-
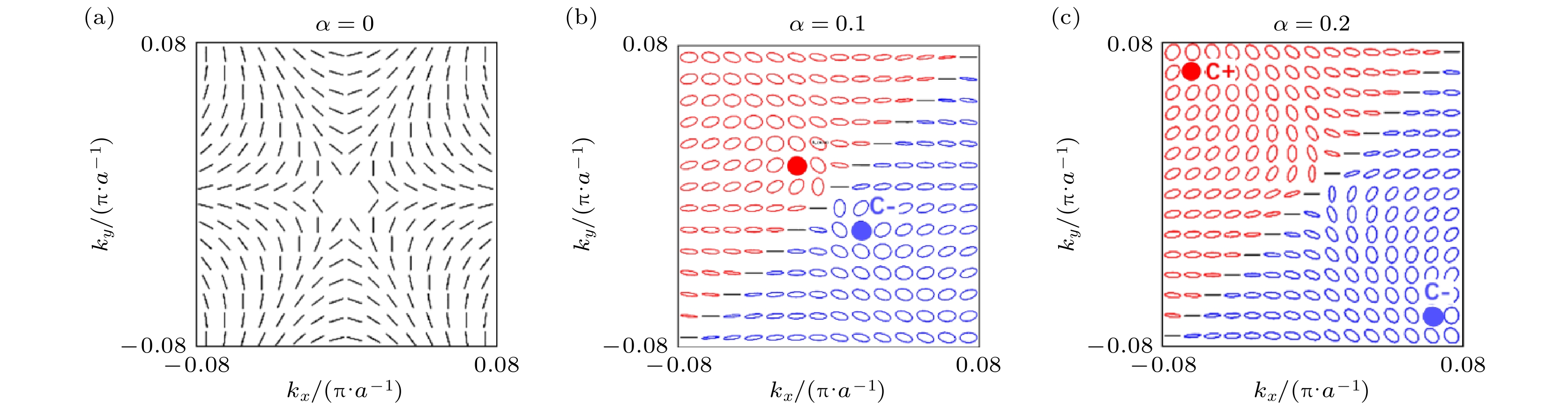
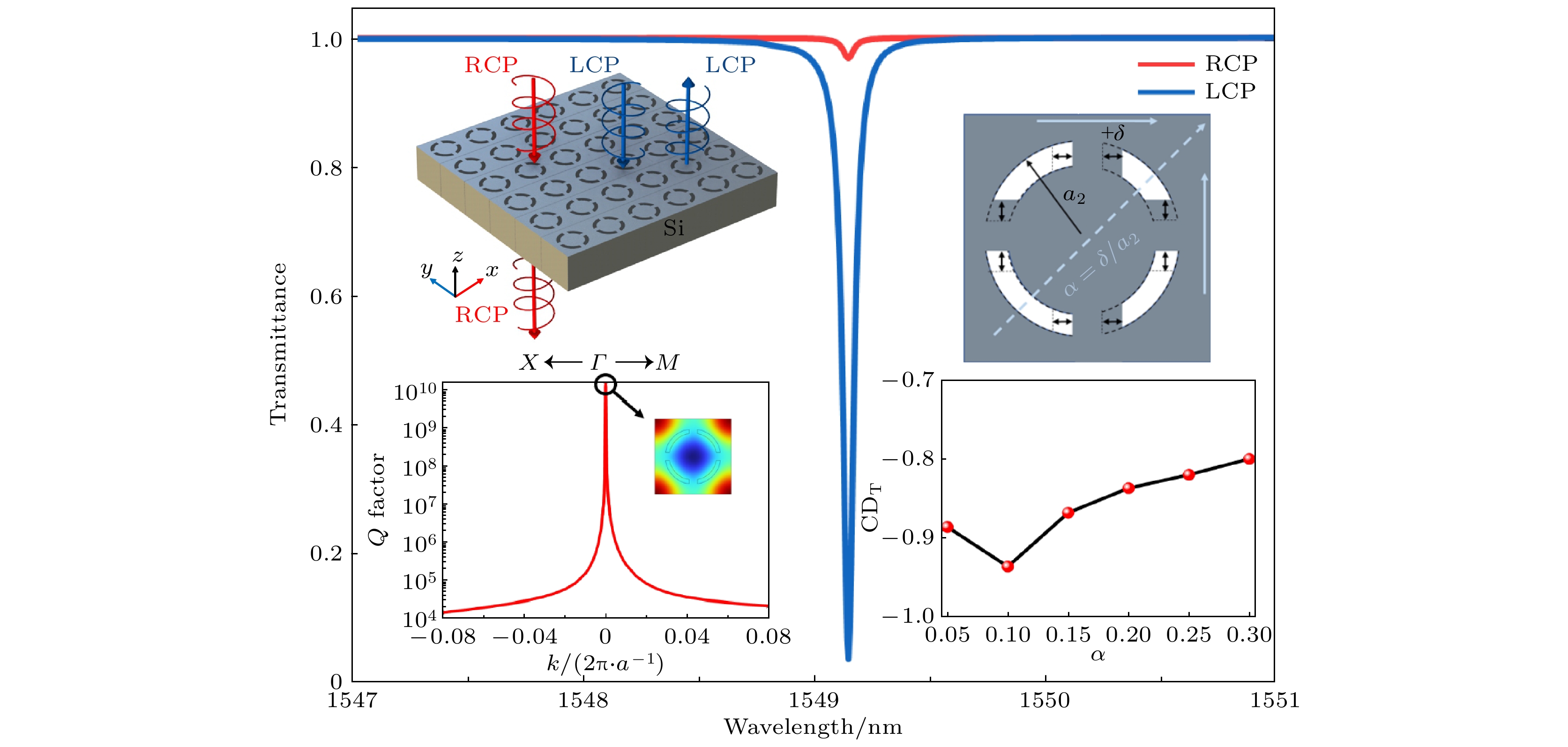
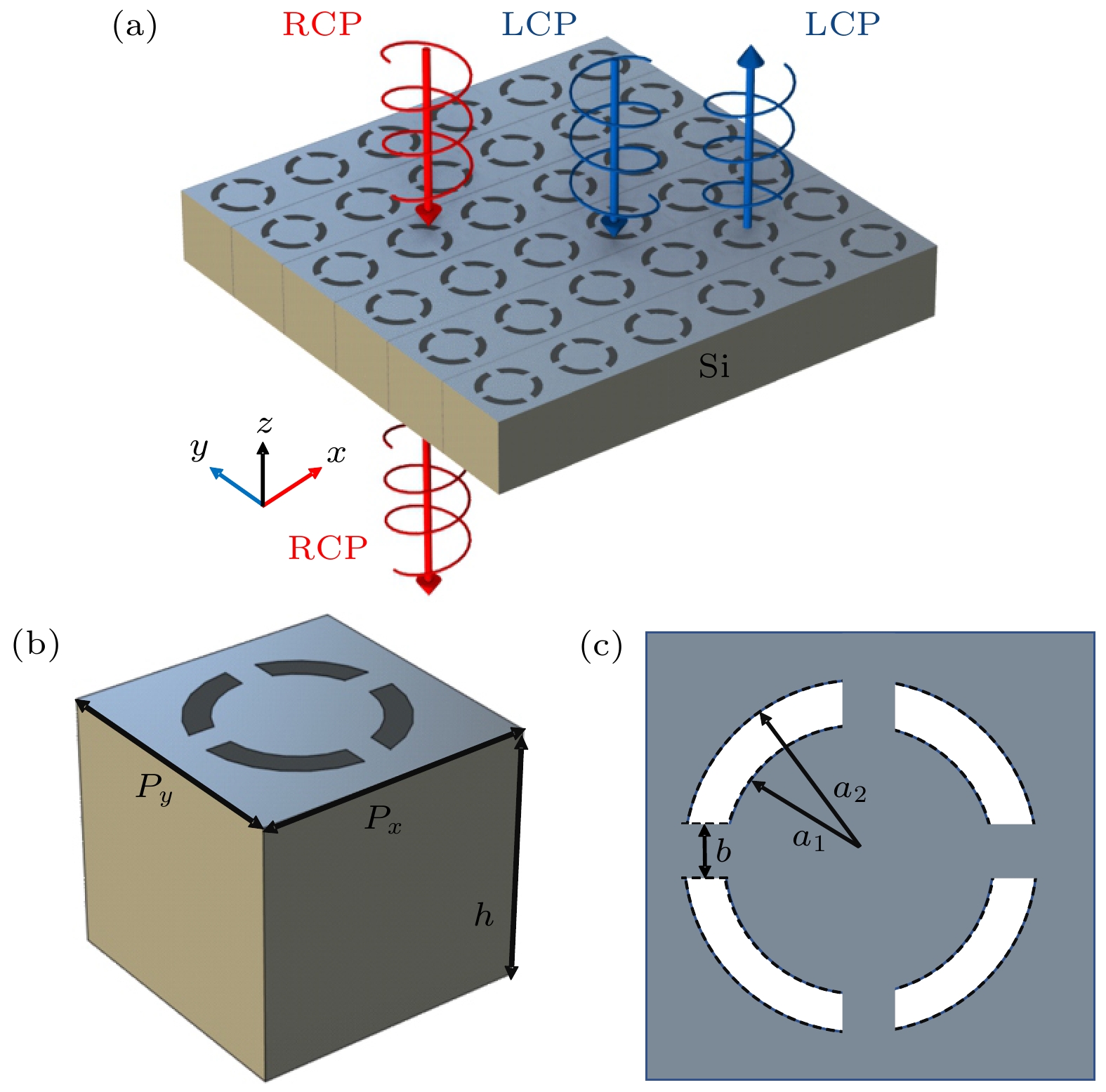
连续域束缚态最初是在量子力学中发现的, 它是一种可保持局域化的波动现象. 这种效应已在各种材料系统中得到广泛研究, 包括压电材料、石墨烯和光子晶体. 本工作提出了一种由中断的环形槽组成的四重旋转对称硅超表面. 通过同时打破晶胞的面内反转对称性, 实现了具有高品质因子和显著手性的准连续域束缚态. 通过对动量空间中拓扑荷的研究, 揭示了由超表面的内部共振机制产生的准连续域束缚态的独特拓扑特征. 在合适的对称破坏下, 具有平面内对称破坏的四重旋转对称超表面表现出–0.93的强圆二色性, 并且其显示出了在对称破坏较大时的强圆二色性. 这项工作所取得的成果在手性生物传感器和低阈值激光器等领域具有广阔的应用前景.Bound states in the continuum (BIC) were initially observed in quantum mechanics as a phenomenon capable of maintaining localized wave behavior. This effect has been extensively studied across various material systems, including piezoelectric materials, graphene, and photonic crystals. Recently, the BIC mode has employed to achieve strong optical chirality in metamaterials with symmetry breaking. In this work, we propose a silicon metasurface with an interrupted ring groove, which has a fourfold rotationally symmetry. By breaking the in-plane inversion symmetry of the unit cell, we achieve quasi-BICs with the high quality factor and conspicuous chirality. Moreover, by analyzing topological charges in momentum space, we reveal that the unique topological characteristics of quasi-BIC are generated by the internal resonance of metasurface. When the symmetry breaking reaches a certain level, our proposed symmetry-broken metasurface shows a strong circular dichroism and its value is –0.93, which indicates that the quasi-BIC mode can has a strong chiral selectivity. For chiral sensing applications, the chiral metasurface exhibits a spectral resolution of approximately 0.003. The findings presented in this work have great potential applications in chiral sensing, nonlinear chiral optics, low-threshold lasers, and other related fields.
-
Keywords:
- bound state in the continuum /
- metasurface /
- chirality /
- quality factor
[1] Borovkova O V, Ignatyeva D O, Sekatskii S K, Karabchevsky A, Belotelov V I 2019 Photonics Res. 8 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Daldosso N, Pavesi L 2009 Laser Photon. Rev. 3 508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kekatpure R D, Brongersma M L 2008 Phys. Rev. A 78 023829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lim W X, Singh R 2018 Nano Converg. 5 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Rybin M V, Koshelev K L, Sadrieva Z F, Samusev K B, Bogdanov A A. Limonov M F, Kivshar Y S 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 243901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Srinivasan K, Stintz A, Krishna S, Painter O 2005 Phys. Rev. B 72 205318.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Azzam S I, Kildishev A V 2020 Adv. Opt. Mater. 9 2001469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Koshelev K, Bogdanov A, Kivshar Y 2019 Science Bulletin 64 836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kupriianov A S, Xu Y, Sayanskiy A, Dmitriev V, Kivshar Y S, Tuz V R 2019 Phys. Rev. Appl. 12 014024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Marinica D C, Borisov A G, Shabanov S V 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 183902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Koshelev K, Lepeshov S, Liu M, Bogdanov A, Kivshar Y 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 193903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kodigala A, Lepetit T, Gu Q, Bahari B, Fainman Y, Kante B 2017 Nature 541 196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Pavlov A, Zabkov I, Klimov V 2018 Opt. Express 26 28948
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xu K, Fang M, Huang Z X 2021 IEEE Photonics J. 13 1500109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Abujetas D R, Barreda Á, Moreno F, Litman A, Geffrin J M, Sánchez‐Gil J A 2020 Laser Photonics Rev. 15 2000263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Volkovskaya I, Xu L, Huang L J, Smirnov A I, Miroshnichenko A E, Smirnova D 2020 Nanophotonics 9 3953
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Koshelev K, Tang Y T, Li K F, Choi D Y, Li G X, Kivshar Y 2019 ACS Photonics 6 1639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Panoiu N C, Sha W E I, Lei D Y, Li G C 2018 J. Opt. 20 083001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ren Q, Feng F, Yao X, Xu Q, Xin M, Lan Z H, You J W, Xiao X F, Sha W E I 2021 Opt. Express 29 5384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Cai Y P, Huang Y, Zhu K Y, Wu H H 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 4049
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yu S L, Wang Y S, Gao Z A, Li H, Song S Z, Yu J G, Zhao T G 2022 Opt. Express 30 4084
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kilchoer C, Abdollahi N, Steiner U, Gunkel I, Wilts B D 2019 APL Photonics 4 126107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wu Z, Liu Y, Hill E H, Zheng Y 2018 Nanoscale 10 18096
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yang S Y, Liu Z, Yang H F, Jin A Z, Zhang S, Li J J, Gu C Z 2019 Adv. Opt. Mater. 8 1901448
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Basiri A, Chen X, Bai J, Amrollahi P, Carpenter J, Holman Z, Wang C, Yao Y 2019 Light Sci. Appl. 8 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Fasold S, Linß S, Kawde T, Falkner M, Decker M, Pertsch T, Staude I 2018 ACS Photonics 5 1773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Kan Y H, Andersen S K H, Ding F, Kumar S, Zhao C Y, Bozhevolnyi S I 2020 Adv. Mater. 32 1907832
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu Z G, Du H F, Li J F, Lu L, Li Z Y, Fang N X 2018 Sci. Adv. 4 eaat4436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhao Y, Askarpour A N, Sun L Y, Shi J W, Li X Q, Alu A 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 14180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Hao C L, Xu L G, Kuang H, Xu C L 2020 Adv. Mater. 32 e1802075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Gorkunov M V, Antonov A A, Kivshar Y S 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 093903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Overvig A, Yu N, Alu A 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 073001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Yu K, Song F, Shi Z, Li H, Liu Y , Wu X 2023 J. Opt. 25 125101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Palik E D 1985 Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids ppxvii-xviii
[35] Zhen B, Hsu C W, Lu L, Stone A D, Soljačić M 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 257401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Chen Y, Yang X D, Gao J 2018 Light Sci. Appl. 7 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
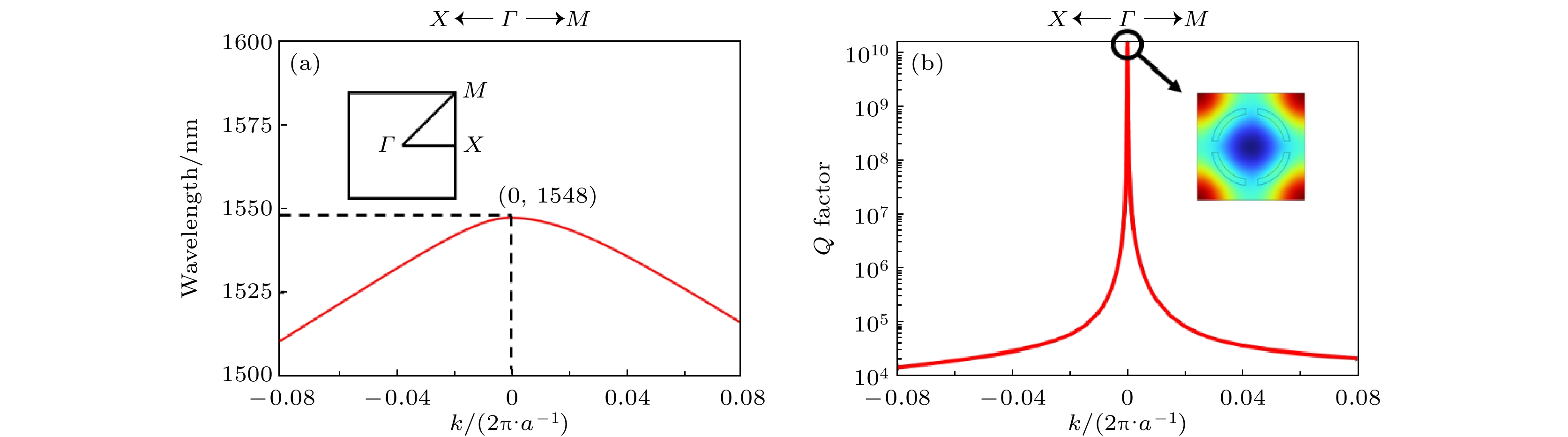
图 2 (a)本征模的位于1500—1600 nm波段的能带结构; (b)本征模在BIC波长(波长为1548 nm)附近的品质因子分布图, 品质因子在k = 0的点处趋向于无穷大, 插图为BIC波长处的结构处的电场分布图
Fig. 2. (a) Band structure of the eigenmodes in the wavelength range of 1500–1600 nm; (b) quality factor distribution of the eigenmodes near the BIC wavelength (1548 nm), with the quality factor approaching infinity at k = 0. The inset shows the electric field distribution at the BIC frequency point.
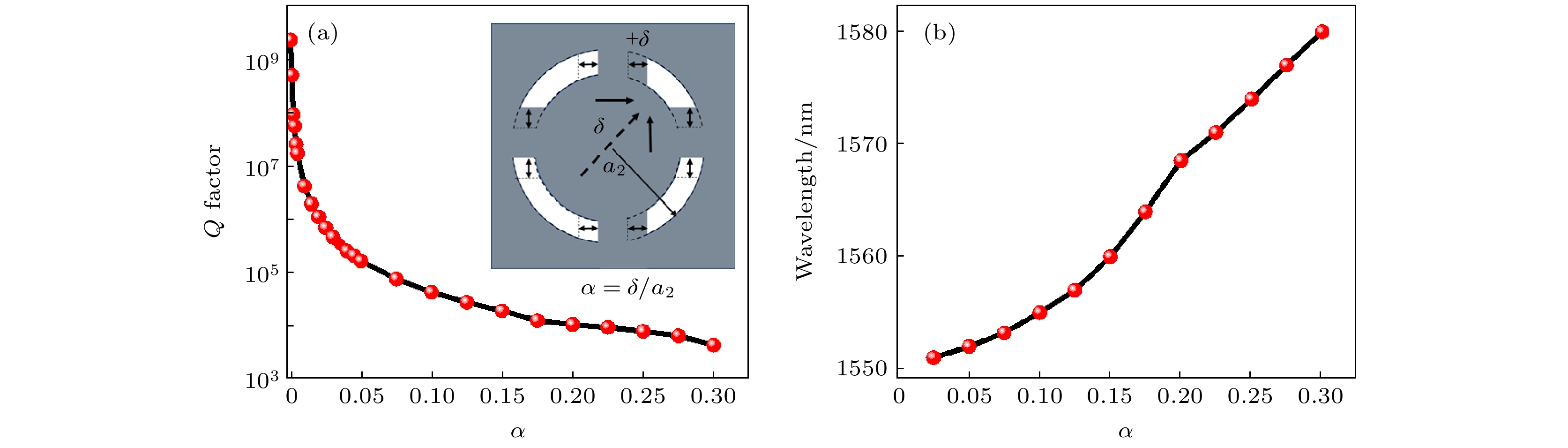
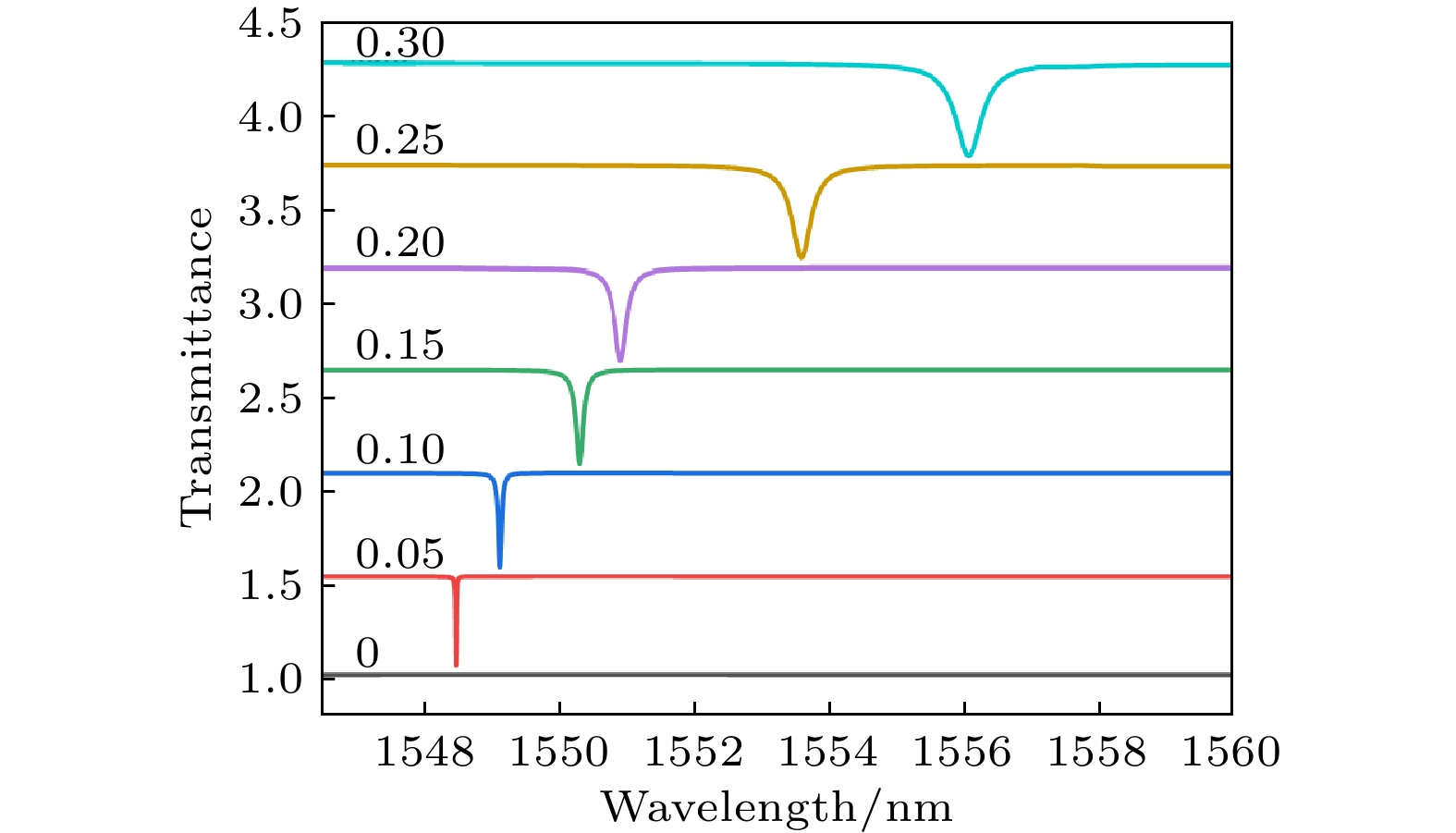
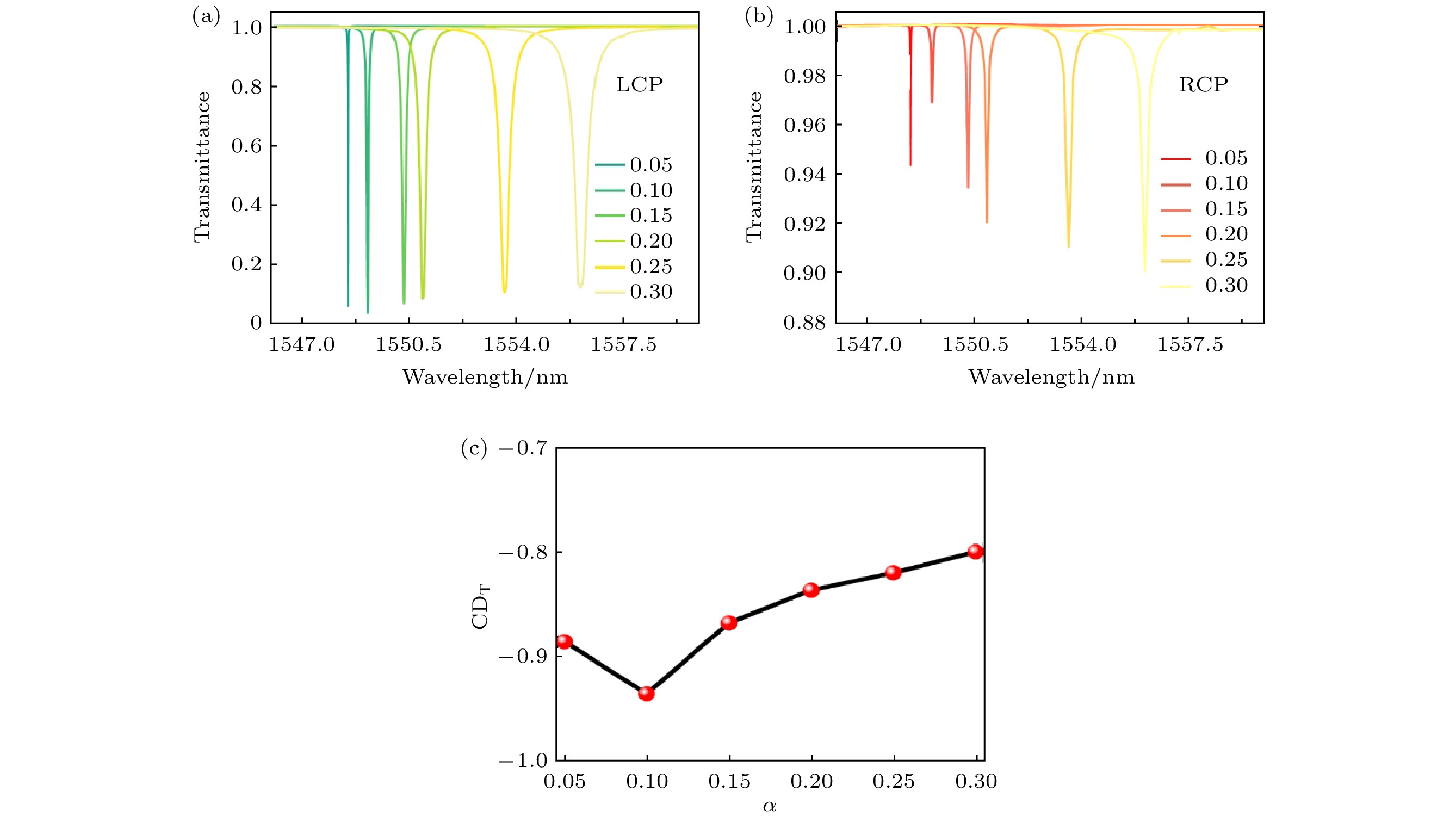
图 3 (a) 超表面处于激发模式下, 扰动因子对高品质因子的影响, 插图为所定义的破坏对称方式的示意图; (b)不同扰动因子下的本征模的波长分布
Fig. 3. (a) Impact of the perturbation factor on the high-quality factor in the excited mode of the metasurface, with the inset showing a schematic diagram of the defined symmetry-breaking method; (b) wavelength distribution of the eigenmodes under different perturbation facors.
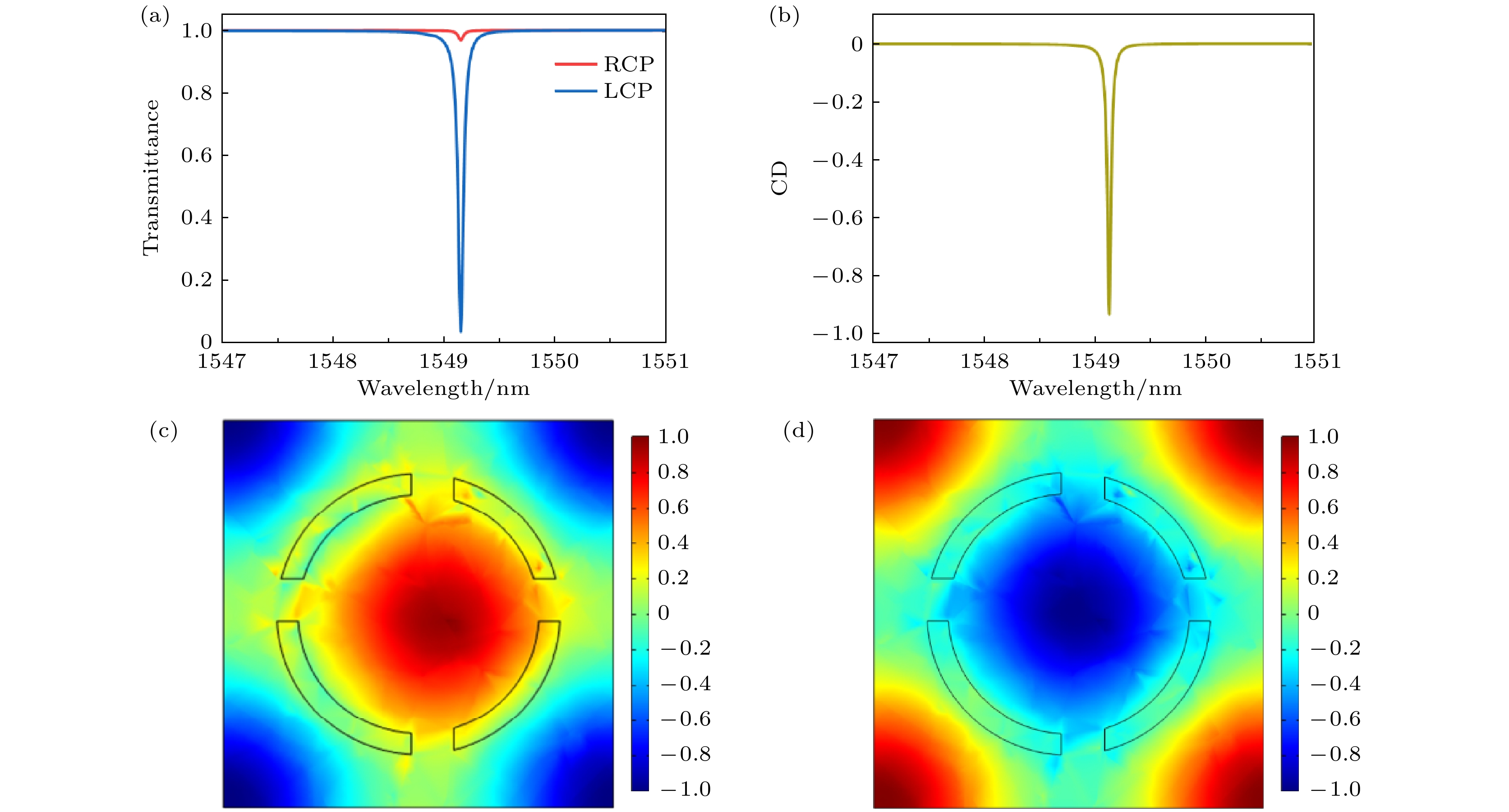
图 6 (a) α = 0.1对称破坏时, C4v超表面使用RCP, LCP光激励的透射光谱; (b)准BIC附近处的圆二色性值; 使用(c) RCP和(d) LCP光激励的准BIC波长处超表面的电场分布
Fig. 6. (a) Transmission spectra of C4v metasurface under α = 0.1 symmetry breaking, excited by RCP and LCP light; (b) circular dichroism values near the quasi-BIC; (c), (d) the electric field distribution of the metasurface at the quasi-BIC wavelength when excited with (c) RCP and (d) LCP light, respectively.
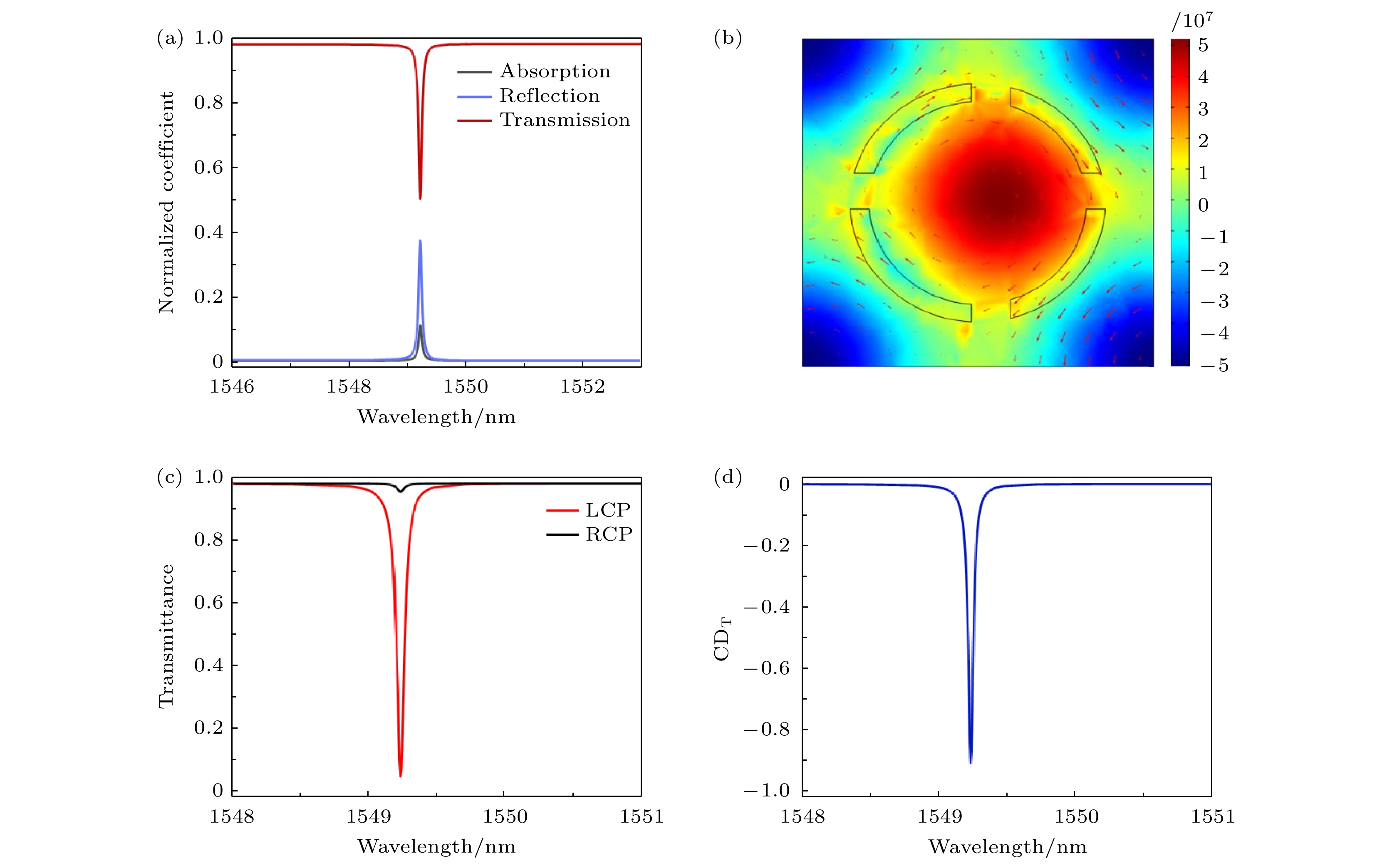
图 8 (a) 考虑损耗的条件下, 超表面破坏对称性后的透射、反射和吸收谱线; (b)考虑损耗的情况下元胞的电场图; 手性超表面在(c) LCP和RCP光下的透射谱线以及(d)圆二色性曲线
Fig. 8. (a) Consideration of losses, transmission, reflection, and absorption spectra of the metasurface after symmetry breaking; (b) electric field distribution in the unit cell considering losses; (c) transmission spectra under LCP and RCP light, and (d) the circular dichroism curve of the chiral metasurface, respectively.
-
[1] Borovkova O V, Ignatyeva D O, Sekatskii S K, Karabchevsky A, Belotelov V I 2019 Photonics Res. 8 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Daldosso N, Pavesi L 2009 Laser Photon. Rev. 3 508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kekatpure R D, Brongersma M L 2008 Phys. Rev. A 78 023829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lim W X, Singh R 2018 Nano Converg. 5 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Rybin M V, Koshelev K L, Sadrieva Z F, Samusev K B, Bogdanov A A. Limonov M F, Kivshar Y S 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 243901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Srinivasan K, Stintz A, Krishna S, Painter O 2005 Phys. Rev. B 72 205318.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Azzam S I, Kildishev A V 2020 Adv. Opt. Mater. 9 2001469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Koshelev K, Bogdanov A, Kivshar Y 2019 Science Bulletin 64 836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kupriianov A S, Xu Y, Sayanskiy A, Dmitriev V, Kivshar Y S, Tuz V R 2019 Phys. Rev. Appl. 12 014024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Marinica D C, Borisov A G, Shabanov S V 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 183902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Koshelev K, Lepeshov S, Liu M, Bogdanov A, Kivshar Y 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 193903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kodigala A, Lepetit T, Gu Q, Bahari B, Fainman Y, Kante B 2017 Nature 541 196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Pavlov A, Zabkov I, Klimov V 2018 Opt. Express 26 28948
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xu K, Fang M, Huang Z X 2021 IEEE Photonics J. 13 1500109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Abujetas D R, Barreda Á, Moreno F, Litman A, Geffrin J M, Sánchez‐Gil J A 2020 Laser Photonics Rev. 15 2000263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Volkovskaya I, Xu L, Huang L J, Smirnov A I, Miroshnichenko A E, Smirnova D 2020 Nanophotonics 9 3953
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Koshelev K, Tang Y T, Li K F, Choi D Y, Li G X, Kivshar Y 2019 ACS Photonics 6 1639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Panoiu N C, Sha W E I, Lei D Y, Li G C 2018 J. Opt. 20 083001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ren Q, Feng F, Yao X, Xu Q, Xin M, Lan Z H, You J W, Xiao X F, Sha W E I 2021 Opt. Express 29 5384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Cai Y P, Huang Y, Zhu K Y, Wu H H 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 4049
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yu S L, Wang Y S, Gao Z A, Li H, Song S Z, Yu J G, Zhao T G 2022 Opt. Express 30 4084
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kilchoer C, Abdollahi N, Steiner U, Gunkel I, Wilts B D 2019 APL Photonics 4 126107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wu Z, Liu Y, Hill E H, Zheng Y 2018 Nanoscale 10 18096
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yang S Y, Liu Z, Yang H F, Jin A Z, Zhang S, Li J J, Gu C Z 2019 Adv. Opt. Mater. 8 1901448
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Basiri A, Chen X, Bai J, Amrollahi P, Carpenter J, Holman Z, Wang C, Yao Y 2019 Light Sci. Appl. 8 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Fasold S, Linß S, Kawde T, Falkner M, Decker M, Pertsch T, Staude I 2018 ACS Photonics 5 1773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Kan Y H, Andersen S K H, Ding F, Kumar S, Zhao C Y, Bozhevolnyi S I 2020 Adv. Mater. 32 1907832
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu Z G, Du H F, Li J F, Lu L, Li Z Y, Fang N X 2018 Sci. Adv. 4 eaat4436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhao Y, Askarpour A N, Sun L Y, Shi J W, Li X Q, Alu A 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 14180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Hao C L, Xu L G, Kuang H, Xu C L 2020 Adv. Mater. 32 e1802075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Gorkunov M V, Antonov A A, Kivshar Y S 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 093903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Overvig A, Yu N, Alu A 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 073001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Yu K, Song F, Shi Z, Li H, Liu Y , Wu X 2023 J. Opt. 25 125101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Palik E D 1985 Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids ppxvii-xviii
[35] Zhen B, Hsu C W, Lu L, Stone A D, Soljačić M 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 257401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Chen Y, Yang X D, Gao J 2018 Light Sci. Appl. 7 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 522
- PDF下载量: 17
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: