-
Vector beams have been used in scientific and engineering researches due to their unique focusing properties. In recent years, many methods of generating the vector beams have been proposed, among which the spatial light modulator (SLM) is widely used based on the superposition principle with using orthogonally polarized beams. However, the energy waste is generally associated with these superposition methods. How to efficiently generate vector beams is still a hot topic. Recently, we proposed an efficient method to generate tunable vector beams by using two triangular common-path interferometers (TCPIs) as the beam splitting and combining system. However, due to the complex structure of the TCPI, the system is difficult to adjust and unstable. In addition, the optical system brings about a long optical path, and the vector beams consisting of non-eigen modes will be distorted obviously with a long distance propagation. In this paper, an improved method is proposed. We replace the TCPIs with a pair of beam displacers, which act as a beam splitter and combiner, respectively. In this setup, we can arbitrarily manipulate the polarization states and phase distributions of vector beams in real time by managing the phase diagrams load on the SLM. The whole optical system does not involve any diffractive optical elements, and has a higher conversion efficiency. The improved optical system is compact and stable, and makes the adjustment of coaxiality easier. The light energy utilization depends mainly on the reflectivity of SLM. The efficiency of generating vector beams is increased to 58% by using an SLM with a reflectivity value of 79%. Several typical vector beams with phases and tunable amplitude, including cylindrical vector beams, fractional vector beams, and vector beams with double singularities, double-mode, radially variant polarization distribution, and azimuthally and radially variant polarization distribution, are generated and verified well experimentally. This method is also expected to create high-power vector beams and play an important role in laser processing and light trapping.
-
Keywords:
- polarization /
- space light modulator /
- vector beam
[1] Zhan Q W 2009 Adv. Opt. Photon. 1 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Quabis S, Dorn R, Eberler M, Glöckl O, Leuchs G 2000 Opt. Commun. 179 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Dorn R, Quabis S, Leuchs G 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 233901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao Y Q, Zhan Q W, Zhang Y, Li Y P 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 848
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kozawa Y, Sato S 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang H F, Shi L P, Lukyanchuk B, Sheppard C, Chong C T 2008 Nat. Photonics 2 501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li P, Guo X Y, Qi S X, Han L, Zhang Y, Liu S, Li Y, Zhao J L 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 9831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu S, Wang M R, Li P, Zhang P, Zhao J L 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 2416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu S, Li P, Zhang Y, Gan X, Wang M, Zhao J 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 20774
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhou J, Zhang W, Liu Y, Ke Y, Liu Y, Luo H, Wen S 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 34276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wei B Y, Chen P, Hu W, Ji W, Zheng L Y, Ge S J, Ming Y, Chigrinov V, Lu Y Q 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 17484
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Cardano F, Marrucci L 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 776
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang Y, Li P, Liu S, Han L, Cheng H, Zhao J 2016 Opt. Express 24 28409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li P, Liu S, Peng T, Xie G, Gan X, Zhao J 2014 Opt. Express 22 7598
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li P, Wu D, Zhang Y, Liu S, Li Y, Qi S, Zhao J 2018 Photon. Res. 6 756
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Cheng H C, Li P, Liu S, Chen P, Han L, Zhang Y, Hu W, Zhao J L 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 111 141901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xie X S, Chen Y Z, Yang K, Zhou J Y 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 263901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Nieminen T A, Heckenberg N R, Rubinsztein D H 2008 Opt. Lett. 33 122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang X L, Chen J, Li Y, Ding J, Guo C S, Wang H T 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 253602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Milione G, Nguyen T A, Leach J, Nolan D A, Alfano R R 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 4887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Pohl D 1972 Appl. Phys. Lett. 20 266
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kozawa Y, Sato S 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 3063
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Bisson J F, Li J, Ueda K, Senatsky Y 2006 Opt. Express 14 3304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lai W J, Lim B C, Phua P B, Tiaw K S, Teo H H, Hong M H 2008 Opt. Express 16 15694
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Bomzon Z, Biener G, Kleiner V, Hasman E 2002 Opt. Lett. 27 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Cardano F, Karimi E, Slussarenko S, Marrucci L, de Lisio C, Santamato E 2012 Appl. Opt. 51 C1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yi X, Ling X, Zhang Z, Li Y, Zhou X, Liu Y, Chen S, Luo H, Wen S 2014 Opt. Express 22 17207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li P, Zhang Y, Liu S, Ma C J, Han L, Cheng H C, Zhao J L 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 2205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang Y, Li P, Ma C J, Liu S, Cheng H C, Zhao J L, Han L 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 4956
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Christian M, Alexander J, Severin F, Stefan B, Monika R M 2007 New J. Phys. 9 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Liu S, Li P, Peng T, Zhao J 2012 Opt. Express 20 21715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wang X L, Ding J P, Ni W J, Guo C S, Wang H T 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 3549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Liu S, Qi S X, Zhang Y, Li P, Wu D J, Han L, Zhao J L 2018 Photon. Res. 6 228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Liu S, Han L, Li P, Zhang Y, Cheng H, Zhao J 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 171112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
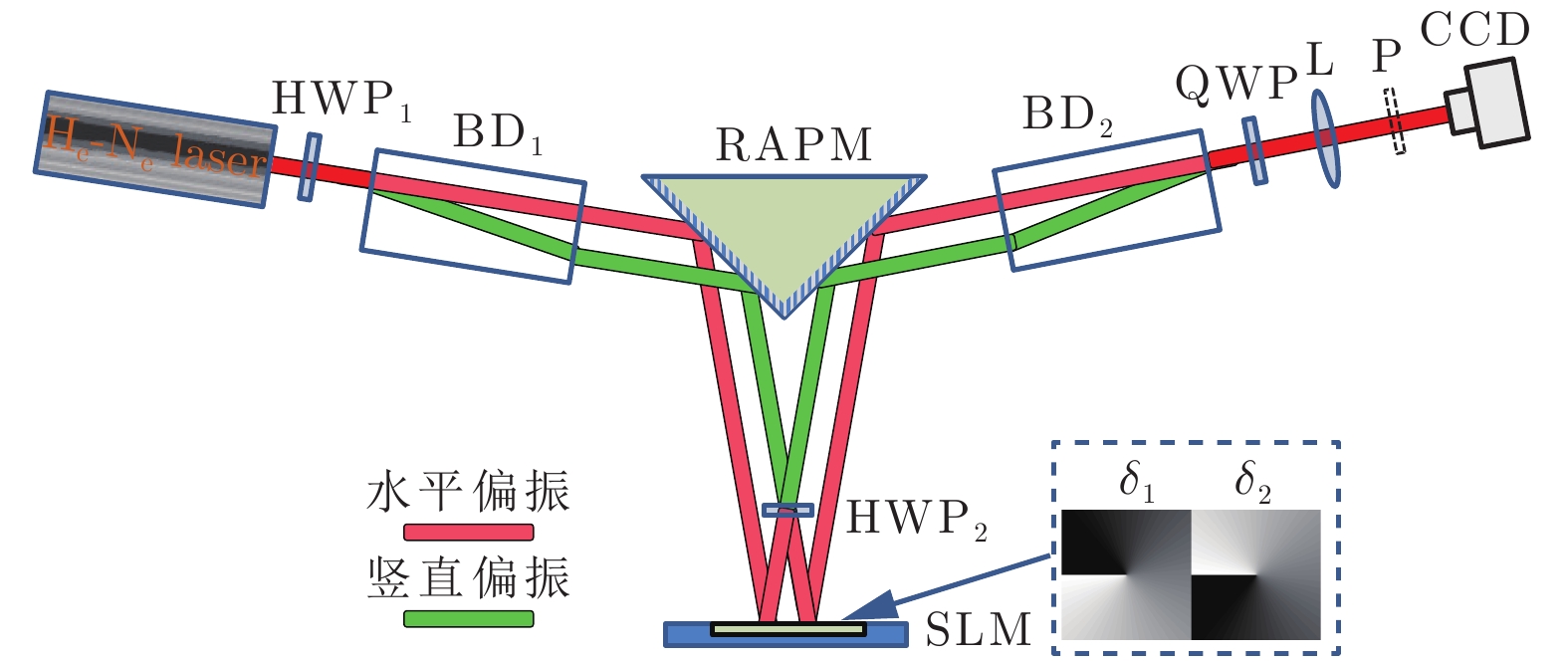
图 1 可产生任意矢量光场的实验光路 HWP, 半波片; BD, 光束偏移器; RAPM, 直角反射棱镜; SLM, 空间光调制器; QWP, 1/4波片; L, 透镜; P, 检偏器; CCD, 电荷耦合器件; 插图表示±1阶相位
Fig. 1. Experimental setup for generating arbitrary vector beams. HWP, half-wave plate; BD, beam displacer; RAPM, right-angle prism mirror; SLM, spatial light modulator; QWP, quarter-wave plate; L, lens; P, polarizer; CCD, charge-coupled device; the inset shows the first-order helix phase map.
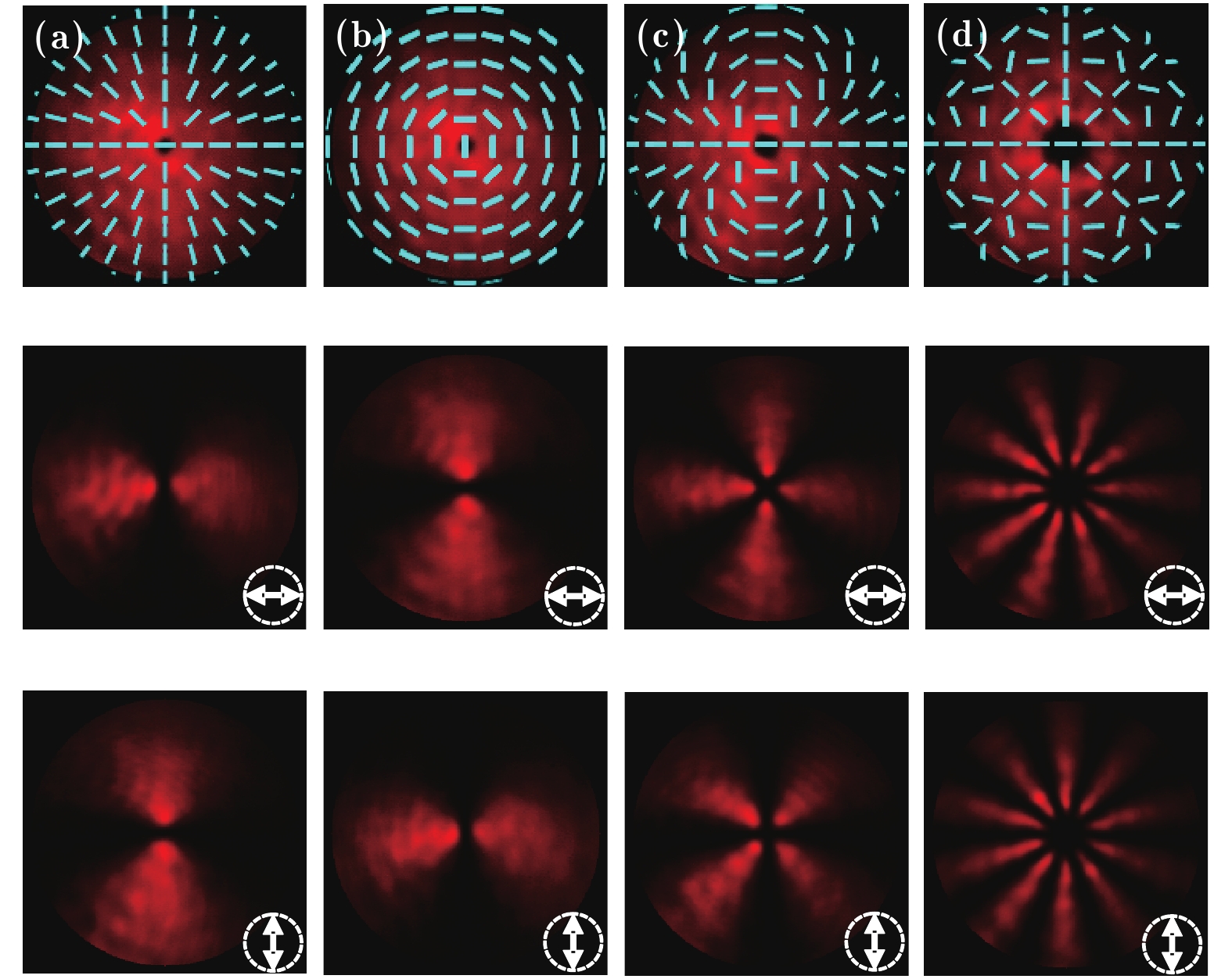
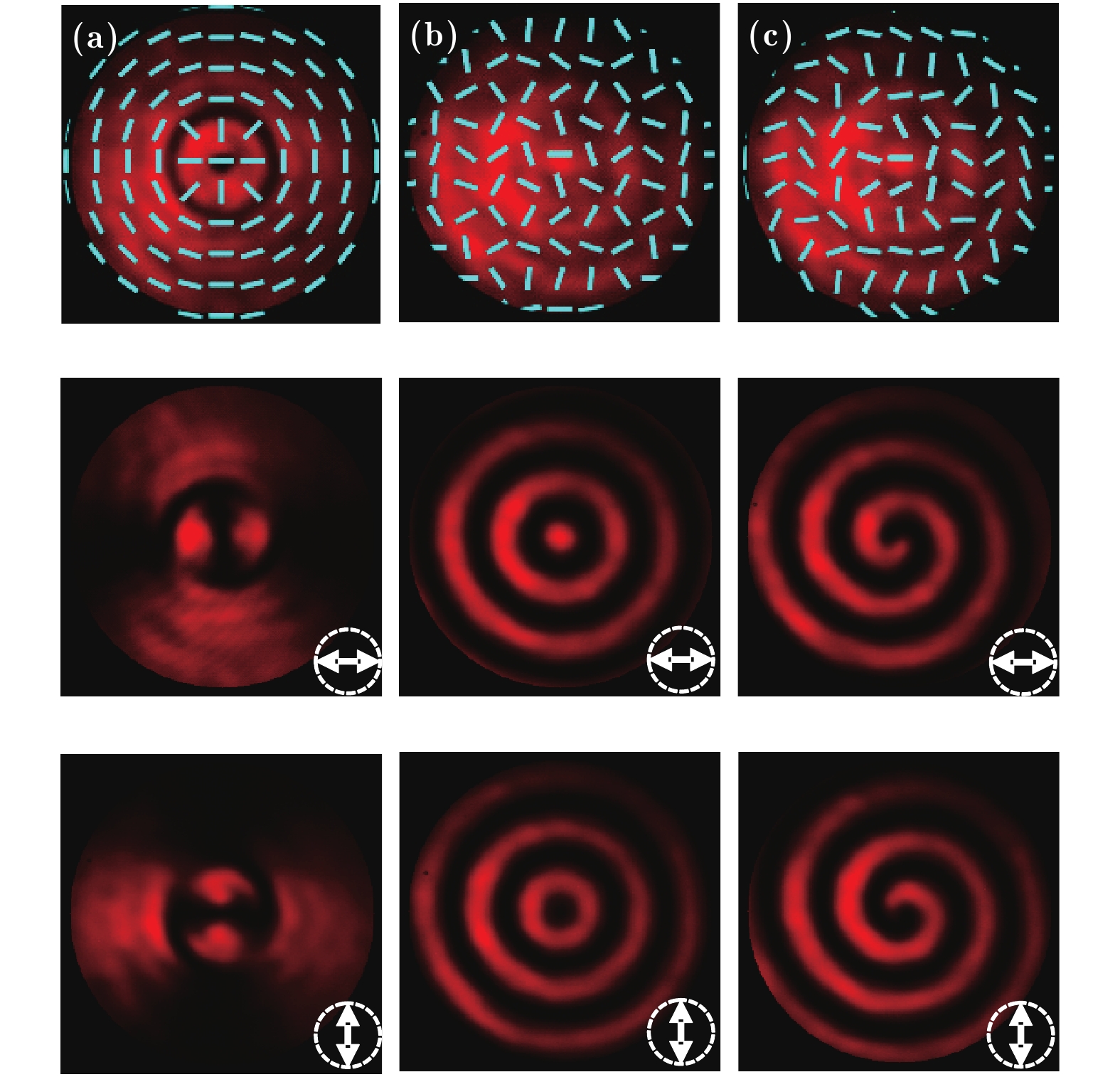
图 2 柱矢量光场的实验产生结果 (a) m = 1,
$ \phi$ 0 = 0; (b) m = 1,$ \phi$ 0 =$ \text{π}$ /2; (c) m = 2,$ \phi$ 0 = 0; (d) m = 5,$ \phi$ 0 = 0; 第一行为光场强度分布和偏振态分布(由短线表示);第二、三行为分别经水平和竖直方向检偏后的光场强度分布Fig. 2. Experiment results of cylindrical vector beams: (a) m = 1,
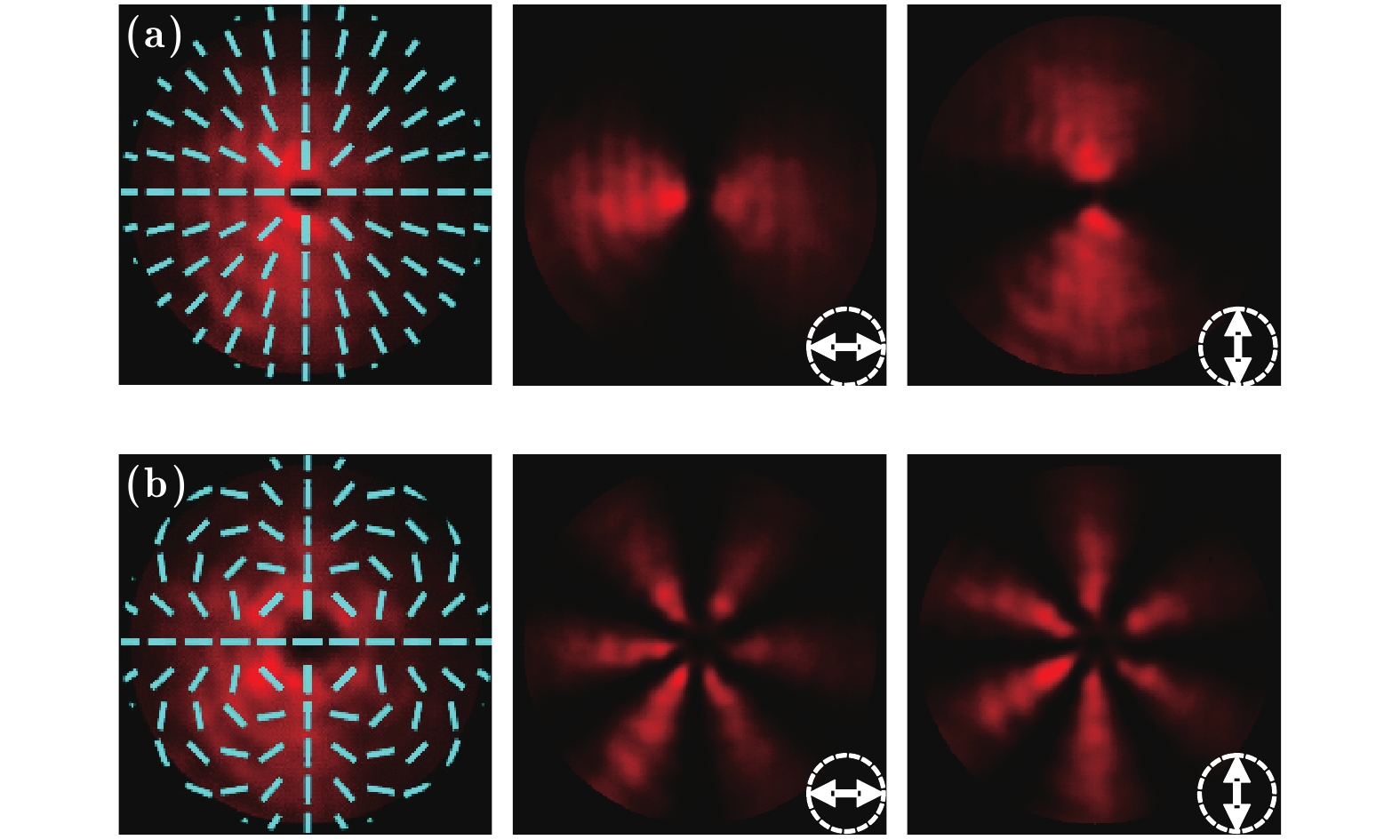
$ \phi$ 0 = 0; (b) m = 1,$ \phi$ 0 =$ \phi$ /2; (c) m = 2,$ \phi$ 0 = 0; (d) m = 5,$ \phi$ 0 = 0. The first column: intensity distributions of light fields with polarizations marked with short lines; the second and third columns: intensity distributions of light fields passing through the horizontal and vertical polarizers, respectively.图 3 携带涡旋相位的柱矢量光场的实验结果 (a) m1 = 2, m2 = 0,
$\phi $ 0 = 0; (b) m1 = 5, m2 = −1,$\phi $ 0 = 0. 第一列为光场强度分布和偏振态分布;第二、三列为分别经水平和竖直方向检偏后的光场强度分布Fig. 3. Experiment results of cylindrical vector beams with vortex phase: (a) m1 = 2, m2 = 0,
$\phi $ 0 = 0; (b) m1 = 5, m2 = −1,$\phi $ 0 = 0. The first column: intensity and polarizations distributions of light fields; the second and third columns: intensity distributions of light field passing through the horizontal and vertical polarizers, respectively.图 4 分数阶矢量光场的实验结果 (a) m = 1/2,
$\phi $ 0 = 0; (b) m = 3/2,$\phi $ 0 = 0. 第一列为光场强度和偏振态分布; 第二、三列为分别经水平和竖直方向检偏后的光场强度分布Fig. 4. Experiment results of fractional vector beams: (a) m = 1/2,
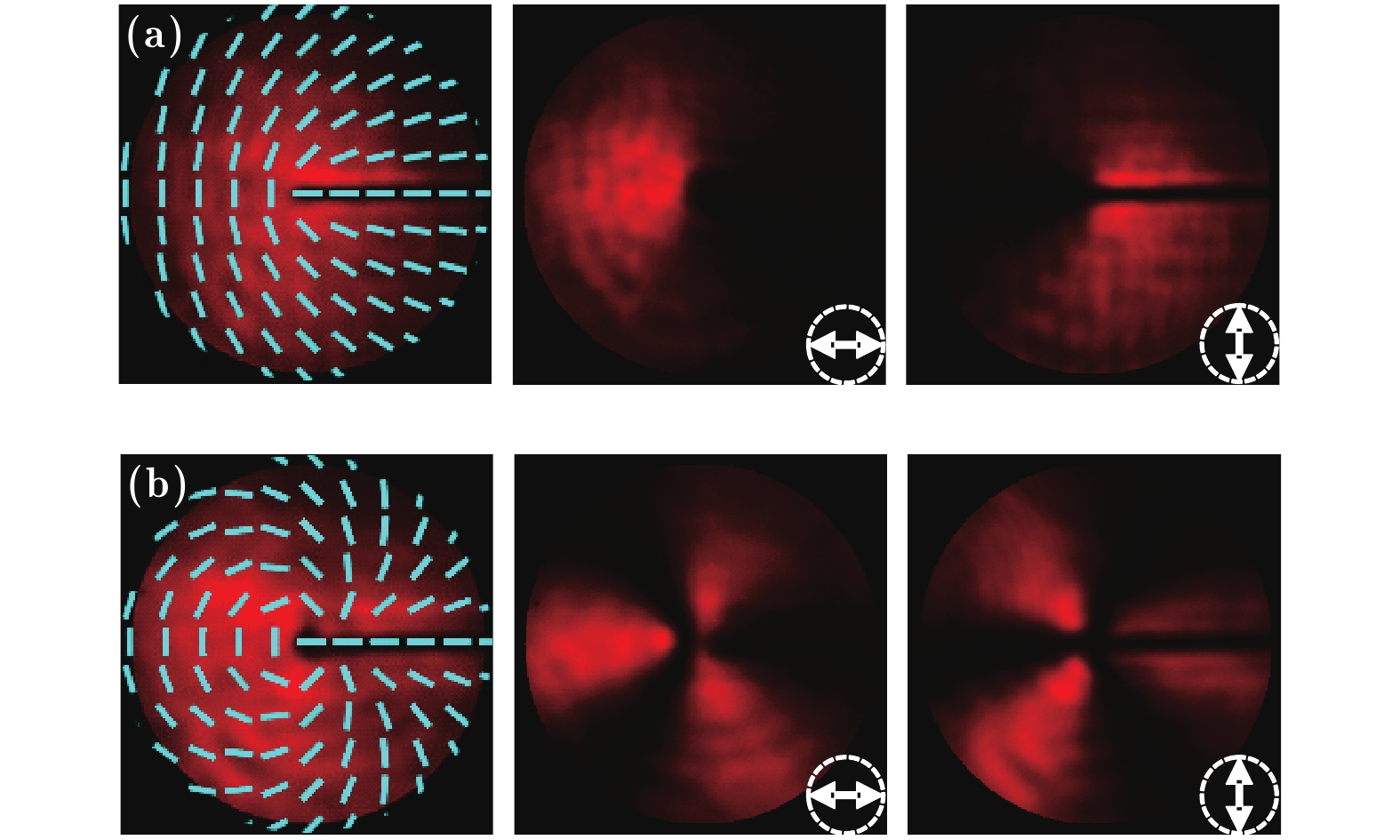
$\phi $ 0 = 0; (b) m = 3/2,$\phi $ 0 = 0. The first column: intensity and polarizations distributions of light fields; the second and third columns: intensity distributions of light field passing through the horizontal and vertical polarizers, respectively.图 5 双奇点矢量光场的实验结果 (a) m1 = m2 = 1,
$\phi $ 0 = 0; (b) m1 = −m2 = 1,$\phi $ 0 = 0. 第一列为光场强度和偏振态分布, 第二、三列为分别经水平和竖直方向检偏后的光场强度分布Fig. 5. Experiment results of vector beams with double singularities: (a) m1 = m2 = 1,
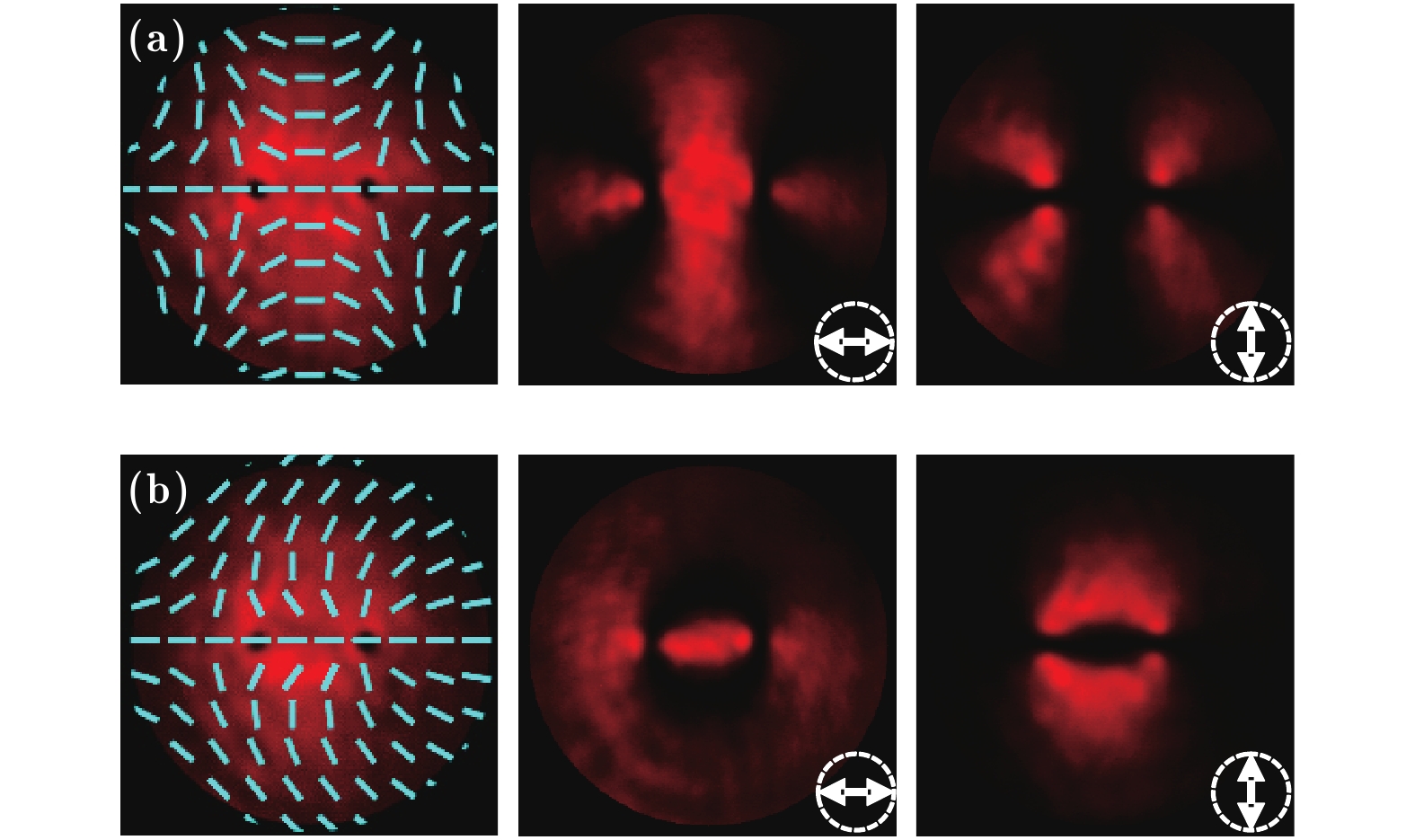
$\phi $ 0 = 0; (b) m1 = −m2 = 1,$\phi $ 0 = 0. The first column: intensity and polarizations distributions of light fields; the second and third columns: intensity distributions of light field passing through the horizontal and vertical polarizers, respectively.图 6 其他几种矢量光场的实验结果 (a) 双模矢量光场; (b) 偏振态沿径向变化矢量光场; (c) 偏振态沿角向与径向同时变化矢量光场. 第一行为光场强度分布和偏振态分布; 第二、三行为分别经水平和竖直方向检偏后的光场强度分布
Fig. 6. Experiment results of other vector beams: (a) Double-mode vector beam; (b) vector beam with radially variant polarization distribution; (c) vector beam with azimuthally and radially variant polarization distribution. The first column: intensity distributions and polarizations of light fields; the second and third columns: intensity distributions of light fields passing through the horizontal and vertical polarizers, respectively.
-
[1] Zhan Q W 2009 Adv. Opt. Photon. 1 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Quabis S, Dorn R, Eberler M, Glöckl O, Leuchs G 2000 Opt. Commun. 179 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Dorn R, Quabis S, Leuchs G 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 233901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao Y Q, Zhan Q W, Zhang Y, Li Y P 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 848
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kozawa Y, Sato S 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang H F, Shi L P, Lukyanchuk B, Sheppard C, Chong C T 2008 Nat. Photonics 2 501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li P, Guo X Y, Qi S X, Han L, Zhang Y, Liu S, Li Y, Zhao J L 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 9831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu S, Wang M R, Li P, Zhang P, Zhao J L 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 2416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu S, Li P, Zhang Y, Gan X, Wang M, Zhao J 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 20774
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhou J, Zhang W, Liu Y, Ke Y, Liu Y, Luo H, Wen S 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 34276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wei B Y, Chen P, Hu W, Ji W, Zheng L Y, Ge S J, Ming Y, Chigrinov V, Lu Y Q 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 17484
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Cardano F, Marrucci L 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 776
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang Y, Li P, Liu S, Han L, Cheng H, Zhao J 2016 Opt. Express 24 28409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li P, Liu S, Peng T, Xie G, Gan X, Zhao J 2014 Opt. Express 22 7598
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Li P, Wu D, Zhang Y, Liu S, Li Y, Qi S, Zhao J 2018 Photon. Res. 6 756
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Cheng H C, Li P, Liu S, Chen P, Han L, Zhang Y, Hu W, Zhao J L 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 111 141901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xie X S, Chen Y Z, Yang K, Zhou J Y 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 263901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Nieminen T A, Heckenberg N R, Rubinsztein D H 2008 Opt. Lett. 33 122
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang X L, Chen J, Li Y, Ding J, Guo C S, Wang H T 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 253602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Milione G, Nguyen T A, Leach J, Nolan D A, Alfano R R 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 4887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Pohl D 1972 Appl. Phys. Lett. 20 266
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kozawa Y, Sato S 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 3063
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Bisson J F, Li J, Ueda K, Senatsky Y 2006 Opt. Express 14 3304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lai W J, Lim B C, Phua P B, Tiaw K S, Teo H H, Hong M H 2008 Opt. Express 16 15694
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Bomzon Z, Biener G, Kleiner V, Hasman E 2002 Opt. Lett. 27 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Cardano F, Karimi E, Slussarenko S, Marrucci L, de Lisio C, Santamato E 2012 Appl. Opt. 51 C1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yi X, Ling X, Zhang Z, Li Y, Zhou X, Liu Y, Chen S, Luo H, Wen S 2014 Opt. Express 22 17207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li P, Zhang Y, Liu S, Ma C J, Han L, Cheng H C, Zhao J L 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 2205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang Y, Li P, Ma C J, Liu S, Cheng H C, Zhao J L, Han L 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 4956
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Christian M, Alexander J, Severin F, Stefan B, Monika R M 2007 New J. Phys. 9 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Liu S, Li P, Peng T, Zhao J 2012 Opt. Express 20 21715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wang X L, Ding J P, Ni W J, Guo C S, Wang H T 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 3549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Liu S, Qi S X, Zhang Y, Li P, Wu D J, Han L, Zhao J L 2018 Photon. Res. 6 228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Liu S, Han L, Li P, Zhang Y, Cheng H, Zhao J 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 171112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 15431
- PDF下载量: 464
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: