-
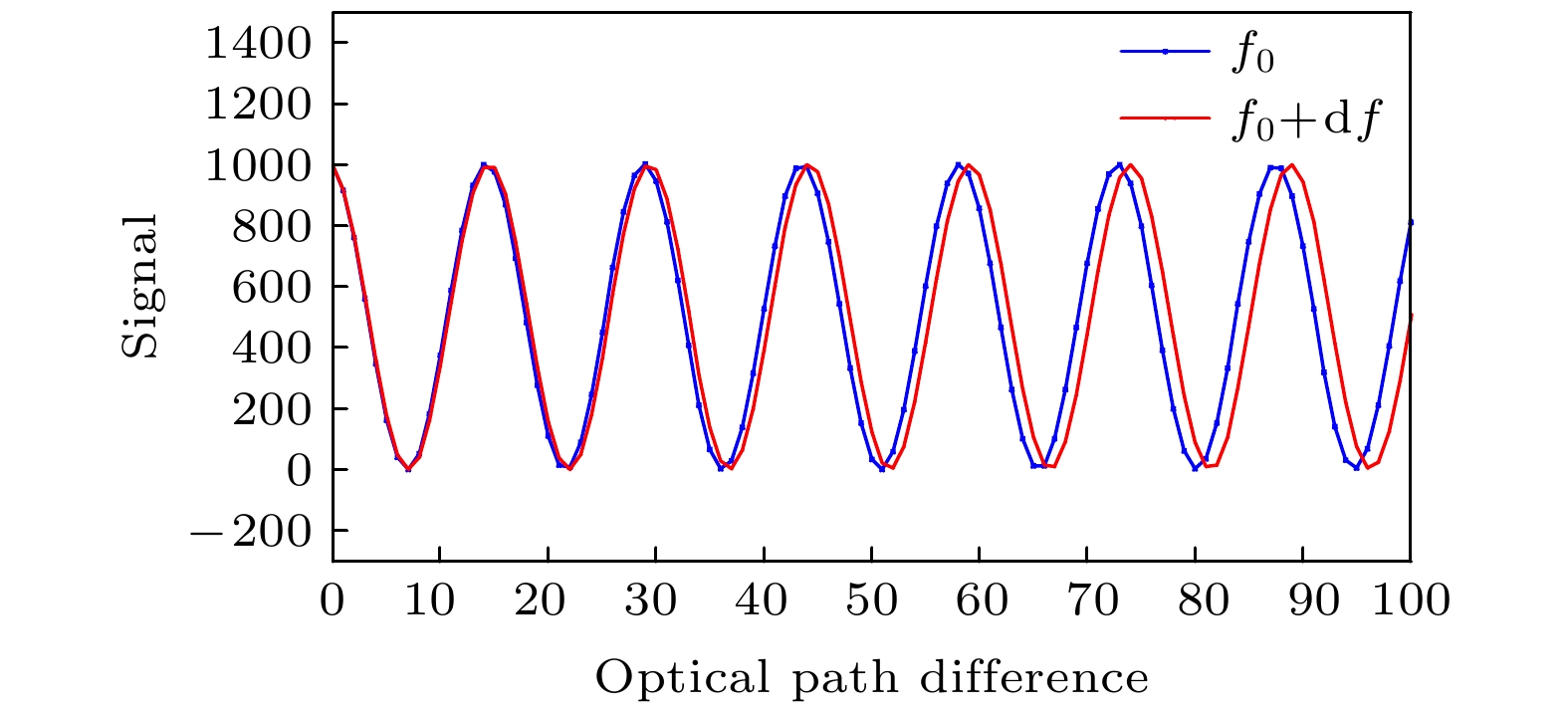
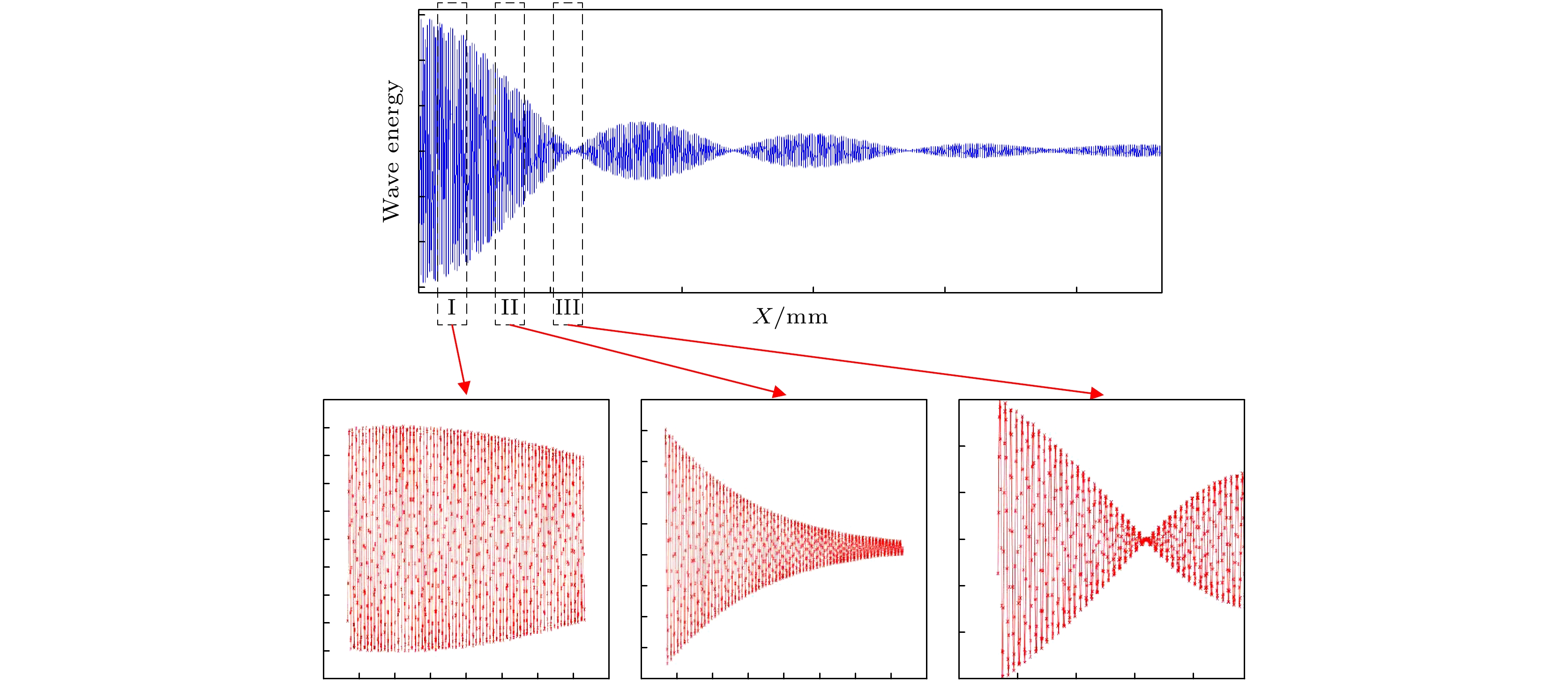
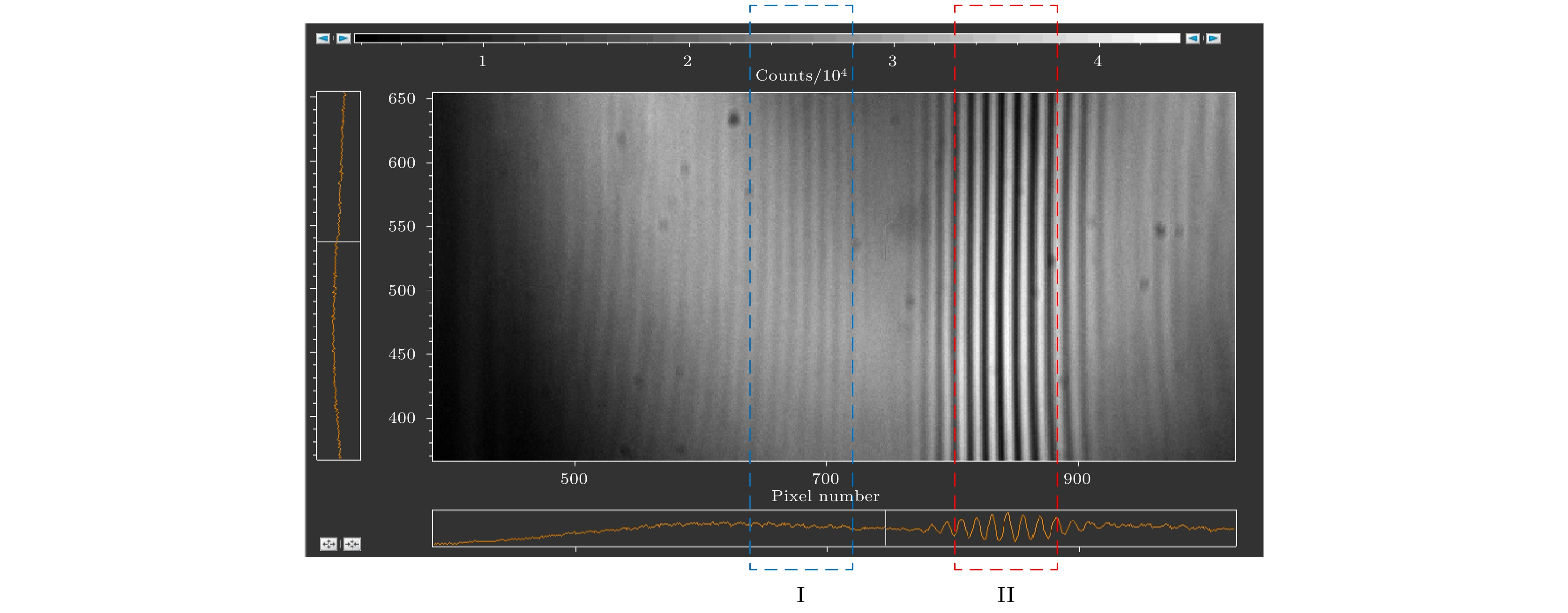
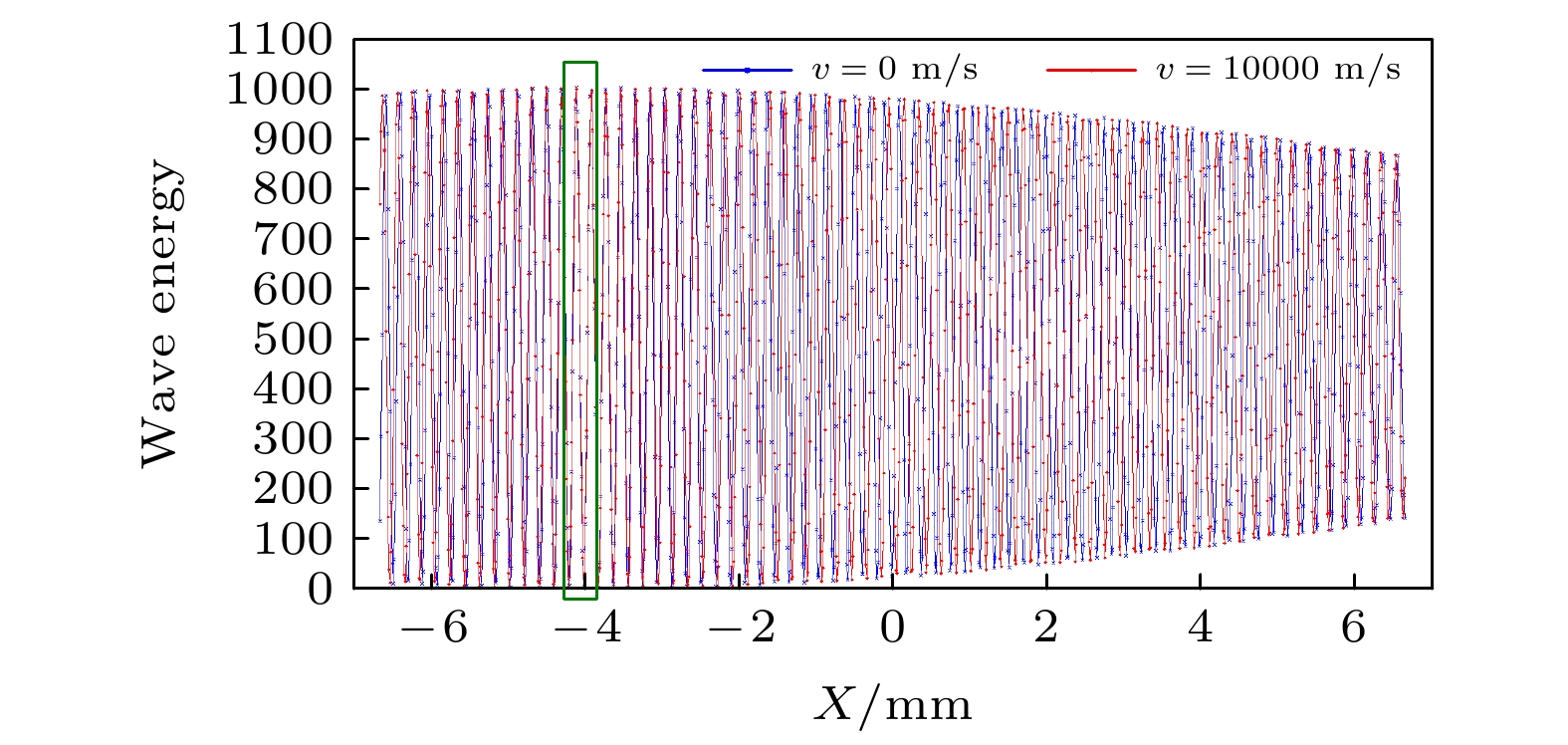
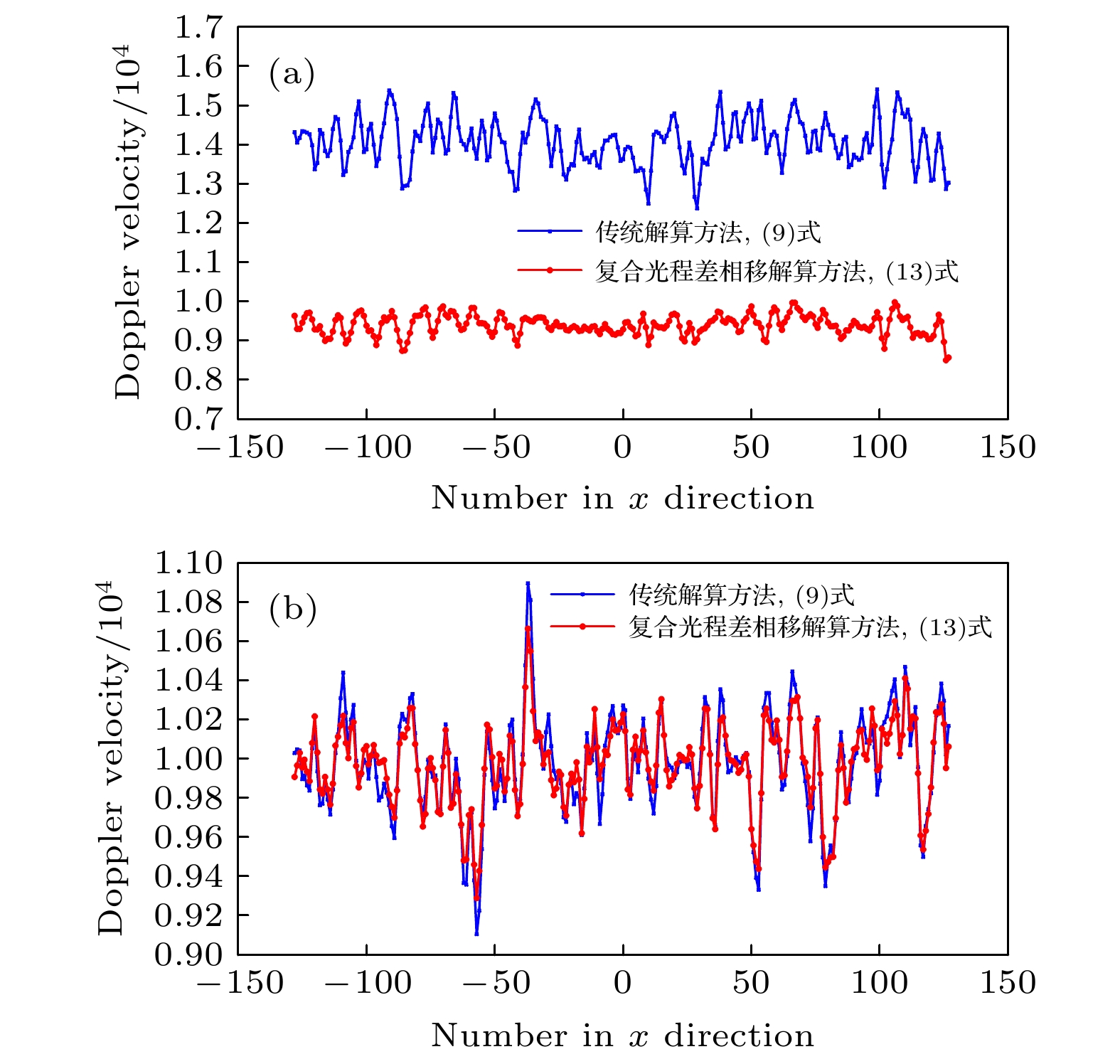
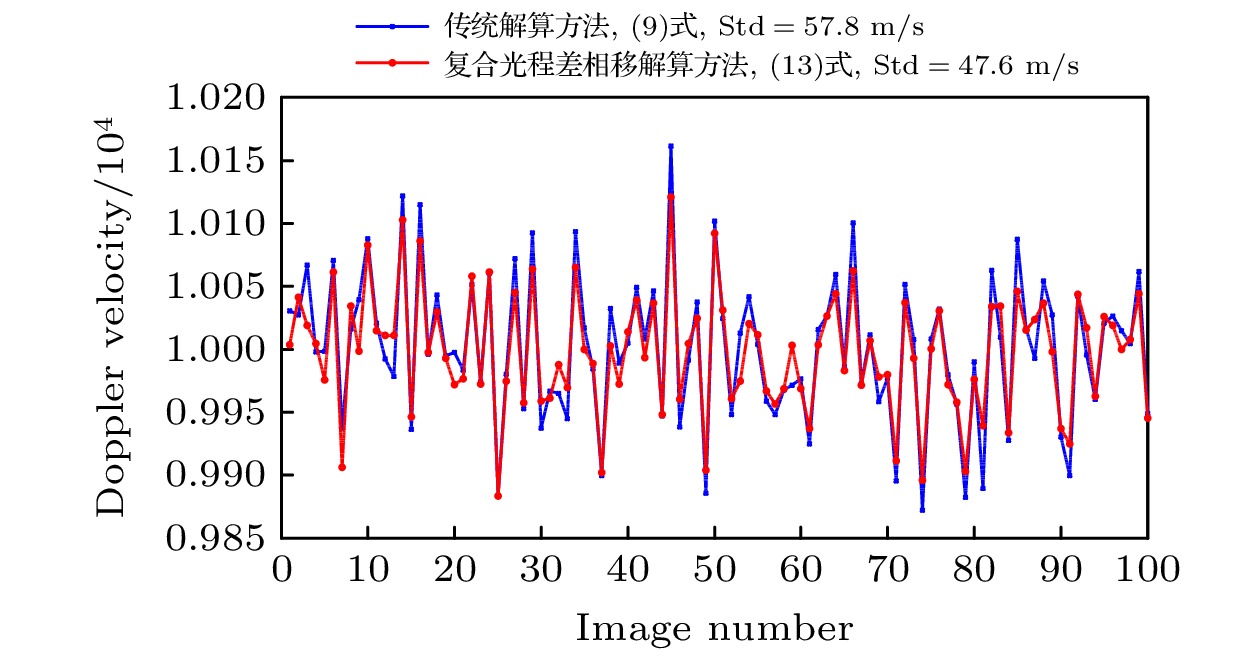
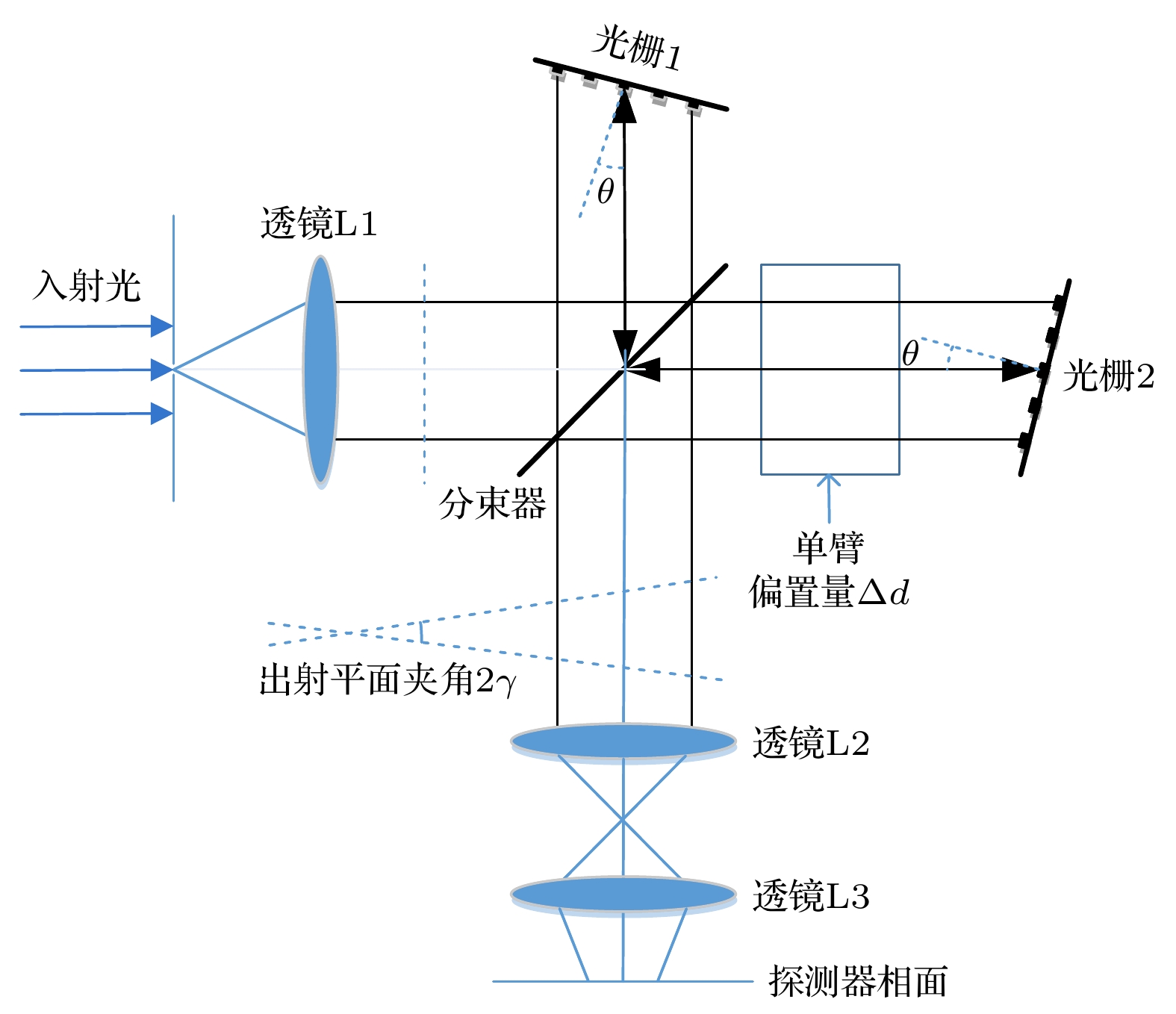
非对称空间外差光谱技术是一种新型的超高分辨率遥感探测技术, 基于其光通量大、体积小、精度高的特点, 适用于深空环境下的高精度探测工作. 也正因其高灵敏度的特性, 使得实验中的各种细节因素都可能对测量结果造成干扰. 本文从实验条件的角度, 重点考虑条纹中心位置偏移、光照不均匀、高斯噪声等因素的影响, 提出了复合光程差相移解算方法. 经仿真计算和数据分析得出, 相位标称点相对中心位置的偏移量会显著影响光谱测速的系统误差, 而复合光程差相移解算方法能够在一定程度上平滑环境噪声和随机干扰造成的光谱测速精度误差. 对于1%程度的高斯噪声干涉条纹图像, 采用复合光程差相移解算方法能够将测速误差控制在5‰以内, 使得非对称空间外差光谱技术能够更好地适用于空间光电精密测量的相关应用中.
-
关键词:
- 多普勒非对称空间外差光谱测速 /
- 深空探测 /
- 复合光程差相移解算 /
- 标称点偏离
Asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectroscopy is a new ultra-high resolution remote sensing detection technology. Based on its features of large luminous flux, small size, and high precision, it is very suitable for high-precision detection in a deep-space environment. Because of its high sensitivity, various details may interfere with the measurement results in experiment. In this paper, from the perspective of experimental condition, considering the influences of factors such as fringe center position offset, uneven illumination, and Gaussian noise, a compound optical path difference phase-shift solution method is proposed. The simulation calculation and data analysis show that the offset of the nominal point relative to the center position will significantly affect the systematic error of spectral velocity measurement. And the compound optical path difference phase-shift solution method can smooth the environmental noise and random interference to a certain extent. For the interference fringe image with 1% Gaussian noise, the velocity measurement error can be controlled within 5‰ by using the compound optical path difference phase-shift solution method, which makes the asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectroscopy technology more suitable for space optoelectronic precision measurement.-
Keywords:
- Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectral velocimetry /
- deep space exploration /
- compound optical path difference phase-shift solution method /
- nominal point deviation
[1] 薛喜平, 张洪波, 孔德庆 2017 天文研究与技术 14 382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xue X P, Zhang H B, Kong D Q 2017 ART 14 382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 张伟 2018 飞控与探测 1 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W 2018 Flight Control Detect. 1 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Babcock D D, Stevens M H, Siskind D E 2006 Atmospheric Optical Modeling, Measurement and Simulation II San Diego, US, August 15–16, 2006 p63030T
[4] Englert C R, Babcock D D, Harlander J M 2007 Appl. Opt. 46 7297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Harlander J M, Englert C R, Babcock D D, Roesler F L 2010 Opt. Express 18 26430
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Emmert J T, Babcock D D, Roesler F L 2010 Opt. Express 18 27416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Solheim B, Brown S, Sioris C, Shepherd G 2015 Atmos. Ocean 53 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 姜通, 施海亮, 沈静, 代海山, 熊伟 2018 光子学报 47 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang T, Shi H L, Shen J, Dai H S, Xiong W 2018 Acta Photon. Sin. 47 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 李志伟, 熊伟, 施海亮, 罗海燕, 乔延利 2016 光谱学与光谱分析 36 2291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Z W, Xiong W, Shi H L, Luo H Y, Qiao Y L 2016 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 36 2291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 况银丽, 方亮, 彭翔, 程欣, 张辉, 刘恩海 2018 67 140703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kuang Y L, Fang L, Peng X, Cheng X, Zhang H, Liu E H 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 140703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Harlander J M, Englert C R, Marr K D, Harding B, Chu K 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 3606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang Y F, Feng Y T, Fu D, Wang P C, Sun J, Bai Q L 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 彭翔, 张嵬 2017 光子学报 46 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng X, Zhang W 2017 Acta Photon. Sin. 46 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王新强, 熊伟, 叶松, 张丽娟 2013 应用光学 34 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X Q, Xiong W, Ye S, Zhang L J 2013 J. Appl. Opt. 34 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 仿真计算所得速度值及误差
Table 1. Speed value and error calculated by simulation
v0/(m·s–1) v1/(m·s–1) v2/(m·s–1) $ \Delta {v_1} $/(m·s–1) $ \Delta {v_2} $/(m·s–1) 10000.0 9991.3 10000.8 8.7 0.8 表 2 不同算法及处理方法对干涉图解算所得速度值的对比
Table 2. Comparison of velocity values calculated on interferograms by different algorithms and processing methods.
v0/(m·s–1) DFT AFT v1/(m·s–1) v2/(m·s–1) v1/(m·s–1) v2/(m·s–1) Mean 10000.0 13989.4 9370.3 10003.8 10001.9 Std 0 516.0 212.6 225.8 185.9 -
[1] 薛喜平, 张洪波, 孔德庆 2017 天文研究与技术 14 382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xue X P, Zhang H B, Kong D Q 2017 ART 14 382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 张伟 2018 飞控与探测 1 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W 2018 Flight Control Detect. 1 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Babcock D D, Stevens M H, Siskind D E 2006 Atmospheric Optical Modeling, Measurement and Simulation II San Diego, US, August 15–16, 2006 p63030T
[4] Englert C R, Babcock D D, Harlander J M 2007 Appl. Opt. 46 7297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Harlander J M, Englert C R, Babcock D D, Roesler F L 2010 Opt. Express 18 26430
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Emmert J T, Babcock D D, Roesler F L 2010 Opt. Express 18 27416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Solheim B, Brown S, Sioris C, Shepherd G 2015 Atmos. Ocean 53 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 姜通, 施海亮, 沈静, 代海山, 熊伟 2018 光子学报 47 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang T, Shi H L, Shen J, Dai H S, Xiong W 2018 Acta Photon. Sin. 47 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 李志伟, 熊伟, 施海亮, 罗海燕, 乔延利 2016 光谱学与光谱分析 36 2291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Z W, Xiong W, Shi H L, Luo H Y, Qiao Y L 2016 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 36 2291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 况银丽, 方亮, 彭翔, 程欣, 张辉, 刘恩海 2018 67 140703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kuang Y L, Fang L, Peng X, Cheng X, Zhang H, Liu E H 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 140703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Harlander J M, Englert C R, Marr K D, Harding B, Chu K 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 3606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang Y F, Feng Y T, Fu D, Wang P C, Sun J, Bai Q L 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 彭翔, 张嵬 2017 光子学报 46 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng X, Zhang W 2017 Acta Photon. Sin. 46 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王新强, 熊伟, 叶松, 张丽娟 2013 应用光学 34 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X Q, Xiong W, Ye S, Zhang L J 2013 J. Appl. Opt. 34 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5446
- PDF下载量: 72
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: