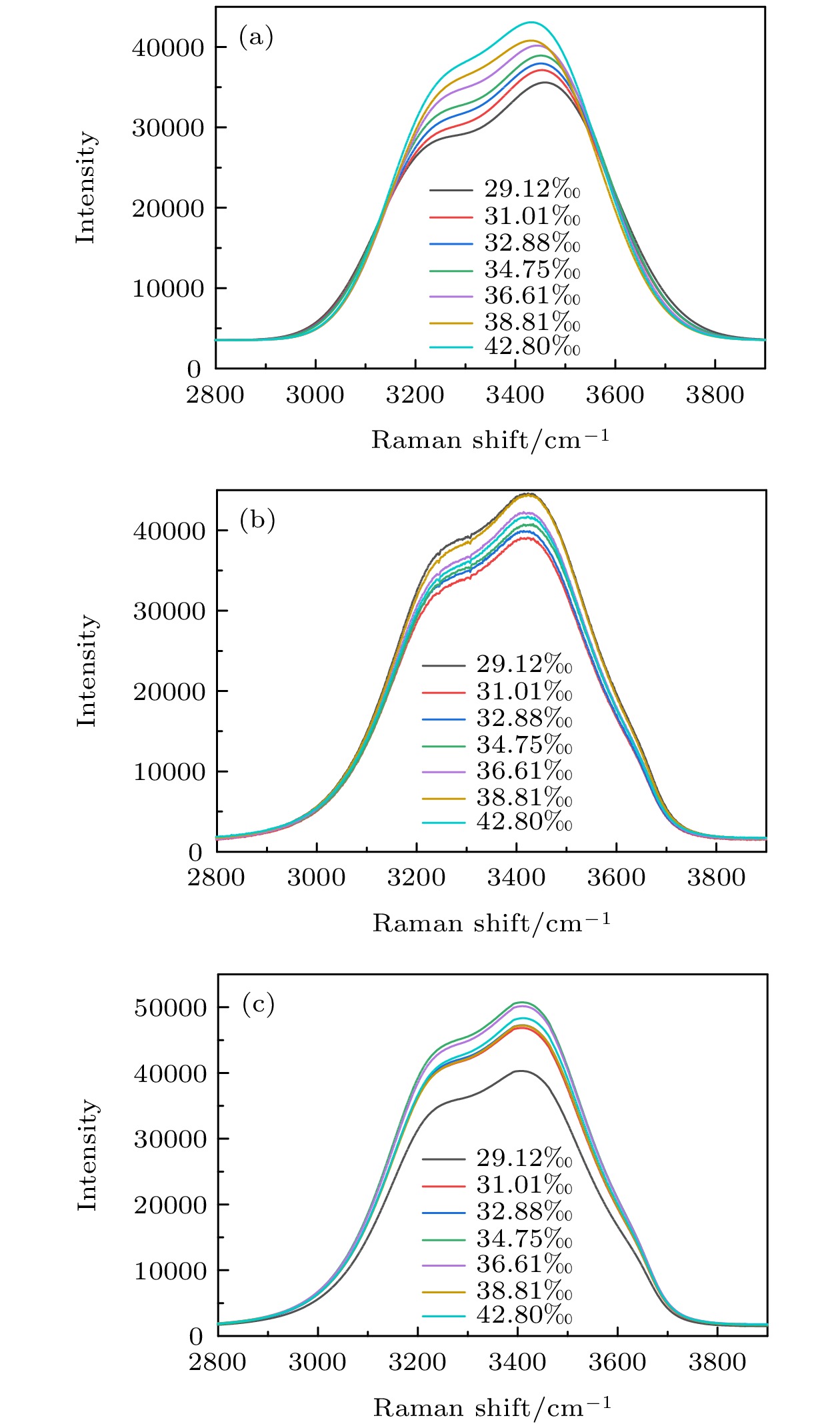
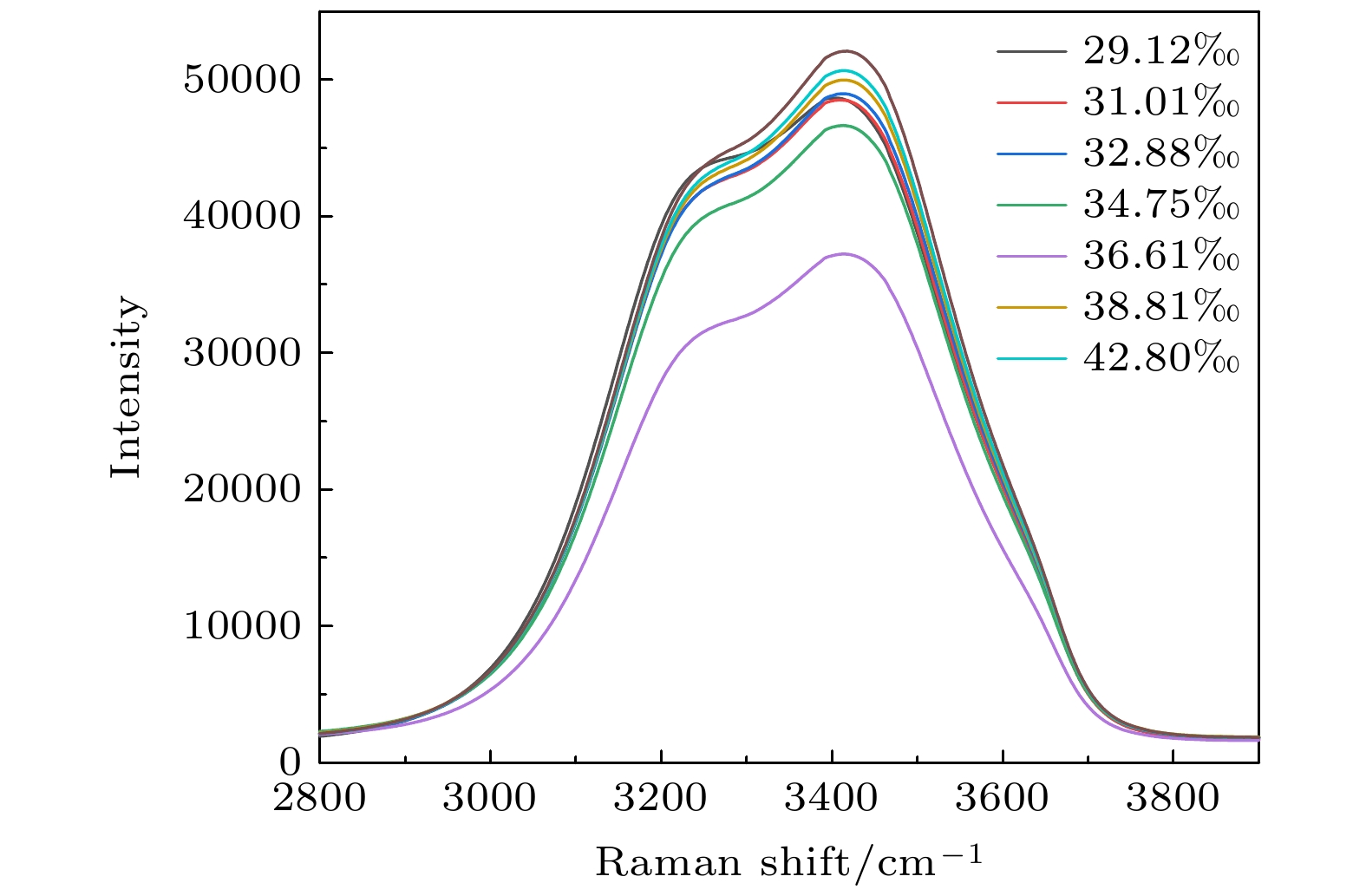
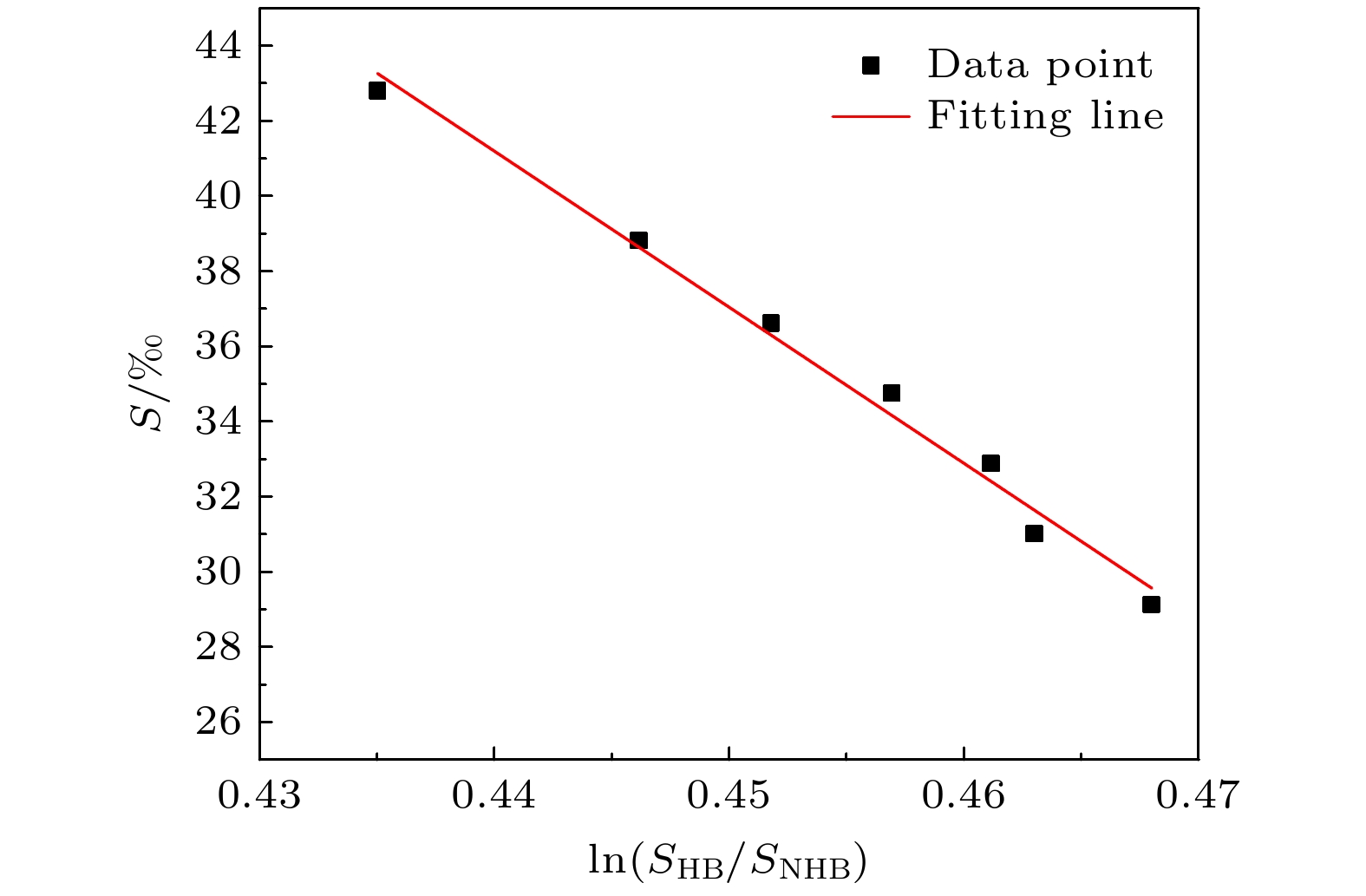
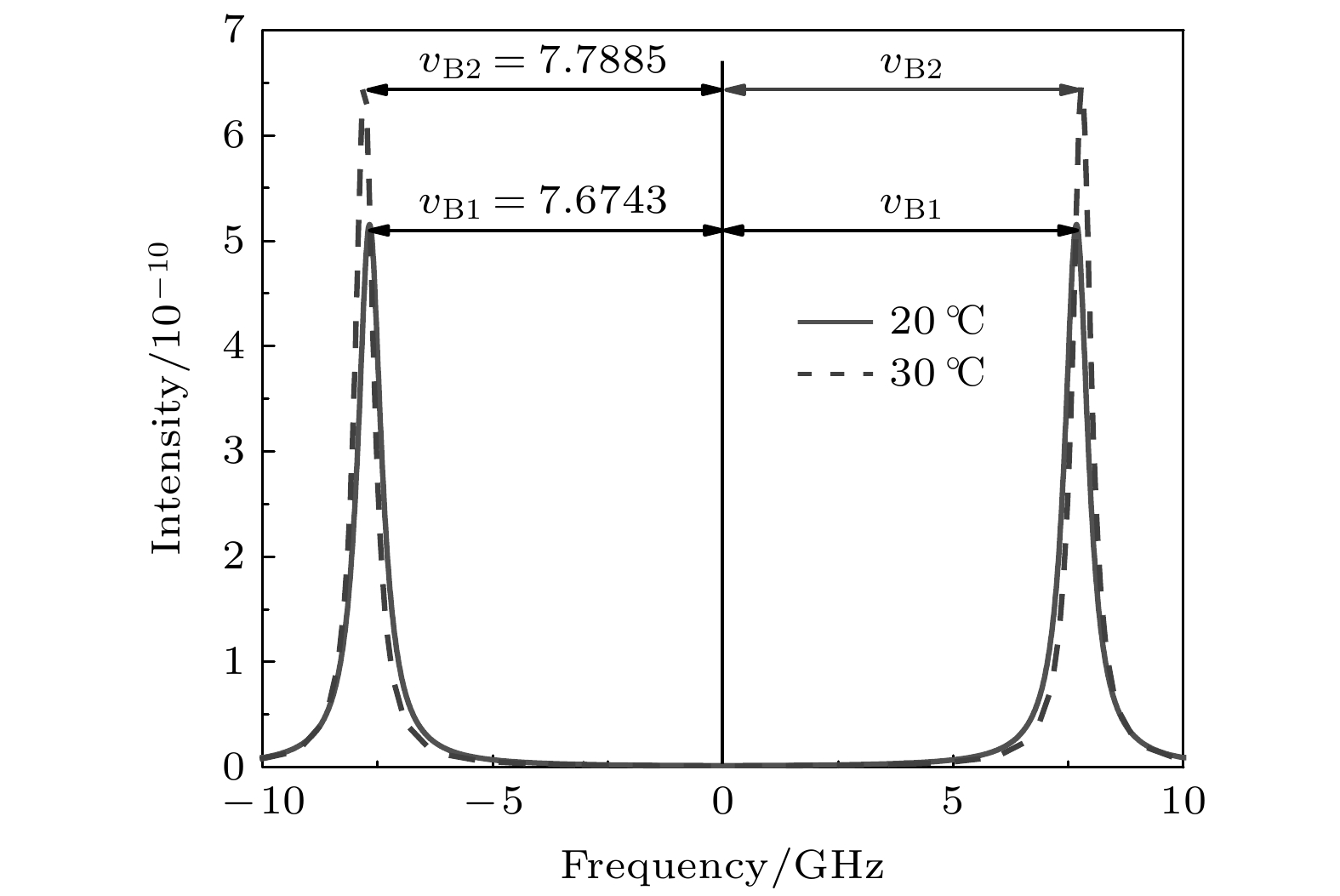
-
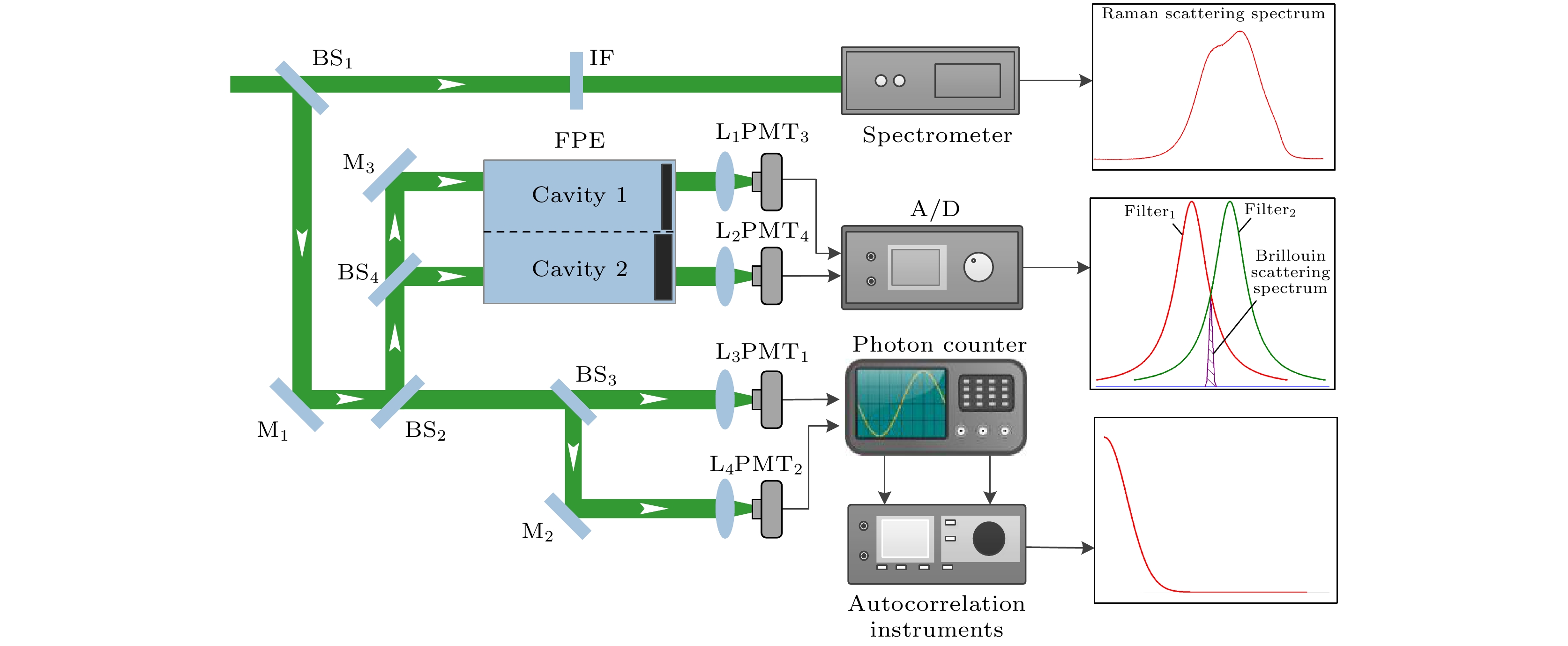
盐度是海洋学中重要的物理参量之一, 其对生物学研究、气候模拟、天气预报以及飓风路径预测都具有极其重要的意义. 在基于拉曼光谱的海洋盐度遥感探测中, 由于拉曼光谱同时与盐度及海水温度相关, 因此反演盐度时, 需要参数假设, 从而降低探测精度. 为实现对盐度的高精度遥感探测, 本文提出了融合水体布里渊散射与拉曼散射光谱的盐度精细反演方法. 文中根据拉曼光谱的低频部分与高频部分的面积比值与水体温度和盐度有定量的关系, 利用最小二乘方法, 建立拉曼光谱与温度和盐度的二元函数方程. 由于布里渊频移量的大小与介质中的声速相关, 而声速变化是由温度和盐度的变化引起, 因此布里渊频移量的大小也同时与盐度及海水温度相关. 激光雷达遥感探测方法可以同时探测拉曼光谱和布里渊频移这两个参量, 因此利用拉曼光谱和布里渊频移与盐度和温度之间的关系, 建立了盐度高精度反演模型, 并分析了探测结果的误差, 得到盐度的反演误差小于0.47‰.Salinity is an important physical parameter in oceanography. The change of seawater salinity is closely related to the change of marine environment and climate. Investigation of seawater salinity is of great significance for marine biology, climate simulation, weather forecast and hurricane path prediction. At present, in the research of seawater salinity detection based on Raman scattering, the influence of temperature change is ignored, which will cause inaccurate detection results. In order to achieve high-precision detection of seawater salinity, in this paper, a method of combining the precision salinity inversion with ocean Brillouin scattering is proposed. According to the influence of temperature and salinity on Raman scattering spectra, the functional relationship between them is established. Raman scattering spectra and Brillouin frequency shift are used to implement the inversion seawater salinity. The Brillouin frequency shift cannot be obtained directly by the lidar remote sensing method. It can only detect the energy of the echo signal through edge detection, and the photon correlation spectroscopy technology is used to detect the spectra width. The Brillouin frequency shift can be calculated by the energy and spectral width of the echo signal. Therefore, the accurate inversion of seawater salinity can be realized by detecting Raman spectra, Brillouin spectra width and energy signal. The experimental results of Raman spectroscopy are used to verify the established functional relationship, and the inversion error of seawater salinity is less than 0.47‰. In the experiment, the influence of seawater temperature control accuracy of ±0.2 ℃ and the detection results of Brillouin spectrum width and energy are analyzed. Through using the error in measurement result of each parameter, the salinity inversion error caused by them is analyzed. Using the Raman spectrum and Brillouin frequency shift, the problem of the accurate inversion of seawater salinity is solved, and the influence of temperature change on salinity inversion is eliminated. This research provides reliable data support for improving the marine environment, early warning of marine disaster and marine meteorological forecast accuracy, and has important research value and significant social benefits. This method also provides a feasible solution for ocean detection lidar used to detect seawater salinity.
-
Keywords:
- salinity /
- Raman scattering /
- Brillouin scattering /
- lidar
[1] Noto V D, Mecozzi M 1997 Appl. Spectrosc. 51 1294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Rudolf A, Walther T 2014 Opt. Eng. 53 051407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 任秀云 2016 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Ren X Y 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[4] Xu Z, Yu Z Z, Fu X Z, Yu X Q 2021 Act. Ocean Sin. 40 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liu Y M, Zhang R H, Yin Y H, Niu T 2005 J. Mereorol. Res-Prc. 19 355
[6] 张兰杰 2019 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Zhang L J 2019 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[7] Artlett C P, Pask H M 2017 Opt. Express 25 2840
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Burikov S A, Churina I V, Dolenko S A, Dolenko T A, Fadeev V V 2004 EARSeL eProceedings 3 298
[9] Wall T T, Hornig D F 1967 J. Chem. Phys. 47 784
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 何兴道, 夏健, 史久林, 刘娟, 李淑静, 刘建安, 方伟 2011 60 054207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He X D, Xia J, Shi J L, Liu J, Li S J, Liu J A, Fang W 2011 Acta Phys. Sin 60 054207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] John M D, Craig R J, Sanford A A 1985 J. Chem. Phys. 82 1732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Eckhardt G, Wagner E G 1966 J. Mol. Spectrosc. 19 407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liang K, Ma Y, Yu Y, Huang J, Li H 2012 Opt. Eng. 51 6002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 赵丽娟 2010 59 6219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao L J 2010 Acta Phys. Sin 59 6219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 史久林, 许锦, 罗宁宁, 王庆, 张余宝, 张巍巍, 何兴道 2019 68 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi J L, Xu J, Luo N N, Wang Q, Zhang Y B, Zhang W W, He X D 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] He X D, Wei H J, Shi J L, Liu J 2012 Opt. Commun. 285 4120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Grosso D V A 1974 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 56 1084
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Fry E S, Emery Y, Quan X H, Katz J W 1997 Appl. Opt. 36 6887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 马泳, 梁琨, 林宏, 冀航 2008 光学学报 28 1508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma Y, Liang K, Lin H, Ji H 2008 Acta. Opt. Sin. 28 1508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ge Y, Shi J L, Zhu K X, He X D 2013 Chin. Opt. Lett. 11 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 任秀云, 田兆硕, 孙兰君, 付石友 2014 63 164209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren X Y, Tian Z S, SUN J L, Fu S Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 164209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Haltrin V I, Kattawar G W 1993 Appl. Opt. 32 5356
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
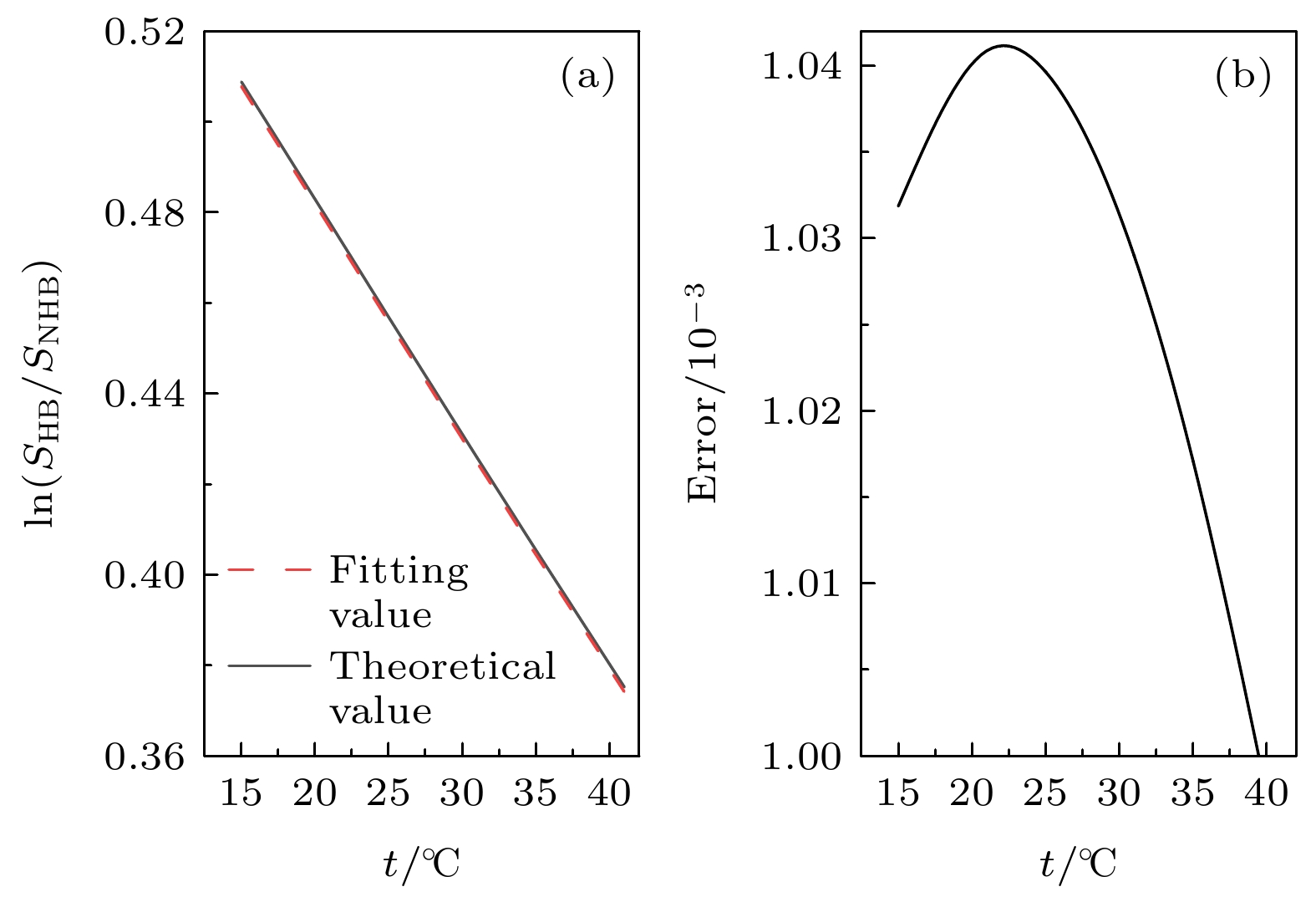
图 9 温度误差对Raman散射光谱低、高频面积比的对数值ln(SHB/SNHB)造成的影响 (a) 恒定盐度, 不同温度下对数面积比理论值与拟合值; (b) 温度误差导致对数面积的误差
Fig. 9. Effect of temperature error on the logarithmic value of the low and high frequency area ratio of Raman scattering spectra: (a) theoretical value and fitting value of log area ratio under constant salinity and different temperatures; (b) error of log area caused by temperature error.
图 10 温度误差对Brillouin散射探测造成的影响 (a) 恒定盐度, 不同温度下谱宽理论值与拟合值; (b) 温度误差导致谱宽探测误差; (c) 恒定盐度, 不同温度下探测能量理论值与拟合值; (d) 温度误差导致能量探测误差
Fig. 10. Effect of temperature error on Brillouin scattering detection: (a) Theoretical and fitting values of spectrum width at different temperatures under constant salinity; (b) temperature error leads to spectrum width detection error; (c) theoretical and fitting values of detection energy at different temperatures under constant salinity; (d) temperature error leads to energy detection error.
图 12 Brillouin散射探测结果对盐度反演的影响 (a) 谱宽改变时, 盐度反演结果理论值与拟合值; (b) 谱宽误差导致盐度反演结果误差; (c) 能量改变时, 盐度反演结果理论值与拟合值; (d) 能量误差导致盐度反演结果误差
Fig. 12. Influence of Brillouin scattering detection results on salinity inversion: (a) Theoretical value and fitting value of salinity inversion results when the spectral width changes; (b) error of spectral width leads to the error of salinity inversion results; (c) theoretical value and fitting value of salinity inversion results when the energy changes; (d) error of energy leads to the error of salinity inversion results.
表 1 恒定盐度下, 不同温度Brillouin线宽、能量和频移计算结果
Table 1. Calculation results of Brillouin spectrum width, energy and frequency shift at different temperatures under constant salinity.
t S ΓB I vB 5 30 1.2732 0.2053 7.38705 10 30 0.9424 0.244 7.48328 15 30 0.7375 0.2859 7.56755 20 30 0.6130 0.3278 7.64070 25 30 0.5376 0.3674 7.70355 30 30 0.4883 0.403 7.75694 -
[1] Noto V D, Mecozzi M 1997 Appl. Spectrosc. 51 1294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Rudolf A, Walther T 2014 Opt. Eng. 53 051407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 任秀云 2016 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Ren X Y 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[4] Xu Z, Yu Z Z, Fu X Z, Yu X Q 2021 Act. Ocean Sin. 40 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liu Y M, Zhang R H, Yin Y H, Niu T 2005 J. Mereorol. Res-Prc. 19 355
[6] 张兰杰 2019 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Zhang L J 2019 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[7] Artlett C P, Pask H M 2017 Opt. Express 25 2840
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Burikov S A, Churina I V, Dolenko S A, Dolenko T A, Fadeev V V 2004 EARSeL eProceedings 3 298
[9] Wall T T, Hornig D F 1967 J. Chem. Phys. 47 784
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 何兴道, 夏健, 史久林, 刘娟, 李淑静, 刘建安, 方伟 2011 60 054207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He X D, Xia J, Shi J L, Liu J, Li S J, Liu J A, Fang W 2011 Acta Phys. Sin 60 054207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] John M D, Craig R J, Sanford A A 1985 J. Chem. Phys. 82 1732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Eckhardt G, Wagner E G 1966 J. Mol. Spectrosc. 19 407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liang K, Ma Y, Yu Y, Huang J, Li H 2012 Opt. Eng. 51 6002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 赵丽娟 2010 59 6219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao L J 2010 Acta Phys. Sin 59 6219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 史久林, 许锦, 罗宁宁, 王庆, 张余宝, 张巍巍, 何兴道 2019 68 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi J L, Xu J, Luo N N, Wang Q, Zhang Y B, Zhang W W, He X D 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] He X D, Wei H J, Shi J L, Liu J 2012 Opt. Commun. 285 4120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Grosso D V A 1974 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 56 1084
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Fry E S, Emery Y, Quan X H, Katz J W 1997 Appl. Opt. 36 6887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 马泳, 梁琨, 林宏, 冀航 2008 光学学报 28 1508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma Y, Liang K, Lin H, Ji H 2008 Acta. Opt. Sin. 28 1508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ge Y, Shi J L, Zhu K X, He X D 2013 Chin. Opt. Lett. 11 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 任秀云, 田兆硕, 孙兰君, 付石友 2014 63 164209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren X Y, Tian Z S, SUN J L, Fu S Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 164209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Haltrin V I, Kattawar G W 1993 Appl. Opt. 32 5356
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8929
- PDF下载量: 97
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: