-
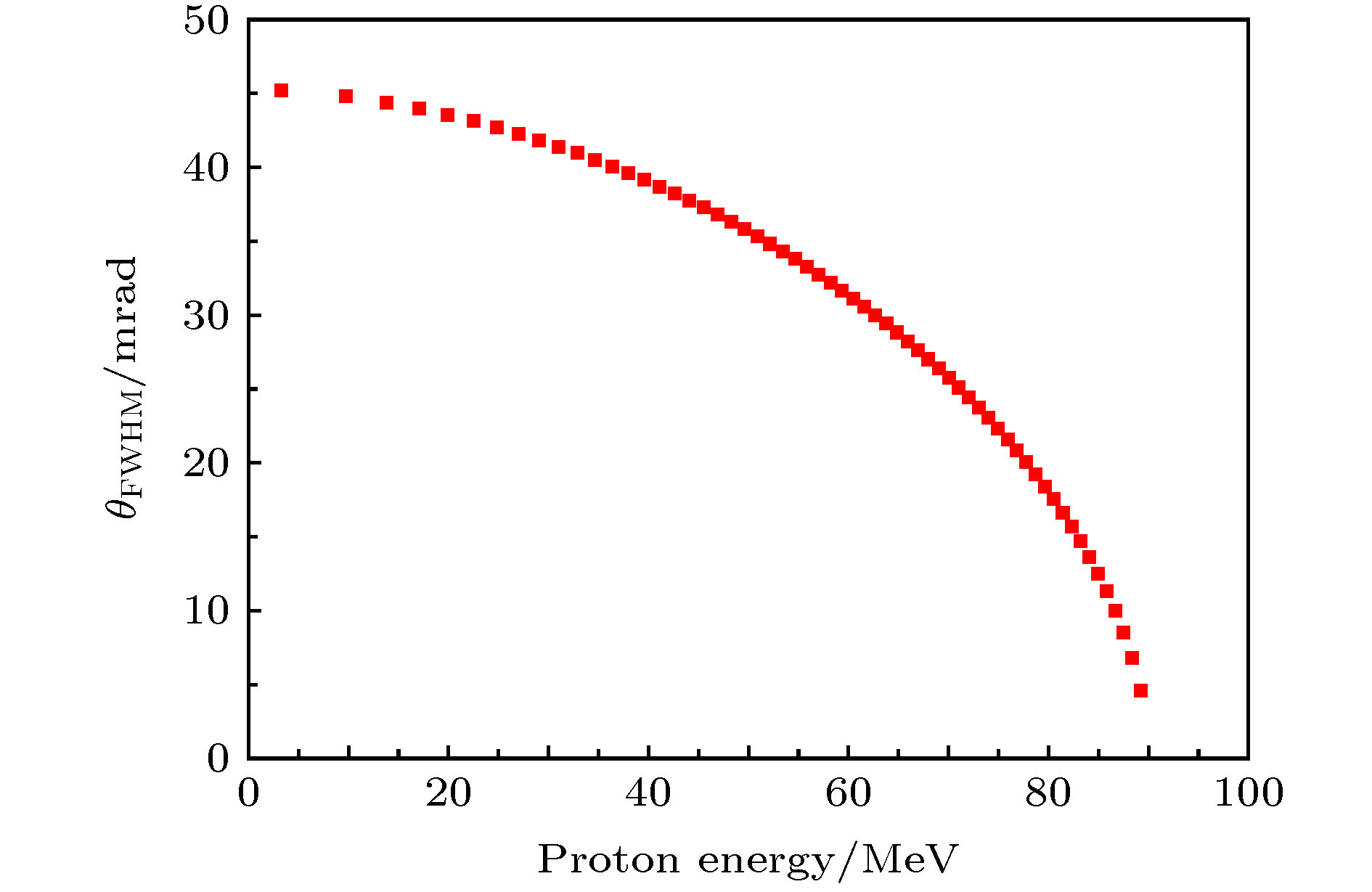
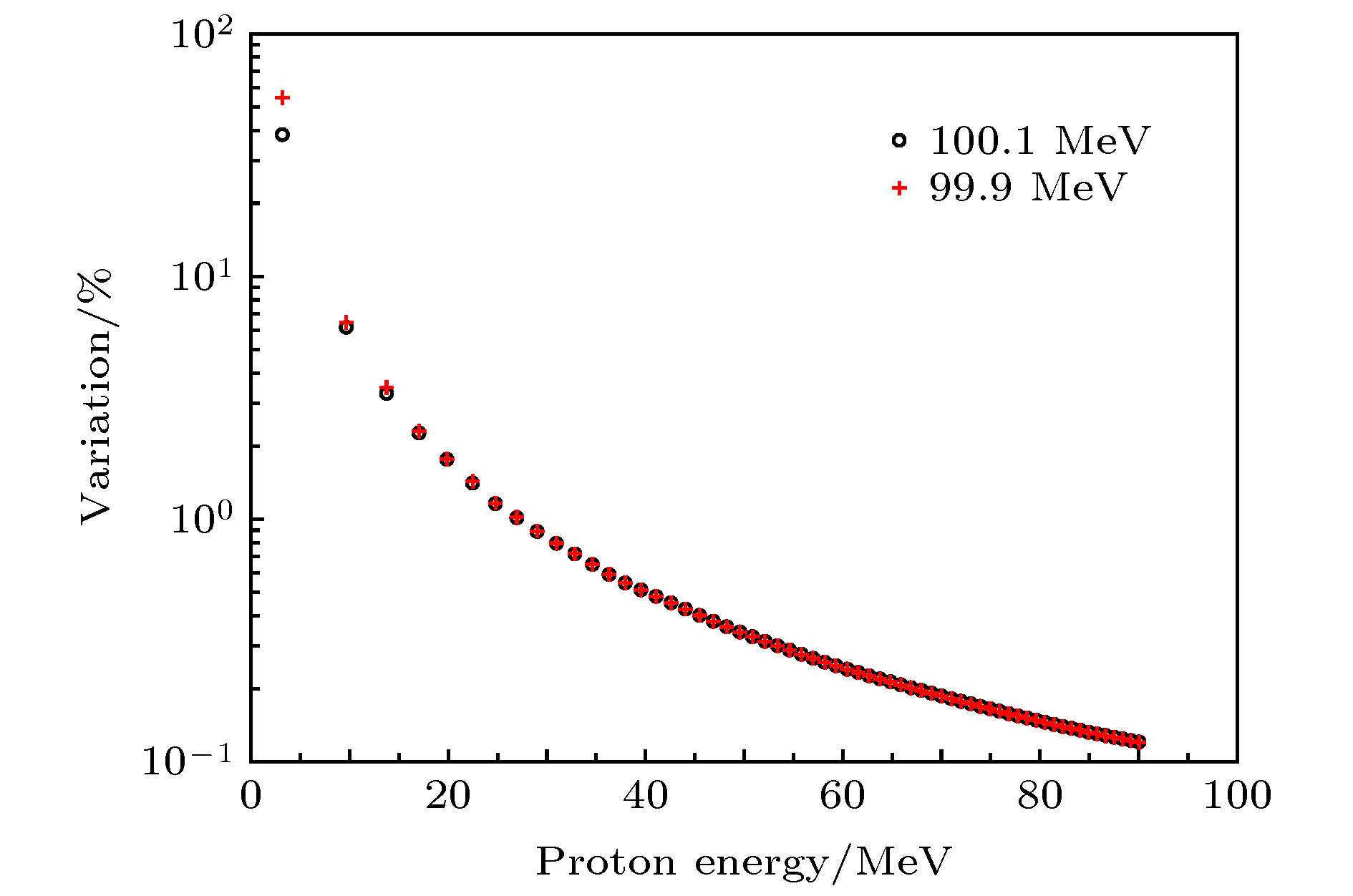
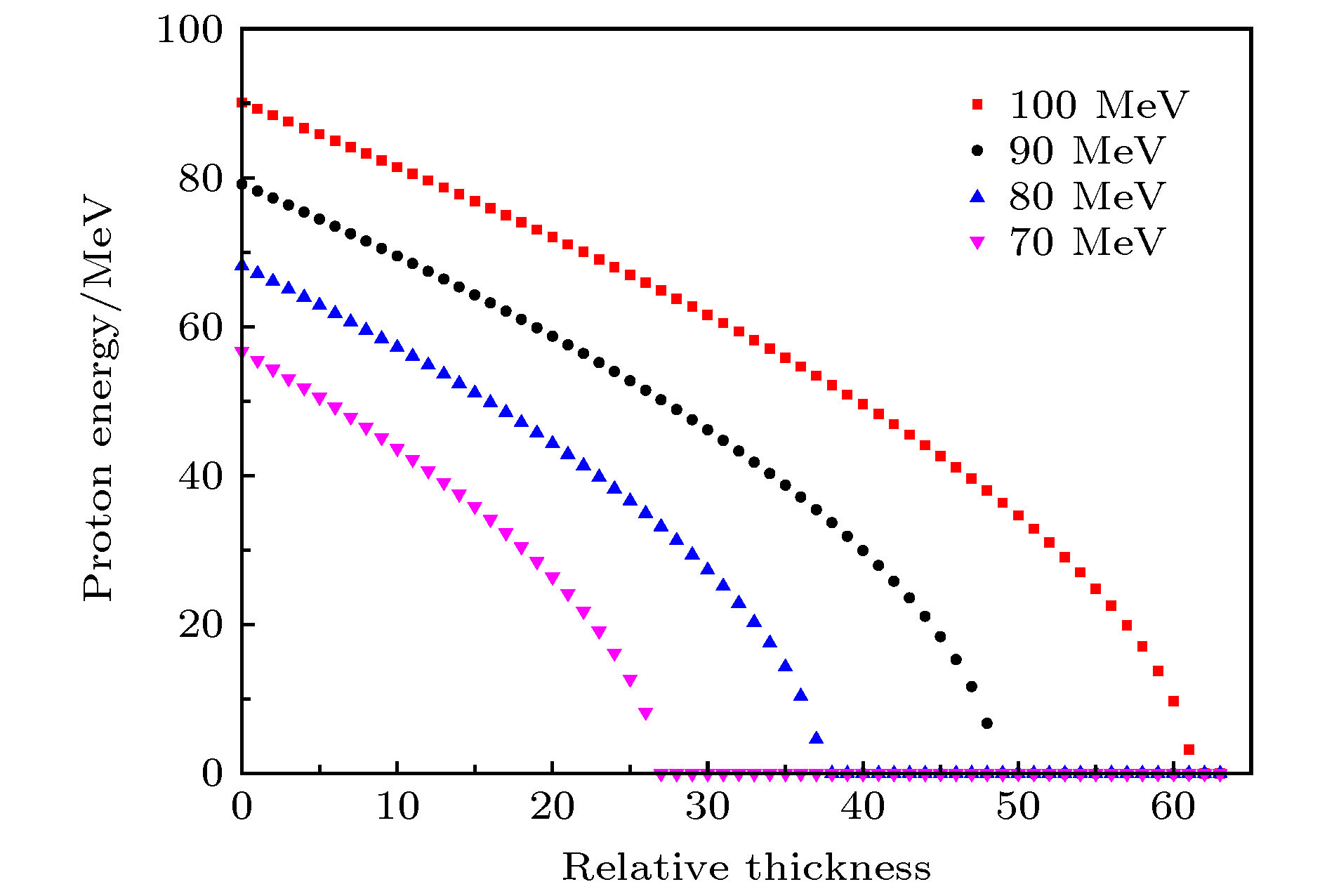
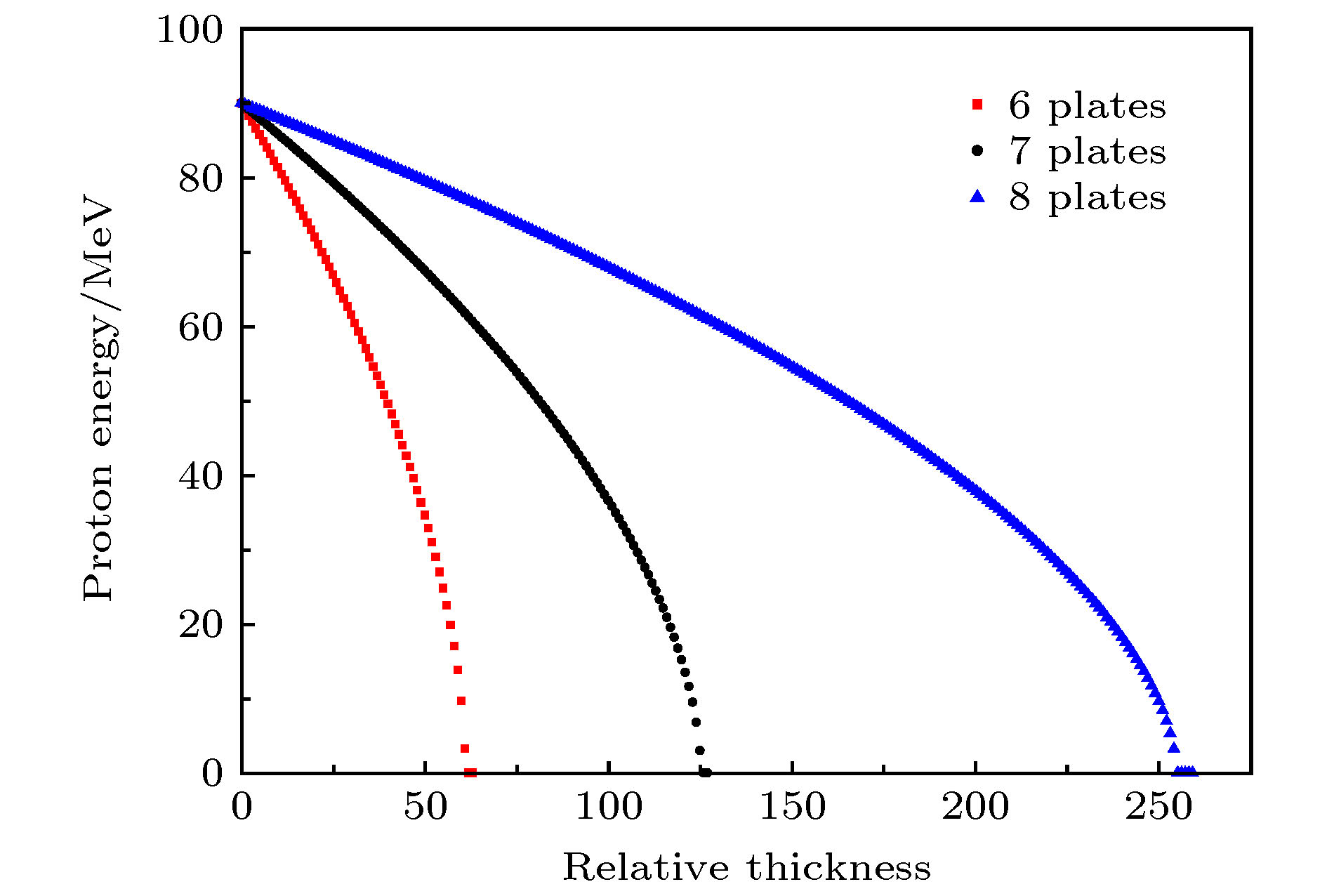
为提升在中国原子能科学研究院的100 MeV质子回旋加速器上进行多能点质子单粒子效应实验的效率, 针对该加速器提供的100 MeV质子设计了一种二进制降能器. 降能器包括6片铝降能片, 厚度分别为0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 mm, 即后一片厚度均为前一片的2倍. 提出相对厚度的概念, 此概念也可用来表示产生的质子能点的次序以及降能器的状态或操作. 降能器产生的9.69 MeV以上的61个质子能点间隔在0.84—4.09 MeV之间, 且能量岐离均在10%以下, 散射角半高宽均在45 mrad以下, 基本可满足质子单粒子效应实验的要求. 对加速器直接提供的质子的能量精度对降能器产生的质子能点的影响进行分析, 发现经降能器产生的质子能量越低, 其影响也就越大. 此外, 降能器对加速器直接能够提供的70—100 MeV能区的质子也是适用的, 且可通过增加降能片数量的方式来获得更加连续化的质子能点. 本文提出的降能器设计方法简单有效, 具有较强的借鉴价值.In order to improve the efficiency of the single event effect (SEE) experiments on the 100 MeV proton cyclotron of China Institute of Atomic Energy, a binary energy degrader that can lower the initial proton energy to other values rapidly is designed for the 100 MeV protons provided by the accelerator. The energy degrader is comprised of six aluminum plates of 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 mm at thickness, where the thickness of the latter plate is twice that of the previous one. We introduce the concept of relative thickness, which can also represent the order of the energy of the produced protons, and the state or operation of the degrader. The energy interval of 61 protons with energy above 9.69 MeV, produced by the degrader, is between 0.84 MeV and 4.09 MeV. And their energy straggling degree is less than 10%, and full width at half maximum of the scattering angle is less than 45 mrad. So the energy degrader basically meets the requirements of the proton SEE experiments. The influence of the initial proton energy accuracy of the protons directly provided by the accelerator on the residual energy after they have passed through the degrader is discussed. It is found that the lower the residual energy, the greater the influence is. In addition, the degrader is also suitable for protons in the 70-100 MeV energy range that the accelerator can directly provide, and more continuous energy can be obtained by using more plates designed with this method. The design method of the energy reducer proposed in this paper is simple and effective, and has a strong reference value.
-
Keywords:
- energy degrader /
- single event effects /
- energy straggling /
- angle straggling
[1] 黄建国, 韩建伟 2004 中国科学G辑 47 540
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang J G, Han J W 2004 Science in China, Ser G 47 540
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Han J H, Guo G 2017 AIP Adv. 7 115220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 罗尹虹, 张凤祁, 郭红霞, 郭晓强, 赵雯, 丁李利, 王园明 2015 64 216103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo Y H, Zhang F Q, Guo H X, Guo X Q, Zhao W, Ding L L, Wang Y M 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 216103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 赵雯, 郭晓强, 陈伟, 邱孟通, 罗尹虹, 王忠明, 郭红霞 2015 64 178501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao W, Guo X Q, Chen W, Qiu M T, Luo Y H, Wang Z M, Guo H X 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 178501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 罗尹虹, 张凤祁, 王燕萍, 王圆明, 郭晓强, 郭红霞 2016 65 068501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo Y H, Zhang F Q, Wang Y P, Wang Y M, Guo X Q, Guo H X 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 068501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 何安林, 郭刚, 陈力, 沈东军, 任义, 刘建成, 张志超, 蔡莉, 史淑廷, 王惠, 范辉, 高丽娟, 孔福全 2014 原子能科学技术 48 2364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He A L, Guo G, Chen L, Shen D J, Ren Y, Liu J C, Zhang Z C, Cai L, Shi S T, Wang H, Fan H, Gao L J, Kong F Q 2014 Atom. Energ. Sci. Technol. 48 2364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 杨海亮, 李国政, 李原春, 姜景和, 贺朝会, 唐本奇 2001 原子能科学技术 35 490
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang H L, Li G Z, Li Y C, Jiang J H, He C H, Tang B Q 2001 Atom. Energ. Sci. Technol. 35 490
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 张付强, 郭刚, 刘建成, 陈启明 2018 原子能科学技术 52 1
Zhang F Q, Guo G, Liu J C, Chen Q M 2018 Atom. Energ. Sci. Technol. 52 1
[9] Hajdas W, Burri F, Eggle C, Harboe-Sorensen R and Marino R 2002 Proc. IEEE Radiat. Effects Data Workshop Phoenix, Arizona, American, 2002 p160
[10] 韩金华, 郭刚, 刘建成, 隋丽, 孔福全, 肖舒颜, 覃英参, 张艳文 2019 68 054104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han J H, Guo G, Liu J C, Sui L, Kong F Q, Xiao S Y, Qin Y C, Zhang Y W 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 054104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ziegler J F http://www.srim.org. [2019-10-6]
[12] Ziegler J F, Ziegler M D, Biersack J P 2010 Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B 268 1818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 复旦大学, 清华大学, 北京大学 1985 原子核物理实验方法(上册) (第2版) (北京: 原子能出版社) 第57−60页
Fudan University, Tsinghua University, Peking University 1985 Nuclear Physics Experimental Methods (Part I) (2nd Ed.) (Beijing: Atomic Energy Press) pp57−60 (in Chinese)
[14] Zhang Z G, Liu J, Hou M D, Sun Y M, Zhao F Z, Liu G, Han Z S, Geng C, Liu J D, Xi K, Duan J L, Yao H J, Mo D, Luo J, Gu S, and Liu T Q 2013 Chin. Phys. B 22 096103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yang Q, O’Connor D J, Wang Z L 1991 Nucl. Instr. and Meth. B 61 149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lynch G R, Dahl O I 1991 Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B 58 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gottschalk B, Koehler A M, Schneider R J, Sisterson J M, Wagner M S 1993 Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B 74 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Particle Data Group 2004 Physics Lett. B 592 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 余建国, 郁庆长 1997 高能物理与核物理 21 851
Yu J G, Yu Q C 1997 High Energ. Phys. Nuc. 21 851
[20] 鞠志萍, 曹午飞, 刘小伟 2009 58 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ju Z P, Cao W F, Liu X W 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] 黄建国, 韩建伟 2004 中国科学G辑 47 540
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang J G, Han J W 2004 Science in China, Ser G 47 540
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Han J H, Guo G 2017 AIP Adv. 7 115220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 罗尹虹, 张凤祁, 郭红霞, 郭晓强, 赵雯, 丁李利, 王园明 2015 64 216103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo Y H, Zhang F Q, Guo H X, Guo X Q, Zhao W, Ding L L, Wang Y M 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 216103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 赵雯, 郭晓强, 陈伟, 邱孟通, 罗尹虹, 王忠明, 郭红霞 2015 64 178501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao W, Guo X Q, Chen W, Qiu M T, Luo Y H, Wang Z M, Guo H X 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 178501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 罗尹虹, 张凤祁, 王燕萍, 王圆明, 郭晓强, 郭红霞 2016 65 068501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo Y H, Zhang F Q, Wang Y P, Wang Y M, Guo X Q, Guo H X 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 068501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 何安林, 郭刚, 陈力, 沈东军, 任义, 刘建成, 张志超, 蔡莉, 史淑廷, 王惠, 范辉, 高丽娟, 孔福全 2014 原子能科学技术 48 2364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He A L, Guo G, Chen L, Shen D J, Ren Y, Liu J C, Zhang Z C, Cai L, Shi S T, Wang H, Fan H, Gao L J, Kong F Q 2014 Atom. Energ. Sci. Technol. 48 2364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 杨海亮, 李国政, 李原春, 姜景和, 贺朝会, 唐本奇 2001 原子能科学技术 35 490
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang H L, Li G Z, Li Y C, Jiang J H, He C H, Tang B Q 2001 Atom. Energ. Sci. Technol. 35 490
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 张付强, 郭刚, 刘建成, 陈启明 2018 原子能科学技术 52 1
Zhang F Q, Guo G, Liu J C, Chen Q M 2018 Atom. Energ. Sci. Technol. 52 1
[9] Hajdas W, Burri F, Eggle C, Harboe-Sorensen R and Marino R 2002 Proc. IEEE Radiat. Effects Data Workshop Phoenix, Arizona, American, 2002 p160
[10] 韩金华, 郭刚, 刘建成, 隋丽, 孔福全, 肖舒颜, 覃英参, 张艳文 2019 68 054104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han J H, Guo G, Liu J C, Sui L, Kong F Q, Xiao S Y, Qin Y C, Zhang Y W 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 054104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ziegler J F http://www.srim.org. [2019-10-6]
[12] Ziegler J F, Ziegler M D, Biersack J P 2010 Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B 268 1818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 复旦大学, 清华大学, 北京大学 1985 原子核物理实验方法(上册) (第2版) (北京: 原子能出版社) 第57−60页
Fudan University, Tsinghua University, Peking University 1985 Nuclear Physics Experimental Methods (Part I) (2nd Ed.) (Beijing: Atomic Energy Press) pp57−60 (in Chinese)
[14] Zhang Z G, Liu J, Hou M D, Sun Y M, Zhao F Z, Liu G, Han Z S, Geng C, Liu J D, Xi K, Duan J L, Yao H J, Mo D, Luo J, Gu S, and Liu T Q 2013 Chin. Phys. B 22 096103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yang Q, O’Connor D J, Wang Z L 1991 Nucl. Instr. and Meth. B 61 149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lynch G R, Dahl O I 1991 Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B 58 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gottschalk B, Koehler A M, Schneider R J, Sisterson J M, Wagner M S 1993 Nucl.Instr. and Meth. B 74 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Particle Data Group 2004 Physics Lett. B 592 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 余建国, 郁庆长 1997 高能物理与核物理 21 851
Yu J G, Yu Q C 1997 High Energ. Phys. Nuc. 21 851
[20] 鞠志萍, 曹午飞, 刘小伟 2009 58 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ju Z P, Cao W F, Liu X W 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 13294
- PDF下载量: 101
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: