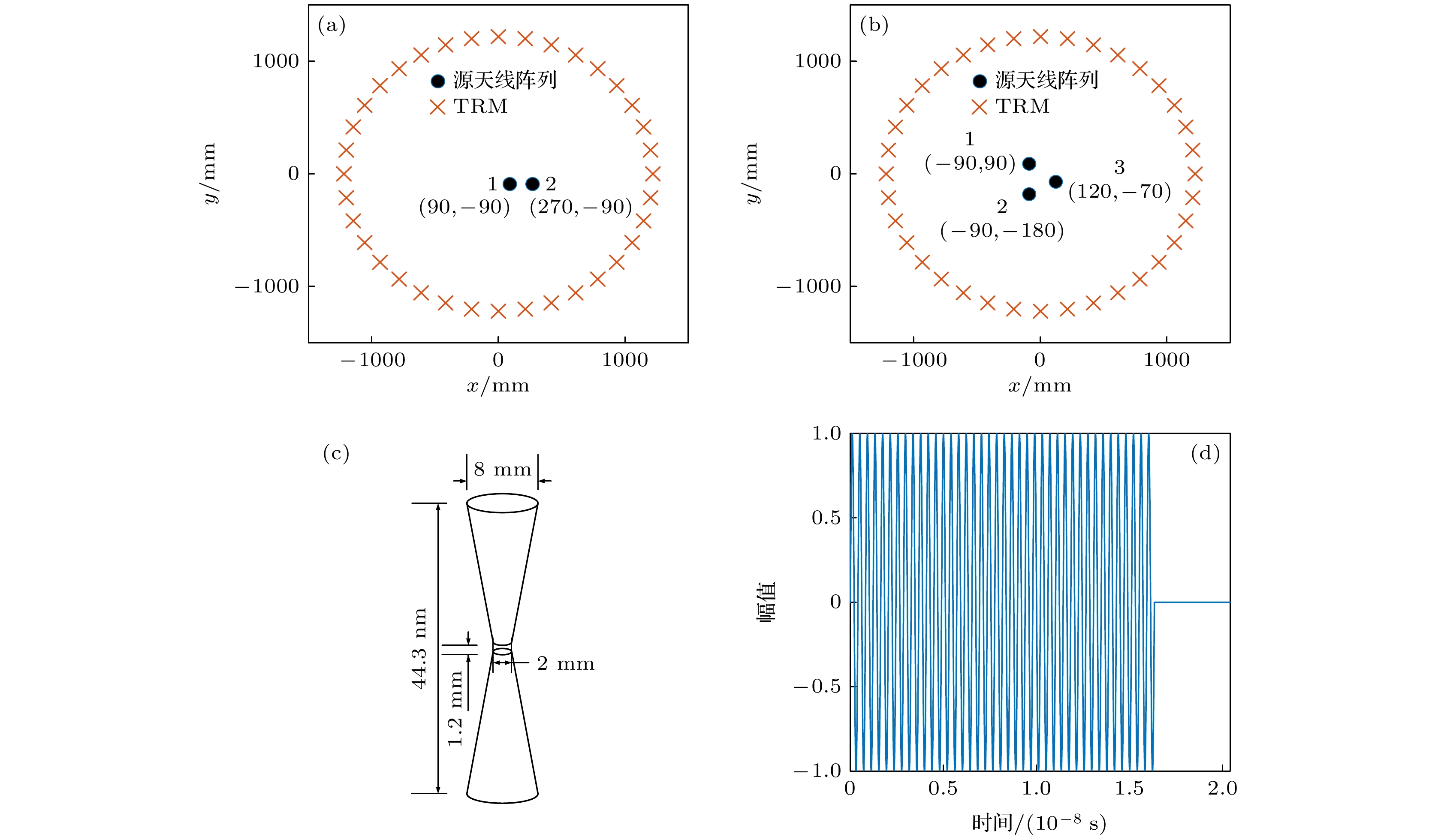
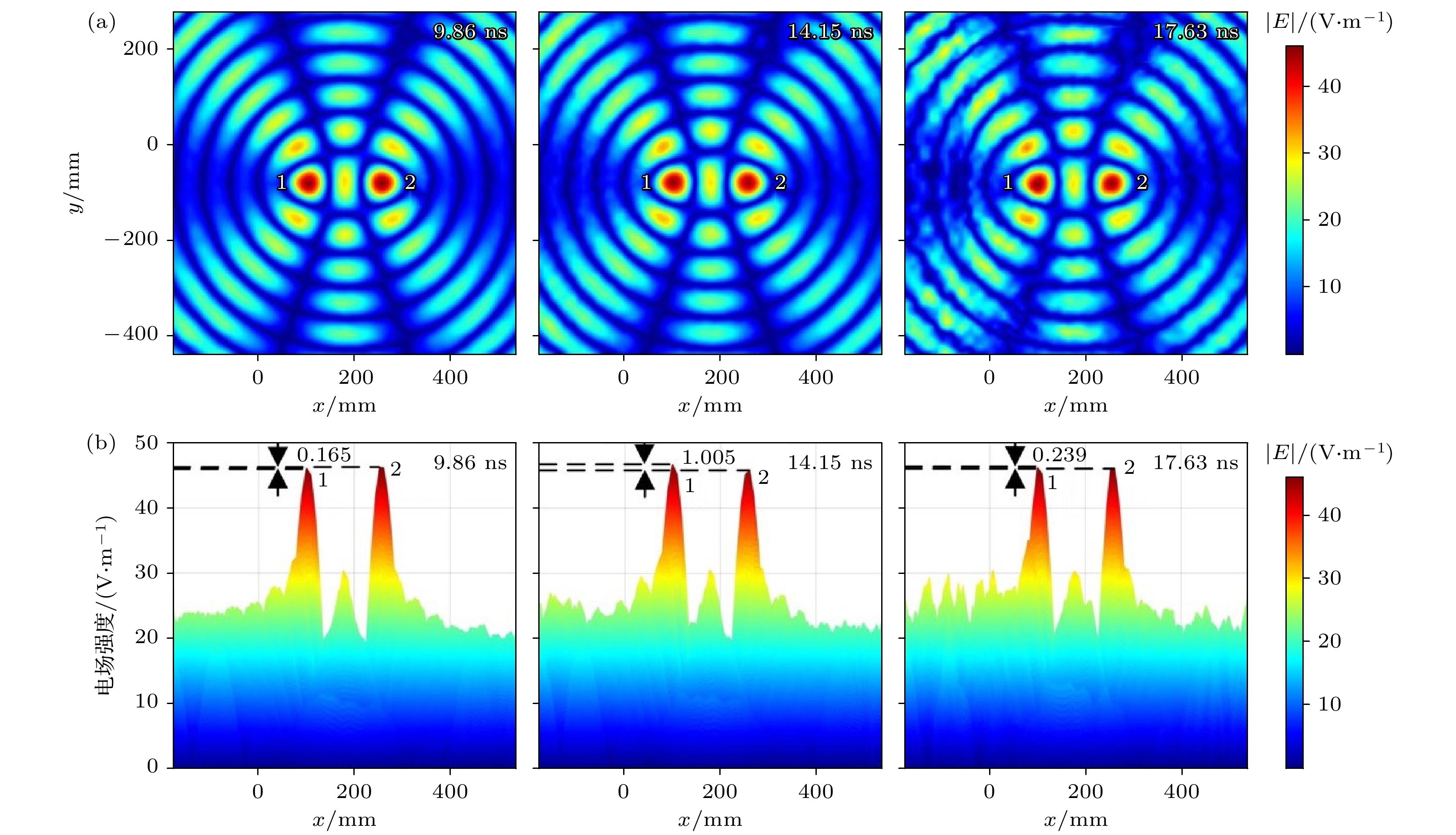
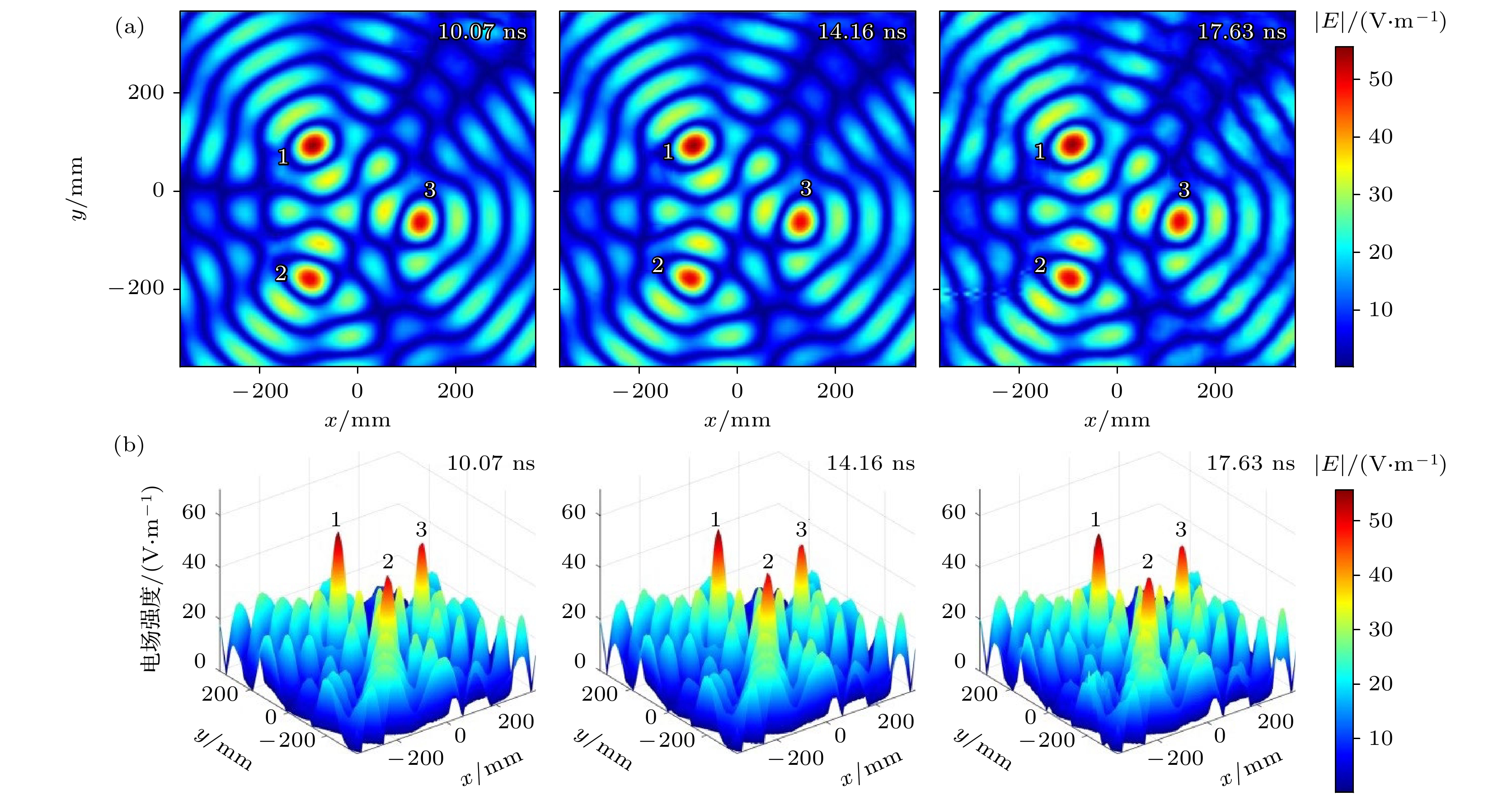
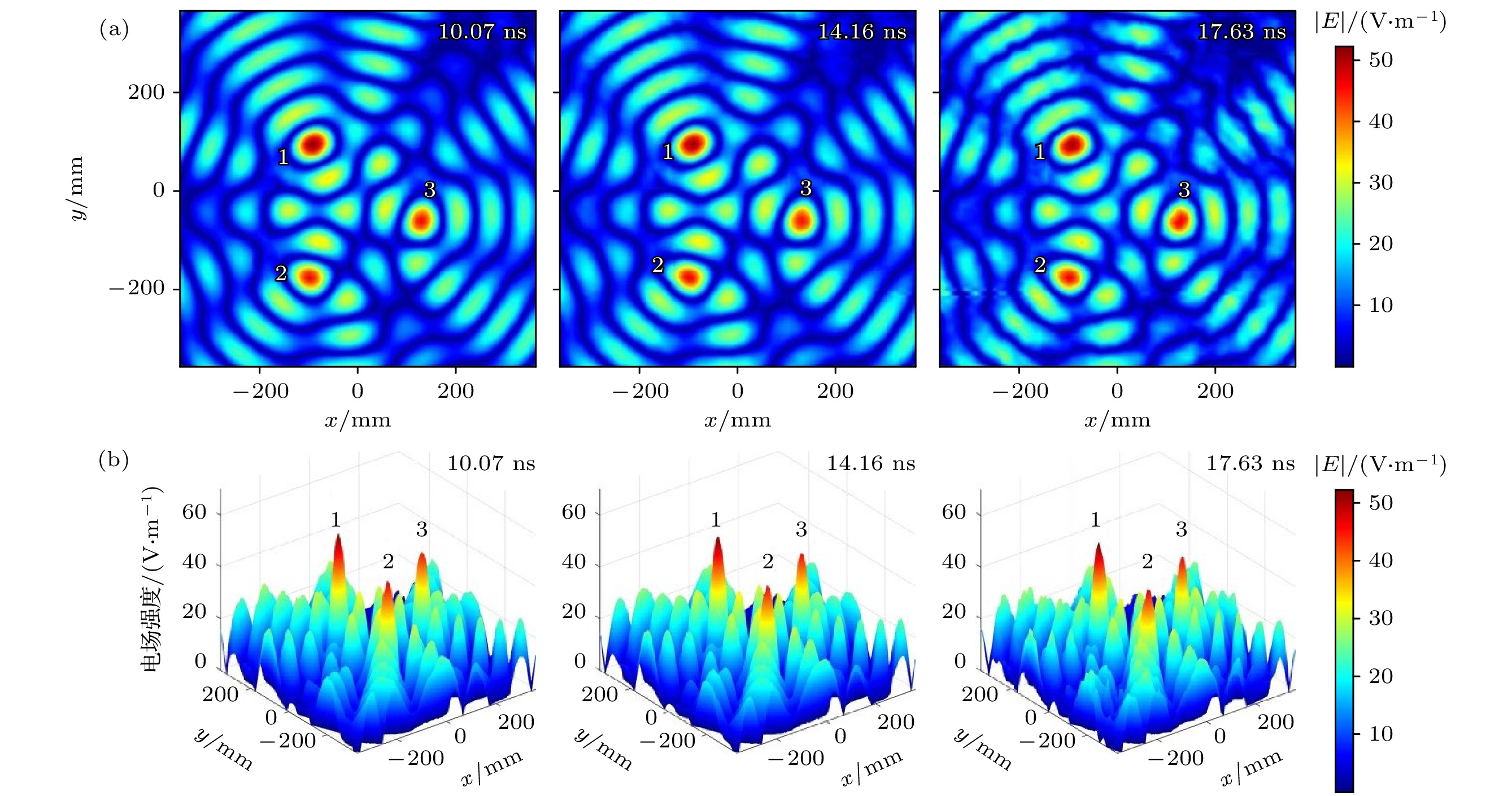
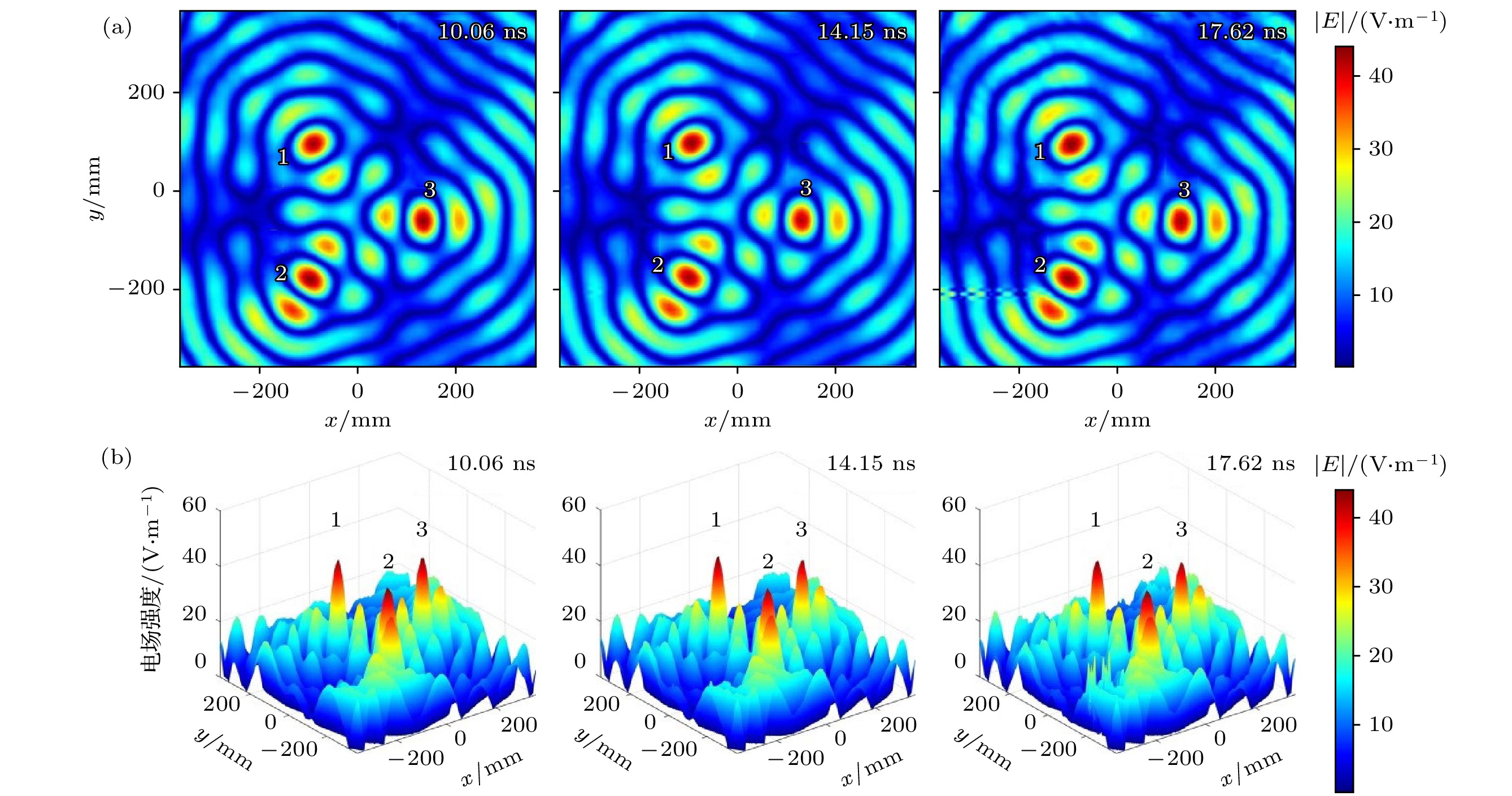
-
在局域有限空间中, 如何保证电磁能量的多目标精准均匀恒定无线传输是亟待解决的科学难题. 本文针对此难题, 以具有时空聚焦特性的时间反演技术为基础, 提出一种自动区域选择信道匹配的恒定均匀无线输能方法. 该方法不仅能够依据多径信号的贡献率, 自适应性地补偿不同目标处的信道差异, 还可以利用距离系数动态划分时间反演镜阵元的工作范围, 降低不同目标间的相互影响. 在提高能量聚焦精度的同时, 解决微波无线输能(microwave power transmission, MPT)中多目标能量非均匀传输的问题, 从而实现长时间恒定的多目标均匀MPT.
-
关键词:
- 时间反演镜 /
- 自动区域选择信道匹配 /
- 微波输能 /
- 均匀输能
The precise, uniform and constant wireless transmission of electromagnetic power to multiple targets in a local finite space is a scientific problem to be solved urgently. Aiming at this problem, in this paper we propose an automatic zone selection channel matching method based on time reversal technique which has the spatiotemporal focusing characteristics. The proposed method can not only adaptively compensate for the channel differences at different targets based on the contribution rate of the multipath signals, but also dynamically divide the working range of the time reversal mirror elements to eliminate the mutual influences between different targets through the use of the distance coefficient. While improving the accuracy of energy focusing, the proposed method also solves the problem that non-uniform microwave power transmission (MPT) of multiple targets, and therefore achieving the constant, uniform and long-time MPT of multi-targets.-
Keywords:
- time reversal mirror /
- automatic zone selection channel matching /
- microwave power transmission /
- uniform power transmission
[1] Zhu X R, Jin K, Hui Q 2021 IEEE J. Emerging Sel. Top. Power Electron. 9 1147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zeng Y, Clerckx B, Zhang R 2017 IEEE Trans. Commun. 65 2264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 倪旺, 丁飞, 宗军, 纪伟伟, 刘兴江 2019 电源技术 43 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ni W, Ding F, Zong J, Ji W W, Liu X J 2019 Chin. J. Power Sources 43 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 殷正刚, 史黎明, 范满义 2021 电工技术学报 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin Z G, Shi L M, Fan M Y 2021 Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Pries J, Galigekere V P N, Onar O C, Su G J 2020 IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35 4500
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 王龙飞 2019 电力电子技术 53 23
Wang L F 2019 Power Electron. 53 23
[7] Lee J, Lee K 2020 IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35 6697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 宋建军, 张龙强, 陈雷, 周亮, 孙雷, 兰军峰, 习楚浩, 李家豪 2021 70 108401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song J J, Zhang L Q, Chen L, Zhou L, Sun L, Lan J F, Xi C H, Li J H 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 108401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Joseph S D, Huang Y, Hsu S S H, Alieldin A, Song C Y 2021 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 69 482
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 黎深根, 陈仲林, 宋磊, 张琳, 李天明, 冯进军, 周碎明 2019 微波学报 35 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S G, Chen Z L, Song L, Zhang L, Li T M, Feng J J, Zhou S M 2019 J. Microw. 35 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fink M 1992 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 39 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lerosey G, Rosny J D, Tourin A, Derode A, Montaldo G, Fink M 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 193904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kaina N, Dupré M, Lerosey G, Fink M 2014 Sci. Rep. 4 6693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhao D S, Zhu M 2016 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 15 1739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhao D S, Guo F 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting San Diego, USA, July 9−14, 2017 p231
[16] Guo S, Zhao D S, Wang B Z, Cao W P 2020 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68 8249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 周洪澄, 王秉中, 丁帅, 欧海燕 2013 62 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou H C, Wang B Z, Ding S, Ou H Y 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ibrahim R, Voyer D, Bréard A, Huillery J, Vollaire C, Allard B, Zaatar Y 2016 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 64 2159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lee S, Zhang R 2017 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65 1685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chettri L, Bera R 2020 IEEE Internet Things J. 7 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ayir N, Riihonen T, Allen M, Fierro M F T 2021 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 69 1917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lee S, Zeng Y, Zhang R 2018 IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 7 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Bellizzi G G, Crocco L, Iero D A M, Isernia T 2017 IEEE International Workshop on Antenna Technology: Small Antennas, Innovative Structures, and Applications Athens, Greece, March 1−3, 2017 p162
[24] Bellizzi G G, Crocco L, Iero D A M, Isernia T 2018 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 17 360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 郭飞 2018 硕士学位论文 (成都: 电子科技大学)
Guo F 2018 M. S. Thesis (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[26] Bellizzi G G, Bevacqua M T, Crocco L, Isernia T 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 4380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bao J L, Zhao D S, Cao W P, Li B, Wang B Z 2019 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology Guangzhou, China, May 19−22, 2019, p1
[28] Li B, Liu S Q, Zhang H L, Hu B J, Zhao D S, Huang Y K 2019 IEEE Access 7 114897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Ku M L, Han Y, Lai H Q, Chen Y, Liu K J R 2016 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64 5819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Kim J H, Lim Y J, Nam S W 2019 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 5750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 李冰 2016 博士学位论文 (广州: 华南理工大学)
Li B 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Guangzhou: South China University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[32] 院琳, 杨雪松, 王秉中 2019 68 170503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan L, Yang X S, Wang B Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 170503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Carminati R, Pierrat R, Rosny J D, Fink M 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 3107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 丁帅, 王秉中, 葛广顶, 王多, 赵德双 2011 60 104101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding S, Wang B Z, Ge G D, Wang D, Zhao D S 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 104101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Fusco V F 2006 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 54 1352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 不同方法在输能时长内各参数均值
Table 1. Average value of each parameter under MPT of different methods.
直接发射 TR 信道补偿 自动区域选择信道匹配 最大场强差值/(V·m–1) 无聚焦 4.278 0.470 0.139 最大场强偏差率 无聚焦 7.46% 1.02% 0.34% 功率差值/mW 无聚焦 2.7 0.225 0.1 功率偏差率 无聚焦 15.92% 2.08% 1.21% 平均输能效率 0.120‰ 0.509‰ 0.310‰ 0.326‰ 面积差值/mm2 无聚焦 227 48.333 102.667 最大主副瓣比/dB 无聚焦 2.666 3.499 4.703 表 2 不同方法在输能时长内各参数均值
Table 2. Average value of each parameter under MPT of different methods.
直接发射 TR 信道补偿 自动区域选择信道匹配 平均最大场强差值/(V·m–1) 无聚焦 3.268 4.655 0.510 平均最大场强偏差率 无聚焦 6.34% 10.18% 1.14% 平均功率差值/mW 无聚焦 1.573 2.251 0.330 平均功率偏差率 无聚焦 11.19% 18.73% 3.18% 平均输能效率 0.139‰ 0.412‰ 0.365‰ 0.664‰ 平均面积差值/mm2 无聚焦 74.667 97.556 43.556 最大主副瓣比/dB 无聚焦 4.016 3.679 3.406 -
[1] Zhu X R, Jin K, Hui Q 2021 IEEE J. Emerging Sel. Top. Power Electron. 9 1147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zeng Y, Clerckx B, Zhang R 2017 IEEE Trans. Commun. 65 2264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 倪旺, 丁飞, 宗军, 纪伟伟, 刘兴江 2019 电源技术 43 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ni W, Ding F, Zong J, Ji W W, Liu X J 2019 Chin. J. Power Sources 43 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 殷正刚, 史黎明, 范满义 2021 电工技术学报 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin Z G, Shi L M, Fan M Y 2021 Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Pries J, Galigekere V P N, Onar O C, Su G J 2020 IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35 4500
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 王龙飞 2019 电力电子技术 53 23
Wang L F 2019 Power Electron. 53 23
[7] Lee J, Lee K 2020 IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35 6697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 宋建军, 张龙强, 陈雷, 周亮, 孙雷, 兰军峰, 习楚浩, 李家豪 2021 70 108401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song J J, Zhang L Q, Chen L, Zhou L, Sun L, Lan J F, Xi C H, Li J H 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 108401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Joseph S D, Huang Y, Hsu S S H, Alieldin A, Song C Y 2021 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 69 482
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 黎深根, 陈仲林, 宋磊, 张琳, 李天明, 冯进军, 周碎明 2019 微波学报 35 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S G, Chen Z L, Song L, Zhang L, Li T M, Feng J J, Zhou S M 2019 J. Microw. 35 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fink M 1992 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 39 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lerosey G, Rosny J D, Tourin A, Derode A, Montaldo G, Fink M 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 193904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kaina N, Dupré M, Lerosey G, Fink M 2014 Sci. Rep. 4 6693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhao D S, Zhu M 2016 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 15 1739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhao D S, Guo F 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting San Diego, USA, July 9−14, 2017 p231
[16] Guo S, Zhao D S, Wang B Z, Cao W P 2020 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68 8249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 周洪澄, 王秉中, 丁帅, 欧海燕 2013 62 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou H C, Wang B Z, Ding S, Ou H Y 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ibrahim R, Voyer D, Bréard A, Huillery J, Vollaire C, Allard B, Zaatar Y 2016 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 64 2159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lee S, Zhang R 2017 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65 1685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chettri L, Bera R 2020 IEEE Internet Things J. 7 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ayir N, Riihonen T, Allen M, Fierro M F T 2021 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 69 1917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lee S, Zeng Y, Zhang R 2018 IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 7 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Bellizzi G G, Crocco L, Iero D A M, Isernia T 2017 IEEE International Workshop on Antenna Technology: Small Antennas, Innovative Structures, and Applications Athens, Greece, March 1−3, 2017 p162
[24] Bellizzi G G, Crocco L, Iero D A M, Isernia T 2018 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 17 360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 郭飞 2018 硕士学位论文 (成都: 电子科技大学)
Guo F 2018 M. S. Thesis (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[26] Bellizzi G G, Bevacqua M T, Crocco L, Isernia T 2018 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 4380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bao J L, Zhao D S, Cao W P, Li B, Wang B Z 2019 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology Guangzhou, China, May 19−22, 2019, p1
[28] Li B, Liu S Q, Zhang H L, Hu B J, Zhao D S, Huang Y K 2019 IEEE Access 7 114897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Ku M L, Han Y, Lai H Q, Chen Y, Liu K J R 2016 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64 5819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Kim J H, Lim Y J, Nam S W 2019 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 5750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 李冰 2016 博士学位论文 (广州: 华南理工大学)
Li B 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Guangzhou: South China University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[32] 院琳, 杨雪松, 王秉中 2019 68 170503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan L, Yang X S, Wang B Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 170503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Carminati R, Pierrat R, Rosny J D, Fink M 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 3107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 丁帅, 王秉中, 葛广顶, 王多, 赵德双 2011 60 104101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding S, Wang B Z, Ge G D, Wang D, Zhao D S 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 104101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Fusco V F 2006 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 54 1352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6840
- PDF下载量: 101
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: