-
光-微波纠缠和光磁纠缠在混合量子网络构建和光学控制等方面有着重要的应用前景. 本文提出了一种在光磁力系统中利用相干反馈机制来增强光-微波纠缠和光磁纠缠的理论方案, 考虑在输入输出腔镜和镀反射膜的YIG桥中间插入薄膜的光磁力系统, 该系统包含了光、微波、机械振子和磁振子四种模式, 其中, 光和微波以机械振子为中介发生相互作用, 磁振子则通过磁偶极相互作用与微波耦合. 我们详细地研究了光-微波纠缠和光磁纠缠随各失谐量、各耦合强度、各衰减率的变化关系, 分析了最优的相干反馈条件、纠缠产生和纠缠转移的物理机制和条件, 讨论了加入反馈回路后的光-微波纠缠和光磁纠缠的增强. 研究结果表明, 加入相干反馈后, 光-微波纠缠和光磁纠缠在较宽的参数范围内均可获得显著且稳定的增强. 研究结果对构建混合量子网络时连接不同物理系统构成的节点、灵活操控磁振子的量子特性以及制备宏观量子态等方面提供了理论依据. 我们的研究结果不仅为实现混合量子网络提供了有力的理论支持, 还为光学控制、设计、检测和传输磁振子状态提供了更多的可能性, 便于未来能够更加灵活地操控和利用磁振子的量子特性.Optomicrowave entanglement and optomagnonic entanglement have significant applications in constructing hybrid quantum network and optical controlling magnons. In this paper, a theoretical scheme of enhancing optomicrowave and optomagnonic entanglements is proposed, based on a coherent-feedback-assisted optomagnomechanical (OMM) system. By inserting a thin membrane between the input-output mirror and the high-reflective-mirror-attached YIG bridge, the system consists of four kinds of modes: optical mode, microwave mode, mechanical mode, and magnon mode. In this system, optical mode and microwave mode interact with each other through the mechanical mode, while the magnon mode couples with the microwave mode through magnetic-dipole interaction. The entanglement is originally generated between optical mode and phonon mode under the two-mode squeezing mechanism (blue-detuned driven), then the generated entanglement is transferred to the optical mode and microwave mode through the state transfer mechanism (red-detuned driven) between the microwave mode and phonon mode and is further transferred to the optical mode and magnon mode by the magnetic-dipole interaction between the microwave mode and magnon mode. Adopting the negative logarithm criterion, the variations of the optomicrowave and optomagnonic entanglements with detuning, coupling strength, and decay rate are thoroughly investigated. Furthermore, the optimal coherent feedback parameters and the physical mechanisms of generating and transferring entanglement are analyzed, and the entanglement enhancements by adding the feedback loop are discussed. The results show that after adding coherent feedback, optomicrowave entanglement and optomagnonic entanglement can be enhanced effectively within a wide range of parameters and the enhancement can also be well maintained. Our findings provide a theoretical basis for connecting different nodes (different physical systems) to construct hybrid quantum networks, flexibly controlling the quantum properties of magnons, and preparing macroscopic quantum states.
-
Keywords:
- optomagnomechanical system /
- coherent feedback /
- quantum entanglement
[1] Lachance-Quirion D, Tabuchi Y, Gloppe A, Usami K, Nakamura Y 2019 Appl. Phys. Express 12 070101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yuan H Y, Cao Y S, Kamra A, Duine R A, Yan P 2022 Phys. Rep. 965 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ast M, Steinlechner S, Schnabel R 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 180801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 郝景晨, 杜培林, 孙恒信, 刘奎, 张静, 杨荣国, 郜江瑞 2024 73 074203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hao J C, Du P L, Sun H X, Liu K, Zhang J, Yang R G, Gao J R 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 074203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang D Y, Bai C H, Xing Y, Liu S T, Zhang S, Wang H F 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 043705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Bai C H, Wang D Y, Zhang S, Liu S T, Wang H F 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 033508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Furusawa A, Sørensen J L, Braunstein S L, Fuchs C A, Kimble H J, Polzik E S 1998 Science 282 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li J, Wallucks A, Benevides R, Fiaschi N, Hensen B, Alegre T P M, Gröblacher S 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 032402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhong C C, Wang Z X, Zou C L, Zhang M Z, Han X, Fu W, Xu M R, Shankar S, Devoret M H, Tang H X, Jiang L 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 010511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Krastanov S, Raniwala H, Holzgrafe J, Jacobs K, Lončar M, Reagor M J, Englund D R 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 127 040503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tian L 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 233602.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bagci T, Simonsen A, Schmid S, Villanueva L G, Zeuthen E, Appel J, Taylor J M, Sørensen A, Usami K, Schliesser A, Polzik E S 2014 Nature 507 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li J, Zhu S Y, Agarwal G S 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 203601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen Y T, Du L, Zhang Y, Wu J H 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 053712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Qiu W Y, Cheng X H, Chen A X, Lan Y H, Nie W J 2022 Phys. Rev. A 105 063718
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张秀龙, 鲍倩倩, 杨明珠, 田雪松 2018 67 104203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X L, Bao Q Q, Yang M Z, Tian X S 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 104203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 周瑶瑶, 田剑锋, 闫智辉, 贾晓军 2019 68 064205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y Y, Tian J F, Yan Z H, Jia X J 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 064205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Fan Z Y, Qiu L, Gröblacher S, Li J 2023 Laser Photonics Rev. 17 2200866
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Luo Y X, Cong L J, Zheng Z G, Liu H Y, Ming Y, Yang R C 2023 Opt. Express 31 34764
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Di K, Tan S, Wang L Y, Cheng A Y, Wang X, Liu Y, Du J J 2023 Opt. Express 31 29491
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Fan Z Y, Qian H, Zuo X, Li J 2023 Phys. Rev. A 108 023501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Fan Z Y, Qian H, Li J 2023 Quantum Sci. Technol. 8 015014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wiseman H M, Milburn G J 1994 Phys. Rev. A 49 4110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lloyd S 2000 Phys. Rev. A 62 022108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gough J E, James M R, Nurdin H I 2010 Phys. Rev. A 81 023804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Jacobs K, Wang X T, Wiseman H M 2014 New J. Phys. 16 073036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Harwood A, Brunelli M, Serafini A 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 023509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li J, Li G, Zippilli S, Vitali D, Zhang T C 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 043819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Peng R, Zhao C S, Yang Z, Yang J Y, Zhou L 2023 Phys. Rev. A 107 013507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Xin J, Pan X Z, Lu X M, Kong J, Li G L, Li X M 2020 Phys. Rev. Appl. 14 024015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zheng Q J, Zhong W X, Cheng G L, Chen A X 2023 Results Phys. 48 106422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Li J, Zhu S Y 2019 New J. Phys. 21 085001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Vidal G, Werner R F 2002 Phys. Rev. A 65 032314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Plenio M B 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 090503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
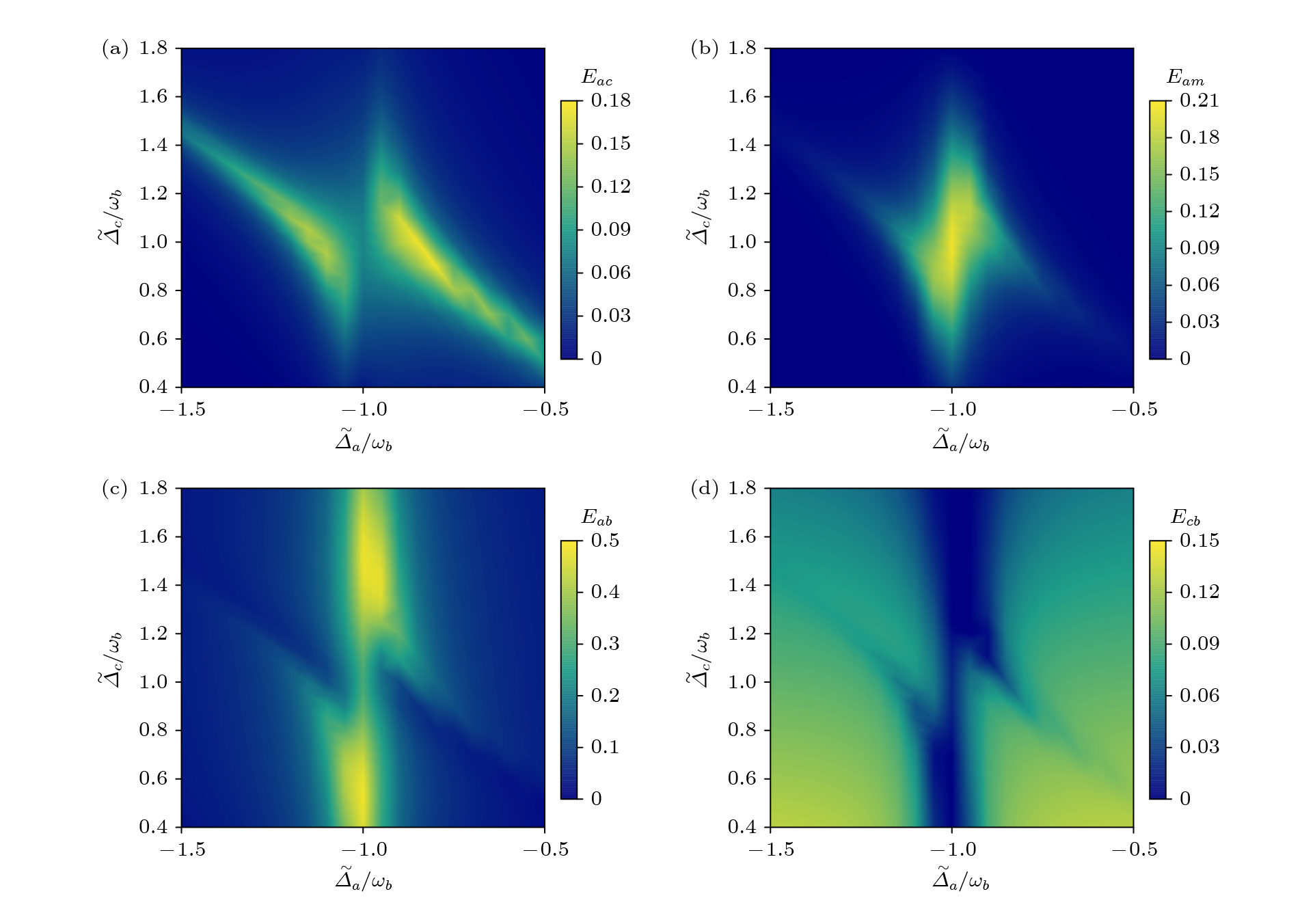
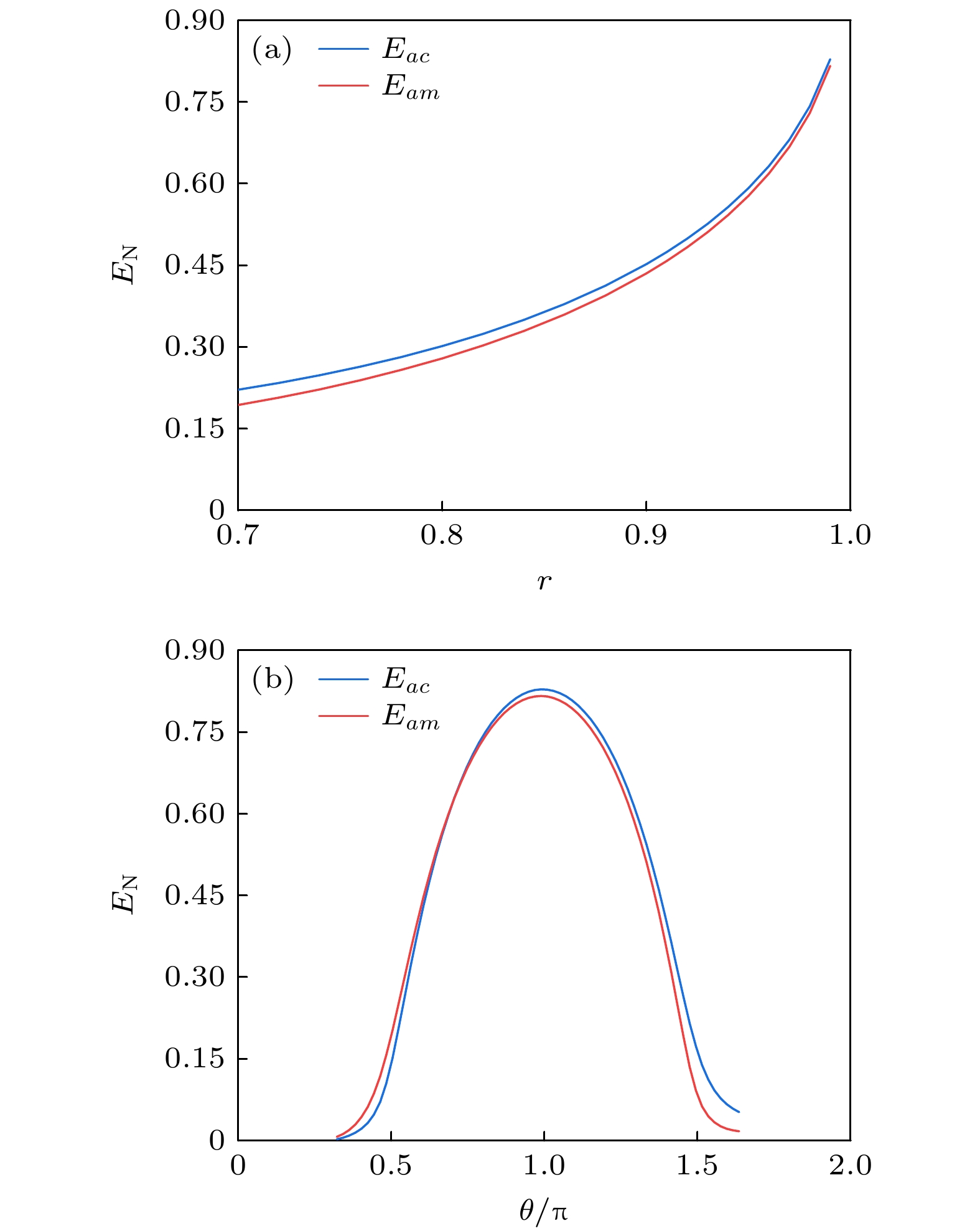
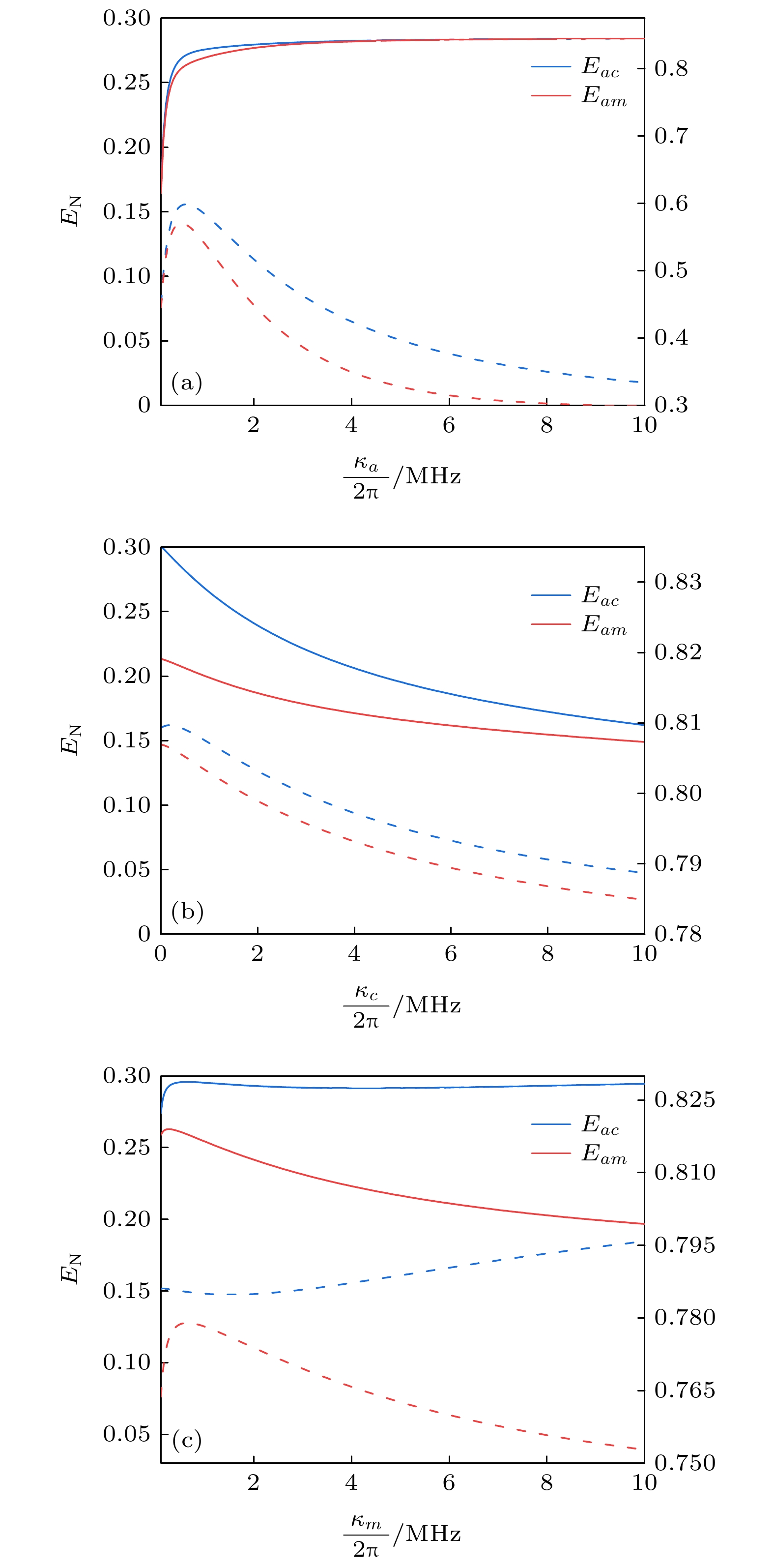
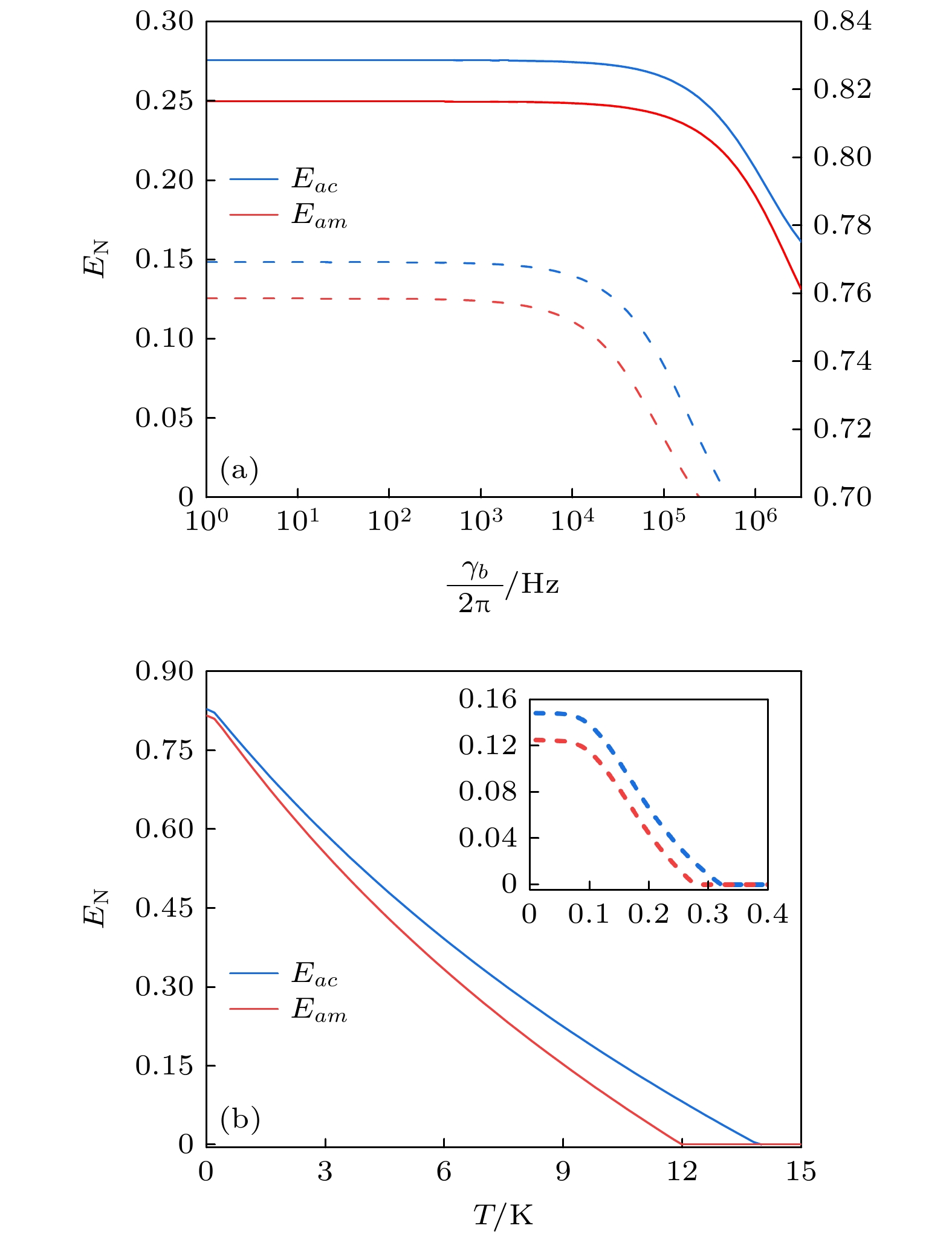
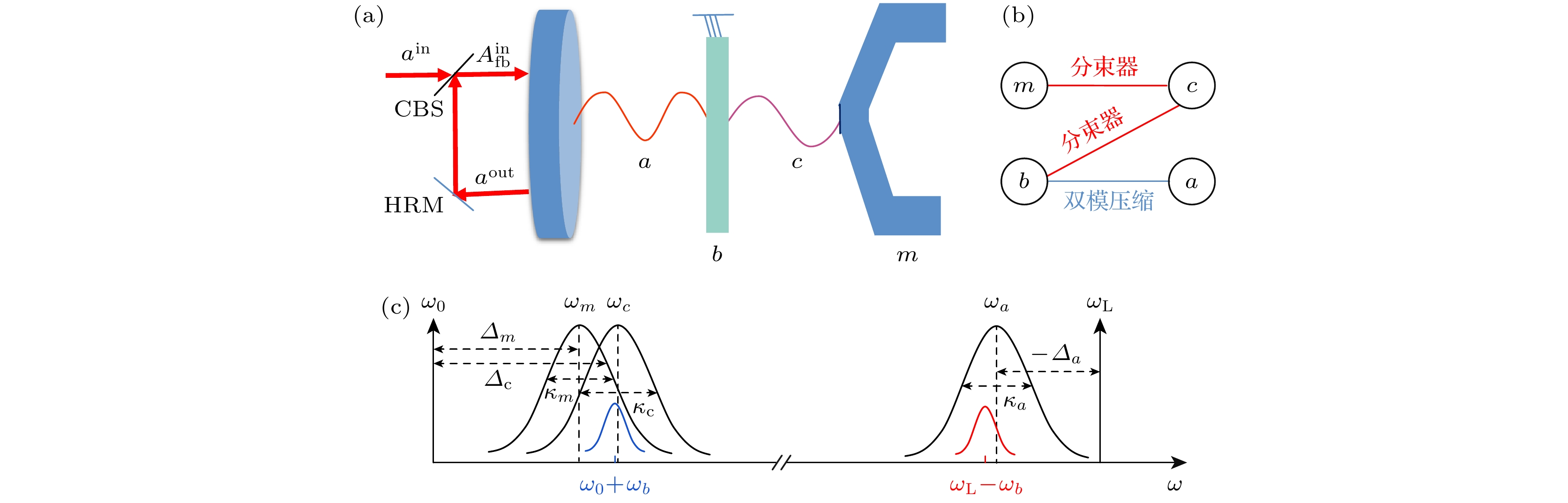
图 1 (a)加入相干反馈回路的光磁力系统示意图, 其中CBS (controllable beam splitter)是可控分束器, HRM (highly reflective mirror)是高反镜; (b)各个模式之间的相互作用, 其中蓝色和红色实线分别对应双模压缩型和分束器型相互作用; (c)各个模式之间的频率关系
Fig. 1. (a) Optomagnomechanics system scheme with a coherent feedback loop, where CBS represents a controllable beam splitter, and HRM represents a highly reflective mirror; (b) the interactions between different modes, where the blue and red solid lines correspond to the two-mode squeezeing and beam-splitter interactions; (c) the frequency relationship between different modes.
-
[1] Lachance-Quirion D, Tabuchi Y, Gloppe A, Usami K, Nakamura Y 2019 Appl. Phys. Express 12 070101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yuan H Y, Cao Y S, Kamra A, Duine R A, Yan P 2022 Phys. Rep. 965 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ast M, Steinlechner S, Schnabel R 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 180801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 郝景晨, 杜培林, 孙恒信, 刘奎, 张静, 杨荣国, 郜江瑞 2024 73 074203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hao J C, Du P L, Sun H X, Liu K, Zhang J, Yang R G, Gao J R 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 074203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang D Y, Bai C H, Xing Y, Liu S T, Zhang S, Wang H F 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 043705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Bai C H, Wang D Y, Zhang S, Liu S T, Wang H F 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 033508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Furusawa A, Sørensen J L, Braunstein S L, Fuchs C A, Kimble H J, Polzik E S 1998 Science 282 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li J, Wallucks A, Benevides R, Fiaschi N, Hensen B, Alegre T P M, Gröblacher S 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 032402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhong C C, Wang Z X, Zou C L, Zhang M Z, Han X, Fu W, Xu M R, Shankar S, Devoret M H, Tang H X, Jiang L 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 010511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Krastanov S, Raniwala H, Holzgrafe J, Jacobs K, Lončar M, Reagor M J, Englund D R 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 127 040503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tian L 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 233602.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bagci T, Simonsen A, Schmid S, Villanueva L G, Zeuthen E, Appel J, Taylor J M, Sørensen A, Usami K, Schliesser A, Polzik E S 2014 Nature 507 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li J, Zhu S Y, Agarwal G S 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 203601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen Y T, Du L, Zhang Y, Wu J H 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 053712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Qiu W Y, Cheng X H, Chen A X, Lan Y H, Nie W J 2022 Phys. Rev. A 105 063718
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张秀龙, 鲍倩倩, 杨明珠, 田雪松 2018 67 104203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X L, Bao Q Q, Yang M Z, Tian X S 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 104203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 周瑶瑶, 田剑锋, 闫智辉, 贾晓军 2019 68 064205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y Y, Tian J F, Yan Z H, Jia X J 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 064205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Fan Z Y, Qiu L, Gröblacher S, Li J 2023 Laser Photonics Rev. 17 2200866
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Luo Y X, Cong L J, Zheng Z G, Liu H Y, Ming Y, Yang R C 2023 Opt. Express 31 34764
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Di K, Tan S, Wang L Y, Cheng A Y, Wang X, Liu Y, Du J J 2023 Opt. Express 31 29491
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Fan Z Y, Qian H, Zuo X, Li J 2023 Phys. Rev. A 108 023501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Fan Z Y, Qian H, Li J 2023 Quantum Sci. Technol. 8 015014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wiseman H M, Milburn G J 1994 Phys. Rev. A 49 4110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lloyd S 2000 Phys. Rev. A 62 022108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gough J E, James M R, Nurdin H I 2010 Phys. Rev. A 81 023804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Jacobs K, Wang X T, Wiseman H M 2014 New J. Phys. 16 073036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Harwood A, Brunelli M, Serafini A 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 023509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li J, Li G, Zippilli S, Vitali D, Zhang T C 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 043819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Peng R, Zhao C S, Yang Z, Yang J Y, Zhou L 2023 Phys. Rev. A 107 013507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Xin J, Pan X Z, Lu X M, Kong J, Li G L, Li X M 2020 Phys. Rev. Appl. 14 024015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zheng Q J, Zhong W X, Cheng G L, Chen A X 2023 Results Phys. 48 106422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Li J, Zhu S Y 2019 New J. Phys. 21 085001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Vidal G, Werner R F 2002 Phys. Rev. A 65 032314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Plenio M B 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 090503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 2299
- PDF下载量: 62
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: