-
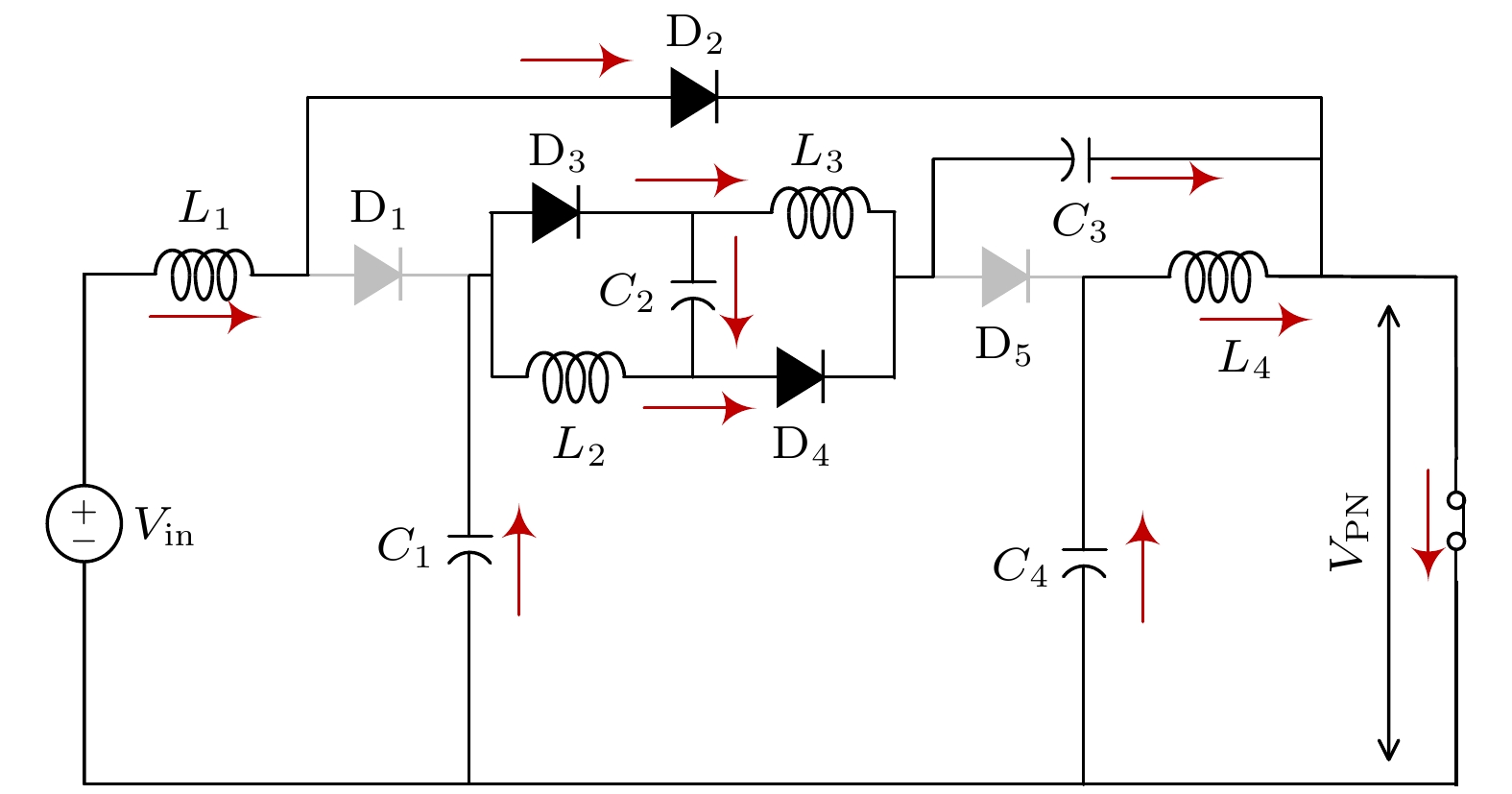
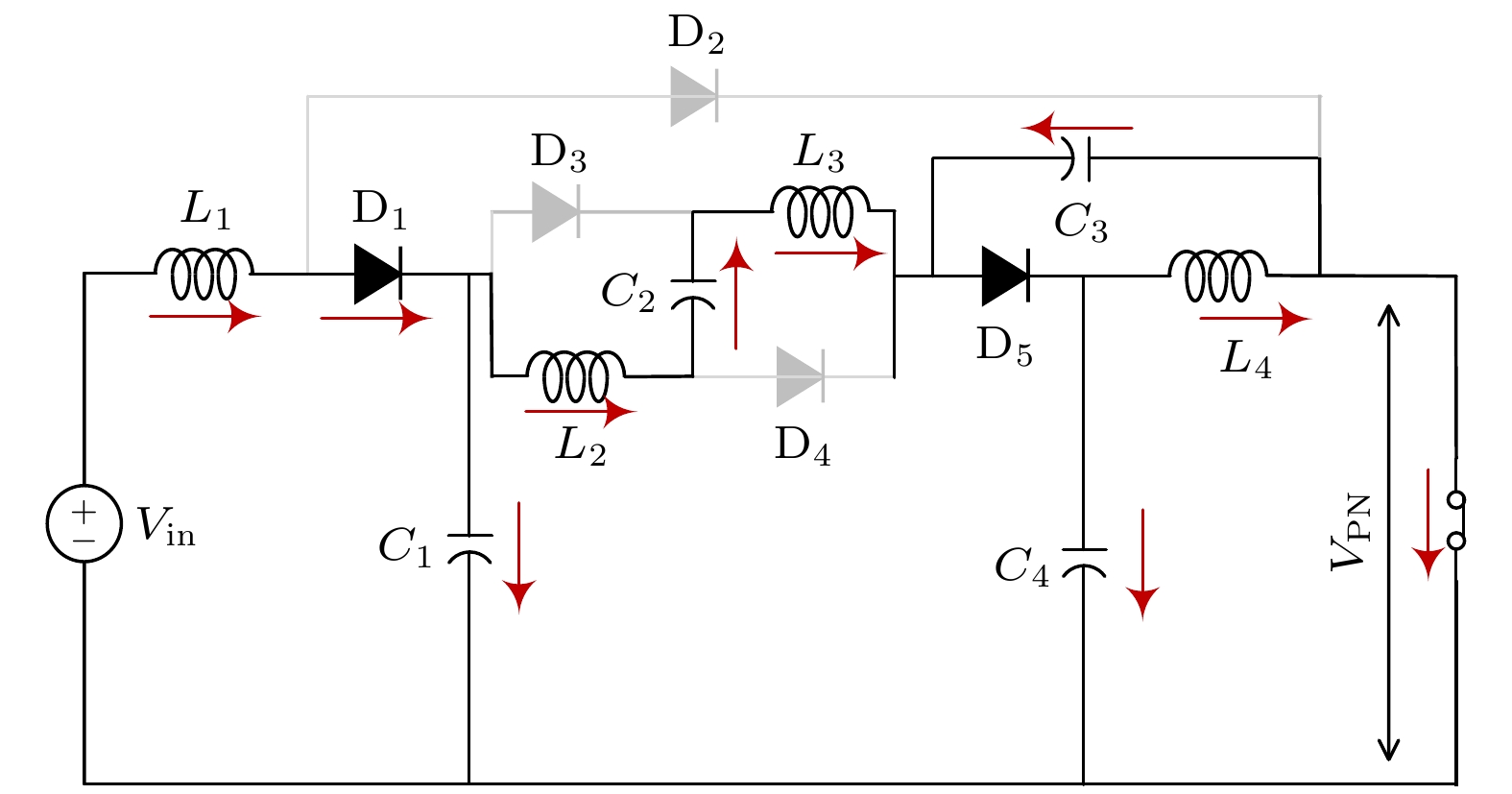
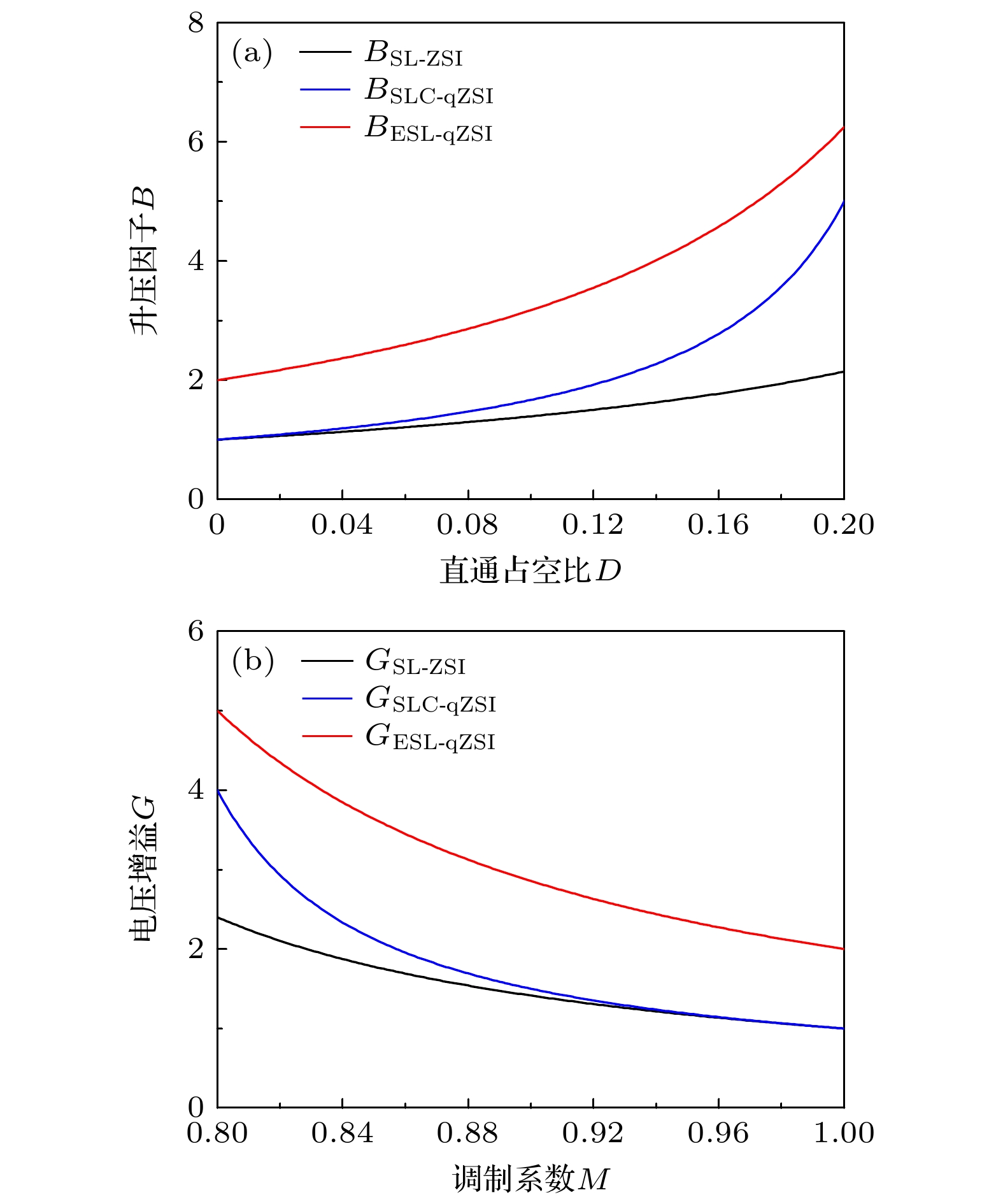
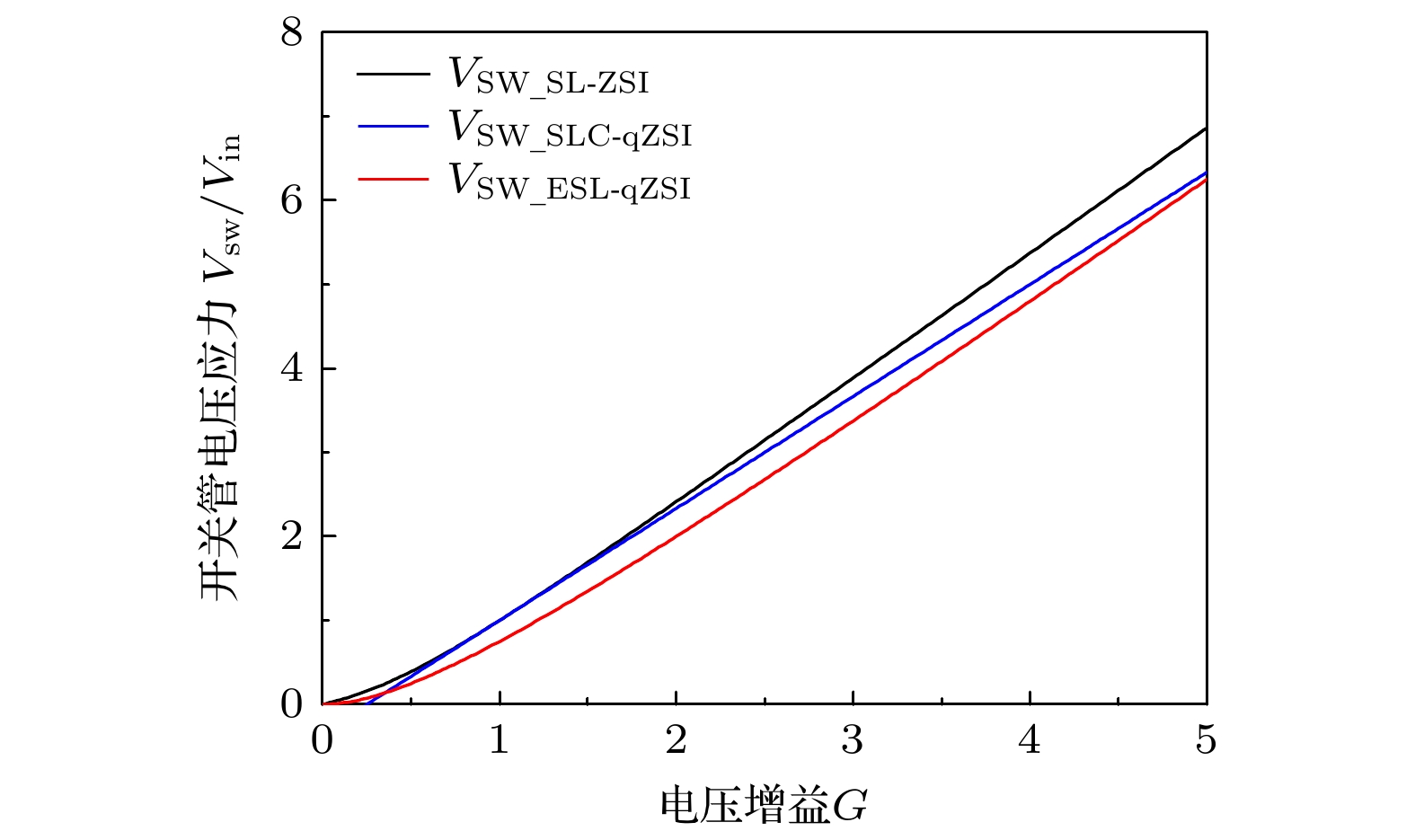
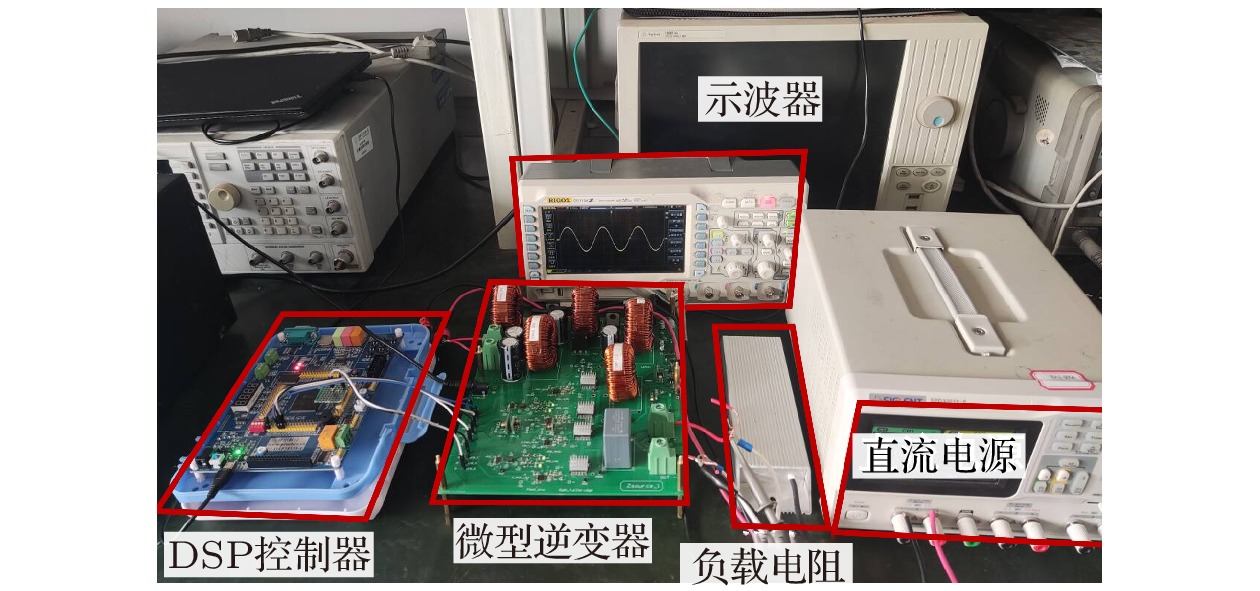
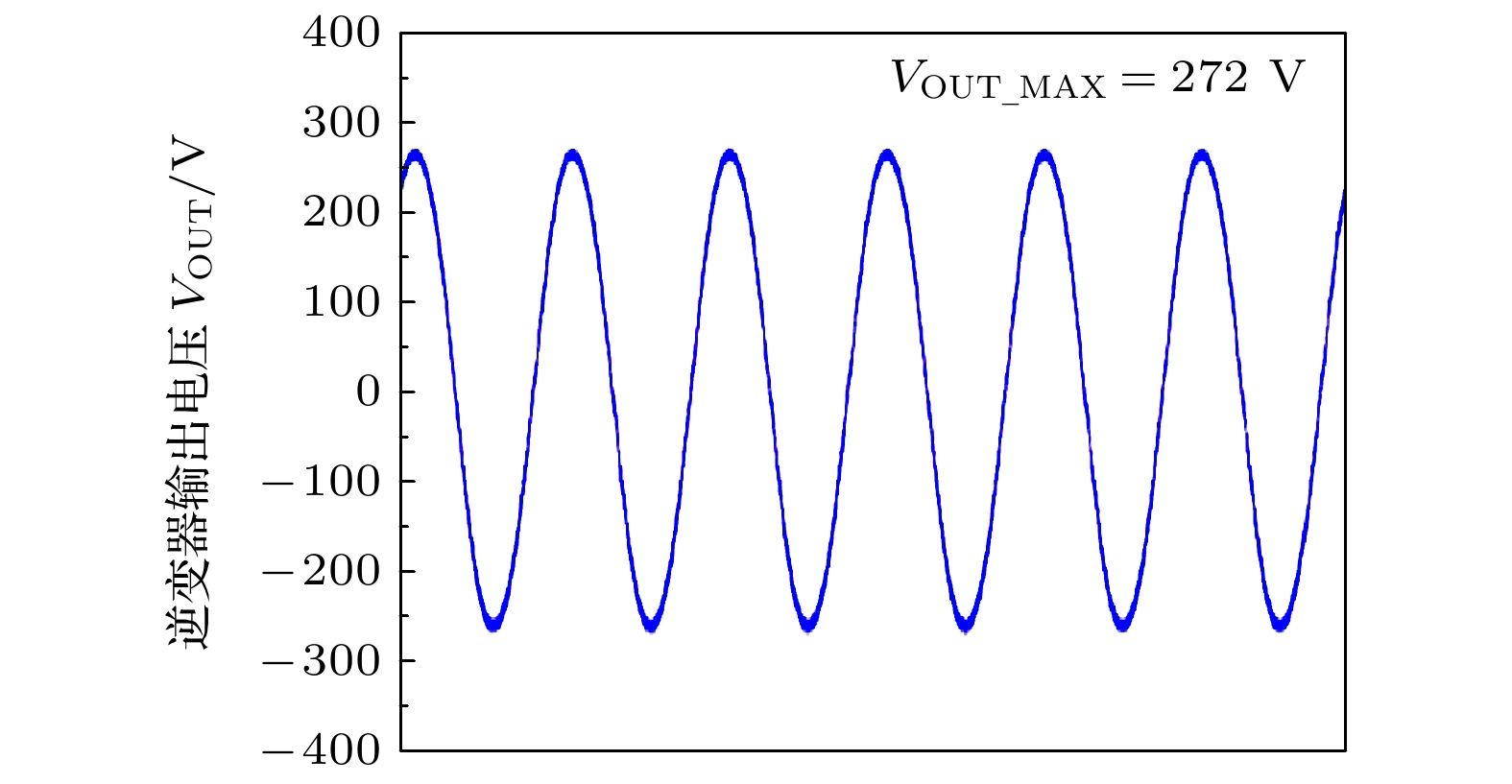
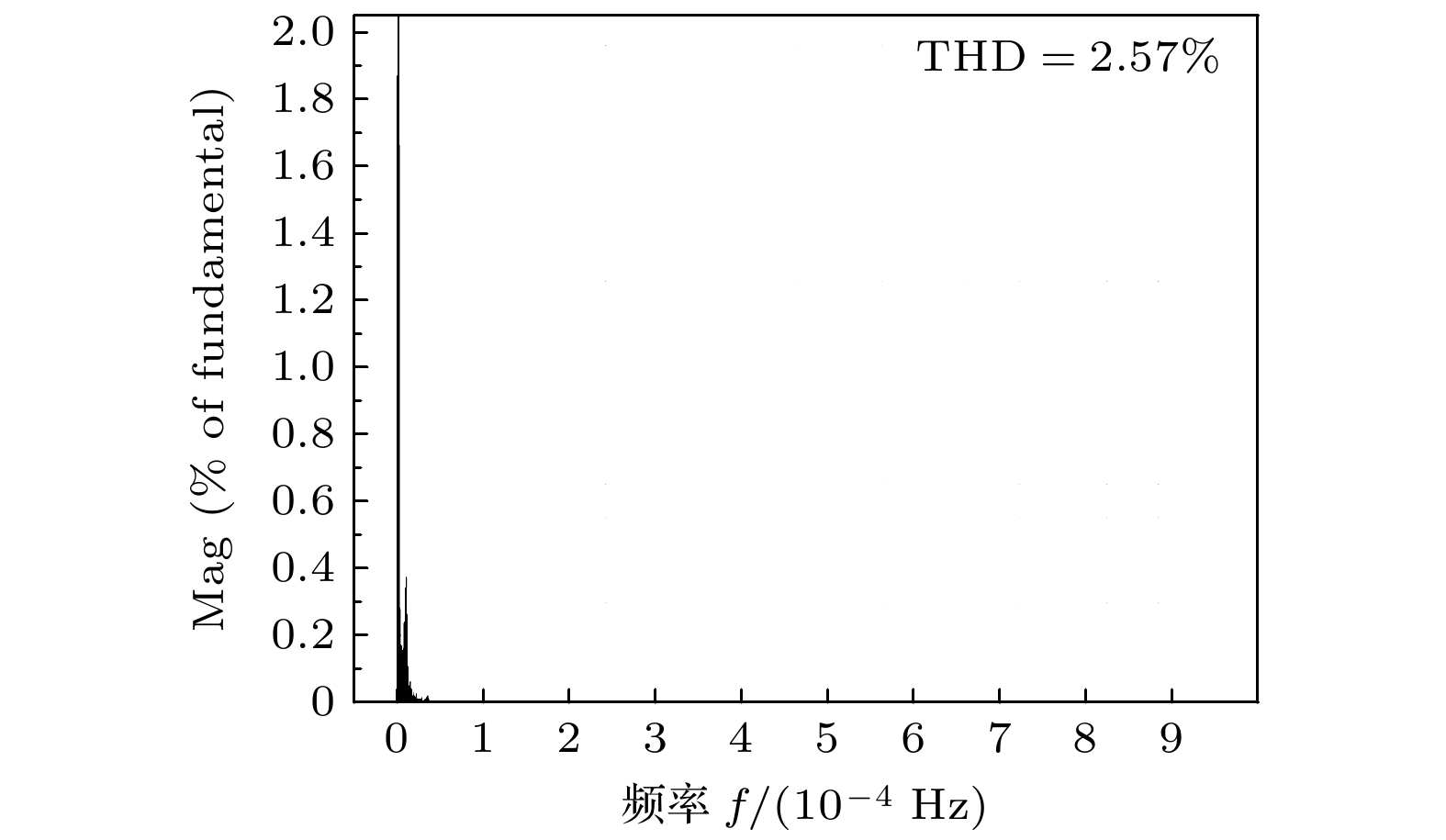
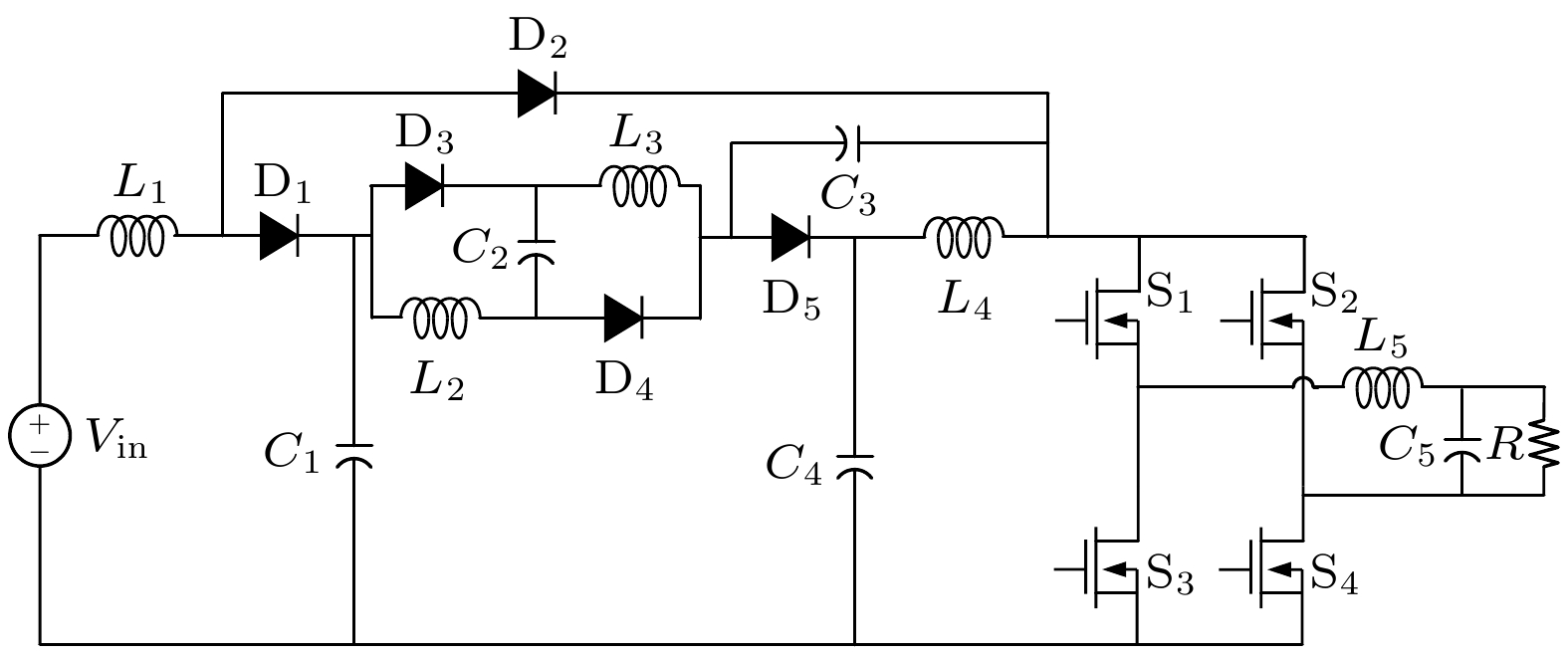
微型逆变器以其模块化、灵活等优势, 近年来已被广泛应用于分布式光伏发电系统中. 然而受拓扑结构和传统功率器件性能的影响, 目前微型逆变器拓扑的电压增益低、可靠性差等问题仍制约着微型逆变器的进一步发展. 为此, 本文提出并研制了一种基于氮化镓高电子迁移率晶体管(GaN HEMT)的增强型开关电感准Z源逆变器. 该逆变器首次采用了辅助升压单元融合开关电感准Z源网络的新型拓扑结构, 显著提高了低直通占空比下的电压增益, 同时降低了开关器件电压应力. 此外, 采用GaN HEMT作为逆变器功率开关器件, 设计了专用负压关断驱动电路, 将功率管开关频率从传统的10 kHz提高到100 kHz, 减小了电感及其他无源器件的体积. 经样机系统测试, 在直通占空比为0.2时, 逆变器实际升压因子达到5.75, 较其他开关电感准Z源型逆变器拓扑提高了15%. 本研究在现有拓扑结构的基础上有效地提高了电压增益, 结合GaN HEMT的应用, 为高效、紧凑的微型逆变器设计提供了新的技术路径.
-
关键词:
- 微型光伏逆变器 /
- 开关电感准Z源逆变器 /
- GaN高电子迁移率晶体管
Microinverters have been widely used in distributed photovoltaic (PV) systems in recent years due to their modularity and flexibility. However, the current development of microinverter topologies faces significant challenges, such as low voltage gain and limited reliability. To solve these problems, an enhanced switched-inductor quasi-Z-Source inverter (ESL-qZSI) based on gallium nitride high electron mobility transistor (GaN HEMT) is proposed in this work. The proposed inverter introduces a novel topology that integrates an auxiliary boost unit with a switched-inductor quasi-Z-source network. This topology significantly enhances the voltage gain at low shoot-through duty ratios and reduces the voltage stress across the switching device. Additionally, the use of GaN HEMT as power switching components increases the switching frequency from the traditional 10 kHz to 100 kHz, in which a specialized negative turn-off gate driver circuit is designed to adapt the characteristics of the GaN HEMT and to ensure reliable switching operation. This increase in frequency reduces the size of passive components, such as inductors. Experimental results show that the proposed inverter achieves a boost factor of 5.75 at a shoot-through duty ratio of 0.2, which indicates that its performance is improved by 15% and 91% greater than the traditional switched-inductor-capacitor quasi-Z-source inverter (SLC-qZSI) and the traditional switched-inductor Z-source inverter (SL-ZSI), respectively. These results confirm that the proposed inverter enhances the voltage gain of existing topologies. Besides, compared with SLC-qZSI, the proposed inverter can obtain a higher efficiency of 90.5%, which shows the advantage of efficiency. In conclusion, the proposed ESL-qZSI with GaN HEMT provides a hopeful solution for high-efficiency and compact microinverter systems in photovoltaic applications.-
Keywords:
- micro photovoltaic inverter /
- switched-inductor quasi-Z-source inverter /
- GaN highelectron mobility transistor
[1] Hmad J, Houari A, Bouzid A E M, Saim A, Trabelsi H 2023 Energies 16 5062
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Iweh C D, Gyamfi S, Tanyi E, Effah-Donyina E 2021 Energies 14 5375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang Q, Zhao B, Sun H D 2020 IEEE 4th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2) Wuhan, China, 2020 p1407
[4] Priyadarshi N, Padmanaban S, Ionel D M, Mihet-Popa L, Azam F 2018 Energies 11 2277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Monjo L, Sainz L, Mesas J J, Pedra J 2021 Energies 14 508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Peng F Z 2003 IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 39 504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yuan J, Yang Y H, Blaabjerg F 2020 Energies 13 1390
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Samanbakhsh R, Koohi P, Ibanez F M, Martin F, Terzija V 2023 Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 147 108819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li Y, Anderson J, Peng F Z, Liu D C 2009 Twenty-Fourth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition Washington, DC, USA, 2009 p918
[10] Rajan V R, Premalatha L 2017 Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 8 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Axelrod B, Berkovich Y, Ioinovici A 2008 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 55 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 刘洪臣, 杨爽, 王国立, 李飞 2013 62 150505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H C, Yang S, Wang G L, Li F 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 150505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhu M, Yu K, Luo F L 2010 IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 25 2150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Nguyen M K, Lim Y C, Cho G B 2011 IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 26 3183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhu X Q, Zhang B, Qiu D Y 2018 IET Power Electron. 11 1774
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Karbalaei A R, Mardaneh M 2021 IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 15 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bolaghi J A, Taheri A, Babaei M H, Gholami M, Harajchi S 2023 IETE J. Res. 70 4231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chaudhary O S, Denaï M, Refaat S S, Pissanidis G 2023 Energies 16 6689
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Y J, Li J G, Wang J H, Zheng T Q, Jia P Y 2022 Energies 15 7791
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 程哲 2021 70 236502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng Z 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 236502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 王帅, 葛晨, 徐祖银, 成爱强, 陈敦军 2024 73 177101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S, Ge C, Xu Z Y, Cheng A Q, Chen D J 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 177101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Morita T, Tamura S, Anda Y, Ishida M, Uemoto Y, Ueda T, Tanaka T, Ueda D 2011 26th Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC) Fort Worth, TX, USA, 2011 p481
[23] Zhao C W, Trento B, Jiang L, Jones E A, Liu B, Zhang Z Y, Costinett D, Wang F, Tolbert L M, Jansen J F, Kress R, Langley R 2016 IEEE J. Emerging Sel. Top. Power Electron. 4 824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jagan V, Ullemgondla G, Thati D, Salveru B, Ongole D, Banoth S 2024 3rd International Conference on Power Electronics and IoT Applications in Renewable Energy and its Control (PARC) Mathura, India, 2024 p475
[25] 谢瑞良, 郝翔, 王跃, 杨旭, 黄浪, 王超, 杨月红 2014 63 120510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie R L, Hao X, Wang Y, Yang X, Huang L, Wang C, Yang Y H 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 120510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 廖志贤, 罗晓曙, 黄国现 2015 64 130503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liao Z X, Luo X S, Huang G X 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 130503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 易龙强, 郜克存 2008 电力电子技术 42 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yi L Q, Gao K C 2008 Power Electron. 42 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 ESL-qZSI拓扑特性
Table 1. Characteristics of ESL-qZSI topology.
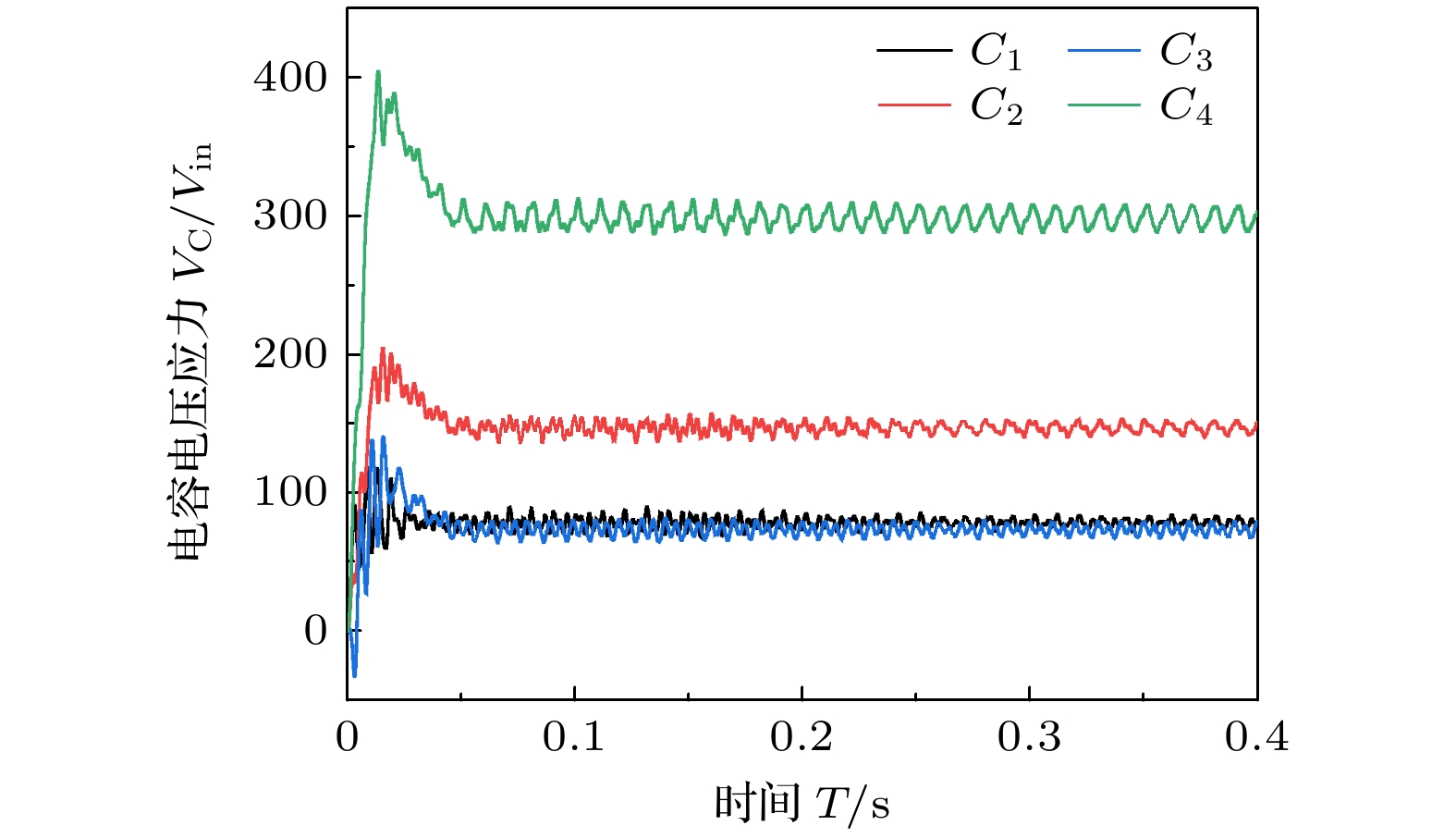
参数名称 参数值 升压因子(B) $ \dfrac{2}{1-4 D+3 D^{2}} $ 电压增益(G) $ \dfrac{2}{3 M-2} $ 开关管电压应力Vsw/Vin $ \dfrac{3 G^{2}}{2 G+2} $ C1电压应力VC1/Vin $ \dfrac{1}{1-D} $ C2电压应力VC2/Vin $ \dfrac{1}{1-3 D} $ C3电压应力VC3/Vin $ \dfrac{2 D}{1-4 D+3 D^{2}} $ C4电压应力VC4/Vin $ \dfrac{2}{1-3 D} $ D1/D2电压应力VD/Vin $ \dfrac{2}{1-4 D+3 D^{2}} $ D3/D4/D5电压应力VD/Vin $ \dfrac{1-D}{1-4 D+3 D^{2}} $ 表 2 驱动电路关键参数
Table 2. Key parameters of driver circuit.
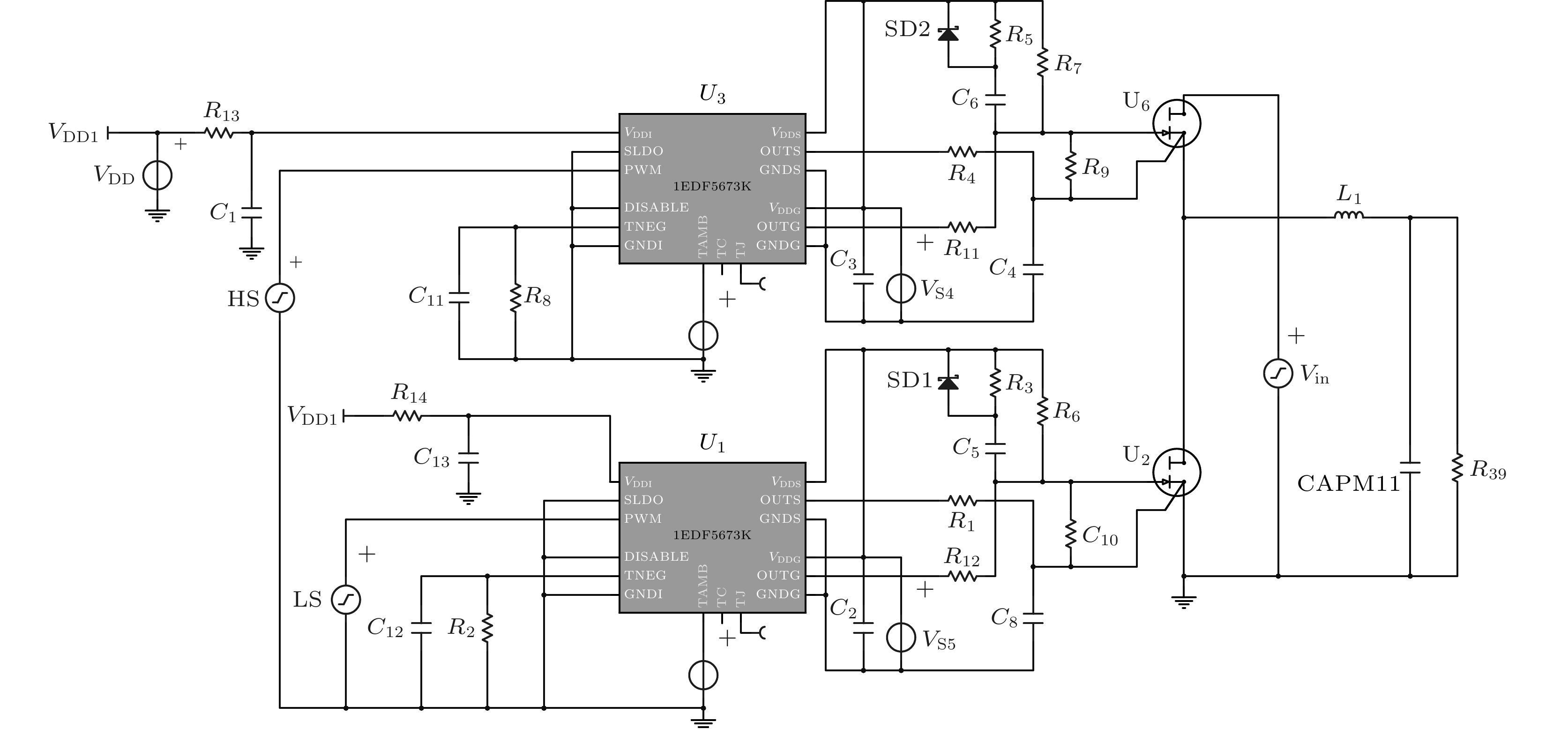
参数名称 R7/Ω R5/Ω R4/Ω C6/nF C3/nF C4/nF 参数值 470 10 3.3 3 100 1 表 3 ESL-qZSI实验参数
Table 3. Experimental parameters of ESL-qZSI.
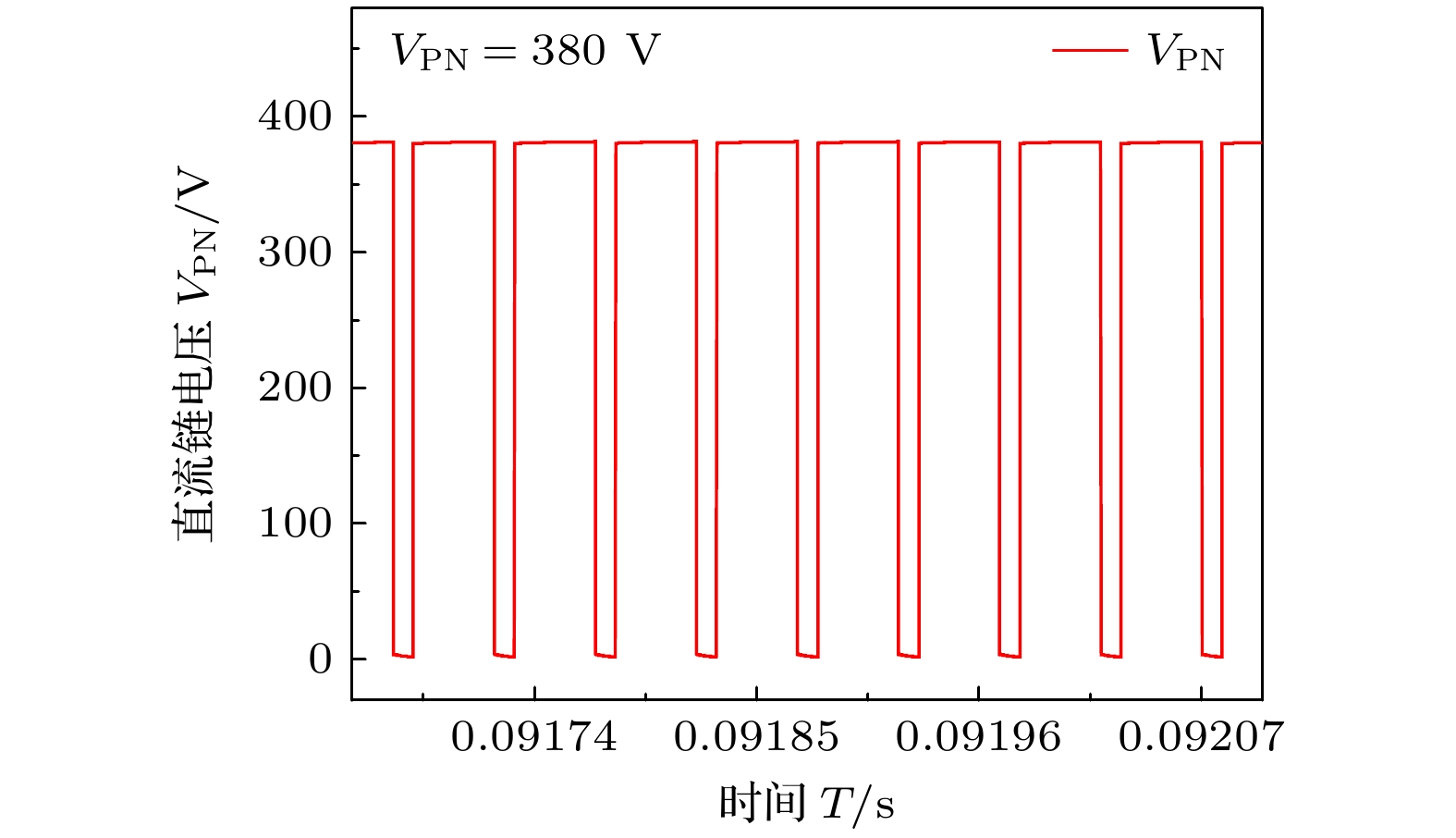
参数名称 参数值 输入电压/V 64 开关频率/kHz 100 准Z源网络电容/μF 100 准Z源网络电感/mH 0.5 LC滤波电容/μF 20 LC滤波电感/mH 1 直通占空比D 0.2 基准频率/Hz 50 表 4 不同拓扑的典型结果对比
Table 4. Typical results of different inverter topologies.
参数 逆变器拓扑类型 SL-ZSI SLC-qZSI ESL-qZSI 数据类型 样机
测试结果理论
计算结果样机
测试结果样机
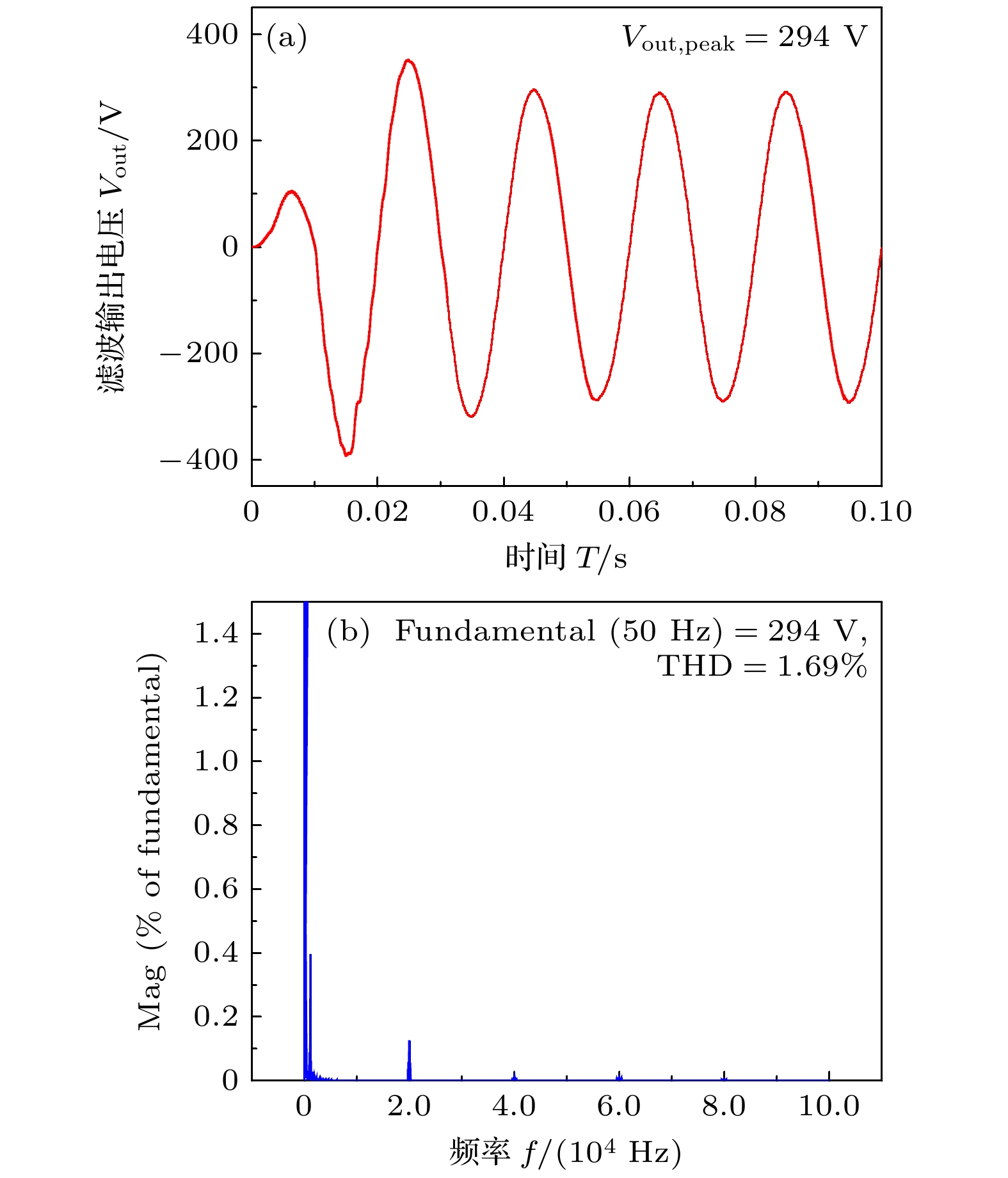
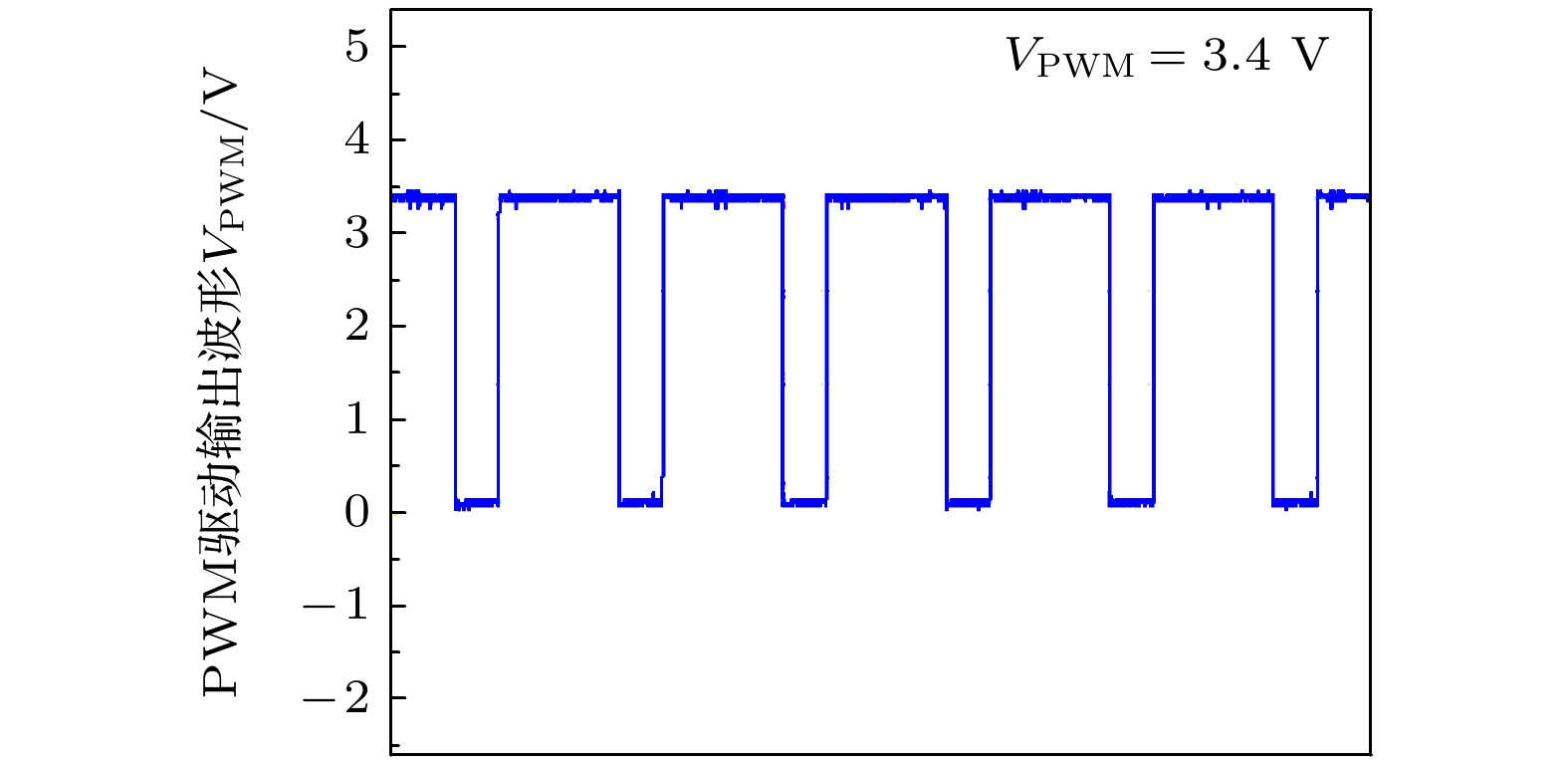
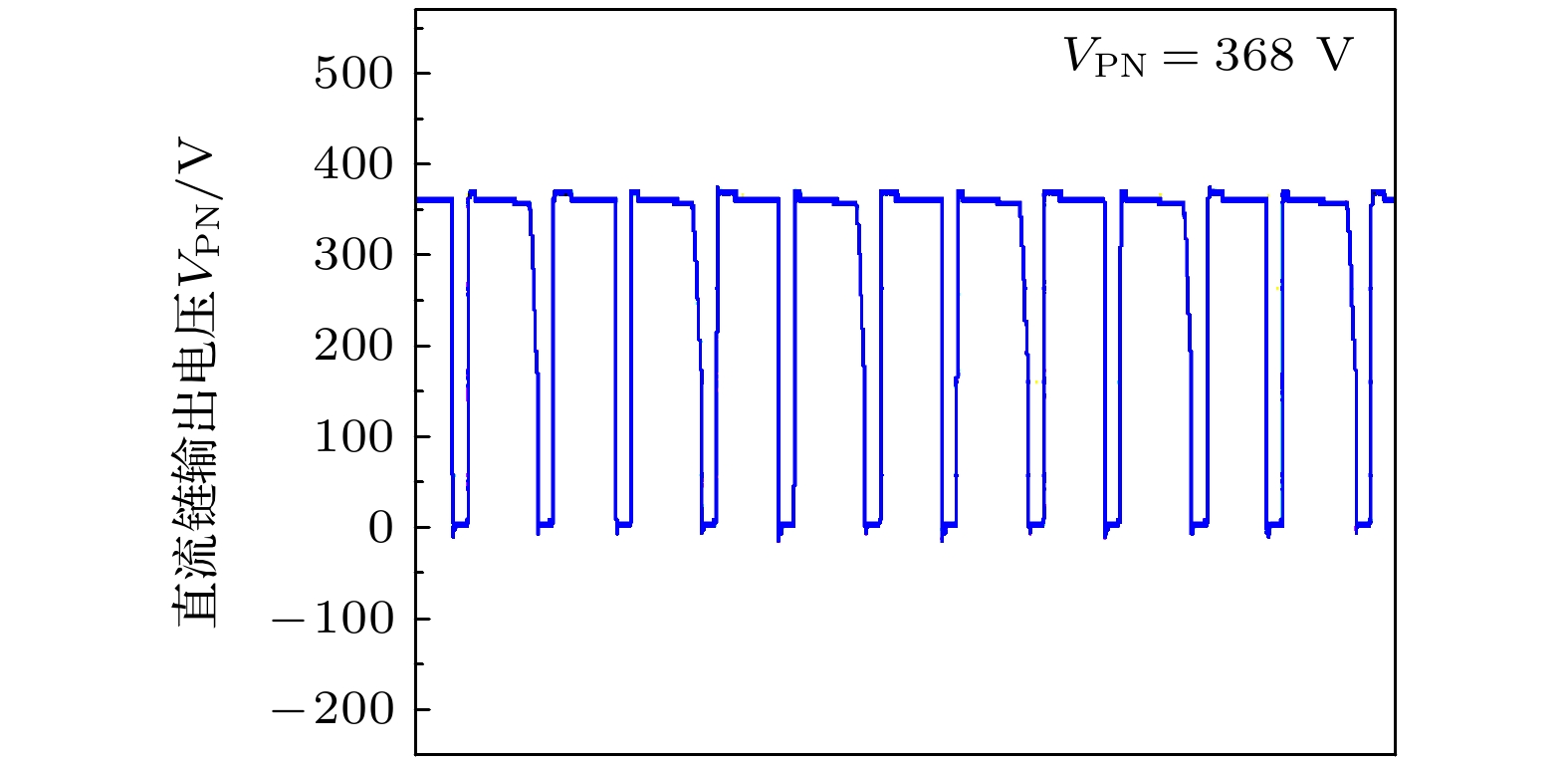
测试结果输入电压Vin/V 36 36 80 64 直通占空比D 0.3 0.2 0.206 0.2 调制系数M 0.7 0.8 0.794 0.8 升压因子B 13 3 5 5.75 开关频率/kHz 10 10 13.3 100 效率/% — — 88.5 90.5 -
[1] Hmad J, Houari A, Bouzid A E M, Saim A, Trabelsi H 2023 Energies 16 5062
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Iweh C D, Gyamfi S, Tanyi E, Effah-Donyina E 2021 Energies 14 5375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang Q, Zhao B, Sun H D 2020 IEEE 4th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2) Wuhan, China, 2020 p1407
[4] Priyadarshi N, Padmanaban S, Ionel D M, Mihet-Popa L, Azam F 2018 Energies 11 2277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Monjo L, Sainz L, Mesas J J, Pedra J 2021 Energies 14 508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Peng F Z 2003 IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 39 504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yuan J, Yang Y H, Blaabjerg F 2020 Energies 13 1390
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Samanbakhsh R, Koohi P, Ibanez F M, Martin F, Terzija V 2023 Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 147 108819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li Y, Anderson J, Peng F Z, Liu D C 2009 Twenty-Fourth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition Washington, DC, USA, 2009 p918
[10] Rajan V R, Premalatha L 2017 Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 8 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Axelrod B, Berkovich Y, Ioinovici A 2008 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 55 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 刘洪臣, 杨爽, 王国立, 李飞 2013 62 150505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H C, Yang S, Wang G L, Li F 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 150505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhu M, Yu K, Luo F L 2010 IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 25 2150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Nguyen M K, Lim Y C, Cho G B 2011 IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 26 3183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhu X Q, Zhang B, Qiu D Y 2018 IET Power Electron. 11 1774
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Karbalaei A R, Mardaneh M 2021 IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 15 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bolaghi J A, Taheri A, Babaei M H, Gholami M, Harajchi S 2023 IETE J. Res. 70 4231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chaudhary O S, Denaï M, Refaat S S, Pissanidis G 2023 Energies 16 6689
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Y J, Li J G, Wang J H, Zheng T Q, Jia P Y 2022 Energies 15 7791
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 程哲 2021 70 236502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng Z 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 236502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 王帅, 葛晨, 徐祖银, 成爱强, 陈敦军 2024 73 177101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S, Ge C, Xu Z Y, Cheng A Q, Chen D J 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 177101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Morita T, Tamura S, Anda Y, Ishida M, Uemoto Y, Ueda T, Tanaka T, Ueda D 2011 26th Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC) Fort Worth, TX, USA, 2011 p481
[23] Zhao C W, Trento B, Jiang L, Jones E A, Liu B, Zhang Z Y, Costinett D, Wang F, Tolbert L M, Jansen J F, Kress R, Langley R 2016 IEEE J. Emerging Sel. Top. Power Electron. 4 824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jagan V, Ullemgondla G, Thati D, Salveru B, Ongole D, Banoth S 2024 3rd International Conference on Power Electronics and IoT Applications in Renewable Energy and its Control (PARC) Mathura, India, 2024 p475
[25] 谢瑞良, 郝翔, 王跃, 杨旭, 黄浪, 王超, 杨月红 2014 63 120510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie R L, Hao X, Wang Y, Yang X, Huang L, Wang C, Yang Y H 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 120510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 廖志贤, 罗晓曙, 黄国现 2015 64 130503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liao Z X, Luo X S, Huang G X 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 130503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 易龙强, 郜克存 2008 电力电子技术 42 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yi L Q, Gao K C 2008 Power Electron. 42 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 800
- PDF下载量: 59
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: