-
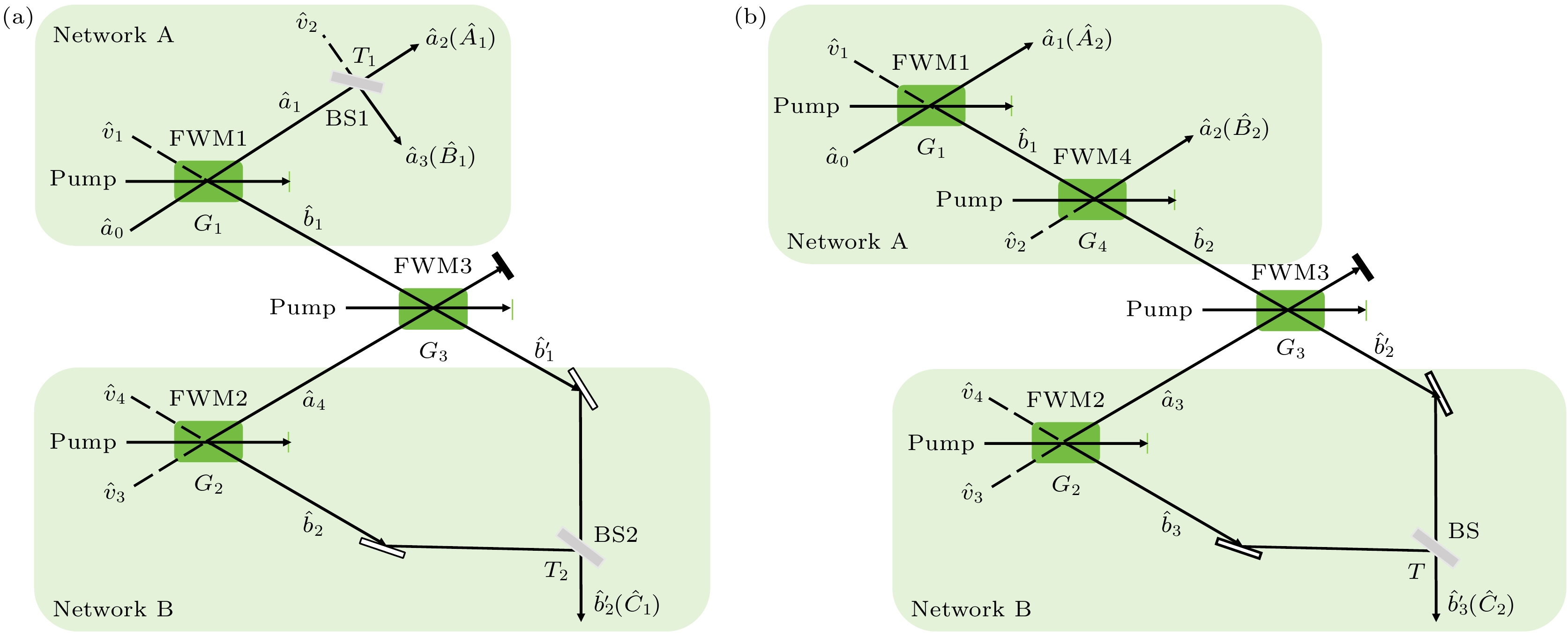
量子导引, 作为一种特殊的量子关联, 相较于量子纠缠和贝尔非局域性, 展现出了特有的不对称性. 这种不对称性使得两个独立的光学模式之间, 通过量子导引交换可以建立单向或双向的导引, 这对构建非对称量子网络具有至关重要的意义. 本文提出了基于三组份与两组份纠缠态的全光学量子导引交换方案, 这一方案利用低噪声、高带宽的四波混频过程, 无测量地实现了传统方案中贝尔态测量的功能, 避免了光电和电光转换. 在导引交换操作后, 原本独立的无直接相互作用的两个纠缠态产生了量子导引. 具体研究了四波混频过程联合线性分束器或非线性分束器两种交换方案, 发现通过调节线性分束器的透射率和四波混频过程的增益, 可以实现三模间的量子导引. 这为单向量子通信和量子信息处理提供了新的可能性, 使得量子资源的利用更加安全和可控.Quantum resource swapping is crucial for establishing quantum networks and achieving efficient quantum communication and it allows quantum resources to be shared and allocated between nodes in a quantum network, thereby enhancing network flexibility and quantum information processing capabilities. Quantum steering is a special type of quantum correlation that exhibits unique asymmetry compared with quantum entanglement and Bell nonlocality. This asymmetry enables quantum steering swapping to establish one-way or two-way asymmetry quantum steering between two independent optical modes, which is crucial for constructing asymmetric quantum networks. In this work, an all-optical quantum steering swapping scheme is proposed based on tripartite entangled state and bipartite entangled state. The all-optical scheme does not involve optic-electro conversion nor electro-optic conversion, but utilizes a low-noise, high-bandwidth four-wave mixing process to achieve the function of Bell state measurement in traditional schemes without measurement. After the steering swapping operation, the two originally independent entangled states without direct interaction generate quantum steering. In this work, two swapping schemes in the four-wave mixing processes, combined with linear beam splitter and nonlinear beam splitter, are investigated. By analyzing the steering characteristics of the output modes, both schemes exhibit varieties of multipartite steering types. By adjusting the transmissivity of the linear beam splitter and the gain of the four-wave mixing process, the steering relationship can be flexibly manipulated to achieve one-way and two-way asymmetry steering. This provides new possibilities for one-way quantum communication and quantum information processing, making the utilization of quantum resources more efficient and controllable. Through in-depth analysis of the steering characteristics after swapping, it is found that compared with the linear beam splitter scheme, the nonlinear beam splitter scheme not only significantly improves the capability of quantum steering, but also allows for more flexible manipulation of monogamy relations of quantum steering. By optimizing the gain parameters of the nonlinear beam splitter, the precise manipulation of the monogamy relations can be achieved over a wider range. This not only expands broader application prospects for information processing and quantum communication in quantum networks, but also lays an important foundation for building efficient and secure quantum information processing systems.
-
Keywords:
- quantum steering swapping /
- four-wave mixing process /
- multipartite steering /
- quantum communication
[1] Einstein A, Podolsky B, Rosen N 1935 Phys. Rev. 47 777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Schrödinger E 1935 Math. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 32 446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wiseman H M, Jones S J, Doherty A C 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 140402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Horodecki R, Horodecki P, Horodecki M, Horodecki K 2009 Rev. Mod. Phys. 81 865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Schrödinger E 1935 Naturwissenschaften 23 807
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Brunner N, Cavalcanti D, Pironio S, Scarani V, Wehner S 2014 Rev. Mod. Phys. 86 419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bowles J, Vértesi T, Quintino M T, Brunner N 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 200402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sun K, Ye X J, Xu J S, Xu X Y, Tang J S, Wu Y C, Chen J L, Li C F, Guo G C 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 160404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] He Q Y, Gong Q H, Reid M D 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 060402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Branciard C, Cavalcanti E G, Walborn S P, Scarani V, Wiseman H M 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 010301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Walk N, Hosseini S, Geng J, Thearle O, Haw J Y, Armstrong S, Assad S M, Janousek J, Ralph T C, Symul T, Wiseman H M, Lam P K 2016 Optica 3 634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Reid M D 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 062338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] He Q Y, Rosales-Zárate L, Adesso G, Reid M D 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 180502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Cleve R, Gottesman D, Lo H K 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xiang Y, Kogias I, Adesso G, He Q Y 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 010101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hillery M, Bužek V, Berthiaume A 1999 Phys. Rev. A 59 1829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lau H K, Weedbrook C 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 042313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xiang Y, Liu Y, Cai Y, Li F, Zhang Y P, He Q Y 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 053834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu Y, Cai Y, Xiang Y, Li F, Zhang Y P, He Q Y 2019 Opt. Express 27 33070
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yuan Z S, Chen Y A, Zhao B, Chen S, Schmiedmayer J, Pan J W 2008 Nature 454 1098
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Duan L M, Lukin M D, Cirac J I, Zoller P 2001 Nature 414 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu S S, Lou Y B, Chen Y X, Jing J T 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 128 060503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Polkinghorne R E S, Ralph T C 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 2095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Pan J W, Bouwmeester D, Weinfurter H, Zeilinger A 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 3891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Jennewein T, Weihs G, Pan J W, Zeilinger A 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 017903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ma L X, Lei X, Cheng J L, Yan Z H, Jia X J 2023 Opt. Express 31 8257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang M H, Qin Z Z, Su X L 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 052311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang M H, Qin Z Z, Wang Y, Su X L 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 022307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang N, Wang M H, Tian C X, Deng X W, Su X L 2023 Laser Photonics Rev. 18 2300653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Hu Q W, Wang J B, Liu S S, Jing J T 2024 Opt. Lett. 49 2585
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Liu S S, Lou Y B, Jing J T 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 3875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Liu S S, Lou Y B, Jing J T 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 113602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Kogias I, Lee A R, Ragy S, Adesso G 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 060403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Ralph T C 1999 Opt. Lett. 24 348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
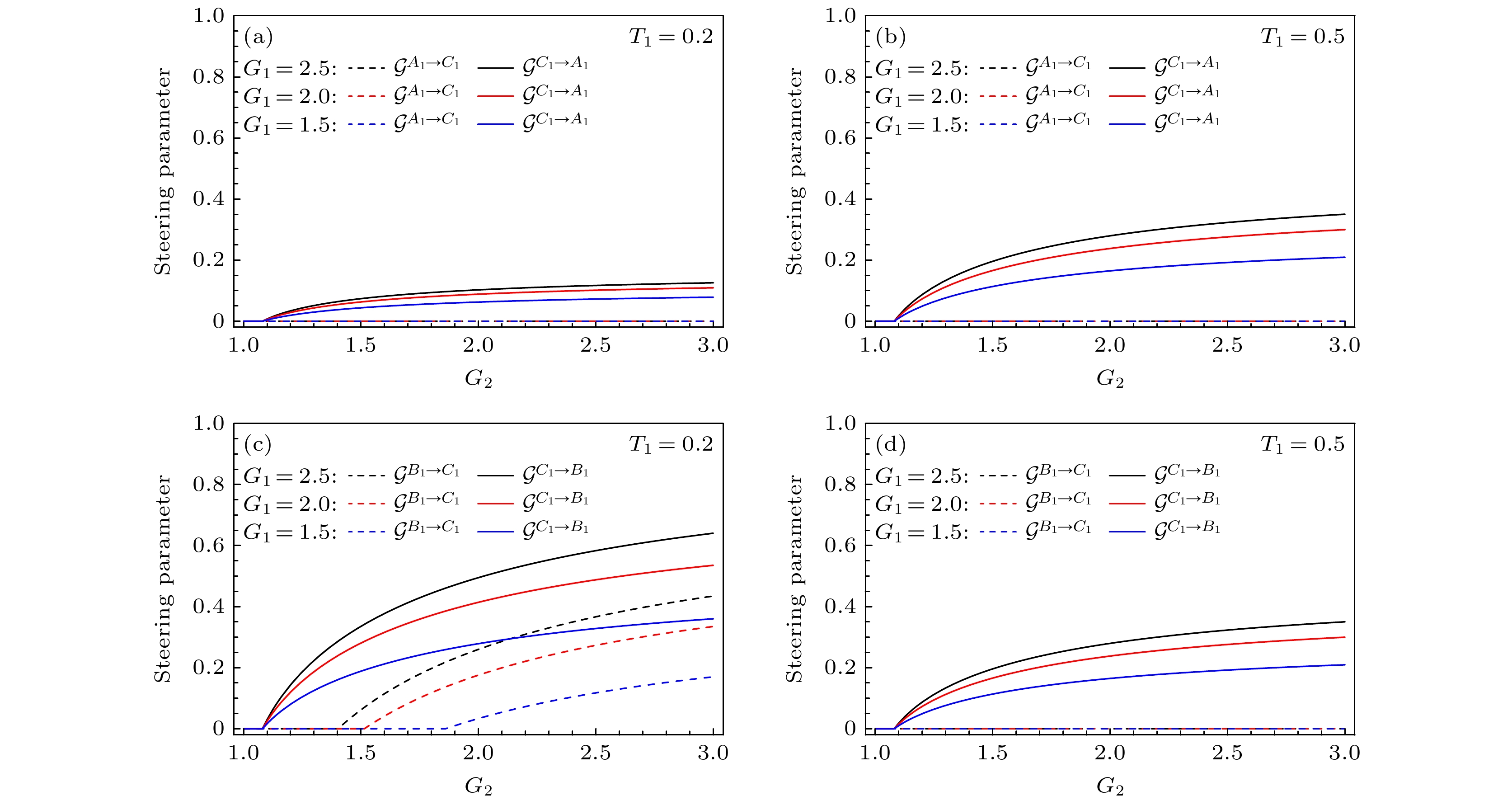
图 2 在不同透射率${T_1}$和增益${G_1}$下, 两模间的量子导引参数随${G_2}$的变化 (a) ${T_1} = 0.2$时, 模${\hat A_1}$和${\hat C_1}$之间的导引; (b) ${T_1} = 0.5$时, 模${\hat A_1}$和${\hat C_1}$之间的导引; (c) ${T_1} = 0.2$时, 模${\hat B_1}$和${\hat C_1}$之间的导引; (d) ${T_1} = 0.5$时, 模${\hat B_1}$和${\hat C_1}$之间的导引
Fig. 2. Steering parameter between any two modes versus ${G_2}$ under different transmissivity ${T_1}$and gain ${G_1}$: (a) The steering between ${\hat A_1}$ and ${\hat C_1}$ $\left( {{T_1} = 0.2} \right)$; (b) the steering between ${\hat A_1}$ and ${\hat C_1}$$\left( {{T_1} = 0.5} \right)$; (c) the steering between ${\hat B_1}$ and ${\hat C_1}$$\left( {{T_1} = 0.2} \right)$; (d) the steering between ${\hat B_1}$and ${\hat C_1}$$\left( {{T_1} = 0.5} \right)$.
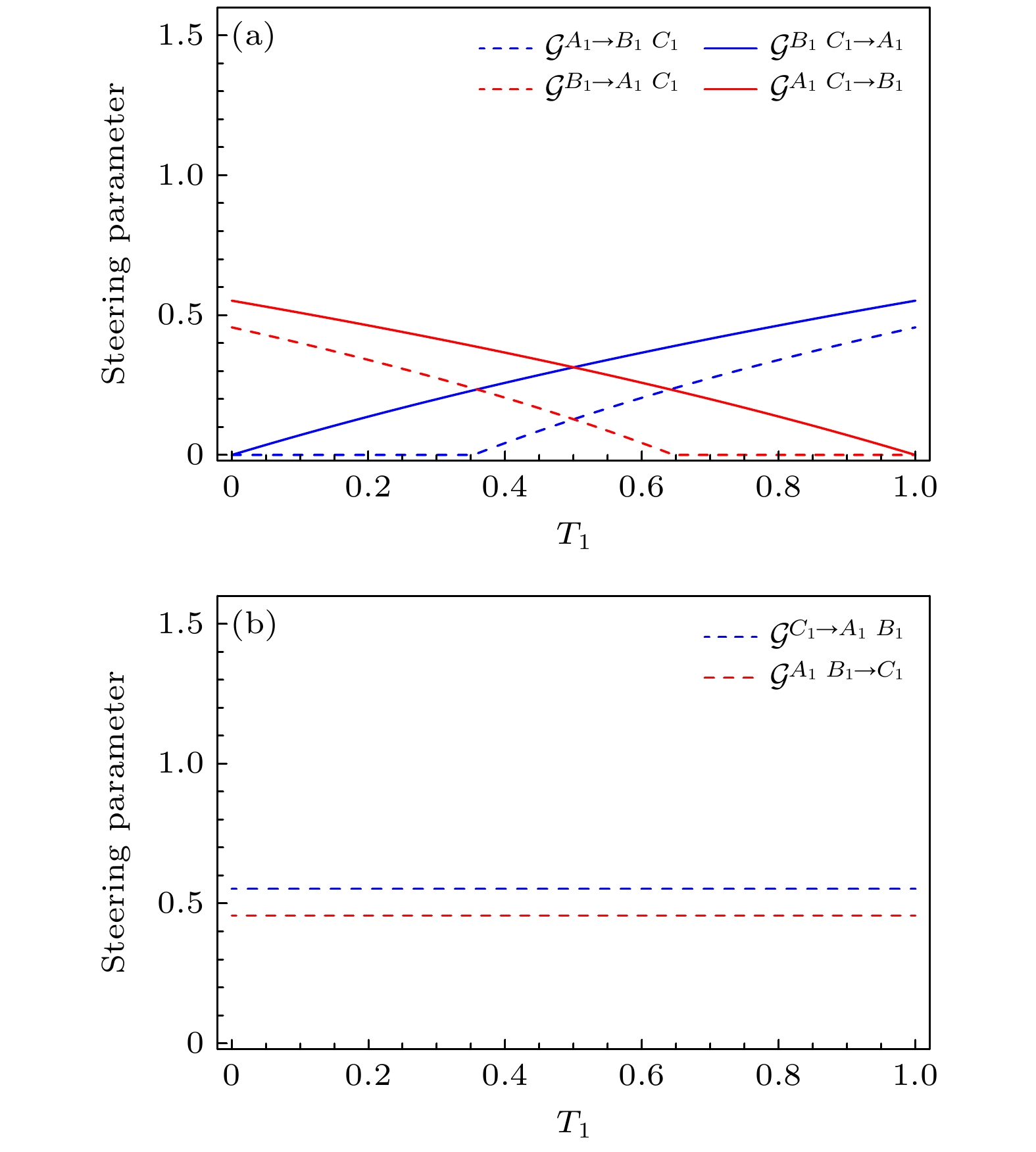
图 4 一个模式与另外两个模式之间的量子导引参数随透射率${T_1}$的变化$ ({G}_{1}={G}_{2}=2) $ (a) 模式$ {\hat A_1} $和${\hat B_1}$分别作为导引方和被导引方; (b) 模式$ {\hat C_1} $作为导引方和被导引方
Fig. 4. Quantum steering parameter between one and the other two modes versus ${T_1}$$ ({G}_{1}={G}_{2}=2) $: (a) Modes $ {\hat A_1} $ and ${\hat B_1}$ serve as steering party and steered party, respectively; (b) mode $ {\hat C_1} $ serves as steering party and steered party.
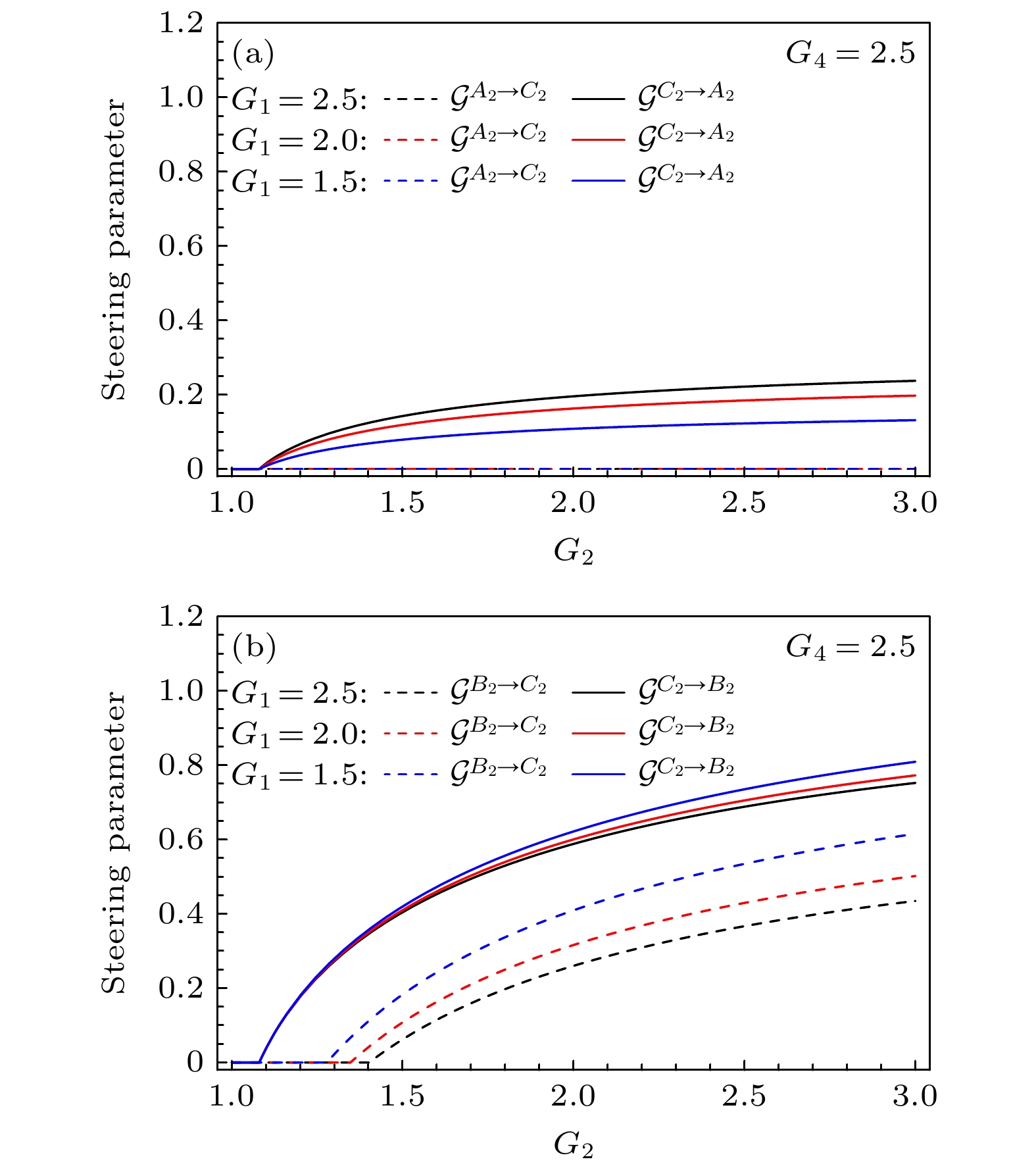
图 5 在不同增益${G_1}$下, 两模间的量子导引参数随增益${G_2}$的变化$\left( {{G_4} = 2.5} \right)$ (a) 模${\hat A_2}$和${\hat C_2}$之间的导引; (b) 模${\hat B_2}$和${\hat C_2}$之间的导引
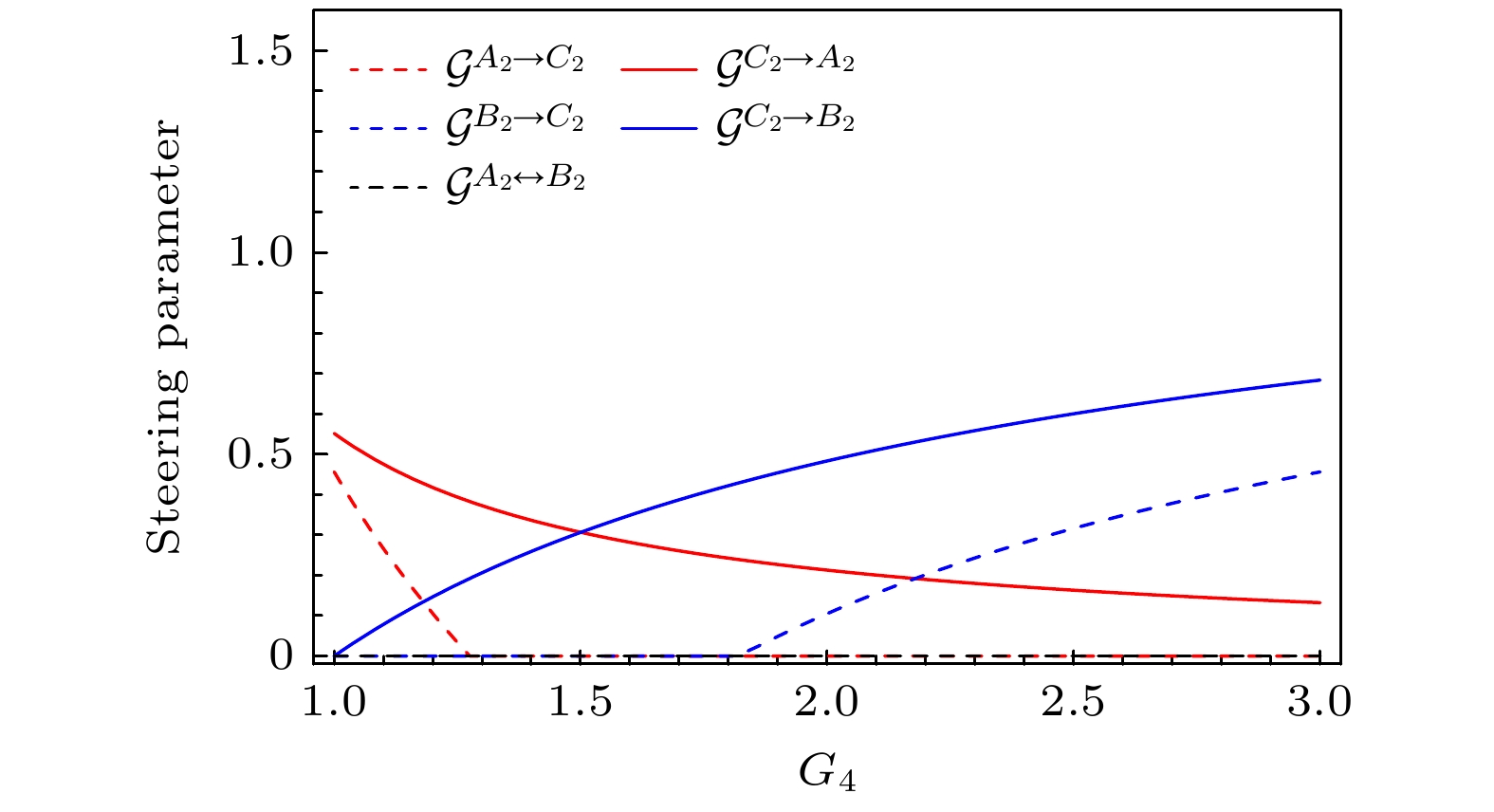
Fig. 5. Steering parameter between any two modes versus ${G_2}$ under different gain ${G_1}$$\left( {{G_4} = 2.5} \right)$: (a) The steering between ${\hat A_2}$ and ${\hat C_2}$; (b) the steering between ${\hat B_2}$ and ${\hat C_2}$
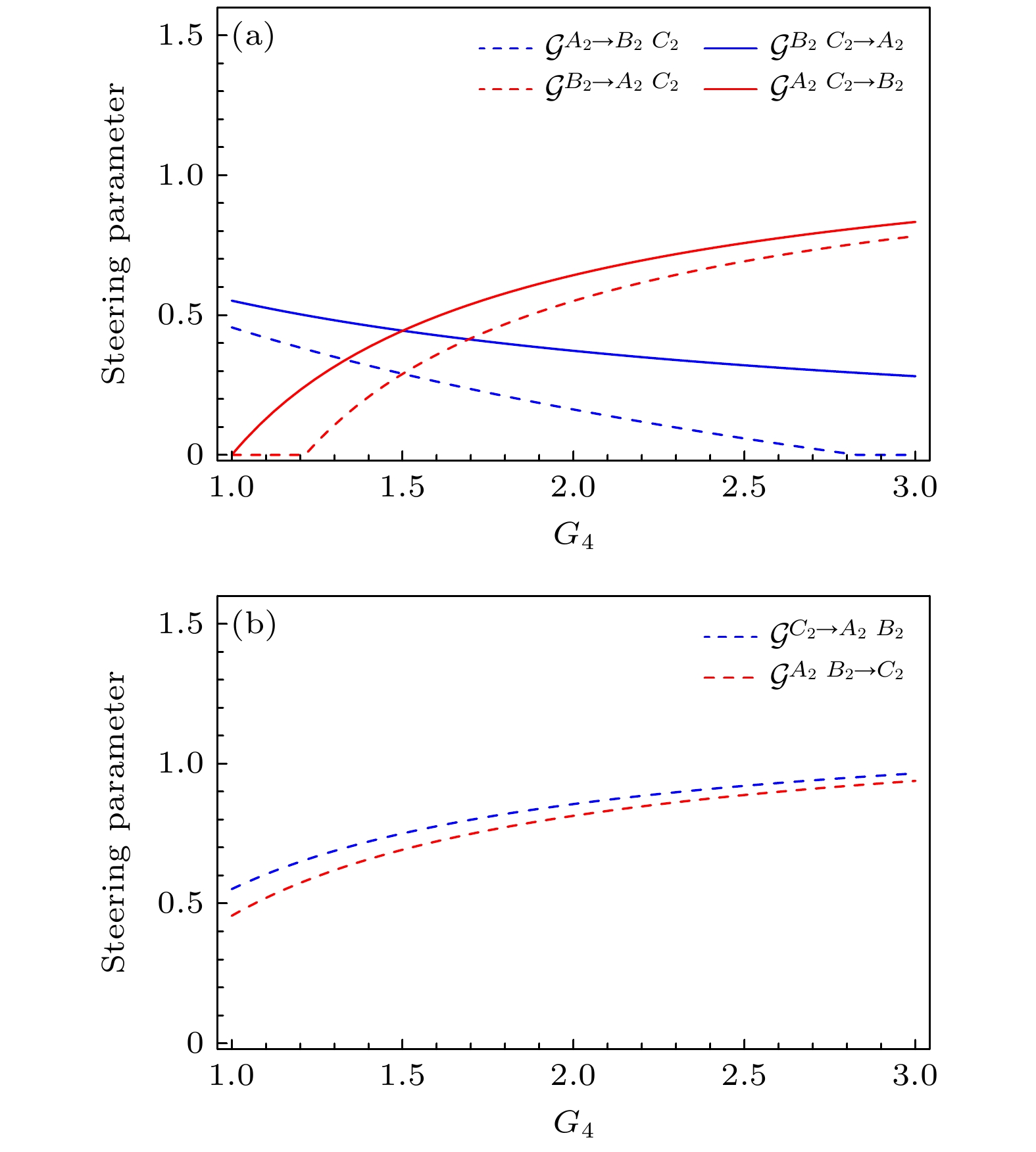
图 7 一个模式与另外两个模式之间的量子导引参数随增益${G_4}$的变化$ ({G}_{1}={G}_{2}=2) $: (a) 模式$ {\hat A_2} $和${\hat B_2}$分别作为导引方和被导引方; (b) 模式$ {\hat C_2} $作为导引方和被导引方
Fig. 7. Quantum steering parameter between one and the other two modes versus ${G_4}$$ ({G}_{1}={G}_{2}=2) $: (a) Modes $ {\hat A_2} $ and ${\hat B_2}$ serve as steering party and steered party, respectively; (b) mode $ {\hat C_2} $ serves as steering party and steered party.
-
[1] Einstein A, Podolsky B, Rosen N 1935 Phys. Rev. 47 777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Schrödinger E 1935 Math. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 32 446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wiseman H M, Jones S J, Doherty A C 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 140402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Horodecki R, Horodecki P, Horodecki M, Horodecki K 2009 Rev. Mod. Phys. 81 865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Schrödinger E 1935 Naturwissenschaften 23 807
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Brunner N, Cavalcanti D, Pironio S, Scarani V, Wehner S 2014 Rev. Mod. Phys. 86 419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bowles J, Vértesi T, Quintino M T, Brunner N 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 200402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sun K, Ye X J, Xu J S, Xu X Y, Tang J S, Wu Y C, Chen J L, Li C F, Guo G C 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 160404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] He Q Y, Gong Q H, Reid M D 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 060402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Branciard C, Cavalcanti E G, Walborn S P, Scarani V, Wiseman H M 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 010301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Walk N, Hosseini S, Geng J, Thearle O, Haw J Y, Armstrong S, Assad S M, Janousek J, Ralph T C, Symul T, Wiseman H M, Lam P K 2016 Optica 3 634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Reid M D 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 062338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] He Q Y, Rosales-Zárate L, Adesso G, Reid M D 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 180502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Cleve R, Gottesman D, Lo H K 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xiang Y, Kogias I, Adesso G, He Q Y 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 010101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hillery M, Bužek V, Berthiaume A 1999 Phys. Rev. A 59 1829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lau H K, Weedbrook C 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 042313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xiang Y, Liu Y, Cai Y, Li F, Zhang Y P, He Q Y 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 053834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu Y, Cai Y, Xiang Y, Li F, Zhang Y P, He Q Y 2019 Opt. Express 27 33070
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yuan Z S, Chen Y A, Zhao B, Chen S, Schmiedmayer J, Pan J W 2008 Nature 454 1098
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Duan L M, Lukin M D, Cirac J I, Zoller P 2001 Nature 414 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu S S, Lou Y B, Chen Y X, Jing J T 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett. 128 060503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Polkinghorne R E S, Ralph T C 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 2095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Pan J W, Bouwmeester D, Weinfurter H, Zeilinger A 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 3891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Jennewein T, Weihs G, Pan J W, Zeilinger A 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 017903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ma L X, Lei X, Cheng J L, Yan Z H, Jia X J 2023 Opt. Express 31 8257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang M H, Qin Z Z, Su X L 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 052311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang M H, Qin Z Z, Wang Y, Su X L 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 022307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang N, Wang M H, Tian C X, Deng X W, Su X L 2023 Laser Photonics Rev. 18 2300653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Hu Q W, Wang J B, Liu S S, Jing J T 2024 Opt. Lett. 49 2585
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Liu S S, Lou Y B, Jing J T 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 3875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Liu S S, Lou Y B, Jing J T 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 113602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Kogias I, Lee A R, Ragy S, Adesso G 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 060403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Ralph T C 1999 Opt. Lett. 24 348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 2433
- PDF下载量: 87
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: