-
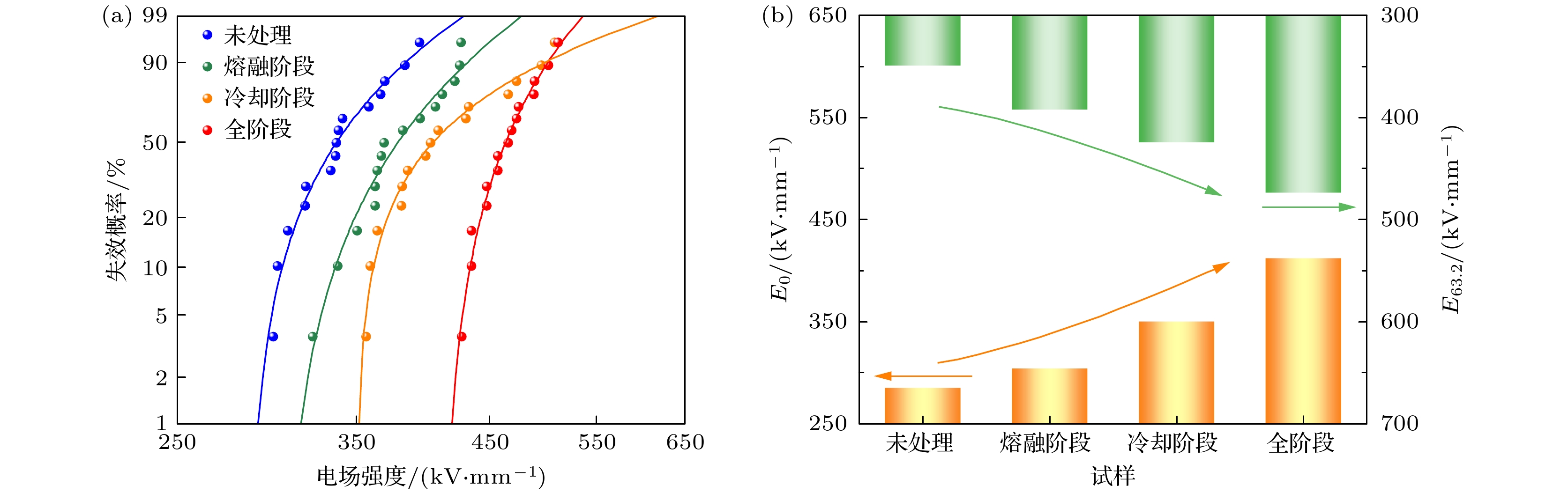
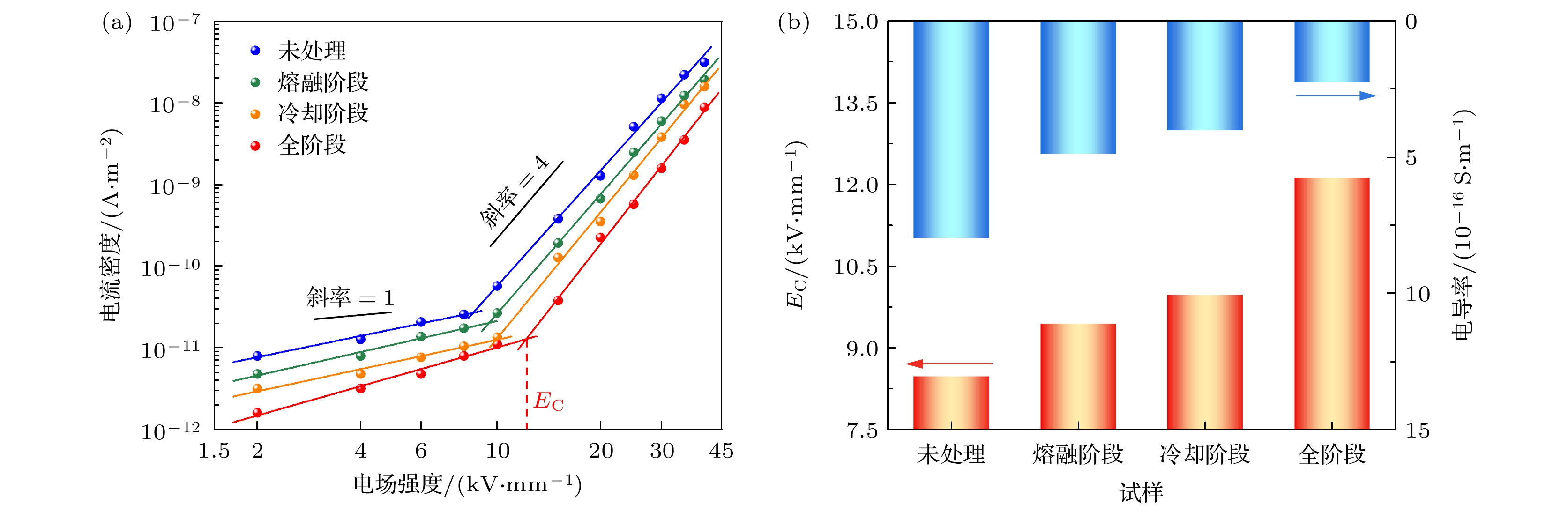
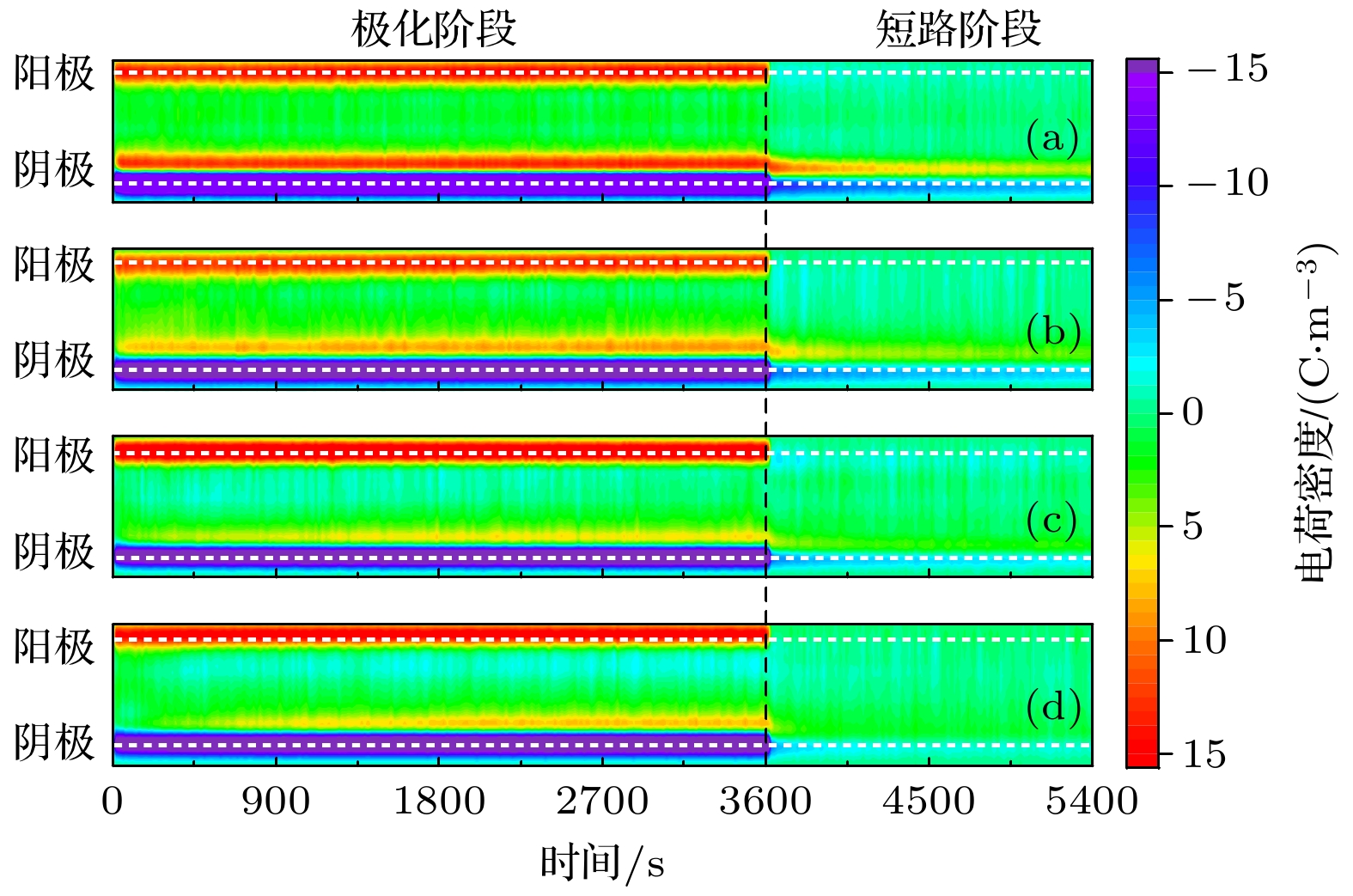
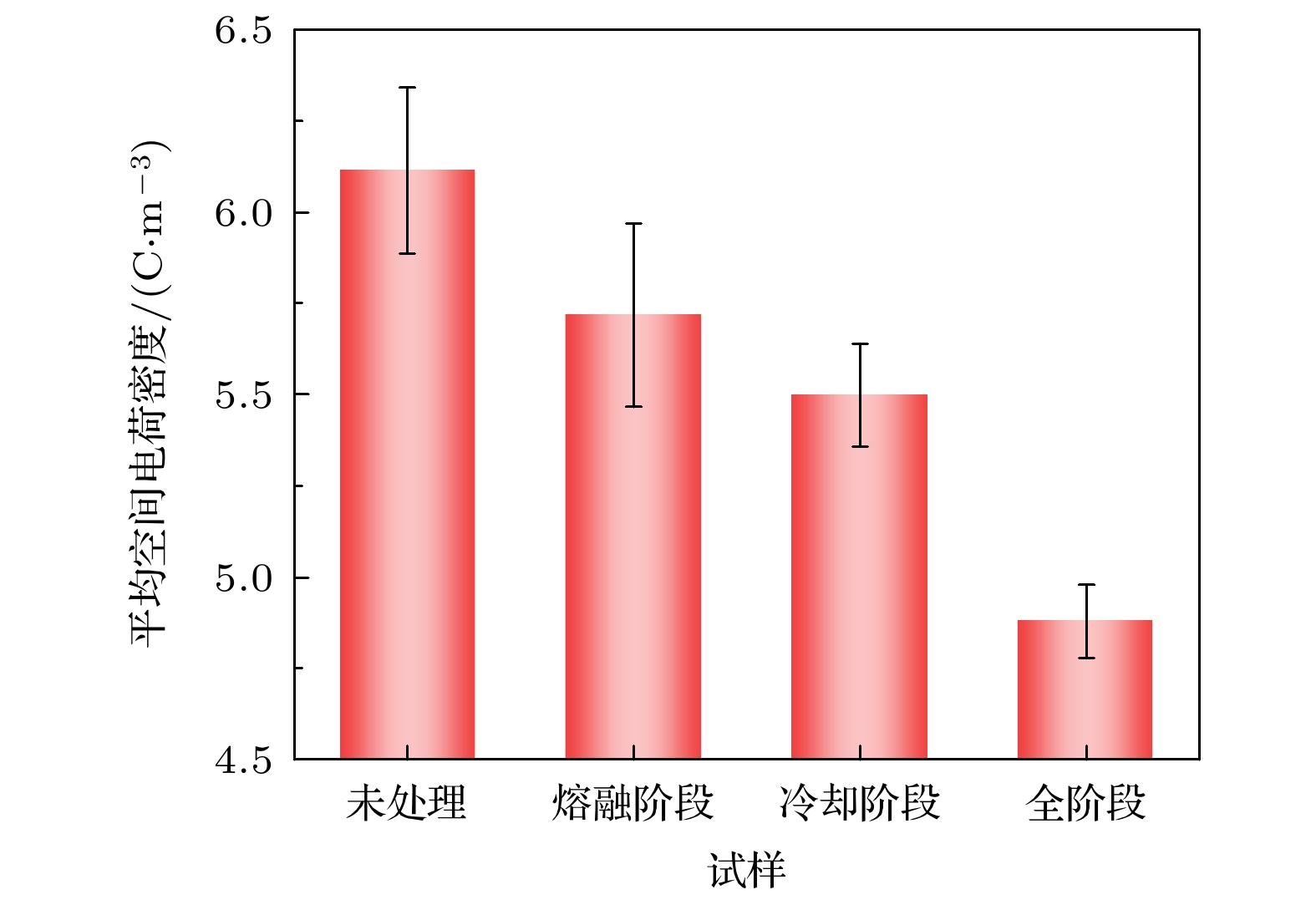
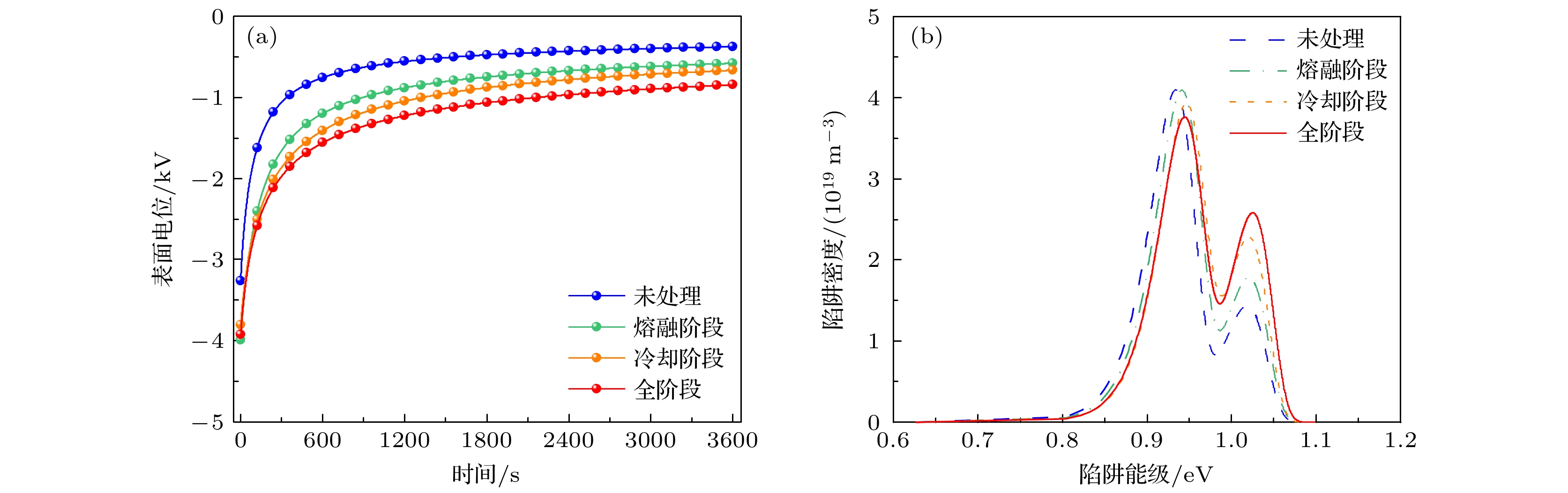
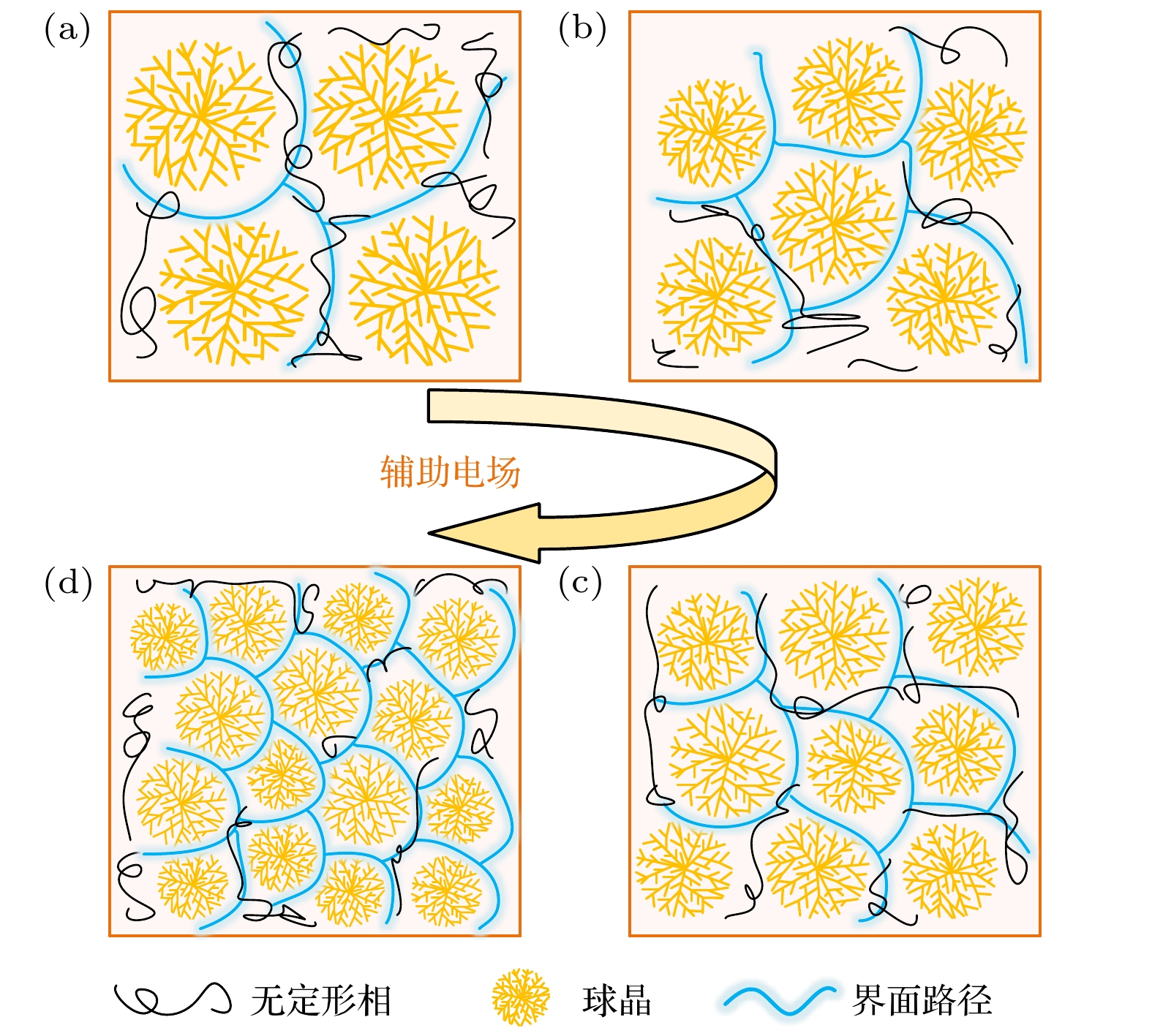
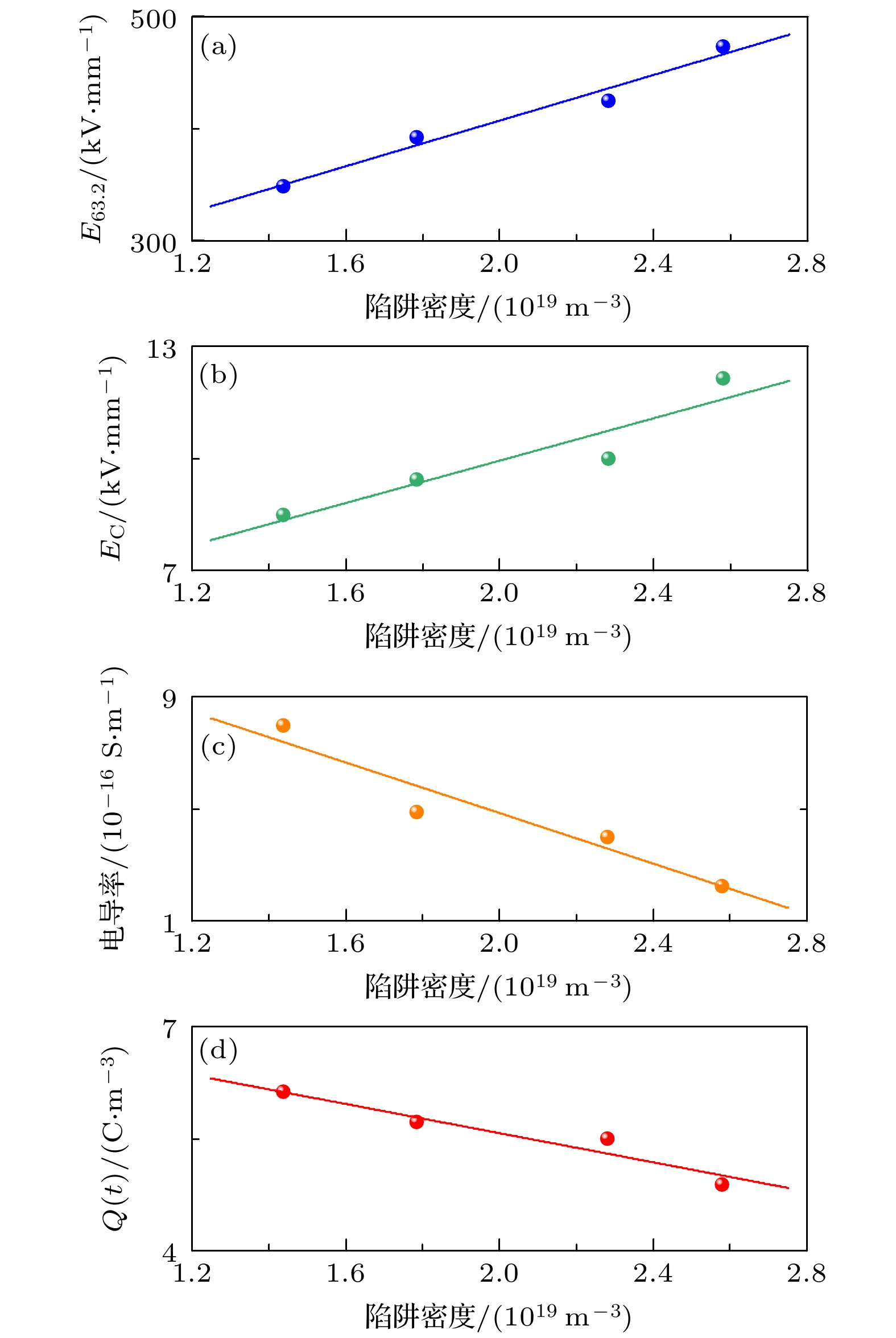
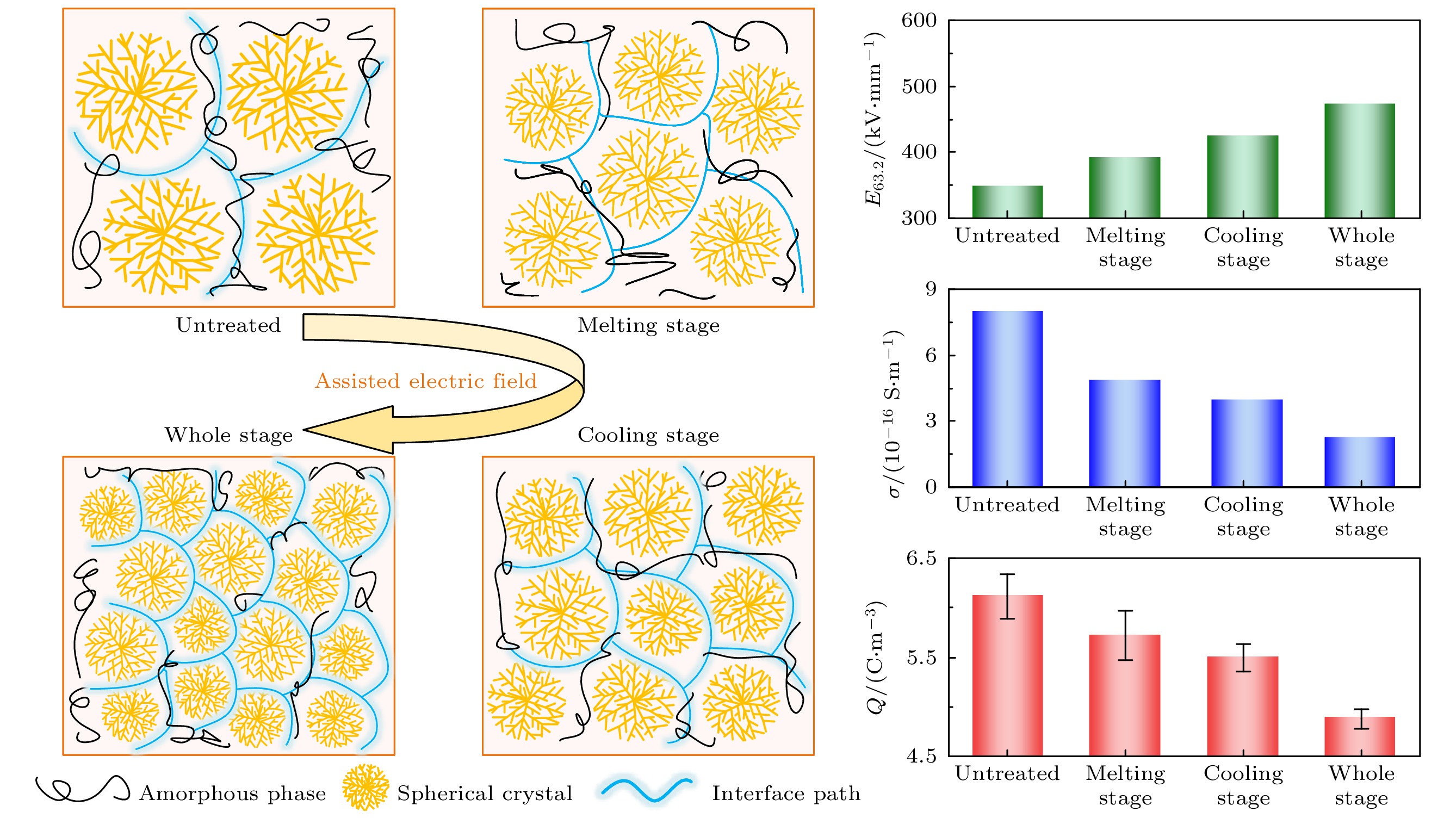
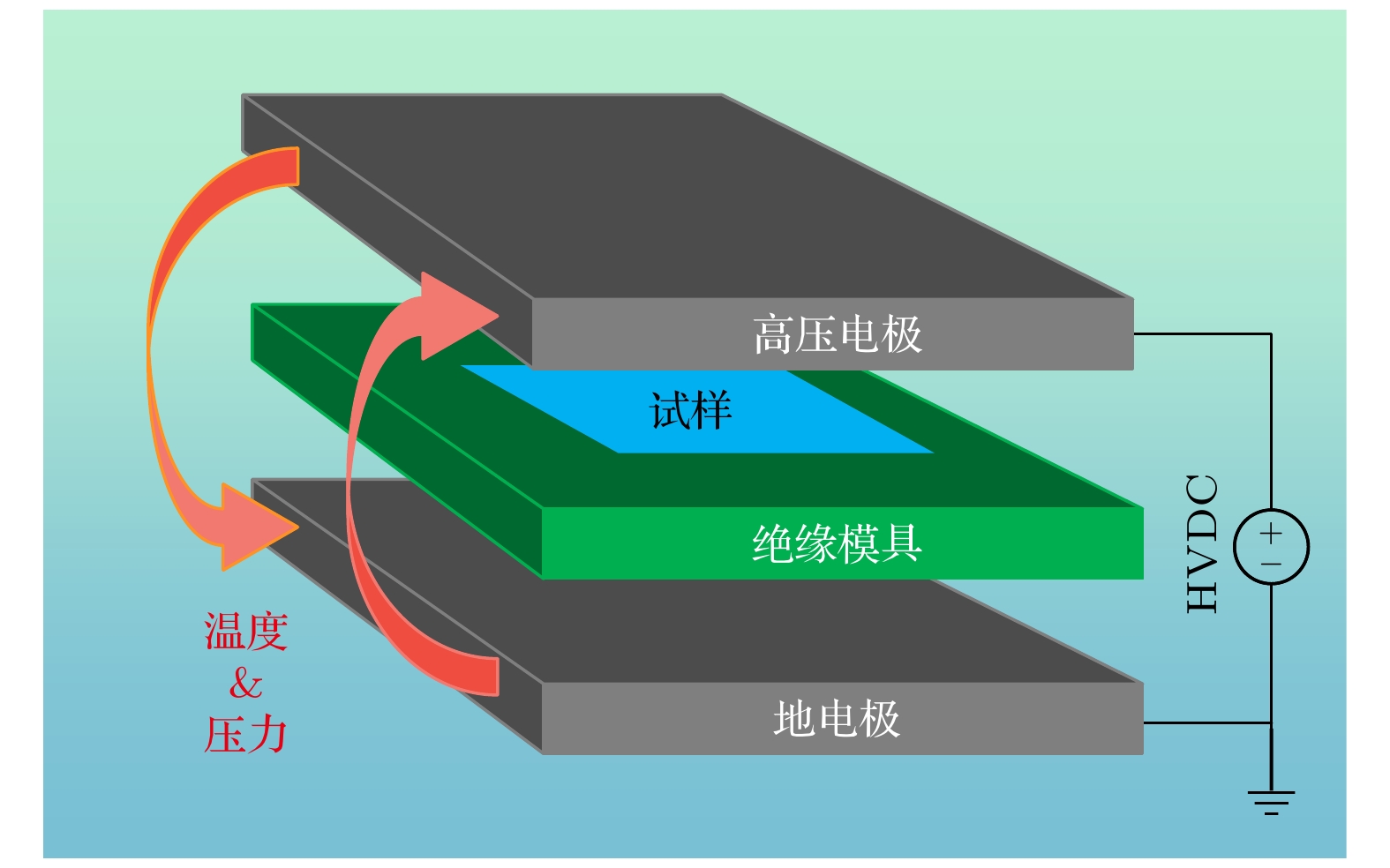
低密度聚乙烯(low-density polyethylene, LDPE)是电缆绝缘的基础材料. 辅助电场可以调控聚合物的微观结构, 但是其目前在电气绝缘领域的应用却鲜有报道. 分别在LDPE试样成型过程中的熔融、冷却结晶及全阶段(即熔融及冷却结晶全阶段)施加辅助电场, 制备了基于电场辅助的LDPE试样. 探究了在不同阶段施加辅助电场对LDPE的微观结构演变、直流击穿特性、电导特性、空间电荷特性和陷阱特性的影响规律. 结果表明, 与未处理的LDPE相比, 在熔融阶段、冷却阶段和全阶段施加辅助电场的LDPE具有更多更小的球晶, 在全阶段施加辅助电场的LDPE的球晶数量最多, 尺寸最小. 同时, 辅助电场能够明显提升LDPE的直流电气特性. 其中, 全阶段施加辅助电场的LDPE与未处理LDPE相比, 击穿场强提升了35.8%, 电导率降低了72.0%, 平均空间电荷密度降低了20.2%. 本研究为电气绝缘聚合物的微观结构调控和直流电气特性提升提供了新的思路.Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is the basic material of the high-voltage direct current (DC) power cable insulation. The assisted electric field is a common way to regulate the microstructure of polymers, but its application in the field of electrical insulating polymers is rarely reported. In order to study the influence of the assisted electric field on the microstructure evolution and DC electrical properties of LDPE, the LDPEs without and with being treated with assisted electric field are prepared in the melting stage, cooling stage, and the whole stage (i.e. the melting stage and cooling stage), respectively. The influence of the assisted electric field applied in the different stages on the microstructure evolution of LDPE is characterized by the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The DC electrical properties of the untreated LDPE and the treated LDPE are investigated via measuring their breakdown strengths, conductivities, space charges and surface potential decays. The results show that, compared with the untreated LDPE, the LDPE treated with the assisted electric field in the whole stage has the smallest spherulite size and the largest spherulite number, followed by the LDPE treated in the cooling stage and the melting stage. The assisted electric field applied in different stages can significantly improve the DC electrical properties of LDPE. Compared with the untreated LDPE, the LDPE treated in the melting stage, the cooling stage and the whole stage increases the breakdown strength but greatly reduces the conductivity and space charge accumulation. The DC electrical properties of LDPE treated with the assisted electric field in the whole-stage are the best. Compared with untreated LDPE, the LDOE treated in whole stage increases the breakdown field strength by 35.8%, reduces the conductivity by 72.0%, and the space charge accumulation by 20.2%. More and smaller spherulites lead to the formation of more interface paths and introduce more deep-traps, which contributes to improving the DC electrical characteristics of the electric field assisted LDPE. This work provides a new idea for improving the DC electrical properties of polymers.
-
Keywords:
- low-density polyethylene /
- assisted electric field /
- microstructure /
- direct current electrical properties
[1] 杜伯学, 李忠磊, 周硕凡, 范铭升 2021 电气工程学报 16 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du B X, Li Z L, Zhou S F, Fan M S 2021 J. Electr. Eng. 16 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li Y J, Han Y S, Sun Y L, Li Z H 2024 Compos. Sci. Technol. 247 110437
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 俞葆青, 夏兵, 杨晓砚, 万宝全, 查俊伟 2023 72 068402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu B Q, Xia B, Yang X Y, Wan B Q, Zha J W 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 068402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 王赫宇, 李忠磊, 杜伯学 2024 73 127702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H Y, Li Z L, Du B X 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 127702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Huang X Y, Zhang J, Jiang P K, Tanaka T 2019 IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 35 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 聂永杰, 赵现平, 李盛涛 2019 68 227201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie Y J, Zhao X P, Li S T 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 227201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 李盛涛, 黄奇峰, 孙健, 张拓, 李建英 2010 59 422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S T, Huang Q F, Sun J, Zhang T, Li J Y 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang Y Y, Wang C, Chen W G, Xiao K 2016 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23 1713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xing Y Q, Liu J H, Su J G, Zha J W, Li G C, Guo Z, Zhao X Z, Feng M J 2024 High Volt. 9 429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Schmidt K, Schoberth H G, Ruppel M, Zettl H, Hänsel H, Weiss T M, Urban V, Krausch G, Böker A 2008 Nat. Mater. 7 142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wu Y, Du B X, Li Z L, Wang H Y, Zheng Z 2023 Polymer 280 126072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 李剑, 沈健, 杨丽君, 章华中, 赵玉顺 2010 高电压技术 36 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J, Shen J, Yang L J, Zhang H Z, Zhao Y S 2010 High Voltage Eng. 36 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zeng S X, Li Q, Liu H X, Wang J Q, Wang K 2023 J. Polym. Eng. 43 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liedel C, Schindler K A, Pavan M J, Lewin C, Pester C W, Ruppel M, Urban V S, Shenhar R, Böker A 2013 Small 9 3276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ruppel M, Pester C W, Langner K M, Sevink G J A, Schoberth H G, Schmidt K, Urban V S, Mays J W, Böker A 2013 ACS nano 7 3854
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Adrjanowicz K, Paluch M, Richert R 2017 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 925
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Pester C W, Liedel C, Ruppel M, Böker A 2017 Prog. Polym. Sci. 64 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wu Y F, Wang S H, Zhou H, Liu H J, Li S T, Wen D K 2023 IEEE 4th International Conference on Electrical Materials and Power Equipment Shanghai, China, May 7–10, 2023 p1
[19] Han Y S, Zhao C G, Sun J, Li Z H 2023 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 30 2706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Vaughan A S, Zhao Y, Barré L L, Sutton S J, Swingler S G 2003 Eur. Polym. J. 39 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Xu N, Zhong L S, Sui R, Ahmed M, Li F, Liu Y B, Gao J H 2022 Macromolecules 55 8186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li Y J, Han Y S, Pang J J, Jin D, Sun Y L, Li Z H 2024 Macromolecules 57 5497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yang K, Ren Y R, Wu K N, Li J Y, Jing Z H, Zhang Z J, Dong J Y 2022 Compos. Sci. Technol. 223 109422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 易姝慧, 王亚林, 吴建东, 尹毅 2018 电气工程学报 13 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yi S H, Wang Y L, Wu J D, Yin Y 2018 J. Electr. Eng. 13 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 阴凯, 郭其阳, 张添胤, 李静, 陈向荣 2024 73 127703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin K, Guo Q Y, Zhang T Y, Li J, Chen X R 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 127703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Han Y S, Li S T, Min D M 2018 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 25 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Schmelzer J W P 2008 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 354 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu J P, Du B Y, Xie F C, Zhang F J, He T B 2002 Polymer 43 1903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Li S T, Nie Y J, Wang W W, Yang L Q, Min D M 2016 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23 3215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Li Z L, Zhong Z Y, Du B X 2019 Polymer 185 121935
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 蔡姝娆, 高梓巍, 纪民尊, 姚佳池, 李鹏新, 闵道敏, 李盛涛, 武庆周 2021 电气工程学报 16 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai S R, Gao Z W, Ji M Z, Yao J C, Li P X, Min D M, Li S T, Wu Q Z 2021 J. Electr. Eng. 16 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 高雅涵, 黄兴溢, 江平开, 闵道敏, 李盛涛 2020 中国电机工程学报 40 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao Y H, Huang X Y, Jiang P K, Min D M, Li S T 2020 Proc. CSEE 40 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
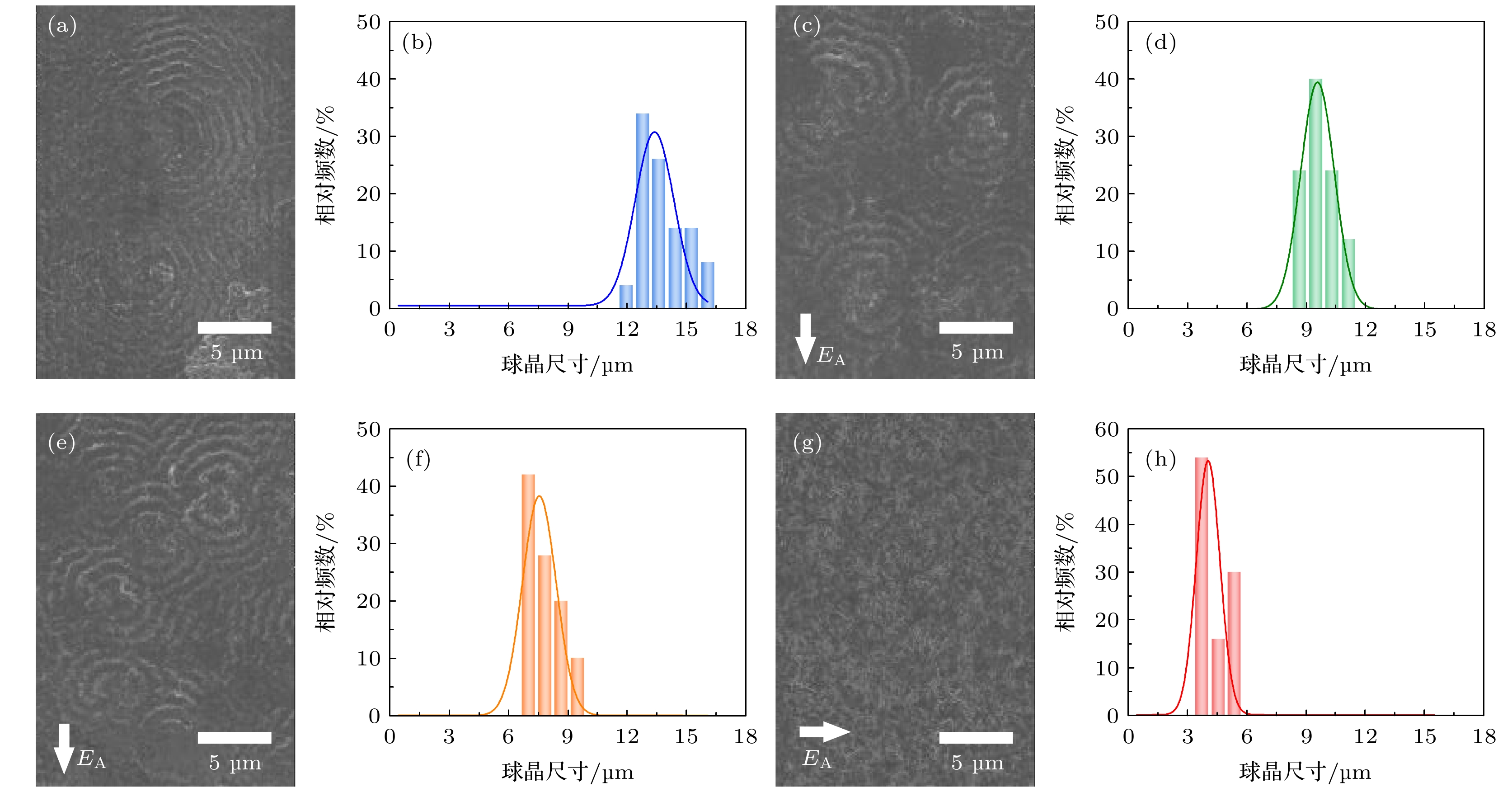
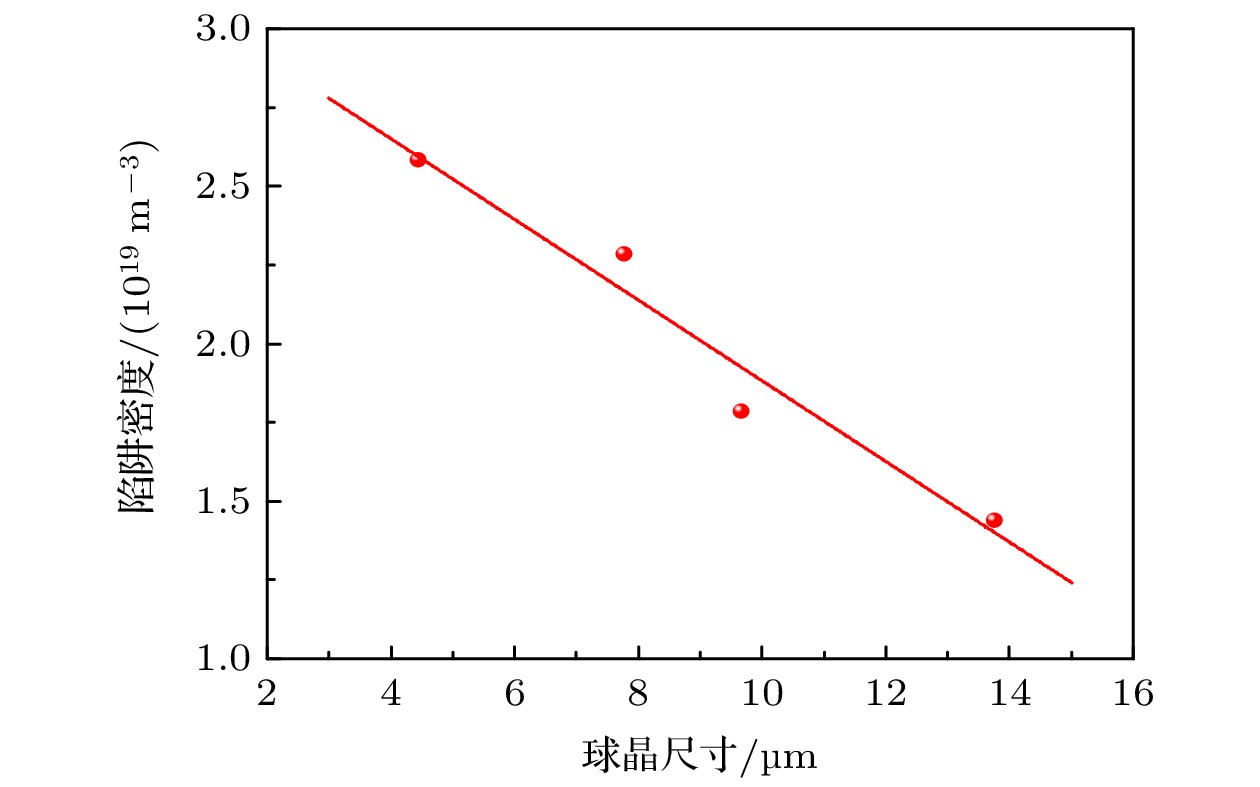
图 2 在不同阶段施加辅助电场的LDPE的球晶形貌与球晶尺寸分布 (a) 未处理的球晶形貌; (b) 未处理的球晶尺寸分布; (c)熔融阶段的球晶形貌; (d) 熔融阶段的球晶尺寸分布; (e) 冷却阶段的球晶形貌; (f) 冷却阶段的球晶尺寸分布; (g) 全阶段的球晶形貌; (h) 全阶段的球晶尺寸分布
Fig. 2. Spherulite morphology and size distribution of LDPE treated with assisted electric field at different stages: (a) Morphology of the untreated spherulite; (b) size distribution of untreated spherulite; (c) spherulite morphology of melting stage; (d) spherulite size distribution of melting stage; (e) spherulite morphology of cooling stage; (f) spherulite size distribution of cooling stage; (g) spherulite morphology of whole stage; (h) spherulite size distribution of whole stage.
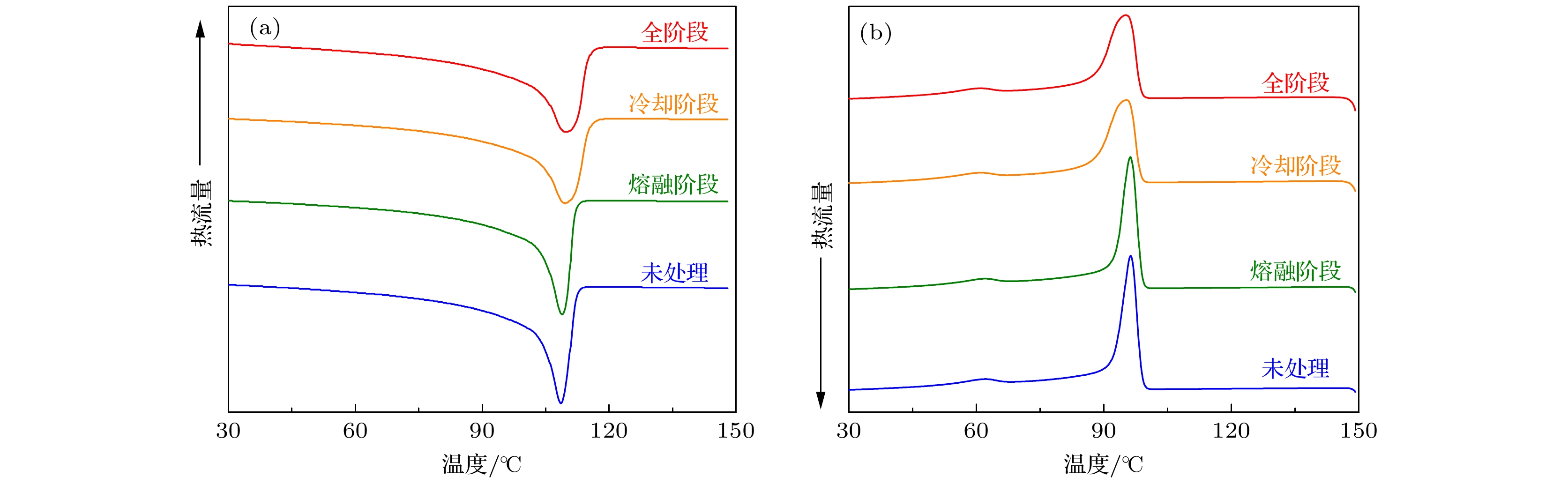
表 1 不同阶段施加辅助电场处理LDPE的结晶温度、熔融温度、熔融焓和结晶度
Table 1. Crystallization temperature, melting temperature, melting enthalpy and crystallinity of electric field assisted LDPE at different stages.
试样 Tc/℃ Tm/℃ ΔHm/(J·g–1) Xc/% 未处理 96.28 108.47 124.96 43.33 熔融阶段 96.28 108.98 126.26 43.78 冷却阶段 95.26 109.66 127.90 44.35 全阶段 95.26 109.83 129.25 44.82 -
[1] 杜伯学, 李忠磊, 周硕凡, 范铭升 2021 电气工程学报 16 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du B X, Li Z L, Zhou S F, Fan M S 2021 J. Electr. Eng. 16 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li Y J, Han Y S, Sun Y L, Li Z H 2024 Compos. Sci. Technol. 247 110437
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 俞葆青, 夏兵, 杨晓砚, 万宝全, 查俊伟 2023 72 068402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu B Q, Xia B, Yang X Y, Wan B Q, Zha J W 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 068402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 王赫宇, 李忠磊, 杜伯学 2024 73 127702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H Y, Li Z L, Du B X 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 127702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Huang X Y, Zhang J, Jiang P K, Tanaka T 2019 IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 35 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 聂永杰, 赵现平, 李盛涛 2019 68 227201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie Y J, Zhao X P, Li S T 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 227201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 李盛涛, 黄奇峰, 孙健, 张拓, 李建英 2010 59 422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S T, Huang Q F, Sun J, Zhang T, Li J Y 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang Y Y, Wang C, Chen W G, Xiao K 2016 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23 1713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xing Y Q, Liu J H, Su J G, Zha J W, Li G C, Guo Z, Zhao X Z, Feng M J 2024 High Volt. 9 429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Schmidt K, Schoberth H G, Ruppel M, Zettl H, Hänsel H, Weiss T M, Urban V, Krausch G, Böker A 2008 Nat. Mater. 7 142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wu Y, Du B X, Li Z L, Wang H Y, Zheng Z 2023 Polymer 280 126072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 李剑, 沈健, 杨丽君, 章华中, 赵玉顺 2010 高电压技术 36 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J, Shen J, Yang L J, Zhang H Z, Zhao Y S 2010 High Voltage Eng. 36 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zeng S X, Li Q, Liu H X, Wang J Q, Wang K 2023 J. Polym. Eng. 43 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Liedel C, Schindler K A, Pavan M J, Lewin C, Pester C W, Ruppel M, Urban V S, Shenhar R, Böker A 2013 Small 9 3276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ruppel M, Pester C W, Langner K M, Sevink G J A, Schoberth H G, Schmidt K, Urban V S, Mays J W, Böker A 2013 ACS nano 7 3854
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Adrjanowicz K, Paluch M, Richert R 2017 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 925
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Pester C W, Liedel C, Ruppel M, Böker A 2017 Prog. Polym. Sci. 64 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wu Y F, Wang S H, Zhou H, Liu H J, Li S T, Wen D K 2023 IEEE 4th International Conference on Electrical Materials and Power Equipment Shanghai, China, May 7–10, 2023 p1
[19] Han Y S, Zhao C G, Sun J, Li Z H 2023 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 30 2706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Vaughan A S, Zhao Y, Barré L L, Sutton S J, Swingler S G 2003 Eur. Polym. J. 39 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Xu N, Zhong L S, Sui R, Ahmed M, Li F, Liu Y B, Gao J H 2022 Macromolecules 55 8186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li Y J, Han Y S, Pang J J, Jin D, Sun Y L, Li Z H 2024 Macromolecules 57 5497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yang K, Ren Y R, Wu K N, Li J Y, Jing Z H, Zhang Z J, Dong J Y 2022 Compos. Sci. Technol. 223 109422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 易姝慧, 王亚林, 吴建东, 尹毅 2018 电气工程学报 13 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yi S H, Wang Y L, Wu J D, Yin Y 2018 J. Electr. Eng. 13 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 阴凯, 郭其阳, 张添胤, 李静, 陈向荣 2024 73 127703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin K, Guo Q Y, Zhang T Y, Li J, Chen X R 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 127703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Han Y S, Li S T, Min D M 2018 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 25 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Schmelzer J W P 2008 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 354 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu J P, Du B Y, Xie F C, Zhang F J, He T B 2002 Polymer 43 1903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Li S T, Nie Y J, Wang W W, Yang L Q, Min D M 2016 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23 3215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Li Z L, Zhong Z Y, Du B X 2019 Polymer 185 121935
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 蔡姝娆, 高梓巍, 纪民尊, 姚佳池, 李鹏新, 闵道敏, 李盛涛, 武庆周 2021 电气工程学报 16 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai S R, Gao Z W, Ji M Z, Yao J C, Li P X, Min D M, Li S T, Wu Q Z 2021 J. Electr. Eng. 16 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 高雅涵, 黄兴溢, 江平开, 闵道敏, 李盛涛 2020 中国电机工程学报 40 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao Y H, Huang X Y, Jiang P K, Min D M, Li S T 2020 Proc. CSEE 40 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 2295
- PDF下载量: 49
- 被引次数: 0















 下载:
下载: