-
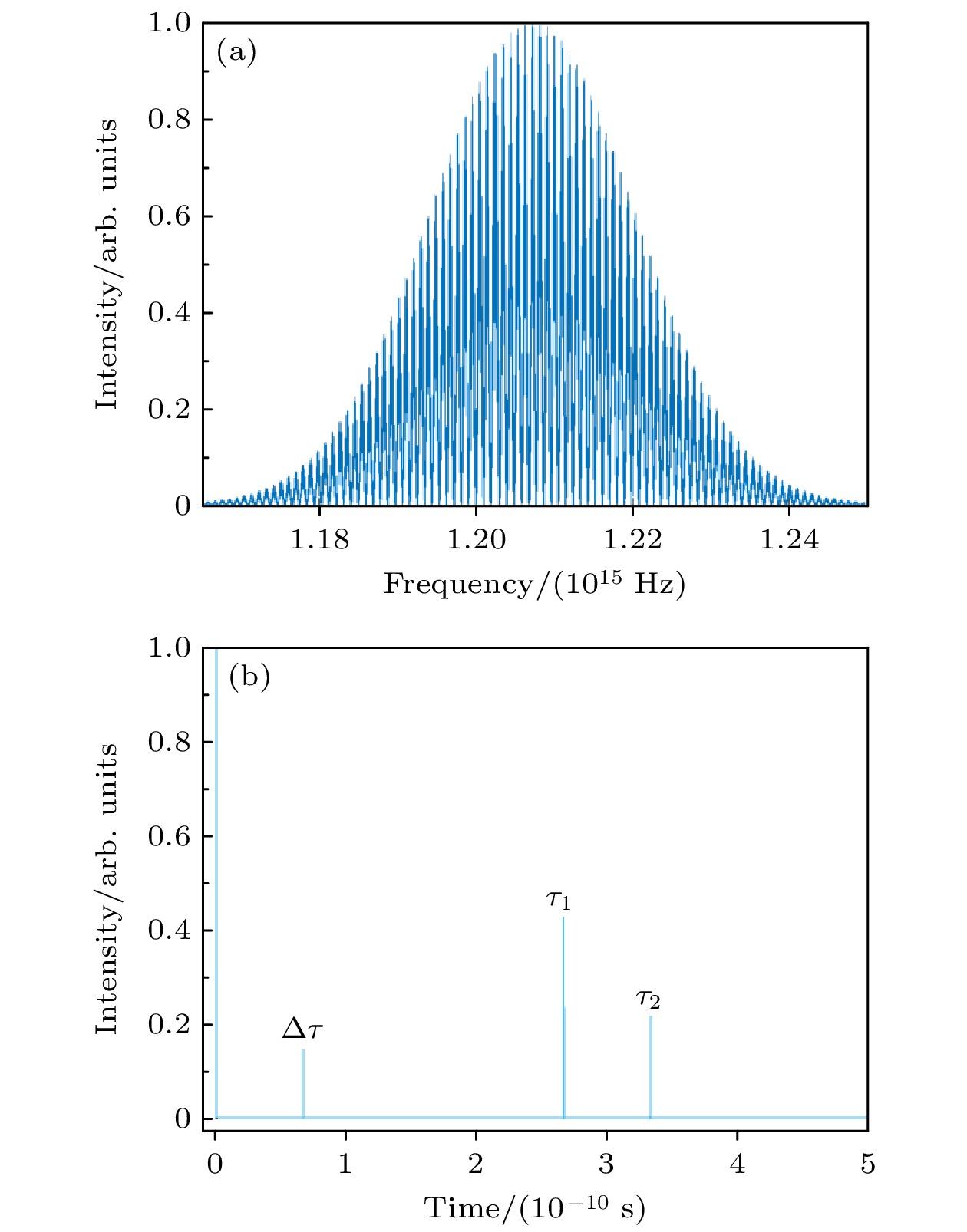
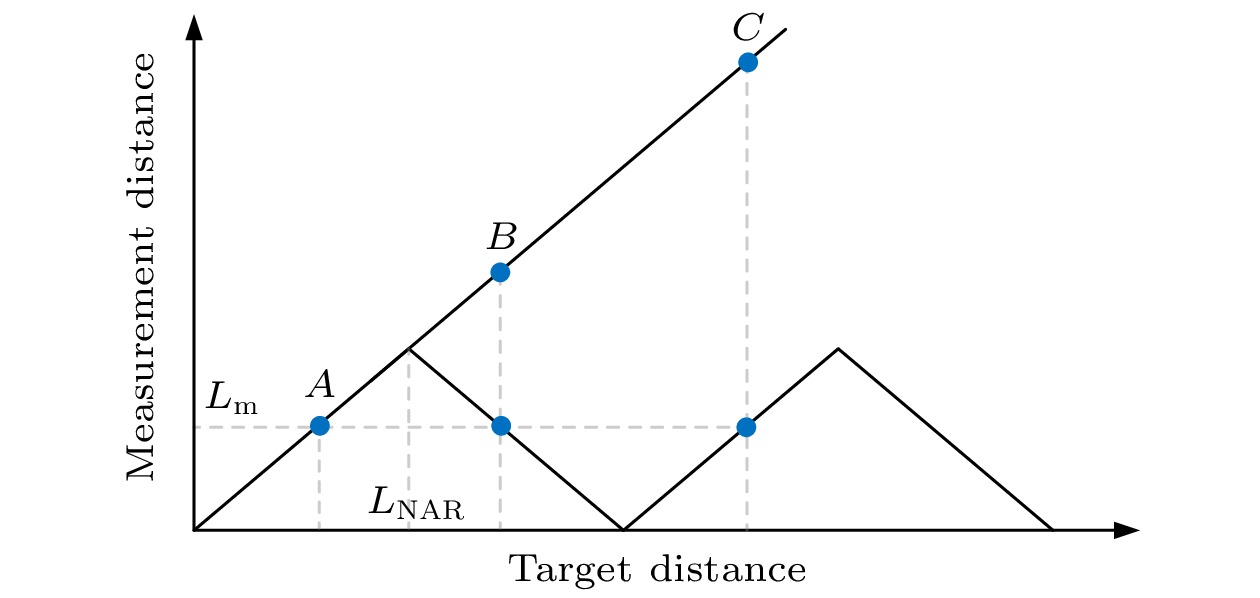
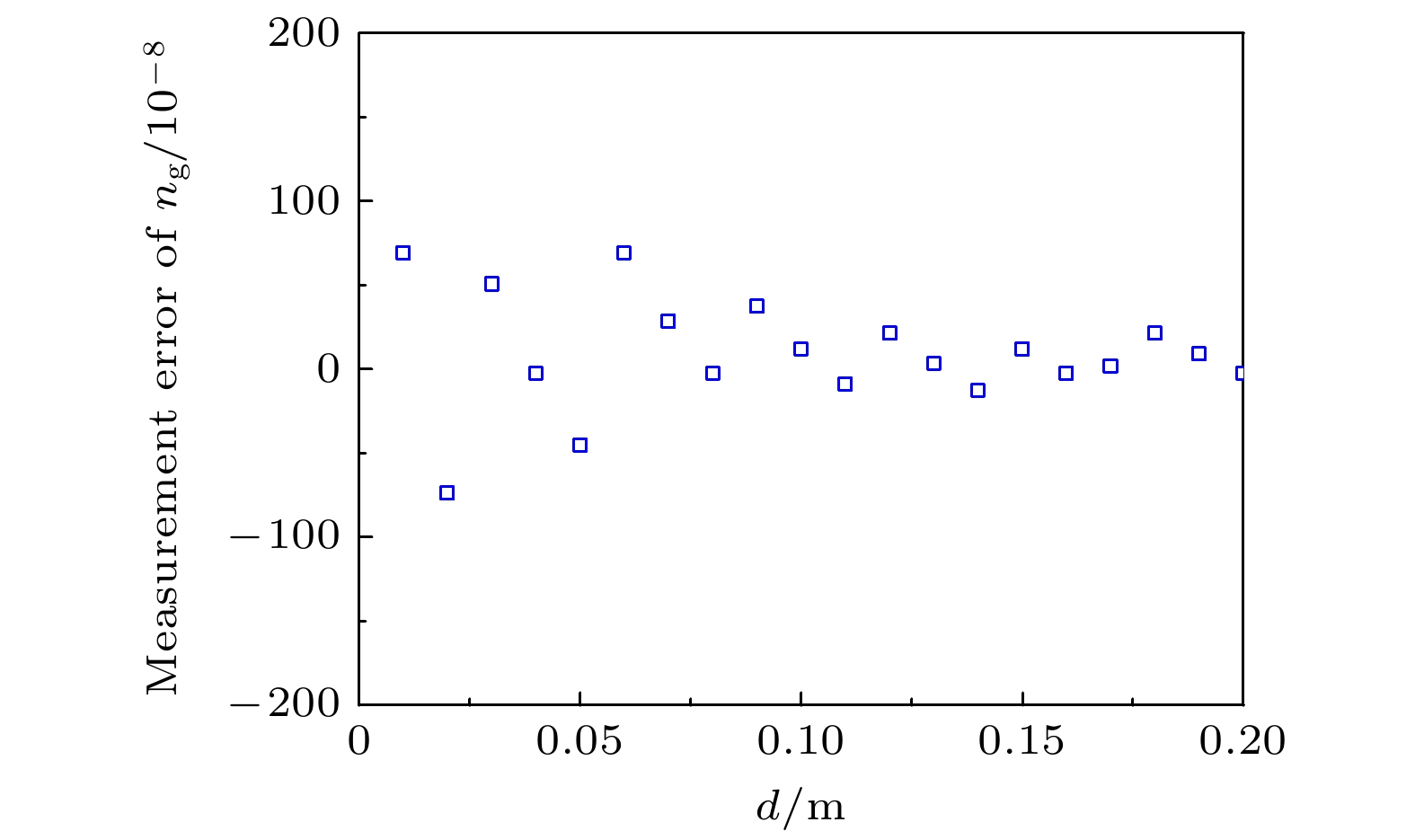
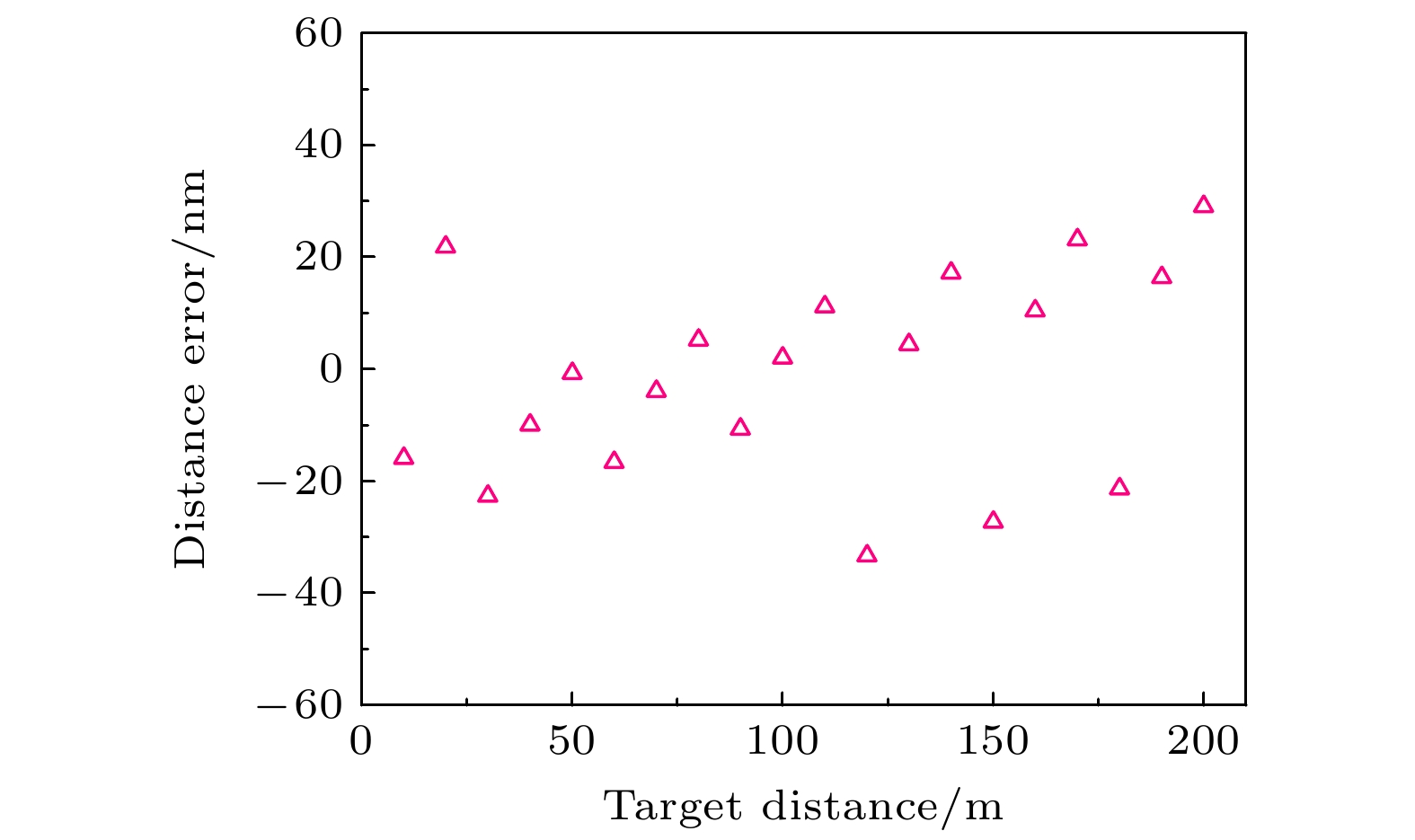
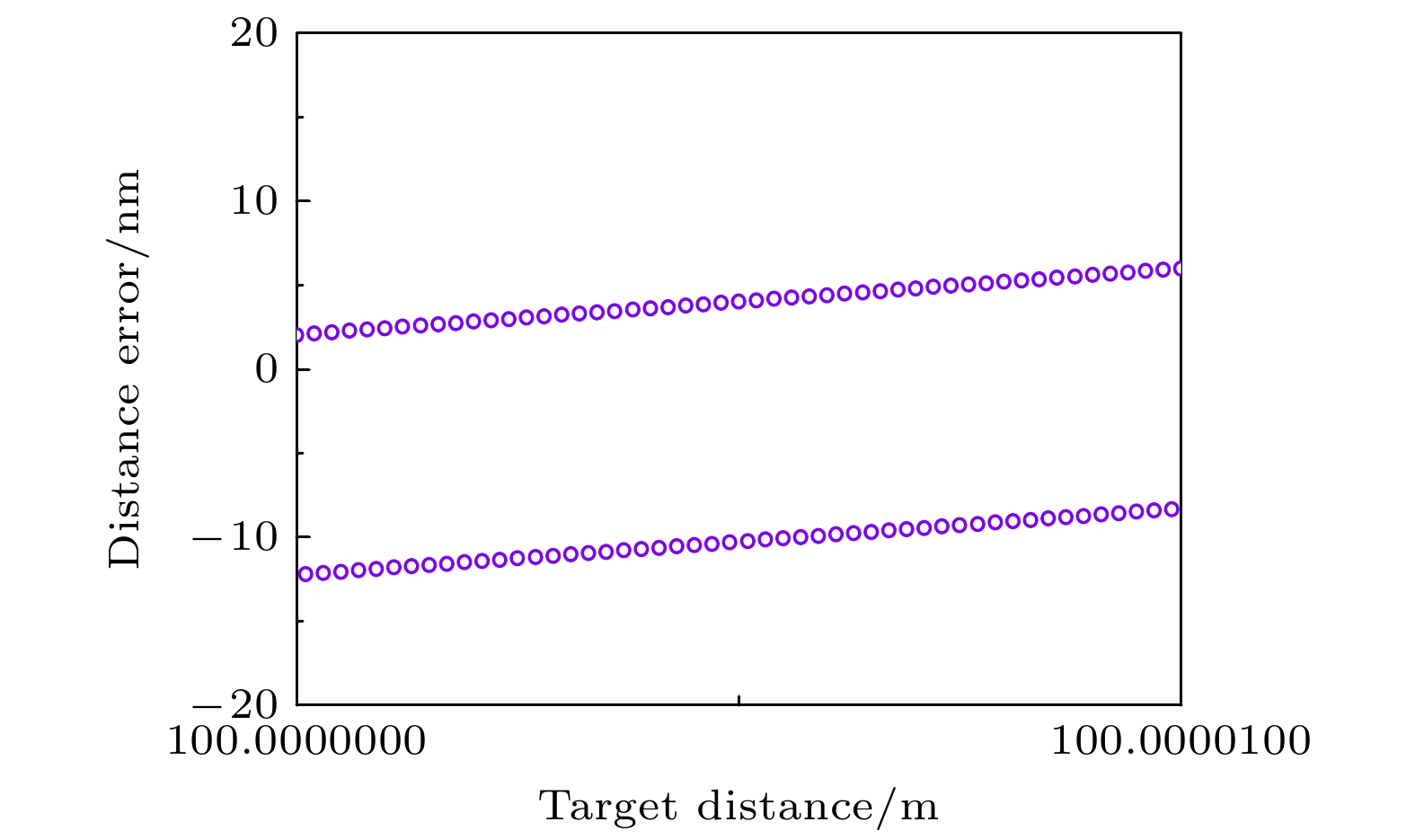
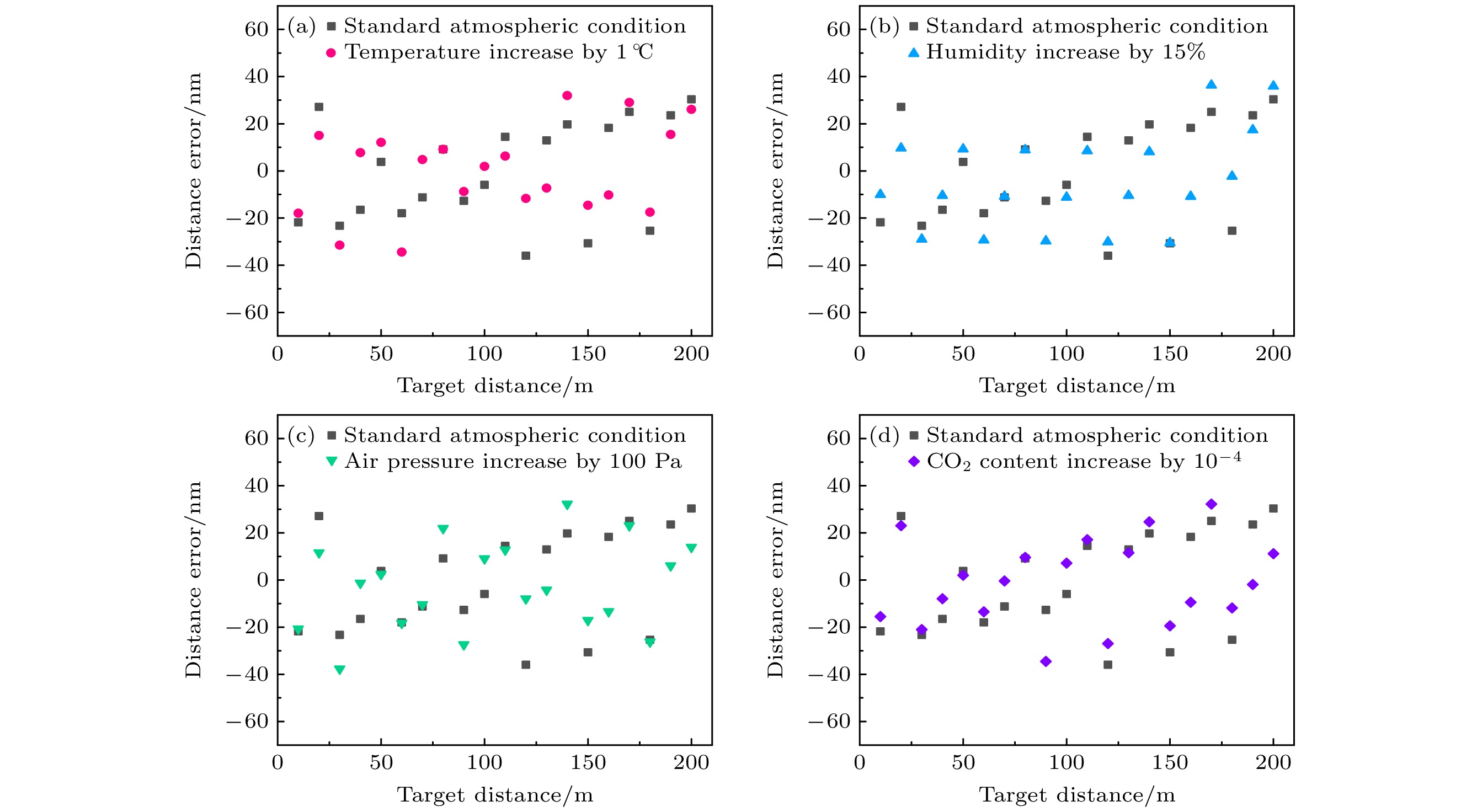
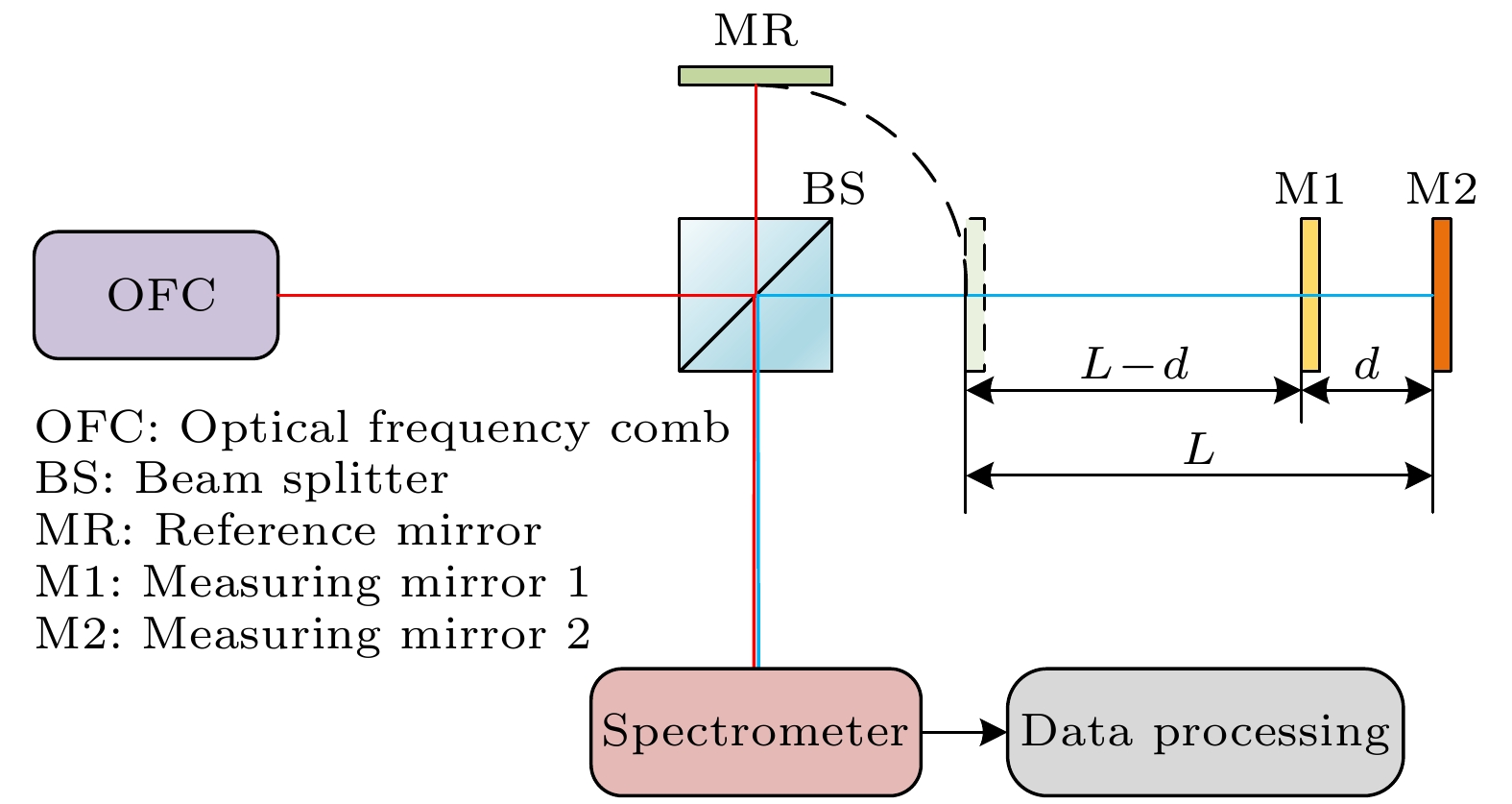
在工业现场或室外长距离测距场景中, 空气折射率难以精确测量且修正过程复杂, 这是影响精密测距的关键因素. 为此, 本文提出了一种基于光频梳的多脉冲光谱干涉绝对测距方法, 建立了相应的数学模型, 分析了利用伪时域同步确定测量光路群折射率和被测距离的方法, 通过微调重复频率和差分计算, 将测距范围由传统光谱干涉测距的非模糊范围拓展至任意长度, 并进行了大量的数值模拟和分析. 模拟结果表明, 当参考间距为0.1 m时, 群折射率测量的绝对误差最大为0.12×10–6; 在考虑空气折射率测量误差的情况下, 被测距离在0—200 m时的测距误差最大为33 nm; 在大气条件发生改变时, 通过实时修正群折射率波动引入的测距误差, 最终测距误差最大为38 nm, 保证了在大量程测距中亚微米级的测距精度. 研究结果表明, 该方法可以应用于大尺寸高精度的绝对距离测量.In industrial sites and outdoor long-distance measurements, the difficulty in accurately measuring and correcting the refractive index of air is a critical factor affecting precise distance measurement. In order to develop a simple, long-range, and high-precision absolute distance measurement technique, in this work an absolute distance measurement method is presented based on multi-pulse spectral interferometry by using an optical frequency comb. This method can dynamically correct the measurement errors introduced by group refractive index fluctuations. Firstly, a mathematical model for multi-pulse spectral interferometry is established. By performing a single Fourier transform on the multi-pulse spectral interference signal, the time delay measured in the pseudo-time domain can be used to simultaneously determine the group refractive index of the measurement path and the measured distance. Secondly, by fine-tuning the repetition frequency and using difference computation, the measurement range can be extended from the non-ambiguity range of traditional spectral interferometry to arbitrary lengths. Finally, extensive numerical simulations and analyses are conducted to validate the performance of the proposed method. The simulation results demonstrate that with a reference distance of 0.1 m, the maximum absolute error in group refractive index measurement is 0.12×10–6, and the maximum distance measurement error is 33 nm in a range of 0—200 m. In order to measure the group refractive index in real time under changing atmospheric conditions and compensate for ranging errors caused by changes in air refractive index, even under changing atmospheric conditions, the maximum distance measurement error is 38 nm, ensuring sub-micron-level measurement accuracy over long distances. The research results indicate that this method can be applied to large-scale and high-precision absolute distance measurement.
-
Keywords:
- optical frequency comb /
- multi-pulse spectral interferometry /
- absolute distance measurement /
- air refractive index
[1] 贾琳华, 郑继辉, 张福民, 曲兴华 2023 机械工程学报 59 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia L H, Zheng J H, Zhang F M, Qu X H 2023 J. Mech. Eng. 59 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ahn C M, Na Y J, Kim J 2023 Opt. Laser Eng. 162 107414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yu D R, Chen Z Y, Yang X, Xu Y L, Jin Z Y, Ma P X, Zhang Y F, Yu S, Lo B, Guo H 2023 Photon. Res. 11 2222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ray P, Salido-Monzu D, Presl R, Butt J, Wieser A 2024 Opt. Express 32 12667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liang X, Wu T F, Lin J R, Yang L H, Zhu J G 2023 Nanomanuf. Metrol. 6 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Cui M, Zeitouny M G, Bhattacharya N, Van Den Berg S A, Urbach H P, Braat J J M 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 1982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wei D, Takahashi S, Uehara K, Minoshima K, Hong F L, Nakajima M, Nakamura K 2011 Opt. Express 19 4881
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zheng J, Wang Y, Wang X, Zhang F, Zhang W 2021 Appl. Phys. Lett. 118 261106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 梁旭, 林嘉睿, 吴腾飞, 赵晖, 邾继贵 2022 71 090602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang X, Lin J R, Wu T F, Zhao H, Zhu J G 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 090602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhou S Y, Xiong S L, Zhu Z B, Wu G H 2019 Opt. Express 27 22868
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wright H, Sun J H, McKendrick D, Weston N, Reid D T 2021 Opt. Express 29 37037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou S Y, Jiang R L, Zhang R X, Shi L H, Zhang D, Wu G H 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 1104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Han S M, Yang L H, Song Y J, Niu Q, Shi Y Q, Yu H Y, Hu X Y, Zhu J G 2024 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 95 043703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Doloca N R, Meiners-Hagen K, Wedde M, Pollinger F, Abou-Zeid A 2010 Meas. Sci. Technol. 21 115302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhao X Y, Qu X H, Zhang F M, Zhao Y H, Tang G Q 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 807
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 王国超, 李星辉, 颜树华, 谭立龙, 管文良 2021 70 040601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G C, Li X H, Yan S H, Tan L L, Guan W L 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 040601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wu H Z, Zhang F M, Meng F, Liu T Y, Li J S, Pan L, Qu X H 2016 Meas. Sci. Technol. 27 015202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Gao H R, Huang L, Xu X, Wang D G, Ge P X, Zhao H N 2024 Meas. Sci. Technol. 35 105009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang J D, Huang J S, Liu Q H, Du W, Zhang F M, Zhu T 2024 Photon. Res. 12 313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Niu Q, Zheng J H, Cheng X R, Liu J C, Jia L H, Ni L M, Nian J, Zhang F M, Qu X H 2022 Opt. Express 30 35029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Xia H Y, Zhang C X 2010 Opt. Express 18 4118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wang J D, Lu Z Z, Wang W Q, Zhang F M, Chen J W, Wang Y, Zheng J H, Chu S T, Zhao W, Brent E, Qu X H, Zhang W F 2020 Photon. Res. 8 1964
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Jang Y S, Liu H, Yang J H, Yu M B, Kwong D L, Wong C W 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 023903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 徐昕阳, 赵海涵, 钱治文, 刘超, 翟京生, 吴翰钟 2021 70 220601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu X Y, Zhao H H, Qian Z W, Liu C, Zhai J S, Wu H Z 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 220601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] 贾琳华, 郑继辉, 张福民, 曲兴华 2023 机械工程学报 59 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia L H, Zheng J H, Zhang F M, Qu X H 2023 J. Mech. Eng. 59 244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ahn C M, Na Y J, Kim J 2023 Opt. Laser Eng. 162 107414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yu D R, Chen Z Y, Yang X, Xu Y L, Jin Z Y, Ma P X, Zhang Y F, Yu S, Lo B, Guo H 2023 Photon. Res. 11 2222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ray P, Salido-Monzu D, Presl R, Butt J, Wieser A 2024 Opt. Express 32 12667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liang X, Wu T F, Lin J R, Yang L H, Zhu J G 2023 Nanomanuf. Metrol. 6 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Cui M, Zeitouny M G, Bhattacharya N, Van Den Berg S A, Urbach H P, Braat J J M 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 1982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wei D, Takahashi S, Uehara K, Minoshima K, Hong F L, Nakajima M, Nakamura K 2011 Opt. Express 19 4881
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zheng J, Wang Y, Wang X, Zhang F, Zhang W 2021 Appl. Phys. Lett. 118 261106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 梁旭, 林嘉睿, 吴腾飞, 赵晖, 邾继贵 2022 71 090602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang X, Lin J R, Wu T F, Zhao H, Zhu J G 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 090602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhou S Y, Xiong S L, Zhu Z B, Wu G H 2019 Opt. Express 27 22868
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wright H, Sun J H, McKendrick D, Weston N, Reid D T 2021 Opt. Express 29 37037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou S Y, Jiang R L, Zhang R X, Shi L H, Zhang D, Wu G H 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 1104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Han S M, Yang L H, Song Y J, Niu Q, Shi Y Q, Yu H Y, Hu X Y, Zhu J G 2024 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 95 043703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Doloca N R, Meiners-Hagen K, Wedde M, Pollinger F, Abou-Zeid A 2010 Meas. Sci. Technol. 21 115302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhao X Y, Qu X H, Zhang F M, Zhao Y H, Tang G Q 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 807
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 王国超, 李星辉, 颜树华, 谭立龙, 管文良 2021 70 040601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G C, Li X H, Yan S H, Tan L L, Guan W L 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 040601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wu H Z, Zhang F M, Meng F, Liu T Y, Li J S, Pan L, Qu X H 2016 Meas. Sci. Technol. 27 015202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Gao H R, Huang L, Xu X, Wang D G, Ge P X, Zhao H N 2024 Meas. Sci. Technol. 35 105009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang J D, Huang J S, Liu Q H, Du W, Zhang F M, Zhu T 2024 Photon. Res. 12 313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Niu Q, Zheng J H, Cheng X R, Liu J C, Jia L H, Ni L M, Nian J, Zhang F M, Qu X H 2022 Opt. Express 30 35029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Xia H Y, Zhang C X 2010 Opt. Express 18 4118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wang J D, Lu Z Z, Wang W Q, Zhang F M, Chen J W, Wang Y, Zheng J H, Chu S T, Zhao W, Brent E, Qu X H, Zhang W F 2020 Photon. Res. 8 1964
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Jang Y S, Liu H, Yang J H, Yu M B, Kwong D L, Wong C W 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 023903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 徐昕阳, 赵海涵, 钱治文, 刘超, 翟京生, 吴翰钟 2021 70 220601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu X Y, Zhao H H, Qian Z W, Liu C, Zhai J S, Wu H Z 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 220601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 935
- PDF下载量: 50
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: