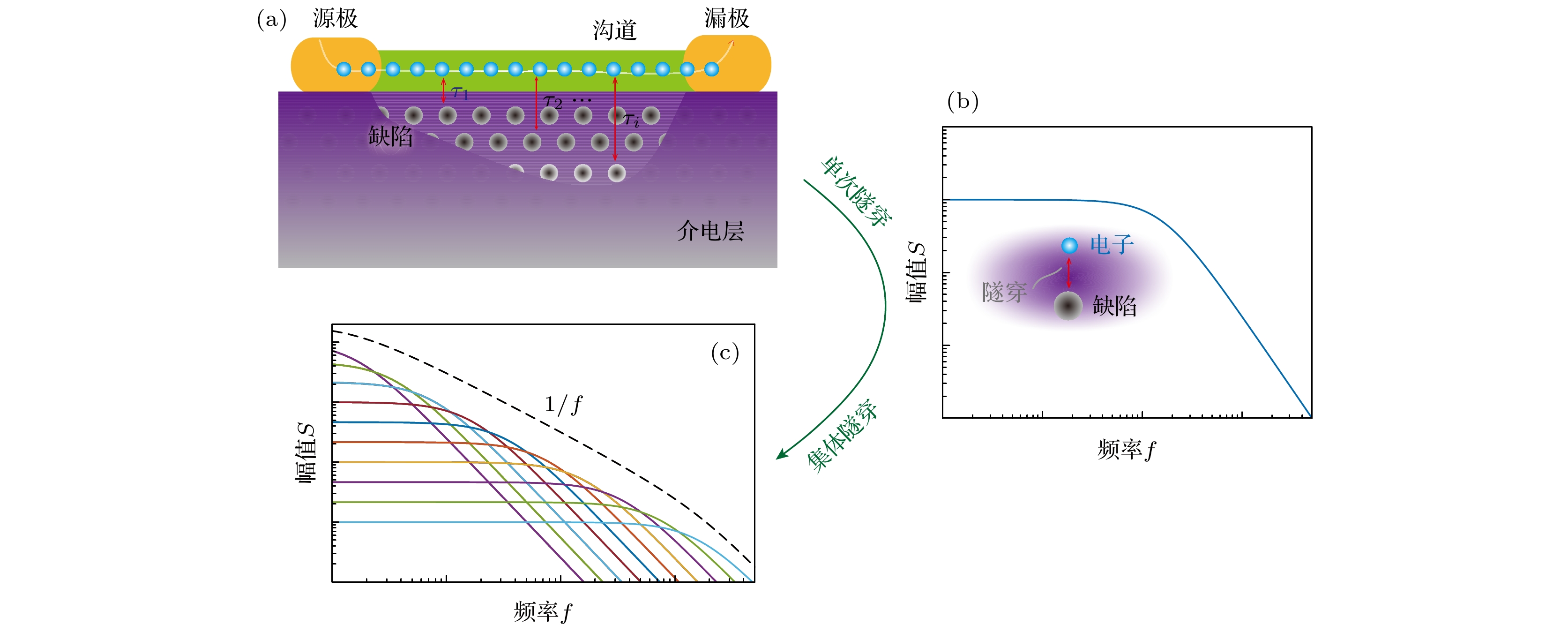
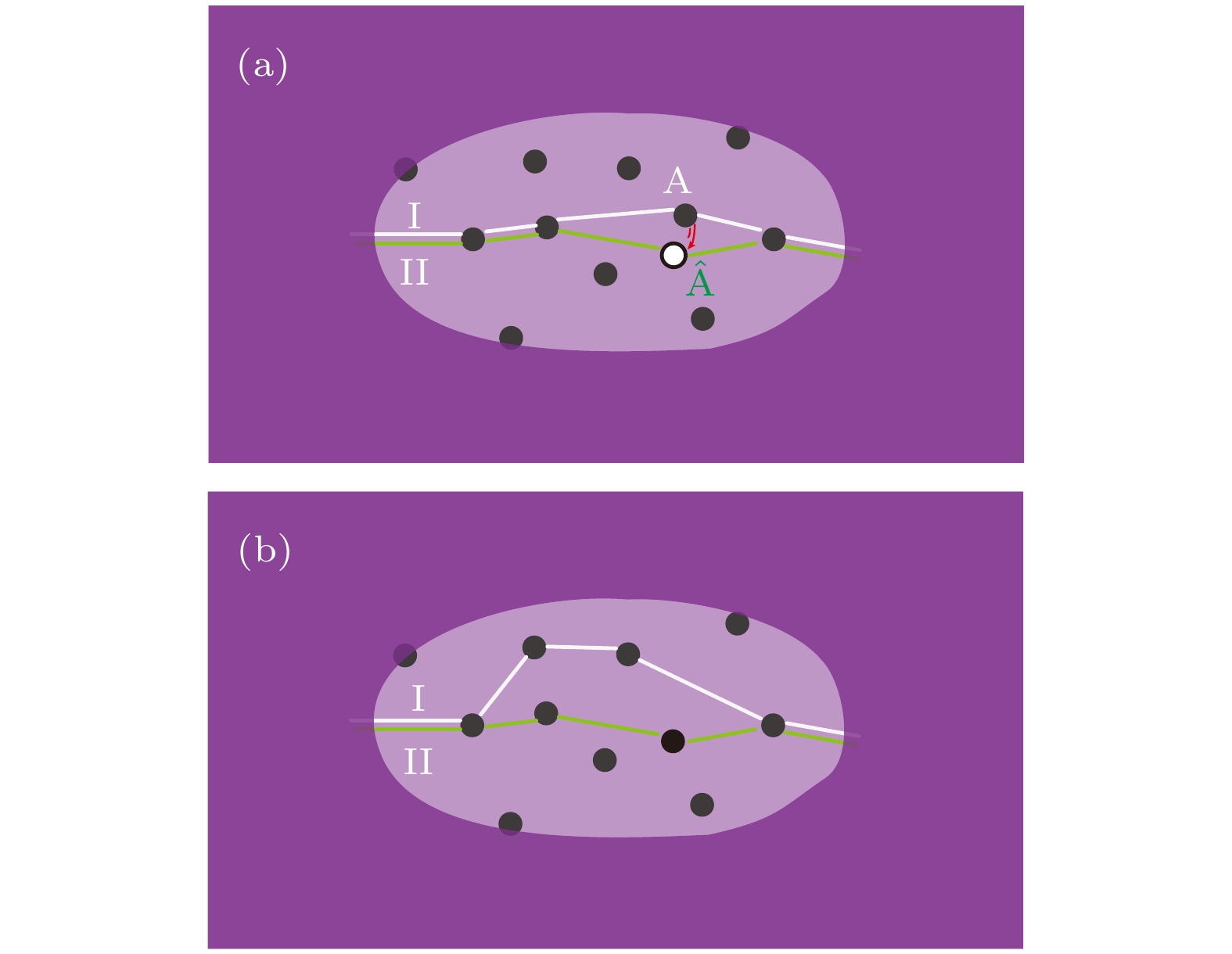
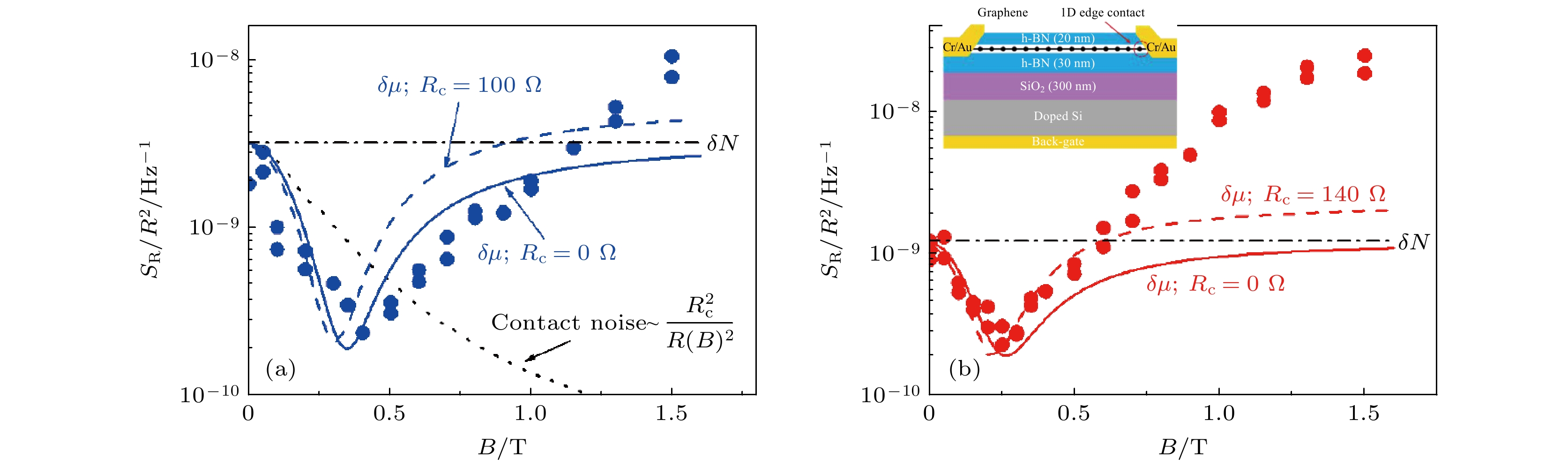
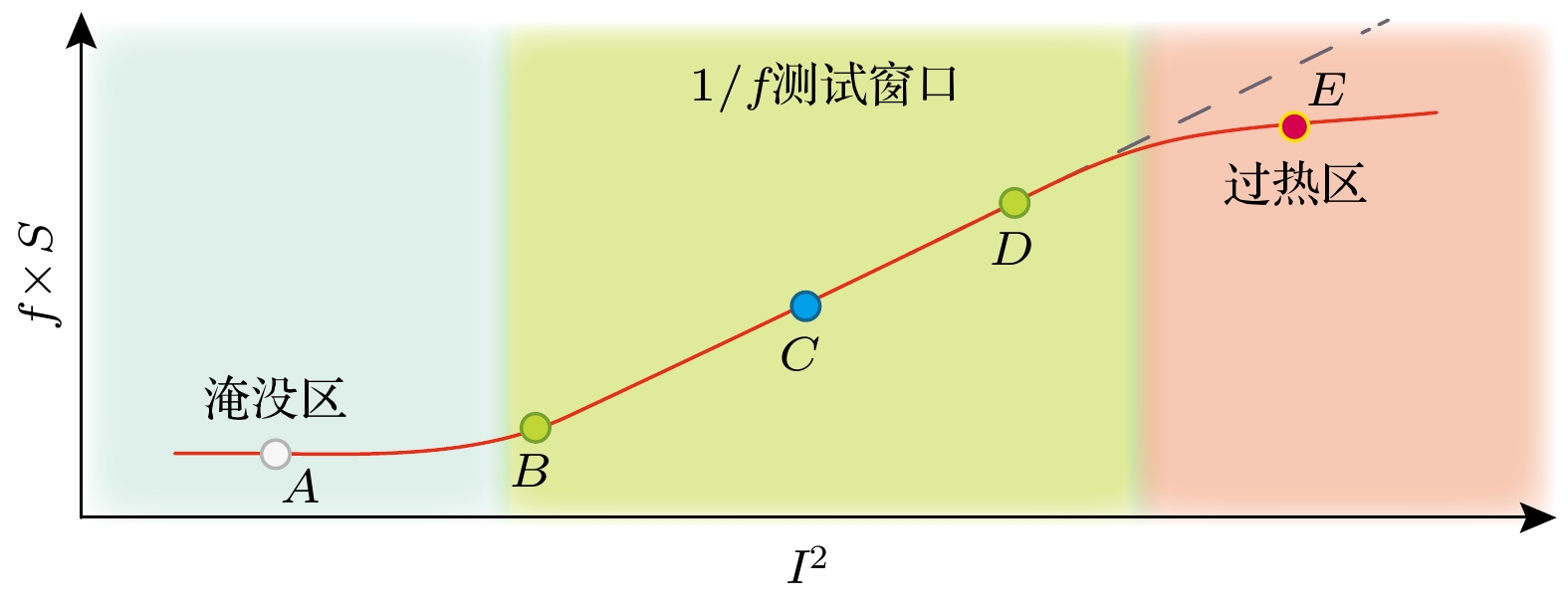
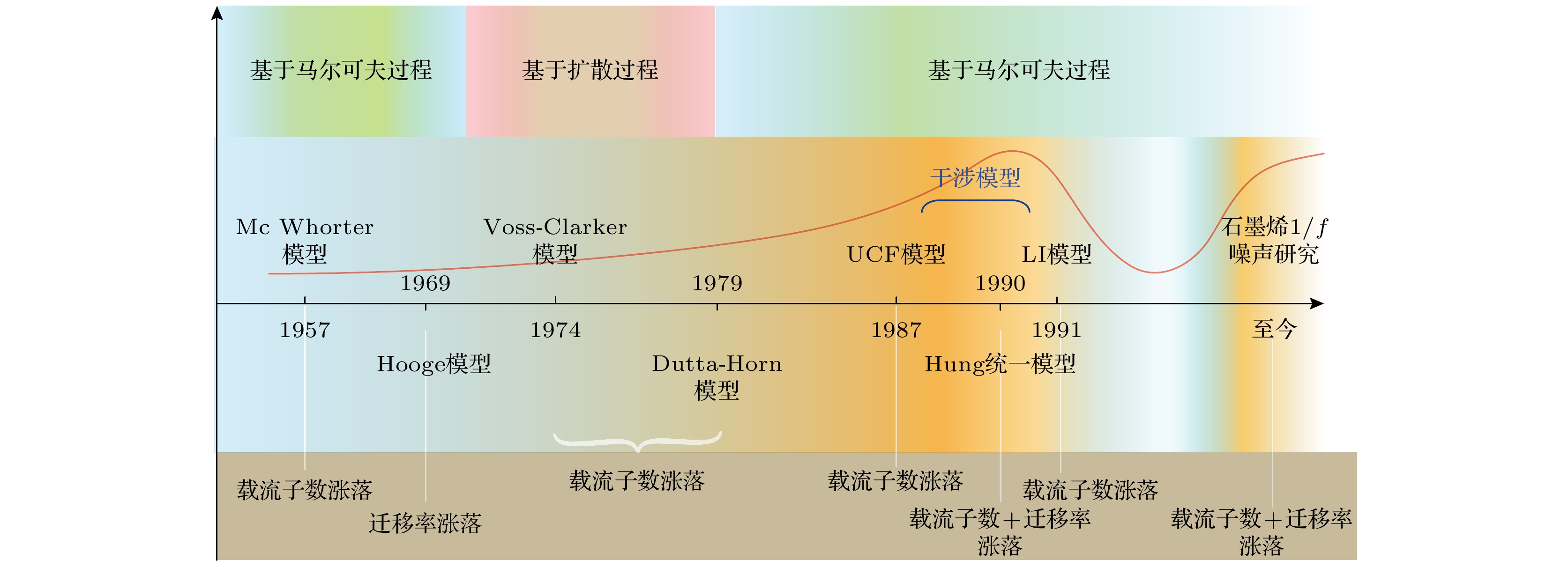
-
1/f噪声具有丰富的物理内涵, 既是科学研究的量化工具, 也是电子器件重要性能指标. 本文从通用数学形式和物理背景两个方面归纳总结1/f噪声模型. 首先介绍了基于马尔可夫过程和基于扩散过程的1/f噪声通用数学模型. 在此基础上, 溯源1/f噪声物理模型的发展历程, 总结五类典型物理模型, 包括Mc Whorter模型、Hooge模型、Voss-Clarker模型、Dutta-Horn模型、干涉模型以及Hung统一模型. 二维材料石墨烯让1/f噪声研究重归学术热点, 本文梳理了当前石墨烯1/f噪声研究中形成的共识性研究成果, 提出石墨烯低频噪声研究的三层次分类分析模型, 分析了不同层面噪声机理研究代表性成果, 归纳总结了各层面可能的主导机制. 通过比较不同团队报道的石墨烯1/f噪声栅极调控特征谱型及测试条件, 分析了复杂多变栅控谱型形成原因. 基于分析结论, 为避免非本征噪声干扰, 提出了石墨烯本征背景1/f噪声规范性测量方案, 为厘清和揭示石墨烯1/f噪声机制及特性探索可行技术途径.Noise is a signal. Low-frequency noise with a 1/f-type spectral density (1/f noise) has been observed in a wide variety of systems. There are plenty of physical processes under the 1/f noise phenomenon. It is not only a useful tool for scientific research, but also a quantitative probe for the performance of electronic devices. In this paper, the 1/f noise models are summarized from the general mathematical forms to physical processes. Based on Markov process and diffusion process, two general mathematical models of 1/f noise are introduced respectively. On this basis, tracing the development history, several typical physical models are described, including Mc Whorter model, Hooge model, Voss-Clarker model, Dutta-horn model, interference model and unified Hung model. The advent of the two-dimensional material graphene offers unique opportunities for studying the mechanism of 1/f noise. In the fact of the cloudy and even contradictory conclusions from different reports, this paper combs the consensus accepted widely. An analysis model based on three-level classification for the graphene low-frequency noise study is built, which divides the noise into intrinsic background 1/f noise, 1/f-like noise and Lorentz-like noise. Typical research on the related mechanism at each level is analyzed, and the dominant mechanisms are summarized. Further, we focus on the gate-modulated characteristic spectrum shape of 1/f noise from different reported experiments, which may be a key to the material internal scattering mechanism and charge distribution. The experimental measurements show that the characteristic shape is variable, and mainly exists in three forms: V-type, Λ-type and M-type. Through the comparative analysis of graphene cleanliness, bias current (voltage) and other experimental parameters, the possible causes of the complexity and variability of the characteristic shape are analyzed, showing that the main reason may be that the experimental parameters are not strictly controlled, and the selection of measuring point is unreasonable. In order to capture the accurate noise characteristics and reveal the noise mechanism clearly, a standard 1/f noise measurement paradigm is proposed in this work to guide the effective research on graphene 1/f noise and the distinction betweenintrinsic noise and extrinsic noise. The standard paradigm includes three processes. The first process is to prepare suspended graphene samples, the second one is to remove the surface contamination by using the methods such as current annealing, and the third one is to test the curve of the 1/f noise amplitude versus the bias voltage or current. Based on this curve, suitable test points can be selected for different measurement schemes. The proposed standard intrinsic background 1/f noise measurement paradigm may be expected to clarify and reveal the characteristics of graphene 1/f noise.
-
Keywords:
- 1/f noise /
- noise mechanism /
- graphene /
- characteristic spectrum shape
[1] Vandamme L, Hooge F 2005 Phys. B Condens. Matter 357 507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wilamowski B M, Irwin J D 2011 Fundamentals of Industrial Electronics: The Industrial Electronics Handbook (1st Ed.) (CRC Press) p11
[3] Liu G, Stillman W, Rumyantsev S, Shur M, Balandin A A 2011 Int. J. High Speed Electron. Syst. 20 161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Johnson J B 1925 Phys. Rev. 26 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Voss R F, Clarke J 1975 Nature 258 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Daniel A 2015 Ph D Dissertation (Nottingham: The University of Nottingham)
[7] 庄奕琪, 马中发, 杜磊 1999 世界科技研究与发展 21 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhuang Y Q, Ma Z F, Du L 1999 World Sci-Tech R. D. 21 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Dutta P, Dimon P, Horn P 1979 Phys. Rev. Lett. 43 646
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Clarke J, Voss R F 1974 Phys. Rev. Lett. 33 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Burstein E, McWhorter A L, Miller P H, Stevenson D T, Weisz P B 1957 Semiconductor Surface Physics (University of Pennsylvania Press) p207
[11] Hooge F, Kleinpenning T, Vandamme L 1981 Rep. Prog. Phys. 44 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hooge F 1972 Physica 60 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hung K K, Ko P K, Hu C, Cheng Y C 1990 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 37 1323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Peransin J, Vignaud P, Rigaud D, Vandamme L K J 1990 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 37 2250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pellegrini B 1988 Phys. Rev. B 38 8279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Dmitriev A P, Levinshtein M E, Rumyantsev S L, Shur M S 2005 J. Appl. Phys. 97 123706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu Y, Tan Z, Kumar M, Abhilash T S, Liu G J, Hakonen P 2018 APL Mater. 6 091102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 杜磊, 庄奕琪, 薛丽君 2002 51 2836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du L, Zhuang Y Q, Xue L J 2002 Acta Phys. Sin. 51 2836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Song X X, Li H O, You J, Han T Y, Cao G, Tu T, Xiao M, Guo G C, Jiang H W, Guo G P 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 8142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Paladino E, Galperin Y M, Falci G, Altshuler B L 2014 Rev. Mod. Phys. 86 361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Dutta P, Horn P 1981 Rev. Mod. Phys. 53 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Macdonald K C, Lindsay R B 1963 Phys. Today 16 74
[23] Landauer R 1998 Nature 392 658
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kogan S 2008 Electronic Noise and Fluctuations in Solids (Cambridge University Press) pp24
[25] Surdin M 1939 J. Phys. Radium 10 188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] M. Richardson J 1950 Bell Syst. Tech. J. 29 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Weissman M B 1975 Phys. Rev. Lett. 35 689
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Kirton M J, Uren M J 1989 Adv. Phys. 38 367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Hooge F N 1994 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 41 1926
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Voss R F, Clarke J 1976 Phys. Rev. Lett. 36 42
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Voss R F, Clarke J 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 556
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Hershfield S 1988 Phys. Rev. B 37 8557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Raychaudhuri A K 2002 Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 6 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Pelz J, Clarke J 1987 Phys. Rev. B 36 4479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Ralls K S, Buhrman R A 1991 Phys. Rev. B 44 5800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Hung K K, Ko P K, Hu C, Cheng Y C 1990 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 37 654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Koga J, Takagi S, Toriumi A Proceedings of 1994 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA 11-14 Dec. 1994 pp475–478
[38] Vandamme E P, Vandamme L K 2000 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 47 2146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Xi'an: Xidian University) 张鹏 2010 博士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学
Zhang P 2010 Ph. D. Dissertation (in Chinese)
[40] Lin Y-M, Avouris P 2008 Nano Lett. 8 2119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Heller I, Chatoor S, Männik J, Zevenbergen M A, Oostinga J B, Morpurgo A F, Dekker C, Lemay S G 2010 Nano Lett. 10 1563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Liu G, Stillman W, Rumyantsev S, Shao Q, Shur M, Balandin A 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 033103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Chen Z, Lin Y M, Rooks M J, Avouris P 2007 Phys. E (Amsterdam, Neth. ) 40 228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Kumar M, Laitinen A, Cox D, Hakonen P J 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 106 263505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Rumyantsev S, Liu G, Stillman W, Shur M, Balandin A A 2010 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 22 395302 7
[46] Liu G X, Rumyantsev S, Shur M S, Balandin A A 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 093111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Zhang Y, Mendez E E, Du X 2011 ACS nano 5 8124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Cheng Z, Li Q, Li Z, Zhou Q, Fang Y 2010 Nano Lett. 10 1864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Zahid Hossain M, Rumyantsev S, Shur M S, Balandin A A 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 153512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Rehman A, Delgado Notario J A, Salvador Sanchez J, Meziani Y M, Cywiński G, Knap W, Balandin A A, Levinshtein M, Rumyantsev S 2022 Nanoscale 14 7242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Kamada M, Laitinen A, Zeng W, Will M, Sarkar J, Tappura K, Seppä H, Hakonen P 2021 Nano Lett. 21 7637
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Pal A N, Ghatak S, Kochat V, Sneha E, Sampathkumar A, Raghavan S, Ghosh A 2011 ACS Nano 5 2075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Kaverzin A A, Mayorov A S, Shytov A, Horsell D W 2012 Phys. Rev. B 85 075435 5
[54] Macucci M, Marconcini P 2020 J. Sens. 2020 2850268
[55] Pellegrini B, Marconcini P, Macucci M, Fiori G, Basso G 2016 J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2016 054017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Pellegrini B 2013 Eur. Phys. J. B 86 373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[57] Rumyantsev S, Liu G X, Shur M S, Potyrailo R A, Balandin A A 2012 Nano Lett. 12 2294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[58] Kazi R A, Aveek B 2014 Curr. Sci. India 107 430
[59] Cui Y, Liu Y M, Yu J C, Hayasaka T, Li X Q, Cai W H, Liu H L, Lin L W 2017 Ieee 19th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Taiwan China pp246–249
[60] Xu G, Torres C M, Jr., Zhang Y, Liu F, Song E B, Wang M, Zhou Y, Zeng C, Wang K L 2010 Nano Lett. 10 3312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[61] Takeshita S, Matsuo S, Tanaka T, Nakaharai S, Tsukagoshi K, Moriyama T, Ono T, Arakawa T, Kobayashi K 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 103106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[62] Arnold H N, Sangwan V K, Schmucker S W, Cress C D, Luck K A, Friedman A L, Robinson J T, Marks T J, Hersam M C 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 073108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[63] Kayyalha M, Chen Y P 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 113101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[64] Stolyarov M A, Liu G, Rumyantsev S L, Shur M, Balandin A A 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 023106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[65] Karnatak P, Sai T P, Goswami S, Ghatak S, Kaushal S, Ghosh A 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 13703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[66] Mavredakis N, Garcia Cortadella R, Bonaccini Calia A, Garrido J A, Jiménez D 2018 Nanoscale 10 14947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
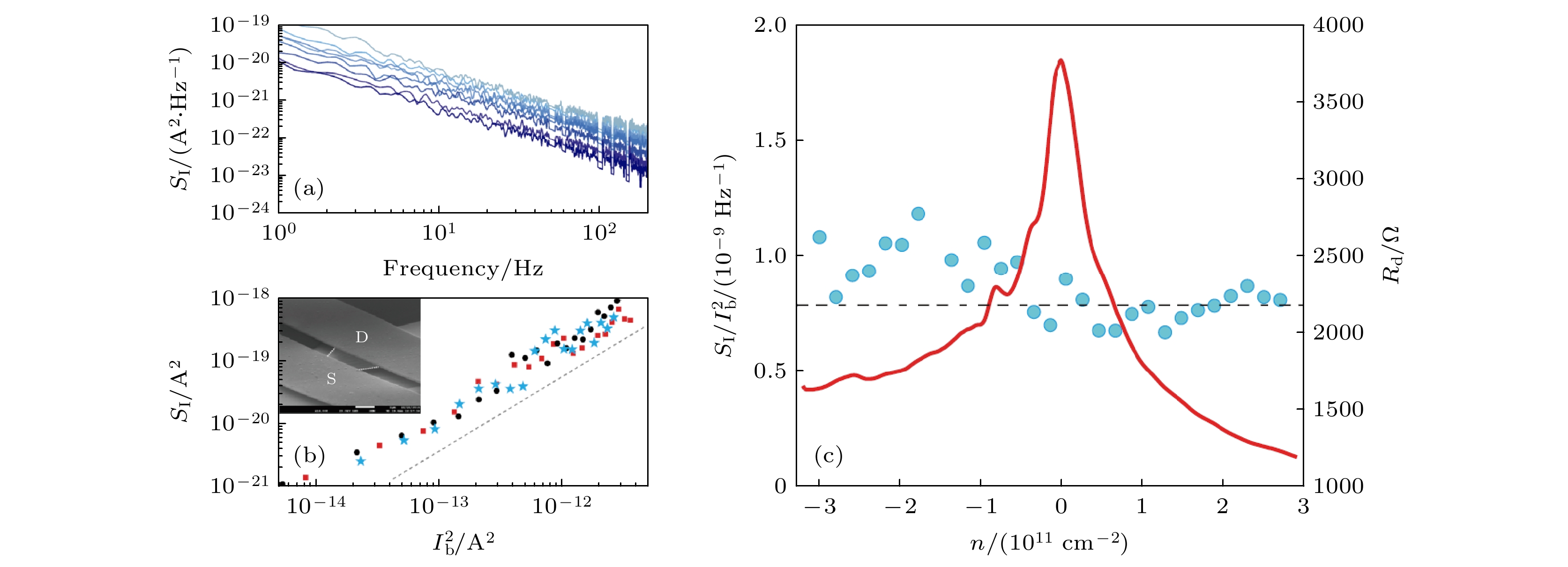
图 7 (a)石墨烯晶体管及两种噪声机制示意图; (b)不同载流子浓度下时域电导涨落; (c)不同栅压下典型电导归一化噪声功率谱; (d)1 Hz处噪声幅值的栅极调控特性及模型拟合结果
Fig. 7. (a) Schematic of the GraFET device showing two different charge noise mechanisms; (b) time domain conductivity fluctuations at different carrier densities; (c) typical noise power spectra at various backgate voltages; (d) noise amptitude at 1 Hz vs. density, fitted by the equation.
表 1 不同研究层次石墨烯噪声主导机制
Table 1. The main noise mechanisms for graphene at different levels.
层次分类 散射截面(迁移率)涨落 载流子数
涨落短程无序散射 长程无序散射 随机隧穿 本征背景噪声 靠近DP ●
(结合电阻网络模型)远离DP ● 类1/f噪声 靠近DP ●
(结合电阻网络模型)远离DP ● ● ● 洛伦兹类噪声 ● ● ● 表 2 石墨烯1/f噪声特征谱型对比
Table 2. comparison of the characteristic shape of 1/f noise in graphene.
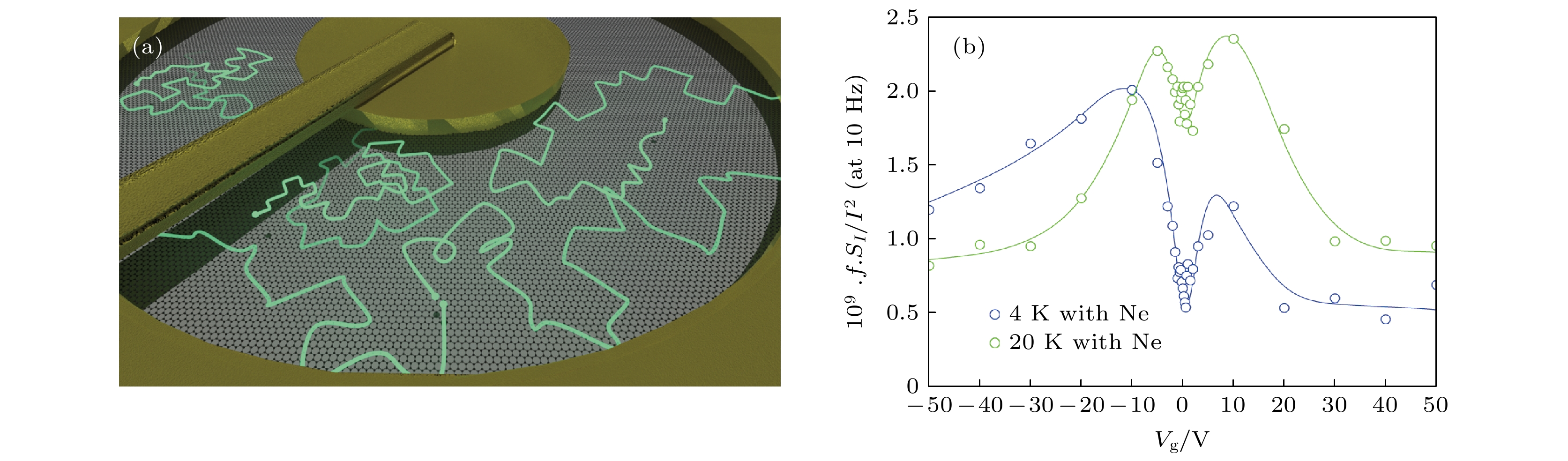
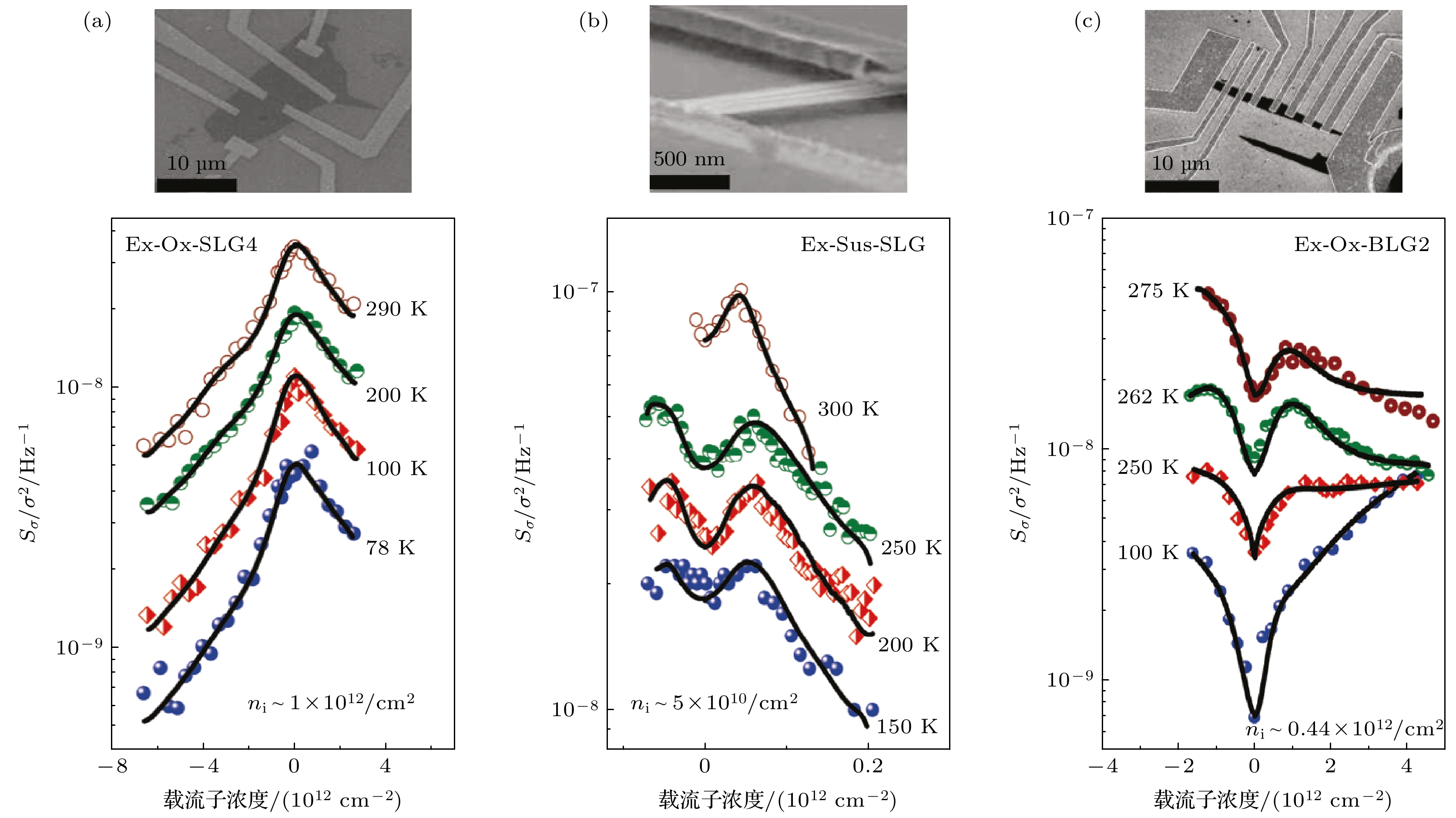
参考文献 特征谱型 ${{\Lambda }} $型 V型 M型 Kaverzin et al.[53] √, T = 60 K, Vb = ?, D √, T = 40 K, Vb = ?, D √, T=40 K, Vb=?, H2O 吸附, D Heller et al.[41] — √, RT, Vb < 5 mV, D √, RT, Vb < 5 mV, D Lin el al.[40] — √, RT, Vb=100 mV, Bi , D √, RT, Vb=100 mV, D Pal el al.[52] √, T = 78–290 K, Ib=50 μA, D √, T = 100 K, Ib=50 μA, Bi, D √, T = 262–275 K,
Ib=50 μA , Bi, D√, T = 150–300 K, Ib=50 μA , Sus, D √, T = 78–90 K, Ib=50 μA, Multi, D Zhang el al.[47] — √, T = 30–50 K, Vb = ?, D √, T = 145–300 K, Vb = ?, D √, T = 30–300 K, Vb = ?, Sus, C Xu el al.[60] — √, T = 70–300 K, Vb = ?, Bi, D √, T = 90-300 K, Vb = ?, D Takeshita el al.[61] √, T = 1.6 K,
Vb < 0.6 mV, D作者认为Heller, Zhang Y, Xu G S,
Rumyantsev, Kaverzin, Stolyarov
等实验偏置电压过大√, T = 1.6 K, Vb > 0.6 mV, D Arnold el al.[62] √, RT, Vb = 0.3 V, D √, RT, Vb=0.3 V, D √, RT, Vb = 0.3 V, D Mavredakis el al.[66] — — √, RT, Vb = 20–60 mV, D Kayyalha el al.[64] √, RT, Vb = 40 mV,
C, BN-encapsulated— √, RT, Vb = 40 mV, D Stolyarov el al.[65] √, RT, Vb = ?, C, BN-encapsulated — √, RT, Vb = ?, D, Pellegrini el al.[55] √ 理论仿真模型 √ Karnatak el al.[66] √, T = 80–300 K,
Ib = 100 nA, C,
BN-encapsulated— — Vb表示样品偏置电压, Vb = ?表示偏置电流未知; Ib表示样品偏置电流; RT表示室温; Bi表示双层石墨烯, Multi表示多层石墨烯, 其他未标注的均为单层石墨烯; Sus表示悬浮石墨烯, BN-encapsulated表示六方氮化硼(h-BN)包覆的石墨烯, 其他未标注的均为二氧化硅基底上的石墨烯; D表示非洁净石墨烯, C表示洁净石墨烯. -
[1] Vandamme L, Hooge F 2005 Phys. B Condens. Matter 357 507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wilamowski B M, Irwin J D 2011 Fundamentals of Industrial Electronics: The Industrial Electronics Handbook (1st Ed.) (CRC Press) p11
[3] Liu G, Stillman W, Rumyantsev S, Shur M, Balandin A A 2011 Int. J. High Speed Electron. Syst. 20 161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Johnson J B 1925 Phys. Rev. 26 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Voss R F, Clarke J 1975 Nature 258 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Daniel A 2015 Ph D Dissertation (Nottingham: The University of Nottingham)
[7] 庄奕琪, 马中发, 杜磊 1999 世界科技研究与发展 21 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhuang Y Q, Ma Z F, Du L 1999 World Sci-Tech R. D. 21 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Dutta P, Dimon P, Horn P 1979 Phys. Rev. Lett. 43 646
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Clarke J, Voss R F 1974 Phys. Rev. Lett. 33 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Burstein E, McWhorter A L, Miller P H, Stevenson D T, Weisz P B 1957 Semiconductor Surface Physics (University of Pennsylvania Press) p207
[11] Hooge F, Kleinpenning T, Vandamme L 1981 Rep. Prog. Phys. 44 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hooge F 1972 Physica 60 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hung K K, Ko P K, Hu C, Cheng Y C 1990 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 37 1323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Peransin J, Vignaud P, Rigaud D, Vandamme L K J 1990 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 37 2250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pellegrini B 1988 Phys. Rev. B 38 8279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Dmitriev A P, Levinshtein M E, Rumyantsev S L, Shur M S 2005 J. Appl. Phys. 97 123706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu Y, Tan Z, Kumar M, Abhilash T S, Liu G J, Hakonen P 2018 APL Mater. 6 091102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 杜磊, 庄奕琪, 薛丽君 2002 51 2836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du L, Zhuang Y Q, Xue L J 2002 Acta Phys. Sin. 51 2836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Song X X, Li H O, You J, Han T Y, Cao G, Tu T, Xiao M, Guo G C, Jiang H W, Guo G P 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 8142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Paladino E, Galperin Y M, Falci G, Altshuler B L 2014 Rev. Mod. Phys. 86 361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Dutta P, Horn P 1981 Rev. Mod. Phys. 53 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Macdonald K C, Lindsay R B 1963 Phys. Today 16 74
[23] Landauer R 1998 Nature 392 658
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kogan S 2008 Electronic Noise and Fluctuations in Solids (Cambridge University Press) pp24
[25] Surdin M 1939 J. Phys. Radium 10 188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] M. Richardson J 1950 Bell Syst. Tech. J. 29 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Weissman M B 1975 Phys. Rev. Lett. 35 689
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Kirton M J, Uren M J 1989 Adv. Phys. 38 367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Hooge F N 1994 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 41 1926
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Voss R F, Clarke J 1976 Phys. Rev. Lett. 36 42
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Voss R F, Clarke J 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 556
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Hershfield S 1988 Phys. Rev. B 37 8557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Raychaudhuri A K 2002 Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 6 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Pelz J, Clarke J 1987 Phys. Rev. B 36 4479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Ralls K S, Buhrman R A 1991 Phys. Rev. B 44 5800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Hung K K, Ko P K, Hu C, Cheng Y C 1990 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 37 654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Koga J, Takagi S, Toriumi A Proceedings of 1994 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA 11-14 Dec. 1994 pp475–478
[38] Vandamme E P, Vandamme L K 2000 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 47 2146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Xi'an: Xidian University) 张鹏 2010 博士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学
Zhang P 2010 Ph. D. Dissertation (in Chinese)
[40] Lin Y-M, Avouris P 2008 Nano Lett. 8 2119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Heller I, Chatoor S, Männik J, Zevenbergen M A, Oostinga J B, Morpurgo A F, Dekker C, Lemay S G 2010 Nano Lett. 10 1563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Liu G, Stillman W, Rumyantsev S, Shao Q, Shur M, Balandin A 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 033103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Chen Z, Lin Y M, Rooks M J, Avouris P 2007 Phys. E (Amsterdam, Neth. ) 40 228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Kumar M, Laitinen A, Cox D, Hakonen P J 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 106 263505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Rumyantsev S, Liu G, Stillman W, Shur M, Balandin A A 2010 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 22 395302 7
[46] Liu G X, Rumyantsev S, Shur M S, Balandin A A 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 093111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Zhang Y, Mendez E E, Du X 2011 ACS nano 5 8124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Cheng Z, Li Q, Li Z, Zhou Q, Fang Y 2010 Nano Lett. 10 1864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Zahid Hossain M, Rumyantsev S, Shur M S, Balandin A A 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 153512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Rehman A, Delgado Notario J A, Salvador Sanchez J, Meziani Y M, Cywiński G, Knap W, Balandin A A, Levinshtein M, Rumyantsev S 2022 Nanoscale 14 7242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Kamada M, Laitinen A, Zeng W, Will M, Sarkar J, Tappura K, Seppä H, Hakonen P 2021 Nano Lett. 21 7637
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Pal A N, Ghatak S, Kochat V, Sneha E, Sampathkumar A, Raghavan S, Ghosh A 2011 ACS Nano 5 2075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Kaverzin A A, Mayorov A S, Shytov A, Horsell D W 2012 Phys. Rev. B 85 075435 5
[54] Macucci M, Marconcini P 2020 J. Sens. 2020 2850268
[55] Pellegrini B, Marconcini P, Macucci M, Fiori G, Basso G 2016 J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2016 054017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Pellegrini B 2013 Eur. Phys. J. B 86 373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[57] Rumyantsev S, Liu G X, Shur M S, Potyrailo R A, Balandin A A 2012 Nano Lett. 12 2294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[58] Kazi R A, Aveek B 2014 Curr. Sci. India 107 430
[59] Cui Y, Liu Y M, Yu J C, Hayasaka T, Li X Q, Cai W H, Liu H L, Lin L W 2017 Ieee 19th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Taiwan China pp246–249
[60] Xu G, Torres C M, Jr., Zhang Y, Liu F, Song E B, Wang M, Zhou Y, Zeng C, Wang K L 2010 Nano Lett. 10 3312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[61] Takeshita S, Matsuo S, Tanaka T, Nakaharai S, Tsukagoshi K, Moriyama T, Ono T, Arakawa T, Kobayashi K 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 103106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[62] Arnold H N, Sangwan V K, Schmucker S W, Cress C D, Luck K A, Friedman A L, Robinson J T, Marks T J, Hersam M C 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 073108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[63] Kayyalha M, Chen Y P 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 113101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[64] Stolyarov M A, Liu G, Rumyantsev S L, Shur M, Balandin A A 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 107 023106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[65] Karnatak P, Sai T P, Goswami S, Ghatak S, Kaushal S, Ghosh A 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 13703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[66] Mavredakis N, Garcia Cortadella R, Bonaccini Calia A, Garrido J A, Jiménez D 2018 Nanoscale 10 14947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8862
- PDF下载量: 193
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: