-
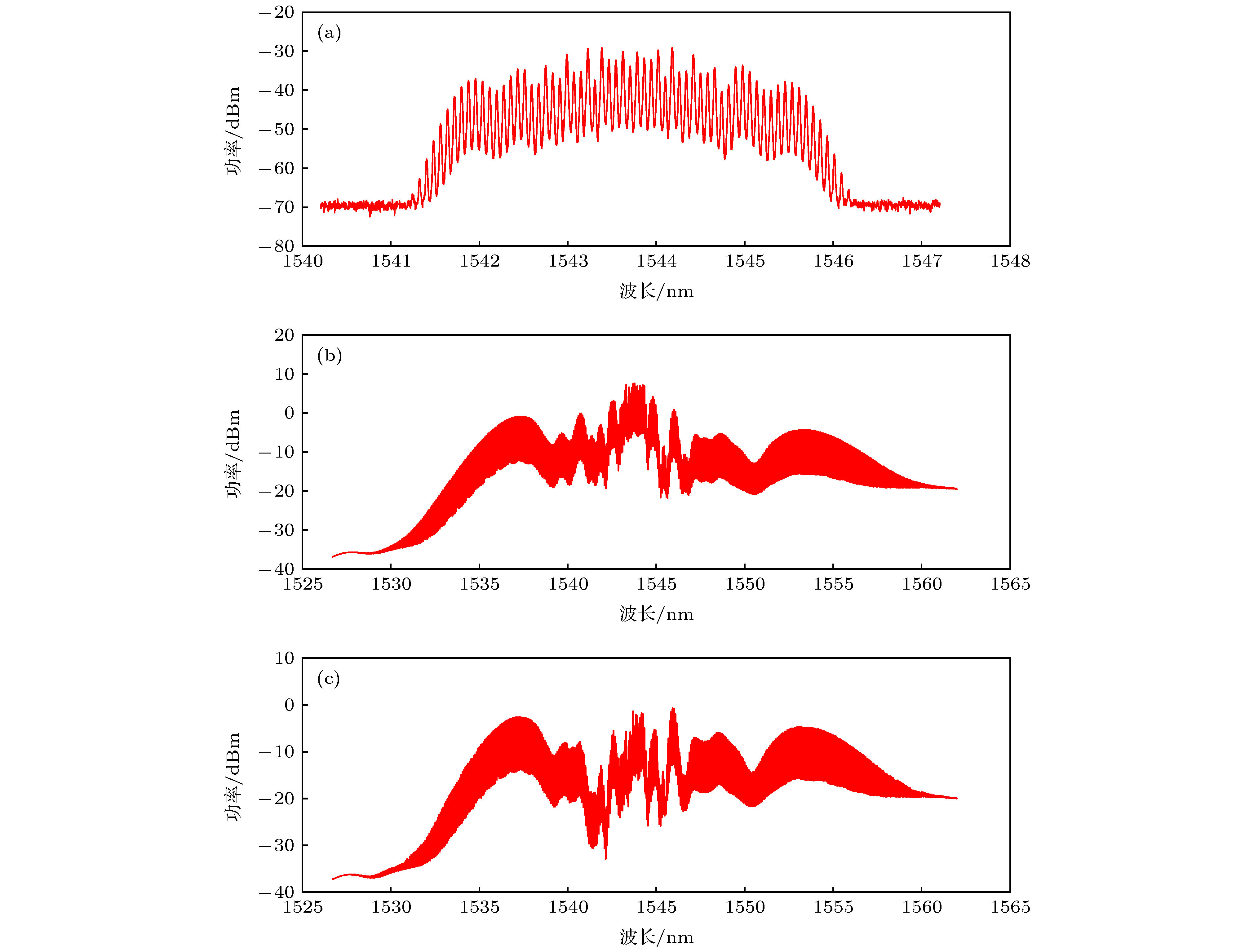
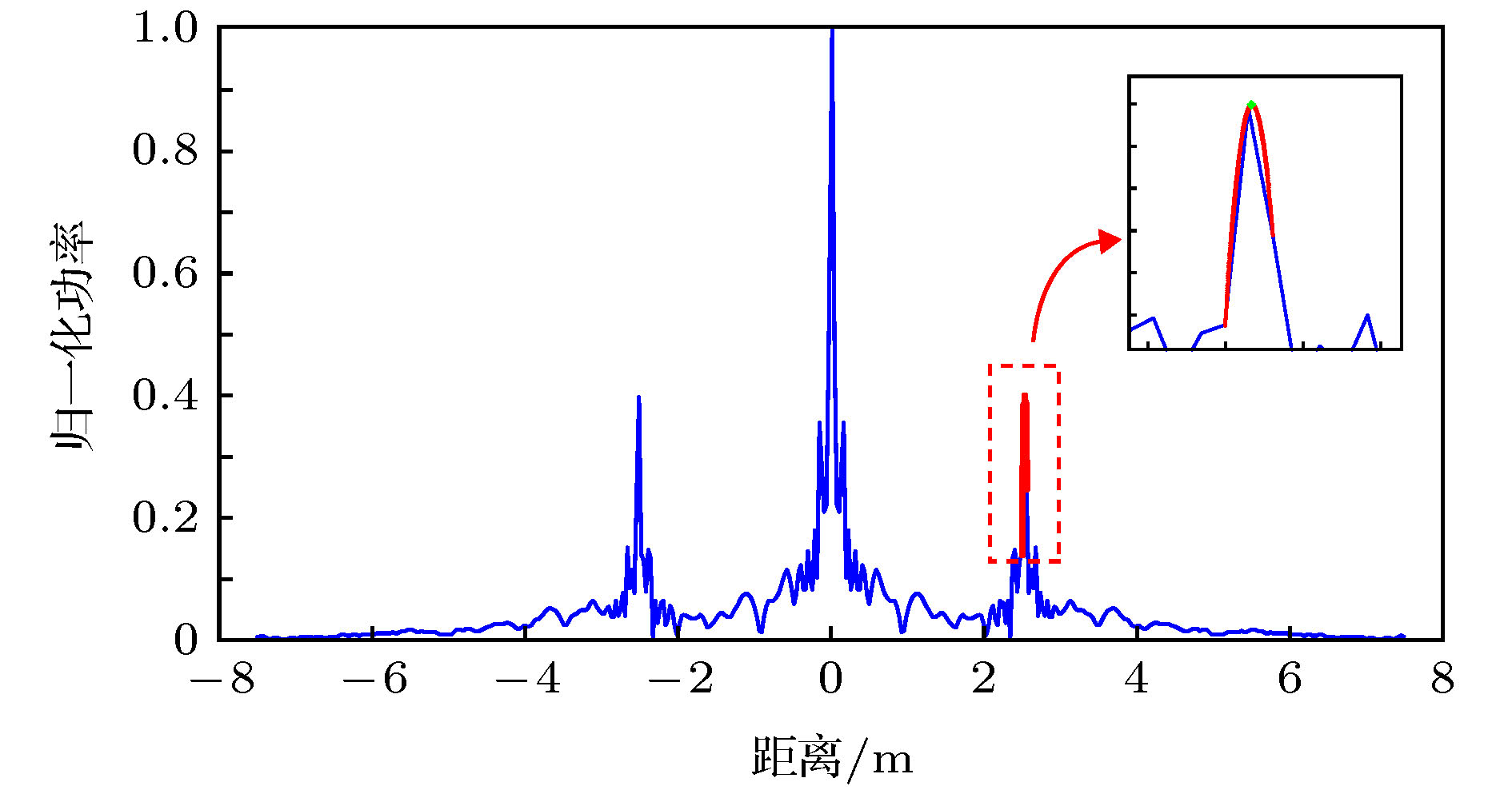
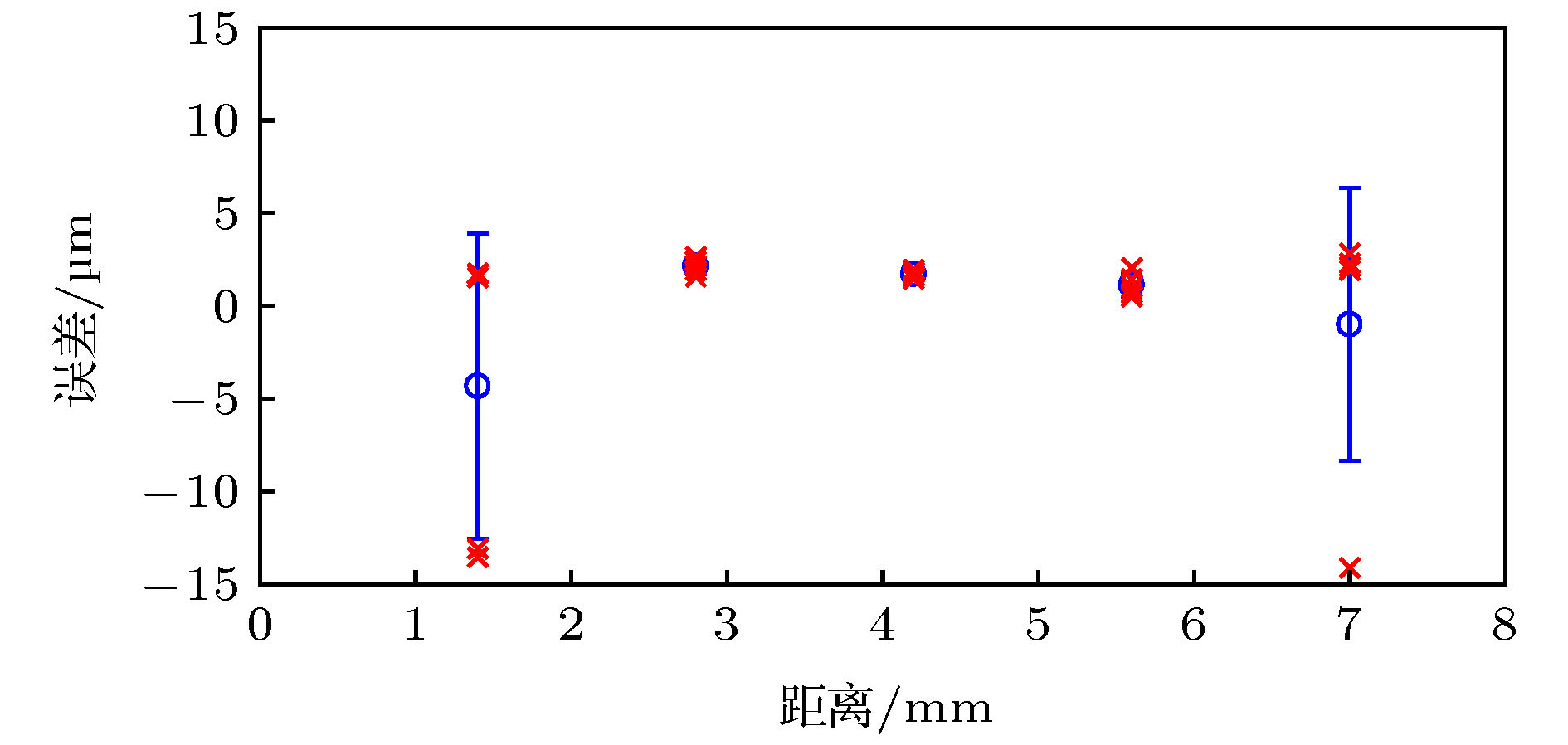
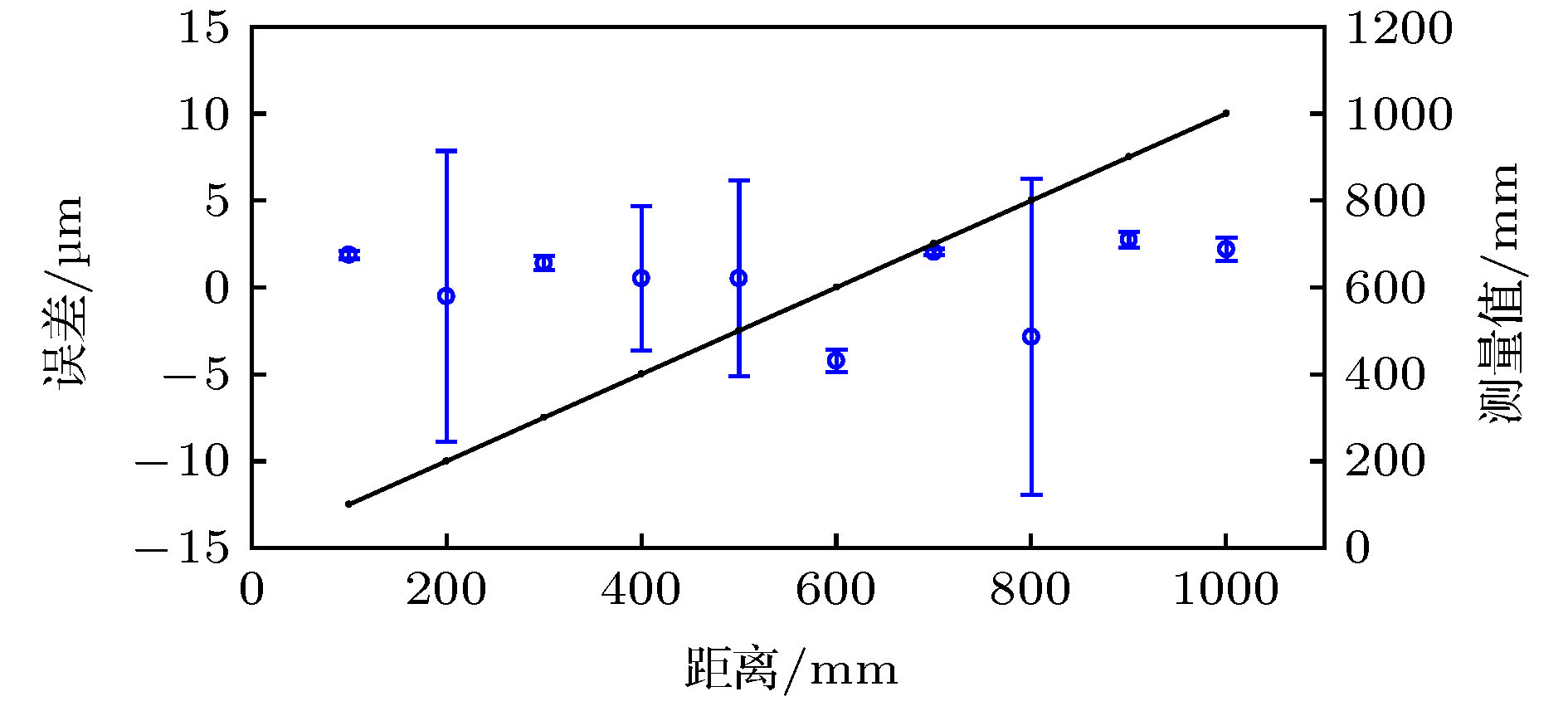
提出了一种基于电光调制光学频率梳的光谱干涉测距方法. 理论分析了电光调制光学频率梳的数学模型和光谱扩展原理, 并分析得出了光谱干涉测距方法的非模糊范围和分辨力的影响因素. 在实验中, 使用三只级联的电光相位调制器调制单频连续波激光生成了40多阶高功率梳齿状边带, 并通过单模光纤和高非线性光纤对电光调制器输出的激光进行光谱扩展, 得到重复频率为10 GHz, 光谱宽度达30 nm的光学频率梳. 将该光频梳作为光谱干涉测距装置的光源, 可以实现无“死区”的绝对距离测量. 另外, 使用等频率间隔重采样和二次方程脉冲峰值拟合算法对测量结果进行数据处理, 可以修正系统误差, 提升测距精度. 实验结果表明, 在1 m的测量范围内, 使用该装置可以在任意位置达到 ± 15 μm以内的绝对测距精度.To explore a new generation of ranging method suitable for industrial applications, in this paper, a spectral interferometry ranging method based on electro-optic (EO) comb is proposed. The mathematical model of EO comb and the principle of spectral expansion are analyzed in detail. Besides, the factors affecting the non-ambiguous range and resolution of the spectral interferometry method are also discussed. According to the theoretical analysis, the resolution of spectral interference ranging is mainly affected by the spectrum width of the optical frequency comb, and the non-ambiguous range is affected by the resolution of the optical spectrum analyzer (equal to the highest sampling rate of the optical spectrum analyzer). In the experiment, triple cascaded EO phase modulator is used to modulate a single frequency laser to generate more than 40 high-power sidebands. Then, the laser spectrum output from the EO modulator is expanded by single mode fiber and high nonlinearity fiber. Owing to the use of erbium doped fiber amplifier between the dispersion compensation fiber (single mode fiber) and the highly nonlinearity fiber, the polarization disturbance does not affect the spectrum width of the optical frequency comb significantly. However, the width of spectrum will be still affected by the phases of light, and the phases of light can be adjusted by the phase shifters in the front of the electro-optic modulators. Finally, the EO comb with a repetition frequency of 10 GHz and spectrum width of 30 nm is obtained. The EO comb can be used as the source of spectral interferometry scheme. Since the repetition frequency of the EO comb is high enough, which can meet the distortion-free sampling of optical spectrum analyzer. Hence, there is no “dead zone” in the measurement range. Besides, the equal frequency interval resampling algorithm and quadratic equation fitting algorithm are used in the data processing. Through the use of these algorithms, we can eliminate the measurement errors caused by non-equal frequency interval sampling of the optical spectrum analyzer and improve the ranging accuracy. The experimental results show that within the range of 1 m, the absolute ranging accuracy of 15 μm can be achieved at arbitrary position.
-
Keywords:
- optical frequency comb /
- electro-optic modulation /
- spectral interferometry /
- absolute distance measurement
[1] Minoshima K, Matsumoto H 2000 Appl. Opt. 39 5512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Sudatham W, Matsumoto H, Takahashi S, Takamasu K 2016 Measurement 78 381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kayes M I, Rochette M 2019 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 31 775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu Y, Yang L, Guo Y, Lin J, Cui P, Zhu J 2018 Opt. Lasers Eng. 101 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Coddington I, Swann W C, Nenadovic L, Newbury N R 2009 Nat. Photonics 3 351
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Suh M G, Vahala K J 2018 Science 359 884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 邢书剑, 张福民, 曹士英, 王高文, 曲兴华 2013 62 170603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xing S J, Zhang F M, Cao S Y, Wang G W, Qu X H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 170603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhu Z, Xu G, Ni K, Zhou Q, Wu G 2018 Opt. Express 26 5747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang R, Pollinger F, Meiners H K, Krystek M, Tan J, Bosse H 2015 Meas. Sci. Technol. 26 084001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao X, Qu X, Zhang F, Zhao Y, Tang G 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 807
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 刘亭洋, 张福民, 吴翰钟, 李建双, 石永强, 曲兴华 2016 65 020601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu T Y, Zhang F M, Wu H Z, Li J S, Shi Y Q, Qu X H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 020601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Joo K N, Kim S W 2006 Opt. Express 14 5954
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] van den Berg S A, van Eldik S, Bhattacharya N 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 14661
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 崔成君, 劳达宝, 高书苑, 郝春艳, 周维虎 2016 光学精密工程 24 2561
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui C J, Lao D B, Gao S Y, Hao C Y, Zhou W H 2016 Opt. Precision Eng. 24 2561
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 胡坤, 黎尧, 纪荣祎, 周维虎, 刘德明 2015 仪表技术与传感器 6 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu K, Li Y, Ji R, Zhou W, Liu D 2015 Intstrument Technique and Sensor 6 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lesundak A, Voigt D, Cip O, Van B S 2017 Opt. Express 25 32570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kourogi M, Nakagawa K, Ohtsu M 1993 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 29 2693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] He C, Pan S, Guo R, Zhao Y, Pan M 2012 Opt. Lett. 37 3834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Morohashi I, Sakamoto T, Sekine N, Kasamatsu A, Hosako I 2016 Nano Commun. Netw. 10 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen C, Zhang F, Pan S 2013 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 25 2164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Nakajima Y, Inaba H, Hosaka K, Minoshima K, Onae A, Yasuda M, Kohno T, Kawato S, Kobayashi T, Katsuyama T, Hong F L 2010 Opt. Express 18 1667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yan J, Zhang S, Xia Z, Bai M, Zheng Z 2015 Opt. Laser Technol. 72 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wu R, Supradeepa V R, Long C M, Leaird D E, Weiner A M 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 3234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu R, Torres C V, Leaird D E, Weiner A M 2013 Opt. Express 21 6045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yang R, Pollinger F, Meiners H K, Tan J, Bosse H 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 5834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 陈嘉伟, 王金栋, 曲兴华, 张福民 2019 68 190602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen J, Wang J, Qu X, Zhang F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 190602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bonsch G, Potulski E 1998 Metrologia 35 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 3 等频率间隔重采样处理示意图 (a)光谱仪等波长间隔采样得到的信号; (b)对横坐标进行波长-频率变换后的信号; (c)对横坐标进行线性坐标转换后的信号; (d)对转换后的信号进行等频率间隔重采样的结果
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of equal frequency interval resampling: (a) Signal obtained by spectrometer with equal wavelength interval sampling; (b) the signal after wavelength-frequency transformed; (c) the signal after linear coordinate transformation on the abscissa; (d) the signal after equal frequency interval resampling.
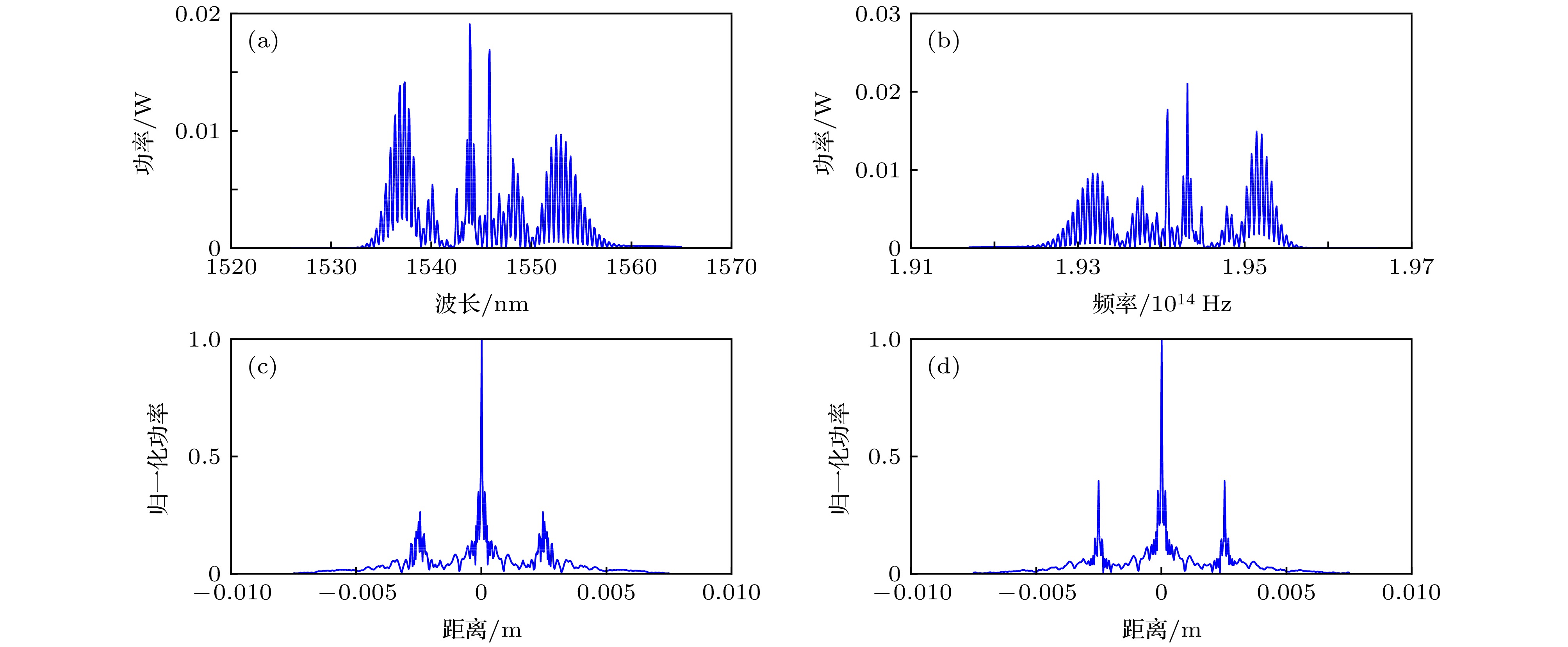
图 7 等频率间隔重采样数据处理过程图 (a)寻峰算法处理后的光谱干涉图; (b)横坐标转化成频率后的光谱干涉图; (c)对图(a)做傅里叶变换后的结果; (d)对图(b)做傅里叶变换后的结果
Fig. 7. Data processing of equal frequency interval resampling. (a) Spectral interferogram processed by peak seeking algorithm; (b) spectrum interferogram after the abscissa is converted into frequency; (c) Fourier transform of panel (a); (d) Fourier transform of panel (b).
-
[1] Minoshima K, Matsumoto H 2000 Appl. Opt. 39 5512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Sudatham W, Matsumoto H, Takahashi S, Takamasu K 2016 Measurement 78 381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kayes M I, Rochette M 2019 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 31 775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu Y, Yang L, Guo Y, Lin J, Cui P, Zhu J 2018 Opt. Lasers Eng. 101 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Coddington I, Swann W C, Nenadovic L, Newbury N R 2009 Nat. Photonics 3 351
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Suh M G, Vahala K J 2018 Science 359 884
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 邢书剑, 张福民, 曹士英, 王高文, 曲兴华 2013 62 170603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xing S J, Zhang F M, Cao S Y, Wang G W, Qu X H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 170603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhu Z, Xu G, Ni K, Zhou Q, Wu G 2018 Opt. Express 26 5747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang R, Pollinger F, Meiners H K, Krystek M, Tan J, Bosse H 2015 Meas. Sci. Technol. 26 084001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao X, Qu X, Zhang F, Zhao Y, Tang G 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 807
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 刘亭洋, 张福民, 吴翰钟, 李建双, 石永强, 曲兴华 2016 65 020601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu T Y, Zhang F M, Wu H Z, Li J S, Shi Y Q, Qu X H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 020601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Joo K N, Kim S W 2006 Opt. Express 14 5954
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] van den Berg S A, van Eldik S, Bhattacharya N 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 14661
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 崔成君, 劳达宝, 高书苑, 郝春艳, 周维虎 2016 光学精密工程 24 2561
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui C J, Lao D B, Gao S Y, Hao C Y, Zhou W H 2016 Opt. Precision Eng. 24 2561
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 胡坤, 黎尧, 纪荣祎, 周维虎, 刘德明 2015 仪表技术与传感器 6 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu K, Li Y, Ji R, Zhou W, Liu D 2015 Intstrument Technique and Sensor 6 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lesundak A, Voigt D, Cip O, Van B S 2017 Opt. Express 25 32570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kourogi M, Nakagawa K, Ohtsu M 1993 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 29 2693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] He C, Pan S, Guo R, Zhao Y, Pan M 2012 Opt. Lett. 37 3834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Morohashi I, Sakamoto T, Sekine N, Kasamatsu A, Hosako I 2016 Nano Commun. Netw. 10 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen C, Zhang F, Pan S 2013 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 25 2164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Nakajima Y, Inaba H, Hosaka K, Minoshima K, Onae A, Yasuda M, Kohno T, Kawato S, Kobayashi T, Katsuyama T, Hong F L 2010 Opt. Express 18 1667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yan J, Zhang S, Xia Z, Bai M, Zheng Z 2015 Opt. Laser Technol. 72 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wu R, Supradeepa V R, Long C M, Leaird D E, Weiner A M 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 3234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu R, Torres C V, Leaird D E, Weiner A M 2013 Opt. Express 21 6045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yang R, Pollinger F, Meiners H K, Tan J, Bosse H 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 5834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 陈嘉伟, 王金栋, 曲兴华, 张福民 2019 68 190602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen J, Wang J, Qu X, Zhang F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 190602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bonsch G, Potulski E 1998 Metrologia 35 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 18251
- PDF下载量: 286
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: