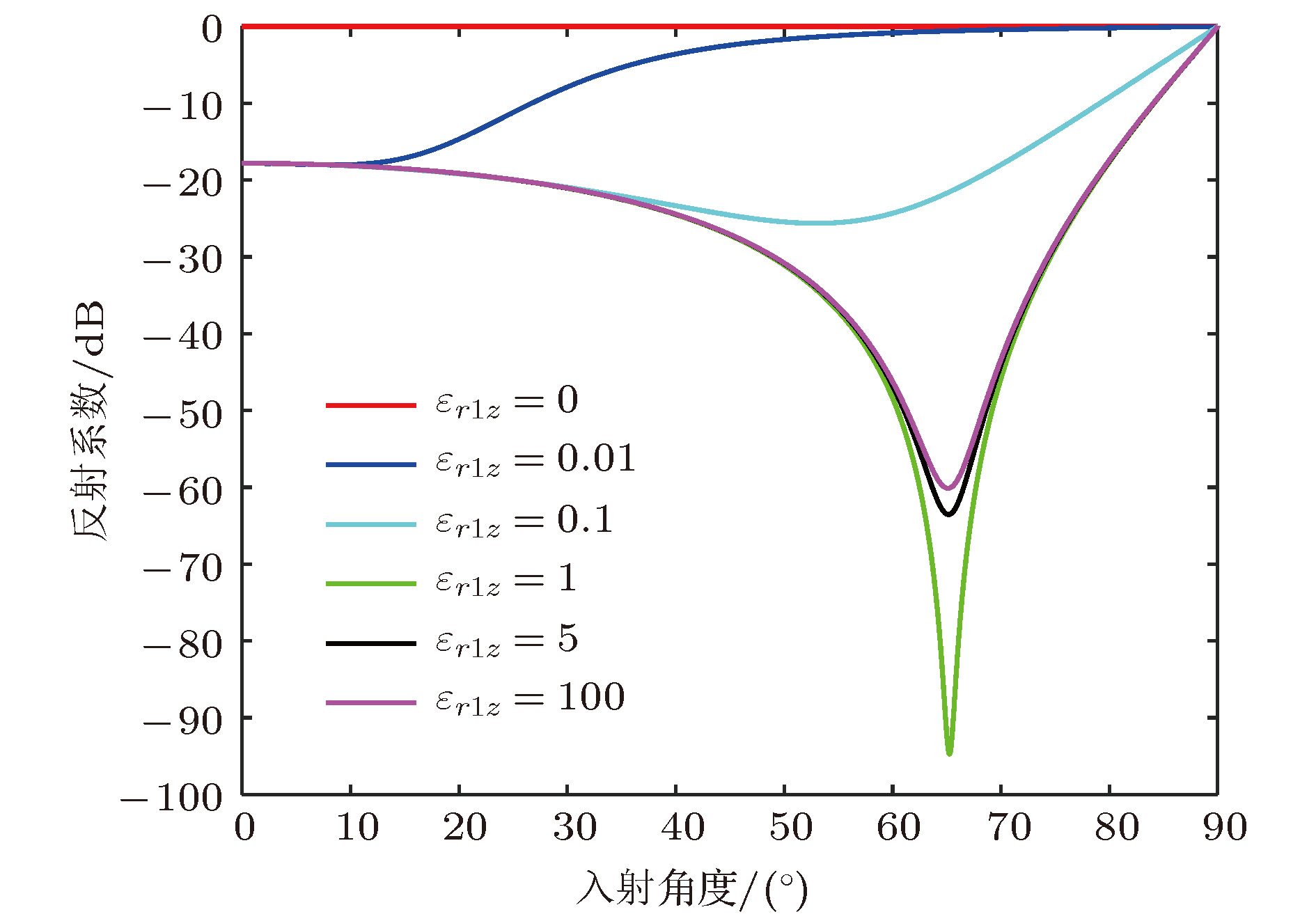
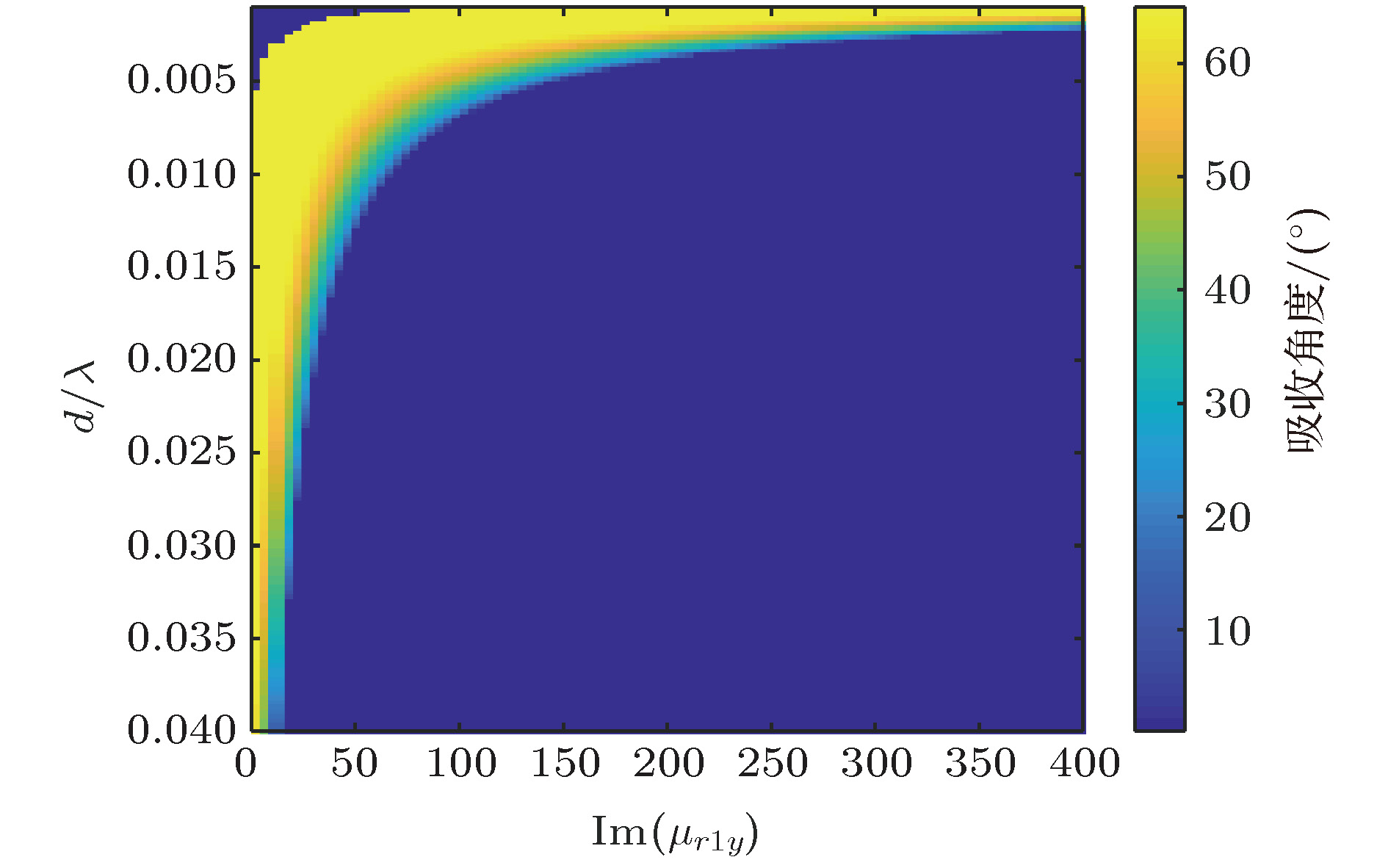
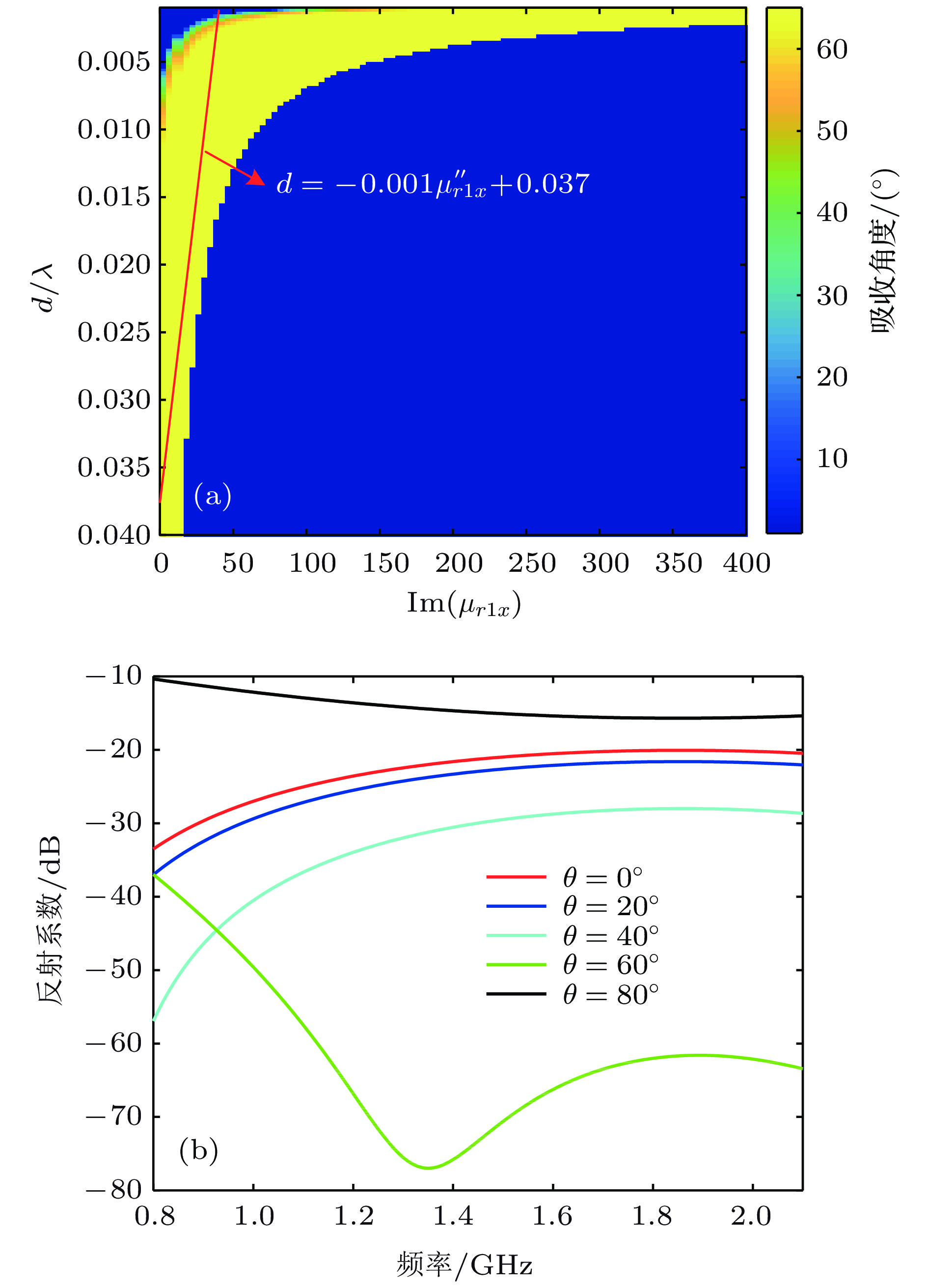
-
目前, 很少有文章就如何实现宽角度吸波材料进行详细的理论分析和设计指导, 设计宽角度吸波材料仍然是一件很困难的事情. 本文基于等效介质理论对带有反射地板的单层介质超材料吸波体进行较为详细的理论分析. 从基础电磁理论出发, 推导TE波(横电波, 电场方向与入射面垂直的平面电磁波)和TM波(横磁波, 磁场方向与入射面垂直的平面电磁波)照射下吸波体的反射系数, 分析实现宽角度吸波效果所需的等效电磁参数, 为宽角度超材料吸波体的设计提供了理论基础. 此外, 论文还理论分析了实现宽带宽角吸波等效电磁参数所要满足的条件, 并做了计算检验. 结果表明, 当介质等效电磁参数按照特殊曲线随频率发生变化时, 理论上能实现宽带宽角的吸波效果.In the past decade, most of researchers have been devoted to broadening the bandwidth of absorber. There are few researches on how to achieve wide-angle absorbing materials by detailed theoretical analysis and design guidance. It is still difficult to design wide-angle absorbers. In this paper, based on the equivalent medium theory, the reflectivity of the metamaterial absorber with a single-layered medium backed with metal reflector is analyzed in detail. Starting from the basic electromagnetic theory, the reflection coefficient of the absorber under transverse electric(TE) plane wave and transverse magnetic (TM) plan wave irradiation are derived. And the equivalent electromagnetic parameters of realizing the wide-angle absorbing effect are analyzed, which provide a theoretical basis for designing the wide-angle metamaterial absorber. The theoretical analysis results show that the equivalent electromagnetic parameters required for the medium to achieve low-profile and wide-angle absorbing effect are mainly related to the equivalent permeability and have little relationship with the equivalent permittivity. Moreover, the equivalent electromagnetic parameter value for achieving ultra-wide-angle absorber under TE wave and that under TM wave irradiation are different from each other. In other words, the anisotropic metamaterial with appropriate equivalent permeability has the potential to be used to design the ultra-wide-angle absorbers which are not sensitive to TE waves nor TM waves. In addition, in order to find the theoretically achievable widest absorbing angle value under TE wave and TM wave irradiation, the reflection coefficients at all angles must be less than or equal to –10 dB to obtain the relationship among the equivalent electromagnetic parameters, thickness and angle. The results show that the theoretically achievable widest absorbing angle value is 86.56° under TE wave and TM wave irradiation. The designer can choose the corresponding thickness and permeability from the data obtained from the analysis according to the design requirements. The narrow-band absorbers have limited applications. Therefore, in this paper we also theoretically analyze the values of the equivalent electromagnetic parameters for ahcieving wide-band and wide-angle absorbing materials, and make theoretical verification. The results show that the wide-band and wide-angle absorber can be achieved theoretically, while the equivalent electromagnetic parameters of the medium vary with frequency as some special curves indicate. Although this method is based on the equivalent medium theory and has no direct relationship with the actual structure, it does provide theoretical guidance for designing the wide-angle absorbers.
[1] Fante R L, McCormack M T 1988 IEEE Trans. Antenna. Propag. 36 1443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Landy N I, Sajuyigbe S, Mock J J, Smith D R, Padilla W J 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 207402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang B X, Zhai X, Wang G Z, Huang W Q, Wang L L 2015 IEEE Photonics J. 7 4600108
[4] Ding F, Cui X, Ge C, Jin Y, He S L 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 103506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lin X Q, Mei P, Zhang P C, Chen Z Z D, Fan Y 2016 IEEE Trans. Antenna. Propag. 64 4910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hao J P, Lheurette E, Burgnies L, Okada E, Lippens D 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 105 081102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Deng T W, Li Z W, Chen Z N 2017 IEEE Trans. Antenna. Propag. 65 5886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Shang Y P, Shen Z X, Xiao S Q 2013 IEEE Trans. Antenna. Propag. 61 6022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Rozanov K N 2000 IEEE Trans. Antenna. Propag. 48 1230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen H T 2012 Opt. Express 20 7165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 顾超, 屈绍波, 裴志斌, 徐卓, 林宝勤, 周航, 柏鹏, 顾巍, 彭卫东, 马华 2011 60 087802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu C, Qu S B, Pei Z B, Xu Z, Lin B Q, Zhou H, Bai P, Gu W, Peng W D, Ma H 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 087802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 程用志, 聂彦, 龚荣洲, 王鲜 2013 62 044103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y Z, Nie Y, Gong R Z, Wang X 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 044103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 熊益军, 王岩, 王强, 王春齐, 黄小忠, 张芬, 周丁 2018 67 084202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiong Y J, Wang Y, Wang Q, Wang C Q, Huang X Z, Zhang F, Zhou D 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 084202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 李宇涵, 邓联文, 罗衡, 贺龙辉, 贺君, 徐运超, 黄生祥 2019 68 095201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y H, Deng L W, Luo H, He L H, He J, Xu Y C, Huang S X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 095201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Tao H, Bingham C M, Strikwerda A C, Pilon D, Shrekenhamer D, Landy N I, Fan K, Zhang X, Padilla, Averitt 2008 Phys. Rev. B 78 241103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang B N, Koschny T, Soukouli Costa M 2009 Phys. Rev. B 80 033108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lee D, Hwang J G, Lim D, Hara T, Lim S 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 27155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Nguyen T T, Lim S 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 3204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lim D, Lee D, Lim S 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 39686
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang J Y, Yang R C, Tian J P, Chen X W, Zhang W M 2018 IEEE Antenna. Wireless Propag. Lett. 17 1242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Jin Y, Xiao S S, Mortensen N A, He S L 2011 Opt. Express 19 11114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Feng S M, Halterman K 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 165103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhong S M, He S L 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 2083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chen W C, Bingham C M, Mak K M, Caira N W, Padilla W J 2012 Phys. Rev. B 85 201104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li C L, Guo J, Zhang P, Yu Q Q, Ma W T, Miao X G, Zhao Z Y, Luan L 2014 Chin. Phys. Lett. 31 077801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Fante R L, McCormack M T 1988 IEEE Trans. Antenna. Propag. 36 1443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Landy N I, Sajuyigbe S, Mock J J, Smith D R, Padilla W J 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 207402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang B X, Zhai X, Wang G Z, Huang W Q, Wang L L 2015 IEEE Photonics J. 7 4600108
[4] Ding F, Cui X, Ge C, Jin Y, He S L 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 103506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lin X Q, Mei P, Zhang P C, Chen Z Z D, Fan Y 2016 IEEE Trans. Antenna. Propag. 64 4910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hao J P, Lheurette E, Burgnies L, Okada E, Lippens D 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 105 081102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Deng T W, Li Z W, Chen Z N 2017 IEEE Trans. Antenna. Propag. 65 5886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Shang Y P, Shen Z X, Xiao S Q 2013 IEEE Trans. Antenna. Propag. 61 6022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Rozanov K N 2000 IEEE Trans. Antenna. Propag. 48 1230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen H T 2012 Opt. Express 20 7165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 顾超, 屈绍波, 裴志斌, 徐卓, 林宝勤, 周航, 柏鹏, 顾巍, 彭卫东, 马华 2011 60 087802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu C, Qu S B, Pei Z B, Xu Z, Lin B Q, Zhou H, Bai P, Gu W, Peng W D, Ma H 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 087802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 程用志, 聂彦, 龚荣洲, 王鲜 2013 62 044103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y Z, Nie Y, Gong R Z, Wang X 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 044103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 熊益军, 王岩, 王强, 王春齐, 黄小忠, 张芬, 周丁 2018 67 084202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiong Y J, Wang Y, Wang Q, Wang C Q, Huang X Z, Zhang F, Zhou D 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 084202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 李宇涵, 邓联文, 罗衡, 贺龙辉, 贺君, 徐运超, 黄生祥 2019 68 095201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y H, Deng L W, Luo H, He L H, He J, Xu Y C, Huang S X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 095201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Tao H, Bingham C M, Strikwerda A C, Pilon D, Shrekenhamer D, Landy N I, Fan K, Zhang X, Padilla, Averitt 2008 Phys. Rev. B 78 241103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang B N, Koschny T, Soukouli Costa M 2009 Phys. Rev. B 80 033108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lee D, Hwang J G, Lim D, Hara T, Lim S 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 27155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Nguyen T T, Lim S 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 3204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lim D, Lee D, Lim S 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 39686
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang J Y, Yang R C, Tian J P, Chen X W, Zhang W M 2018 IEEE Antenna. Wireless Propag. Lett. 17 1242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Jin Y, Xiao S S, Mortensen N A, He S L 2011 Opt. Express 19 11114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Feng S M, Halterman K 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 165103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhong S M, He S L 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 2083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chen W C, Bingham C M, Mak K M, Caira N W, Padilla W J 2012 Phys. Rev. B 85 201104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li C L, Guo J, Zhang P, Yu Q Q, Ma W T, Miao X G, Zhao Z Y, Luan L 2014 Chin. Phys. Lett. 31 077801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9265
- PDF下载量: 374
- 被引次数: 0













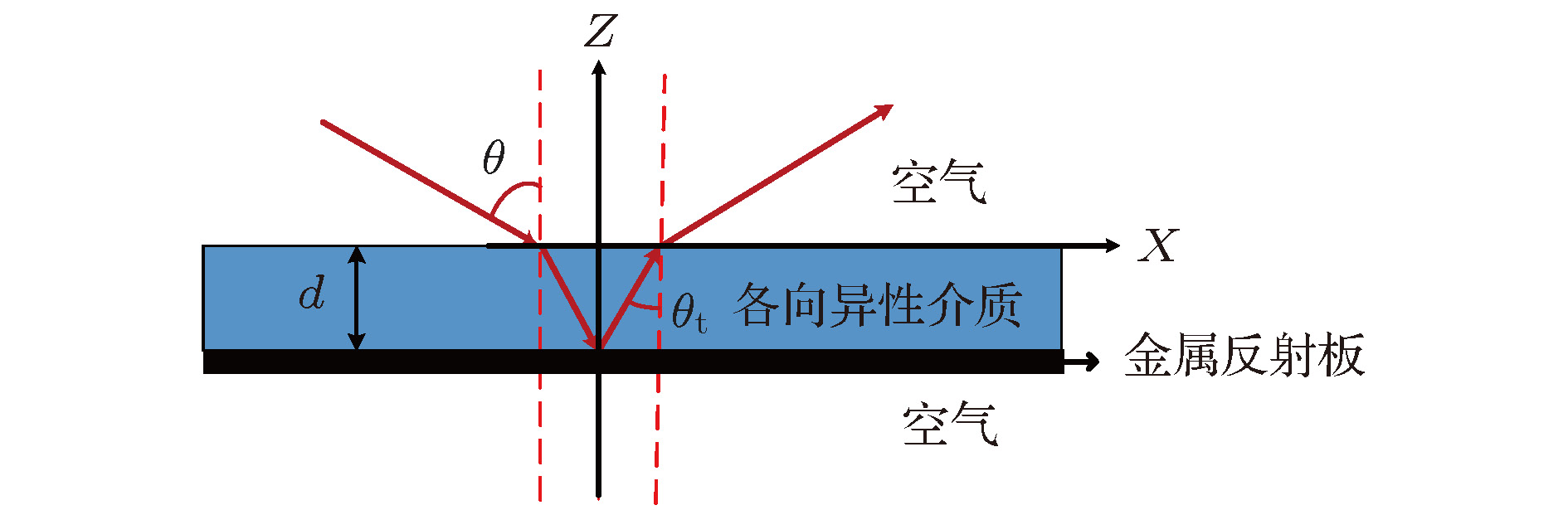
 下载:
下载: