-
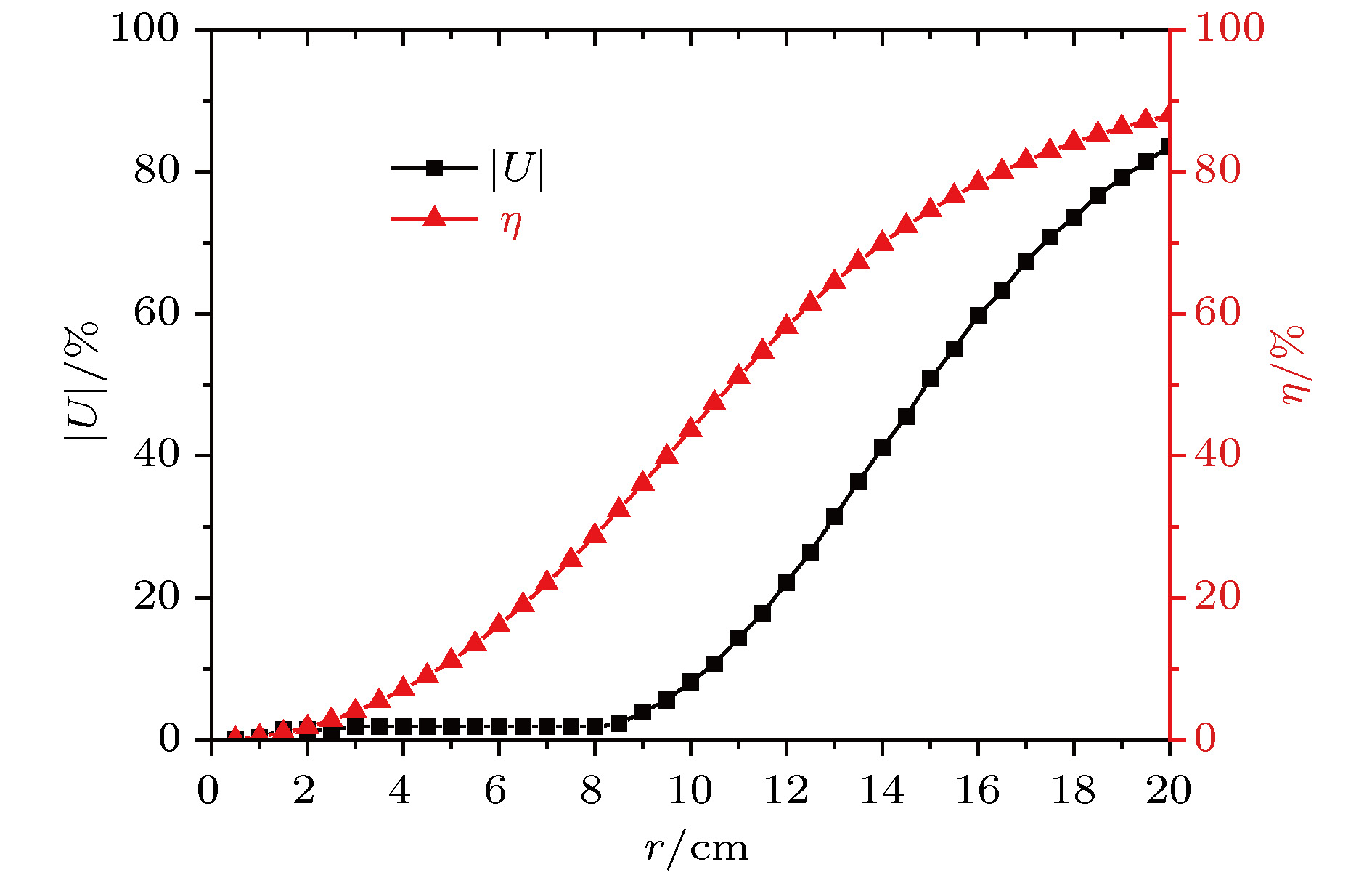
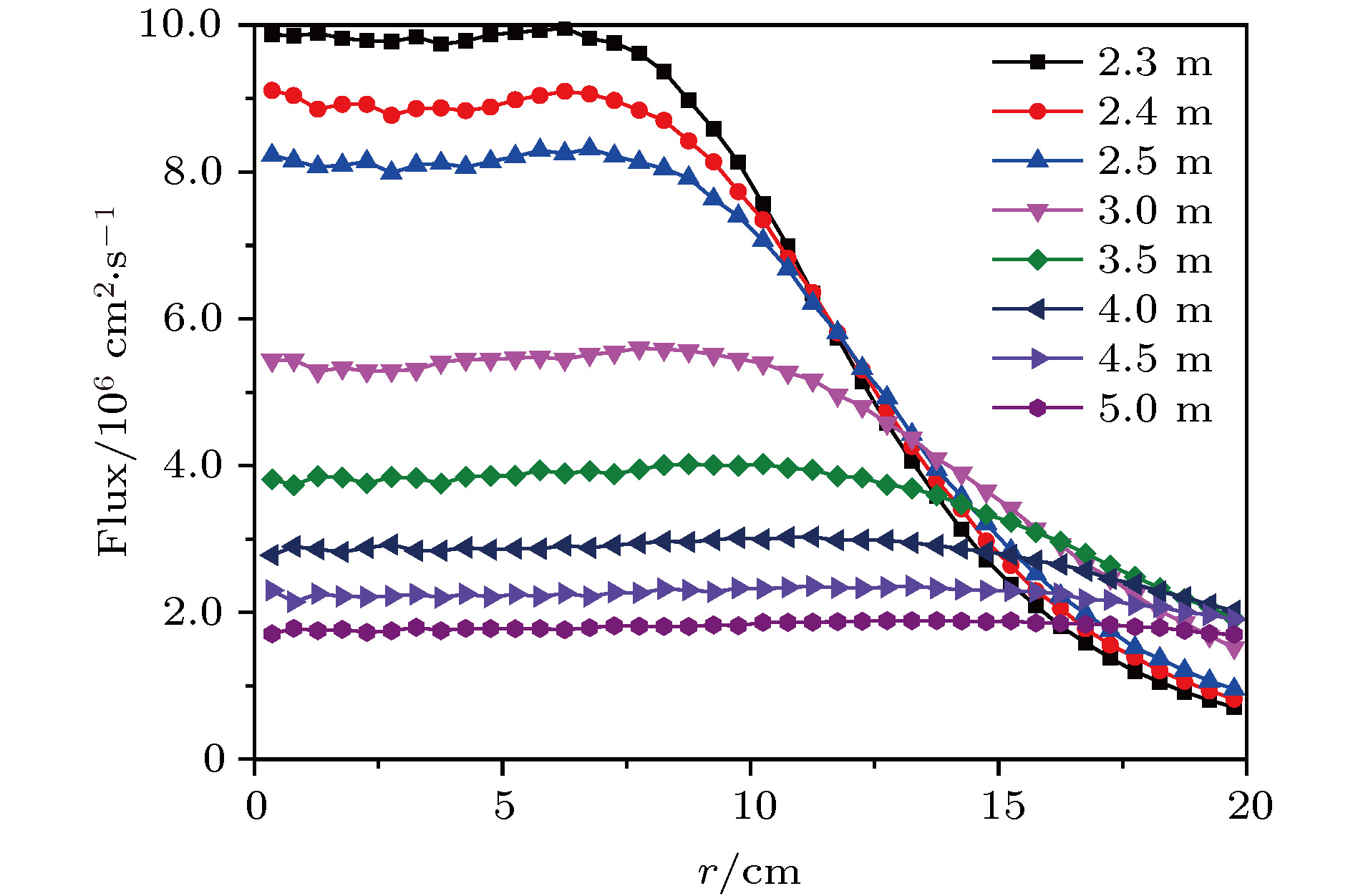
为满足质子单粒子效应实验对大面积、均匀化质子束流的需求, 针对中国原子能科学研究院100 MeV质子回旋加速器提供的100 MeV质子进行了双环双散射体扩束方案设计. Geant4模拟表明该方案可在2.4 m位置产生一个均匀性为 ±1.89%、半径为8 cm的照射野, 在5 m位置产生一个均匀性为 ±5.32%、半径为20 cm的照射野. 此外, 利用Geant4对双环双散射体扩束方法的基本原理进行了进一步探索, 并对第二散射体后加速器管道、初始束斑尺寸、照射野形成距离、改变入射质子能量等实际中各种可能因素对该方案扩束效果的影响进行了讨论.To obtain a large uniform beam field for proton single event effect (SEE) experiments, the double-ring double scattering method (DDSM) is employed for spreading the 100 MeV proton beam provided by the 100 MeV proton cyclotron at China Institute of Atomic Energy. With the Geant 4 simulations, the fundamentals of the DDSM are further explored, the achieved effect of our DDSM scheme design is presented, and the influences of some possible factors in practice on the produced beam field are discussed. We find that the the outer part of the second scatter plays an important role in enlarging the area of the uniform field and improving its uniformity. We also find that the first scatter and the inner part of the second scatter play a decisive role in determining the proton flux of the uniform area. The scattering between the spread proton beam and the accelerator tube behind the second scatter damages the uniformity and leads the energy of the produced beam field to straggle. Therefore, the tube should be made as short as possible. The size of the initial beam spot on the first scatter affects the produced beam field to some extent. The spot should be focused as much as possible in a circle with a radius of 0.5 cm. At a larger distance, a larger uniform field can be produced due to the spreading of the proton beam along the space. The decrease in the incident proton energy causes the flux and uniformity to decrease, and also leads the energy loss to increase and the energy of the produced proton beam field to straggle. Using our DDSM schematic design, the simulations show that an 8-cm-diameter beam field with a uniformity of ±1.89% can be produced at a distance of 2.4 m, thereby meeting the need for an SEE experiment of a device-level sample, and that a 20-cm-radius beam field with a uniformity of ±5.32% can be created at a distance of 5.0 m, thereby meeting the need for an SEE experiment of a system-level sample of comparable size. By taking into consideration the uniformity and energy straggling, our design is basically applicable to the protons in the 70−100 MeV energy region that the accelerator can provide directly.
-
Keywords:
- dual-ring double scattering /
- single event effects /
- beam spreading /
- uniformity
[1] 赵雯, 郭晓强, 陈伟, 邱孟通, 罗尹虹, 王忠明, 郭红霞 2015 64 178501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao W, Guo X Q, Chen W, Qiu M T, Luo Y H, Wang Z M, Guo H X 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 178501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Mcmahan M A, Blackmore E, Cascio E W, Castaneda C, Przewoski B, Eisen H 2008 Proc. IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop Tucson, Arizona, American, 2008 p135
[3] Hajdas W, Burri F, Eggle C, Harboe-Sorensen R, Marino R 2002 Proc. IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop Phoenix, Arizona, American, 2002 p160
[4] Blackmore E W 2000 Proc. IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop Reno Nevada, American, 2000 p1
[5] Przewoski B, Rinckel T, Manwaring W, Broxton G, Chipara M, Ellis T, Hall E R, Kinser A, Foster C C, Murray K M 2004 Proc. IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop Atlanta, Georgia, American, 2004 p145
[6] 鞠志萍 2009 博士学位论文(广州: 中山大学)
Ju Zh P 2009 Ph. D. Dissertation (Guangzhou: Sun Yat-sen University) (in Chinese)
[7] 余建国, 郁庆长 1997 高能物理与核物理 21 851
Yu J G, Yu Q C 1997 High Energy Physics and Nuclear Physics 21 851
[8] 鞠志萍, 曹午飞, 刘小伟 2009 58 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ju Z P, Cao W F, Liu X W 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Koehler A M, Schnelder R J, Sisterson J M 1977 Med. Phys. 4 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 鞠志萍, 曹午飞, 刘小伟 2010 59 199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ju Z P, Cao W F, Liu X W 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Grusell E, Montelius A, Brahme A, Rikner G, Russell K 1994 Phys. Med. Biol. 39 2201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Takada Y 1994 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 33 353
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Himukai T, Furukawa T, Takeshita E, Inaniwa T, Mizushima K, Katagiri K, Takada Y 2011 Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 269 2891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Highland V L 1975 Nucl. Instr. Meth. 129 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lynch G R, Dahl O I 1991 Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 58 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ziegler J F, Ziegler M D, Biersack J P 2010 Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 268 1818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Agostinelli S, Allisonet J, Amako K, et al. 2003 Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 506 250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Geant4 User’s Guide for Application Developers, available online at: http://geant4-userdoc.web.cern.ch/geant4-userdoc/UsersGuides/ForApplicationDeveloper/fo/BookForAppliDev.pdf [2018-9-1]
[19] Gottschalk B, Koehler A M, Schneider R J, Sisterson J M, Wagner M S 1993 Nucl. Instr. Meth. 74 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 丁富荣, 班勇, 夏宗璜 2004 辐射物理 (北京: 北京大学出版社) 第10页
Ding F R, Ban Y, Xia Z H 2004 Radiation Physics (Beijing: Peking University Press) p10 (in Chinese)
[21] 复旦大学, 清华大学, 北京大学 1985 原子核物理实验方法(上册) (第二版)(北京: 原子能出版社) 第57—60页
Fudan University, Tsinghua University, Peking University 1985 Nuclear Physics Experimental Methods (Part I) (2nd edn.) (Beijing: Atomic Energy Press) pp57–60 (in Chinese)
-
图 2 以Pb, Ta, Cu, Al四种材料做第一散射体时, 100 MeV质子在其中损失的能量
$\Delta {E_1}$ 与束流在DUT位置形成的高斯分布的${1 / {\rm e}}$ 半径${R_1}$ 之间的关系Fig. 2. Relations between the 1/e radii of the produced Gaussian distributions at the DUT position and the energy losses for the 100 MeV protons with the Pb, Ta, Cu and Al foils as the first scatters.
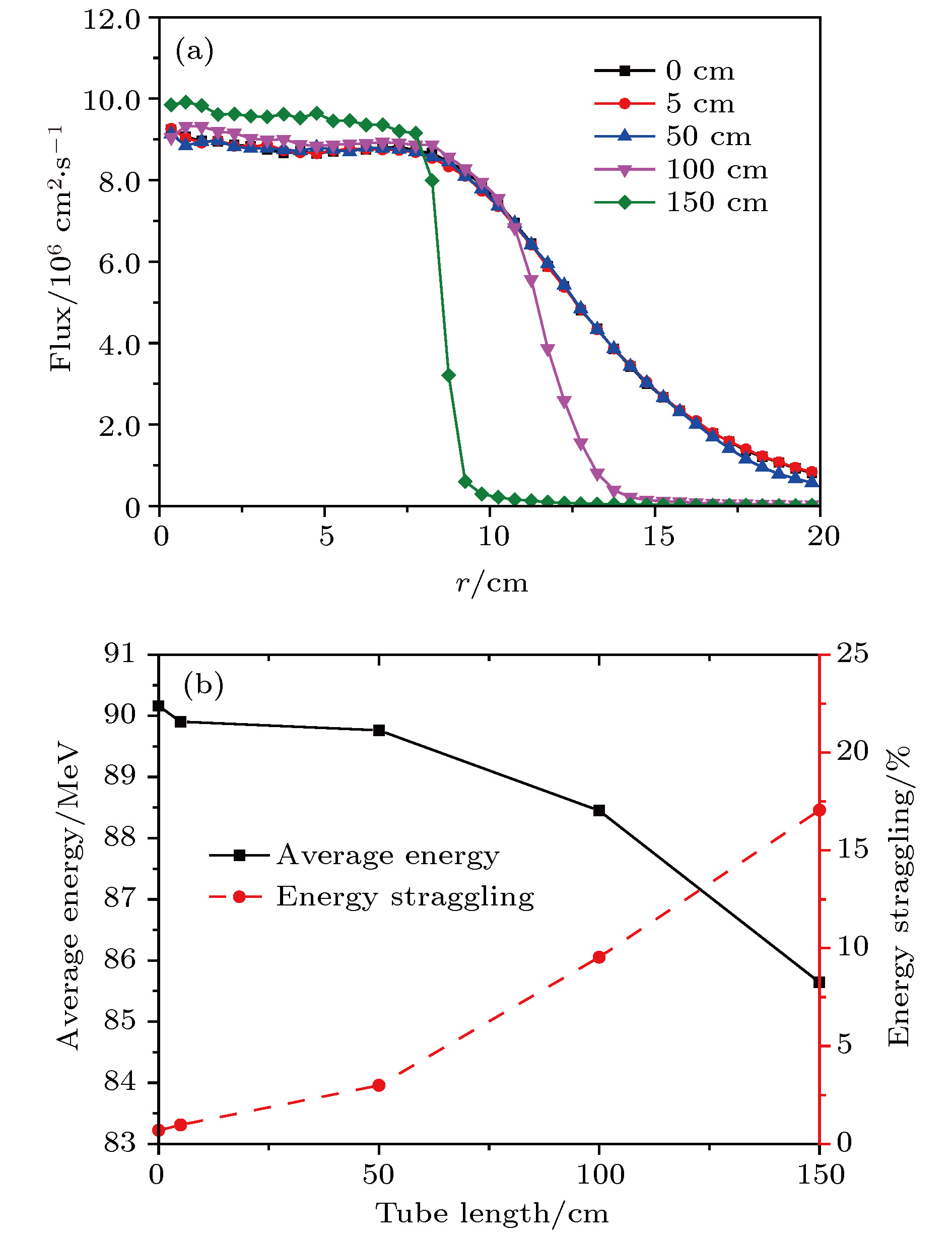
图 5 入射质子流强为1 nA时, 第二散射体之后采用0, 5, 50, 100, 150 cm长的管道时在DUT位置所产生的质子注量率分布(a)以及质子的平均能量和能散(b)
Fig. 5. Flux distributions (a), average energy and energy straggling (b) of the protons in the produced beam fields at the DUT position with the 0, 5, 50, 100 and 150 cm accelerator tubes behind the second scatter for 1 nA incident proton beams.
-
[1] 赵雯, 郭晓强, 陈伟, 邱孟通, 罗尹虹, 王忠明, 郭红霞 2015 64 178501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao W, Guo X Q, Chen W, Qiu M T, Luo Y H, Wang Z M, Guo H X 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 178501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Mcmahan M A, Blackmore E, Cascio E W, Castaneda C, Przewoski B, Eisen H 2008 Proc. IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop Tucson, Arizona, American, 2008 p135
[3] Hajdas W, Burri F, Eggle C, Harboe-Sorensen R, Marino R 2002 Proc. IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop Phoenix, Arizona, American, 2002 p160
[4] Blackmore E W 2000 Proc. IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop Reno Nevada, American, 2000 p1
[5] Przewoski B, Rinckel T, Manwaring W, Broxton G, Chipara M, Ellis T, Hall E R, Kinser A, Foster C C, Murray K M 2004 Proc. IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop Atlanta, Georgia, American, 2004 p145
[6] 鞠志萍 2009 博士学位论文(广州: 中山大学)
Ju Zh P 2009 Ph. D. Dissertation (Guangzhou: Sun Yat-sen University) (in Chinese)
[7] 余建国, 郁庆长 1997 高能物理与核物理 21 851
Yu J G, Yu Q C 1997 High Energy Physics and Nuclear Physics 21 851
[8] 鞠志萍, 曹午飞, 刘小伟 2009 58 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ju Z P, Cao W F, Liu X W 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Koehler A M, Schnelder R J, Sisterson J M 1977 Med. Phys. 4 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 鞠志萍, 曹午飞, 刘小伟 2010 59 199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ju Z P, Cao W F, Liu X W 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Grusell E, Montelius A, Brahme A, Rikner G, Russell K 1994 Phys. Med. Biol. 39 2201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Takada Y 1994 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 33 353
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Himukai T, Furukawa T, Takeshita E, Inaniwa T, Mizushima K, Katagiri K, Takada Y 2011 Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 269 2891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Highland V L 1975 Nucl. Instr. Meth. 129 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lynch G R, Dahl O I 1991 Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 58 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ziegler J F, Ziegler M D, Biersack J P 2010 Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 268 1818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Agostinelli S, Allisonet J, Amako K, et al. 2003 Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 506 250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Geant4 User’s Guide for Application Developers, available online at: http://geant4-userdoc.web.cern.ch/geant4-userdoc/UsersGuides/ForApplicationDeveloper/fo/BookForAppliDev.pdf [2018-9-1]
[19] Gottschalk B, Koehler A M, Schneider R J, Sisterson J M, Wagner M S 1993 Nucl. Instr. Meth. 74 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 丁富荣, 班勇, 夏宗璜 2004 辐射物理 (北京: 北京大学出版社) 第10页
Ding F R, Ban Y, Xia Z H 2004 Radiation Physics (Beijing: Peking University Press) p10 (in Chinese)
[21] 复旦大学, 清华大学, 北京大学 1985 原子核物理实验方法(上册) (第二版)(北京: 原子能出版社) 第57—60页
Fudan University, Tsinghua University, Peking University 1985 Nuclear Physics Experimental Methods (Part I) (2nd edn.) (Beijing: Atomic Energy Press) pp57–60 (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 9163
- PDF下载量: 82
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: