-
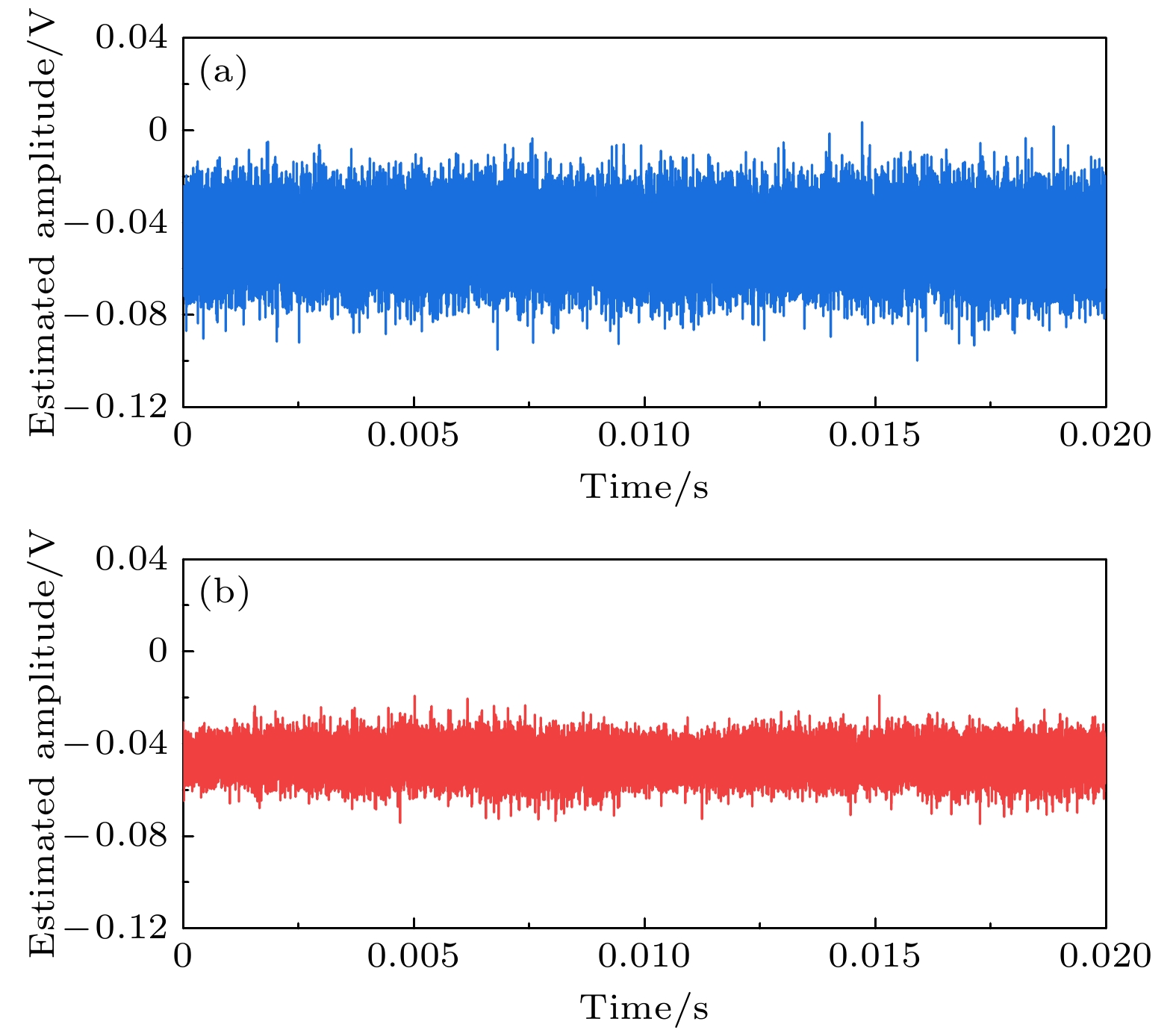
量子增强型光学相位追踪作为高精度跟踪和测量光学相位的量子光学技术, 在目标定位、量子测距以及相控阵雷达和唢呐等领域中有着重要应用. 本文提出一种基于压缩态光场的量子增强型光学相位追踪协议. 采用中心波长为1064 nm的连续固体激光光源, 结合光学参量振荡器以及Pound-Drever-Hall (PDH)锁定技术, 制备得到初始压缩度为(8.0±0.2) dB的相位压缩态光场. 通过信号调制及解调技术, 实现对压缩态光场相位的控制, 从而实现对光学相位0—2π范围内的量子增强型追踪. 与经典协议相比, 这一协议可以将相位追踪的噪声起伏抑制至散粒噪声基准以下至少6.27 dB, 实现了相位追踪精度至少76.4%的量子增强. 由于到达角估计、相控阵雷达、相控阵唢呐等应用领域对相位测量精度要求极高, 这一协议有望将相位估计的精度提高至突破散粒噪声极限, 为相关领域提供压缩光源, 也为更高精度的空间定位及量子测距技术提供理论和实验基础.Quantum-enhanced optical phase tracking is a quantum optical technique for tracking and measuring optical phases with high accuracy. It has important applications in laser interferometry, spectral analysis, and optical measurements. In this study, we propose a quantum-enhanced optical phase tracking protocol based on squeezed state optical fields. By using a continuous solid-state laser source with a central wavelength of 1064 nm, combing second harmonic generation, optical parametric oscillator, and PDH (Pound-Drever-Hall) locking technology, we prepare an initial squeezed state with a squeezing level of (8.0±0.2) dB. Through signal modulation technique and demodulation technique, we control the phase of the squeezed state optical field, thereby realizing the quantum-enhanced tracking of optical phases within the range of 0-2π. Compared with classical protocols, this protocol can suppress the noise fluctuations of phase tracking to at least 6.27 dB below the shot noise limit, improving the phase tracking accuracy by more than 76.4%. Because of the high requirements for phase measurement accuracy in applications such as angle estimation, phased array radar, and phased array sonar, this protocol is expected to improve the phase estimation accuracy beyond the shot noise limit. It provides compressed light sources for relevant fields, laying a theoretical and experimental foundation for higher-precision spatial positioning and quantum ranging techniques. The probe is made of amino acids arranged in a linear chain and joined together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is determined by a gene and encoded in the genetic code. This can happen either before the protein is used in the cell, or as part of control mechanism.
-
Keywords:
- optical parametric oscillation /
- squeezed state /
- phase estimation /
- optical phase tracking
[1] Giovannetti V, Lloyd S, Maccone L 2011 Nat. Photon. 5 222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pezze L, Smerzi A, Oberthaler M K, Schmied R, Treutlein P 2018 Rev. Mod. Phys. 90 035005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Caves C M 1981 Phys. Rev. D 23 1693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tse M, Yu H, Kijbunchoo N, et al. 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 231107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li B B, Blek J, Hoff U B, Madsen L S, Forstner S, Prakash V, Schäfermeier C, Gehring T, Bowen W P, Andersen U L 2018 Optica 5 850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Taylor M A, Janousek J, Daria V, Knittel J, Hage B, Bachor H A, Bowen W P, 2013 Nat. Photon. 7 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Low G H, Yoder T J, Chuang I L 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 100801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 徐涵, 陈树新, 吴昊, 陈坤, 洪磊 2019 68 024204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu H, Chen S X, Wu H, Chen K, Hong L 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 024204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li T C, Song Y, Fan H Q 2023 Signal Process. 205 108883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shi C, Wang Y, Salous S, Zhou J, Yan J 2022 IEEE T. Aero. Elec. Sys. 58 2762
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Guo X, Breum C R, Borregaard J, Izumi S, Larsen M V, Gehring T, Christandl M, Neergaard-Nielsen J S, Andersen U L 2020 Nat. Phys. 16 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Xia Y, Li W, Clark W, Hart D, Zhuang Q T, Zhang Z S 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 150502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xia Y, Li W, Zhuang Q T, Zhang Z S 2021 Phys. Rev. X 11 021047
[14] Sun X C, Li W, Tian Y H, Li F, Tian L, Wang Y J, Zheng Y H 2022 Photonics Res. 10 2886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 田龙, 郑立昂, 张晓莉, 武奕淼, 王庆伟, 秦博, 王雅君, 李卫, 史少平, 陈力荣, 郑耀辉 2023 72 148502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian L, Zheng L A, Zhang X L, Wu Y M, Wang Q W, Qin B, Wang Y J, Li W, Shi S P, Chen L R, Zheng Y H 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 148502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张晓莉, 王庆伟, 姚文秀, 史少平, 郑立昂, 田龙, 王雅君, 陈力荣, 李卫, 郑耀辉 2022 71 184203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X L, Wang Q W, Yao W X, Shi S P, Zheng L A, Tian L, Wang Y J, Chen L R, Li W, Zheng Y H 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 184203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sun X C, Wang Y J, Tian L J, Zheng Y H, Peng K C 2019 Chin. Opt. Lett. 17 072701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Shi S P, Wang Y J, Yang W H, Zheng Y H, Peng K C 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 5411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhou H J, Wang W, Chen C, Zheng Y H 2015 IEEE Sens. J. 15 2101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhou H J, Yang W H, Li Z X, Li X F, Zheng Y H 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 013111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
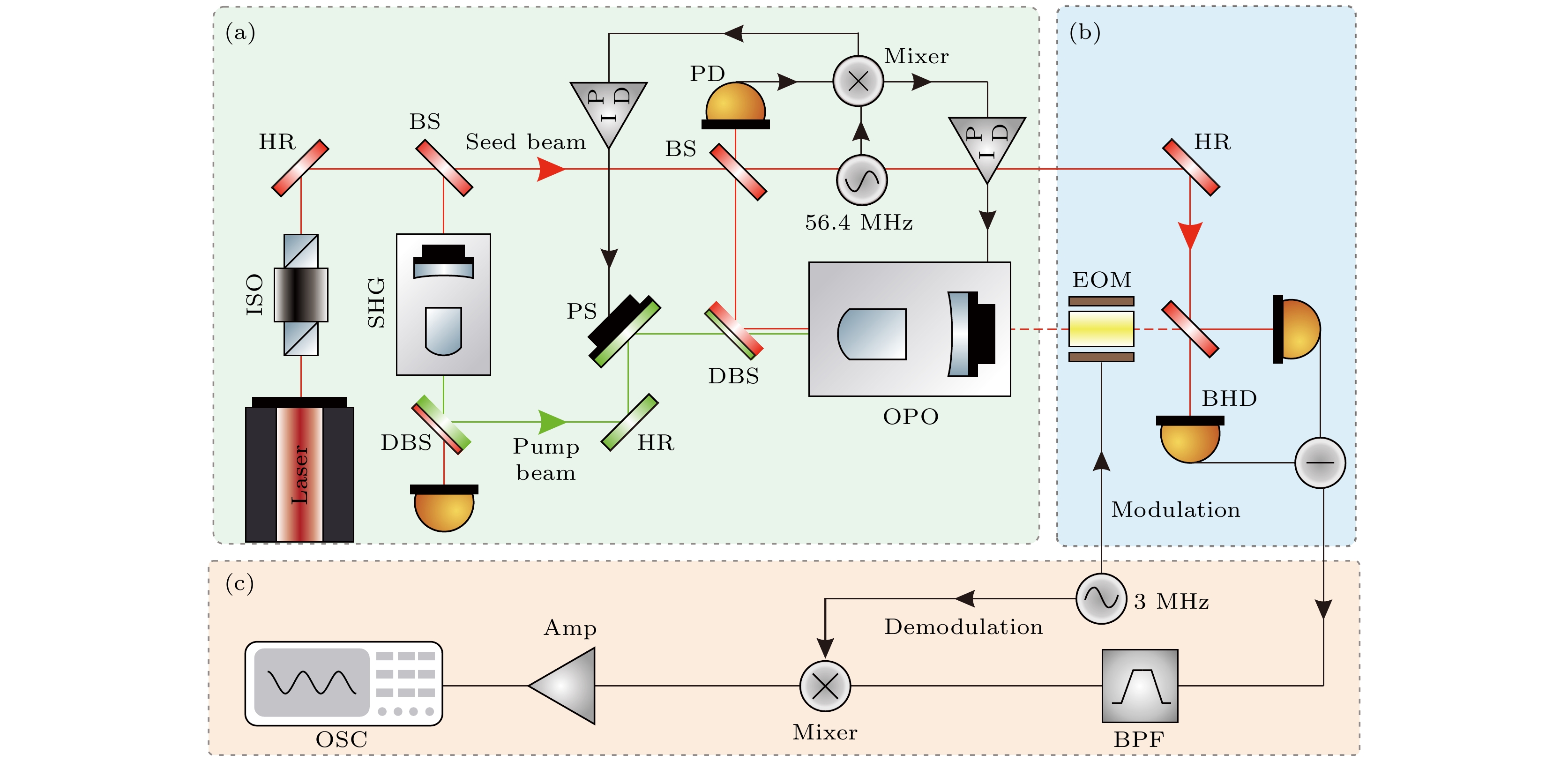
图 1 基于压缩态光场的QOPT实验装置图. ISO-隔离器; EOM-电光相位调制器; HR-高反镜; PD-光电探测器; BS-分束镜; DBS-双色镜; SHG-二次谐波产生; OPO-光学参量振荡器; PS-移相器; BHD-平衡零拍探测器; BPF-带通滤波器; amp-前置放大器; OSC-示波器
Fig. 1. Experimental setup for QOPT protocol via squeezed state. ISO-isolator; EOM-electro-optic phase modulator; HR- high reflectivity mirror; PD-photoelectric detector; BS-beam splitter; DBS-dichroic beam splitter; SHG-second harmonic generator; OPO-optical parametric oscillator; PS-phase shifter; BHD-balanced homodyne detection; BPF-band-pass filter; amp-amplifier; OSC-oscilloscope.
-
[1] Giovannetti V, Lloyd S, Maccone L 2011 Nat. Photon. 5 222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pezze L, Smerzi A, Oberthaler M K, Schmied R, Treutlein P 2018 Rev. Mod. Phys. 90 035005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Caves C M 1981 Phys. Rev. D 23 1693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tse M, Yu H, Kijbunchoo N, et al. 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 231107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li B B, Blek J, Hoff U B, Madsen L S, Forstner S, Prakash V, Schäfermeier C, Gehring T, Bowen W P, Andersen U L 2018 Optica 5 850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Taylor M A, Janousek J, Daria V, Knittel J, Hage B, Bachor H A, Bowen W P, 2013 Nat. Photon. 7 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Low G H, Yoder T J, Chuang I L 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 100801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 徐涵, 陈树新, 吴昊, 陈坤, 洪磊 2019 68 024204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu H, Chen S X, Wu H, Chen K, Hong L 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 024204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li T C, Song Y, Fan H Q 2023 Signal Process. 205 108883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shi C, Wang Y, Salous S, Zhou J, Yan J 2022 IEEE T. Aero. Elec. Sys. 58 2762
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Guo X, Breum C R, Borregaard J, Izumi S, Larsen M V, Gehring T, Christandl M, Neergaard-Nielsen J S, Andersen U L 2020 Nat. Phys. 16 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Xia Y, Li W, Clark W, Hart D, Zhuang Q T, Zhang Z S 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 124 150502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xia Y, Li W, Zhuang Q T, Zhang Z S 2021 Phys. Rev. X 11 021047
[14] Sun X C, Li W, Tian Y H, Li F, Tian L, Wang Y J, Zheng Y H 2022 Photonics Res. 10 2886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 田龙, 郑立昂, 张晓莉, 武奕淼, 王庆伟, 秦博, 王雅君, 李卫, 史少平, 陈力荣, 郑耀辉 2023 72 148502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian L, Zheng L A, Zhang X L, Wu Y M, Wang Q W, Qin B, Wang Y J, Li W, Shi S P, Chen L R, Zheng Y H 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 148502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张晓莉, 王庆伟, 姚文秀, 史少平, 郑立昂, 田龙, 王雅君, 陈力荣, 李卫, 郑耀辉 2022 71 184203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X L, Wang Q W, Yao W X, Shi S P, Zheng L A, Tian L, Wang Y J, Chen L R, Li W, Zheng Y H 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 184203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sun X C, Wang Y J, Tian L J, Zheng Y H, Peng K C 2019 Chin. Opt. Lett. 17 072701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Shi S P, Wang Y J, Yang W H, Zheng Y H, Peng K C 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 5411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhou H J, Wang W, Chen C, Zheng Y H 2015 IEEE Sens. J. 15 2101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhou H J, Yang W H, Li Z X, Li X F, Zheng Y H 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 013111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 4932
- PDF下载量: 192
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: