-
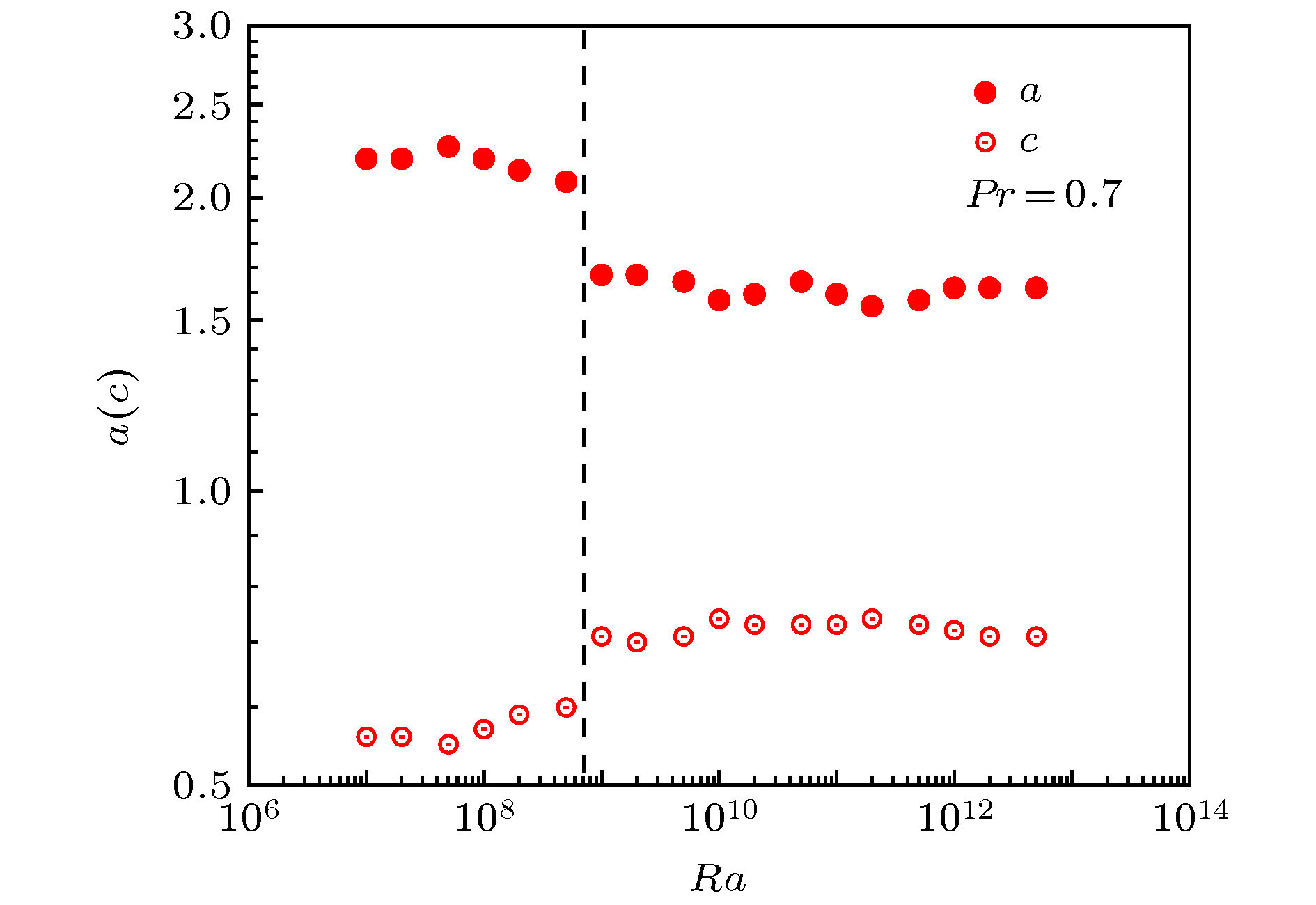
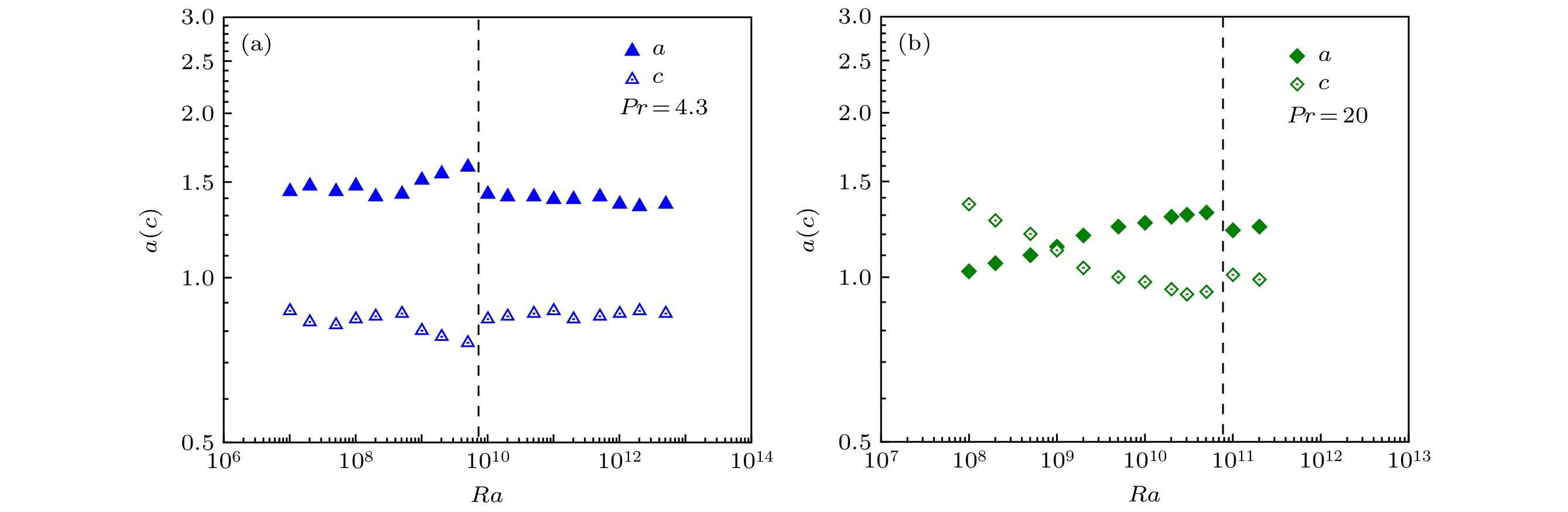
采用高效并行的直接数值模拟方法计算了三个Pr数的系列Ra数的二维热对流. 对所有计算结果的平均场温度边界层特性进行研究, 采用考虑脉动作用的双参数温度边界层理论对温度边界层剖面进行拟合, 得到了拟合参数a和参数c的分布. 参数a决定了温度剖面的基本特性, 而参数c起到了对温度剖面外区的修正作用, 使得在5个边界层厚度温度边界层剖面的计算值与理论解符合良好. 参数c的变化特性与参数a的相反, a值增大则c值减小. 不同的Pr数拟合参数a随Ra数变化具有不同的分布特性, 但都存在突然减小的间断. 参数a的间断变化是由湍流热对流流动状态由椭圆形大尺度环流突变到圆形大尺度环流造成的, 且随着Pr数变大间断点的特征Ra数增高. 相同Ra数时Pr数越大温度剖面的拟合参数a值越小, 表明温度边界层中脉动的影响越小. 传热特性
$Nu/R{a^{0.3}}$ 、表征羽流运动特性的大尺度环流路径周长, 及温度边界层拟合参数a三者随Ra数的变化都存在转折或间断, 且对应相同的特征Ra数, 显示三者具有很好的相关性并与流动形态变化直接关联.The two-dimensional thermal convection with three-Pr series Ra number is calculated by using the highly efficient parallel DNS method. The two-parameter temperature boundary layer theory, with the pulsation influence taken into account, is used to fit the temperature boundary layer profile for the field averaged over all calculations. The distributions of the fitted parameters a and c are obtained. Parameter a determines the basic characteristics of the temperature profile, and parameter c plays a role in correcting the outer area of the temperature profile. Therefore, the simulation results of the temperature boundary layer profile is well matched with the theoretical solution in the 5 boundary layers. The variation characteristic of parameter c is the opposite to that of parameter a, and the c value decreases as the a value increases. The fitting parameters for the different Pr numbers have different distribution characteristics as the Ra number changes, but they have all suddenly decreasing interruptions, and as the Pr number becomes large, the characteristic Ra number for the interruption increases. The variation characteristic of parameter c is the opposite to that of parameter a. With the same Ra number, the larger the Pr number, the smaller the fitting parameter of the temperature profile is, indicating that the influence of pulsation in the temperature boundary layer is smaller. The heat transfer characteristic Nu/Ra0.3, the large-scale circulation path circumference for the characteristics of plume movement, and the temperature boundary layer fitting parameter all have the interruptions with the change of Ra number, and their corresponding characteristic Ra numbers are identical. The results show that the three have good correlation and are directly related to the change of flow pattern.-
Keywords:
- 2-dimentional turbulent convection /
- thermal boundary layer profile /
- interruption characteristics /
- heat transfer characteristics /
- large scale circulation path circumference
[1] Ahlers G, Grossmann S, Lohse D 2009 Rev. Mod. Phys. 81 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Grossmann S, Lohse D 2000 J. Fluid Mech. 407 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Grossmann S, Lohse D 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 3316
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lui S L, Xia K Q 1998 Phys. Rev. E 57 5494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhou Q, Xia K Q 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 104301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ahlers G, Bodenschatz E, Funfschilling D, Grossmann S, He X Z, Lohse D, Stevens R J A M, Verzicco R 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 114501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wei P, Ahlers G 2014 J. Fluid Mech. 758 809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ahlers G, Bodenschatz E, He X 2014 J. Fluid Mech. 758 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou Q, Stevens R J A M, Sugiyama K, Grossmann S, Lohse D, Xia K Q 2010 J. Fluid Mech. 664 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhou Q, Sugiyama K, Stevens R J, Grossmann S, Lohse D, Xia K Q 2011 Phys. Fluids 23 125104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Stevens R J A M, Zhou Q, Grossmann S, Verzicco R, Xia K Q, Lohse D 2011 Phys. Rev. E 85 027301
[12] Shishkina O, Horn S, Wagner S 2013 J. Fluid Mech. 730 442
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shishkina O, Horn S, Wagner S, Ching E S C 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 114302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Shishkina O, Horn S, Emran M S, Ching E S C 2017 Phys. Rev. Fluids 2 113502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 何鹏, 黄茂静, 包芸 2018 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 48 124702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He P, Huang M J, Bao Y 2018 Sci. Sin.-Phys. Mech. Astron. 48 124702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 黄茂静, 包芸 2016 65 204702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang M J, Bao Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 204702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang Y, He X Z, Tong P 2016 Phys. Rev. Fluids 1 082301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 包芸, 高振源, 叶孟翔 2018 67 014701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao Y, Gao Z Y, Ye M X 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 014701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bao Y, Luo J H, Ye M X 2018 J. Mech. 34 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Sun C, Xia K Q 2005 Phys. Rev. E 72 067302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 包芸, 何建超, 高振源 2019 68 164701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao Y, He J C, Gao Z Y 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 164701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
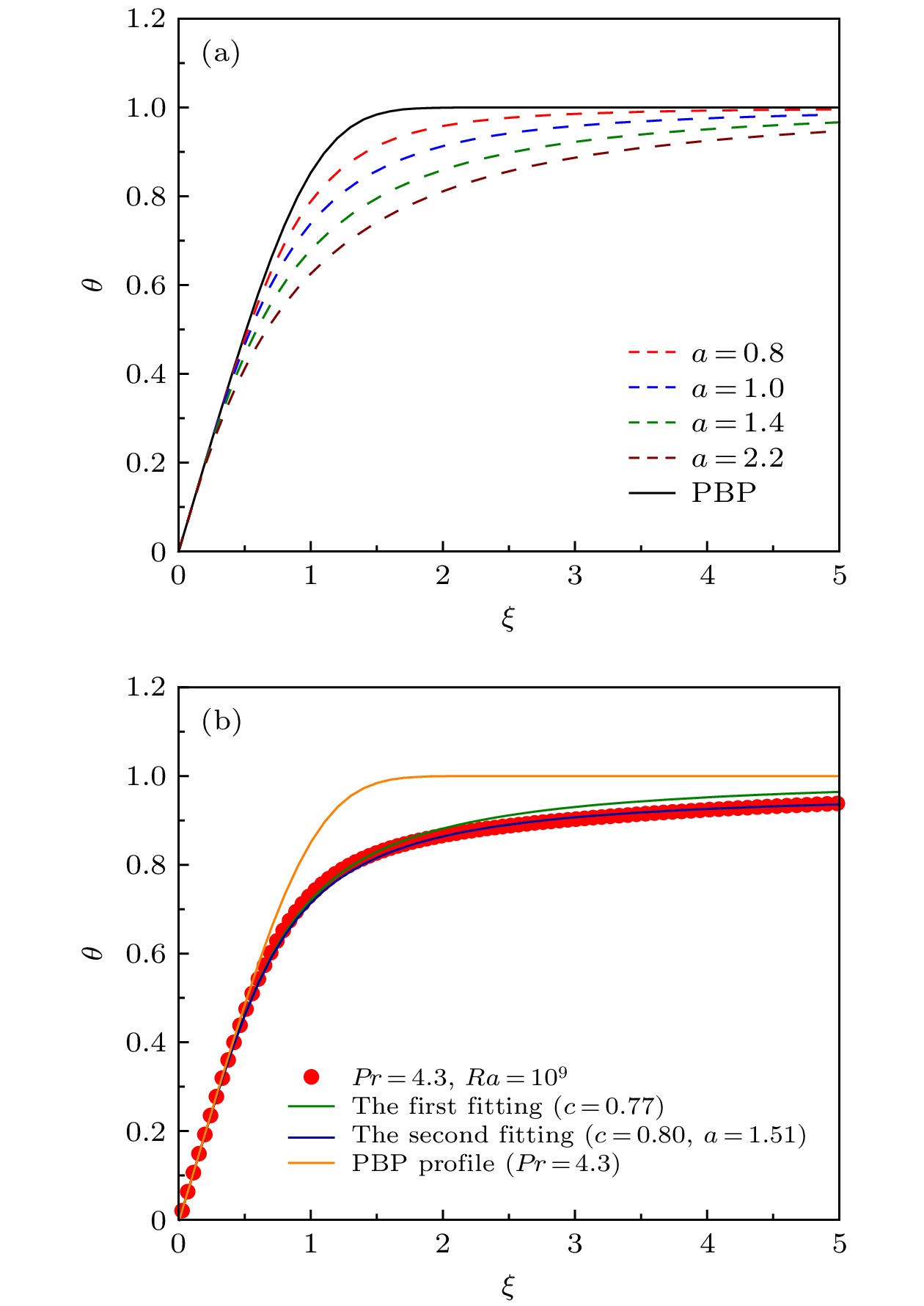
图 1 (a) 不同控制参数a, 双参数理论温度剖面分布, 黑色实线为PBP理论解; (b) Pr = 4.3, Ra = 109, 单、双参数温度剖面拟合
Fig. 1. (a) Two-parameter theoretical temperature profile distribution for different parameters a, the black solid line is the Prandtl-Blasius predictions; (b) Pr = 4.3, Ra = 109, one and two-parameter temperature profile fitting.
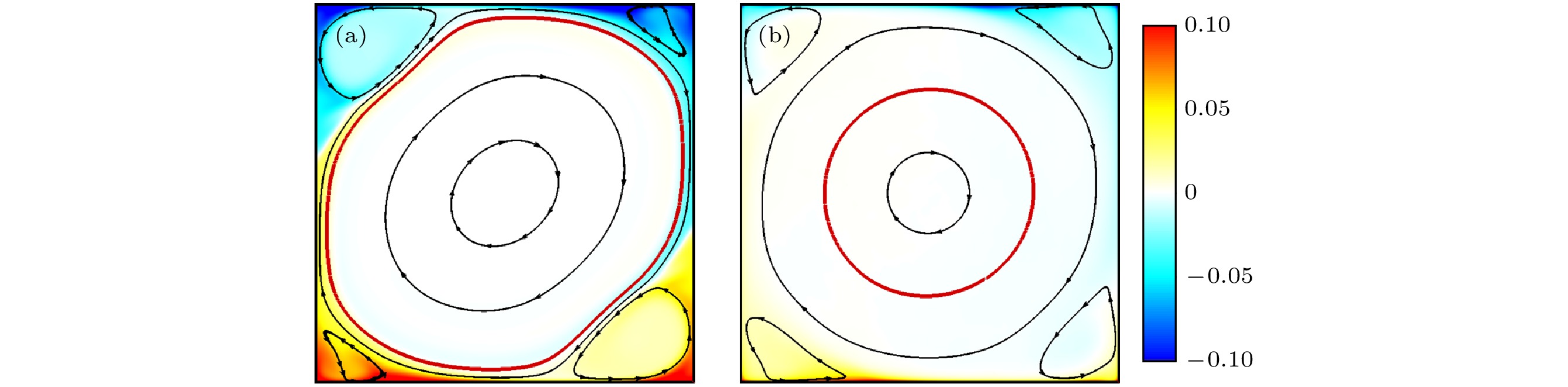
图 4 两个典型热对流平均温度场和流线图, 颜色表示温度分布, 带有箭头的曲线为流线, 其中红色流线代表大尺度环流路径周长[20] (a) Ra = 1 × 108; (b) Ra = 1 × 109
Fig. 4. The time-averaged temperature fields and streamlines in two typical RB convection, the temperature is coded in color, and the arrow indicates the flow direction. The red streamline represents the length of the large-scale circulation path[20]: (a) Ra = 1 × 108; (b) Ra = 1 × 109.
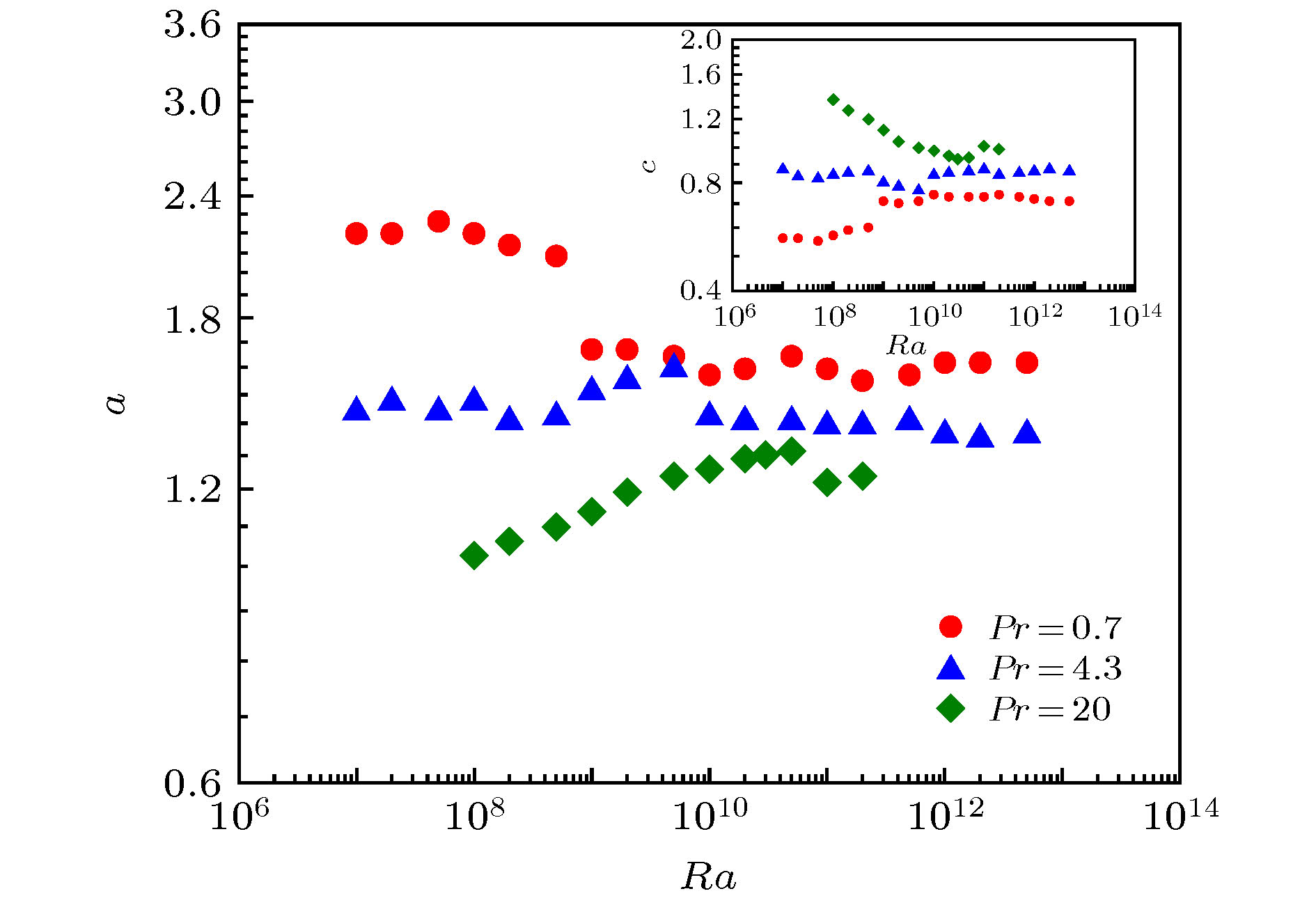
图 7 大尺度环流路径周长、传热Nu数及参数a随Ra数变化, 其中红色空心圆点和蓝色空心三角是包芸等[21]的计算结果, 黑色虚线是GL理论预测倍数线, 红线是特征Ra数位置 (a) Pr = 0.7; (b) Pr = 4.3; (c) Pr = 20
Fig. 7. The variation of large scale circulation path length, Nu number, and parameter a with Ra number, among which the red hollow dots and blue hollow triangles are calculated by Bao Yun[21], etc. The black dotted line is the multiple predicted by the GL theory, the red line is the characteristic Ra number position: (a) Pr = 0.7; (b) Pr = 4.3; (c) Pr = 20.
-
[1] Ahlers G, Grossmann S, Lohse D 2009 Rev. Mod. Phys. 81 503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Grossmann S, Lohse D 2000 J. Fluid Mech. 407 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Grossmann S, Lohse D 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 3316
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lui S L, Xia K Q 1998 Phys. Rev. E 57 5494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhou Q, Xia K Q 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 104301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ahlers G, Bodenschatz E, Funfschilling D, Grossmann S, He X Z, Lohse D, Stevens R J A M, Verzicco R 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 114501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wei P, Ahlers G 2014 J. Fluid Mech. 758 809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ahlers G, Bodenschatz E, He X 2014 J. Fluid Mech. 758 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou Q, Stevens R J A M, Sugiyama K, Grossmann S, Lohse D, Xia K Q 2010 J. Fluid Mech. 664 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhou Q, Sugiyama K, Stevens R J, Grossmann S, Lohse D, Xia K Q 2011 Phys. Fluids 23 125104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Stevens R J A M, Zhou Q, Grossmann S, Verzicco R, Xia K Q, Lohse D 2011 Phys. Rev. E 85 027301
[12] Shishkina O, Horn S, Wagner S 2013 J. Fluid Mech. 730 442
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shishkina O, Horn S, Wagner S, Ching E S C 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 114302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Shishkina O, Horn S, Emran M S, Ching E S C 2017 Phys. Rev. Fluids 2 113502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 何鹏, 黄茂静, 包芸 2018 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 48 124702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He P, Huang M J, Bao Y 2018 Sci. Sin.-Phys. Mech. Astron. 48 124702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 黄茂静, 包芸 2016 65 204702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang M J, Bao Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 204702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang Y, He X Z, Tong P 2016 Phys. Rev. Fluids 1 082301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 包芸, 高振源, 叶孟翔 2018 67 014701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao Y, Gao Z Y, Ye M X 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 014701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bao Y, Luo J H, Ye M X 2018 J. Mech. 34 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Sun C, Xia K Q 2005 Phys. Rev. E 72 067302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 包芸, 何建超, 高振源 2019 68 164701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao Y, He J C, Gao Z Y 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 164701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7862
- PDF下载量: 68
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: