-
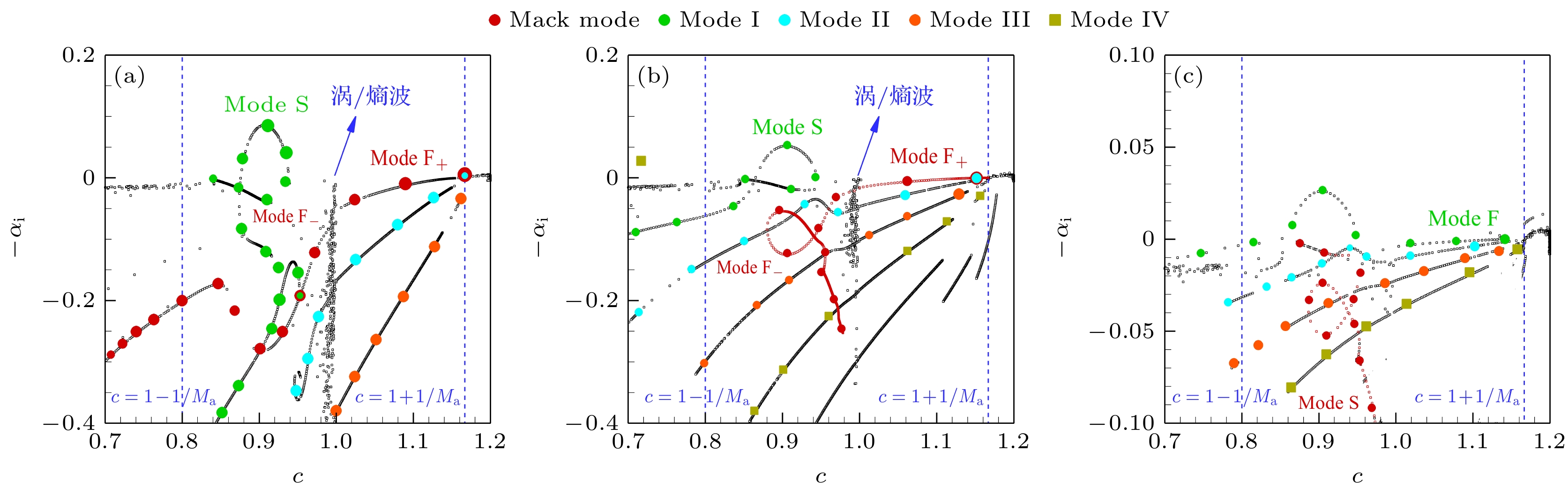
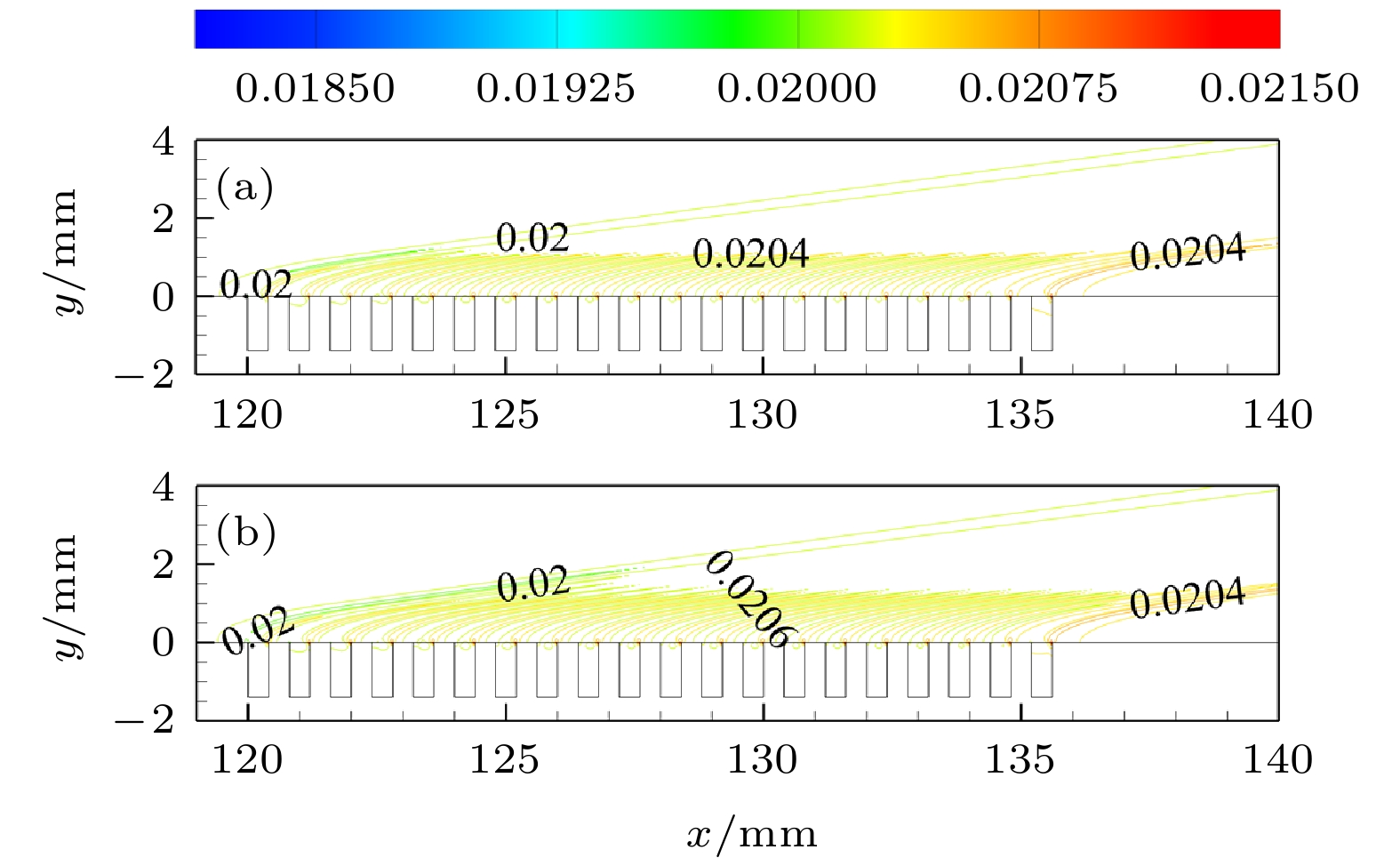
针对高超声速飞行器边界层转捩控制问题, 以马赫数6平板边界层的第二模态扰动波为研究对象, 采用线性稳定性理论(LST)和直接数值模拟(DNS)分别开展了离散模态的同步模式研究和大尺寸(0.4 mm宽)横向矩形微槽开槽位置对第二模态扰动波的控制作用研究. LST分析表明: 涡/熵波会导致Mack第二模态和“mode I”模态(通常来源于快声波)的分支类型发生改变. 通过DNS发现, 开槽表面对基本流的影响程度与边界层流向位置(或厚度)相关, 随着开槽位置后移(边界层厚度增加), 开槽表面对基本流动的影响程度减弱, 摩擦阻力系数和压差阻力系数也逐渐减小. DNS结果还表明, 位于快/慢模态同步区间之前的开槽工况对第二模态扰动波依然有抑制效果, 这与文献中关于小尺寸(微米量级)微孔隙位置对第二模态控制作用的结论不同, 同时发现, 当矩形微槽布置在最大增长率区间范围内或快/慢模态同步区间位置时, 对第二模态扰动的抑制效果最佳.Aiming at delaying boundary-layer transition of hypersonic vehicles, the second-mode wave in the boundary layer of a Mach 6 flat plate is studied. Linear stability theory (LST) and direct numerical simulations (DNS) are used to investigate the discrete modes and the relation between the suppressing effect of second-mode wave and the location of transverse rectangular micro-groove (0.4 mm in width), respectively. The LST results show that vortex/entropy waves cause the branch types of Mack’s second mode and “mode I” modes (usually derived from fast acoustic waves) to change. The DNS results show that the influence of the grooved surface on the base flow depends on the streamwise location (or boundary-layer thickness). As the grooved surface shifts backward (or thickness increases), the influence of intensity on the base flow decreases, and the friction resistance coefficient
$ C{d_{\text{f}}} $ , differential pressure resistance coefficient$ C{d_{\text{p}}} $ and total resistance coefficient$ C{d_x} $ of the grooved surface also decrease. It is found that the grooves located in front of the synchronization region of the fast mode and slow mode still have an inhibitory effect on the second-mode wave, which is different from the effect of small-sized (micrometer scale) micro-pores reported in the literature. It is also found that the suppression effect on the second-mode wave is best when the grooves are arranged in the vicinity of the maximum growth-rate point or at the location of the synchronization interval of the fast mode and slow mode.-
Keywords:
- hypersonic /
- linear stability /
- transition control /
- rectangular micro-grooves
[1] Richie G 1999 AIAA 4435
[2] Bertin J J, Cummings R M 2006 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech 38 129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Whitehead A 1989 AIAA 5013
[4] Morkovin M V 1994 Bull. Am. Phys. Soc 39 1882
[5] Fedorov A 2011 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech 43 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Malmuth N, Fedorov A, Shalaev V, Cole J, Khokhlov A, Hites M, Williams D 1998 Theoretical Fluid Mechanics Meeting Albuquerque, NM, USA, June 15–18, 1998 p2695
[7] Fedorov A V, Malmuth N D, Rasheed A, Hornung H G 2001 AIAA J 39 605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Rasheed A, Hornung H G, Fedorov A V, Malmuth N D 2002 AIAA J 40 481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chokani N, Bountin D A, Shiplyuk A N, Maslov A A 2005 AIAA J 43 149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Egorov I V, Fedorov A V, Soudakov V G 2008 J. Fluid Mech 601 165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Egorov I V, Fedorov A V, Novikov A V, Soudakov V G 2007 AIAA 948
[12] Dong M, Li C 2021 AIAA J 59 2368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Long T H, Dong Y, Zhao R, Wen Z Y 2021 Phys. Fluids 33 054105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Brès G A, Colonius T, Fedorov A V 2010 AIAA J 48 267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhao R, Liu T, Wen C Y, Zhu J, Chen L 2018 AIAA J 56 2942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 涂国华, 陈坚强, 袁先旭, 杨强, 张毅锋 2018 空气动力学报 36 273
Tu G H, Chen J Q, Yuan X X, Yang Q, Zhang Y F 2018 Acta Aerodyn. Sin. 36 273 (in Chinese)
[17] 郭启龙, 涂国华, 陈坚强, 袁先旭, 万兵兵 2020 航空动力学报 35 135
Guo Q L, Tu G H, Chen J Q, Yuan X X, Wan B B 2020 J. Aerosp. Power 35 135 (in Chinese)
[18] Guo Q L, Li C, Tu G H, Chen J J, Wan B B, Liu Y 2021 Asia Conference on Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Athens, Greece, July 14–17, 2020 p012053
[19] Wang X W, Zhong X L 2008 AIAA 4382
[20] Wang X W, Zhong X L 2012 Phys. Fluids 24 1441
[21] Lukashevich S V, Morozov S O, Shiplyuk A N 2016 J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys 57 873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhao R, Wen C Y, Long T H, Tian X D, Zhou L, Wu Y 2019 AIAA J 57 5061
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 孔维萱, 闫超, 赵瑞 2013 航空学报 34 2249
Kong W X, Yan C, Zhao R 2013 Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 34 2249 (in Chinese)
[24] Brès G A, Inkman M, Colonius T, Fedorov A V 2013 J. Fluid Mech 726 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhao R, Liu T, Wen C Y, Zhu J, Chen L 2019 Phys. Rev. Appl 11 044015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhao R, Dong Y, Zhang X X, Wen Z Y, Long T H, Wu Y 2021 AIAA J 59 1893
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Ma Y B, Zhong X L 2003 J. Fluid Mech 488 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Tumin A, Wang X W, Zhong X L 2011 AIAA J 49 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Liu Y, Guo Q L, Tu G H, Yang Q, Yuan X X, Wan B B 2021 International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Automation Science, Seoul, South Korea, October 28–30, 2021 p132
[30] Zhang H X, Zhang L P, Zhang S H, Li Q 2017 Comput. Fluids 154 371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Sandham N D, Lüdeke H 2009 AIAA 1288
[32] Tullio N D, Sandham N D 2010 Phys. Fluids 22 094105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zhao R, Wen C Y, Tian X D, Yuan W 2018 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 121 986
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Wartemann V, Lüdeke H, Sandham N 2009 AIAA 7202
[35] Fedorov A V, Tumin A 2010 AIAA 5003
[36] Liu Z Y, Yu M 2017 AIAA 2247
[37] Deng X G, Mao M L, Tu G H, Zhang H X, Zhang Y F 2012 Commun. Comput. Phys 11 1081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
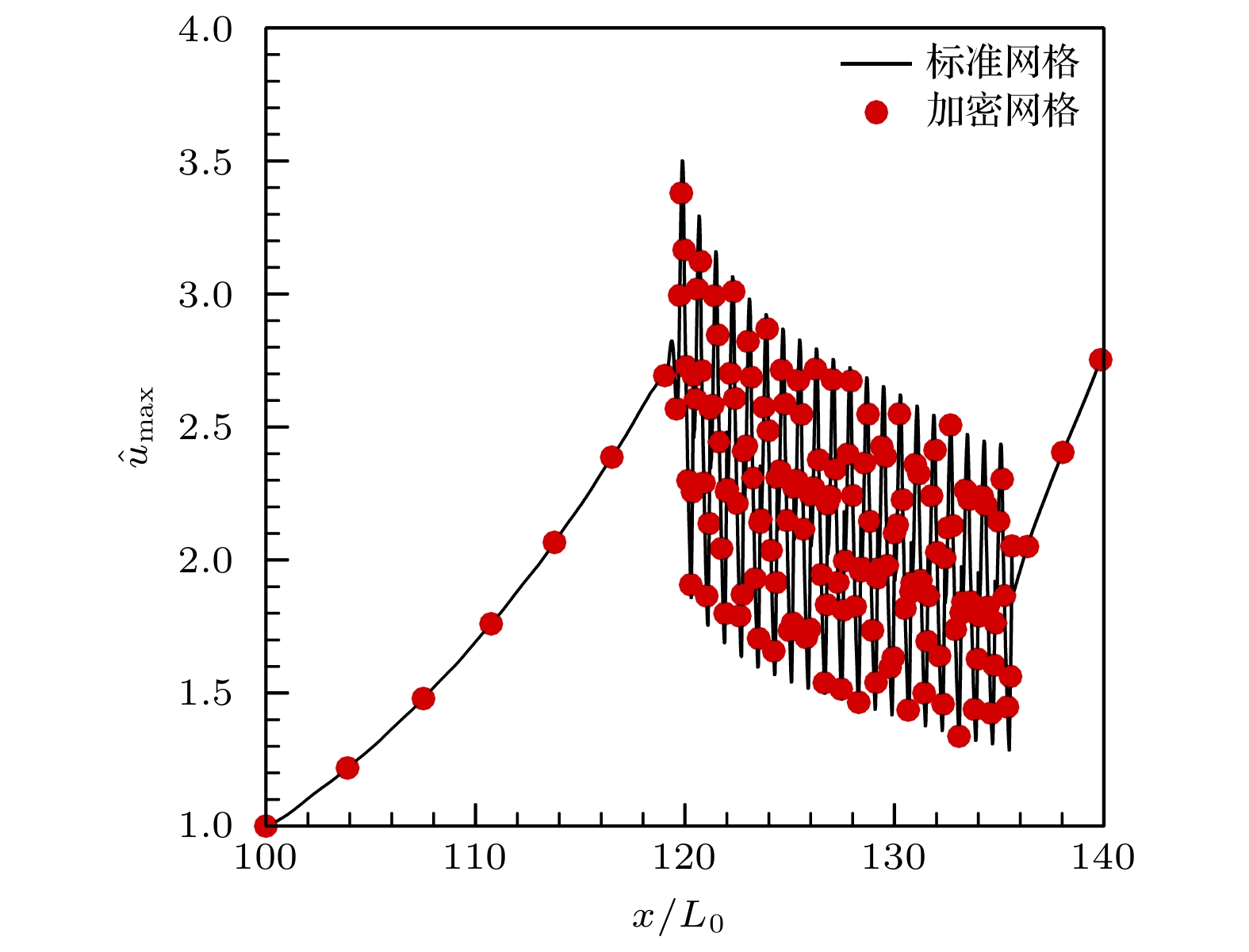
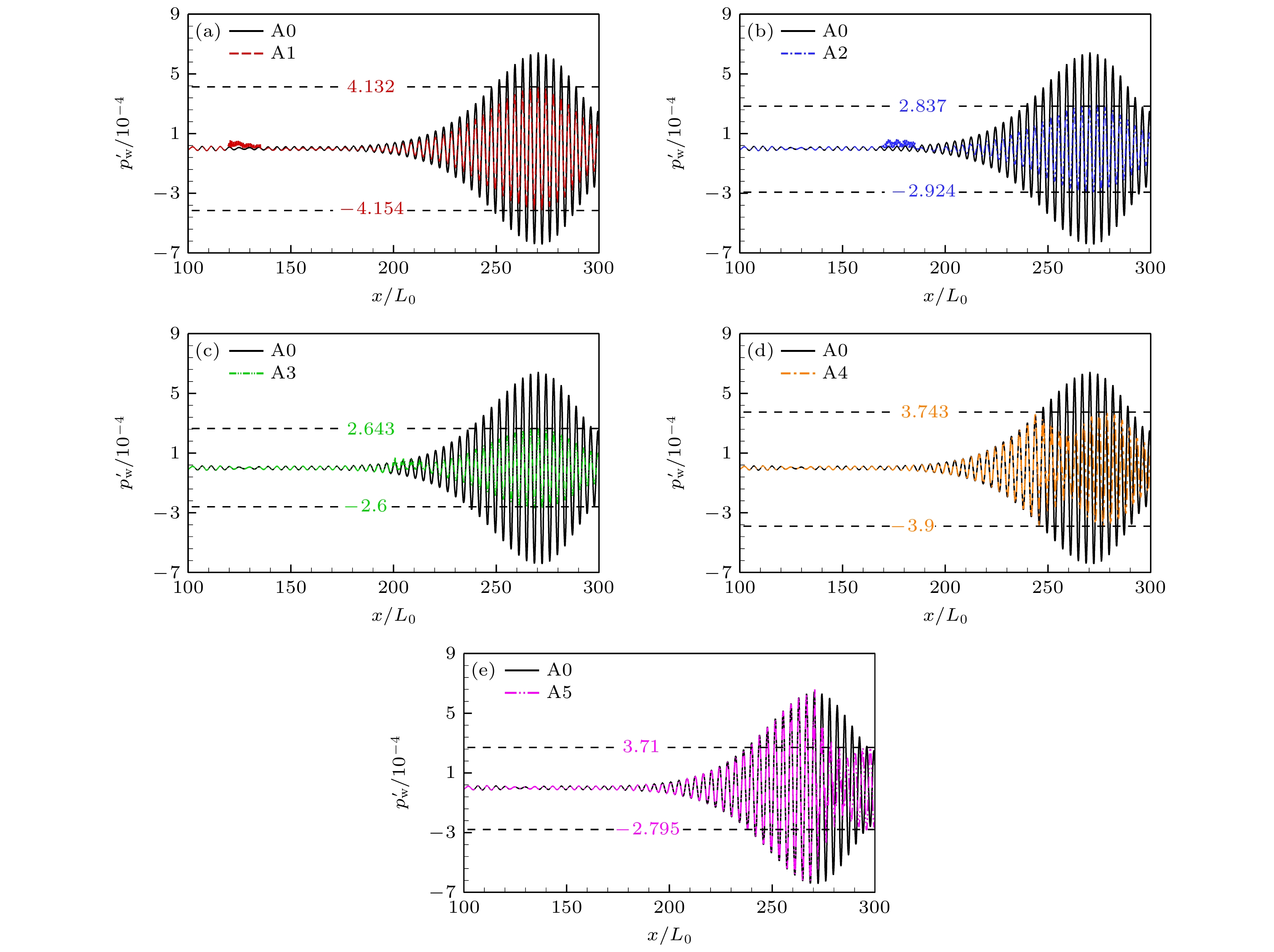
图 16 400 kHz第二模态沿流向的发展 (a) A0—A5工况流向[100, 300] mm扰动幅值; (b) A0, A4, A5工况在加长区[300, 400] mm扰动幅值
Fig. 16. Development of the 400 kHz second mode along the streamwise direction: (a) A0–A5 cases flow direction[100, 300] mm disturbance amplitude; (b) A0, A4, and A5 cases in the extended area of [300, 400] mm.
表 1 来流参数设置
Table 1. Free stream parameter setting.
马赫数Ma 单位
雷诺数 Re/m壁温 Tw/K 来流
密度
ρ/(kg·m–3)来流
温度 Te/K普朗
特数 Pr比热比 γ 6.0 $1 \times {10^7}$ $300{\text{ }}$ $0.0184{\text{ }}$ 216.65 0.72 1.4 表 2 开槽位置参数
Table 2. Grooving location parameters.
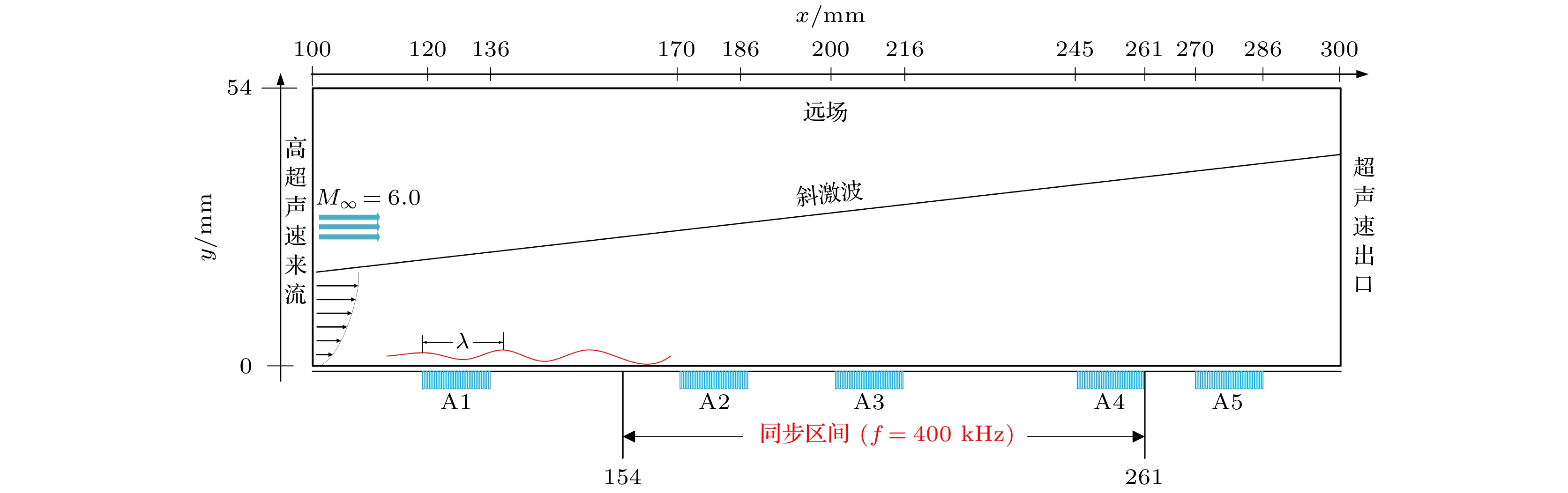
Cases 开槽起始位置${x_{\text{l}}}/{L_0}$ 开槽区间 A0 — — A1 120 (120, 136) A2 170 (170, 186) A3 200 (200, 216) A4 245 (245, 261) A5 270 (270, 286) -
[1] Richie G 1999 AIAA 4435
[2] Bertin J J, Cummings R M 2006 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech 38 129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Whitehead A 1989 AIAA 5013
[4] Morkovin M V 1994 Bull. Am. Phys. Soc 39 1882
[5] Fedorov A 2011 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech 43 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Malmuth N, Fedorov A, Shalaev V, Cole J, Khokhlov A, Hites M, Williams D 1998 Theoretical Fluid Mechanics Meeting Albuquerque, NM, USA, June 15–18, 1998 p2695
[7] Fedorov A V, Malmuth N D, Rasheed A, Hornung H G 2001 AIAA J 39 605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Rasheed A, Hornung H G, Fedorov A V, Malmuth N D 2002 AIAA J 40 481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chokani N, Bountin D A, Shiplyuk A N, Maslov A A 2005 AIAA J 43 149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Egorov I V, Fedorov A V, Soudakov V G 2008 J. Fluid Mech 601 165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Egorov I V, Fedorov A V, Novikov A V, Soudakov V G 2007 AIAA 948
[12] Dong M, Li C 2021 AIAA J 59 2368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Long T H, Dong Y, Zhao R, Wen Z Y 2021 Phys. Fluids 33 054105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Brès G A, Colonius T, Fedorov A V 2010 AIAA J 48 267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhao R, Liu T, Wen C Y, Zhu J, Chen L 2018 AIAA J 56 2942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 涂国华, 陈坚强, 袁先旭, 杨强, 张毅锋 2018 空气动力学报 36 273
Tu G H, Chen J Q, Yuan X X, Yang Q, Zhang Y F 2018 Acta Aerodyn. Sin. 36 273 (in Chinese)
[17] 郭启龙, 涂国华, 陈坚强, 袁先旭, 万兵兵 2020 航空动力学报 35 135
Guo Q L, Tu G H, Chen J Q, Yuan X X, Wan B B 2020 J. Aerosp. Power 35 135 (in Chinese)
[18] Guo Q L, Li C, Tu G H, Chen J J, Wan B B, Liu Y 2021 Asia Conference on Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Athens, Greece, July 14–17, 2020 p012053
[19] Wang X W, Zhong X L 2008 AIAA 4382
[20] Wang X W, Zhong X L 2012 Phys. Fluids 24 1441
[21] Lukashevich S V, Morozov S O, Shiplyuk A N 2016 J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys 57 873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhao R, Wen C Y, Long T H, Tian X D, Zhou L, Wu Y 2019 AIAA J 57 5061
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 孔维萱, 闫超, 赵瑞 2013 航空学报 34 2249
Kong W X, Yan C, Zhao R 2013 Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 34 2249 (in Chinese)
[24] Brès G A, Inkman M, Colonius T, Fedorov A V 2013 J. Fluid Mech 726 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhao R, Liu T, Wen C Y, Zhu J, Chen L 2019 Phys. Rev. Appl 11 044015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhao R, Dong Y, Zhang X X, Wen Z Y, Long T H, Wu Y 2021 AIAA J 59 1893
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Ma Y B, Zhong X L 2003 J. Fluid Mech 488 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Tumin A, Wang X W, Zhong X L 2011 AIAA J 49 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Liu Y, Guo Q L, Tu G H, Yang Q, Yuan X X, Wan B B 2021 International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Automation Science, Seoul, South Korea, October 28–30, 2021 p132
[30] Zhang H X, Zhang L P, Zhang S H, Li Q 2017 Comput. Fluids 154 371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Sandham N D, Lüdeke H 2009 AIAA 1288
[32] Tullio N D, Sandham N D 2010 Phys. Fluids 22 094105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zhao R, Wen C Y, Tian X D, Yuan W 2018 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 121 986
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Wartemann V, Lüdeke H, Sandham N 2009 AIAA 7202
[35] Fedorov A V, Tumin A 2010 AIAA 5003
[36] Liu Z Y, Yu M 2017 AIAA 2247
[37] Deng X G, Mao M L, Tu G H, Zhang H X, Zhang Y F 2012 Commun. Comput. Phys 11 1081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5105
- PDF下载量: 73
- 被引次数: 0




















 下载:
下载: