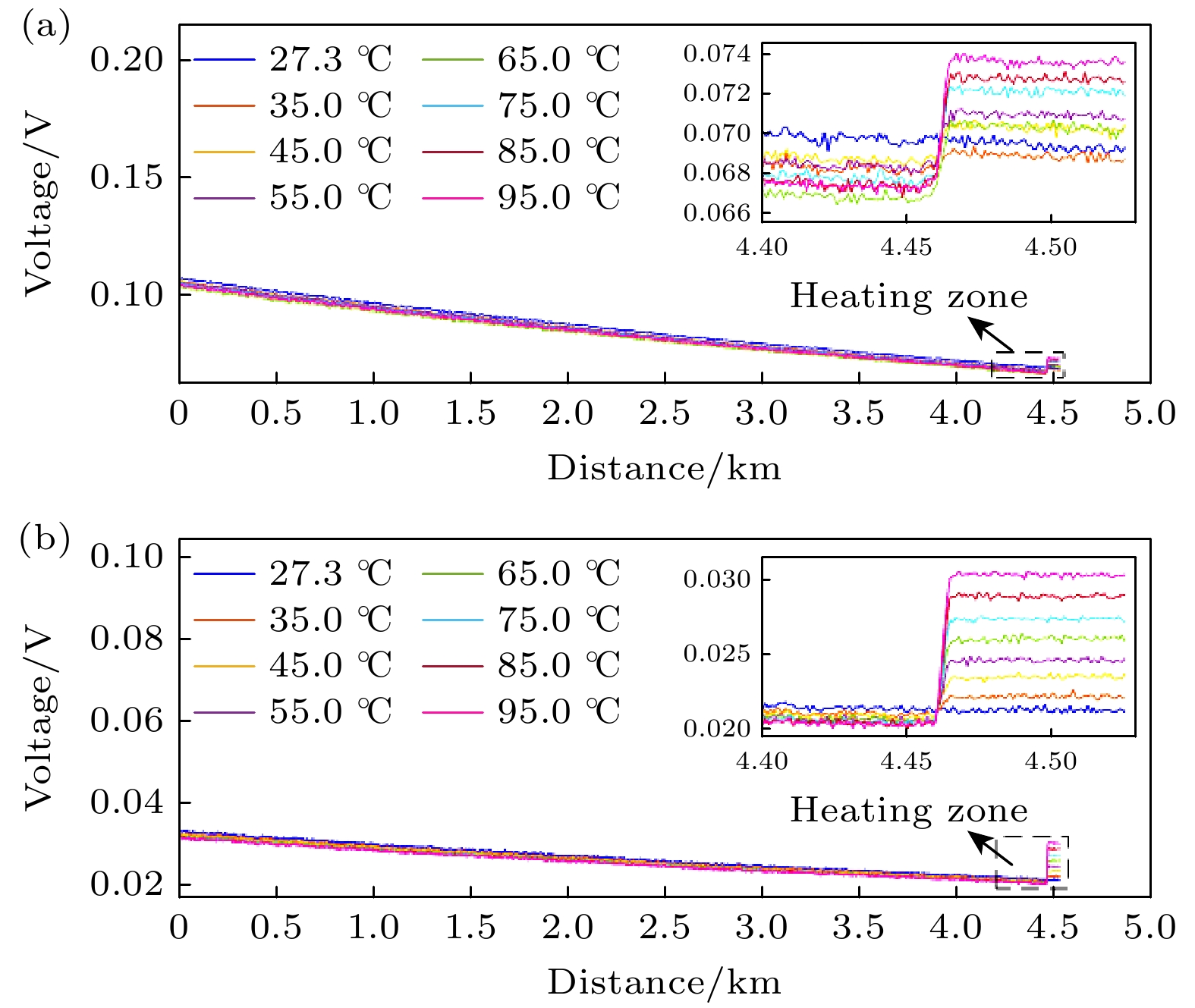
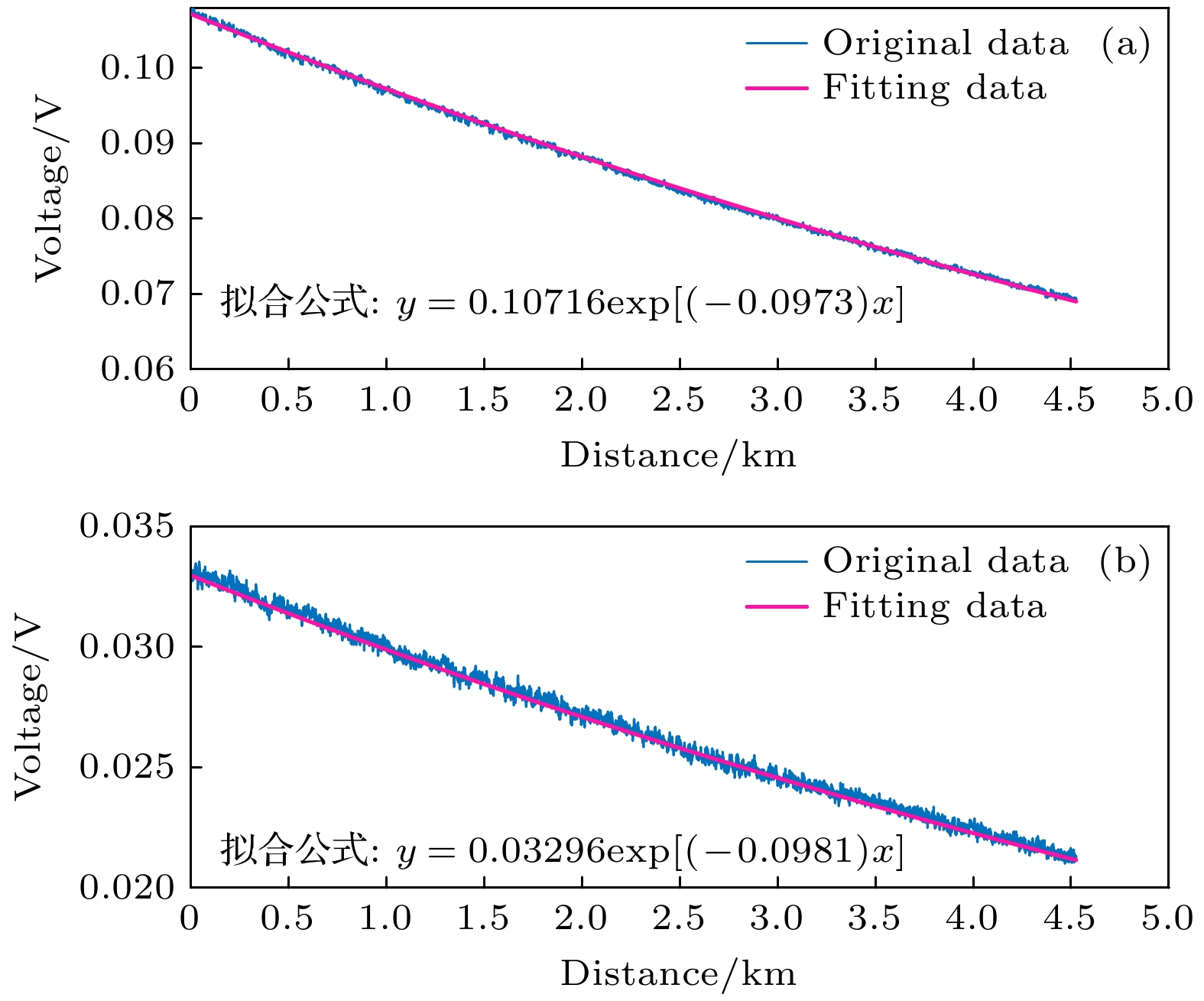
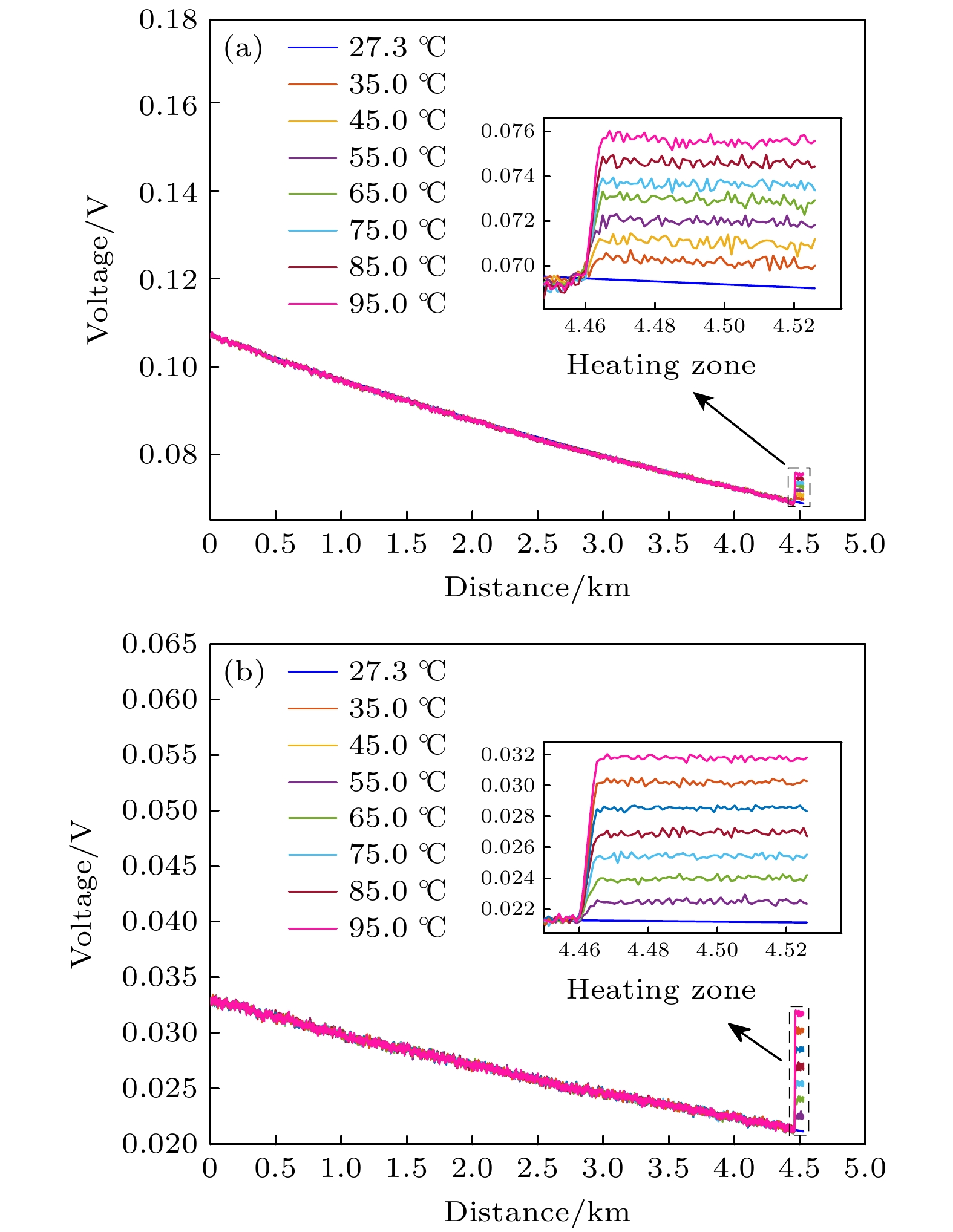
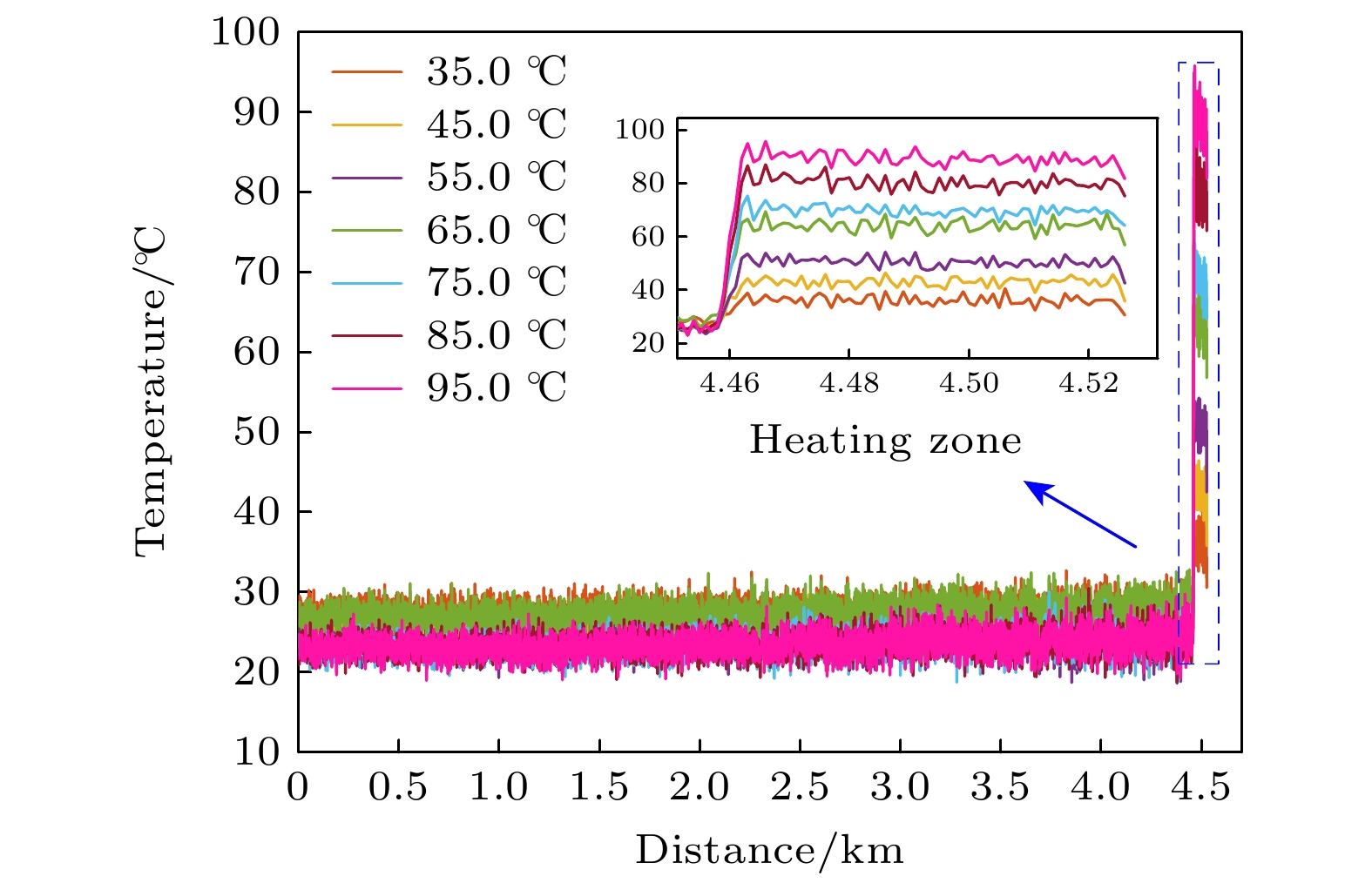
-
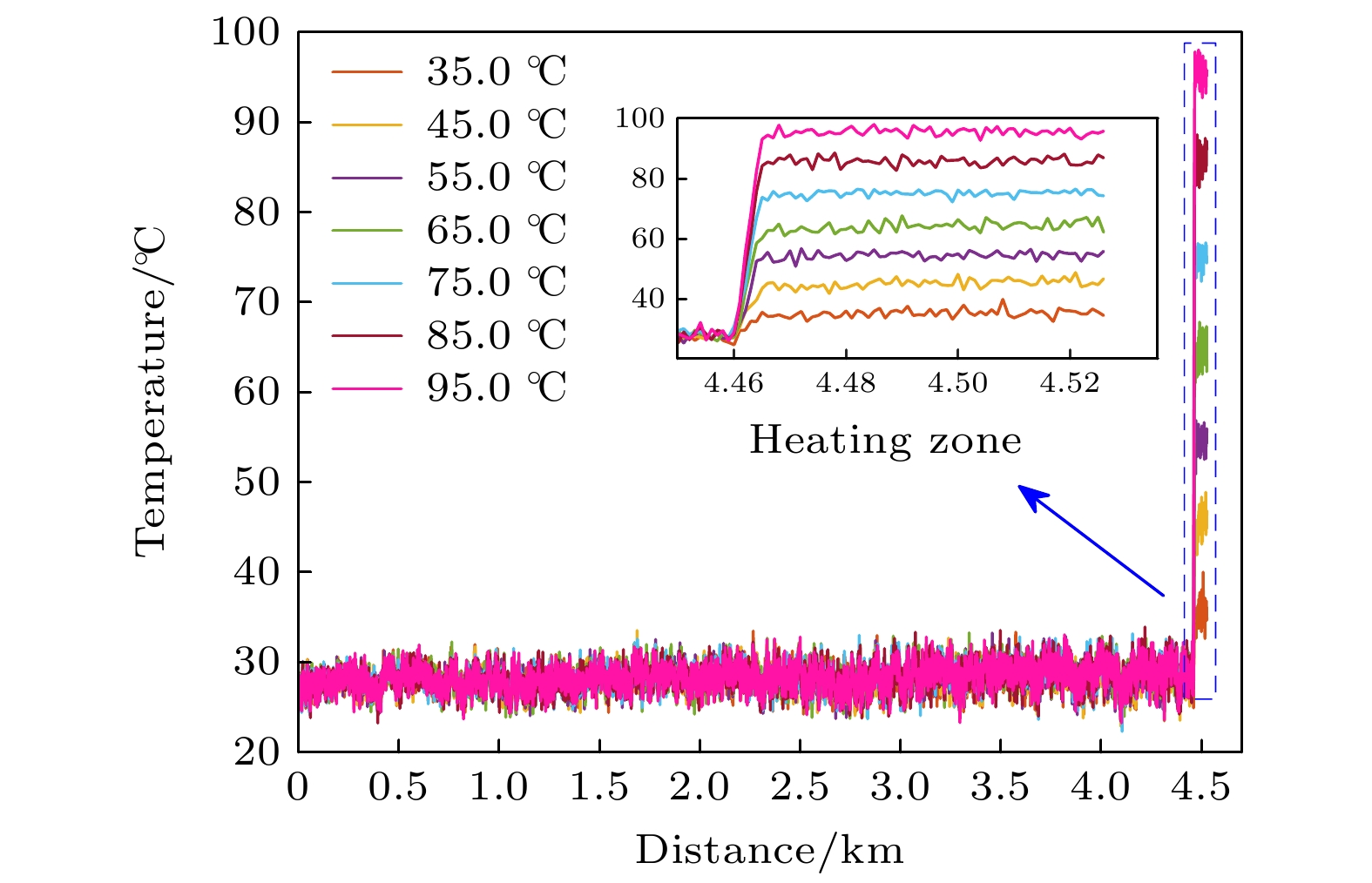
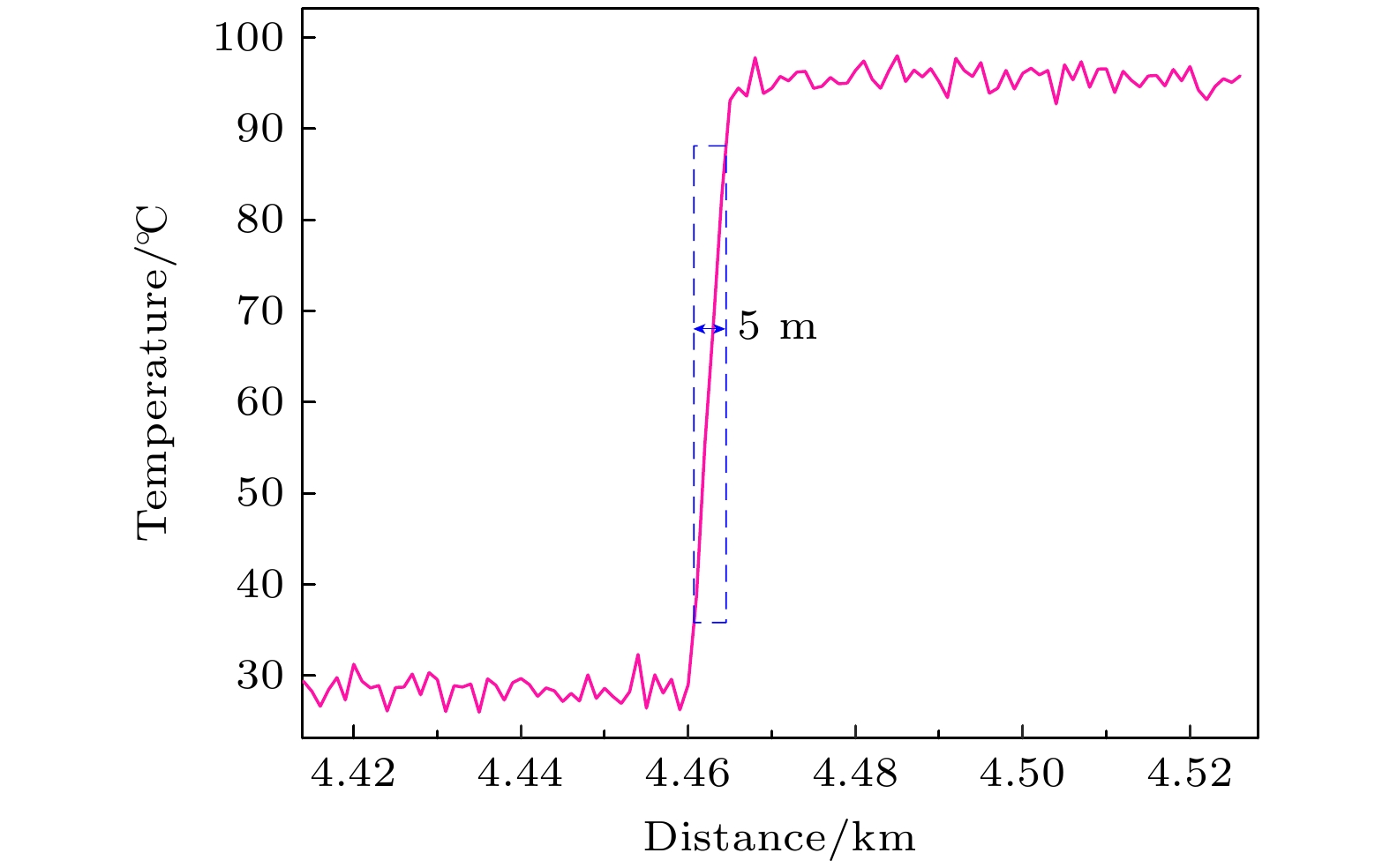
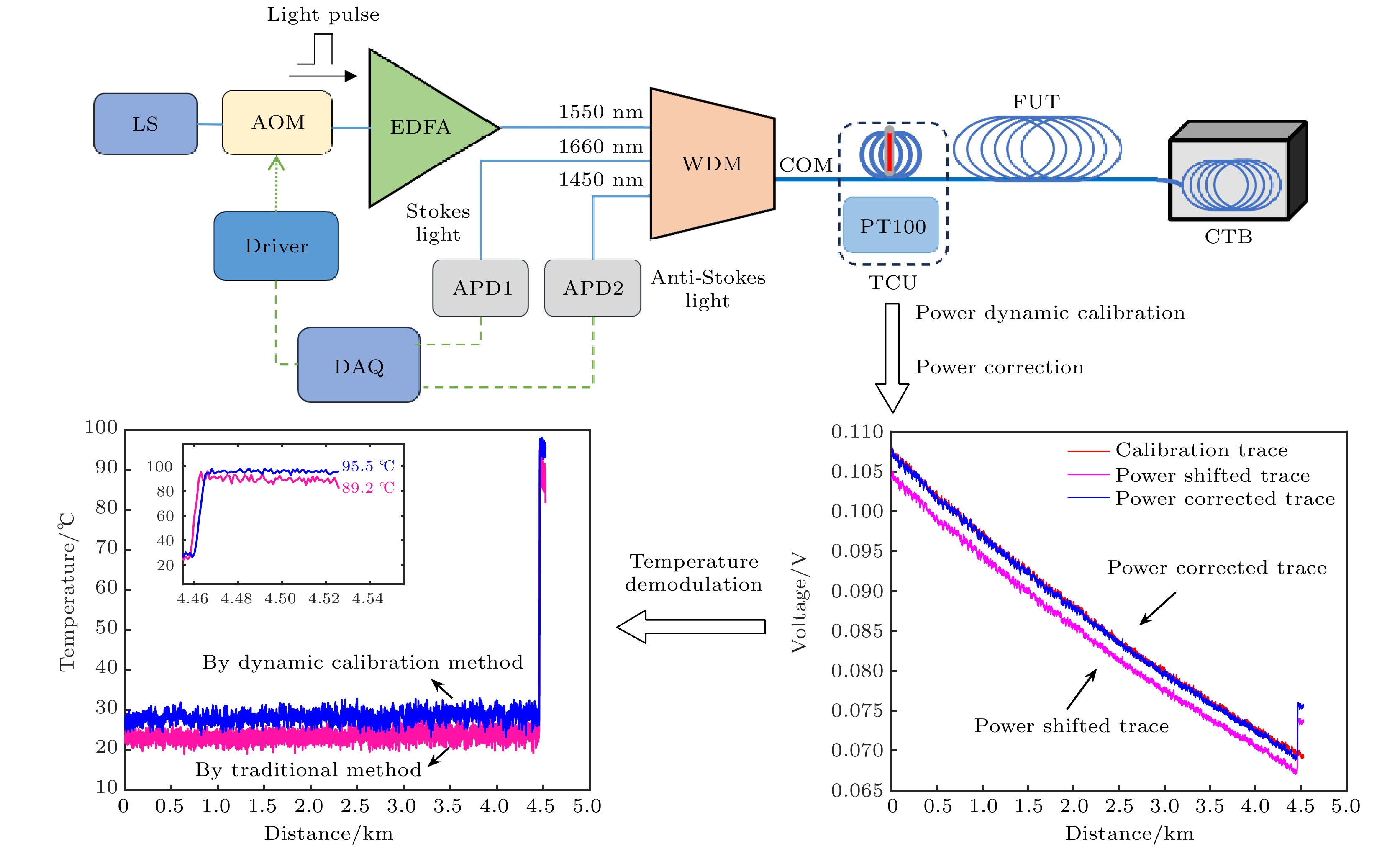
拉曼分布式光纤测温系统基于拉曼斯托克斯(Stokes)散射光和反斯托克斯(anti-Stokes)散射光功率进行温度解调, 拉曼散射光功率直接影响测温精度. 系统中激光脉冲功率以及雪崩光电探测器增益均可能出现随机变化, 从而导致获取的拉曼散射光功率波动, 因此本文提出一种基于动态标定的拉曼分布式光纤测温系统方案, 通过设置温度标定单元并结合提出的功率校正算法, 消除标定单元的温度的动态变化对拉曼散射光功率的贡献, 再基于先前标定的数据, 分别将拉曼Stokes散射光和拉曼anti-Stokes散射光功率校正到同一激光脉冲功率及雪崩光电探测器增益水平, 从而提升系统的测温精度. 系统采用50 ns的激光脉冲, 在4.6 km长的单模光纤上开展测温试验, 结果显示: 在35—95 ℃的测温区间, 基于传统的温度解调算法, 测温偏差为–5.8—1.0 ℃, 均方根误差为4.0 ℃, 而基于动态标定的校正算法, 测温偏差为–0.8—0.9 ℃, 均方根误差为0.5 ℃. 本文提出新的拉曼分布式光纤测温系统具备拉曼散射光功率动态校正功能, 有工程推广价值.Distributed optical fiber temperature measurement system is widely used in the fields of substation, power cable, natural gas transmission pipeline and other temperature measurement systems. It can continuously measure the temperature information at each location along the sensing direction. Raman distributed optical fiber temperature measurement system demodulates the temperature information based on Raman Stokes scattered light and anti-Stokes scattered light power, and the Raman scattering light power directly affects the temperature measurement accuracy. So, it is a challenging task to control the hardware of the system to ensure the feasiblity of the Raman sacttering signals. The laser pulse power, and the gain of avalanche photodetector may vary randomly in the system, resulting in fluctuations in the acquired Raman scattered light power data. Therefore, a scheme of Raman distributed fiber temperature measurement system based on dynamic calibration is proposed in this work, and by setting up the temperature calibration unit and combining the proposed power correction algorithm and previous calibration data, the Raman Stokes scattering light and Raman anti-Stokes scattering light power are calibrated at the same laser pulse power level and avalanche photodetector gain, thereby improving the temperature measurement accuracy of the system. For the performance demonstration of the new scheme, the experimental system adopts 50-ns laser pulse to carry out temperature measurement experiments with a 4.6-km long single-mode fiber. The results show that in the temperature measurement range from 35 ℃ to 95 ℃, based on the traditional temperature demodulation algorithm, the temperature deviation measured is in the range from –5.8 ℃ to 1.0 ℃, and the root mean square error is 4.0 ℃, and by the dynamic calibration algorithm, the deviation of deviation measured is within –0.8 ℃ to 0.9 ℃ and the root mean square error is 0.5 ℃. Therefore, the novel Raman-type distributed optical fiber temperature measurement system proposed in this work has the function to dynamically correct the Raman-type scattered light power to suppress the influence caused by instability of the key devices such as pulsed laser and avalanche photodetector and improve the temperature measurement accuracy, which is valuable in practical engineering applications.
-
Keywords:
- distributed optical fiber sensing /
- Raman scattered light /
- dynamic calibration /
- power correction
[1] Zhang Z L, Lu Y G, Peng J Q, Ji Z Y 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 1776
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ding Z Y, Wang C H, Liu K, Jiang J F, Yang D, Pan G Y, Pu Z L, Liu T G 2018 Sensors 18 1072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liang C S, Bai Q, Yan M, Wang Y, Zhang H J, Jin B Q 2021 IEEE Access 9 41647
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 黄尚廉, 梁大巍, 刘龚 1991 仪器仪表学报 04 25
Huang S L, Liang D W, Liu G 1991 Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 04 25
[5] 饶云江 2017 66 074207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Rao Y J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 074207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 尚盈, 王昌 2021 应用科学学报 39 843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shang Y, Wang C 2021 J. Appl. Sci. 39 843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 介瑞敏, 肖春, 刘旭, 朱琛, 饶云江, 刘波 2024 光学学报 44 0106011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jie R M, Xiao C, Liu X, Zhu C, Rao Y J, Liu B 2024 Acta Opt. Sin. 44 0106011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 段绍辉, 田杰, 周正仙, 王晓华, 徐邦联 2014 激光杂志 35 47
Duan S H, Tian J, Zhou Z X, Wang X H, Xu B L 2014 Laser J. 35 47
[9] Zhan Z W, Cantono M, Kamalov V, Mecozzi A, Müller R, Yin S, Castellanos J C 2021 Science 371 931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 黄程, 翟富超, 范高 2016 化学工程与装备 10 67
Huang C, Zhai F C, Fan G 2016 Chem. Eng. Equip. 10 67
[11] 王雪辉 2019 石油化工安全环保技术 35 41
Wang X H 2019 Petrotrochem. Saf. Environ. Prot. Technol. 35 41
[12] 胡子昂, 王强, 谷小红, 朱凯, 徐晓萌, 吴琳琳, 胡栋 2023 激光与红外 53 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Z A, Wang Q, Gu X H, Zhu K, Xu X M, Wu L L, Hu D 2023 Laser Infrared 53 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 张明江, 李健, 刘毅, 张建忠, 李云亭, 黄琦, 刘瑞霞, 杨帅军 2017 中国激光 44 0306002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang M J, Li J, Liu Y, Zhang J Z, Li Y T, Huang Q, Liu R X, Yang S J 2017 Chin. J. Lasers 44 0306002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 谢孔利, 饶云江, 冉曾令 2008 光学学报 28 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie K L, Rao Y J, Ran Z L 2008 Acta. Opt. Sin. 28 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 刘云鹏, 李欢, 高树国, 王佳雪, 范晓舟, 李昕烨, 田源, 尹钧毅 2022 中国电机工程学报 42 6126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y P, Li H, Gao S G, Wang J X, Fan X Z, Li X Y, Tian Y, Yi J Y 2022 Proc. CSEE 42 6126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 何祖源, 刘银萍, 马麟, 杨晨, 童维军 2019 红外与激光工程 48 0422002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He Z Y, Liu Y P, Ma L, Yang C, Tong W J 2019 Infrared Laser Eng. 48 0422002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李政颖, 孙文丰, 李子墨, 王洪海 2015 64 234207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Z Y, Sun W F, Li L M, Wang H H 2015 Acta. Phys. Sin. 64 234207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 鲁佳慧, 万成功, 金恺, 王敏, 黄光明 2023 激光杂志 44 62
Lu J H, Wan C G, Jin K, Wang M, Huang G M 2023 Laser J. 44 62
[19] Li J, Li Y T, Zhang M J, Liu Y, Zhang J Z, Yan B Q, Wang D, Jin B Q 2018 Photonic Sensors 8 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 孙苗, 杨爽, 汤玉泉, 赵晓虎, 张志荣, 庄飞宇 2022 71 200701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun M, Yang S, Tang Y Q, Zhao X H, Zhang Z R, Zhuang F Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 200701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 马天兵, 訾保威, 郭永存, 凌六一, 黄友锐, 贾晓芬 2020 69 030701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma T B, Zi B W, Guo Y C, Ling L Y, Huang Y R, Jia X F 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 030701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 李硕, 王纪强, 高忠国, 高建新, 侯泽民, 姜龙, 侯墨语 2023 红外与激光工程 52 20230076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S, Wang J Q, Gao Z G, Gao J X, Hou Z M, Jiang L, Hou M Y 2023 Infrared Laser Eng. 52 20230076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chai D D, Zhang H J, Gao Y 2022 IEEE Sens. J. 23 2204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lu L D, Yong M C, Wang Q S, Bu X D, Gao Q H 2023 Opt. Commun. 529 129096
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li J, Yan B Q, Zhang M J, Zhang J Z, Qiao L J, Wang T 2018 App. Opt. 58 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 冯玉祥, 刘志凯, 黄闽南, 王一山, 吕立冬 2024 光学精密工程 32 2645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng Y X, Liu Z K, Huang M N, Wang Y S, Lü L D 2024 Opt. Precis. Eng. 32 2645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
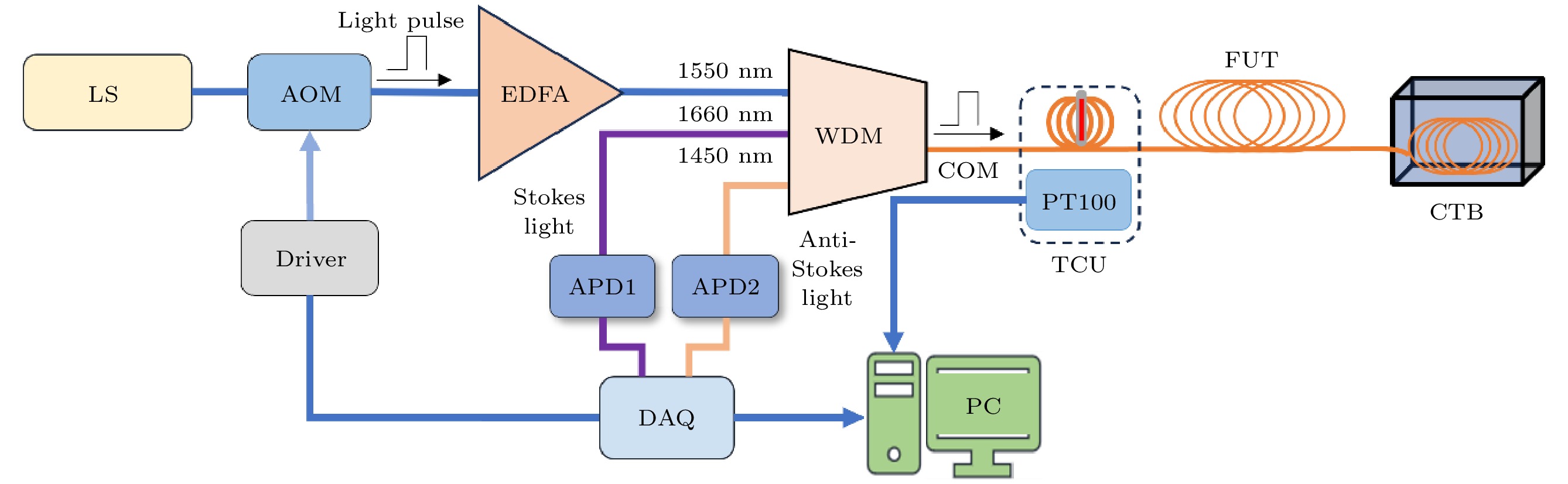
图 1 实验系统原理图
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of experimental system. LS, laser source; AOM, acousto-optic modulator; EDFA, erbium doped fiber amplifier; WDM, wavelength division multiplexer; TCU, temperature calibration unit; FUT, fiber under test; CTB, constant temperature box; APD, avalanche photo detector; DAQ, data acquisition card; PC, personal computer.
表 1 传统双路温度数据对比
Table 1. Traditional dual-channel temperature data comparison.
实际温度/℃ 测得温度/℃ 误差/℃ 35.0 36.0 +1.0 45.0 43.0 –2.0 55.0 50.4 –4.6 65.0 64.1 –0.9 75.0 69.6 –5.4 85.0 80.2 –4.8 95.0 89.2 –5.8 表 2 基于动态标定及校正算法温度数据对比
Table 2. Temperature data comparison based on dynamic calibration and calibration algorithm
实际温度/℃ 测得温度/℃ 比值H1 比值H2 误差/℃ 35.0 35.4 1.0180 1.0150 +0.4 45.0 45.3 1.0100 1.0225 +0.3 55.0 54.6 1.0141 1.0350 –0.4 65.0 64.2 1.0365 1.0366 –0.8 75.0 75.2 1.0204 1.0443 +0.2 85.0 85.9 1.0250 1.0478 +0.9 95.0 95.5 1.0263 1.0500 +0.5 -
[1] Zhang Z L, Lu Y G, Peng J Q, Ji Z Y 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 1776
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ding Z Y, Wang C H, Liu K, Jiang J F, Yang D, Pan G Y, Pu Z L, Liu T G 2018 Sensors 18 1072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liang C S, Bai Q, Yan M, Wang Y, Zhang H J, Jin B Q 2021 IEEE Access 9 41647
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 黄尚廉, 梁大巍, 刘龚 1991 仪器仪表学报 04 25
Huang S L, Liang D W, Liu G 1991 Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 04 25
[5] 饶云江 2017 66 074207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Rao Y J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 074207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 尚盈, 王昌 2021 应用科学学报 39 843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shang Y, Wang C 2021 J. Appl. Sci. 39 843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 介瑞敏, 肖春, 刘旭, 朱琛, 饶云江, 刘波 2024 光学学报 44 0106011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jie R M, Xiao C, Liu X, Zhu C, Rao Y J, Liu B 2024 Acta Opt. Sin. 44 0106011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 段绍辉, 田杰, 周正仙, 王晓华, 徐邦联 2014 激光杂志 35 47
Duan S H, Tian J, Zhou Z X, Wang X H, Xu B L 2014 Laser J. 35 47
[9] Zhan Z W, Cantono M, Kamalov V, Mecozzi A, Müller R, Yin S, Castellanos J C 2021 Science 371 931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 黄程, 翟富超, 范高 2016 化学工程与装备 10 67
Huang C, Zhai F C, Fan G 2016 Chem. Eng. Equip. 10 67
[11] 王雪辉 2019 石油化工安全环保技术 35 41
Wang X H 2019 Petrotrochem. Saf. Environ. Prot. Technol. 35 41
[12] 胡子昂, 王强, 谷小红, 朱凯, 徐晓萌, 吴琳琳, 胡栋 2023 激光与红外 53 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Z A, Wang Q, Gu X H, Zhu K, Xu X M, Wu L L, Hu D 2023 Laser Infrared 53 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 张明江, 李健, 刘毅, 张建忠, 李云亭, 黄琦, 刘瑞霞, 杨帅军 2017 中国激光 44 0306002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang M J, Li J, Liu Y, Zhang J Z, Li Y T, Huang Q, Liu R X, Yang S J 2017 Chin. J. Lasers 44 0306002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 谢孔利, 饶云江, 冉曾令 2008 光学学报 28 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie K L, Rao Y J, Ran Z L 2008 Acta. Opt. Sin. 28 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 刘云鹏, 李欢, 高树国, 王佳雪, 范晓舟, 李昕烨, 田源, 尹钧毅 2022 中国电机工程学报 42 6126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y P, Li H, Gao S G, Wang J X, Fan X Z, Li X Y, Tian Y, Yi J Y 2022 Proc. CSEE 42 6126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 何祖源, 刘银萍, 马麟, 杨晨, 童维军 2019 红外与激光工程 48 0422002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He Z Y, Liu Y P, Ma L, Yang C, Tong W J 2019 Infrared Laser Eng. 48 0422002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李政颖, 孙文丰, 李子墨, 王洪海 2015 64 234207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Z Y, Sun W F, Li L M, Wang H H 2015 Acta. Phys. Sin. 64 234207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 鲁佳慧, 万成功, 金恺, 王敏, 黄光明 2023 激光杂志 44 62
Lu J H, Wan C G, Jin K, Wang M, Huang G M 2023 Laser J. 44 62
[19] Li J, Li Y T, Zhang M J, Liu Y, Zhang J Z, Yan B Q, Wang D, Jin B Q 2018 Photonic Sensors 8 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 孙苗, 杨爽, 汤玉泉, 赵晓虎, 张志荣, 庄飞宇 2022 71 200701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun M, Yang S, Tang Y Q, Zhao X H, Zhang Z R, Zhuang F Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 200701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 马天兵, 訾保威, 郭永存, 凌六一, 黄友锐, 贾晓芬 2020 69 030701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma T B, Zi B W, Guo Y C, Ling L Y, Huang Y R, Jia X F 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 030701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 李硕, 王纪强, 高忠国, 高建新, 侯泽民, 姜龙, 侯墨语 2023 红外与激光工程 52 20230076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S, Wang J Q, Gao Z G, Gao J X, Hou Z M, Jiang L, Hou M Y 2023 Infrared Laser Eng. 52 20230076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chai D D, Zhang H J, Gao Y 2022 IEEE Sens. J. 23 2204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lu L D, Yong M C, Wang Q S, Bu X D, Gao Q H 2023 Opt. Commun. 529 129096
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li J, Yan B Q, Zhang M J, Zhang J Z, Qiao L J, Wang T 2018 App. Opt. 58 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 冯玉祥, 刘志凯, 黄闽南, 王一山, 吕立冬 2024 光学精密工程 32 2645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng Y X, Liu Z K, Huang M N, Wang Y S, Lü L D 2024 Opt. Precis. Eng. 32 2645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3065
- PDF下载量: 284
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: