-
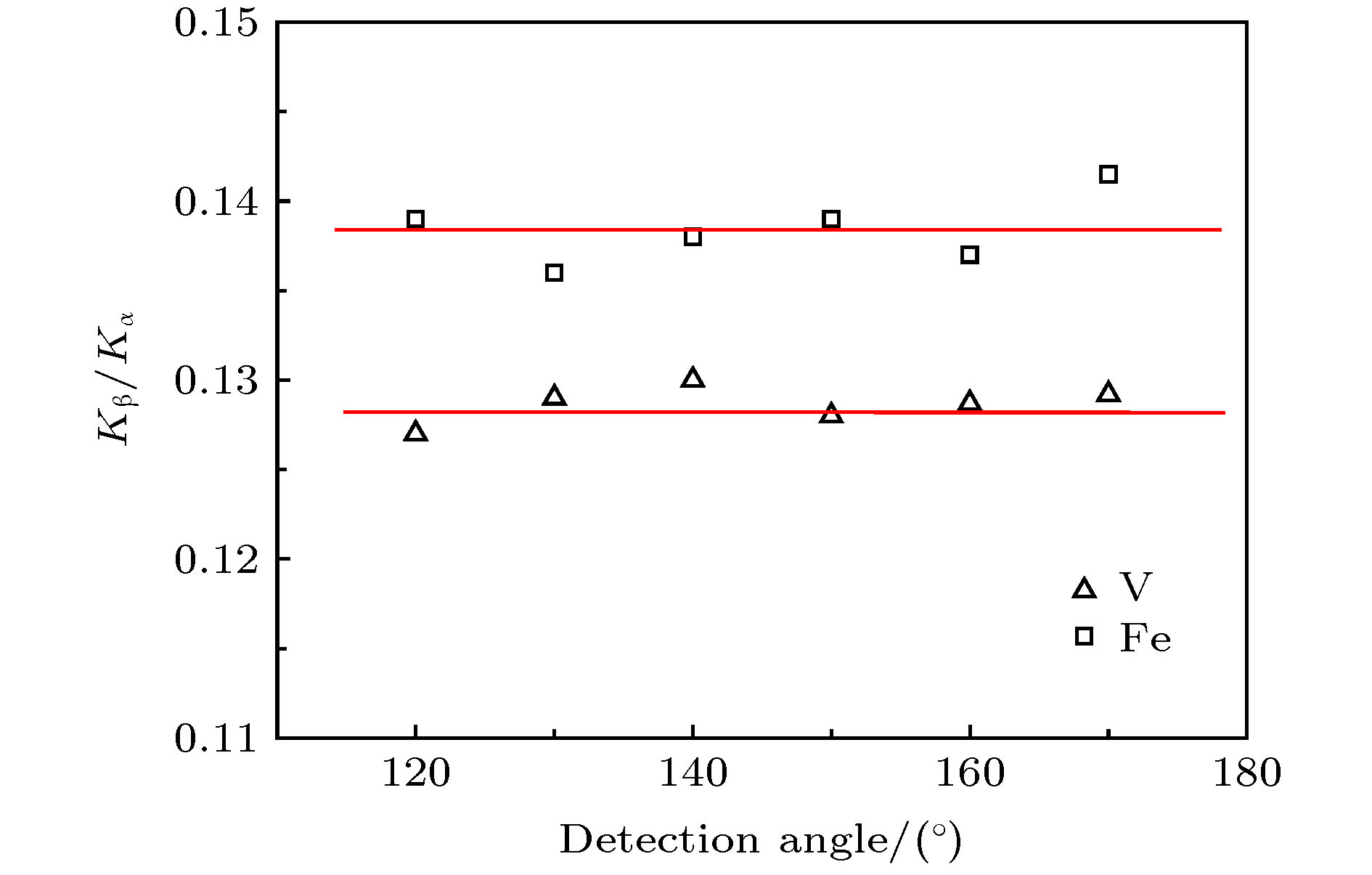
在发射角120°—170°的范围内, 应用硅漂移探测器以10°为间隔对中心能量为13.1 keV的韧致辐射诱发Fe靶和V靶发射的典型K系X射线光谱进行了测量. 得到特征X射线Kα和Kβ的特征谱线, 考虑探测器对特征X射线的探测效率、靶对入射光子和出射光子吸收的校准及大气对特征X射线的吸收后, 结果显示不同探测角度下Kβ与Kα的强度比为一常数. 将本次实验探测角度为150°时的Kβ/Kα强度比值的实验值、理论计算值和Ertuğral的实验结果进行对比, 发现实验结果与预期相符. 对比不同探测角度下的强度比变化趋势推断特征X射线的角度依赖关系, 分析认为Kα和Kβ在探测范围内是各向同性发射的.
The de-excitation process of vacancy in the inner shell of the target atom caused by collision ionization produces the characteristic X-ray or Auger electrons. The precise measurement of ionization cross sections plays an important role in many basic research fields, as well as in practical fields, such as chemical analysis of Particle Induced X-ray Emission (PIXE), atomic and nuclear processes, and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy. As we know, when ionization cross sections are measured precisely, whether the emission of X-ray is isotropic in collision process must be considered. However, there have been few experimental results for angular dependence of Kβ/Kα intensity ratios in the literature until now. Therefore, this study aims to verify that the Kα and Kβ X-rays originated from filling of the K shell vacancies with total angular momentum quantum number 1/2 (J = 1/2) are isotropic. In this work, the typical K-shell X-ray spectra for Fe and V, which induced by bremsstrahlung with central energy of 13.1 keV, have been measured at emission angles varied from 120° to 170° at intervals of 10°. The characteristic X-ray spectra obtained by the detector are fitted by Gauss function, where the absorption of incident X-rays by the detector, the absorption of emitted X-rays by the atmosphere and the self-absorption correction factor of incident and emitted X-rays by the target are all taken into account. The experimental results of Kβ/Kα intensity ratio in this experiment coincide with those of theoretical calculation, as well as the Ertuğral’s experimental result. The experimental results show that the intensity ratio of Kβ/Kα is a constant at different detection angles. Therefore it can be concluded that the emission of Kα and Kβ is isotropic in the detection range. Since the K shell has no sub-shell, there is no Coster-Kronig transition in the collision ionization process. In the process of photoionization, the vacancies in the K shell are produced by direct ionization. As a result, the cross section ratio of K shell X-ray generation is independent of the K shell photoionization cross section. In addition, the experimental results show that the Kβ/Kα characteristic X-ray intensity ratio of target Fe is 8% higher than that of target V, which are consistent with the theoretical analysis results that the characteristic X-ray intensity ratio depends on the target atomic number Z. -
Keywords:
- angular distribution /
- photoionization /
- isotropy
[1] 王兴, 赵永涛, 程锐, 周贤明, 徐戈, 孙渊博, 雷瑜, 王瑜玉, 任洁茹, 虞洋, 李永峰, 张小安, 李耀宗, 梁昌慧, 肖国青 2012 61 193201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X, Zhao Y T, Cheng R, Zhou X M, Xu G, Sun Y B, Lei Y, Wang Y Y, Ren J R, Yu Y, Li Y F, Zhang X A, Li Y Z, Liang C H, Xiao G Q 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 193201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Horvat V, Watson R L, Blackadar J M 2008 Phys. Rev. A 77 032724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 梁昌慧, 张小安, 李耀宗, 赵永涛, 周贤明, 王兴, 梅策香, 肖国青 2018 67 243201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang C H, Zhang X A, Li Y Z, Zhao Y T, Zhou X M, Wang X, Mei C X, Xiao G Q 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 243201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Han I, Şahin M, Demir L 2009 Appl. Radiat. Isot. 67 1027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Salem S, Stöhlker, T, Demian A B, Hagmann S, Kozhuharov C, Liesen D, Gumberidze A 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 012701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Šmit Ž 2005 Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 240 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Romo-Kröger C M 2010 Vacuum 84 1250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ma K, Dong C Z, Xie L Y, Qu Y Z 2014 Chin. Phys.Lett. 31 103201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 牟致栋, 魏琦瑛 2014 63 083402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mu Z D, Wei Q Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 083402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Freemantle C S, Sacks N, Topic M, Pineda-vargas C A 2014 Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 318 168
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kada W, Kishi A, Sueyasu M, Sato F, Kato Y, Iida T 2014 Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 318 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fernandez J E, Scot V, Verardi L, Salvat F 2014 Radiat. Phys. Chem. 95 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Flugge S, Mehlhorn W, Schmidt V 1972 Phys. Rev. Lett. 29 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 马堃, 颉录有, 张登红, 董晨钟, 屈一至 2016 65 083201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma K, Xie L Y, Zhang D H, Dong C Z, Qu Y Z 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 083201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang X, Xu Z F, Cheng L 2016 Radiat. Phys. Chem. 122 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Slivinsky V W, Ebert P J 1969 Phys. Lett. A 29 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ertugrul M, Sogut O, Simsek O, Buyukkasap E 2001 J. Phys. B: At.Mol. Opt. Phys. 34 909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Richard P, Bonner T I, Furuta T, Morgan I L, Rhodes J R 1970 Phys. Rev. A 1 1044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li T K, Watson R L 1974 Phys. Rev. A 9 1574
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Salem S I, Wimmer R J 1970 Phys. Rev. A 2 1121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yalçın P 2007 Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 254 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Apaydın G, Aylıkcı V, Cengiz E, Kaya N, Kobya Y, Tıraşoğlu E 2008 Radiat. Phys. Chem. 77 923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Akkus T, Sahin Y, Yılmaz D, Tuzluca F N 2017 Can. J. Phys. 95 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ertuğral B, Apaydın G, Cevika U, Ertuğrul M, Kobya A I 2007 Radiat.Phys.Chem. 76 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Scofield J H 1974 Phys. Rev. A 9 1041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Scofield J H 1974 At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 14 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Manson S T, Kennedy D J 1974 At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 14 111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Berezhko E G, Kabachnik N M 1977 J. Phys. B: At.Mol. Opt. Phys. 10 2467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kanaya K, Okayama S 1972 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 5 43
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yadav N, Bhatt P, Singh R, Llovet X, Shanker R 2011 Appl. Radiat. Isot. 69 1380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] 王兴, 赵永涛, 程锐, 周贤明, 徐戈, 孙渊博, 雷瑜, 王瑜玉, 任洁茹, 虞洋, 李永峰, 张小安, 李耀宗, 梁昌慧, 肖国青 2012 61 193201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X, Zhao Y T, Cheng R, Zhou X M, Xu G, Sun Y B, Lei Y, Wang Y Y, Ren J R, Yu Y, Li Y F, Zhang X A, Li Y Z, Liang C H, Xiao G Q 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 193201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Horvat V, Watson R L, Blackadar J M 2008 Phys. Rev. A 77 032724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 梁昌慧, 张小安, 李耀宗, 赵永涛, 周贤明, 王兴, 梅策香, 肖国青 2018 67 243201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang C H, Zhang X A, Li Y Z, Zhao Y T, Zhou X M, Wang X, Mei C X, Xiao G Q 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 243201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Han I, Şahin M, Demir L 2009 Appl. Radiat. Isot. 67 1027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Salem S, Stöhlker, T, Demian A B, Hagmann S, Kozhuharov C, Liesen D, Gumberidze A 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 012701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Šmit Ž 2005 Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 240 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Romo-Kröger C M 2010 Vacuum 84 1250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ma K, Dong C Z, Xie L Y, Qu Y Z 2014 Chin. Phys.Lett. 31 103201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 牟致栋, 魏琦瑛 2014 63 083402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mu Z D, Wei Q Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 083402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Freemantle C S, Sacks N, Topic M, Pineda-vargas C A 2014 Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 318 168
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kada W, Kishi A, Sueyasu M, Sato F, Kato Y, Iida T 2014 Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 318 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fernandez J E, Scot V, Verardi L, Salvat F 2014 Radiat. Phys. Chem. 95 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Flugge S, Mehlhorn W, Schmidt V 1972 Phys. Rev. Lett. 29 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 马堃, 颉录有, 张登红, 董晨钟, 屈一至 2016 65 083201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma K, Xie L Y, Zhang D H, Dong C Z, Qu Y Z 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 083201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang X, Xu Z F, Cheng L 2016 Radiat. Phys. Chem. 122 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Slivinsky V W, Ebert P J 1969 Phys. Lett. A 29 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ertugrul M, Sogut O, Simsek O, Buyukkasap E 2001 J. Phys. B: At.Mol. Opt. Phys. 34 909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Richard P, Bonner T I, Furuta T, Morgan I L, Rhodes J R 1970 Phys. Rev. A 1 1044
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li T K, Watson R L 1974 Phys. Rev. A 9 1574
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Salem S I, Wimmer R J 1970 Phys. Rev. A 2 1121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yalçın P 2007 Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 254 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Apaydın G, Aylıkcı V, Cengiz E, Kaya N, Kobya Y, Tıraşoğlu E 2008 Radiat. Phys. Chem. 77 923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Akkus T, Sahin Y, Yılmaz D, Tuzluca F N 2017 Can. J. Phys. 95 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ertuğral B, Apaydın G, Cevika U, Ertuğrul M, Kobya A I 2007 Radiat.Phys.Chem. 76 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Scofield J H 1974 Phys. Rev. A 9 1041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Scofield J H 1974 At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 14 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Manson S T, Kennedy D J 1974 At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 14 111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Berezhko E G, Kabachnik N M 1977 J. Phys. B: At.Mol. Opt. Phys. 10 2467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kanaya K, Okayama S 1972 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 5 43
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yadav N, Bhatt P, Singh R, Llovet X, Shanker R 2011 Appl. Radiat. Isot. 69 1380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8767
- PDF下载量: 96
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: