-
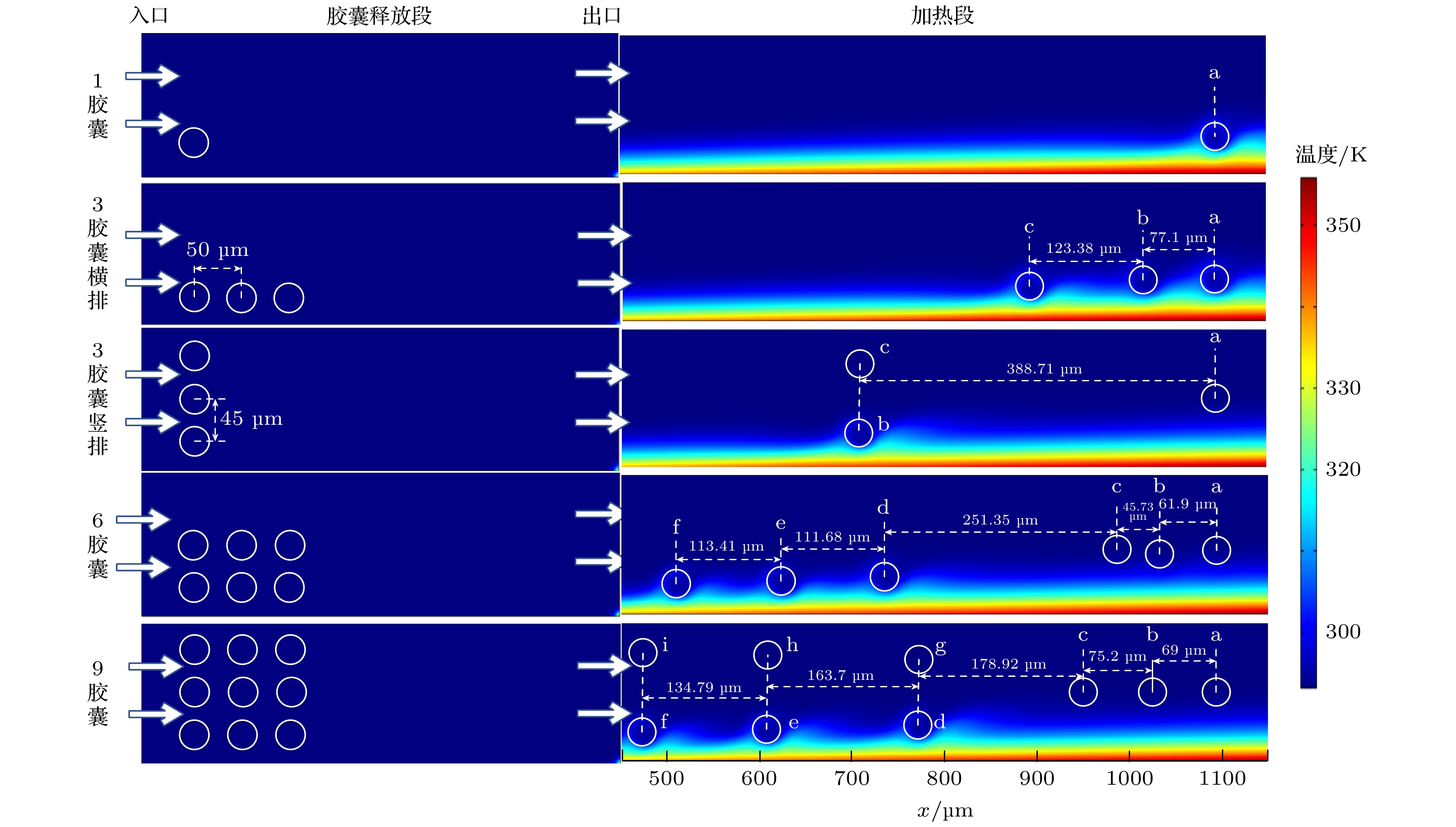
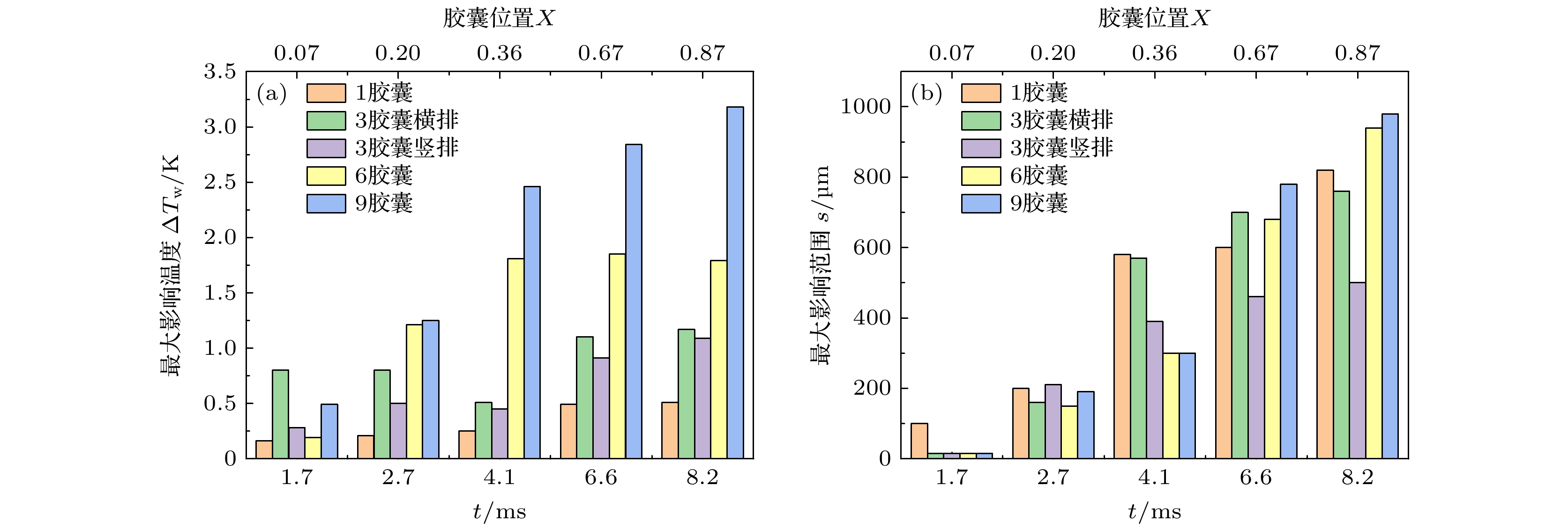
相变微胶囊悬浮液是一种新型的蓄热-传热功能流体, 目前对相变微胶囊与基液流固传递作用认识的欠缺, 导致宏观上对悬浮液流动传热性能的研究结果存在较大的差异. 为此, 本文采用任意拉格朗日-欧拉方法模拟相变微胶囊在液冷微通道内流固作用下的流动传热特性, 对比普通颗粒及相变胶囊对液冷微通道壁面温升的抑制作用, 考察胶囊位置、形状及数量对壁面温升抑制的影响. 结果表明: 胶囊及颗粒均对它们上游区域的壁面温升产生抑制作用, 而胶囊的相变使得抑制效果更加明显; 胶囊越靠近壁面自旋运动越快, 越有利于流体与壁面的换热, 对壁面温升抑制效果越强, 尤其是靠近受热面时; 相比椭圆形胶囊, 圆形胶囊自旋运动更激烈, 对壁面温升抑制效果更优; 随着加热区内胶囊数的增加, 最大抑制效果在逐渐提升.Phase change microcapsule suspension is a new type of heat-storage and heat-transfer functional fluid. Owing to the lack of understanding of flow-solid interaction, there exists a difference in research result of the heat transfer performance of suspension fluid. Therefore, the arbitrary Lagrangian-Euler method is used to simulate the flow-solid transfer characteristics of phase-change microcapsules in the liquid-cooled microchannel. Furthermore, the comparison of heat-transfer between particle and phase-change capsules is conducted. The influences of the position, shape, and number of capsules on the inhibition of the wall temperature rise are investigated. The results show that the wall-temperature-rise inhibition mainly occurs in the upstream area of the capsules. The phase change of capsules can reduce the wall temperature rise. On the other hand, the spin movement is faster when the capsule is closer to the wall, and the heat transfer is enhanced. As a result, the inhibitory effect on the wall temperature rise becomes stronger, especially near the heating surface. The circular capsules spin movement is faster and the inhibition performance is better than the ellipse. With the capsules number increasing, the wall temperature inhibition effect also gradually strengthens.
-
Keywords:
- phase change microcapsule /
- microchannel liquid cooling /
- fluid-particle interaction /
- wall-temperature inhibition
[1] Zhang Y, Ding B, Zhao D Y, Zhao S, Gong L 2023 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 201 123566
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xiu L 2019 IEEE Solid-State Circuits Magazine 11 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang Q, Deng K, Wilkens L, Reith H, Nielsch K 2022 Nat. Electron. 5 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ding B, Feng W C, Fang J, Li S Z, Gong L 2022 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 184 122272
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ding B, Feng W C, Mu M F, Gong L, Li L 2023 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 203 123773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 黄豪杰, 钱吉裕, 魏涛 2022 中国电子科学研究院学报 17 842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang H J, Qian J Y, Wei T 2022 J. Chin. Acad. Electron. Sci. 17 842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Vinoth R, Sachuthananthan B 2021 Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 123 105194
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hou T, Chen Y 2020 Chem. Eng. Process 153 107931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang F, Wu B, Du B 2022 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 172 107357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Alnaimat F, Varghese D, Mathew B 2022 Int. J. Thermo. fluids 16 100213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Roumpea E, Kovalchuk N M, Chinaud M, Nowak E, Simmons M J H, Angeli P 2019 Chem. Eng. Sci. 195 507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liang C P, Ture F, Dai Y J, Wang R Z, Ge T S 2021 Energy Build. 231 110622
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen Z, Qian P, Huang Z, Zhang W, Liu M 2023 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 183 107840
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sarafraz M M, Arjomandi M 2018 Appl. Therm. Eng. 137 700
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Martínez V A, Vasco D A, García-Herrera C M, Ortega-Aguilera R 2019 Appl. Therm. Eng. 161 114130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 刘中淼, 孙其诚, 宋世雄, 史庆藩 2014 63 034702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z M, Sun Q C, Song S X, Shi Q P 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 034702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hetsroni G, Mosyak A, Pogrebnyak E 2002 Int. J. Multiph. Flow 28 1873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hashemi Z, Abouali O, Kamali R 2013 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 65 235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu C, Tang S, Dong Y 2017 Appl. Math Mech. Engl. 38 1149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 段总样, 赵云华, 徐璋 2021 力学学报 53 2656
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan Z Y, Zhao Y H, Xu Z 2021 Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 53 2656
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 赵维维 2019 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Zhao W W 2019 M. S. Thesis (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[22] 崔智文, 王泽, 蒋新宇, 赵立豪 2022 力学进展 52 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui Z W, Wang Z, Jiang X Y, Zhao L H 2022 Adv. Mech. 52 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Rao Y, Dammel F, Stephan P, Lin G 2007 Heat Mass Transf. 44 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 杨杰, 王艳 2020 农业装备与车辆工程 58 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang J, Wang Y 2020 Agric. Equip. Veh. Eng. 58 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
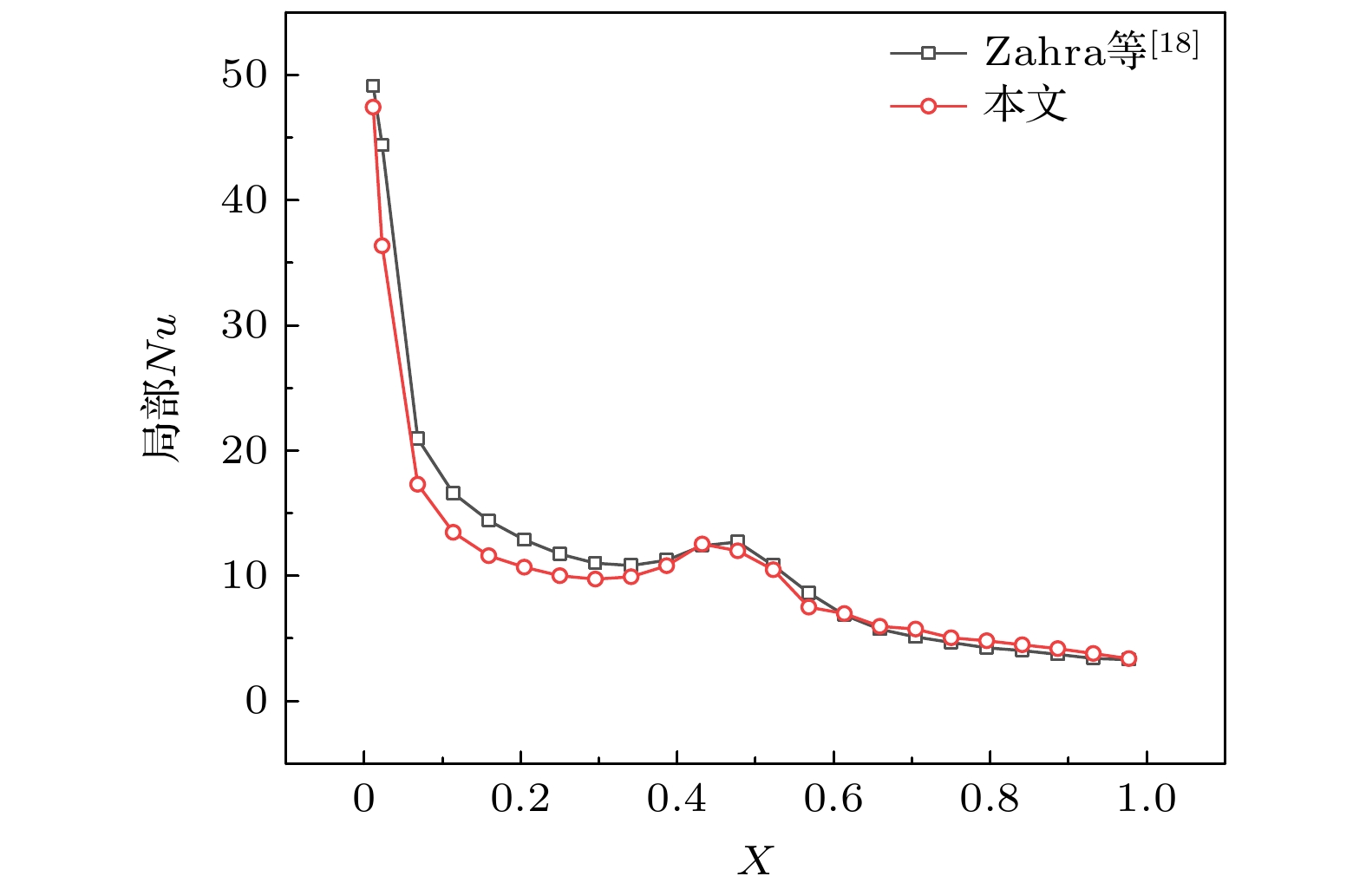
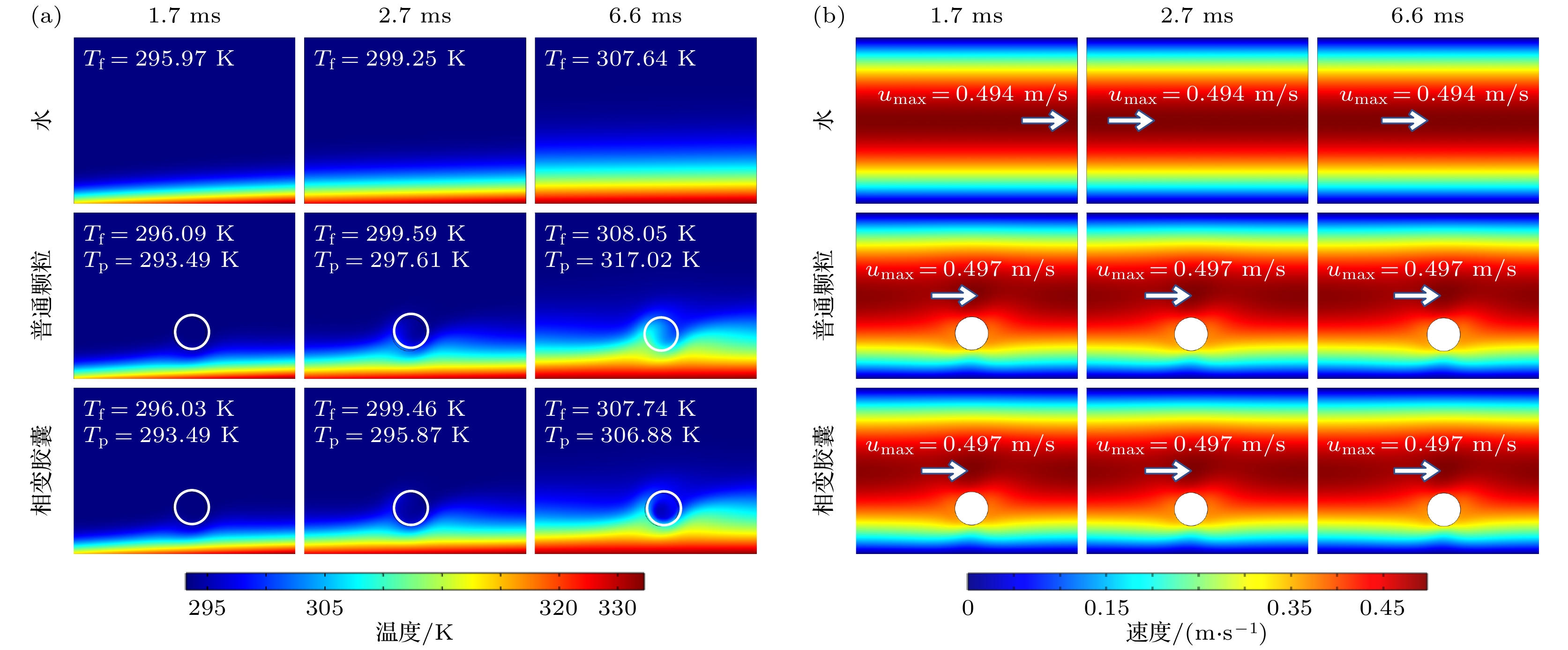
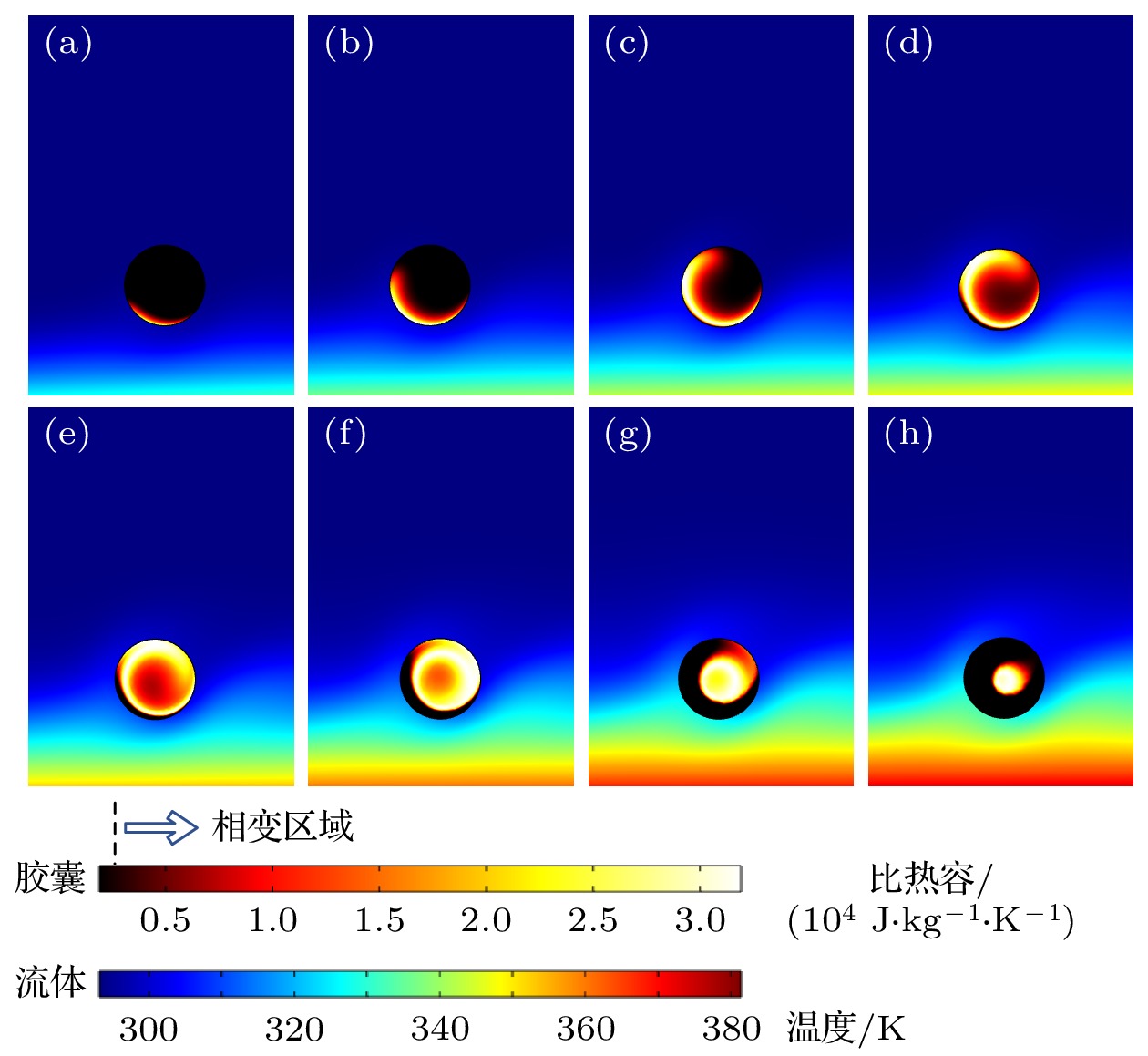
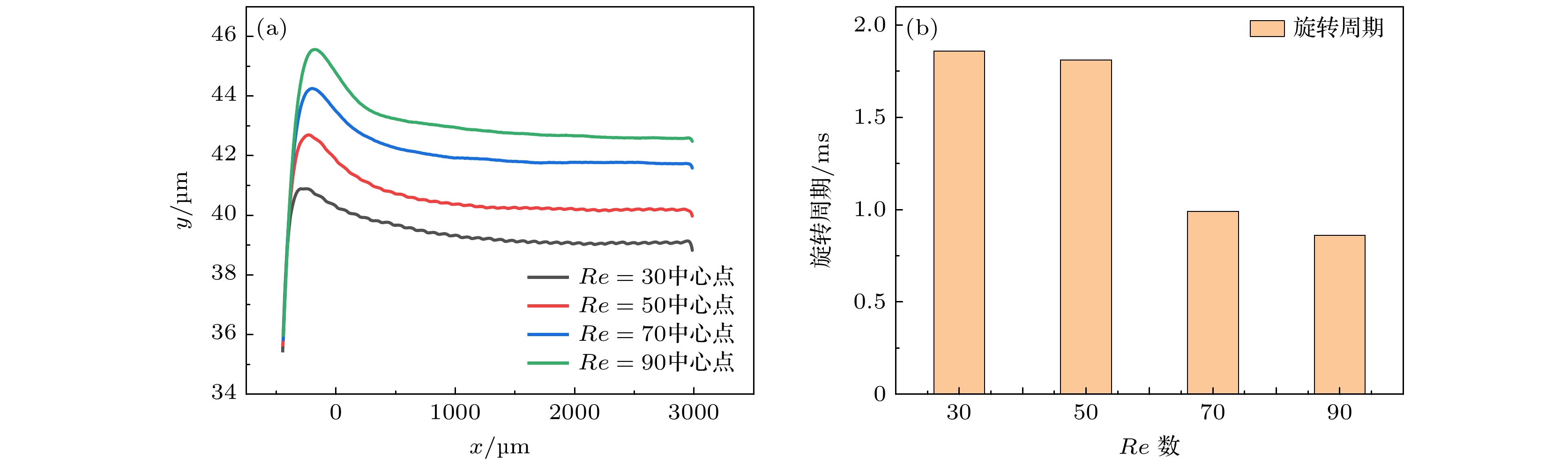
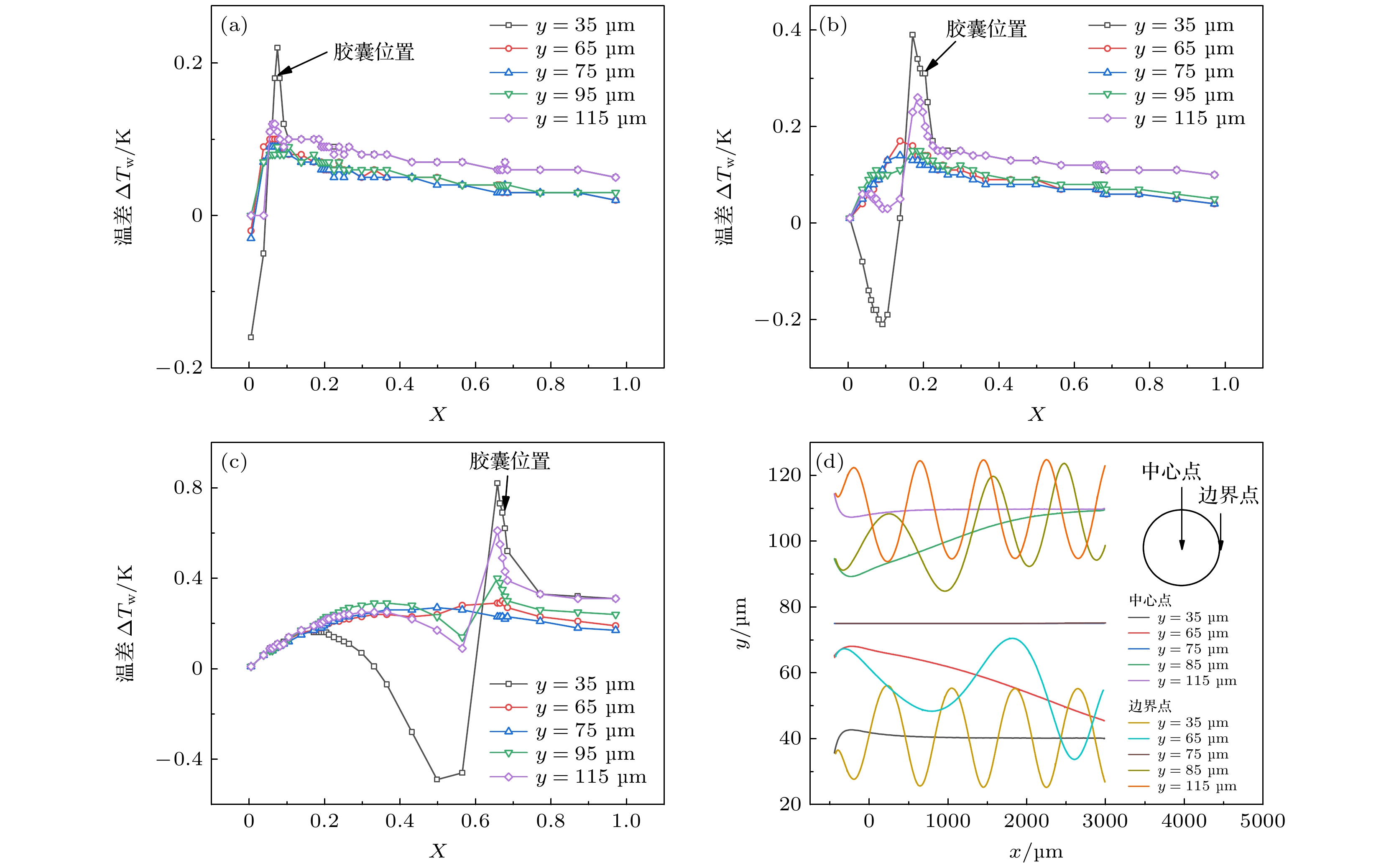
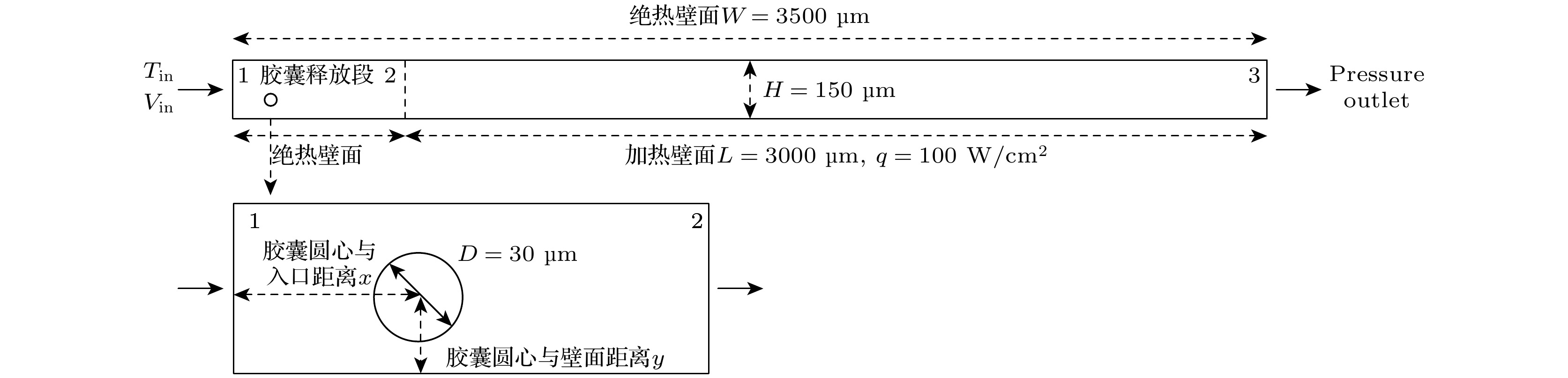
图 12 胶囊位置的影响 (a) 胶囊在1.7 ms时
$ \Delta {T}_{{\rm{w}}} $ ; (b) 胶囊在2.7 ms时$ \Delta {T}_{{\rm{w}}} $ ; (c) 胶囊在6.6 ms时$ \Delta {T}_{{\rm{w}}} $ ; (d) 胶囊迁移及自旋Fig. 12. Effect of microcapsule position: (a)
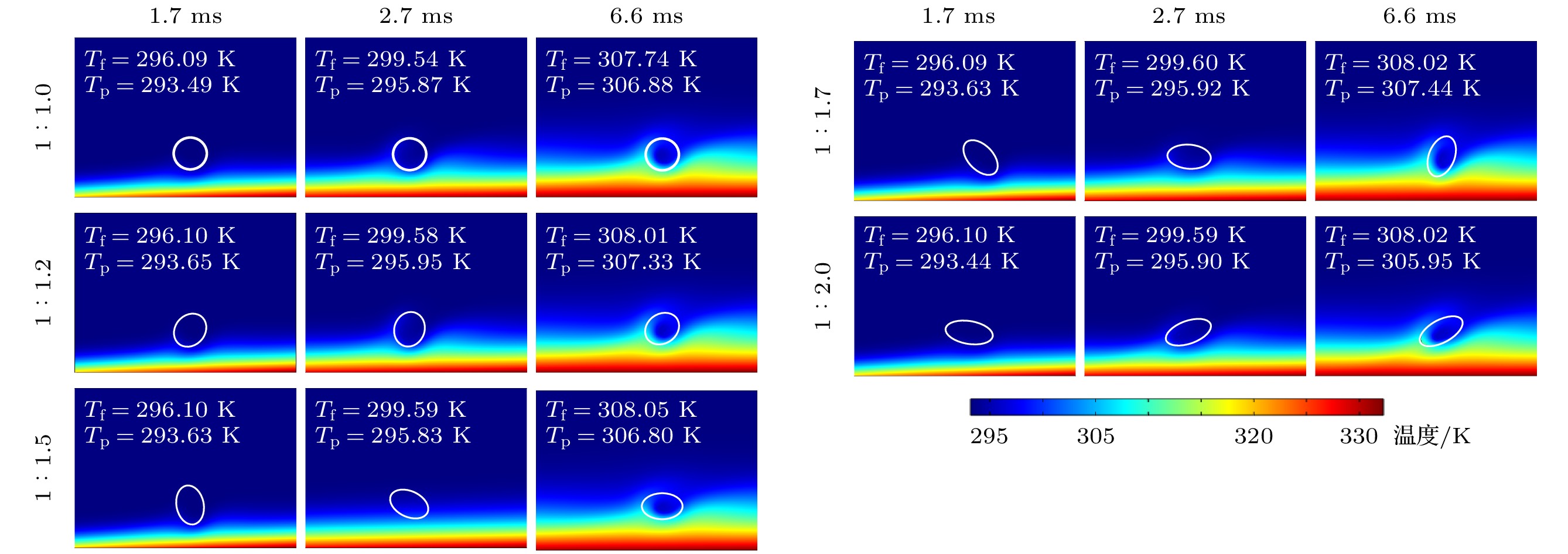
$ \Delta $ Tw in 1.7 ms; (b)$ {\Delta } $ Tw in 2.7 ms; (c)$ \Delta $ Tw in 6.6 ms; (d) phase change microcapsule migration and spin.表 1 基液及相变胶囊、普通颗粒的物性参数
Table 1. Thermophysical properties of the base fluid and particle.
材料 ρ/(kg·m–3) Cp/(J·kg–1·K–1) k/(W·m–1·K–1) μ/(10–3 Pa·s) hsf/(kJ·kg–1) 水 998.2 4189 0.599 1.005 — 相变胶囊 1094 (1)式 0.1644 — 241 普通颗粒 1094 1893.04 0.1644 — — -
[1] Zhang Y, Ding B, Zhao D Y, Zhao S, Gong L 2023 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 201 123566
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xiu L 2019 IEEE Solid-State Circuits Magazine 11 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang Q, Deng K, Wilkens L, Reith H, Nielsch K 2022 Nat. Electron. 5 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ding B, Feng W C, Fang J, Li S Z, Gong L 2022 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 184 122272
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ding B, Feng W C, Mu M F, Gong L, Li L 2023 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 203 123773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 黄豪杰, 钱吉裕, 魏涛 2022 中国电子科学研究院学报 17 842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang H J, Qian J Y, Wei T 2022 J. Chin. Acad. Electron. Sci. 17 842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Vinoth R, Sachuthananthan B 2021 Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 123 105194
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hou T, Chen Y 2020 Chem. Eng. Process 153 107931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhang F, Wu B, Du B 2022 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 172 107357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Alnaimat F, Varghese D, Mathew B 2022 Int. J. Thermo. fluids 16 100213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Roumpea E, Kovalchuk N M, Chinaud M, Nowak E, Simmons M J H, Angeli P 2019 Chem. Eng. Sci. 195 507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liang C P, Ture F, Dai Y J, Wang R Z, Ge T S 2021 Energy Build. 231 110622
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Chen Z, Qian P, Huang Z, Zhang W, Liu M 2023 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 183 107840
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sarafraz M M, Arjomandi M 2018 Appl. Therm. Eng. 137 700
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Martínez V A, Vasco D A, García-Herrera C M, Ortega-Aguilera R 2019 Appl. Therm. Eng. 161 114130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 刘中淼, 孙其诚, 宋世雄, 史庆藩 2014 63 034702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z M, Sun Q C, Song S X, Shi Q P 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 034702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hetsroni G, Mosyak A, Pogrebnyak E 2002 Int. J. Multiph. Flow 28 1873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hashemi Z, Abouali O, Kamali R 2013 Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 65 235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu C, Tang S, Dong Y 2017 Appl. Math Mech. Engl. 38 1149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 段总样, 赵云华, 徐璋 2021 力学学报 53 2656
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan Z Y, Zhao Y H, Xu Z 2021 Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 53 2656
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 赵维维 2019 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Zhao W W 2019 M. S. Thesis (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[22] 崔智文, 王泽, 蒋新宇, 赵立豪 2022 力学进展 52 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui Z W, Wang Z, Jiang X Y, Zhao L H 2022 Adv. Mech. 52 623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Rao Y, Dammel F, Stephan P, Lin G 2007 Heat Mass Transf. 44 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 杨杰, 王艳 2020 农业装备与车辆工程 58 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang J, Wang Y 2020 Agric. Equip. Veh. Eng. 58 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5170
- PDF下载量: 181
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: