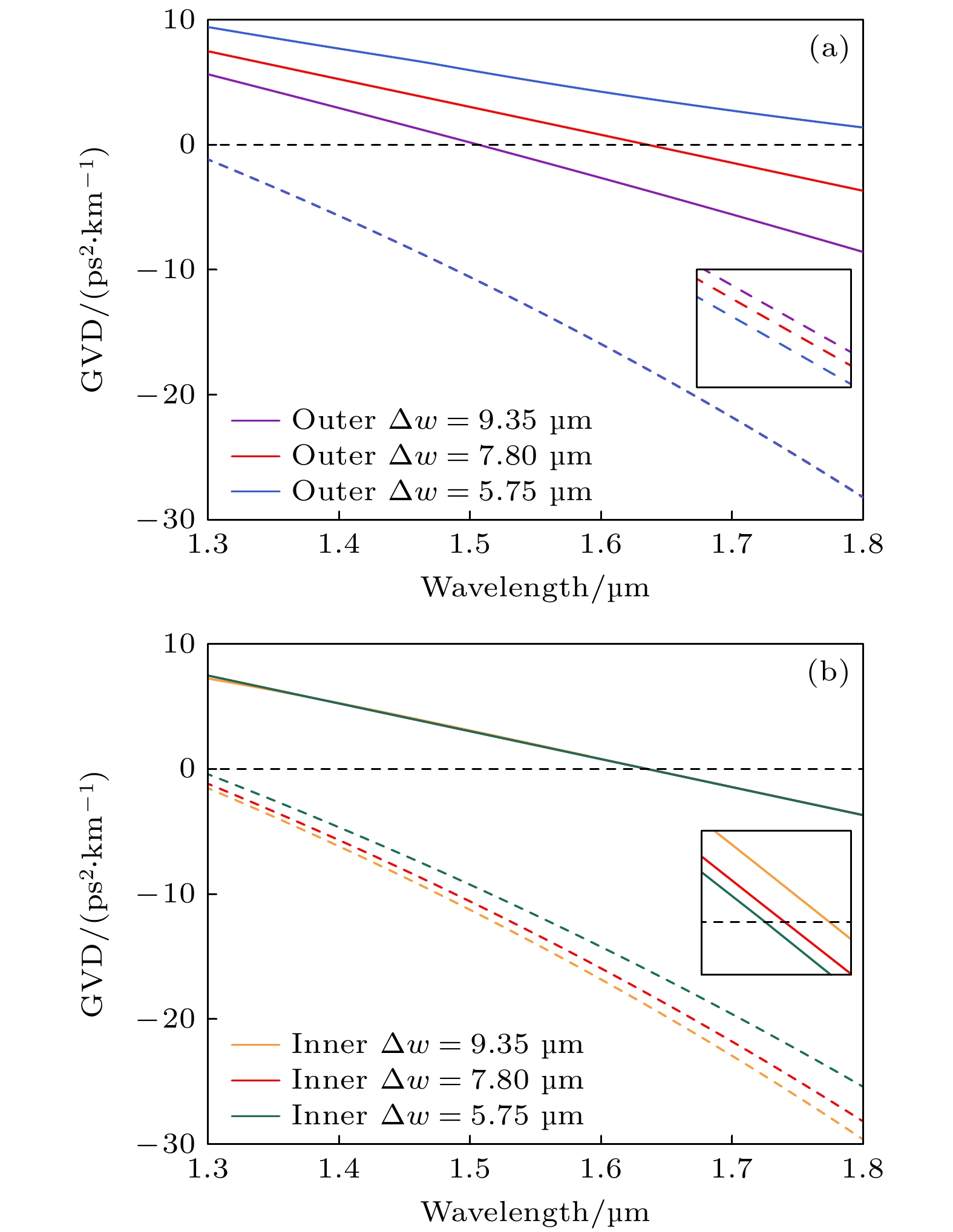
图 10 (a)双势阱GRIN微腔的折射率分布$ n(r) $和势函数$ V(r) $; (b)内层基模径向模场; (c)外层基模径向模场
Fig. 10. (a) Refractive index distribution $ n(r) $ and potential function $ V(r) $ of the double-potential-well GRIN microresonator; (b) radial mode field of the inner fundamental mode; (c) radial mode field of the outer fundamental mode.
-
[1] Vahala K 2003 Nature 424 839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 孟令俊, 王梦宇, 沈远, 杨煜, 徐文斌, 张磊, 王克逸 2020 69 014203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Meng L J, Wang M Y, Shen Y, Yang Y, Xu W B, Zhang L, Wang K Y 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 014203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu W, Li W, Wang R, Xing E, Jing N, Zhou Y, Tang J, Liu J 2021 Opt. Commun. 497 127148
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wan H, Liu L, Ding Z, Wang J, Xiao Y, Zhang Z 2018 Opt. Laser Technol. 102 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jiang S, Guo C, Fu H, Che K, Xu H, Cai Z 2020 Opt. Express 28 38304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Strekalov D V, Marquardt C, Matsko A B, Schwefel H G L, Leuchs G 2016 J. Opt. 18 123002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wu X Y, Wang K, Wang H, Lu B, Gao Y P, Wang C 2023 EPL 141 25001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Fuerst J U, Strekalov D V, Elser D, Aiello A, Andersen U L, Marquardt C, Leuchs G 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 263904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cheng S, Zhang X, Shang M, Liu X, Jia K, Xie Z, Zhu S 2024 Phys. Rev. A 109 L011502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Del’Haye P, Schliesser A, Arcizet O, Wilken T, Holzwarth R, Kippenberg T J 2007 Nature 450 1214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nakagawa Y, Mizumoto Y, Kato T, Kobatake T, Itobe H, Kakinuma Y, Tanabe T 2016 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 33 1913
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Xu L, Xie C, Wang M, Guo Z, Wei B, Zhang H, Zhang L, He X 2023 Opt. Express 31 38365
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sturman B, Breunig I 2015 New J. Phys. 17 125006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tian J, Lin G 2024 J. Lightwave Technol. 42 2118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kippenberg T J, Gaeta A L, Lipson M, Gorodetsky M L 2018 Science 361 eaan8083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Fujii S, Tanabe T 2020 Nanophotonics 9 1087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Grudinin I S, Yu N 2015 Optica 2 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhou C, Du J, He Z 2017 IEEE Photon. J. 9 7908008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jin X, Wang J, Wang M, Dong Y, Li F, Wang K 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 8023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ke C, Ma J, Huang Y, Zeng Z, Xu C, Qin J 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 1522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ilchenko V, Savchenkov A, Matsko A, Maleki L 2003 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 20 157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhu D, Zhou Y, Yu X, Shum P, Luan F 2012 Opt. Express 20 26285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen T, Kang Z, Yang Y, Zhao S, Zhang J, Zhang L, Wang K 2023 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 40 1208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chen T, Kang Z, Zhang J, Huang Z, Tang D, Yang B, Yang Y, Wang K 2024 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 41 486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Ba Q, Zhou Y, Li J, Xiao W, Ye L, Liu Y, Chen J H, Chen H 2022 eLight 2 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Dadashi K, Kurt H, Ustun K, Esen R 2014 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 31 2239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 王克逸, 汪景昌 1989 38 1334
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang K Y, Wang J C 1989 Acta Phys. Sin. 38 1334
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Sellmeier W 1872 Annalen der Physik 223 386
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Nie M, Jia K, Xie Y, Zhu S, Xie Z, Huang S W 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 6395
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3004
- PDF下载量: 105
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: