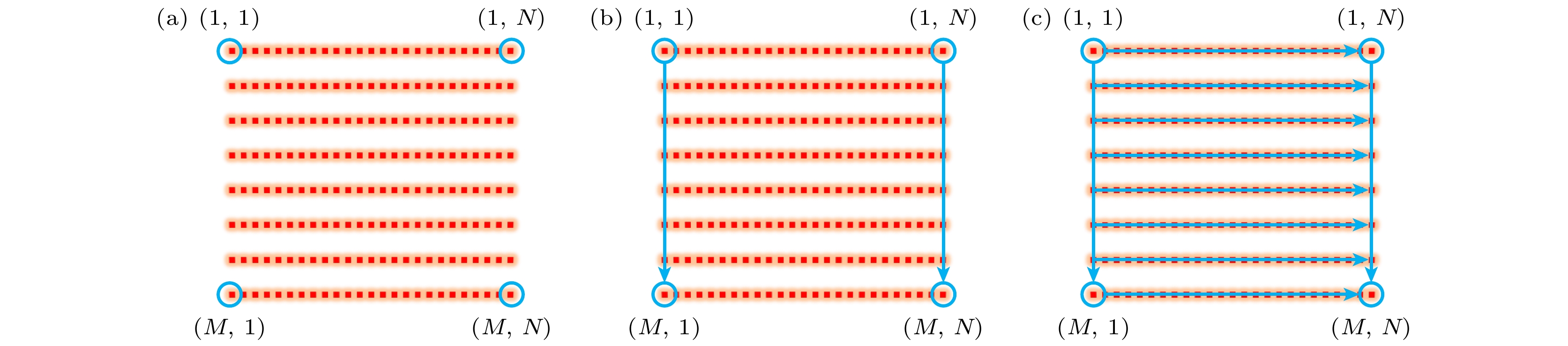
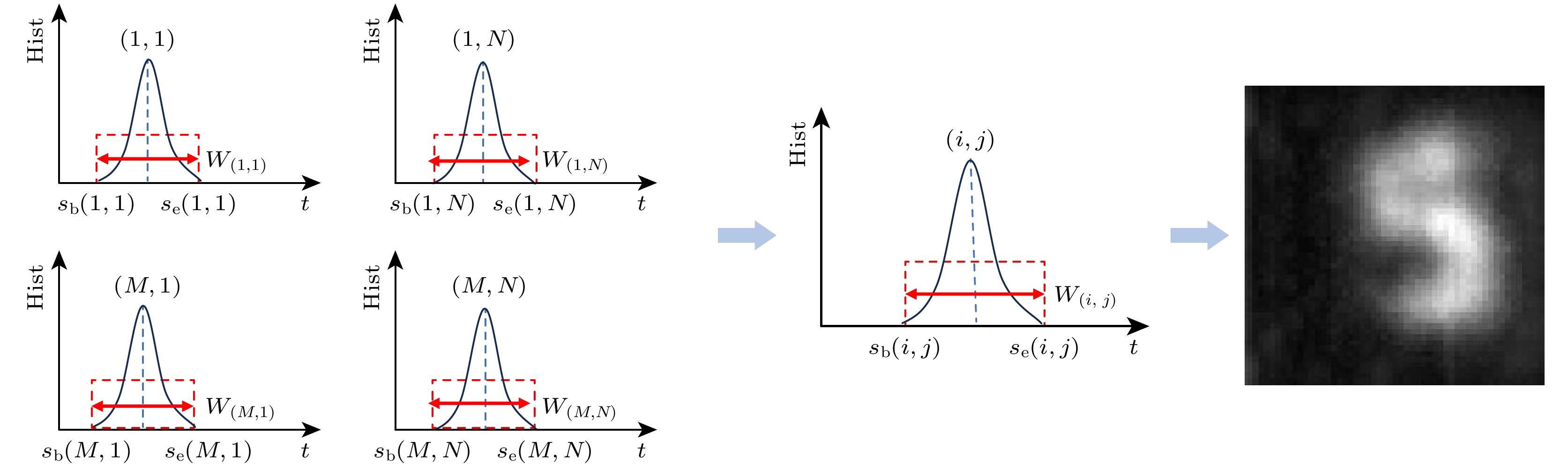
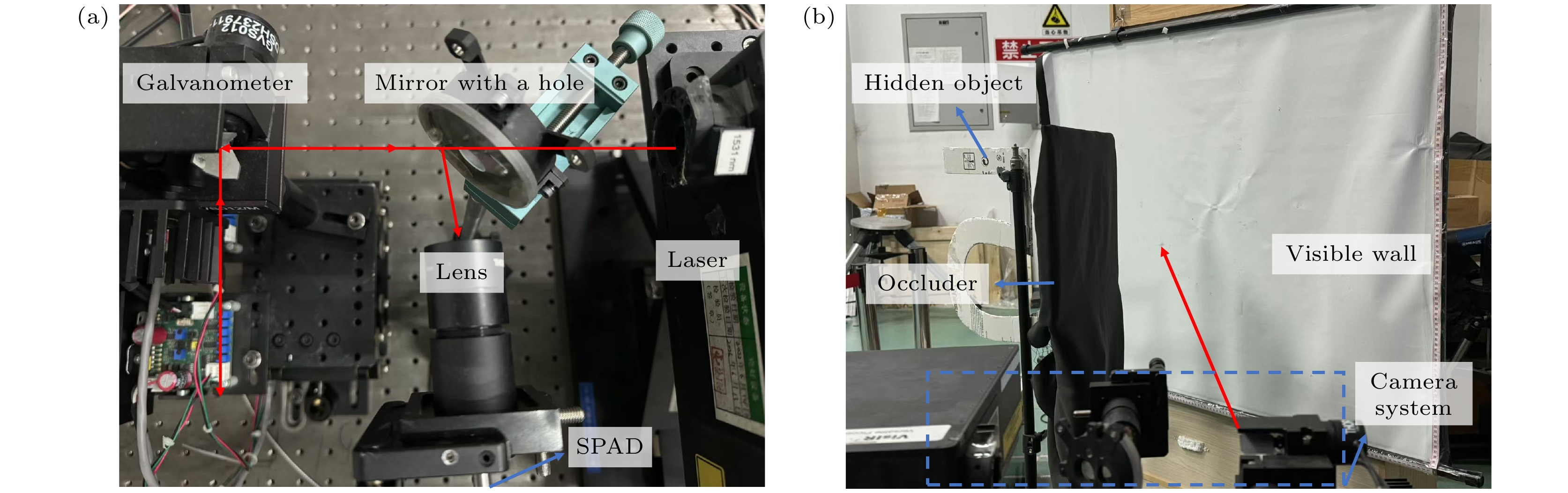
-
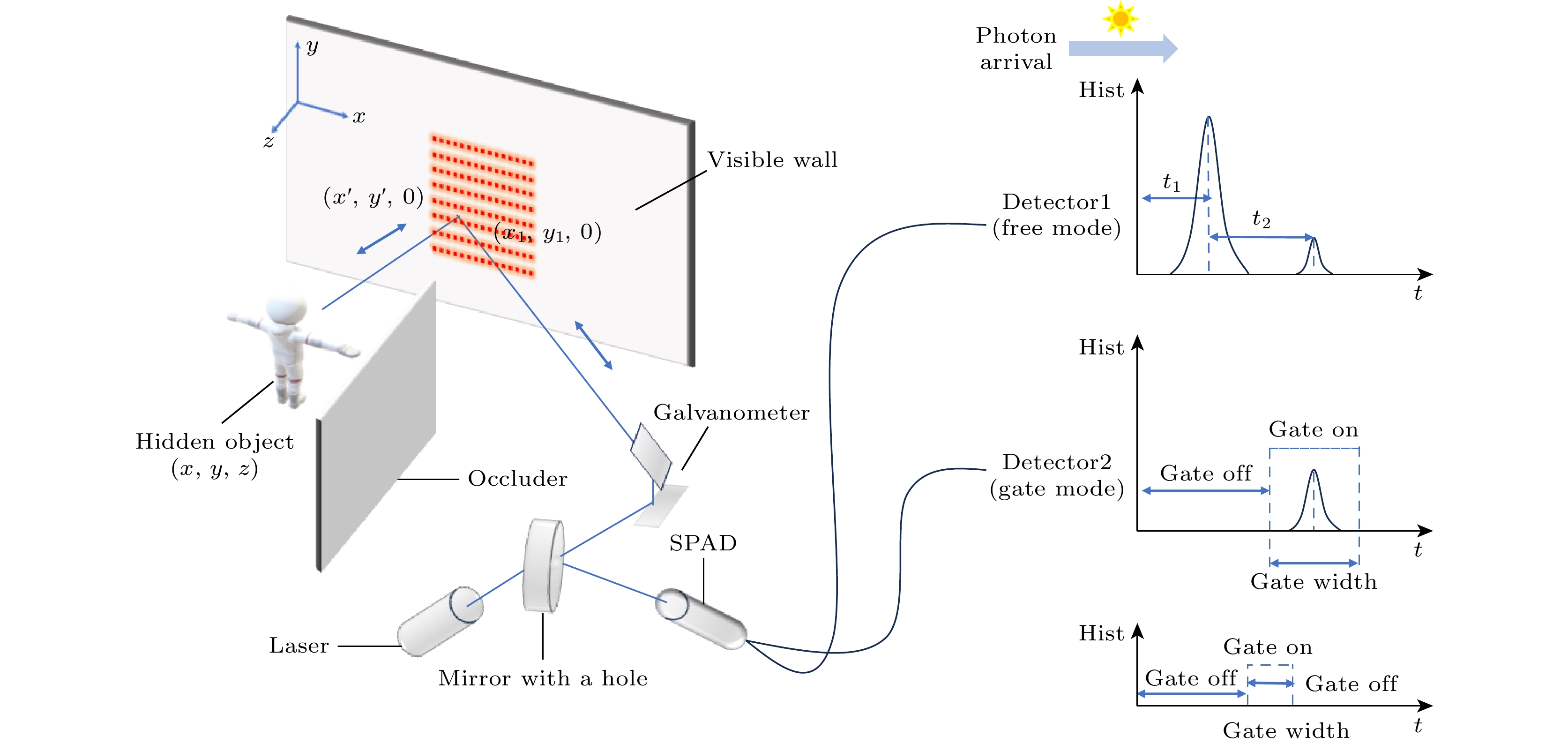
Non-line-of-sight (NLOS) imaging is an emerging optical imaging technique used for detecting hidden targets outside the line of sight. Due to multiple diffuse reflections, the signal echoes are weak, and gated single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD) plays a pivotal role in signal detection under low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions. However, when gated SPAD is used for detecting a target signal, existing methods often depend on prior information to preset the gate width, which cannot fully mitigate non-target signal interference or signal loss. Additionally, these methods encountered some problems such as large data acquisition volumes and lengthy processing times. To address these challenges, an adaptive gating algorithm is proposed in this work based on the principle of maximizing the distance from the vertex of a triangle to its base. The algorithm possesses advantages of the linear variation in scan point positions and the echo information from specific feature points. It can automatically identify echo signals and compute their widths without additional prior information or manual intervention. This method reduces the amount of data collected, improves processing efficiency, and has other benefits. Moreover, a confocal NLOS imaging system based on gated SPAD is developed to validate the proposed algorithm. The work further quantitatively evaluates the enhancement of target signal detection and image quality achieved by gated SPAD, and compares its imaging performance with leading NLOS image reconstruction algorithms. Experimental results demonstrate that the adaptive gating algorithm can effectively identify echo signals, facilitate automatic adjustment of gating parameters, and significantly improve target imaging quality while reducing data acquisition volume and enhancing processing efficiency.
-
Keywords:
- non-line-of-sight imaging /
- adaptive gating /
- signal-to-noise ratio
[1] Kirmani A, Hutchison T, Davis J, Raskar R 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Kyoto, Japan, September 29–October 2, 2009 p159
[2] Velten A, Willwacher T, Gupta O, Veeraraghavan A, Bawendi M G, Raskar R 2012 Nat. Commun. 3 745
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Victor A, Diego G, Adrian J 2017 Opt. Express 25 11574
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] O’Toole M, Lindell D B, Wetzstein G 2018 Nature 555 338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lindell D B, Wetzstein G, O’Toole M 2019 ACM T. Graphic. 38 116
[6] Xin S, Nousias S, Kutulakos K N, Sankaranarayanan A C, Narasimhan S G, Gkioulekas I 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Long Beach, CA, USA, June 15–19, 2019 p6793
[7] Liu X C, Guillén I, La Manna M, Nam J H, Reza S A, Huu Le T, Jarabo A, Gutierrez D, Velten A 2019 Nature 572 620
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Young S I, Lindell D B, Girod B, Taubman D, Wetzstein G 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Seattle, WA, USA, June 14–19, 2020 p1404
[9] Chen X J, Li M Y, Chen T T, Zhan S Y 2023 Photonics 10 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Plack M, Callenberg C, Schneider M, Hullin M B 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) Waikoloa, HI, USA, January 2–7, 2023 p3066
[11] Shen S Y, Wang Z, Liu P, Pan Z Q, Li R Q, Gao T, Li S Y, Yu J Y 2021 IEEE T. Pattern Anal. 43 2257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 吴嘉伟 2021 硕士学位论文 (长沙: 湖南大学)
Wu J W 2021 M. S. Thesis (Changsha: Hunan University
[13] 任禹, 罗一涵, 徐少雄, 马浩统, 谭毅 2021 光电工程 48 84
Ren Y, Luo Y H, Xu S X, Ma H T, Tan Y 2021 Opto-Electron. Eng. 48 84
[14] 唐佳瑶, 罗一涵, 谢宗良, 夏诗烨, 刘雅卿, 徐少雄, 马浩统, 曹雷 2023 72 014210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang J Y, Luo Y H, Xie Z L, Xia S Y, Liu Y Q, Xu S X, Ma H T, Cao L 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 014210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 郑海洋, 罗一涵, 李泰霖, 唐佳瑶, 刘雅卿, 夏诗烨, 吴琼雁, 谢宗良 2023 光电工程 50 101
Zheng H Y, Luo Y H, Li T L, Tang J Y, Liu Y Q, Xia S Y, Wu Q Y, Xie Z L 2023 Opto-Electron. Eng. 50 101
[16] Wang B, Zheng M Y, Han J J, Huang X, Xie X P, Xu F H, Zhang Q, Pan J W 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 127 053602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wu C, Liu J J, Huang X, Li Z P, Yu C, Ye J T, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Dou X K, Goyal V K, Xu F H, Pan J W 2021 PNAS 118 e2024468118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu X T, Wang J Y, Xiao L P, Shi Z Q, Fu X, Qiu L Y 2023 Nat. Commun. 14 3230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Laurenzis M, Velten A 2014 J. Electron. Imag. 23 063003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Buttafava M, Zeman J, Tosi A, Eliceiri K, Velten A 2015 Opt. Express 23 20997
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhu S Y, Sua Y M, Rehain P, Huang Y P 2021 Opt. Express 29 40865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhao J X, Gramuglia F, Keshavarzian P, Toh E H, Tng M, Lim L 2024 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 30 8000110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Luo Y H, Xie Z L, Xu S X, Ma H T, Ren Y, Cao L 2020 China Patent CN202010742670.6 [2020-06-28]
-
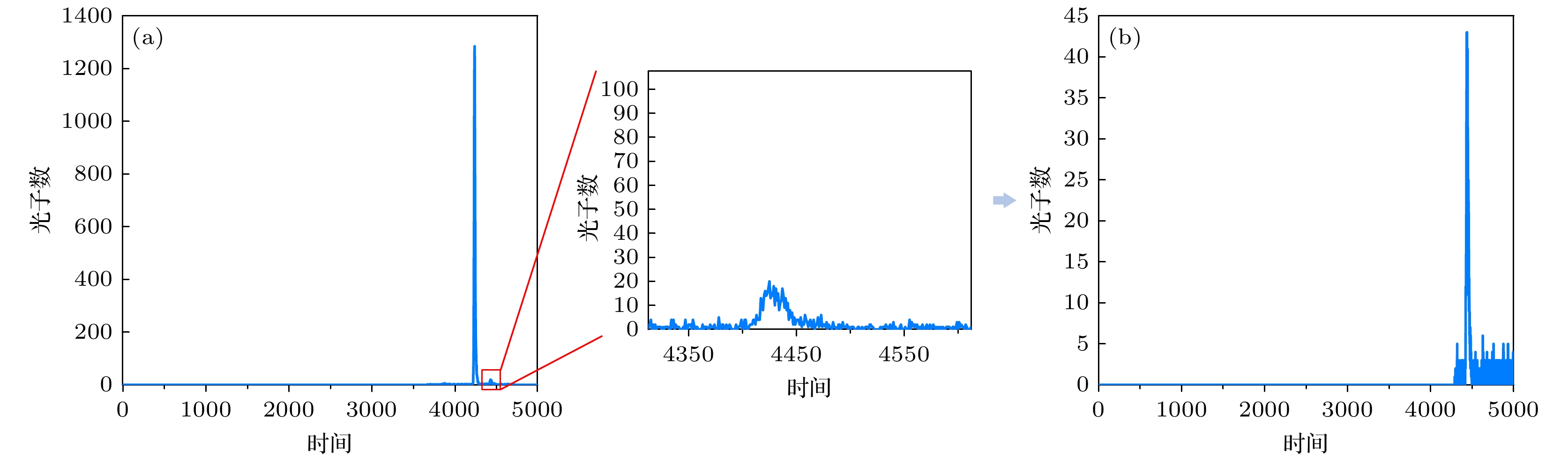
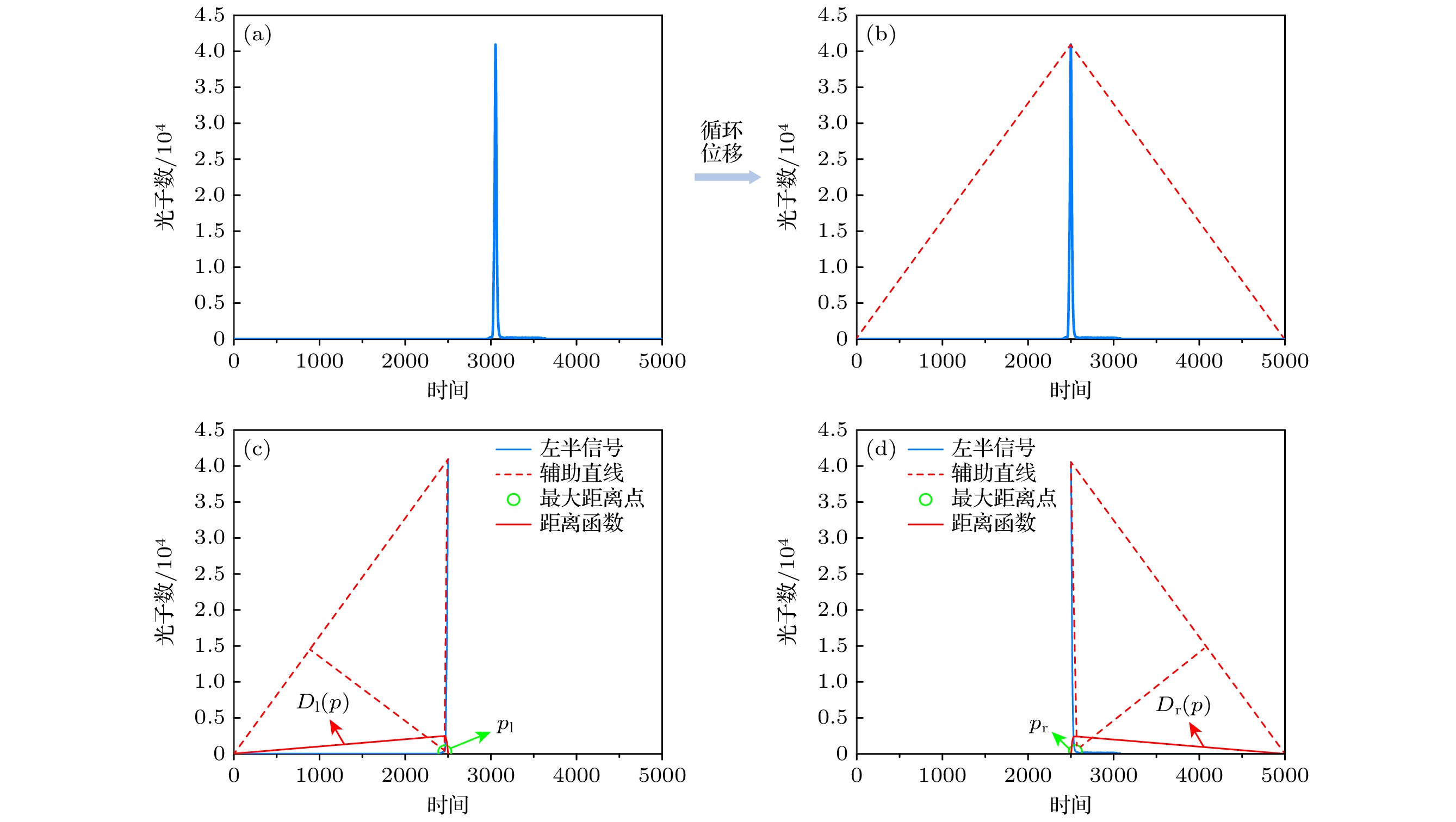
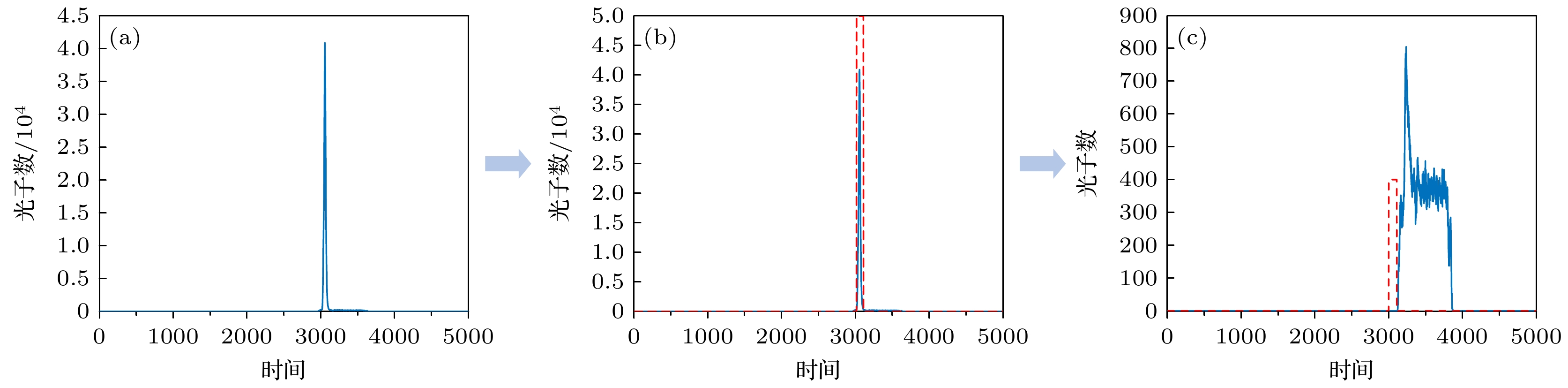
图 4 中介面回波信号处理过程 (a) 使用门控SPAD采集的某点回波信号; (b) 该回波信号循环位移后的结果; (c) 左半信号处理结果; (d) 右半信号处理结果
Figure 4. Signal processing procedure for the interface echo signal: (a) Echo signal acquired using gated SPAD at a certain point; (b) result after cyclic shift of the echo signal; (c) result of processing the left half of the signal; (d) result of processing the right half of the signal.
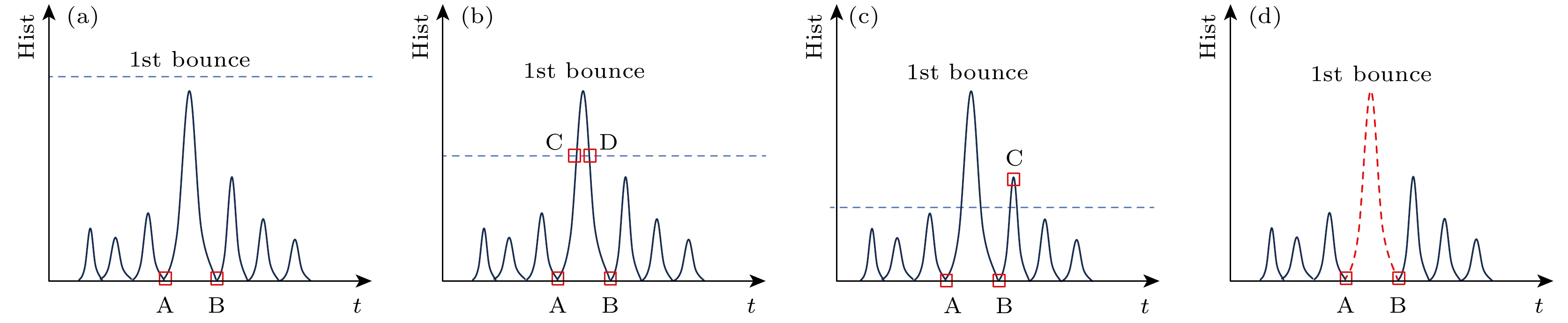
图 10 中介面回波信号抑制结果 (a)某点中介面回波信号; (b)某点中介面回波信号识别结果; (c)抑制中介面回波信号后的目标回波信号
Figure 10. Suppression results of intermediate surface echo signal: (a) Echo signal for the intermediate interface midpoint; (b) result of identifying the echo signal of an intermediary surface at a certain point; (c) target echo signal after suppressing the intermediate interface echo signal.
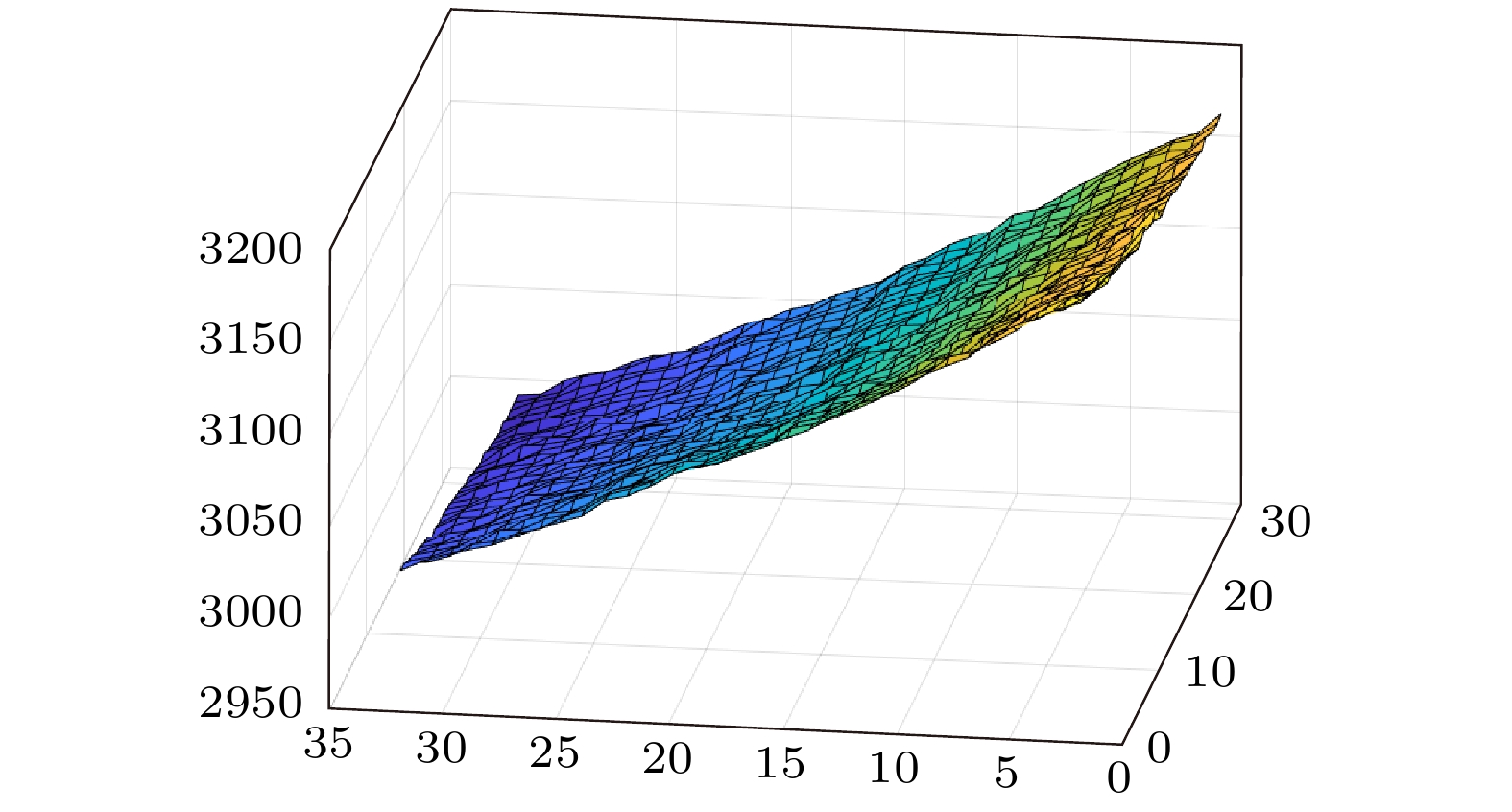
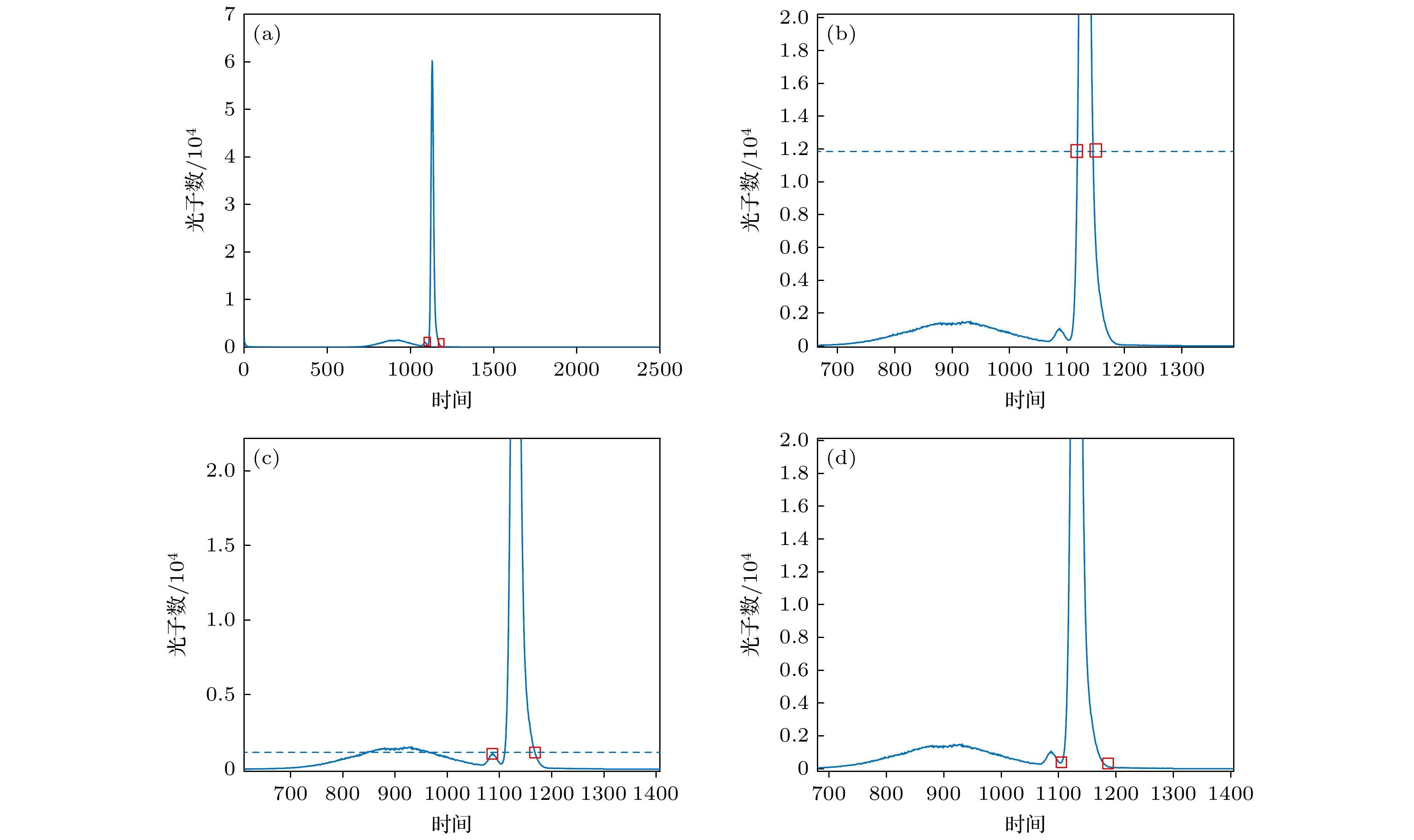
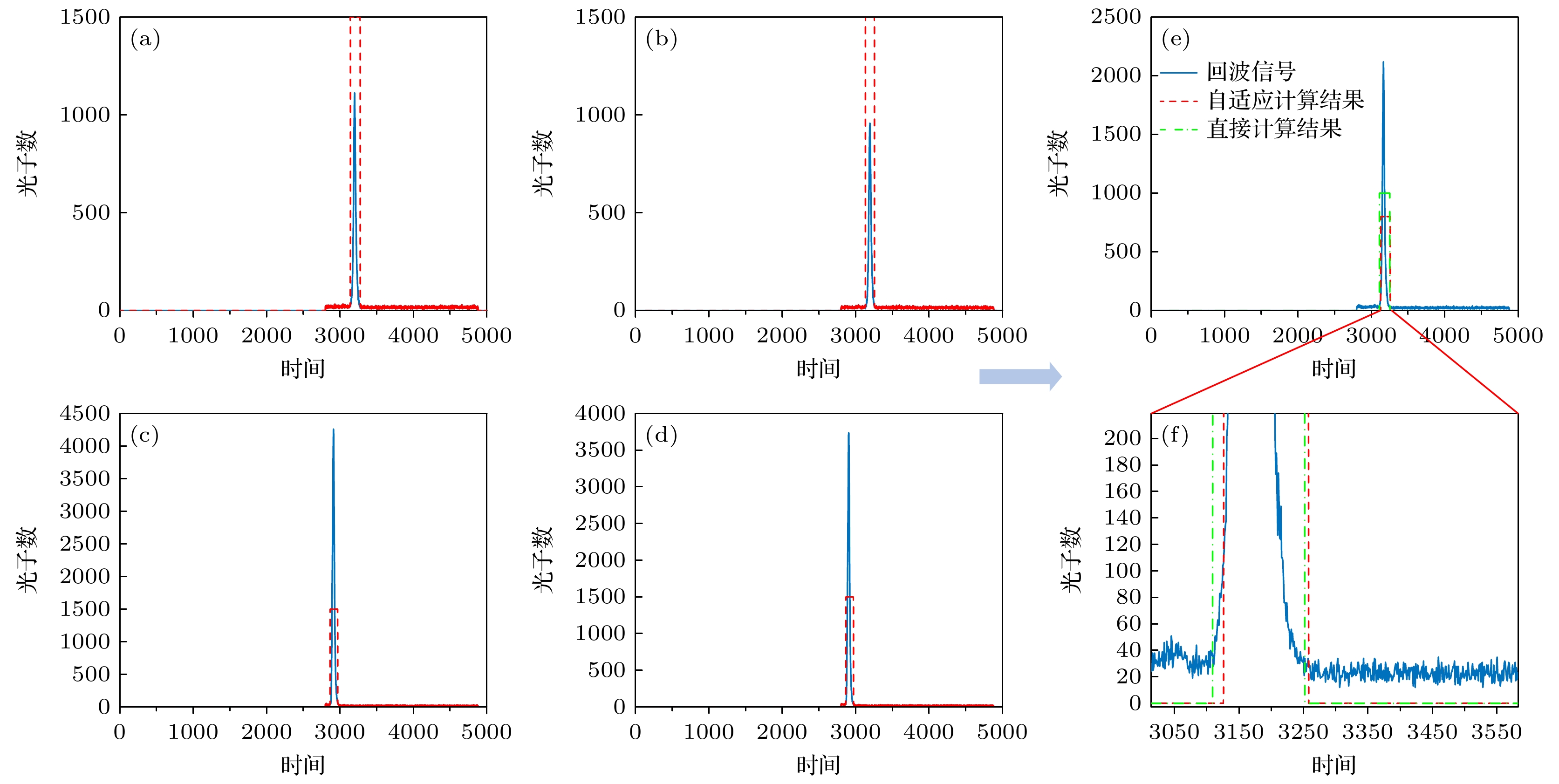
图 11 中介面回波信号位置与宽度计算结果 (a)左上顶点中介面回波信号位置与宽度计算结果; (b)右上顶点中介面回波信号位置与宽度计算结果; (c)左下顶点中介面回波信号位置与宽度计算结果; (d)右下顶点中介面回波信号位置与宽度计算结果; (e)自适应计算结果和直接计算结果对比图; (f)计算结果细节图
Figure 11. Results of the adaptive gated control algorithm: (a) Calculated position and width of the interface echo signal at the top-left vertex; (b) calculated position and width of the interface echo signal at the top-right vertex; (c) calculated position and width of the interface echo signal at the bottom-left vertex; (d) calculated position and width of the interface echo signal at the bottom-right vertex; (e) comparison of adaptive algorithm results and direct calculation results; (f) detailed plot of the calculated results.
图 12 一次回波对目标信号作用 (a)—(c)移动门位置示意图; (d)未抑制一次回波的回波信号图; (e)抑制一半一次回波的回波信号图; (f)完全抑制一次回波的回波信号图
Figure 12. Effect of single echo on the target signal: (a)–(c) Schematic diagram of the moving gate position; (d) echo signal diagram without suppressing the single echo; (e) diagram of the echo signal with half of the single echo suppressed; (f) diagram of the echo signal with the single echo completely suppressed.
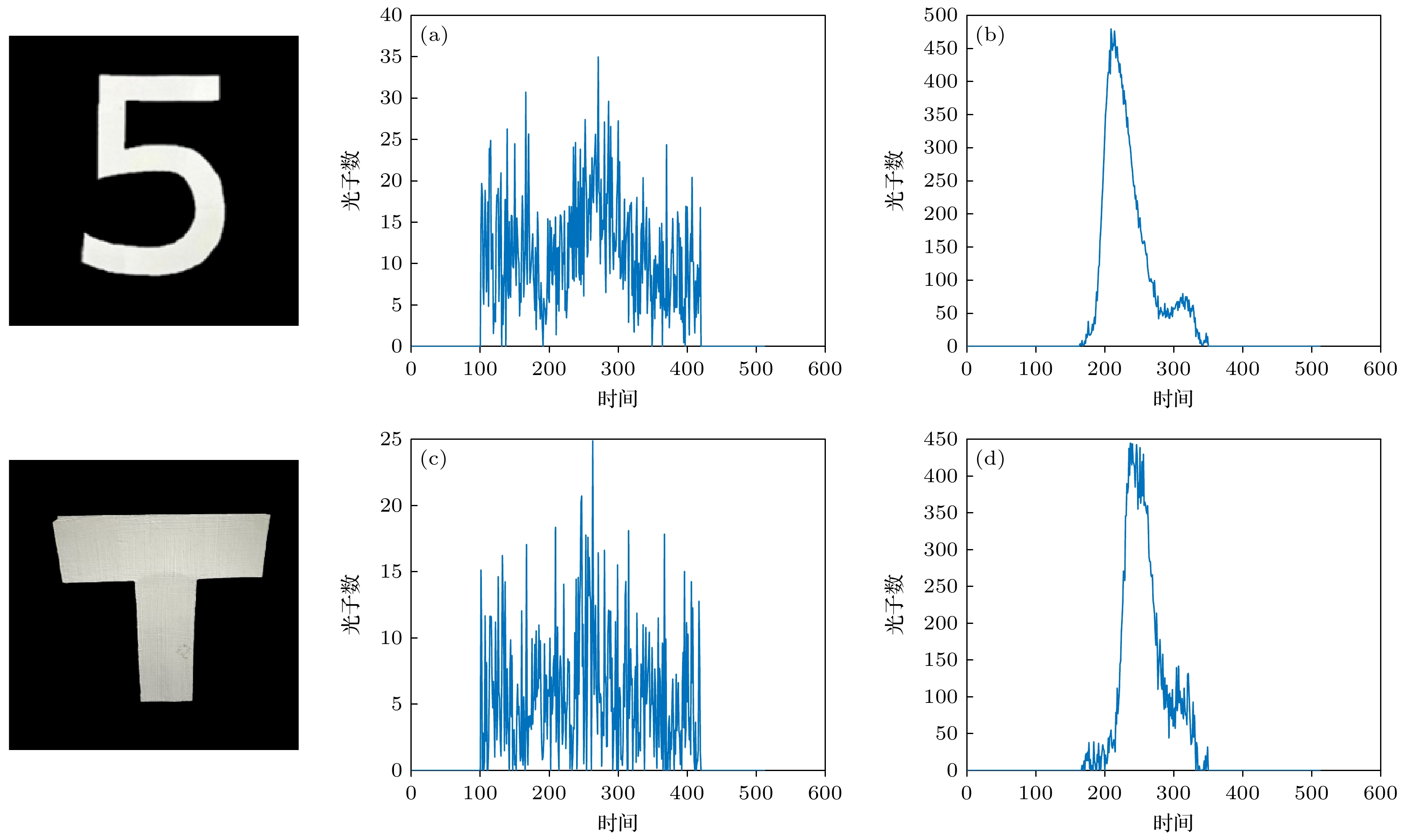
图 13 门控SPAD对目标回波信号影响 (a)自由模式下隐藏目标5回波信号; (b)门控模式下隐藏目标5回波信号; (c)自由模式下隐藏目标T回波信号; (d)门控模式下隐藏目标T回波信号
Figure 13. Impact of gated SPAD on target echo signals: (a) Hidden target 5 echo signal in free-running mode; (b) hidden target 5 echo signal in gated mode; (c) hidden target T echo signal in free-running mode; (d) hidden target T echo signal in gated mode.
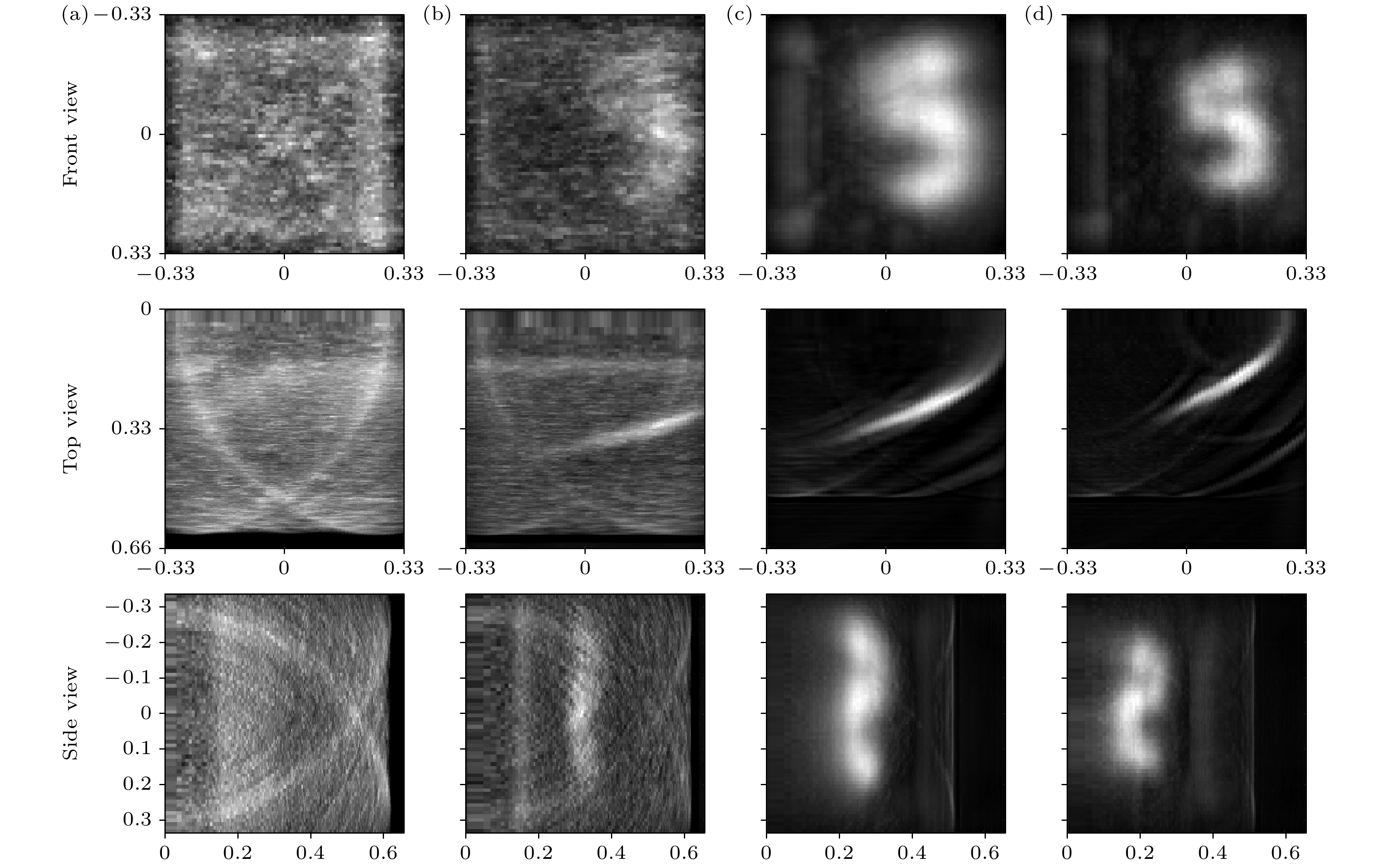
图 14 不同模式重建结果对比 (a)自由模式下目标重构结果; (b)固定门宽未抑制一次回波的目标重构结果; (c)固定门宽抑制一次回波的目标重构结果; (d)本文自适应门控控制算法目标重构结果
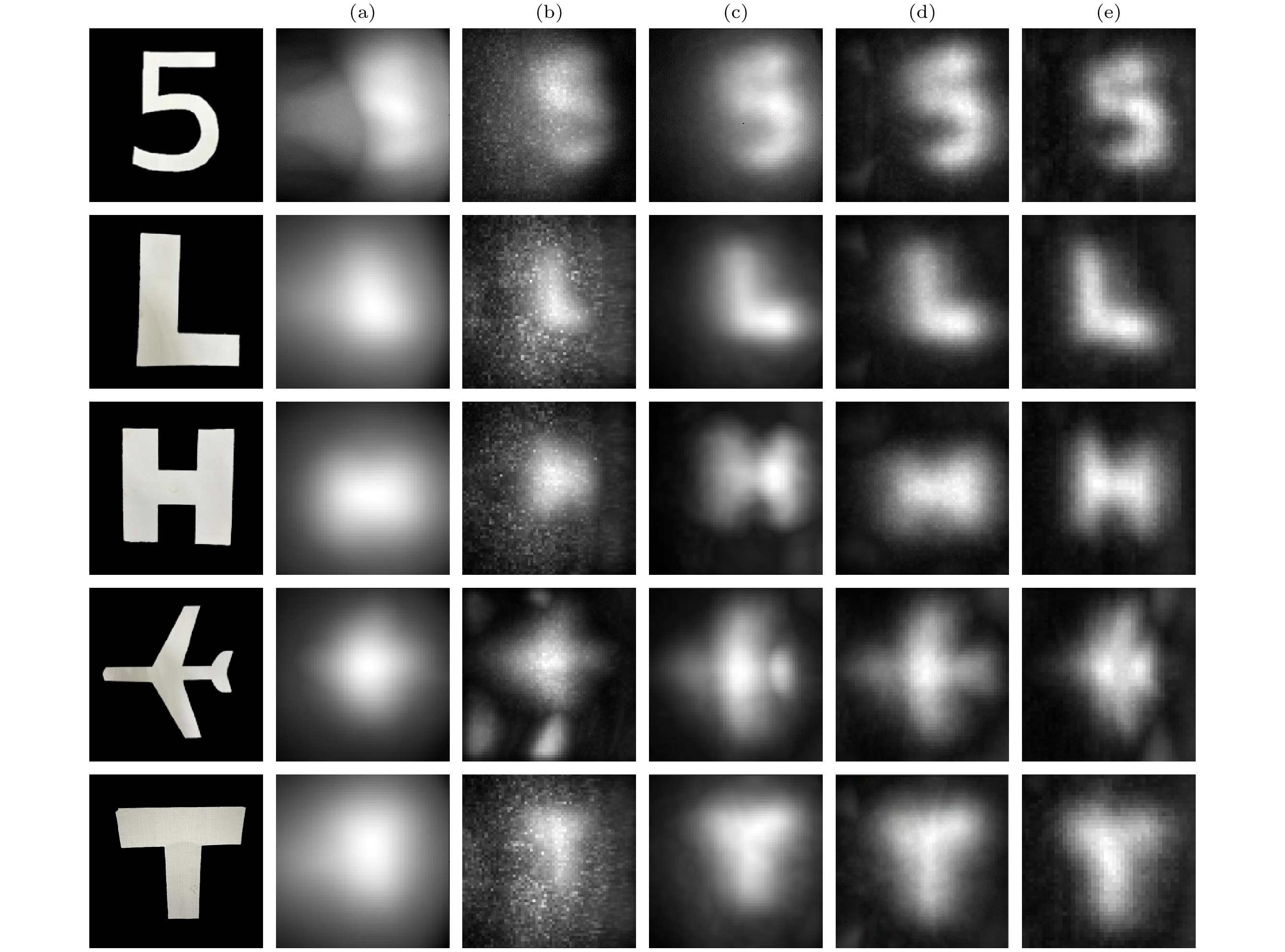
Figure 14. Comparison of different mode reconstruction results: (a) Reconstruction result under free mode; (b) reconstruction result without suppressing the first echo with fixed gate width; (c) reconstruction result with fixed gate width suppressing the first echo; (d) reconstruction result using the proposed adaptive gate control algorithm in this paper.
表 1 不同方法中介面位置的对比
Table 1. Comparison of the results of different method.
采集信号 常规方法
抑制常规方法
抑制三角定位法
抑制起点 1103 1118 1090 1105 终点 1181 1145 1170 1178 宽度/ns 0.78 0.27 0.8 0.73 表 2 不同方法对中介面回波信号抑制结果偏差对比
Table 2. Comparison of the deviation in suppression results of interface echo signals using different methods.
起点 终点 宽度/ns 常规方法抑制情形一 15 36 0.51 常规方法抑制情形二 13 9 0.02 三角定位法抑制 2 3 0.05 表 3 自适应计算机果和直接计算结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of adaptive algorithm results and direct calculation results
起点 终点 宽度/ns 自适应计算 3127 3257 1.31 实际采集计算 3110 3251 1.41 偏差/ns 0.17 0.06 0.11 表 4 一次回波对目标回波信号的影响
Table 4. Impact of primary echo on the target echo signal.
未抑制一次
回波信号抑制一半一次
回波信号完全抑制一次
回波信号一次回波峰值 36190 8811 0 目标回波峰值 372 952 805 信号信噪比 16.79 19.48 28.75 主观 目标信号被淹没 目标信号可见 目标信号突出 表 5 门控SPAD对目标回波信号的影响
Table 5. Impact of gated single-photon avalanche diode on the target echo signal.
目标5信号
(自由模式)目标5信号(门控模式) 目标T信号
(自由模式)目标T信号
(门控模式)目标回波峰值 35 480 25 445 信号信噪比 6.79 25.54 6.15 23.21 主观 目标波形可见 目标波形清晰 目标波形可见 目标波形清晰 表 6 不同方法采集数据量、耗时对比
Table 6. Comparison of data collection volume and time consumption across different methods.
数据采集量 耗时/T 自由模式 一次逐点扫描 1 未抑制中介面回波信号 一次逐点扫描 1 抑制中介面回波信号 两次逐点扫描 2 自适应门控控制算法 一次逐点扫描+
四个特征点≈1 表 7 不同模式下成像质量对比
Table 7. Comparison of imaging quality under different modes.
自由模式 未抑制中介面
回波信号抑制中介面
回波信号自适应门控
控制算法峰值
信噪比6.94 9.52 10.70 11.4932 结构
相似度0.56 0.73 0.81 0.8466 相关系数 0.007 0.31 0.56 0.64885 主观 无法识别
目标可见目标
轮廓目标轮廓
清晰目标轮廓
清晰表 8 不同目标重构质量对比
Table 8. Reconstruction quality comparison of different objects.
评价指标 BP F-K V-W LCT 本文 目标5 峰值信噪比 7.0311 10.15 8.9784 10.7017 11.4932 结构相似度 0.6443 0.7873 0.7408 0.8107 0.8466 相关系数 0.4545 0.5098 0.5315 0.5703 0.6489 主观 目标模糊 可见目标轮廓 目标轮廓清晰 目标轮廓清晰 目标轮廓清晰 目标L 峰值信噪比 7.1744 9.543 8.4819 11.179 11.3109 结构相似度 0.6689 0.7781 0.7825 0.8535 0.8621 相关系数 0.386 0.4459 0.5093 0.6014 0.6587 主观 目标模糊 可见目标轮廓 目标轮廓清晰 目标轮廓清晰 目标轮廓清晰 目标H 峰值信噪比 8.8224 9.4324 9.4568 10.1954 10.558 结构相似度 0.7477 0.8071 0.8163 0.8417 0.8564 相关系数 0.6077 0.4839 0.5092 0.6017 0.6275 主观 目标模糊 可见目标轮廓 目标轮廓清晰 目标轮廓清晰 目标轮廓清晰 目标Plane 峰值信噪比 9.8436 11.6533 11.4687 12.2066 11.9239 结构相似度 0.7745 0.8545 0.8465 0.8533 0.8608 相关系数 0.6019 0.5541 0.6223 0.6524 0.6325 主观 目标模糊 可见目标轮廓 目标轮廓清晰 目标轮廓清晰 目标轮廓清晰 目标T 峰值信噪比 7.9285 11.1673 11.2831 12.7401 12.604 结构相似度 0.6883 0.8106 0.8328 0.8812 0.877 相关系数 0.6566 0.6714 0.7388 0.7102 0.7696 主观 目标模糊 可见目标轮廓 目标轮廓清晰 目标轮廓清晰 目标轮廓清晰 -
[1] Kirmani A, Hutchison T, Davis J, Raskar R 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Kyoto, Japan, September 29–October 2, 2009 p159
[2] Velten A, Willwacher T, Gupta O, Veeraraghavan A, Bawendi M G, Raskar R 2012 Nat. Commun. 3 745
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Victor A, Diego G, Adrian J 2017 Opt. Express 25 11574
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] O’Toole M, Lindell D B, Wetzstein G 2018 Nature 555 338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lindell D B, Wetzstein G, O’Toole M 2019 ACM T. Graphic. 38 116
[6] Xin S, Nousias S, Kutulakos K N, Sankaranarayanan A C, Narasimhan S G, Gkioulekas I 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Long Beach, CA, USA, June 15–19, 2019 p6793
[7] Liu X C, Guillén I, La Manna M, Nam J H, Reza S A, Huu Le T, Jarabo A, Gutierrez D, Velten A 2019 Nature 572 620
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Young S I, Lindell D B, Girod B, Taubman D, Wetzstein G 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Seattle, WA, USA, June 14–19, 2020 p1404
[9] Chen X J, Li M Y, Chen T T, Zhan S Y 2023 Photonics 10 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Plack M, Callenberg C, Schneider M, Hullin M B 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) Waikoloa, HI, USA, January 2–7, 2023 p3066
[11] Shen S Y, Wang Z, Liu P, Pan Z Q, Li R Q, Gao T, Li S Y, Yu J Y 2021 IEEE T. Pattern Anal. 43 2257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 吴嘉伟 2021 硕士学位论文 (长沙: 湖南大学)
Wu J W 2021 M. S. Thesis (Changsha: Hunan University
[13] 任禹, 罗一涵, 徐少雄, 马浩统, 谭毅 2021 光电工程 48 84
Ren Y, Luo Y H, Xu S X, Ma H T, Tan Y 2021 Opto-Electron. Eng. 48 84
[14] 唐佳瑶, 罗一涵, 谢宗良, 夏诗烨, 刘雅卿, 徐少雄, 马浩统, 曹雷 2023 72 014210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang J Y, Luo Y H, Xie Z L, Xia S Y, Liu Y Q, Xu S X, Ma H T, Cao L 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 014210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 郑海洋, 罗一涵, 李泰霖, 唐佳瑶, 刘雅卿, 夏诗烨, 吴琼雁, 谢宗良 2023 光电工程 50 101
Zheng H Y, Luo Y H, Li T L, Tang J Y, Liu Y Q, Xia S Y, Wu Q Y, Xie Z L 2023 Opto-Electron. Eng. 50 101
[16] Wang B, Zheng M Y, Han J J, Huang X, Xie X P, Xu F H, Zhang Q, Pan J W 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 127 053602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wu C, Liu J J, Huang X, Li Z P, Yu C, Ye J T, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Dou X K, Goyal V K, Xu F H, Pan J W 2021 PNAS 118 e2024468118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu X T, Wang J Y, Xiao L P, Shi Z Q, Fu X, Qiu L Y 2023 Nat. Commun. 14 3230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Laurenzis M, Velten A 2014 J. Electron. Imag. 23 063003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Buttafava M, Zeman J, Tosi A, Eliceiri K, Velten A 2015 Opt. Express 23 20997
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhu S Y, Sua Y M, Rehain P, Huang Y P 2021 Opt. Express 29 40865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhao J X, Gramuglia F, Keshavarzian P, Toh E H, Tng M, Lim L 2024 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 30 8000110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Luo Y H, Xie Z L, Xu S X, Ma H T, Ren Y, Cao L 2020 China Patent CN202010742670.6 [2020-06-28]
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 624
- PDF Downloads: 11
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: