-
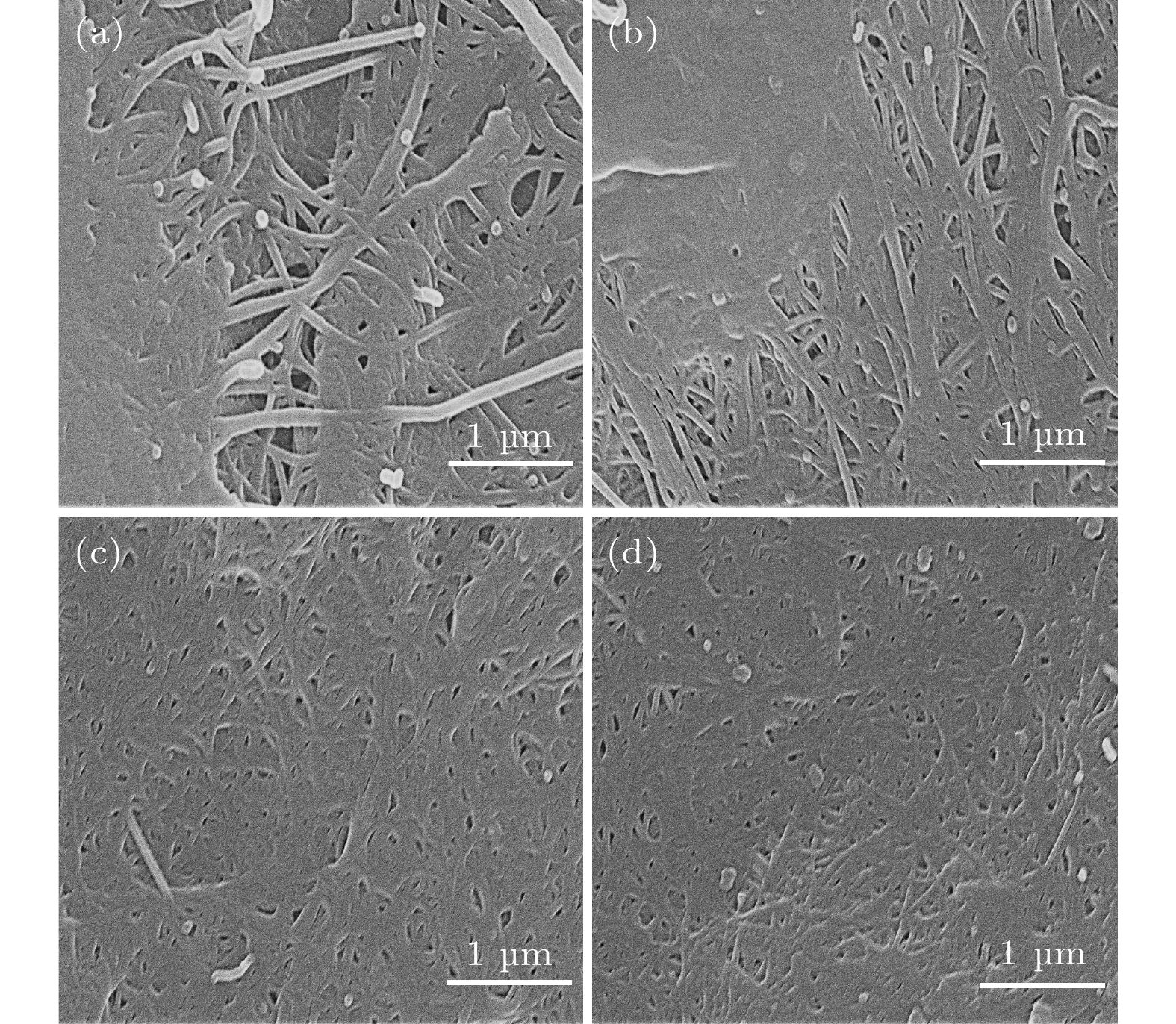
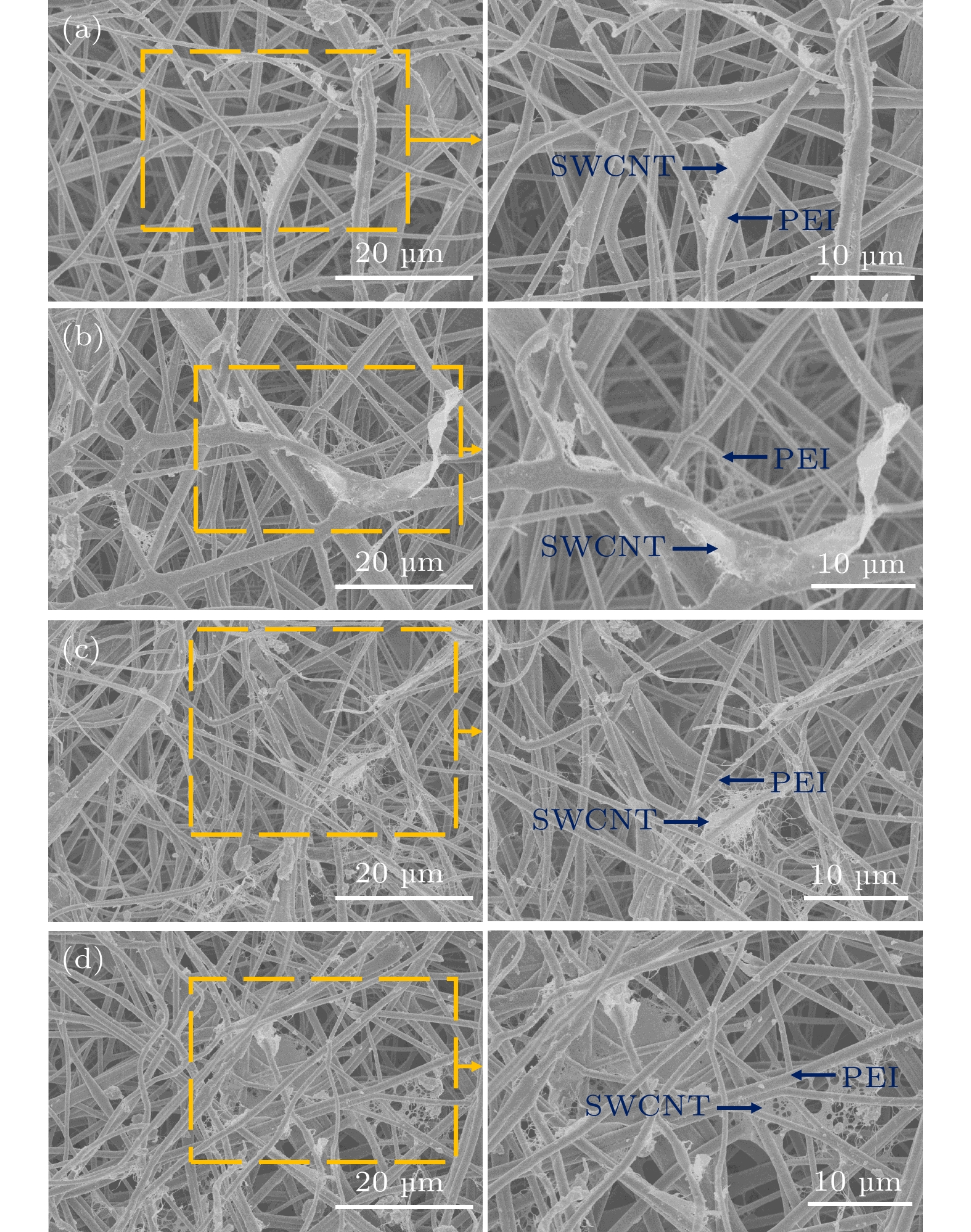
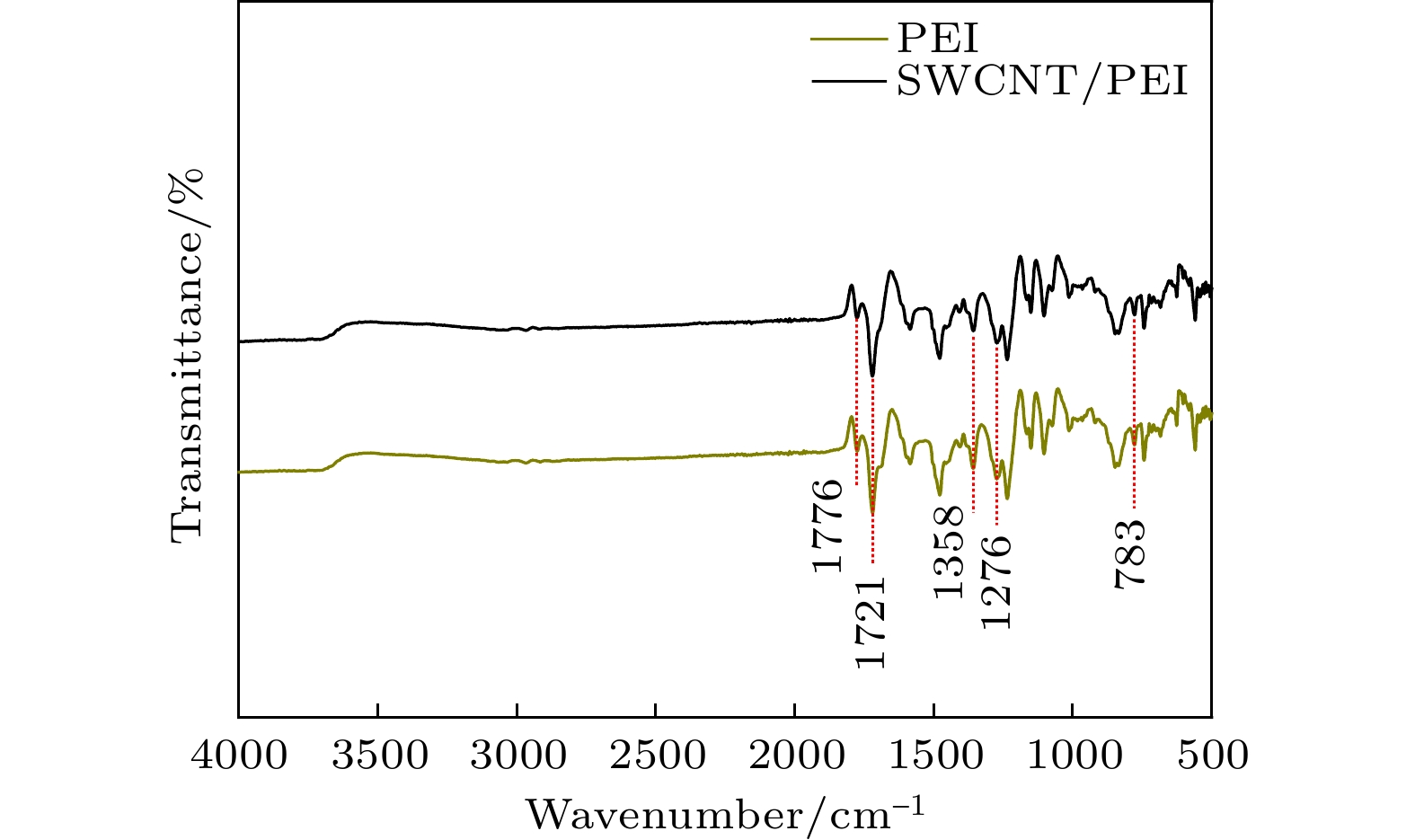
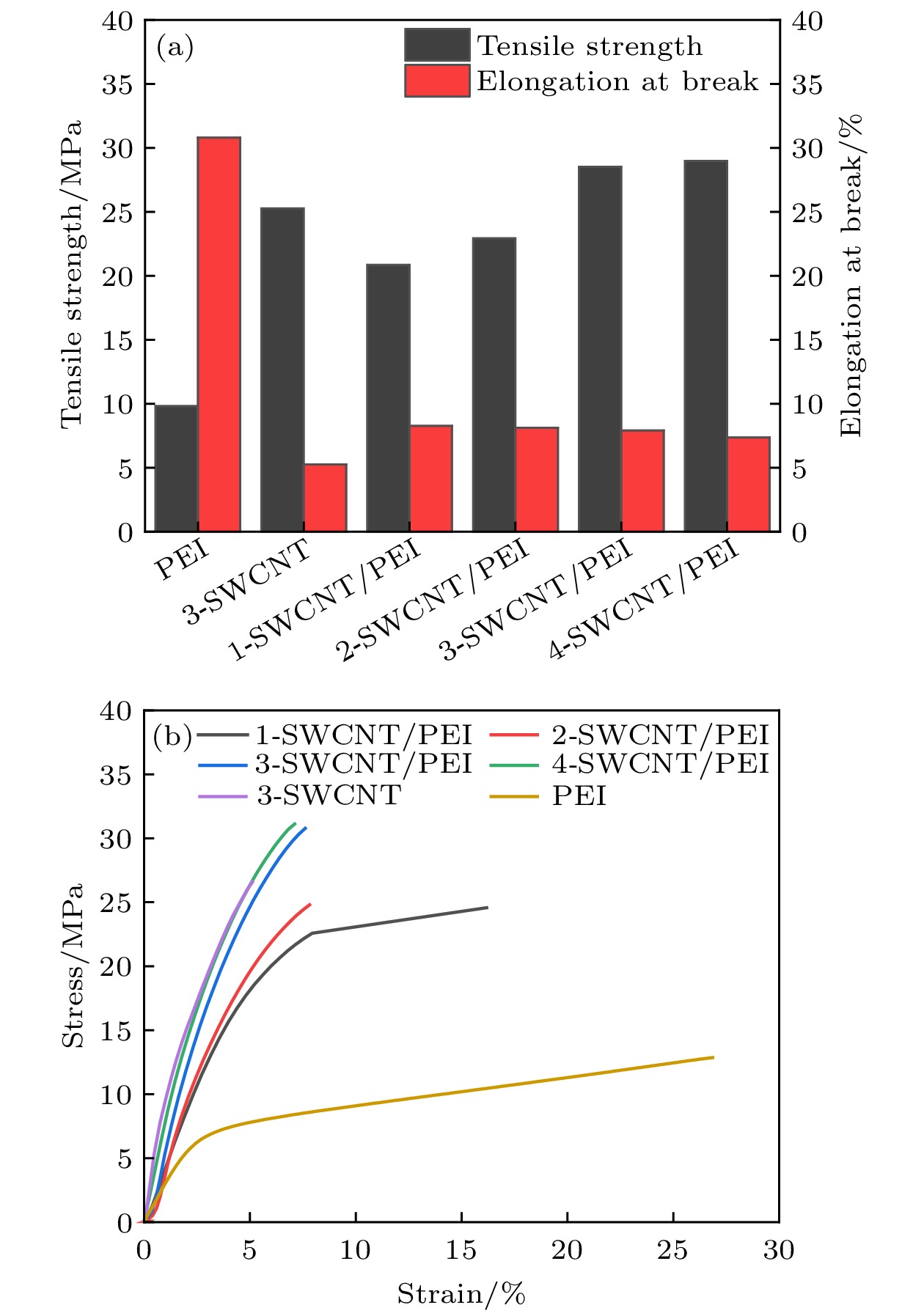
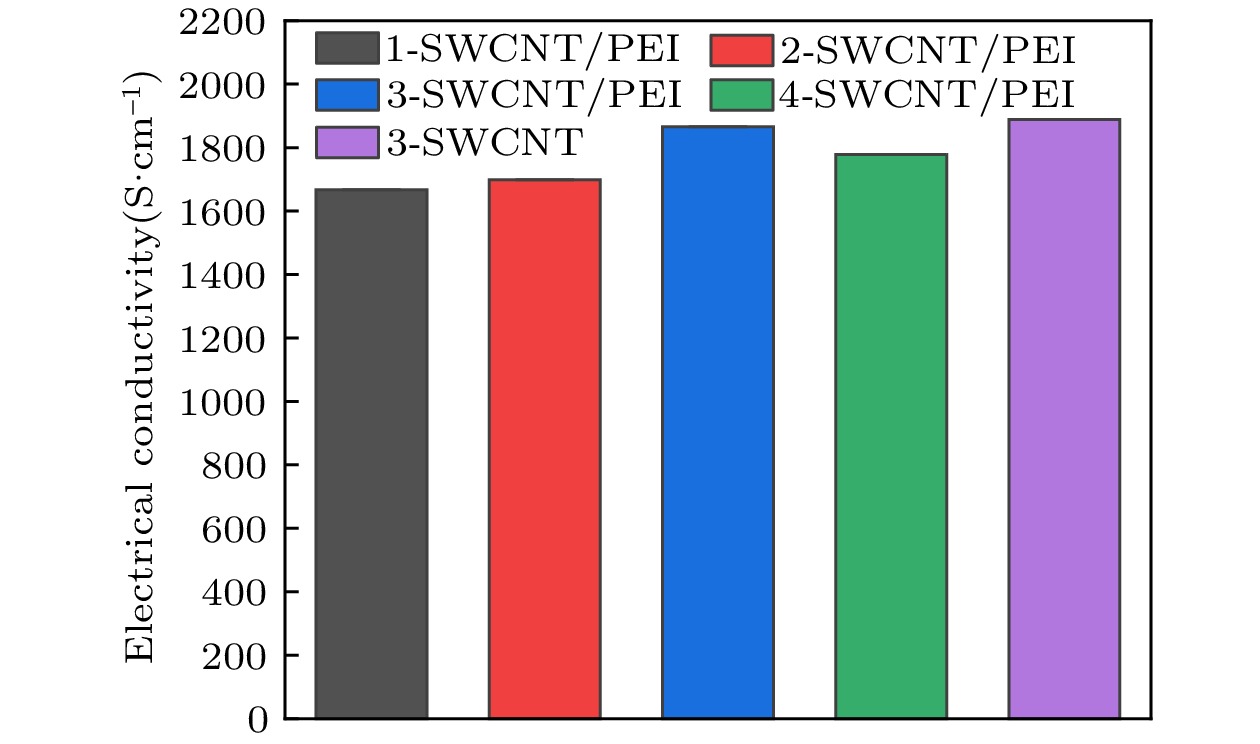
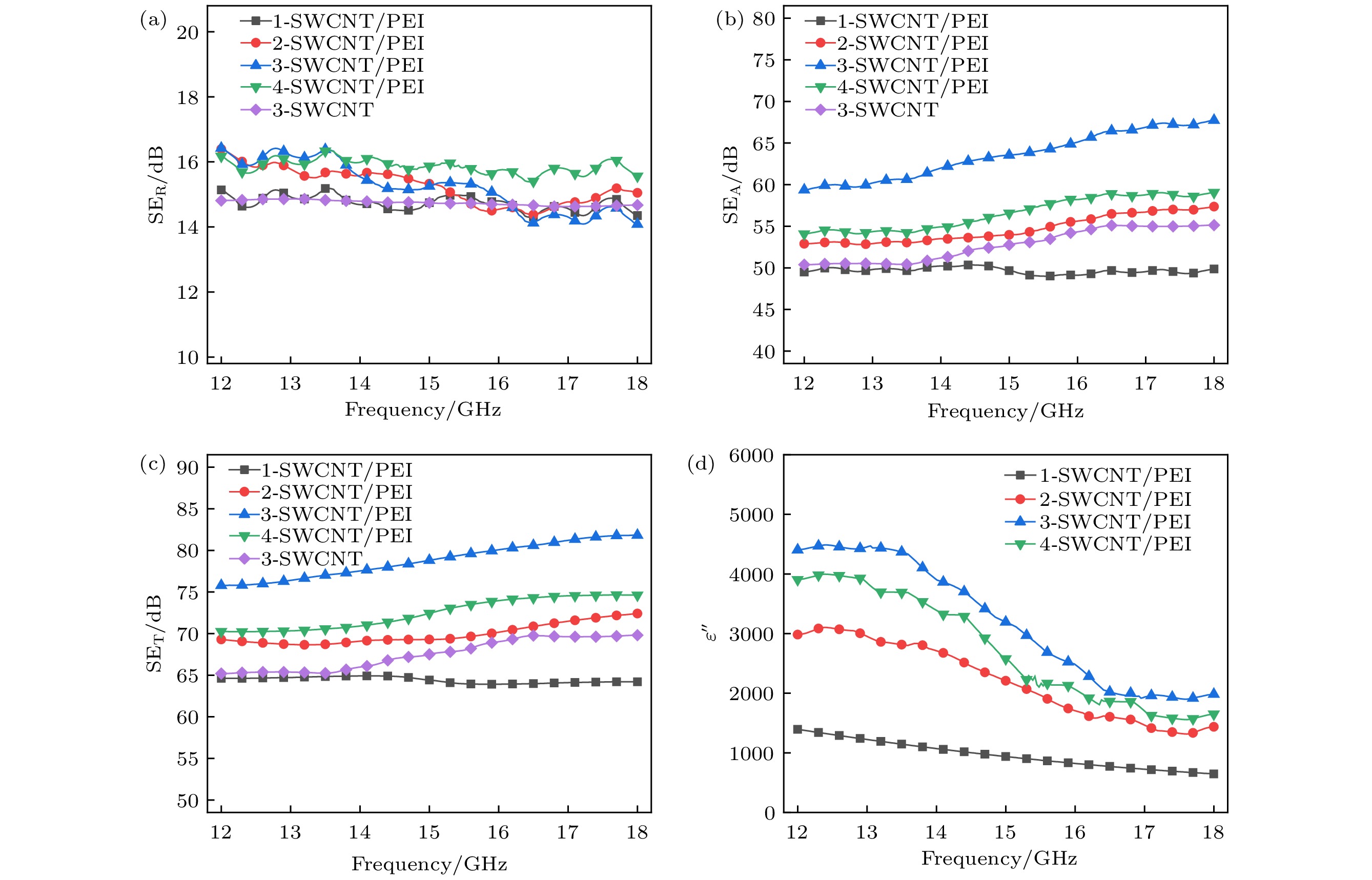
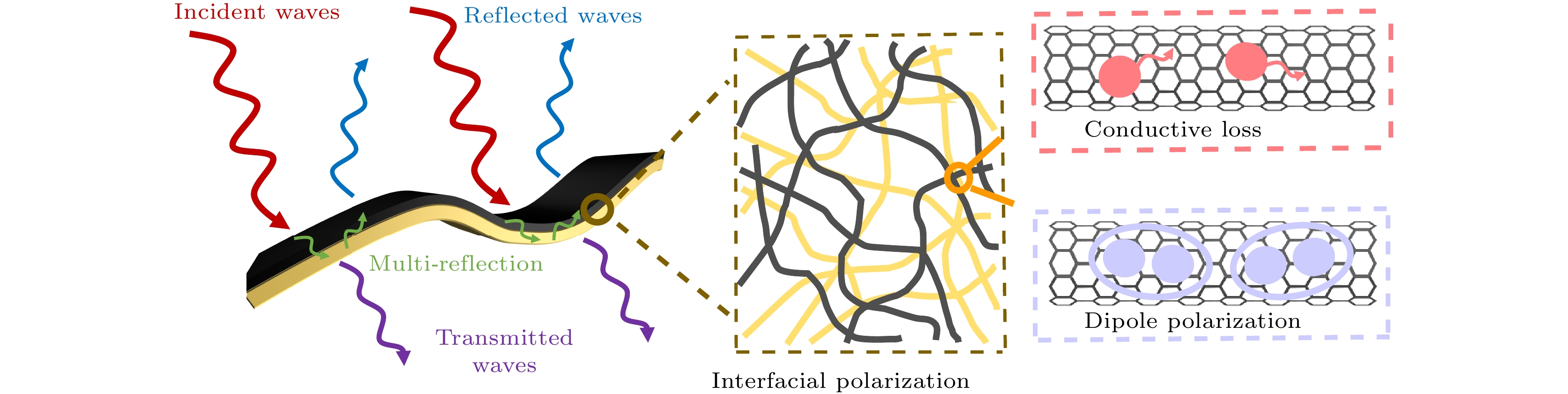
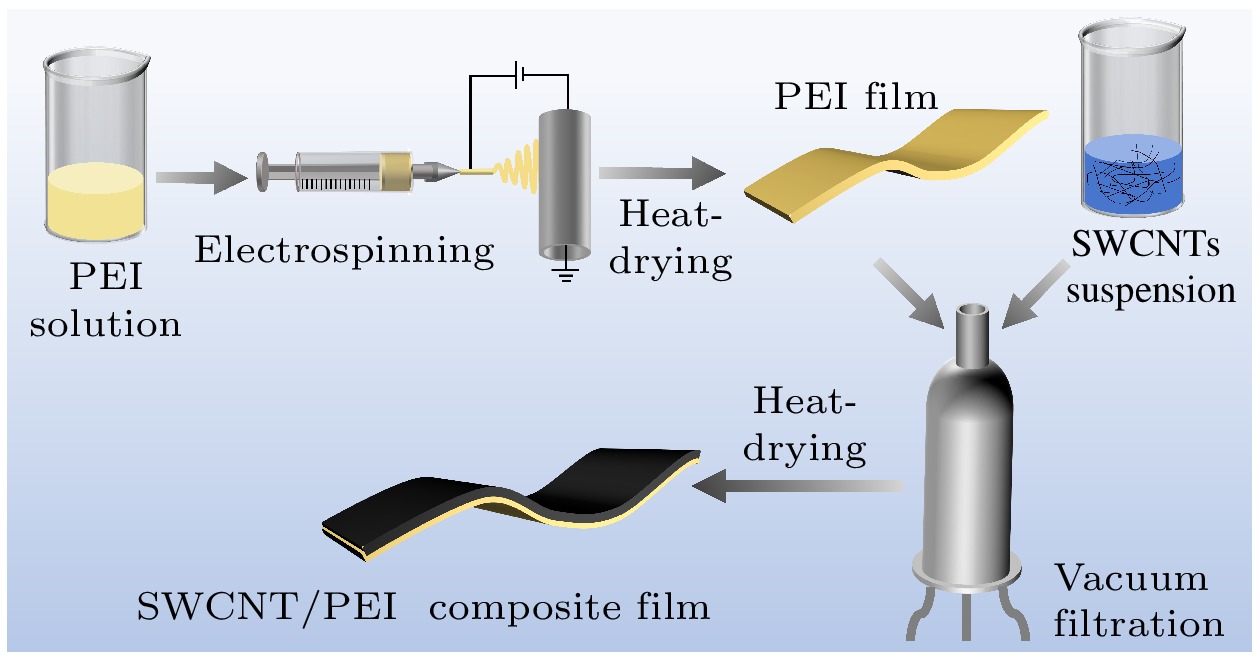
在实际应用中, 柔性、轻质、高性能是聚合物基电磁屏蔽材料应具备的特点. 目前, 制备兼具优异电导率、电磁屏蔽性能和力学性能的聚合物基电磁屏蔽材料仍然是一个巨大挑战. 因此, 本工作以单壁碳纳米管和聚醚酰亚胺为原料, 通过静电纺丝和真空辅助过滤的方法制备了单壁碳纳米管/聚醚酰亚胺复合薄膜. 通过调控单壁碳纳米管的面密度, 复合薄膜的电导率可以提升至1866 S/cm. 对于电磁屏蔽性能, 单壁碳纳米管/聚醚酰亚胺复合薄膜在Ku波段(12—18 GHz)的总电磁屏蔽效能为75.78—81.83 dB, 高于纯单壁碳纳米管薄膜的电磁屏蔽效能(65.19—69.81 dB). 由于聚醚酰亚胺纤维和单壁碳纳米管之间形成了界面, 在一定的单壁碳纳米管面密度范围内, 界面越多, 消耗的电磁波能量越多. 对于力学性能, 单壁碳纳米管/聚醚酰亚胺薄膜的最大拉伸强度和断裂伸长率分别为28.52 MPa和7.91%, 是单壁碳纳米管薄膜的1.13倍和1.5倍, 随着单壁碳纳米管面密度的增大, 单壁碳纳米管之间的相互作用以及聚醚酰亚胺纤维和单壁碳纳米管在界面处的相互作用对复合薄膜的力学性能起到了一定的增强作用. 单壁碳纳米管/聚醚酰亚胺复合薄膜作为一种优异的聚合物基电磁屏蔽复合材料, 可用于如精密电子仪器的防护和可穿戴电子设备等领域.In practical applications, flexibility, lightweight, and high performance are the characteristics that polymer-based electromagnetic shielding materials should have. At present, it is still a great challenge to prepare polymer-based electromagnetic shielding materials with excellent conductivity, electromagnetic shielding properties, and mechanical properties. Therefore, in this work, single-walled carbon nanotubes/polyetherimide composite films are prepared by electrostatic spinning and vacuum-assisted filtration through using single-walled carbon nanotubes and polyetherimide as raw materials. By regulating the surface density of single-walled carbon nanotubes, the conductivity of the composite film can be enhanced to 1866 S/cm. For the electromagnetic shielding performance, the total electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of single-walled carbon nanotubes/polyetherimide composite film in Ku band (12–18 GHz) is in a range of 75.78–81.83 dB, which is higher than that of pure single-walled carbon nanotube film (65.19–69.81 dB). This is attributed to the formation of interfaces between the polyetherimide fibers and the single-walled carbon nanotubes, with more interfaces consuming more electromagnetic wave energy for a given range of single-walled carbon nanotube surface densities. For the mechanical properties, the maximum tensile strength and elongation at the break of the single-walled carbon nanotube/polyetherimide film are 1.13 and 1.5 times higher than those of the single-walled carbon nanotube film, with the values of 28.52 MPa and 7.91%, respectively. As the surface density of single-walled carbon nanotubes increases, the interaction between single-walled carbon nanotubes as well as the interaction between polyetherimide fibers and single-walled carbon nanotubes at the interface plays a role in enhancing the mechanical properties of the composite films. The single-walled carbon nanotube/polyetherimide composite films, as an excellent polymer-based electromagnetic shielding composite material, can be used in fields such as the protection of precision electronic instruments and wearable electronic devices.
-
Keywords:
- single-walled carbon nanotube /
- polyetherimide /
- lectrostatic spinning /
- electromagnetic shielding
[1] Qi Q, Ma L, Zhao B, Wang S, Liu X B, Lei Y, Park C B 2020 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12 36568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Promlok D, Wichaita W, Phongtamrug S, Kaewsaneha C, Sreearunothai P, Suteewong T, Tangboriboonrat P 2024 Prog. Org. Coat. 186 108002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kulkarni G, Kandesar P, Velhal N, Phadtare V, Jatratkar A, Shinde S K, Kim D-Y, Puri V 2019 Chem. Eng. J. 355 196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Qiao Y S, Shen L Z, Guo Y, Liu J H, Meng S M 2014 Mater. Techn. 30 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lai H R, Li W Y, Xu L, Wang X M, Jiao H, Fan Z Y, Lei Z L, Yuan Y 2020 Chem. Eng. J. 400 125322
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ma M, Shao W Q, Chu Q D, Tao W T, Chen S, Shi Y Q, He H W, Zhu Y L, Wang X 2024 J. Mater. Chem. A 12 1617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ren W, Zhu H X, Yang Y Q, Chen Y H, Duan H J, Zhao G Z, Liu Y Q 2020 Compos. Part B: Eng. 184 107745
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang G, Zhou L C, Wang M J, Xiang T T, Pan D, Zhu J Z, Su F M, Ji Y X, Liu C T, Shen C Y 2023 Nano Res. 16 11411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wei L F, Ma J Z, Ma L, Zhao C X, Xu M L, Qi Q, Zhang W B, Zhang L, He X, Park C B 2022 Small Methods 6 2101510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang T, Kong W W, Yu W C, Gao J F, Dai K, Yan D X, Li Z M 2021 Nanomicro Lett. 13 162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li M M, Xu Q Y, Jiang W, Farooq A, Qi Y R, Liu L F 2023 Fiber. Polym. 24 771
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Si Y F, Jin H H, Zhang Q, Xu D W, Xu R X, Ding A X, Liu D 2022 Ceram. Int. 48 24898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Anand S, Pauline S 2021 Nanotechnology 32 475707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang B B, Zhang W Y, Sun J M, Lai C H, Ge S B, Guo H W, Liu Y, Zhang D H 2023 J. Mater. Chem. A 11 8656
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang C B, Guo Y B, Chen J W, Zhu Y T 2023 Compos. Commun. 37 101444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang S, Yan D X, Li Y, Lei J, Li Z M 2021 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 60 9824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Jia F F, Lu Z Q, Liu Y Q, Li J Y, Xie F, Dong J Y 2022 ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 4 6342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Song J W, Xu K J, He J, Ye H J, Xu L X 2023 Polym. Compos. 44 2836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hu P Y, Lyu J, Fu C, Gong W B, Liao J H, Lu W B, Chen Y P, Zhang X T 2020 ACS Nano 14 688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Cao W T, Ma C, Tan S, Ma M G, Wan P B, Chen F 2019 Nanomicro Lett. 11 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Mani D, Vu M C, Lim C S, Kim J B, Jeong T H, Kim H J, Islam M A, Lim J H, Kim K M, Kim S R 2023 Carbon 201 568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lee E S, Lim Y K, Chun Y S, Wang B Y, Lim D S 2017 Carbon 118 650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Khodadadi Yazdi M, Noorbakhsh B, Nazari B, Ranjbar Z 2020 Prog. Org. Coat. 145 105674
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 安萍, 郭浩, 陈萌, 赵苗苗, 杨江涛, 刘俊, 薛晨阳, 唐军 2014 63 237306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
An P, Guo H, Chen M, Zhao M M, Yang J T, Liu J, Xue C Y, Tang J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 237306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zheng X H, Hu Q L, Wang Z Q, Nie W Q, Wang P, Li C L 2021 J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 602 680
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Chauhan S, Nikhil Mohan P, Raju K C J, Ghotia S, Dwivedi N, Dhand C, Singh S, Kumar P 2023 Colloid. Surfaces A 673 131811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang M M, Tian L, Zhang Q Q, You X, Yang J S, Dong S M 2023 Carbon 202 414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Qi Q, Ma L, Zhao B, Wang S, Liu X B, Lei Y, Park C B 2020 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12 36568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Promlok D, Wichaita W, Phongtamrug S, Kaewsaneha C, Sreearunothai P, Suteewong T, Tangboriboonrat P 2024 Prog. Org. Coat. 186 108002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kulkarni G, Kandesar P, Velhal N, Phadtare V, Jatratkar A, Shinde S K, Kim D-Y, Puri V 2019 Chem. Eng. J. 355 196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Qiao Y S, Shen L Z, Guo Y, Liu J H, Meng S M 2014 Mater. Techn. 30 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lai H R, Li W Y, Xu L, Wang X M, Jiao H, Fan Z Y, Lei Z L, Yuan Y 2020 Chem. Eng. J. 400 125322
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ma M, Shao W Q, Chu Q D, Tao W T, Chen S, Shi Y Q, He H W, Zhu Y L, Wang X 2024 J. Mater. Chem. A 12 1617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ren W, Zhu H X, Yang Y Q, Chen Y H, Duan H J, Zhao G Z, Liu Y Q 2020 Compos. Part B: Eng. 184 107745
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang G, Zhou L C, Wang M J, Xiang T T, Pan D, Zhu J Z, Su F M, Ji Y X, Liu C T, Shen C Y 2023 Nano Res. 16 11411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wei L F, Ma J Z, Ma L, Zhao C X, Xu M L, Qi Q, Zhang W B, Zhang L, He X, Park C B 2022 Small Methods 6 2101510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang T, Kong W W, Yu W C, Gao J F, Dai K, Yan D X, Li Z M 2021 Nanomicro Lett. 13 162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li M M, Xu Q Y, Jiang W, Farooq A, Qi Y R, Liu L F 2023 Fiber. Polym. 24 771
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Si Y F, Jin H H, Zhang Q, Xu D W, Xu R X, Ding A X, Liu D 2022 Ceram. Int. 48 24898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Anand S, Pauline S 2021 Nanotechnology 32 475707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang B B, Zhang W Y, Sun J M, Lai C H, Ge S B, Guo H W, Liu Y, Zhang D H 2023 J. Mater. Chem. A 11 8656
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang C B, Guo Y B, Chen J W, Zhu Y T 2023 Compos. Commun. 37 101444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang S, Yan D X, Li Y, Lei J, Li Z M 2021 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 60 9824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Jia F F, Lu Z Q, Liu Y Q, Li J Y, Xie F, Dong J Y 2022 ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 4 6342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Song J W, Xu K J, He J, Ye H J, Xu L X 2023 Polym. Compos. 44 2836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hu P Y, Lyu J, Fu C, Gong W B, Liao J H, Lu W B, Chen Y P, Zhang X T 2020 ACS Nano 14 688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Cao W T, Ma C, Tan S, Ma M G, Wan P B, Chen F 2019 Nanomicro Lett. 11 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Mani D, Vu M C, Lim C S, Kim J B, Jeong T H, Kim H J, Islam M A, Lim J H, Kim K M, Kim S R 2023 Carbon 201 568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lee E S, Lim Y K, Chun Y S, Wang B Y, Lim D S 2017 Carbon 118 650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Khodadadi Yazdi M, Noorbakhsh B, Nazari B, Ranjbar Z 2020 Prog. Org. Coat. 145 105674
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 安萍, 郭浩, 陈萌, 赵苗苗, 杨江涛, 刘俊, 薛晨阳, 唐军 2014 63 237306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
An P, Guo H, Chen M, Zhao M M, Yang J T, Liu J, Xue C Y, Tang J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 237306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zheng X H, Hu Q L, Wang Z Q, Nie W Q, Wang P, Li C L 2021 J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 602 680
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Chauhan S, Nikhil Mohan P, Raju K C J, Ghotia S, Dwivedi N, Dhand C, Singh S, Kumar P 2023 Colloid. Surfaces A 673 131811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang M M, Tian L, Zhang Q Q, You X, Yang J S, Dong S M 2023 Carbon 202 414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 4163
- PDF下载量: 74
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: