-
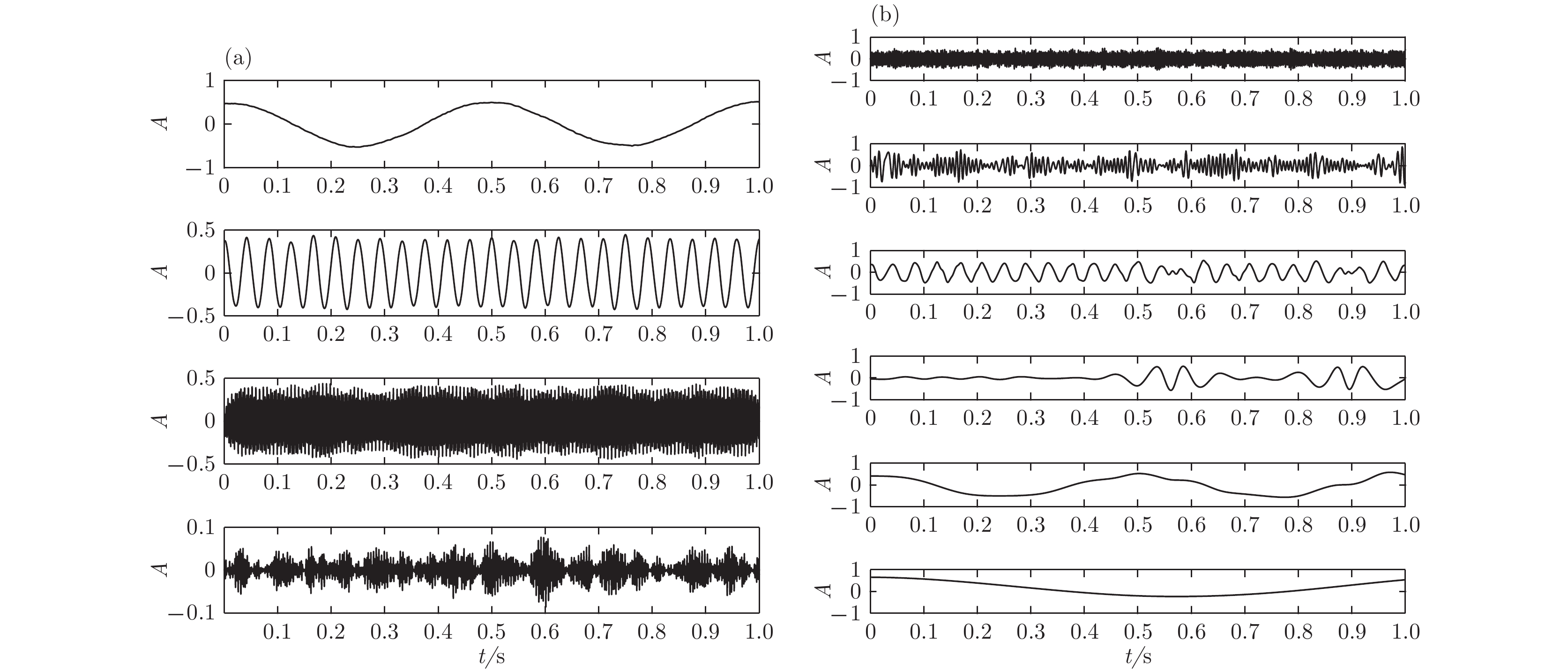
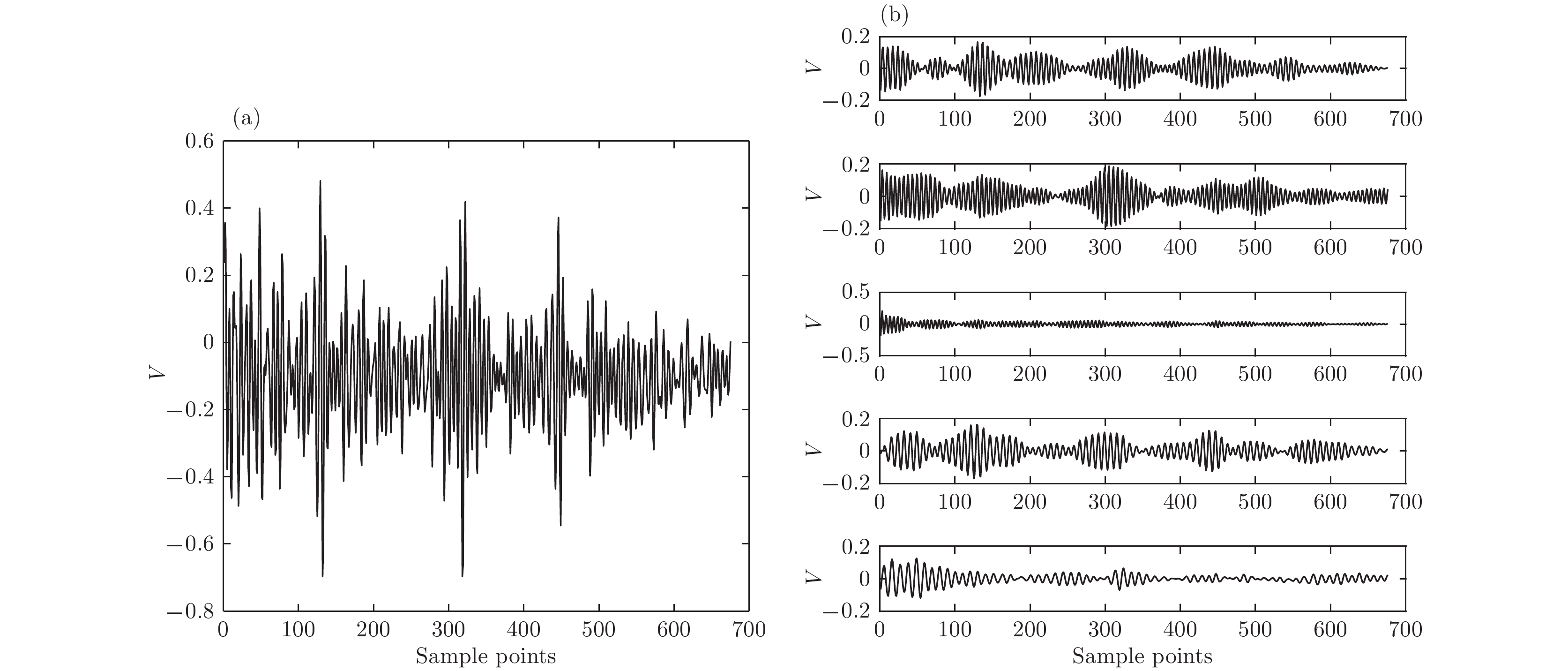
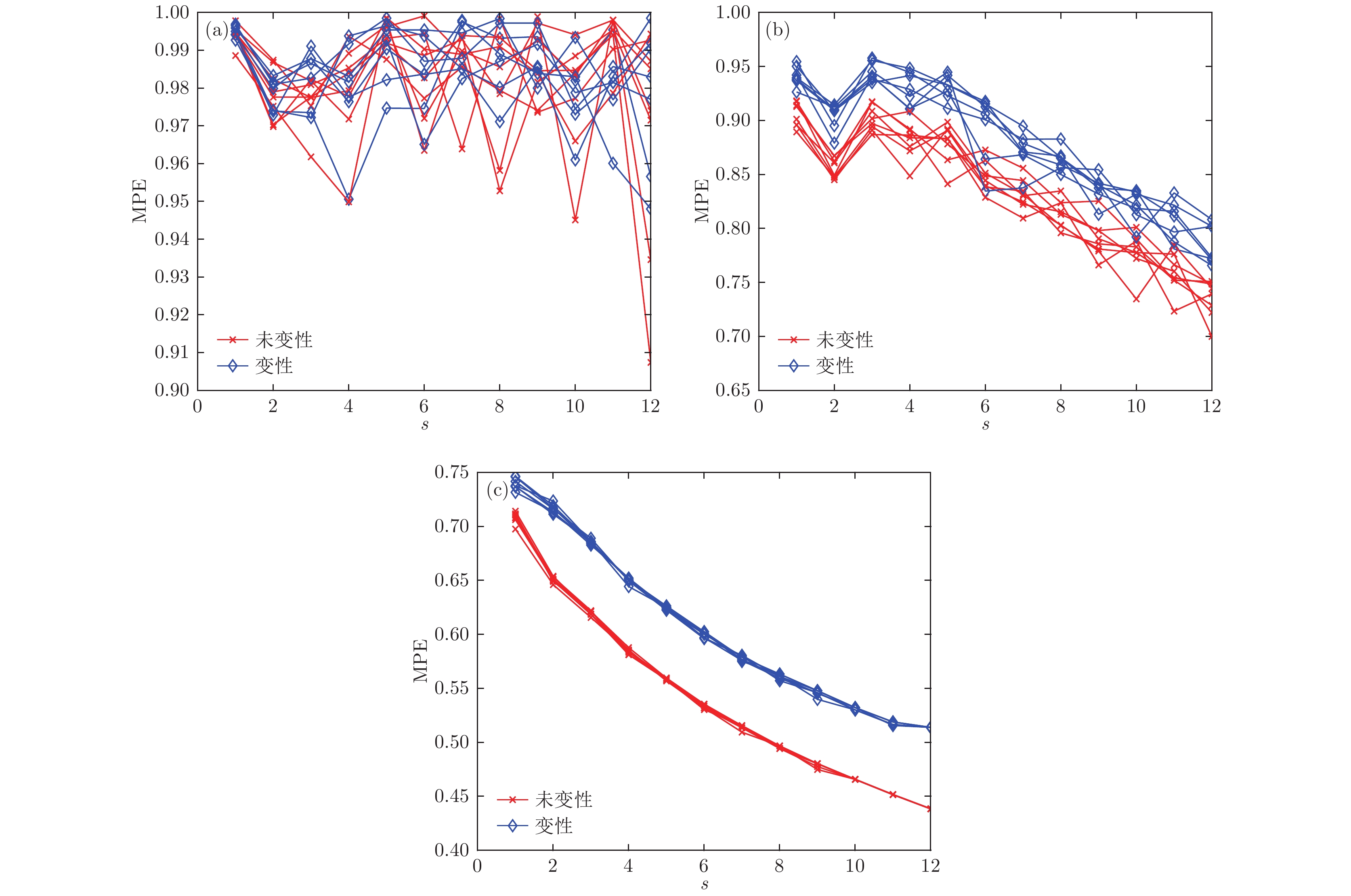
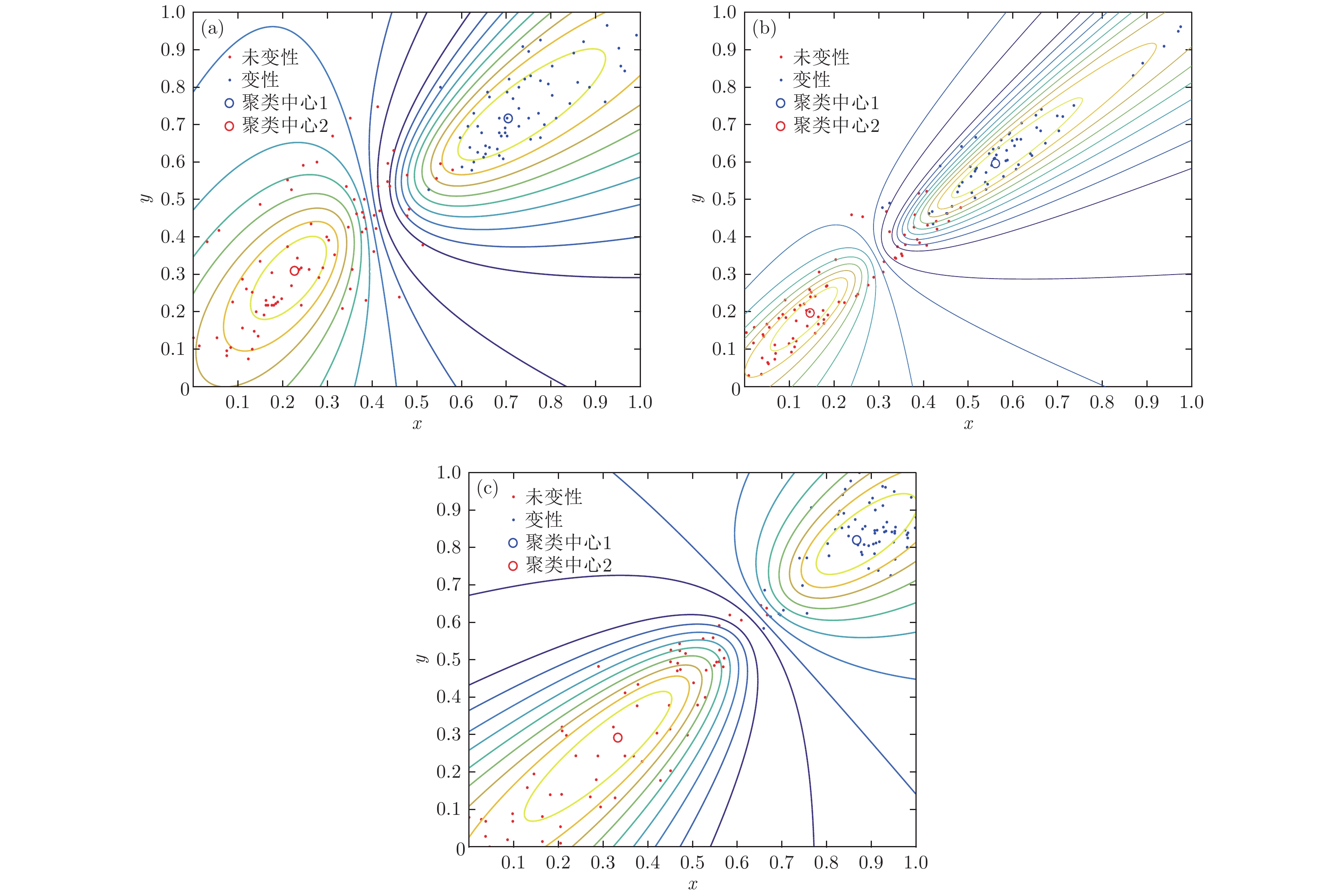
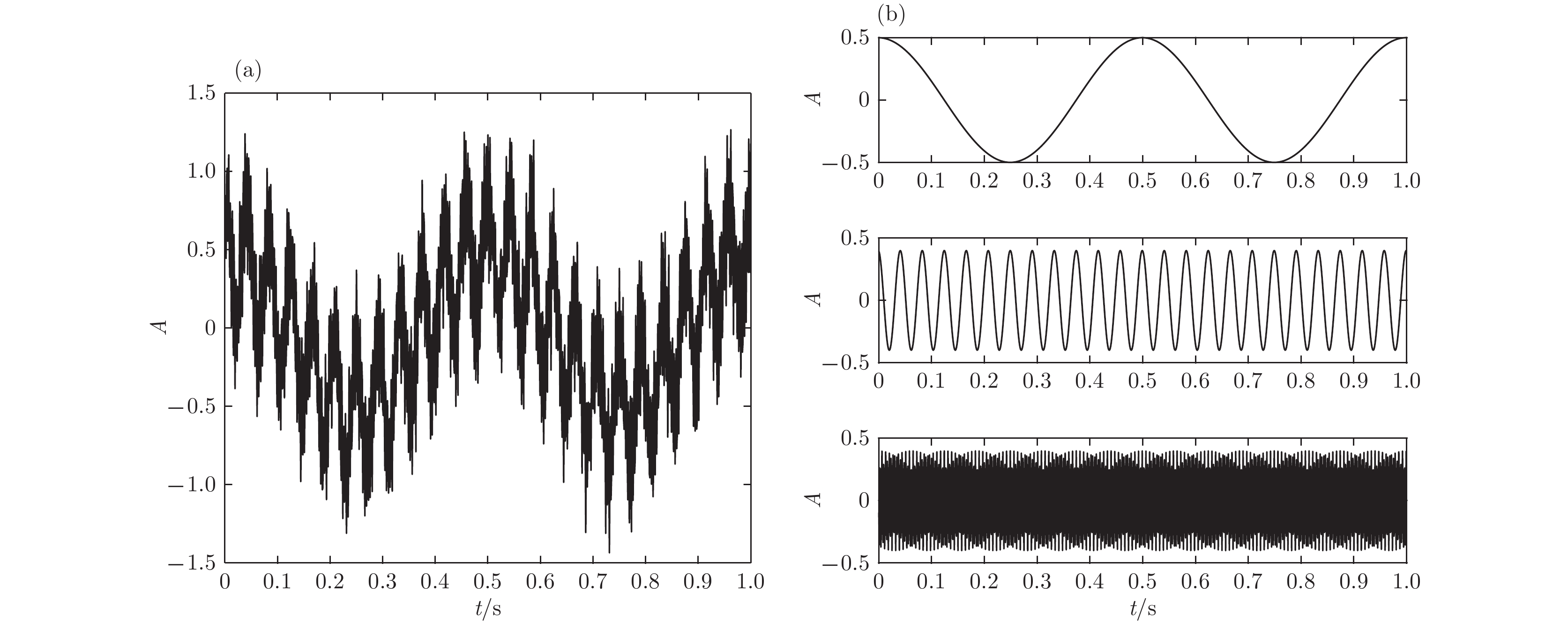
根据高强度聚焦超声(HIFU)治疗中超声散射回波信号的特点, 本文利用变分模态分解(VMD)与多尺度排列熵(MPE)对生物组织变性识别进行了研究. 首先对生物组织中的超声散射回波信号进行变分模态分解, 根据各阶模态的功率谱信息熵值分离出噪声分量和有用分量; 对分离出的有用信号进行重构并提取其多尺度排列熵; 然后通过Gustafson-Kessel (GK)模糊聚类确定聚类中心, 采用欧氏贴近度与择近原则对生物组织进行变性识别. 将所提方法应用于HIFU治疗中超声散射回波信号实验数据, 用遗传算法对多尺度排列熵的参数优化后, 对293例未变性组织和变性组织的超声散射回波信号数据进行了多尺度排列熵分析, 发现变性组织的超声散射回波信号的多尺度排列熵值要高于未变性组织; 多尺度排列熵可以较好地识别生物组织是否变性. 相对于EMD-MPE-GK模糊聚类以及VMD-小波熵(WE)-GK模糊聚类变性识别方法, 本文所提方法中变性与未变性组织特征交叠区域数据点更少, 聚类效果和分类性能更好; 本实验环境下生物组织变性识别结果表明, 该方法的识别率更高, 高达93.81%.It is an important practical problem to accurately recognize whether biological tissue is denatured during high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) treatment. Ultrasonic scattering echo signals are related to some physical properties of biological tissues. According to the characteristics of ultrasonic scattering echo signals, the recognition of denatured biological tissues is studied based on the variational mode decomposition (VMD) and multi-scale permutation entropy (MPE) in this paper. The ultrasonic echo signals are decomposed into various modal components by the VMD. The noise components and the useful components are separated according to the power spectrum information entropy of various modal components. The separated useful signals are reconstructed and the MPE are extracted. Furthermore, Gustafson-Kessel (GK) fuzzy clustering analysis is employed to obtain the standard clustering center, and the recognition of denatured biological tissues is carried out by Euclid approach degree and principle of proximity. The proposed method is applied to ultrasonic scattering echo signal during HIFU treatment. In order to determine the parameters of MPE algorithm for ultrasonic scattering echo signals, the embedding dimension of the MPE is discussed, and the scale factor of the MPE algorithm is optimized by genetic algorithm. When the delay time and the embedding dimension are 2 and 7 respectively, the MPE values decrease with scale factor increasing. Assuming that the scale factor is 12 from optimization results, the 293 ultrasonic scattering echo signals from normal tissues and denatured tissues are analyzed by the MPE. It is found that the MPE values of the denatured tissues are higher than those of the normal tissues. The MPE can be used to distinguish normal tissues and denatured tissues. Comparing with the recognition methods of the EMD-MPE-GK fuzzy clustering method and the VMD-WE-GK fuzzy clustering, the proposed method has good clustering performance and separability. Its partition coefficient (PC) is close to 1 and the Xie-Beni (XB) index is smaller. There are fewer feature points in the overlap region between MPE features of denatured tissues and normal tissues. The recognition results of denatured biological tissues in this experimental environment show that the recognition rate based on this method is higher, reaching up to 93.81%.
-
Keywords:
- high intensity focused ultrasound /
- variational mode decomposition /
- power spectrum information entropy /
- multi-scale permutation entropy
[1] Cranston D 2015 Ultrason. Sonochem. 27 654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ellens N, Hynynen K 2015 Med. Phys. 42 4896
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bailey M, Khokhlova V, Sapozhnikov O, Kargl S, Crum L 2003 Acoust.Phys. 49 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Worthington A E, Tranchtenberg J, Sherar M D 2002 Ultrasound Med. Biol. 10 1311
[5] Damianou C A, Sanghvi N T, Fry F J, Maass-Moreno R 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 102 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 盛磊, 周著黄, 吴水才, 丁琪瑛, 曾毅 2014 北京工业大学学报 40 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sheng L, Zhou Z H, Wu S C, Ding Q Y, Zeng Y 2014 Journal of Beijing Polytechnic University 40 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bamber J C, Hill C R 1979 Ultrasound Med. Biol. 5 149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 明文, 谭乔来, 钱盛友, 邹孝, 廖志远 2015 测试技术学报 5 404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ming W, Tan Q L, Qian S Y, Zou X, Liao Z Y 2015 Journal of Test and Measurement Technology 5 404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Arthur R M, Straube W L, Starman J D, Moros E G 2003 Med. Phys. 30 1021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Seip R, Ebbini E S 1995 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 42 828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Parker K J 1983 Ultrasound Med. Biol. 9 363
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bloch S, Bailey M R, Crum L A, Kaczkowski P J, Keilman G W, Mourad P D 1998 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 103 2868
[13] Wu Z H, Huang N E, Chen X Y 2009 Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 1 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 周彦婷, 汪源源 2010 声学学报 5 495
Zhou Y T, Wang Y Y 2010 Acta Acustica 5 495
[15] Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D 2014 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62 531
[16] Li J, Ning X 2006 Phys. Rev. E 73 88
[17] 杨孝敬, 杨阳, 李淮周, 钟宁 2016 65 218701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang X J, Yang Y, Li H Z, Zhong N 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 218701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 严碧歌, 赵婷婷 2011 60 078701
Yan B G, Zhao T T 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 078701
[19] Bandt C, Pompe B 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 174102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gao Y, Villecco F, Li M, Song W 2017 Entropy 19 176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 姚文坡, 刘铁兵, 戴加飞, 王俊 2014 63 078704
Yao W P, Liu T B, Dai J F, Wang J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 078704
[22] Rahimian S,Tavakkoli J 2013 J. Ther. Ultrasound 1 1
[23] Davari A, Marhaban M H, Noor S, Karimadini M, Karimoddini A 2010 Fuzzy Sets Syst. 163 45
-
表 1 三组样本在嵌入维数m = 7时各尺度下排列熵平均值
Table 1. The average entropy of the three samples at each scale when the embedding dimension m = 7.
尺度因子s 样本1 样本2 样本3 未变性 变性 未变性 变性 未变性 变性 1 0.7068 0.7396 0.7085 0.7408 0.7028 0.7366 2 0.6504 0.7163 0.6491 0.7013 0.6449 0.6958 3 0.6200 0.6855 0.6194 0.6718 0.6145 0.6715 4 0.5836 0.6498 0.5839 0.6361 0.5781 0.6378 5 0.5569 0.6241 0.5575 0.6176 0.5530 0.6151 6 0.5328 0.5994 0.5329 0.5962 0.5273 0.5934 7 0.5142 0.5780 0.5130 0.5771 0.5087 0.5776 8 0.4954 0.5609 0.4958 0.5618 0.4908 0.5602 9 0.4792 0.5458 0.4796 0.5453 0.4737 0.5418 10 0.4657 0.5313 0.4646 0.5325 0.4622 0.5320 11 0.4536 0.5152 0.4506 0.5246 0.4471 0.5173 12 0.4384 0.5139 0.4379 0.5188 0.4350 0.5059 13 0.4364 0.4626 0.4367 0.4686 0.4289 0.5042 表 2 变性与未变性组织识别结果
Table 2. Recognition results of denatured and undenatured tissues.
聚类方法 PC XB 识别率/% VMD-MPE-GK 0.8119 4.498 93.81 EMD-MPE-GK 0.8088 11.589 87.44 VMD-WE-GK 0.790 14.878 85.29 -
[1] Cranston D 2015 Ultrason. Sonochem. 27 654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ellens N, Hynynen K 2015 Med. Phys. 42 4896
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bailey M, Khokhlova V, Sapozhnikov O, Kargl S, Crum L 2003 Acoust.Phys. 49 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Worthington A E, Tranchtenberg J, Sherar M D 2002 Ultrasound Med. Biol. 10 1311
[5] Damianou C A, Sanghvi N T, Fry F J, Maass-Moreno R 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 102 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 盛磊, 周著黄, 吴水才, 丁琪瑛, 曾毅 2014 北京工业大学学报 40 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sheng L, Zhou Z H, Wu S C, Ding Q Y, Zeng Y 2014 Journal of Beijing Polytechnic University 40 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bamber J C, Hill C R 1979 Ultrasound Med. Biol. 5 149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 明文, 谭乔来, 钱盛友, 邹孝, 廖志远 2015 测试技术学报 5 404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ming W, Tan Q L, Qian S Y, Zou X, Liao Z Y 2015 Journal of Test and Measurement Technology 5 404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Arthur R M, Straube W L, Starman J D, Moros E G 2003 Med. Phys. 30 1021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Seip R, Ebbini E S 1995 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 42 828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Parker K J 1983 Ultrasound Med. Biol. 9 363
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bloch S, Bailey M R, Crum L A, Kaczkowski P J, Keilman G W, Mourad P D 1998 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 103 2868
[13] Wu Z H, Huang N E, Chen X Y 2009 Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 1 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 周彦婷, 汪源源 2010 声学学报 5 495
Zhou Y T, Wang Y Y 2010 Acta Acustica 5 495
[15] Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D 2014 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62 531
[16] Li J, Ning X 2006 Phys. Rev. E 73 88
[17] 杨孝敬, 杨阳, 李淮周, 钟宁 2016 65 218701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang X J, Yang Y, Li H Z, Zhong N 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 218701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 严碧歌, 赵婷婷 2011 60 078701
Yan B G, Zhao T T 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 078701
[19] Bandt C, Pompe B 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 174102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gao Y, Villecco F, Li M, Song W 2017 Entropy 19 176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 姚文坡, 刘铁兵, 戴加飞, 王俊 2014 63 078704
Yao W P, Liu T B, Dai J F, Wang J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 078704
[22] Rahimian S,Tavakkoli J 2013 J. Ther. Ultrasound 1 1
[23] Davari A, Marhaban M H, Noor S, Karimadini M, Karimoddini A 2010 Fuzzy Sets Syst. 163 45
计量
- 文章访问数: 13311
- PDF下载量: 96
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: