-
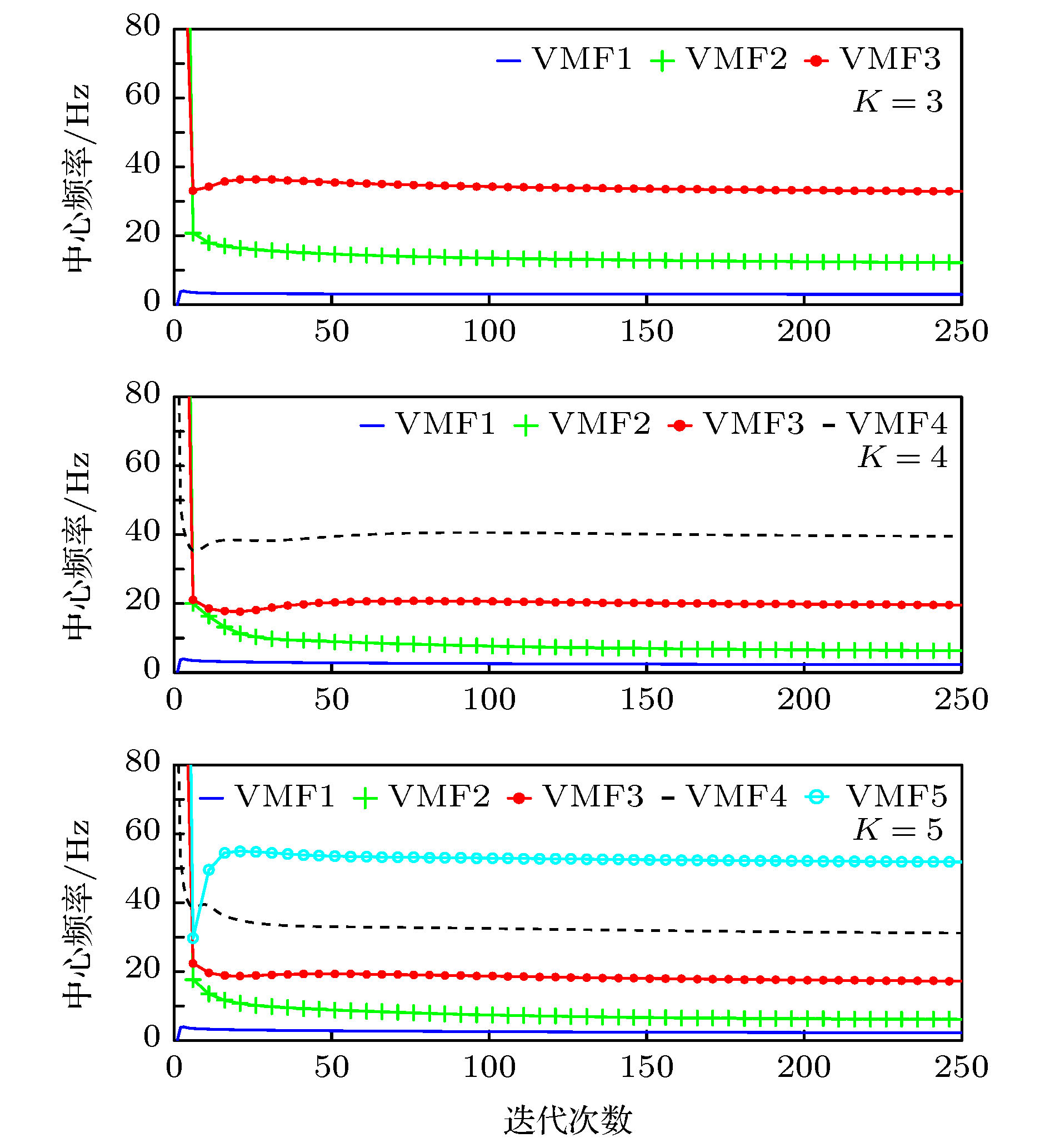
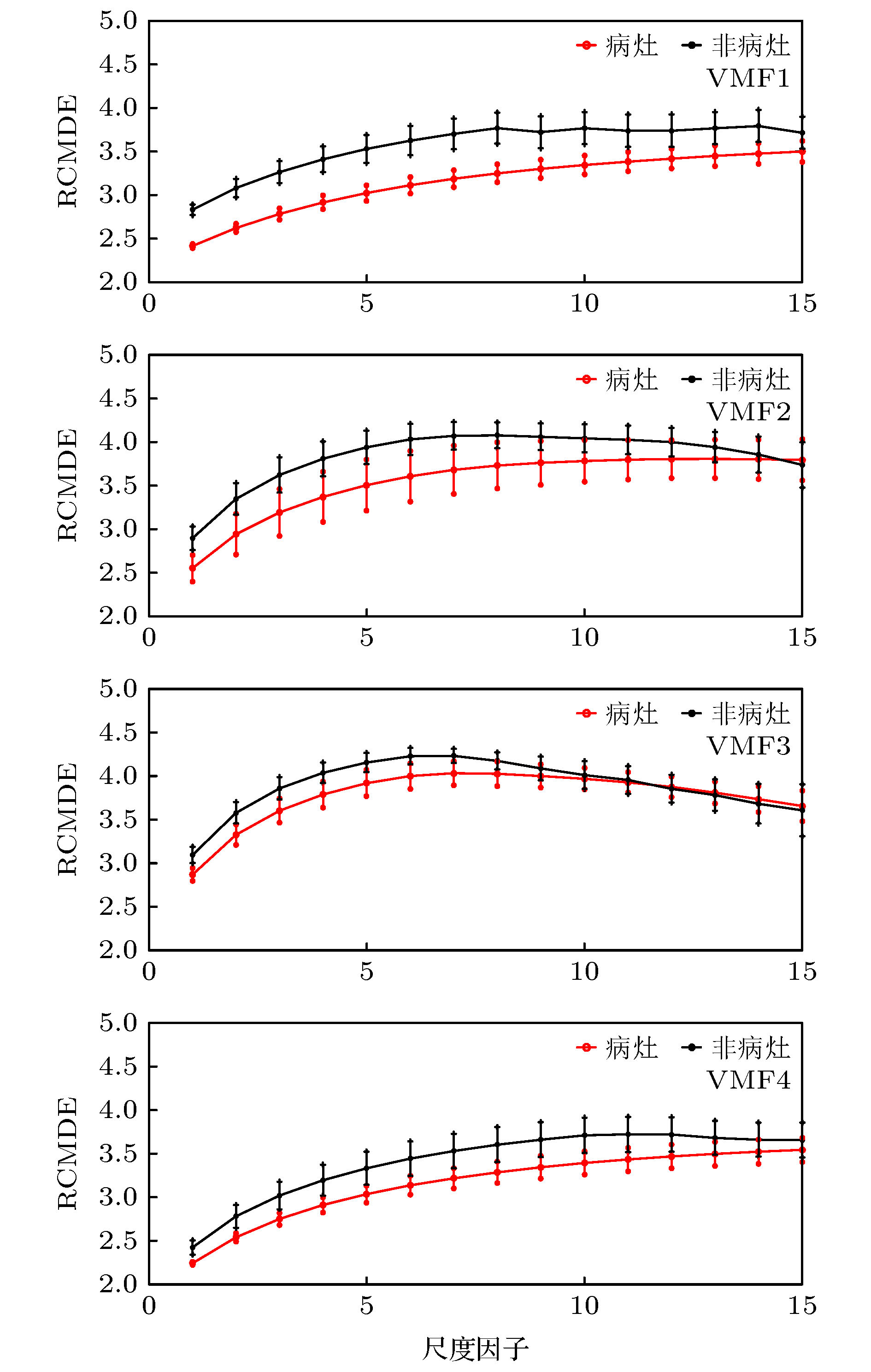
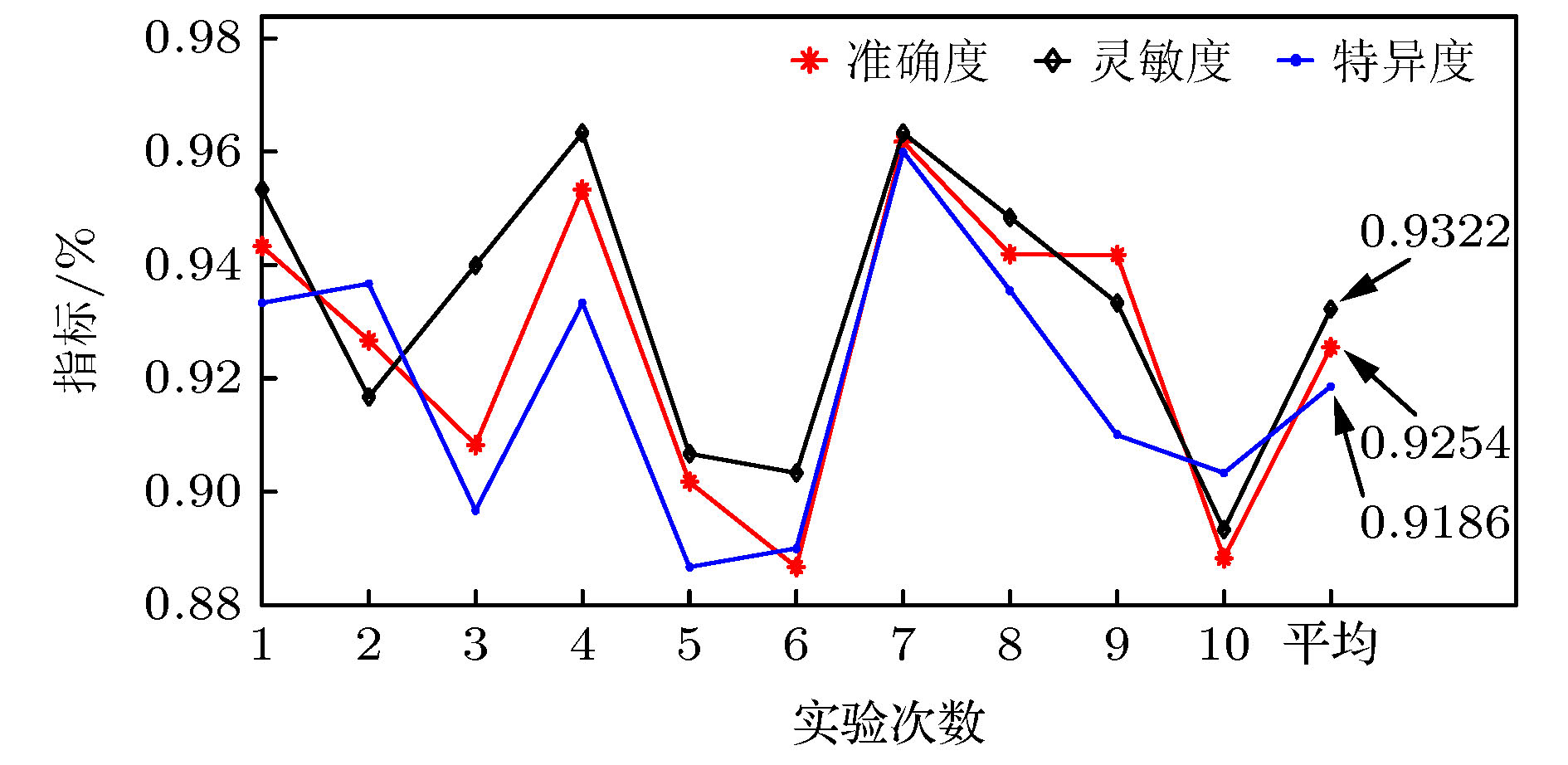
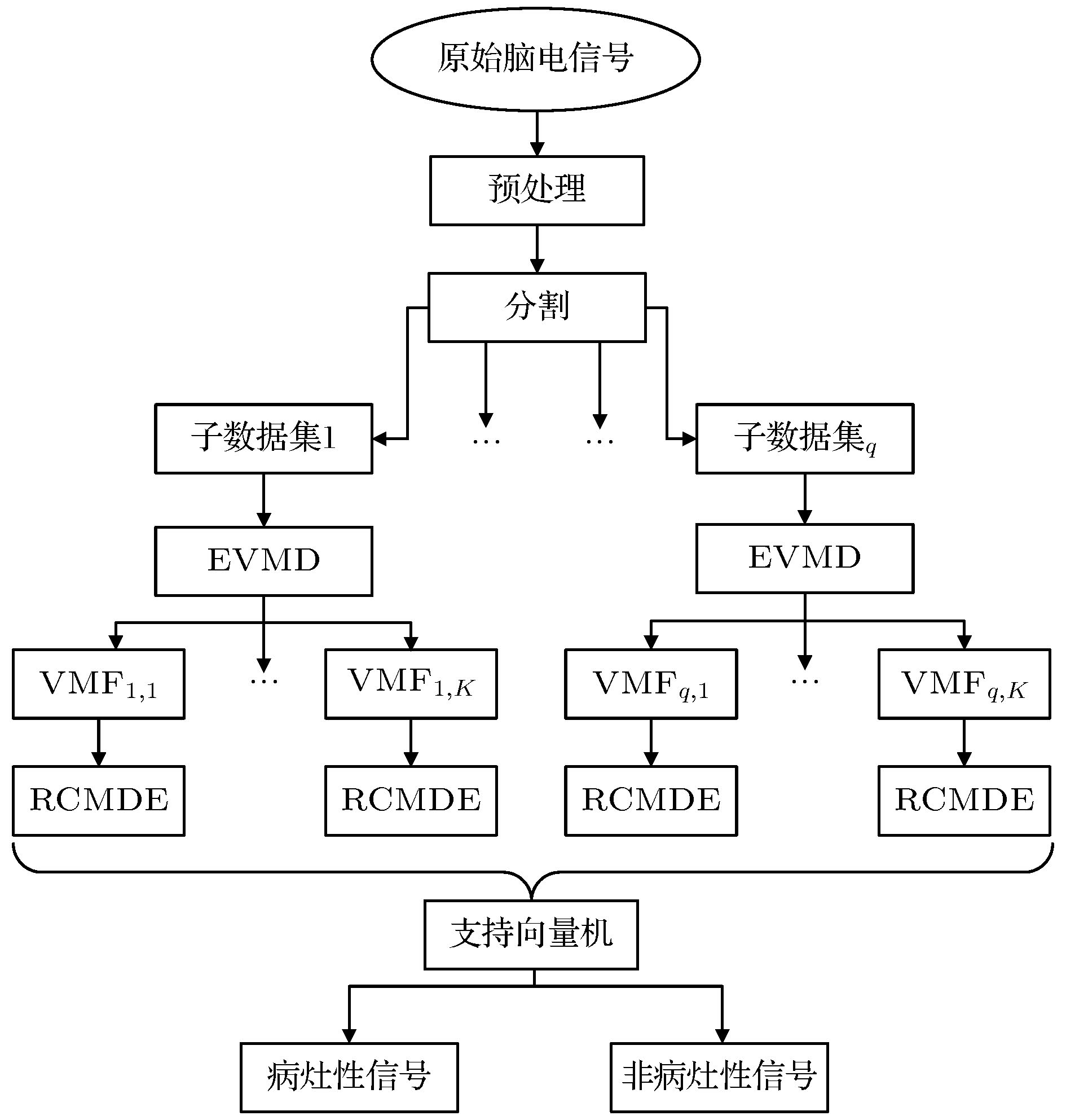
癫痫脑电信号分类对于癫痫诊治具有重要意义. 为了实现病灶性与非病灶性癫痫脑电信号的分类, 本文利用弹性网回归重构变分模态分解算法, 提出弹性变分模态分解算法并将其应用到所提癫痫脑电信号分类方法中. 该方法先将原信号分割成多个子信号, 并对各子信号进行弹性变分模态分解, 然后从分解后的不同变分模态函数中提取精细复合多尺度散布熵作为特征, 最后利用支持向量机进行分类. 针对癫痫脑电的公共数据集, 最终的实验结果表明, 准确率、灵敏度和特异度三个性能指标分别达到92.54%, 93.22%和91.86%.
-
关键词:
- 弹性变分模态分解 /
- 精细复合多尺度散布熵 /
- 癫痫脑电
Epilepsy is an extensive nervous system disease nowadays. Electroencephalogram (EEG) can capture the abnormal discharge of nerves in the brain duration of seizure and provide a non-invasive way to identify epileptogenic sites in the brain. In order to distinguish between focal epilepsy EEG signal and non-focal epilepsy EEG signal, in this paper we propose an automated epileptic EEG detection method based on the elastic variational mode decomposition (EVMD). The proposed EVMD algorithm is a method of analyzing the signals and also a processing method in time-frequency domain, in which the elastic net regression is used to reconstruct a constrained variational model in variational mode decomposition (VMD). Used in the VMD algorithm is the Tikhonov regularization that is also statistically called ridge regression as a solution of recovering the unknown signal and assessing the bandwidth of a mode, namely the variational equation constructed by VMD only has L2 norm. However, the ridge regression cannot select variables when the equation has multiple variables. Another regression method, called lasso regression, only has L1 norm and can select a more accurate model from multiple variables, but it has worse performance when variables have group effect or co-linearity. The elastic net regression has advantages of ridge regression and lasso regression, in other word, the variational equation constructed by EVMD has both L1 regularization item and L2 regularization item, so in this paper we propose the EVMD by elastic net regression. In addition, in this paper the EVMD is used to distinguish between focal epilepsy EEG signal and non-focal epilepsy EEG signal. Firstly, the original EEG signals are divided into several sub-signals where the test signals are divided into sub-signals with shorter durations by time series and a reasonable time overlap is kept between successive sub-signals. After that each sub-signal is decomposed into intrinsic mode functions by using the EVMD. Furthermore, the refined composite multiscale dispersion entropy (RCMDE) as feature is extracted from each intrinsic mode function where a Student’s t-test is used to assess the statistical differences between RCMDEs extracted from focal and non-focal EEG signals respectively. Finally, the support vector machine (SVM) is used to classify their features. For an epilepsy EEG signalspublic data set, the final experimental results show that the performance indices of accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity can reach 92.54%, 93.22% and 91.86% respectively.-
Keywords:
- elastic variational mode decomposition /
- refined composite multiscale dispersion entropy /
- epileptic electroencephalogram
[1] World Health Organization http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy/ [2019-6-20]
[2] Andrzejak R G, Schindler K, Rummel C 2012 Phys. Rev. E 86 046206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 张瑞, 宋江玲, 胡文凤 2016 西北大学学报(自然科学版) 46 781
Zhang R, Song J L, Hu W F 2016 J. Northwest Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 46 781
[4] Alam S, Bhuiyan M 2013 IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 17 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Das A, Bhuiyan M, Alam S 2014 Signal Image Video Process. 10 259
[6] Rahman M, Bhuiyan M, Das A 2019 Biomed. Signal Process. Control 50 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Sharma R, Pachori R, Acharya U 2015 Entropy 17 669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Abhijit B, Ram B P 2017 Entropy 19 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 谢平, 杨芳梅, 李欣欣, 杨勇, 陈晓玲, 张利泰 2016 65 118701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie P, Yang F M, Li X X, Yang Y, Chen X L, Zhang L T 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 118701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王莹, 侯凤贞, 戴加飞, 刘新峰, 李锦, 王俊 2014 63 218701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Hou F Z, Dai J F, Liu X F, Li J, Wang J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 218701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Azami H, Rostaghi M, Abasolo D, Escudero J 2017 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64 2872
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] KiymiK M, Guler I, Dizibuyuk A, Akin M 2005 Comput. Biol. Med. 35 603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 张涛, 陈万忠, 李明阳 2016 65 038703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang T, Chen W Z, Li M Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 038703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso P 2014 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62 531
[15] 张哲, 梁冯珍 2013 哈尔滨商业大学学报 (自然科学版) 29 592
Zhang Z, Liang F Z 2013 J. Harbin Univ. Com. (Nat. Sci.) 29 592
[16] Zou H, Hastie T 2005 J. R. Stat. Soc. 67 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Andrzejak R G http://www.dtic.upf.edu/~ralph/ [2019-3-20]
[18] Andrzejak R G, Schindler K, Rummel C 2012 Physical Review E 86 046206
[19] Chatterjee S, Pratiher S, Bose R 2017 IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 11 1014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Abhijit B, Manish S, Ram B P, Pradip S Rajendra A 2018 Neural Comput. Appl. 29 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li Z P, Chen J L, Zi Y Y, Pan J 2017 Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 85 512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wang X B, Yang Z X, Y an, X A 2018 IEEE-ASME Trans. Mech. 23 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang Z J, He G F, Du W H, Zhou J, Han X F, Wang J T, He H H, Guo X M, Wang J Y, Kou Y F 2019 IEEE Access 7 44871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 从各VMF中提取的RCMDE特征p值
Table 1. The p values of RCMDE computed from VMF.
VMF1 VMF2 VMF3 VMF4 p值 1.17 × 10–4 2.38 × 10–2 4.42 × 10–2 7.50 × 10–3 表 2 EVMD与VMD实验结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of experimental result between EVMD and VMD.
指标 准确度/% 灵敏度/% 特异度/% EMVD 92.54 93.22 91.86 VMD 89.49 87.56 88.12 表 3 本文方法与其他方法对比
Table 3. Comparison between proposed method and previously published methods.
-
[1] World Health Organization http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy/ [2019-6-20]
[2] Andrzejak R G, Schindler K, Rummel C 2012 Phys. Rev. E 86 046206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 张瑞, 宋江玲, 胡文凤 2016 西北大学学报(自然科学版) 46 781
Zhang R, Song J L, Hu W F 2016 J. Northwest Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 46 781
[4] Alam S, Bhuiyan M 2013 IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 17 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Das A, Bhuiyan M, Alam S 2014 Signal Image Video Process. 10 259
[6] Rahman M, Bhuiyan M, Das A 2019 Biomed. Signal Process. Control 50 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Sharma R, Pachori R, Acharya U 2015 Entropy 17 669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Abhijit B, Ram B P 2017 Entropy 19 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 谢平, 杨芳梅, 李欣欣, 杨勇, 陈晓玲, 张利泰 2016 65 118701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie P, Yang F M, Li X X, Yang Y, Chen X L, Zhang L T 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 118701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王莹, 侯凤贞, 戴加飞, 刘新峰, 李锦, 王俊 2014 63 218701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Hou F Z, Dai J F, Liu X F, Li J, Wang J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 218701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Azami H, Rostaghi M, Abasolo D, Escudero J 2017 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64 2872
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] KiymiK M, Guler I, Dizibuyuk A, Akin M 2005 Comput. Biol. Med. 35 603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 张涛, 陈万忠, 李明阳 2016 65 038703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang T, Chen W Z, Li M Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 038703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso P 2014 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62 531
[15] 张哲, 梁冯珍 2013 哈尔滨商业大学学报 (自然科学版) 29 592
Zhang Z, Liang F Z 2013 J. Harbin Univ. Com. (Nat. Sci.) 29 592
[16] Zou H, Hastie T 2005 J. R. Stat. Soc. 67 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Andrzejak R G http://www.dtic.upf.edu/~ralph/ [2019-3-20]
[18] Andrzejak R G, Schindler K, Rummel C 2012 Physical Review E 86 046206
[19] Chatterjee S, Pratiher S, Bose R 2017 IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 11 1014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Abhijit B, Manish S, Ram B P, Pradip S Rajendra A 2018 Neural Comput. Appl. 29 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li Z P, Chen J L, Zi Y Y, Pan J 2017 Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 85 512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wang X B, Yang Z X, Y an, X A 2018 IEEE-ASME Trans. Mech. 23 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang Z J, He G F, Du W H, Zhou J, Han X F, Wang J T, He H H, Guo X M, Wang J Y, Kou Y F 2019 IEEE Access 7 44871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9555
- PDF下载量: 134
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: