-
采用水热法制备了一系列稀土Dy3+, Tb3+, Eu3+掺杂的极性Gd2Te4O11(GTO)亚碲酸盐荧光粉. 对样品的物相结构、形貌和热稳定性等进行了表征, 测试了样品的发光性能. 结果显示, 所制样品均为单相, 呈短杆状形貌, 尺寸在微米量级, 热稳定性能良好. 对于GTO:Dy3+荧光粉, 在紫外光激发下的发光主要位于黄绿光区, 获得最强发光强度的掺杂浓度为2.5%, 色坐标为(0.39, 0.43); 荧光衰减曲线表明GTO:Dy3+样品发光寿命随着掺杂浓度增大逐渐减小, 与Dy3+离子间的交叉弛豫有关. 对于GTO:Eu3+荧光粉, 在紫外光激发下的发光主要位于红光和橙红光区, 其发射强度随着Eu3+掺杂浓度的增大而增强. 当掺杂浓度为10%时, 样品发光的色坐标为(0.62, 0.38), 位于橙红光区, 且样品的发光寿命几乎不受掺杂浓度影响. 对于GTO:Tb3+荧光粉, 随着Tb3+掺杂浓度的增大, 受Tb3+离子间交叉弛豫的影响, 荧光粉在紫外光激发下的发射从蓝紫区向黄绿光区转变; 其中, 当Tb3+浓度为0.5%时, 样品表现为白光发射, 色坐标为(0.33, 0.35), 显色指数达86. 变温荧光光谱测试结果显示, 上述荧光粉具有良好的发光热稳定性. 对三类荧光粉的内量子效率进行了测试, 其中GTO:Eu3+量子效率优于GTO:Dy3+和GTO:Tb3+, 各样品量子效率仍有较大提升空间.A series of rare earth Dy3+, Tb3+, Eu3+ singly doped Gd2Te4O11 (GTO) tellurite phosphors with intrinsic polarity are prepared by hydrothermal method. The phase structures, morphologies and thermal stabilities of these phosphors are characterized. Their luminescence properties are tested in detail. The results show that all those phosphors are crystalized into single phase of digadolinium tellurite with short rod-like shape. The maximum size in the axial direction is microns. The phosphor has good thermal stability. For the GTO:Dy3+, the fluorescence emission under UV excitation is mainly located in the yellow-green region. The optimal doping concentration corresponding to the strongest excitation and emission is 2.5%, and the CIE color coordinates are (0.39, 0.43). The fluorescence decay curve shows that the lifetime of the GTO:Dy3+ on 4F9/2 energy level decreases gradually with doping concentration of Dy3+ increasing, which may be related to the cross relaxation (CR) between Dy3+ ions. For the GTO:Eu3+, the fluorescence emission under UV excitation is mainly located in the red region and orange-red region. The emission intensity is enhanced with the doping concentration of Eu3+ increasing. When the doping concentration is 10%, the CIE color coordinates are (0.62, 0.38), which are located in the orange-red region with high color purity. The fluorescence lifetime of Eu3+ on 5D0 energy level is hardly affected by the change of Eu3+ doping concentration. For the GTO:Tb3+, with the increase of the Tb3+ concentration, the fluorescence emission under UV excitation changes from blue-violet region to yellow-green region, which can be ascribed to the influence of CR between Tb3+ ions. The fluorescence decay behavior reveals that the Tb3+ ions on 5D4 excited state may undergo energy transfer and reabsorption, which can deviate the fluorescence decay from the single exponential model. When the concentration of Tb3+ is 0.5%, the sample exhibits white light emission with the CIE color coordinates of (0.33, 0.35) and color rendering index of 86. The measurements of temperature-dependent emission spectra show that the above-mentioned phosphors have good luminescent thermal stability. The internal quantum efficiencies (IQEs) of those three types of phosphors are measured, and the IQE of GTO:Eu3+ is better than those of GTO:Dy3+ and GTO:Tb3+. There is still much room for improvement in the luminescent performance of all these phosphors. These phosphors have potential to be used in UV-excited white LEDs.
-
Keywords:
- rare earth tellurite oxosalt /
- phosphors /
- luminescent property /
- thermal stability
[1] McKittrick J, Shea-Rohwer L E 2014 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97 1327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fang M H, Bao Z, Huang W T, Liu R S 2022 Chem. Rev. 122 11474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 孙晓园, 范小暄, 何俊杰, 吕启松, 姜光远, 邓昀, 骆永石, 吴春雷 2020 发光学报 41 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun X Y, Fan X X, He J J, Lv Q S, Jiang G Y, Deng Y, Luo Y S, Wu C L 2020 Chin. J. Lumin. 41 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang X H, Lu Z M, Meng F B, Hu L, Xu X W, Lin J, Tang C C 2012 Mater. Lett. 79 292
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yu X F, Yuan D W, Mi X Y 2021 J. Alloys Compd. 857 157585
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 余阳, 刘自军, 陈乔乔, 戴能利, 李进延, 杨旅云 2013 62 017804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu Y, Liu Z J, Chen Q Q, Dai N L, Li J Y, Yang L Y 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 017804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Fang Y C, Huang X R, Juang Y D, Chu S Y 2012 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95 1613
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Christy A G, Mills S J, Kampf A R 2016 Mineral. Mag. 80 415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shannon R D 1976 Acta Crystallogr. 32 751
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Z Q, Qin Z T, Zeng L W, Liu J, Li G N, Li C M, Yang J, Capobianco J A, Tang J F 2022 Ceram. Int. 48 13960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] You P L, Yin G F, Chen X C, Yue B, Huang Z B, Liao X M, Yao Y D 2011 Opt. Mater. 33 1808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Jayasimhadri M, Ratnam B V, Jang K, Lee H S, Chen B J, Yi S S, Jeong J H, Moorthy L R 2010 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93 494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bedyal A K, Kumar V, Prakash R, Ntwaeaborwa O M, Swart H C 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 329 40
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ratnam B V, Jayasimhadri M, Jang K, Lee H S, Yi S S, Jeong J H 2010 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93 3857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gupta S K, Zuniga J P, Abdou M, Thomas M P, Goonatilleke M D A, Guiton B S, Mao Y B 2020 Chem. Eng. J. 379 122314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li W L, Chen Z Y, Zhang B, Zhao P J, Fan Y W 2022 J. Lumin. 246 118824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yu R J, Shin D S, Jang K W, Guo Y, Noh H M, Moon B K, Choi B C, Jeong J H, Yi S S 2014 Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. 125 458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sahu M K, Mula J 2019 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102 6087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 赵旺, 平兆艳, 郑庆华, 周薇薇 2018 67 247801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao W, Ping Z Y, Zheng Q H, Zhou W W 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 247801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang S Y, Wei D L, Zhu R, Huang Y L, Seo H J 2011 Ceram. Int. 37 3697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 李兆, 王永锋, 曹静, 吴坤尧, 王亚楠 2020 光谱学与光谱分析 40 3077
Li Z, Wang Y F, Cao J, Wu K Y, Wang Y N 2020 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 40 3077
[22] G. Blasse 1968 Phys. Lett. A 28 444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Mahakingam V, Mangiarini F, Vetrone F, Venkatramu V, Bettinelli M, Speghini A, Capobianco J A 2008 J. Phys. Chem. C 112 17745
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] McCamy C S 1992 Color Res. Appl. 17 142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wu Y F, Nien Y T, Wang Y J, Chen I G 2012 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95 1360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Kasturi S, Sivakumar V 2017 Mater. Chem. Front. 1 550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Rajendran M, Vaidyanathan S 2020 Chemistry Select 5 5128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 续卓, 郭竞渊, 熊正烨, 唐强, 高沐 2021 70 167801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu Z, Guo J Y, Xiong Z Y, Tang Q, Gao M 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 167801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Szpikowska-Sroka B, Pawlik N, Goryczka T, Bańczyk M, Pisarski W A 2017 J. Lumin. 188 400
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhang L L, Peng M Y, Dong G P, Qiu J R 2012 Opt. Mater. 34 1202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wen Z X, Li L J, Huang W J, Chen S Y, Lei L, Pang T, Guo H 2022 J. Lumin. 250 119095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kim G C, Park H L, Kim T W 2001 Mater. Res. Bull. 36 1603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Hua Y J, Zhang D W, Ma H P, Deng D G, Xu S Q 2016 RSC Adv. 6 113249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Meetei S D, Singh S D 2014 J. Lumin. 147 328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Liu C J, Zhou Z F, Zhang Y 2019 J. Alloy. Compd. 787 1158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Singh N S, Ningthoujam R S, Luwang M N, Singh S D, Vatsa R K 2009 Chem. Phys. Lett. 480 237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] 李瑛, 樊国栋, 阮方毅, 周建锋, 陈茜茜, 王拓 2022 硅酸盐学报 50 2501
Li Y, Fan G D, Ruan F Y, Zhou J F, Chen Q Q, Wang T 2022 J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 50 2501
-
图 1 (a)—(c) XRD图谱; (d) GTO沿[010]向的晶体结构; (e)稀土(RE)掺入 [GdO8]十二面体示意图; (f) Dy3+, Tb3+, Eu3+掺杂样品的DSC曲线
Fig. 1. XRD patterns of (a) GTO : Dy3+, (b) GTO : Tb3+ and (c) GTO : Eu3+; (d) view of the GTO crystal structure along [010]; (e) [GdO8] dodecahedron; (f) DSC curves of Dy3+, Tb3+ and Eu3+ doped samples.
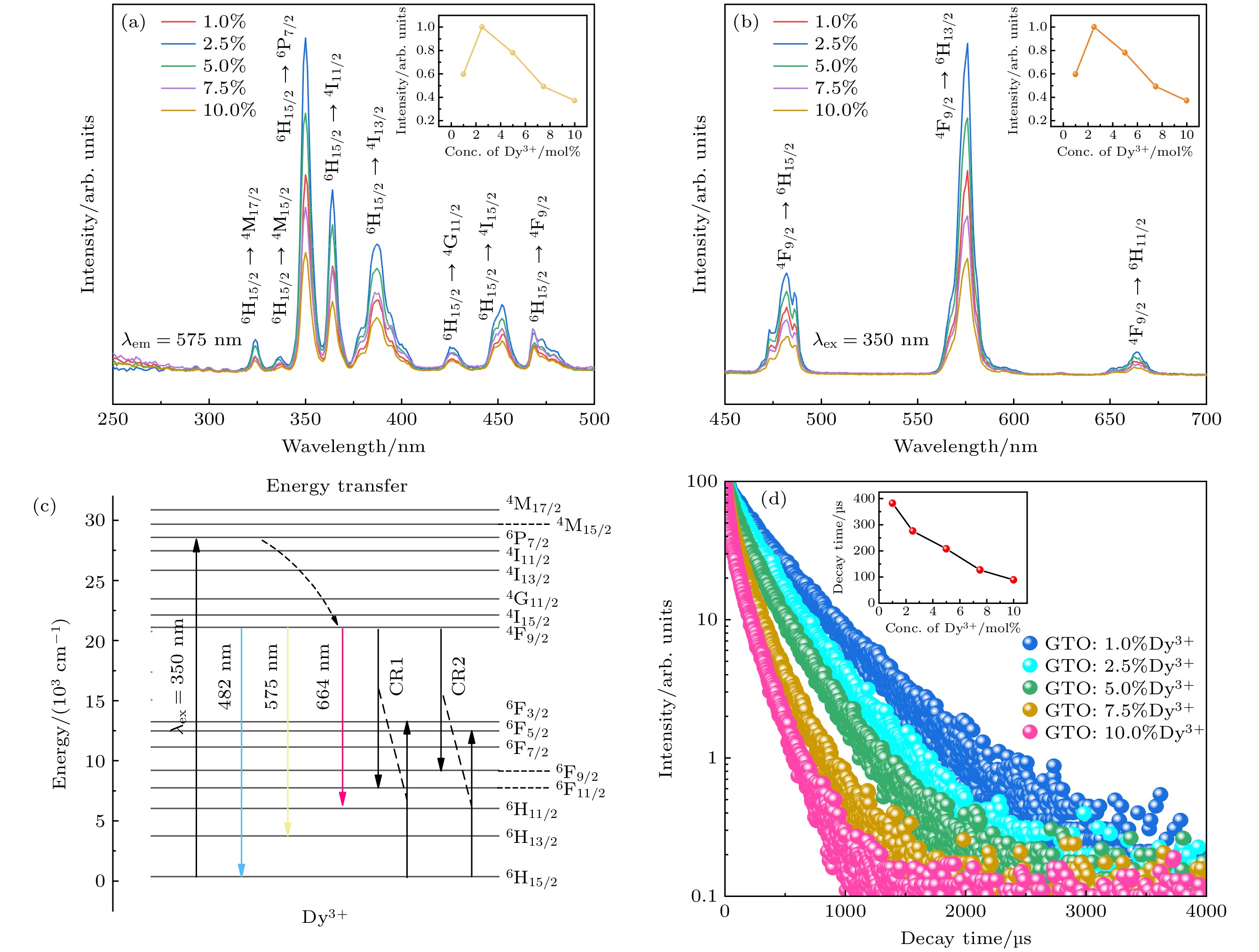
图 3 (a) 在575 nm监测下GTO:Dy3+的激发光谱图; (b) 在350 nm激发下GTO:Dy3+的发射光谱图, 插图为不同Dy3+含量荧光粉在575 nm处的荧光强度变化曲线图; (c) 跃迁示意图; (d) GTO:Dy3+荧光衰减曲线, 350 nm激发, 在575 nm监测, 插图为寿命随浓度变化曲线
Fig. 3. (a) Excitation spectra of GTO:Dy3+ monitored at 575 nm; (b) emission spectra of GTO:Dy3+ under 350 nm excitation, the inset shows the emission intensity around 575 nm versus concentration; (c) schematic diagram of transitions; (d) decay curves of GTO:Dy3+ samples monitored at 575 nm under excitation at 350 nm, inset shows the decay time changing with Dy3+ concentration.
图 4 (a) GTO:Dy3+荧光粉在350 nm激发下的色坐标, 插图为样品在365 nm紫外灯照射下的实物发光图; (b) 350 nm激发下, GTO:2.5% Dy3+的荧光变温光谱瀑布图; (c) 575 nm的发射峰积分强度与温度的关系折线图
Fig. 4. (a) The color coordinates of GTO:Dy3+ phosphor at 350 nm excitation. Inset shows the digital images of sample under 365 nm irradiation; (b) temperature dependence PL spectra of GTO:2.5% Dy3+ under 350 nm; (c) integrated intensity of 575 nm emission peak at different temperatures.
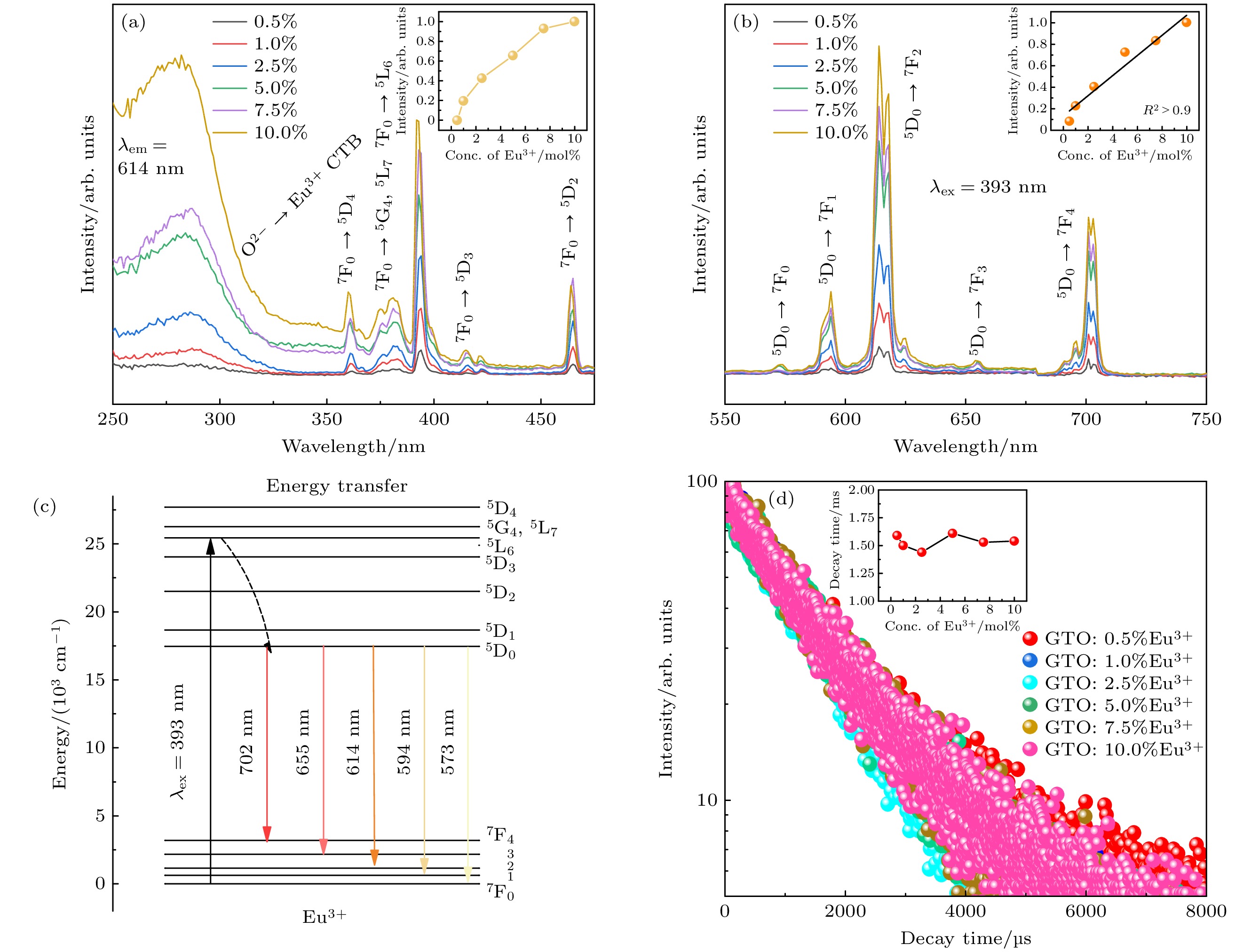
图 5 (a) GTO:Eu3+在614 nm监测下的激发光谱图; (b) GTO:Eu3+在393 nm激发下的发射光谱图, 插图为614 nm处的荧光强度随Eu3+掺杂浓度变化线性拟合结果; (c) Eu3+能级跃迁示意图; (d) GTO:Eu3+在614 nm处监测得到的荧光衰减曲线, 插图表示寿命变化曲线
Fig. 5. (a) Excitation spectra of GTO:Eu3+ phosphors, monitored at 614 nm; (b) emission spectra of GTO:Eu3+ phosphor under 393 nm excitation, the inset shows the linear fitting of emission intensity around 614 nm versus concentration; (c) schematic diagram of transition; (d) decay curves of GTO:Eu3+ samples monitored at 614 nm, inset shows the decay time changing with Eu3+ concentration.
图 6 (a) GTO:x% Eu3+(x = 0.5—10)在350 nm激发下的色坐标; (b) GTO:7.5% Eu3+在393 nm激发下的变温发射光谱图; (c) 614 nm发射峰强度随温度变化曲线
Fig. 6. (a) The color coordinates of GTO:x% Eu3+( x = 0.5–10) phosphor at 350 nm excitation; (b) temperature dependent PL spectra of GTO:7.5% Eu3+ under 393 nm; (c) integrated intensity of 614 nm emission peak at different temperatures.
图 7 (a) GTO:Tb3+荧光粉的激发光谱图; (b) GTO:Tb3+荧光粉的发射光谱图; (c) Tb3+离子能级跃迁示意图; (d)Tb3+荧光衰减曲线, 监测波长为548 nm, 插图表示寿命变化情况
Fig. 7. (a) Excitation spectra of GTO:Tb3+ phosphors; (b) emission spectra of GTO:Tb3+ phosphor; (c) schematic diagram of transitions of Tb3+; (d) decay curves of GTO:Tb3+ samples, monitored at 548 nm, inset shows the decay time changing with Tb3+ concentration.
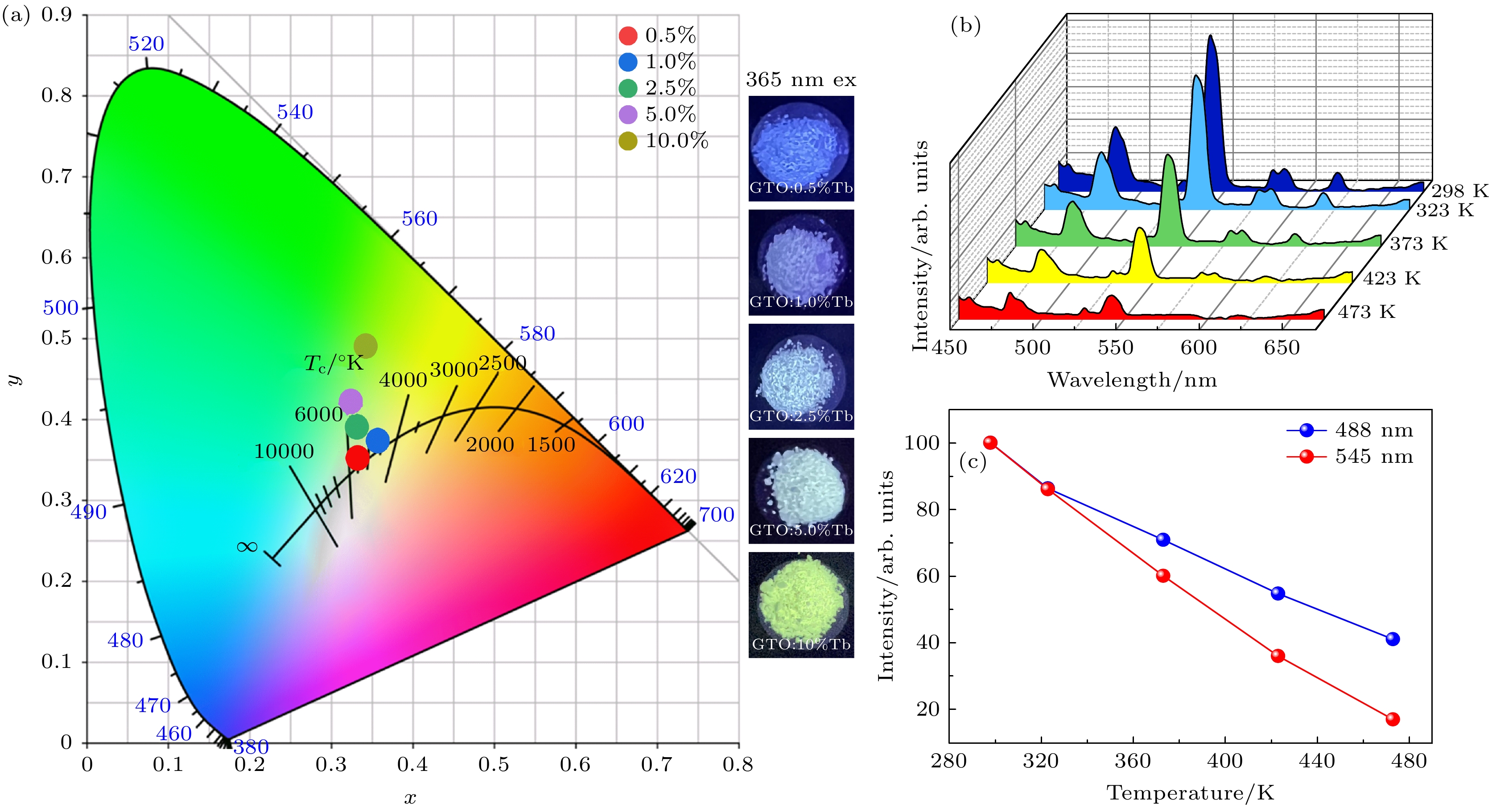
图 8 (a) GTO:x%Tb3+(x = 0.5—10)荧光粉在377 nm激发下的色坐标; (b) 377 nm激发下, GTO:10%Tb的荧光变温光谱图; (c) 488 nm和545 nm的归一化发射峰强度与温度的关系折线图
Fig. 8. (a) The color coordinates of GTO:x% Tb3+( x = 0.5–10) phosphor under 377 nm excitation; (b) temperature dependence emission spectra of GTO:7.5% Eu under 393 nm; (c) integrated intensity of 614 nm emission peak at different temperatures.
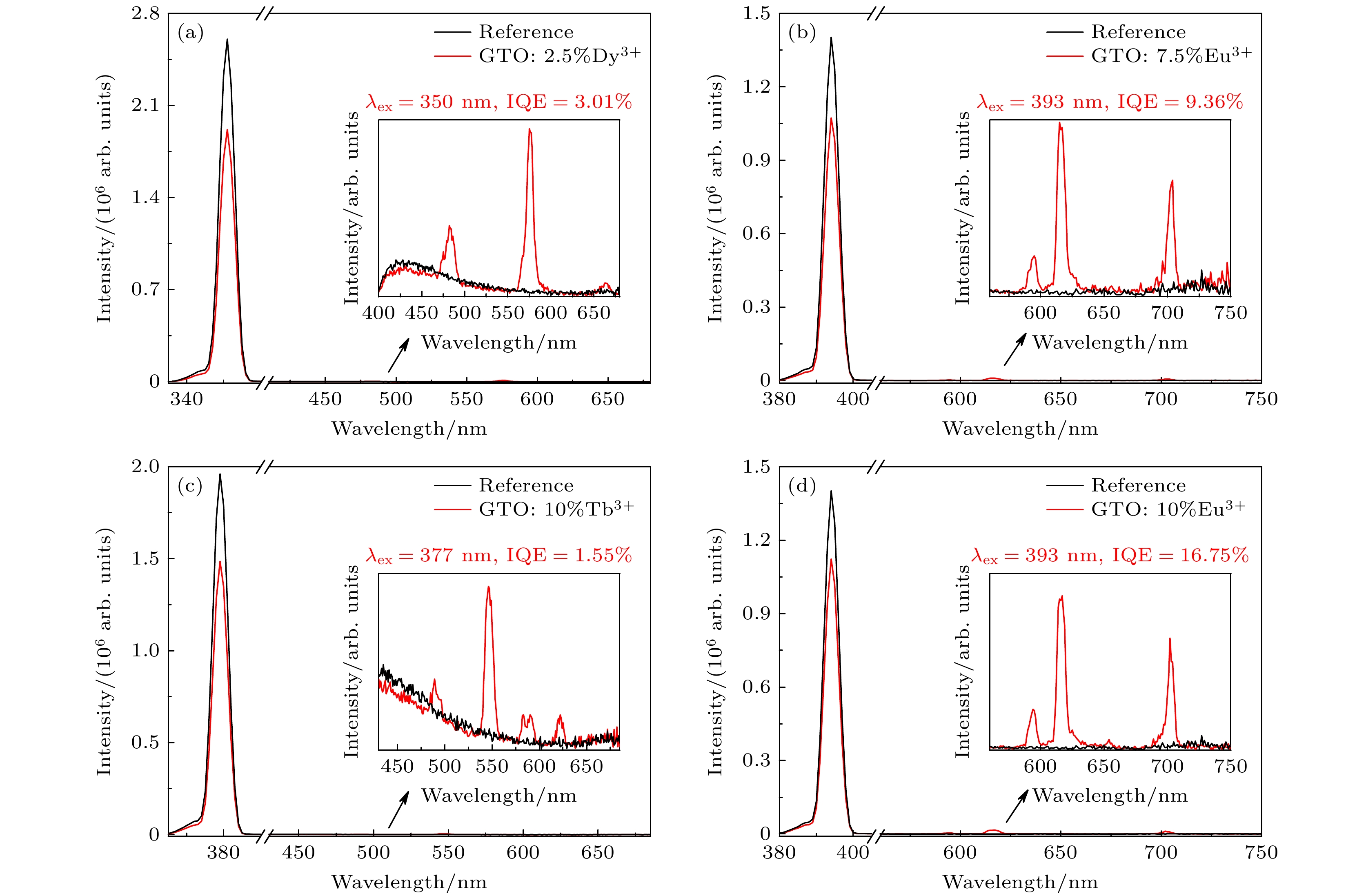
图 9 荧光量子产率测试光谱图 (a) GTO:2.5% Dy3+; (b) GTO:7.5% Eu3+; (c) GTO:10% Tb3+; (d) GTO:10% Eu3+. 黑色线表示空白样发射光谱, 红色线表示样品发射光谱, 插图为各样品发光波段光谱的放大显示
Fig. 9. Fluorescence spectra of phosphors for quantum efficiency measurement: (a) GTO:2.5% Dy3+; (b) GTO:7.5% Eu3+; (c) GTO:10% Tb3+; (d) GTO:10% Eu3+. The spectrum of reference is depicted in black and the spectrum of sample is depicted in red. Insets show the amplification of emission spectra.
表 1 不同材料的发光热稳定性对比
Table 1. Comparison of luminescent thermal stability of different materials.
表 2 GTO:Eu3+的CIE色参数
Table 2. CIE parameters of GTO:Eu3+ with different Eu3+ doping concentration.
掺杂浓度 CIE色坐标 色温/K 色纯度/% 0.5 (0.53, 0.45) 2197 93.96 1.0 (0.56, 0.43) 1857 96.70 2.5 (0.59, 0.40) 1631 97.17 5.0 (0.60, 0.39) 1621 97.14 7.5 (0.62, 0.37) 1752 97.56 10.0 (0.62, 0.38) 1689 98.51 表 3 Tb3+离子5D4能级荧光衰减寿命拟合值(μs)与平均寿命(μs)
Table 3. Fitting values of lifetimes (μs) and average lifetimes(μs) of Tb3+ on 5D4 energy level.
A1 τ1 A2 τ2 A3 τ3 平均荧光寿命 GTO:0.5%Tb3+ 18.9 7.5 69.4 46.9 11.0 180.8 95.4 GTO:1.0%Tb3+ 8.2 3.2 82.3 47.6 9.0 226.4 108.4 GTO:2.5%Tb3+ 34.6 6.6 52.2 48.3 14.1 199.7 123.2 GTO:5.0%Tb3+ 41.5 7.1 46.2 51.3 13.5 214.8 134.2 GTO:10%Tb3+ 21.5 3.9 69.7 48.2 7.3 358.7 181.6 -
[1] McKittrick J, Shea-Rohwer L E 2014 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97 1327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fang M H, Bao Z, Huang W T, Liu R S 2022 Chem. Rev. 122 11474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 孙晓园, 范小暄, 何俊杰, 吕启松, 姜光远, 邓昀, 骆永石, 吴春雷 2020 发光学报 41 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun X Y, Fan X X, He J J, Lv Q S, Jiang G Y, Deng Y, Luo Y S, Wu C L 2020 Chin. J. Lumin. 41 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang X H, Lu Z M, Meng F B, Hu L, Xu X W, Lin J, Tang C C 2012 Mater. Lett. 79 292
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yu X F, Yuan D W, Mi X Y 2021 J. Alloys Compd. 857 157585
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 余阳, 刘自军, 陈乔乔, 戴能利, 李进延, 杨旅云 2013 62 017804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu Y, Liu Z J, Chen Q Q, Dai N L, Li J Y, Yang L Y 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 017804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Fang Y C, Huang X R, Juang Y D, Chu S Y 2012 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95 1613
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Christy A G, Mills S J, Kampf A R 2016 Mineral. Mag. 80 415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shannon R D 1976 Acta Crystallogr. 32 751
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang Z Q, Qin Z T, Zeng L W, Liu J, Li G N, Li C M, Yang J, Capobianco J A, Tang J F 2022 Ceram. Int. 48 13960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] You P L, Yin G F, Chen X C, Yue B, Huang Z B, Liao X M, Yao Y D 2011 Opt. Mater. 33 1808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Jayasimhadri M, Ratnam B V, Jang K, Lee H S, Chen B J, Yi S S, Jeong J H, Moorthy L R 2010 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93 494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bedyal A K, Kumar V, Prakash R, Ntwaeaborwa O M, Swart H C 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 329 40
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ratnam B V, Jayasimhadri M, Jang K, Lee H S, Yi S S, Jeong J H 2010 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93 3857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gupta S K, Zuniga J P, Abdou M, Thomas M P, Goonatilleke M D A, Guiton B S, Mao Y B 2020 Chem. Eng. J. 379 122314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li W L, Chen Z Y, Zhang B, Zhao P J, Fan Y W 2022 J. Lumin. 246 118824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yu R J, Shin D S, Jang K W, Guo Y, Noh H M, Moon B K, Choi B C, Jeong J H, Yi S S 2014 Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. 125 458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sahu M K, Mula J 2019 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102 6087
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 赵旺, 平兆艳, 郑庆华, 周薇薇 2018 67 247801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao W, Ping Z Y, Zheng Q H, Zhou W W 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 247801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang S Y, Wei D L, Zhu R, Huang Y L, Seo H J 2011 Ceram. Int. 37 3697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 李兆, 王永锋, 曹静, 吴坤尧, 王亚楠 2020 光谱学与光谱分析 40 3077
Li Z, Wang Y F, Cao J, Wu K Y, Wang Y N 2020 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 40 3077
[22] G. Blasse 1968 Phys. Lett. A 28 444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Mahakingam V, Mangiarini F, Vetrone F, Venkatramu V, Bettinelli M, Speghini A, Capobianco J A 2008 J. Phys. Chem. C 112 17745
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] McCamy C S 1992 Color Res. Appl. 17 142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wu Y F, Nien Y T, Wang Y J, Chen I G 2012 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95 1360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Kasturi S, Sivakumar V 2017 Mater. Chem. Front. 1 550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Rajendran M, Vaidyanathan S 2020 Chemistry Select 5 5128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 续卓, 郭竞渊, 熊正烨, 唐强, 高沐 2021 70 167801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu Z, Guo J Y, Xiong Z Y, Tang Q, Gao M 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 167801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Szpikowska-Sroka B, Pawlik N, Goryczka T, Bańczyk M, Pisarski W A 2017 J. Lumin. 188 400
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhang L L, Peng M Y, Dong G P, Qiu J R 2012 Opt. Mater. 34 1202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wen Z X, Li L J, Huang W J, Chen S Y, Lei L, Pang T, Guo H 2022 J. Lumin. 250 119095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kim G C, Park H L, Kim T W 2001 Mater. Res. Bull. 36 1603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Hua Y J, Zhang D W, Ma H P, Deng D G, Xu S Q 2016 RSC Adv. 6 113249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Meetei S D, Singh S D 2014 J. Lumin. 147 328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Liu C J, Zhou Z F, Zhang Y 2019 J. Alloy. Compd. 787 1158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Singh N S, Ningthoujam R S, Luwang M N, Singh S D, Vatsa R K 2009 Chem. Phys. Lett. 480 237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] 李瑛, 樊国栋, 阮方毅, 周建锋, 陈茜茜, 王拓 2022 硅酸盐学报 50 2501
Li Y, Fan G D, Ruan F Y, Zhou J F, Chen Q Q, Wang T 2022 J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 50 2501
计量
- 文章访问数: 6384
- PDF下载量: 105
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: