-
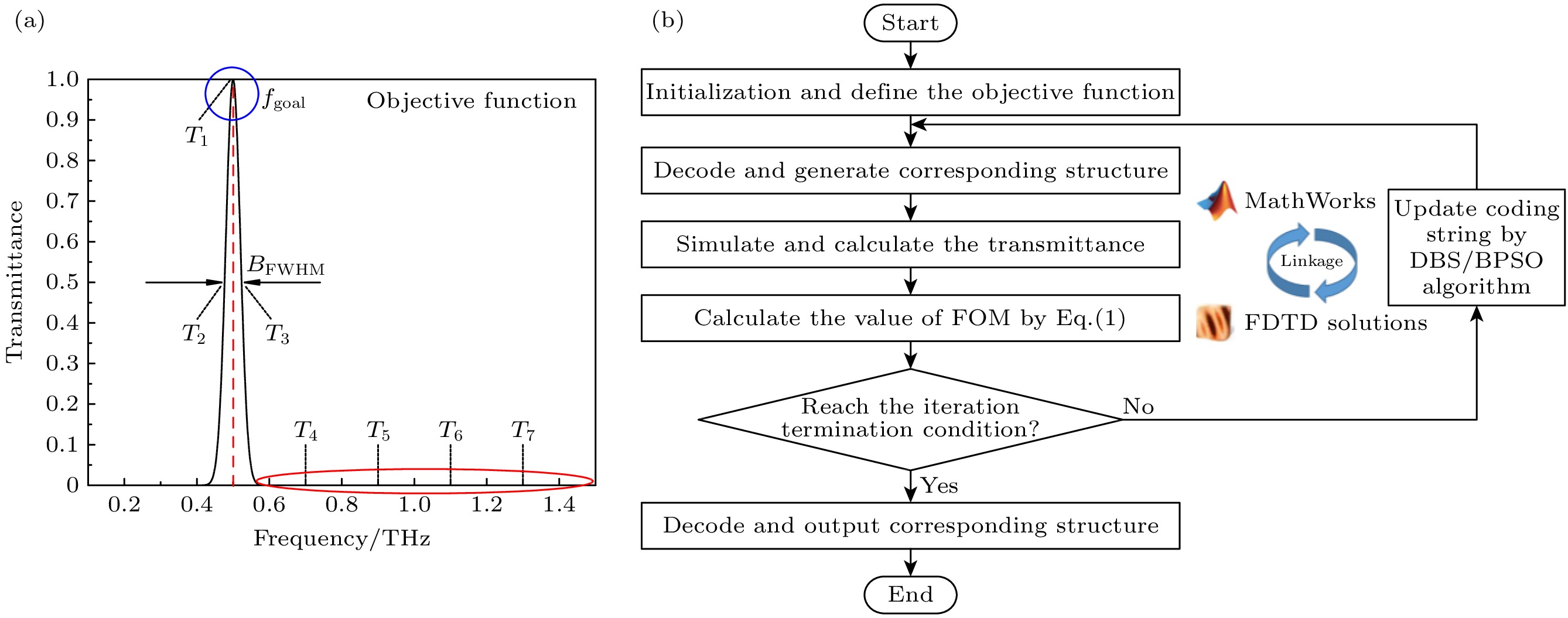
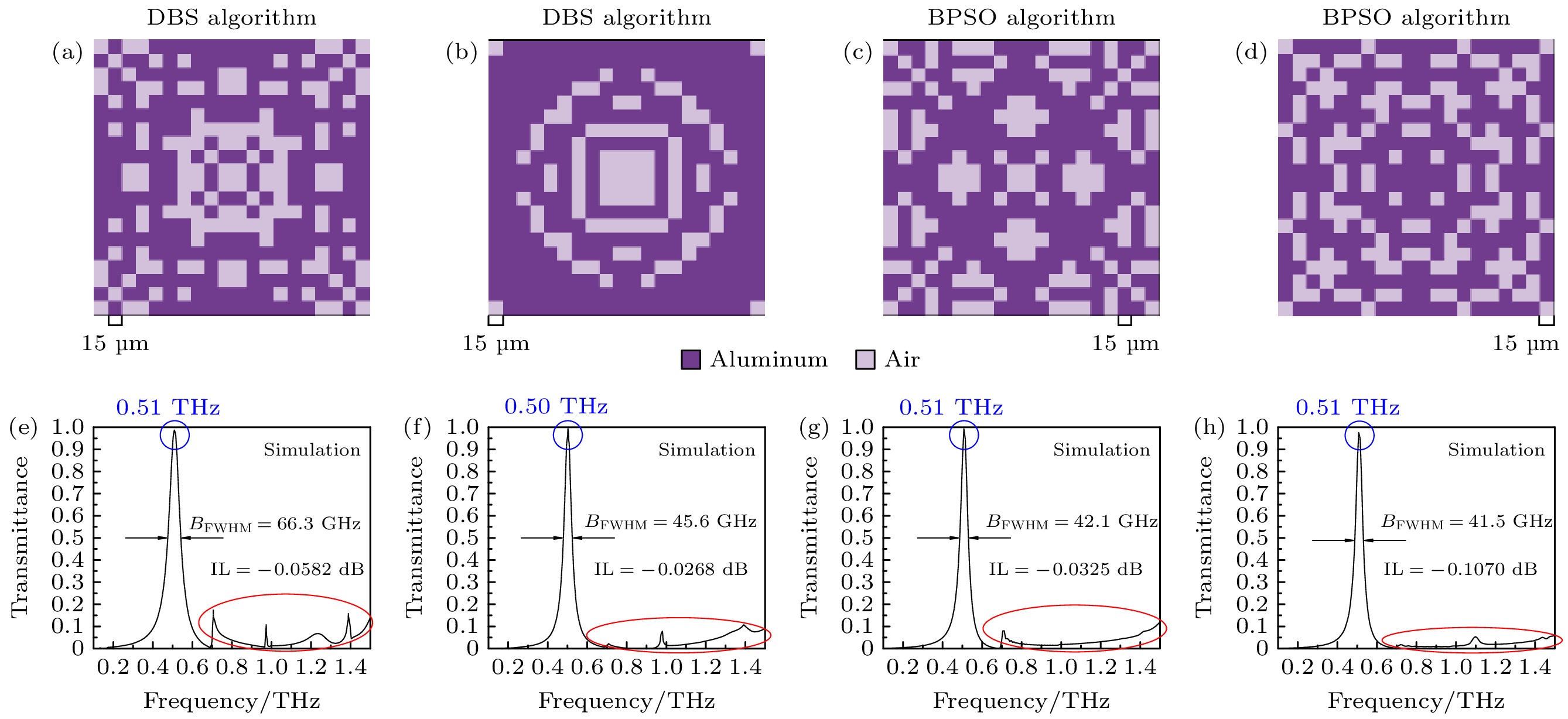
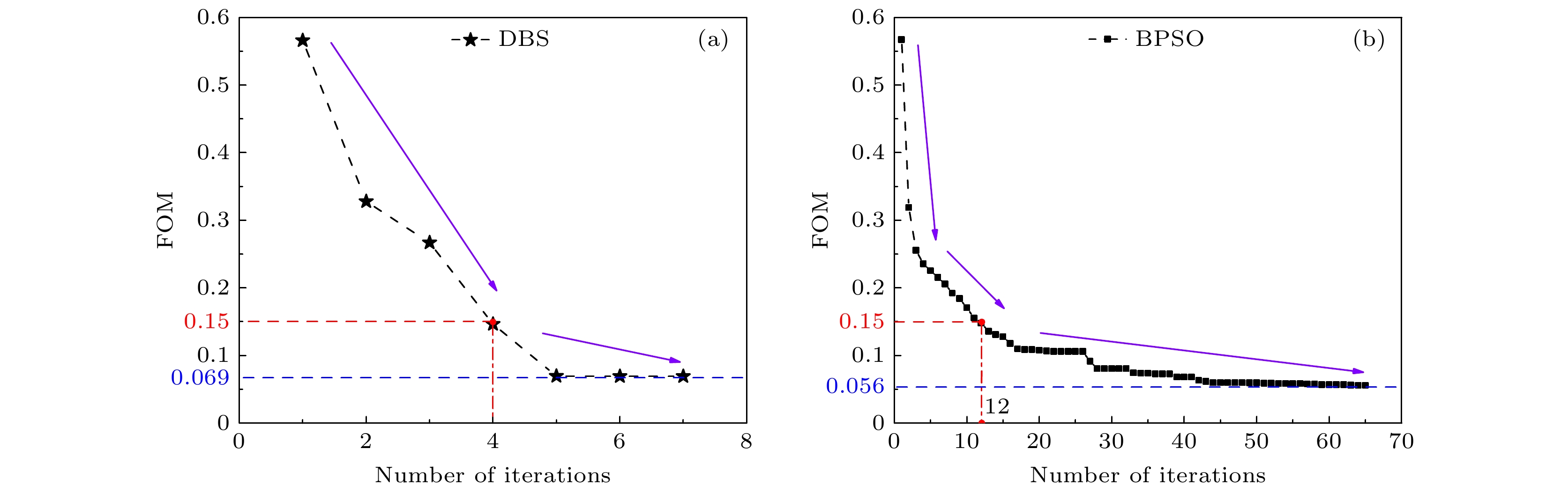
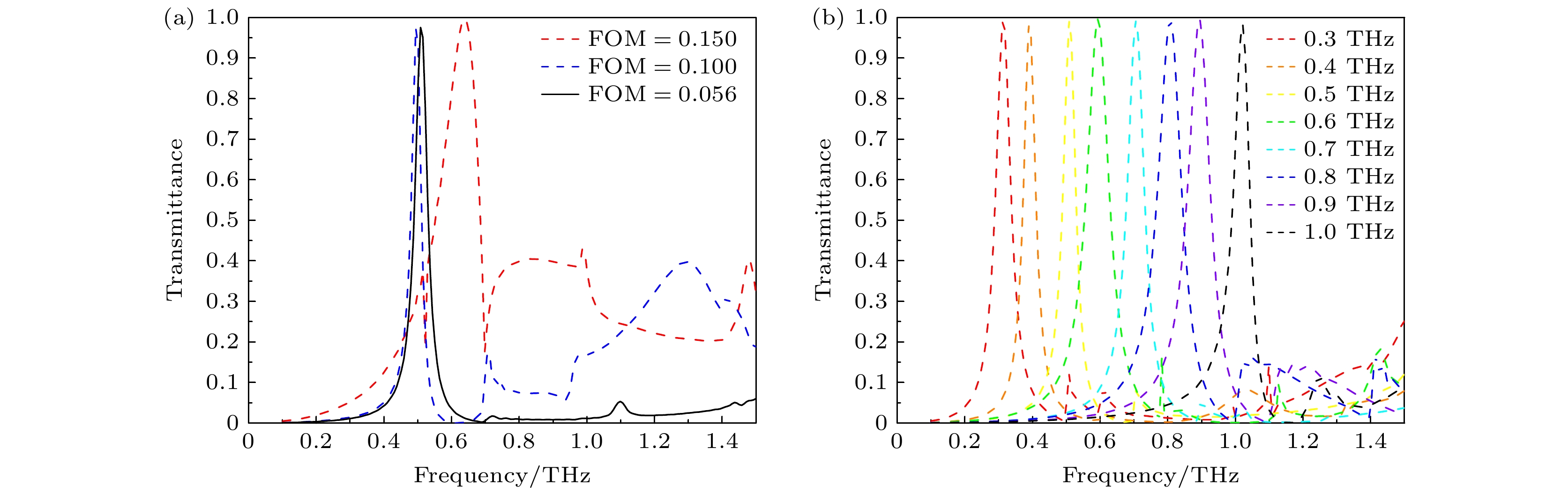
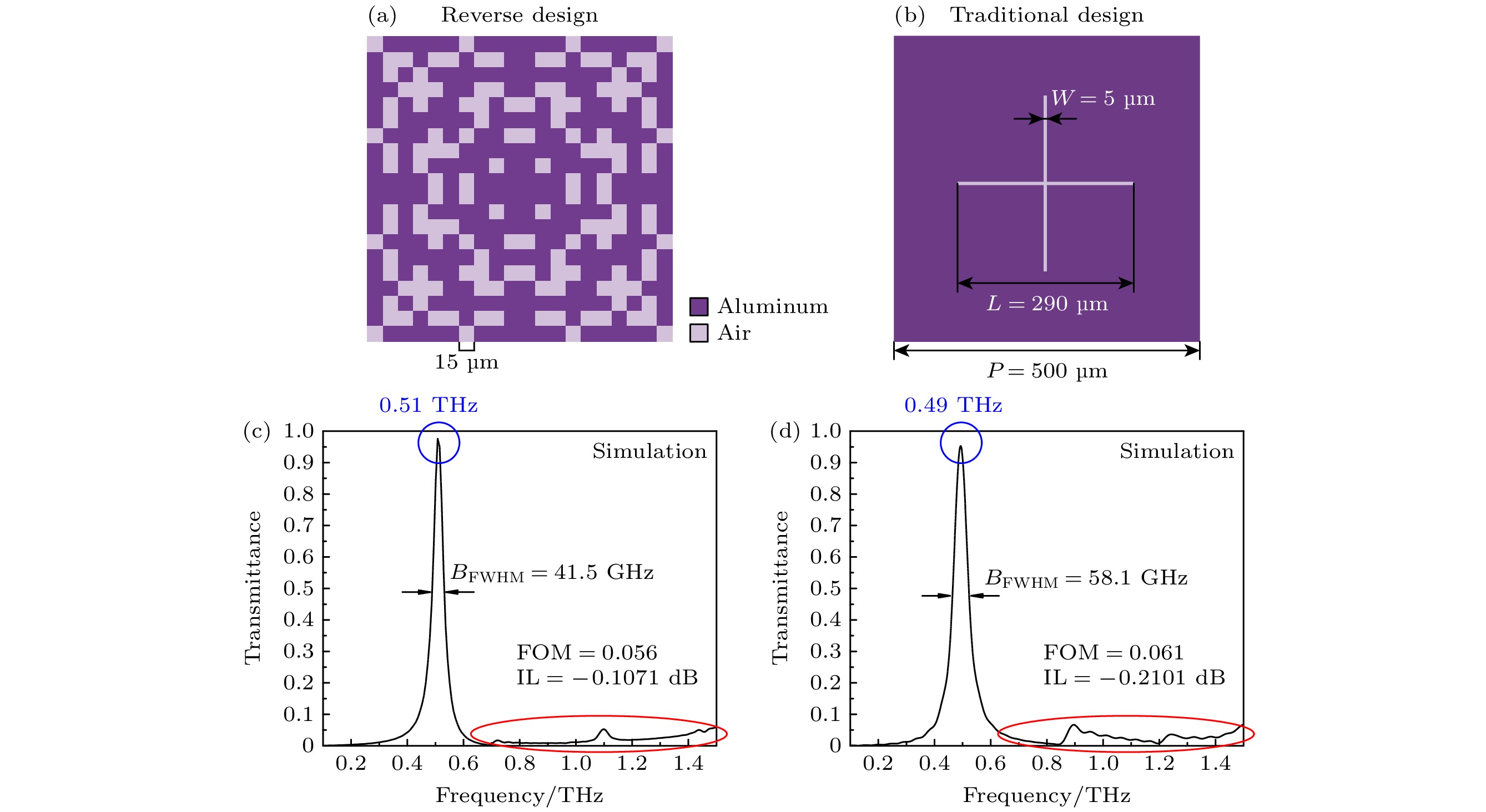
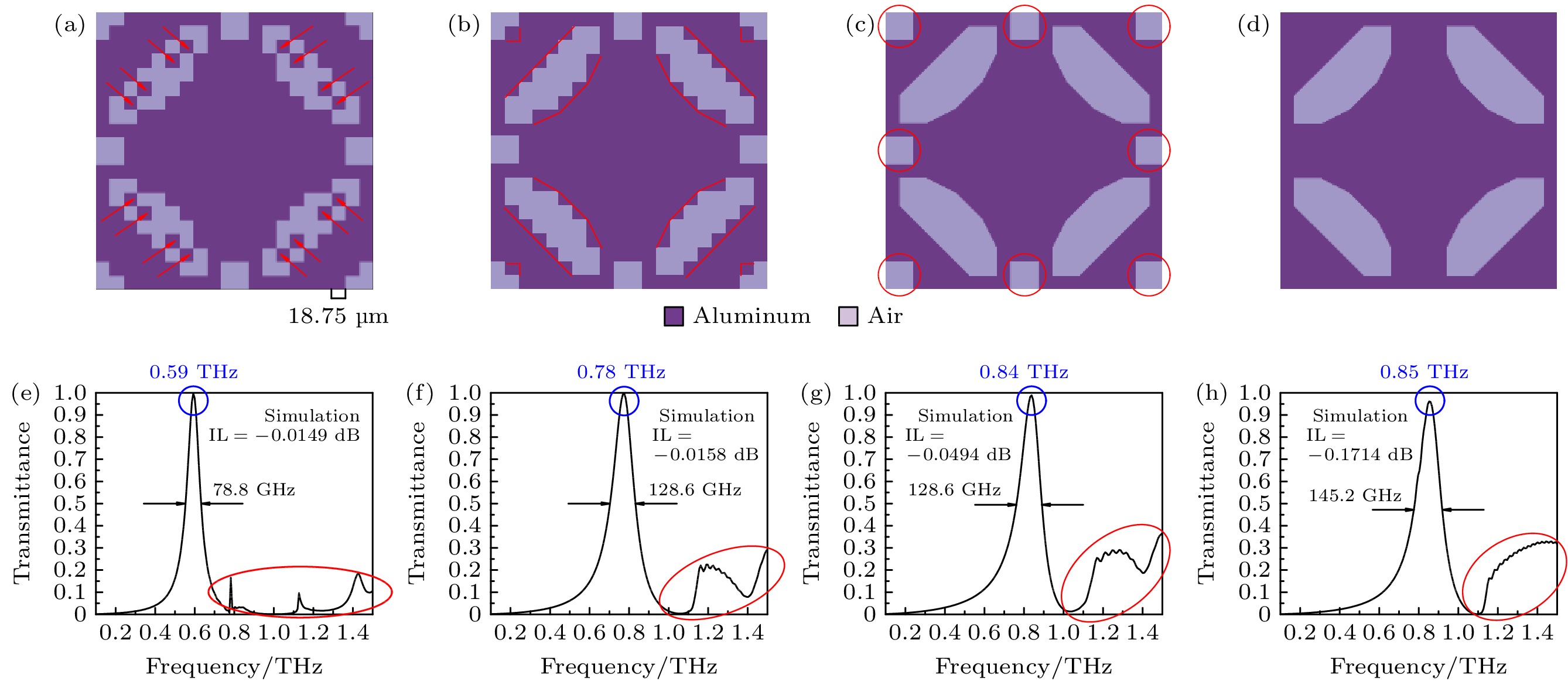
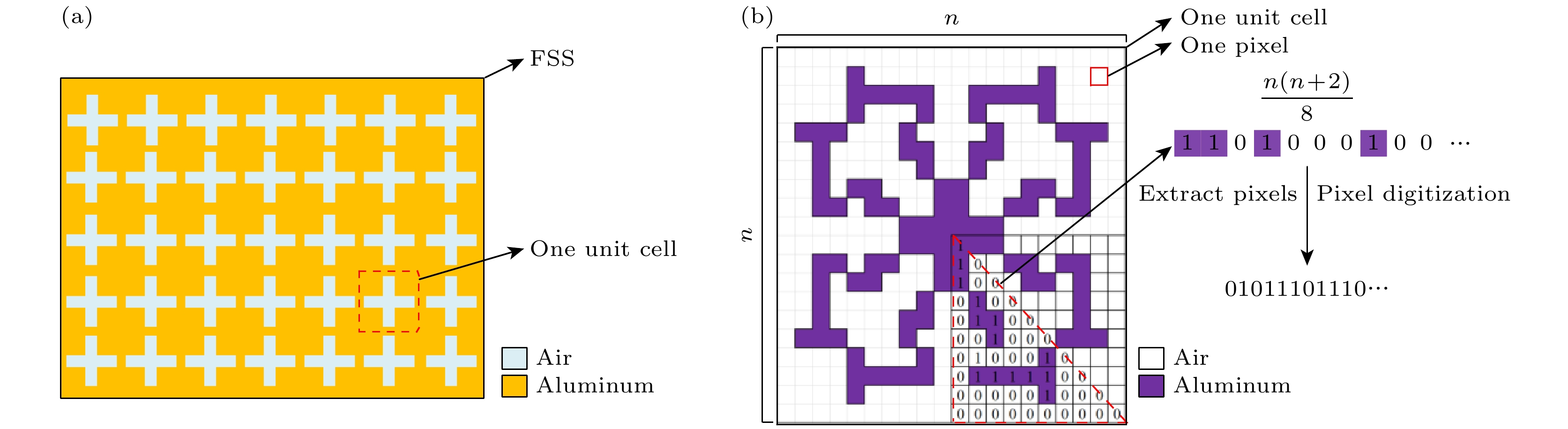
In this paper, an ingenious reverse design method is applied to the design and optimization of terahertz bandpass filters in order to achieve standardized design of high-performance terahertz functional devices. An equivalent model of subwavelength metasurface mapped to digital space is established. Based on ideal objective functions and constraints, intelligent algorithms begin a bold journey to explore the vast potential structure in the solution space. Through iterative refinement, the algorithm reveals optimal structural patterns, unlocking areas of unparalleled performance. The direct binary search (DBS) algorithm and the binary particle swarm optimization (BPSO) algorithm are compared in optimization process. When using the DBS algorithm to optimize the design area, it takes a long time to poll the logic states of all pixel units point by point, and it is easy to get stuck in the local optimal value. However, BPSO algorithm has stronger global search capabilities, faster convergence speed, and higher accuracy. Through a comprehensive comparison of the device performance optimized by the two algorithms, the solution optimized by BPSO algorithm has better out-of-band suppression performance and a narrower full width at half peak, but slightly lower transmittance at the center frequency. The bandpass filter has a center frequency of 0.51 THz, a bandwidth of 41.5 GHz, and an insertion loss of -0.1071 dB. When considering computational efficiency, DBS algorithm lags behind, the simulation time is 11550 s, while BPSO algorithm only needs 9750 s. Compared with the traditional forward design, the reverse design method can achieve the narrower band, lower insertion loss, better out-of-band suppression and polarization stability. The fine structural changes of the optimal results have a significant influence on spectral performance, demonstrating the superiority and uniqueness of reverse design. This technology contributes to the design and optimization of high-performance and novel functional devices.
-
Keywords:
- reverse design /
- terahertz metasurface /
- digital encoding /
- mapping and modeling
[1] Yang X, Zhao X, Yang K, Liu Y, Fu W, Luo Y. Biomedical applications of terahertz spectroscopy and imaging 2016 Trends Biotechnol. 34 810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pengnoo M, Barros M T, Wuttisittikulkij L, Butler B, Davy A, Balasubramaniam S 2020 IEEE Access 8 114580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kumar A, Gupta M, Pitchappa P, Wang N, Szriftgiser P, Ducournau G, Singh R 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 5404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lee E S, Jeon T I. 2012 Opt. Express 20 29605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Savel’ev S, Rakhmanov A L, Nori F 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 157004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lin Y, Yao H, Ju X, Chen Y, Zhong S, Wang X 2017 Opt. Express 25 25125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gao T, Huang F, Chen Y, Zhu W, Ju X 2020 Appl. Sci. 10 5030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hu F, Fan Y, Zhang X, Jiang W, Chen Y, Li P, Yin X, Zhang W 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 洪鹏, 胡珑夏雨, 周子昕, 秦浩然, 陈佳乐, 范烨, 殷同宇, 寇君龙, 陆延青 2023 光子学报 52 0623001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hong P, Hu L X Y, Zhou Z X, Qin H R, Chen J L, Fan Y, Yin T Y, Kou J L, Lu Y Q 2023 Acta Photonnica Sin. 52 0623001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 常红伟, 马华, 张介秋, 张志远, 徐卓, 王甲富, 屈绍波 2014 63 087804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang H W, Ma H, Zhang J Q, Zhang Z Y, Xu Z, Wang J F, Qu S B 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 087804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sui S, Ma H, Wang J, Pang Y, Feng M, Xu Z, Qu S 2018 J. Phys. D 51 065603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhu R, Wang J, Sui S, Meng Y, Qiu T, Jia Y, Wang X, Han Y, Feng M, Zheng L, Qu S 2020 Front. Phys. 8 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu Z H, Liu X H, Xiao Z Y, Lu C C, Wang H Q, Wu Y, Hu X Y, Liu Y C, Zhang H Y, Zhang X D 2019 Optica 6 1367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ma W, Cheng F, Liu Y M 2018 ACS Nano 12 6326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ma H, Kim J S, Choe J H, Park Q H 2023 Nanophotonics 12 2415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang T, Liu Q, Dan Y H, Yu S, Han X, Dai J, Xu K 2020 Opt. Express 28 18899
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang Y Z, Zeng Q L, Wang J Z, Li Y, Fang D N 2022 Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 401 115571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Piggott A Y, Lu J, Lagoudakis K G, Petykiewicz J, Babinec T M, Vučković J 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chang W J, Ren X S, Ao Y Q, Lu L H, Cheng M F, Deng L, Liu D M, Zhang M M 2018 Opt. Express 26 24135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fallahi A, Mishrikey M, Hafner C, Vahldieck R 2008 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 56 1340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ordal M A, Long L L, Bell R J, Bell S E, Bell R R, Alexander R W, Ward C A 1983 Appl. Opt. 22 1099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhu G Y, Ju X W, Zhang W B 2018 Int. J. Prod. Res. 56 4017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hajian M, Ranjbar A M, Amraee T, Mozafari B 2011 Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 33 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ju X W, Hu Z Q, Huang F, Wu H B, Belyanin A, Kono J, Wang X F 2021 Opt. Express 29 9261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Yang X, Zhao X, Yang K, Liu Y, Fu W, Luo Y. Biomedical applications of terahertz spectroscopy and imaging 2016 Trends Biotechnol. 34 810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pengnoo M, Barros M T, Wuttisittikulkij L, Butler B, Davy A, Balasubramaniam S 2020 IEEE Access 8 114580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kumar A, Gupta M, Pitchappa P, Wang N, Szriftgiser P, Ducournau G, Singh R 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 5404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lee E S, Jeon T I. 2012 Opt. Express 20 29605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Savel’ev S, Rakhmanov A L, Nori F 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 157004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lin Y, Yao H, Ju X, Chen Y, Zhong S, Wang X 2017 Opt. Express 25 25125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gao T, Huang F, Chen Y, Zhu W, Ju X 2020 Appl. Sci. 10 5030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hu F, Fan Y, Zhang X, Jiang W, Chen Y, Li P, Yin X, Zhang W 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 洪鹏, 胡珑夏雨, 周子昕, 秦浩然, 陈佳乐, 范烨, 殷同宇, 寇君龙, 陆延青 2023 光子学报 52 0623001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hong P, Hu L X Y, Zhou Z X, Qin H R, Chen J L, Fan Y, Yin T Y, Kou J L, Lu Y Q 2023 Acta Photonnica Sin. 52 0623001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 常红伟, 马华, 张介秋, 张志远, 徐卓, 王甲富, 屈绍波 2014 63 087804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang H W, Ma H, Zhang J Q, Zhang Z Y, Xu Z, Wang J F, Qu S B 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 087804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sui S, Ma H, Wang J, Pang Y, Feng M, Xu Z, Qu S 2018 J. Phys. D 51 065603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhu R, Wang J, Sui S, Meng Y, Qiu T, Jia Y, Wang X, Han Y, Feng M, Zheng L, Qu S 2020 Front. Phys. 8 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu Z H, Liu X H, Xiao Z Y, Lu C C, Wang H Q, Wu Y, Hu X Y, Liu Y C, Zhang H Y, Zhang X D 2019 Optica 6 1367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ma W, Cheng F, Liu Y M 2018 ACS Nano 12 6326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ma H, Kim J S, Choe J H, Park Q H 2023 Nanophotonics 12 2415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang T, Liu Q, Dan Y H, Yu S, Han X, Dai J, Xu K 2020 Opt. Express 28 18899
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang Y Z, Zeng Q L, Wang J Z, Li Y, Fang D N 2022 Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 401 115571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Piggott A Y, Lu J, Lagoudakis K G, Petykiewicz J, Babinec T M, Vučković J 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chang W J, Ren X S, Ao Y Q, Lu L H, Cheng M F, Deng L, Liu D M, Zhang M M 2018 Opt. Express 26 24135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fallahi A, Mishrikey M, Hafner C, Vahldieck R 2008 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 56 1340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ordal M A, Long L L, Bell R J, Bell S E, Bell R R, Alexander R W, Ward C A 1983 Appl. Opt. 22 1099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhu G Y, Ju X W, Zhang W B 2018 Int. J. Prod. Res. 56 4017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hajian M, Ranjbar A M, Amraee T, Mozafari B 2011 Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 33 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ju X W, Hu Z Q, Huang F, Wu H B, Belyanin A, Kono J, Wang X F 2021 Opt. Express 29 9261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 4938
- PDF下载量: 86
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: