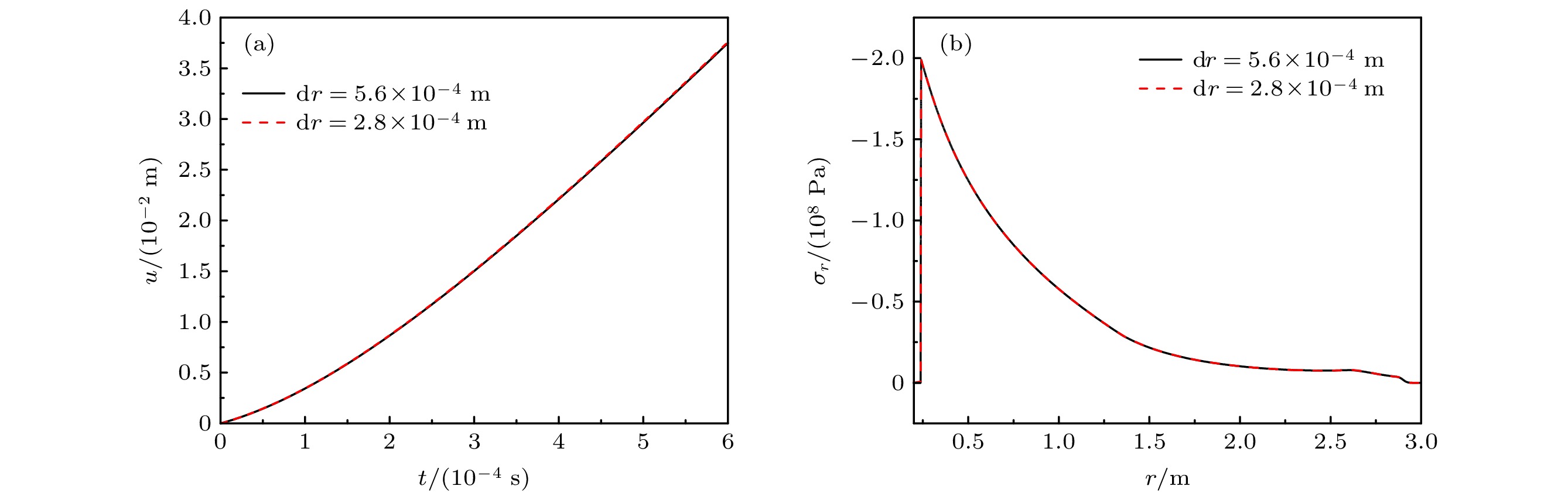
-
基于线性硬化塑性本构模型, 建立了冲击载荷作用下弹塑性球面应力波场的理论求解方法. 首先, 分析了冲击载荷卸载速率对球面应力波传播的影响, 得到了3种不同类型的应力波传播图像. 在此基础上, 建立了弹性阶段、塑性加载阶段以及卸载阶段球面波动方程的理论求解方法, 给出了质点位移、质点速度、应力和应变等物理量的计算方案. 与已有理论方法相比, 该方法考虑了不同载荷卸载速率条件下应力波的不同传播情况, 并且给出了卸载阶段应力波参量计算方法, 具有更广的适用范围. 利用上述方法计算了恒定冲击载荷和不同指数衰减冲击载荷作用下弹塑性球面应力波场参量, 在弹性阶段和塑性加载阶段, 理论计算得到的物理量与已有理论方法和数值模拟结果基本吻合, 在卸载阶段, 已有理论方法不再适用, 而本文理论计算得到的物理量与数值模拟结果基本吻合, 验证了该理论方法的正确性.Based on the linear hardening plastic constitutive model, the theoretical solution of the elastic-plastic spherical stress wave field under impact load is established. Firstly, the influence of the impact load unloading rate on the propagation of the spherical stress wave is analyzed, and three different types of propagation images are obtained. On this basis, the method of theoretically calculating the spherical wave equation in elastic stage, plastic loading stage and unloading stage is established separately, and the calculation scheme of particle displacement, particle velocity, stress and strain is given. Compared with the existing theoretical methods, this method takes into account the different propagation patterns of the stress waves under different unloading rates, and shows how to calculate the stress wave parameters in unloading stage, which is more applicable. This method is used to calculate the elastic-plastic spherical stress wave field under constant shock load and exponential attenuation shock load. The calculated results are in good agreement with those from the existing theoretical method and numerical simulation results in the elastic stage and also in the plastic loading stage. In the unloading stage, the existing theoretical method is no longer applicable, while the results obtained in this paper are in good agreement with the numerical simulation results, which verifies the correctness of the theoretical method.
-
Keywords:
- elastic-plastic /
- spherical stress wave /
- linear hardening model /
- unloading rate
[1] Wlodarczyk E, Zielenkiewicz M 2009 J. Theor. App. Mech. 47 127
[2] Wlodarczyk E, Zielenkiewicz M 2009 J. Theor. App. Mech. 47 761
[3] Wlodarczyk E, Zielenkiewicz M 2009 Shock Waves 18 465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wlodarczyk E, Zielenkiewicz M 2011 J. Theor. App. Mech. 49 457
[5] Biswas S 2021 Indian J. Phys. 95 705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 李孝兰 2000 爆炸与冲击 20 186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X L 2000 Explo. Shock Waves 20 186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 李孝兰 2000 爆炸与冲击 20 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X L 2000 Explo. Shock Waves 20 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 肖建华 2001 石油地球物理勘探 36 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao J H 2001 Oil Geophys. Prospect. 36 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 肖建华 2004 石油地球物理勘探 39 249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao J H 2004 Oil Geophys. Prospect. 39 249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xu C J, Chen Q Z, Zhou J, Cai Y Q 2015 J. Civ. Eng. 19 2035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 卢强, 王占江, 王礼立, 赖华伟, 杨黎明 2013 爆炸与冲击 33 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu Q, Wang Z J, Wang L L, Lai H W, Yang L M 2013 Explo. Shock Waves 33 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 卢强, 王占江 2015 64 108301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu Q, Wang Z J 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 108301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lu Q, Wang Z J 2016 J. Sound Vib. 371 183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 邓德全, 李兆权 1992 第三届全国岩石动力学学术会议论文集, 桂林, 1992, 第152页
Deng D Q, Li Z Q 1992 Proceedings of the 3rd National Conference on Rock Dynamics Guilin, 1992 p152 (in Chinese)
[15] 赖华伟, 王占江, 杨黎明, 王礼立 2013 爆炸与冲击 33 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lai H W, Wang Z J, Yang L M, Wang L L 2013 Explo. Shock Waves 33 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang C Y 1970 Int. J. Solids Struct. 6 757
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Morland L W 1971 J. Mech. Phys. Solids 19 295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Milne P C, Morland L W, Yeung W 1988 J. Mech. Phys. Solids 36 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Milne P C, Morland L W 1988 J. Mech. Phys. Solids 36 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Rapoport L, Katzir Z, Rubin M B 2011 Wave Motion 48 441
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Santos T, Brezolin A, Rossi R, Rodriguez-Martinez J A 2020 Acta Mech. 231 2381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 肖建华, 孙文涛 1997 石油地球物理勘探 32 809
Xiao J H, Sun W T 1997 Oil Geophys. Prospect. 32 809
[23] Chen S, Wu J, Zhang Z 2017 J. Eng. Mech. 143 04017034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 王礼立 2005 应力波基础 (第二版) (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第236页
Wang L L 2005 Foundation of Stress Waves (2nd Ed.) (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) p236 (in Chinese)
-
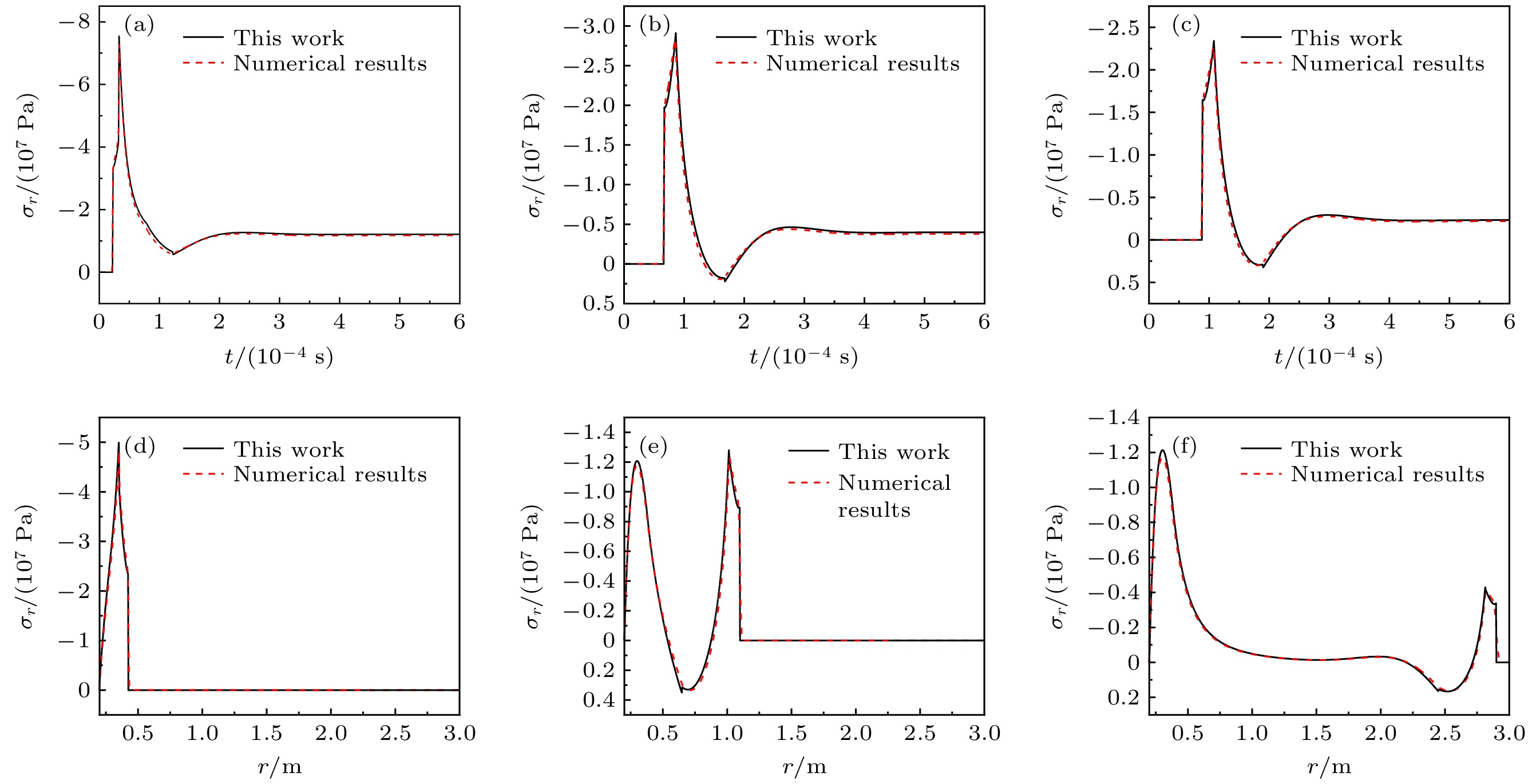
图 4 径向应力时间历程 (a) r = 0.5 m; (b) r = 0.8 m; (c) r = 1.4 m和径向应力空间分布 (d) t = 0.1 ms; (e) t = 0.2 ms; (f) t = 0.3 ms (恒定冲击载荷)
Fig. 4. Time history of the radial stress: (a) r = 0.5 m; (b) r = 0.8 m; (c) r = 1.4 m and the radial stress distribution: (d) t = 0.1 ms; (e) t = 0.2 ms; (f) t = 0.3 ms (constant impact loading).
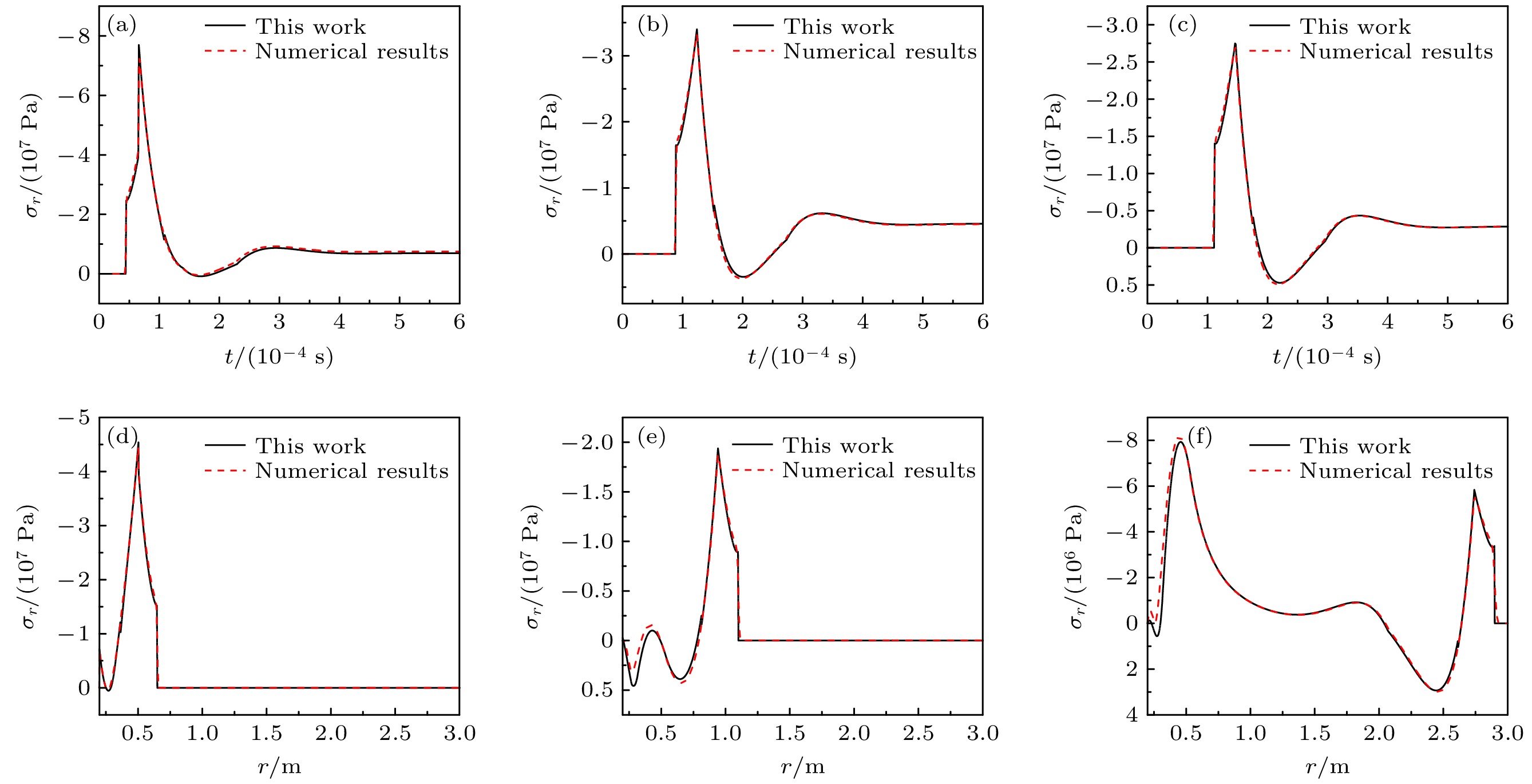
图 5 径向应力时间历程 (a) r = 0.3 m; (b) r = 0.5 m; (c) r = 0.6 m和径向应力空间分布 (d) t = 0.05 ms; (e) t = 0.2 ms; (f) t = 0.6 ms (T0 = 0.01 ms)
Fig. 5. Time history of the radial stress: (a) r = 0.3 m; (b) r = 0.5 m; (c) r = 0.6 m and the radial stress distribution: (d) t = 0.05 ms; (e) t = 0.2 ms; (f) t = 0.6 ms (T0 = 0.01 ms).
图 7 径向应力时间历程 (a) r = 0.4 m; (b) r = 0.6 m; (c) r = 0.7 m和径向应力空间分布 (d) t = 0.1 ms; (e) t = 0.2 ms; (f) t = 0.6 ms (T0 = 0.03 ms)
Fig. 7. Time history of the radial stress: (a) r = 0.4 m; (b) r = 0.6 m; (c) r = 0.7 m; and the radial stress distribution: (d) t = 0.1 ms; (e) t = 0.2 ms; (f) t = 0.6 ms (T0 = 0.03 ms).
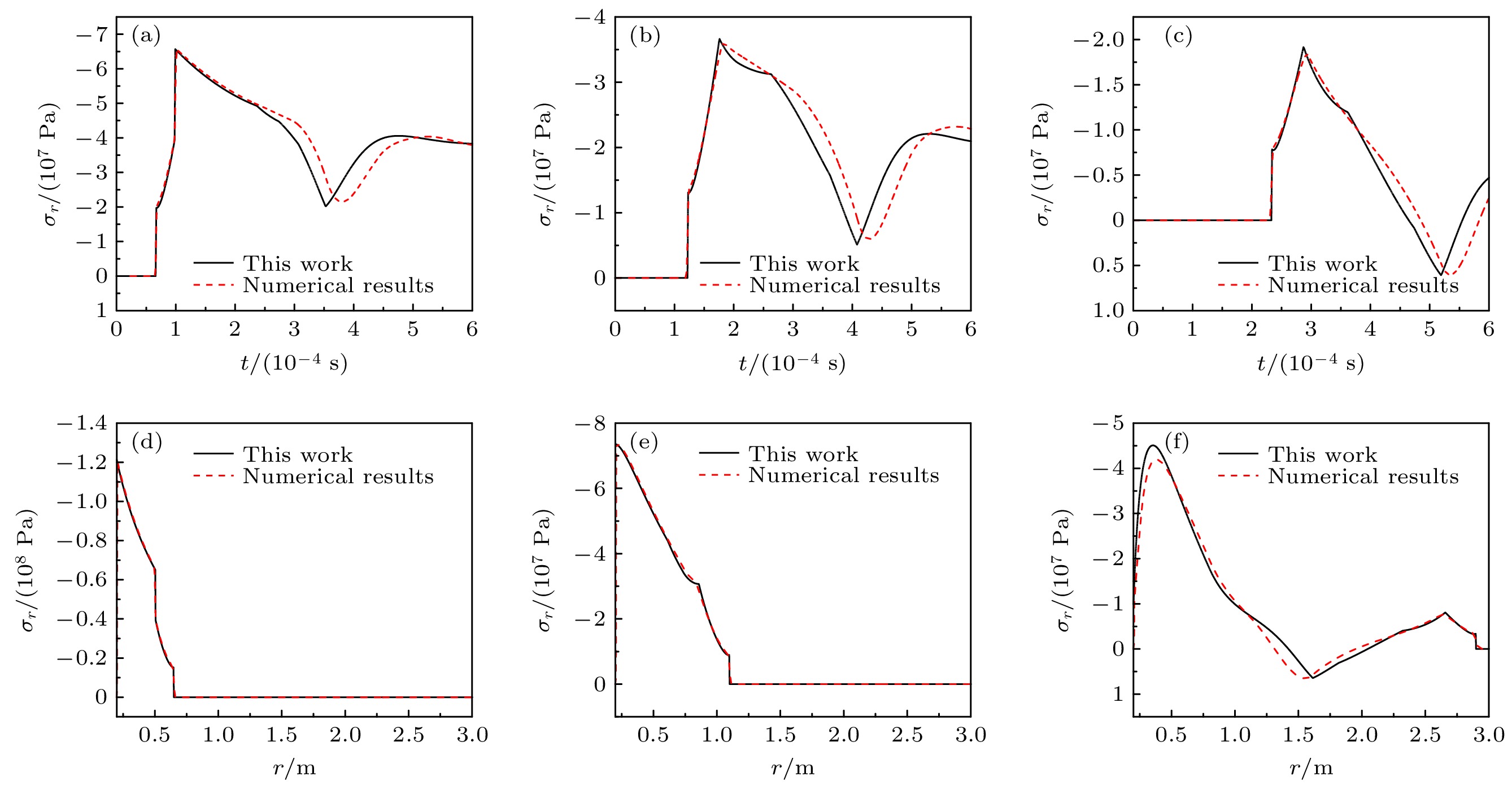
图 6 径向应力时间历程 (a) r = 0.5 m; (b) r = 0.75 m; (c) r = 1.25 m和径向应力空间分布 (d) t = 0.1 ms; (e) t = 0.2 ms; (f) t = 0.6 ms (T0 = 0.2 ms)
Fig. 6. Time history of the radial stress: (a) r = 0.5 m; (b) r = 0.75 m; (c) r = 1.25 m and the radial stress distribution: (d) t = 0.1 ms; (e) t = 0.2 ms; (f) t = 0.6 ms (T0 = 0.2 ms).
-
[1] Wlodarczyk E, Zielenkiewicz M 2009 J. Theor. App. Mech. 47 127
[2] Wlodarczyk E, Zielenkiewicz M 2009 J. Theor. App. Mech. 47 761
[3] Wlodarczyk E, Zielenkiewicz M 2009 Shock Waves 18 465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wlodarczyk E, Zielenkiewicz M 2011 J. Theor. App. Mech. 49 457
[5] Biswas S 2021 Indian J. Phys. 95 705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 李孝兰 2000 爆炸与冲击 20 186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X L 2000 Explo. Shock Waves 20 186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 李孝兰 2000 爆炸与冲击 20 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X L 2000 Explo. Shock Waves 20 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 肖建华 2001 石油地球物理勘探 36 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao J H 2001 Oil Geophys. Prospect. 36 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 肖建华 2004 石油地球物理勘探 39 249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao J H 2004 Oil Geophys. Prospect. 39 249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xu C J, Chen Q Z, Zhou J, Cai Y Q 2015 J. Civ. Eng. 19 2035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 卢强, 王占江, 王礼立, 赖华伟, 杨黎明 2013 爆炸与冲击 33 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu Q, Wang Z J, Wang L L, Lai H W, Yang L M 2013 Explo. Shock Waves 33 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 卢强, 王占江 2015 64 108301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu Q, Wang Z J 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 108301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lu Q, Wang Z J 2016 J. Sound Vib. 371 183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 邓德全, 李兆权 1992 第三届全国岩石动力学学术会议论文集, 桂林, 1992, 第152页
Deng D Q, Li Z Q 1992 Proceedings of the 3rd National Conference on Rock Dynamics Guilin, 1992 p152 (in Chinese)
[15] 赖华伟, 王占江, 杨黎明, 王礼立 2013 爆炸与冲击 33 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lai H W, Wang Z J, Yang L M, Wang L L 2013 Explo. Shock Waves 33 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang C Y 1970 Int. J. Solids Struct. 6 757
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Morland L W 1971 J. Mech. Phys. Solids 19 295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Milne P C, Morland L W, Yeung W 1988 J. Mech. Phys. Solids 36 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Milne P C, Morland L W 1988 J. Mech. Phys. Solids 36 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Rapoport L, Katzir Z, Rubin M B 2011 Wave Motion 48 441
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Santos T, Brezolin A, Rossi R, Rodriguez-Martinez J A 2020 Acta Mech. 231 2381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 肖建华, 孙文涛 1997 石油地球物理勘探 32 809
Xiao J H, Sun W T 1997 Oil Geophys. Prospect. 32 809
[23] Chen S, Wu J, Zhang Z 2017 J. Eng. Mech. 143 04017034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 王礼立 2005 应力波基础 (第二版) (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第236页
Wang L L 2005 Foundation of Stress Waves (2nd Ed.) (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) p236 (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 7558
- PDF下载量: 134
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: