-
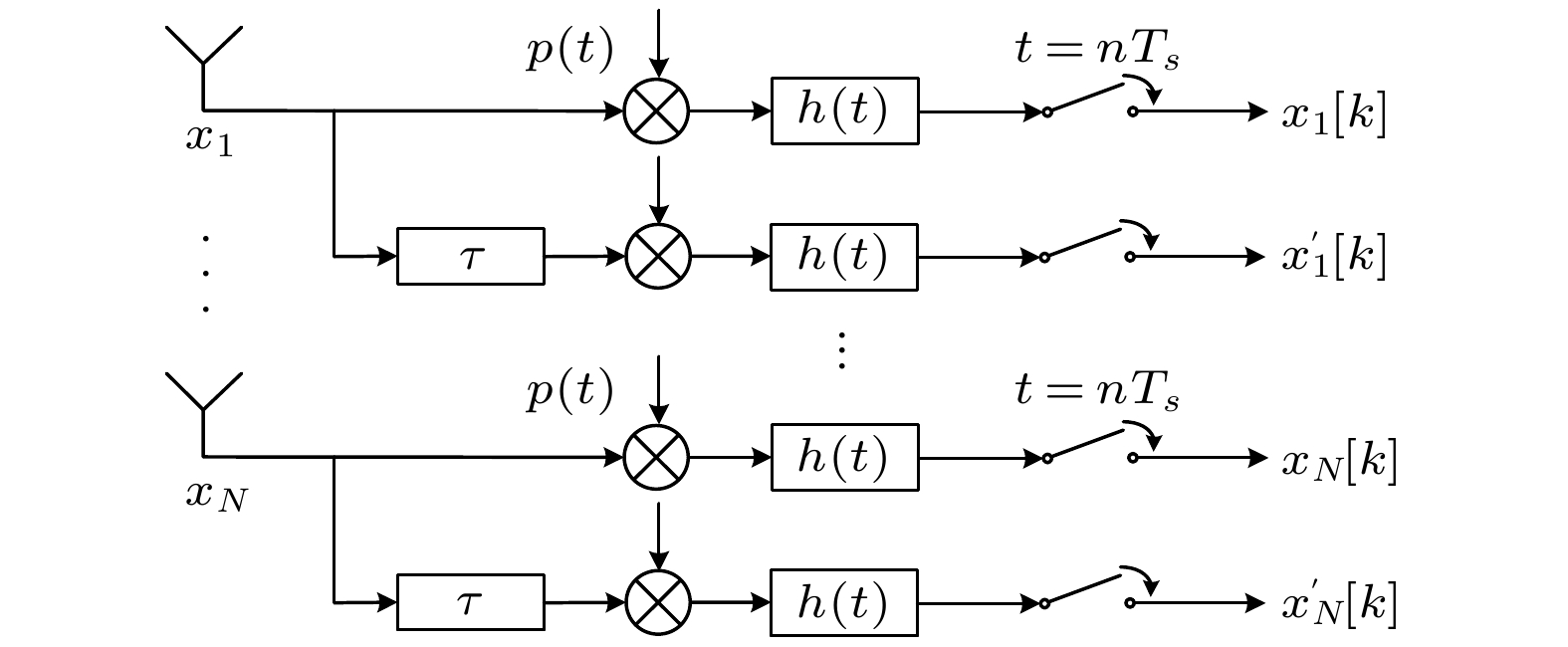
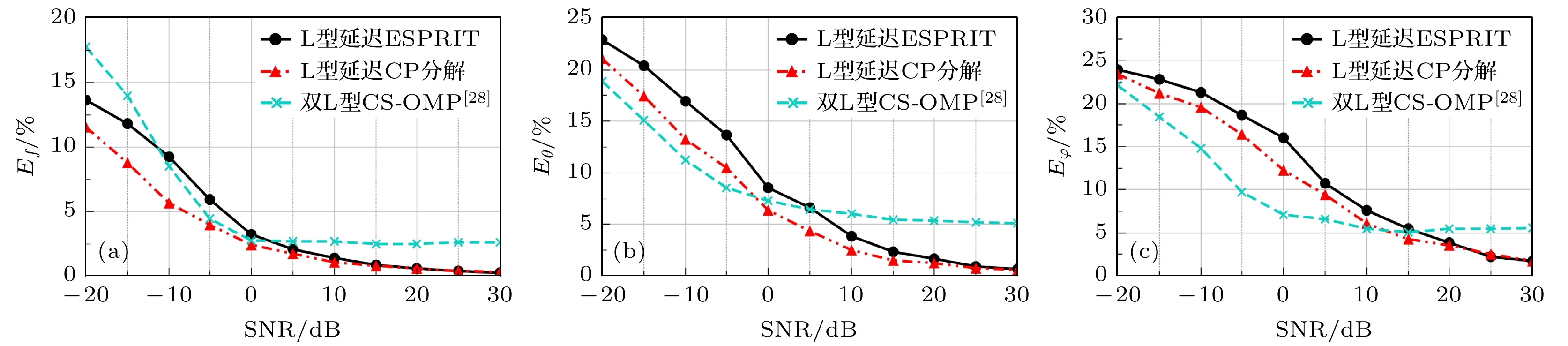
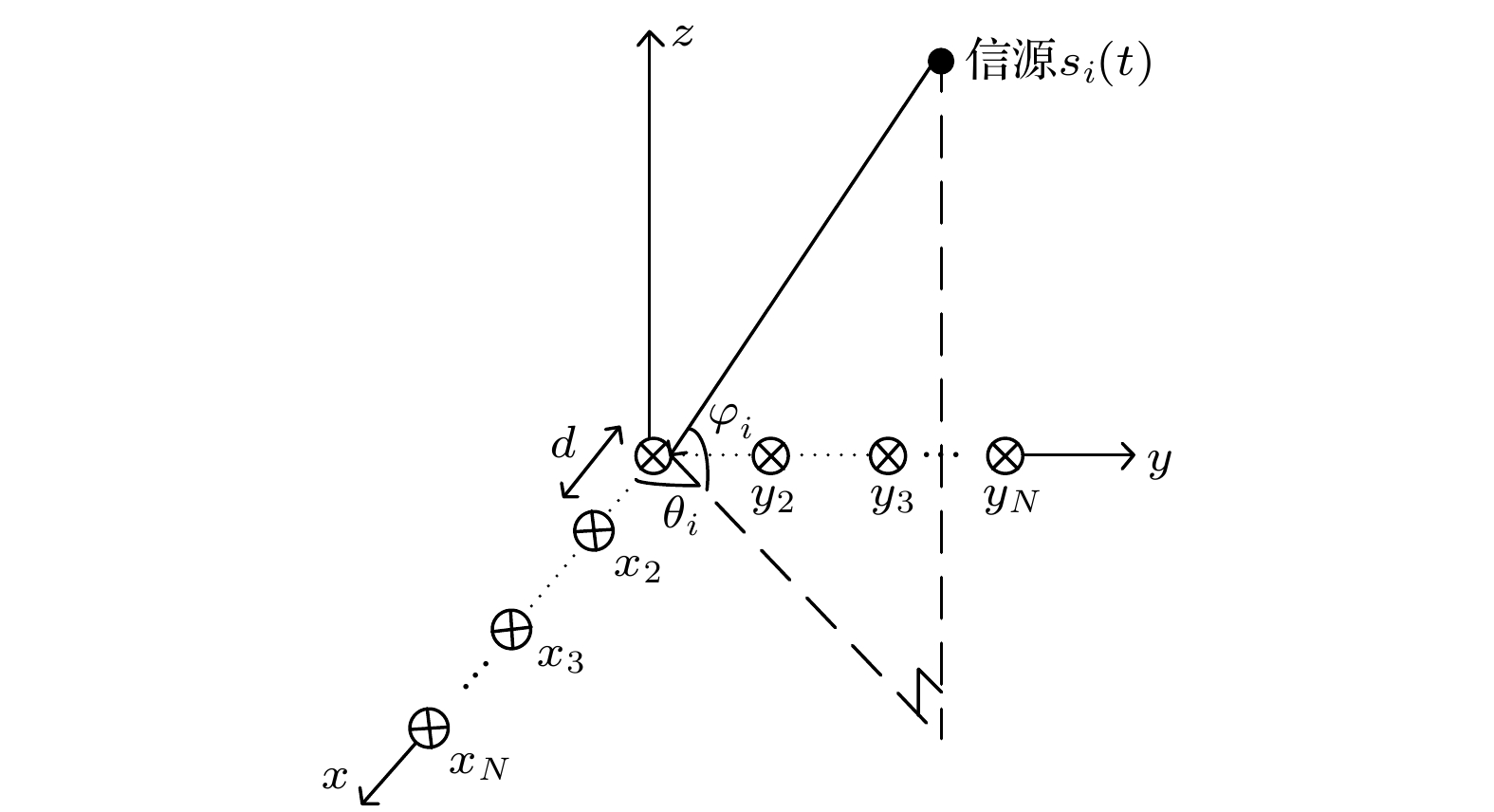
针对现有的基于欠采样的频率和二维到达角的联合估计存在结构复杂问题, 本文提出了一种基于调制宽带转换器技术的L型延迟阵列接收结构. 利用延迟通道与未延迟通道采样值之间的相位差可直接估计载频, 进而计算二维到达角, 无需额外的参数配对操作, 避免了配对步骤引入的误差和复杂度的提升. 并结合所提L型延迟阵列结构的特点构造相关矩阵和三线性模型, 提出了两种参数估计算法, 一种基于旋转不变子空间算法, 计算量小, 适用于需要实时处理的场景; 另一种基于正则分解技术, 鲁棒性较好, 适用于信噪比较低的应用场景. 仿真实验表明该方法能较好地从欠奈奎斯特样本中估计目标的载频和二维到达角参数.
-
关键词:
- 压缩感知 /
- 阵列参数联合估计 /
- 二维到达角 /
- 阵列式调制宽带转换器
As the signal spectrum in modern information technology becomes wider and wider, multi-band signals are distributed in a frequency range of tens of GHz. It covers a very wide spectrum but each RF signal has a very narrow band, and the distribution location of the band (or carrier frequency) is completely unknown. For the receiver, the single-band signals transmitted together constitute a multi-band signal. The sampling rate required to jointly estimate the space domain and frequency domain parameters of these signals is getting higher and higher. Modulated wideband converter system is an analog information conversion system for multiband analog signals, which is based on compressed sensing theory and greatly reduces the sampling rate. First, we propose an L-shaped delay array structure based on modulated wideband converter, which can estimate carrier frequency and two-dimensional arrival angles with a small number of samples. Secondly, two parameter-estimating algorithms are proposed based on the proposed structure. One is based on the estimating of signal parameter via rotational invariance technique (ESPRIT), which requires a small number of computations and is suitable for real-time processing application scenarios; the other algorithm is based on CANDECOMP/PARAFAC (CP) technique, which has better robustness and is suitable for applications with low signal-to-noise ratio. The samples of the delay channels can be directly used to estimate the carrier frequencies, and then the two-dimensional arrival angles are calculated. No additional pairing issue is required between the parameters. Then we give the time complexity analysis and space complexity analysis of the two methods. It can be found that the computational complexity and space storage occupation of the method based on ESPRIT are lower than those of the CP decomposition method. Then the conditions for unique parameter estimation are given. Finally, simulation experiments show that the proposed methods can estimate the carrier frequencies and two-dimensional arrival angles from sub-Nyquist samples. It can be found that the estimation method based on CP decomposition is more robust than the method based on ESPRIT, but at the cost of increased complexity of the algorithm.-
Keywords:
- compressed sensing /
- joint estimation of array parameters /
- two-dimensional direction of arrival /
- array modulated wideband converter structure
[1] Hassanien A, Vorobyov S A 2011 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59 2669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 谢磊, 孙超, 刘雄厚, 蒋光禹 2016 65 144303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie L, Sun C, Liu X H, Jiang G Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 144303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 孙梅, 周士弘 2016 65 164302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun M, Zhou S H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 164302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yang C, Xia B, Xie W, Huang K, Yao Y, Zhao Y 2018 IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 67 842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 巴斌, 刘国春, 李韬, 林禹丞, 王瑜 2015 64 078403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ba B, Liu G C, Li T, Lin Y C, Wang Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 078403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Donoho D L 2006 IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52 1289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Candes E J, Wakin M B 2008 IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 25 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 康志伟, 吴春艳, 刘劲, 马辛, 桂明臻 2018 67 099701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kang Z W, Wu C Y, Liu J, Ma X, Gui M Z 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 099701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 冷雪冬, 王大鸣, 巴斌, 王建辉 2017 66 090703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Leng X D, Wang D M, Bang B, Wang J H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 090703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao Y, Hu Y H, Wang H 2012 IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 61 579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tropp J A, Wakin M B, Duarte M F, et al. 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Toulouse, France, May 14–19, 2006 p873
[12] Kirolos S, Laska J, Wakin M, et al. 2006 IEEE Dallas/CAS Workshop on Design, Applications, Integration and Software, Richardson, Texas, USA, October 29–30, 2006 p71
[13] Mishali M, Eldar Y C 2009 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57 993
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Mishali M, Eldar Y C 2010 IEEE J. Sel. Topics Signal Process. 4 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Mishali M, Eldar Y C, Dounaevsky O, Shoshan E 2009 IET Circ. Device. Syst. 5 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 黄翔东, 刘明卓, 杨琳, 刘琨, 刘铁根 2017 66 188401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang X D, Liu M Z, Yang L, Liu K, Liu T G 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 188401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 沈志博, 赵国庆, 董春曦, 黄龙 2014 航空学报 35 1357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen Z B, Zhao G Q, Dong C X, Huang L 2014 Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 35 1357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu L, Gu J F, Wei P 2019 Signal Process. 154 87
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu L, Wei P, Zhang H G 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, December 13–16, 2017 p843
[20] Sidiropoulos N D, Giannakis G B, Bro R 2000 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 48 810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu L, Wei P 2017 IET Radar Sonar Navigation 11 1798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu L, Wei P 2016 IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 25 1285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Stein S, Yair O, Cohen D, Eldar Y C 2015 IEEE International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications Stockholm, Sweden, June 28–July 1, 2015 p331
[24] Stein S, Yair O, Cohen D, Eldar Y C 2017 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65 2645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Cui C, Wu W, Wang W Q 2017 IEEE Sensors J. 17 7470
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Chen T, Liu L Z, Guo L M 2018 IET Radar, Sonar Navigation 12 873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 陈玉龙, 黄登山 2012 计算机工程与应用 48 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y L, Huang D S 2012 Computer Engineering and Applications 48 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Esmaeil R, Farzan S M, Mohammad S S 2018 IET Radar, Sonar Navigation 12 889
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 不同方法的复杂度对比
Table 1. Complexity comparison of different methods.
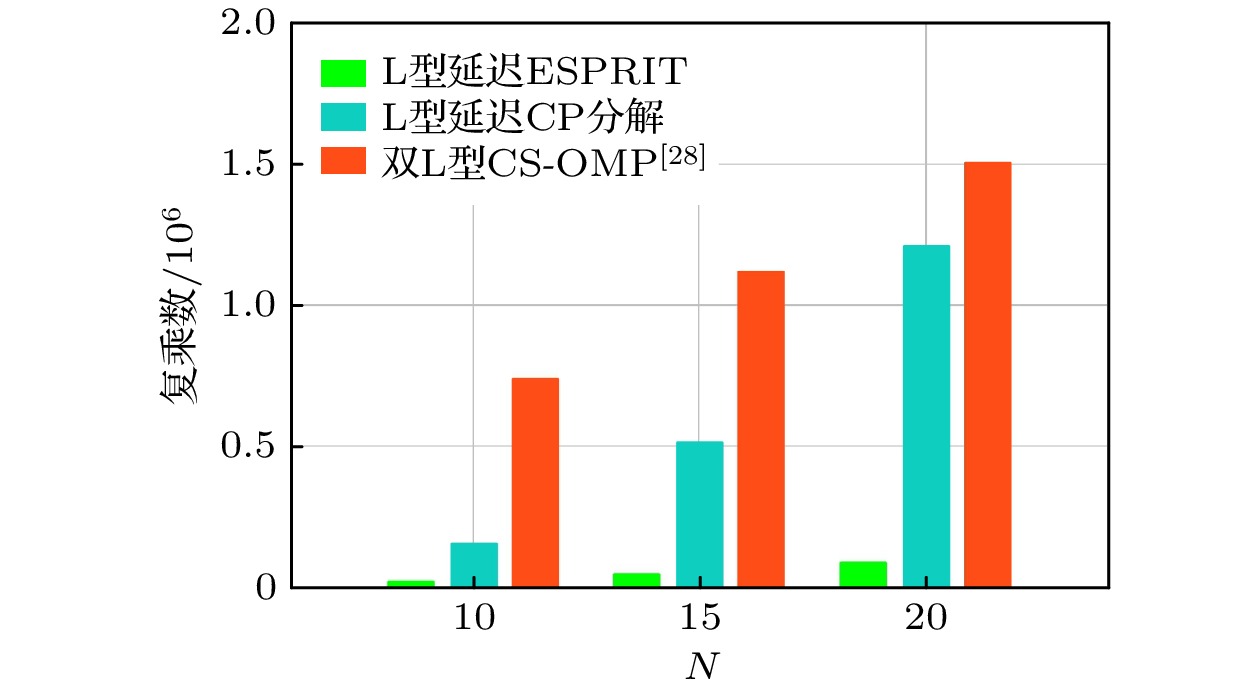
基于ESPRIT的方法 基于CP分解的方法 CS-OMP方法[28] 时间复杂度 $O({N^3} + {N^2}Q + {M^2})$ $O(IM \cdot {N^3} + IN{M^2} + {N^2}Q)$ $O(N{M^2}{P^2} + {N^3} + {N^2}(M + Q))$ 空间复杂度 $O({N^2} + {M^2})$ $O({N^3})$ $O(N{P^2} + {N^2} + NM)$ -
[1] Hassanien A, Vorobyov S A 2011 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59 2669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 谢磊, 孙超, 刘雄厚, 蒋光禹 2016 65 144303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie L, Sun C, Liu X H, Jiang G Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 144303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 孙梅, 周士弘 2016 65 164302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun M, Zhou S H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 164302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yang C, Xia B, Xie W, Huang K, Yao Y, Zhao Y 2018 IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 67 842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 巴斌, 刘国春, 李韬, 林禹丞, 王瑜 2015 64 078403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ba B, Liu G C, Li T, Lin Y C, Wang Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 078403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Donoho D L 2006 IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52 1289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Candes E J, Wakin M B 2008 IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 25 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 康志伟, 吴春艳, 刘劲, 马辛, 桂明臻 2018 67 099701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kang Z W, Wu C Y, Liu J, Ma X, Gui M Z 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 099701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 冷雪冬, 王大鸣, 巴斌, 王建辉 2017 66 090703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Leng X D, Wang D M, Bang B, Wang J H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 090703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao Y, Hu Y H, Wang H 2012 IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 61 579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tropp J A, Wakin M B, Duarte M F, et al. 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Toulouse, France, May 14–19, 2006 p873
[12] Kirolos S, Laska J, Wakin M, et al. 2006 IEEE Dallas/CAS Workshop on Design, Applications, Integration and Software, Richardson, Texas, USA, October 29–30, 2006 p71
[13] Mishali M, Eldar Y C 2009 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57 993
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Mishali M, Eldar Y C 2010 IEEE J. Sel. Topics Signal Process. 4 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Mishali M, Eldar Y C, Dounaevsky O, Shoshan E 2009 IET Circ. Device. Syst. 5 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 黄翔东, 刘明卓, 杨琳, 刘琨, 刘铁根 2017 66 188401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang X D, Liu M Z, Yang L, Liu K, Liu T G 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 188401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 沈志博, 赵国庆, 董春曦, 黄龙 2014 航空学报 35 1357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen Z B, Zhao G Q, Dong C X, Huang L 2014 Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 35 1357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu L, Gu J F, Wei P 2019 Signal Process. 154 87
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu L, Wei P, Zhang H G 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, December 13–16, 2017 p843
[20] Sidiropoulos N D, Giannakis G B, Bro R 2000 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 48 810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu L, Wei P 2017 IET Radar Sonar Navigation 11 1798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu L, Wei P 2016 IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 25 1285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Stein S, Yair O, Cohen D, Eldar Y C 2015 IEEE International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications Stockholm, Sweden, June 28–July 1, 2015 p331
[24] Stein S, Yair O, Cohen D, Eldar Y C 2017 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65 2645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Cui C, Wu W, Wang W Q 2017 IEEE Sensors J. 17 7470
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Chen T, Liu L Z, Guo L M 2018 IET Radar, Sonar Navigation 12 873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 陈玉龙, 黄登山 2012 计算机工程与应用 48 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y L, Huang D S 2012 Computer Engineering and Applications 48 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Esmaeil R, Farzan S M, Mohammad S S 2018 IET Radar, Sonar Navigation 12 889
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6302
- PDF下载量: 69
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: