-
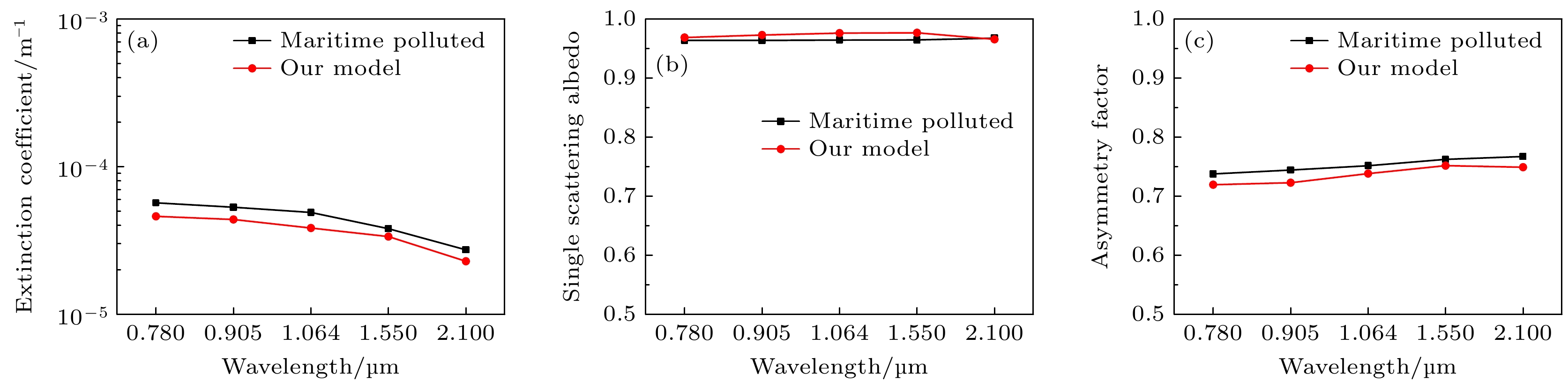
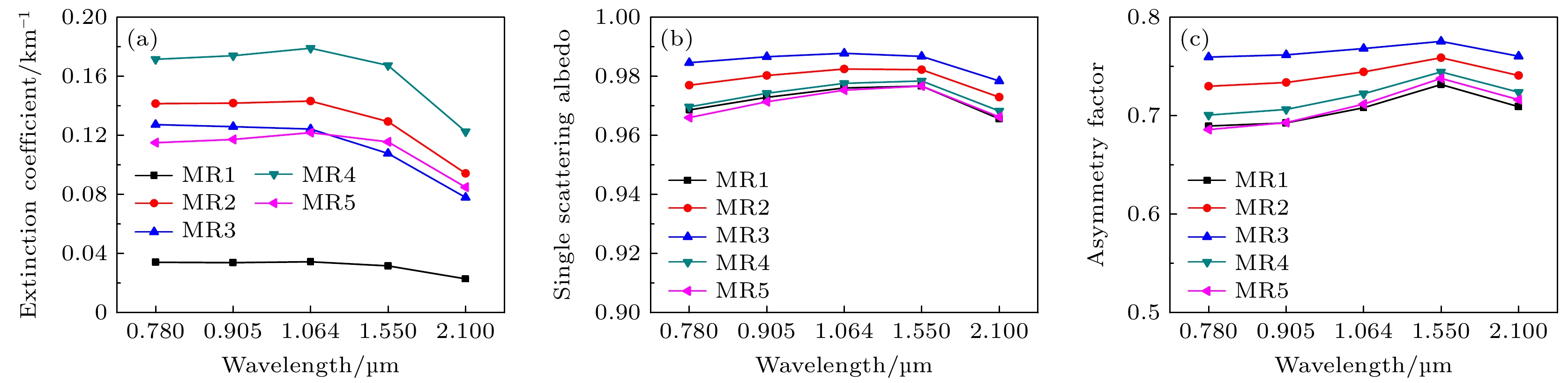
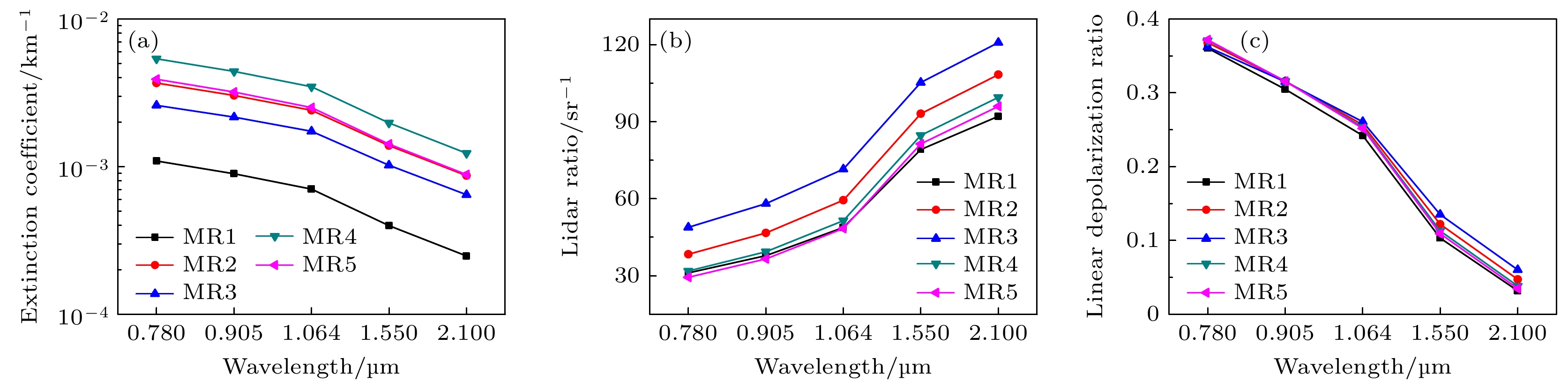
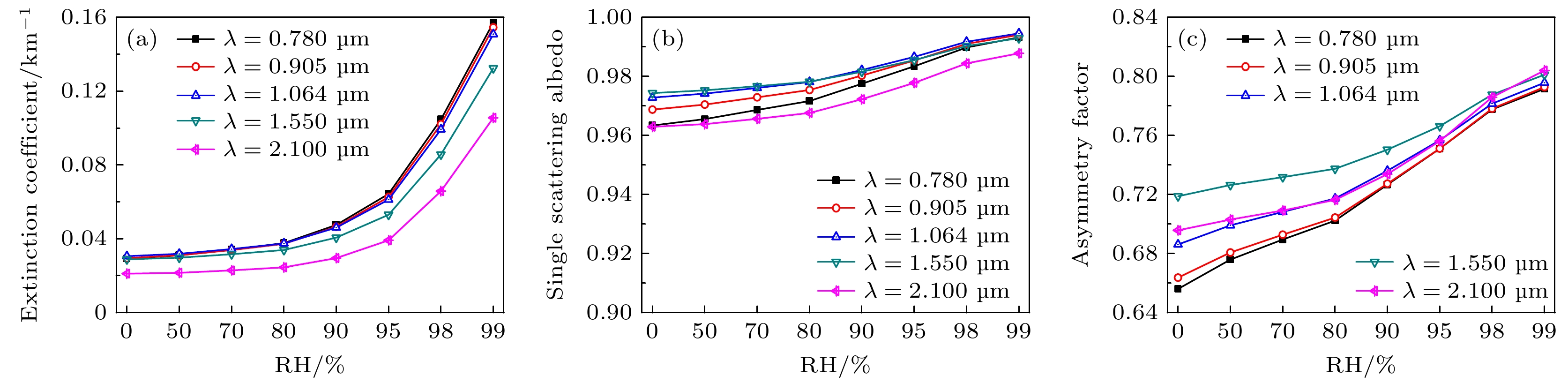
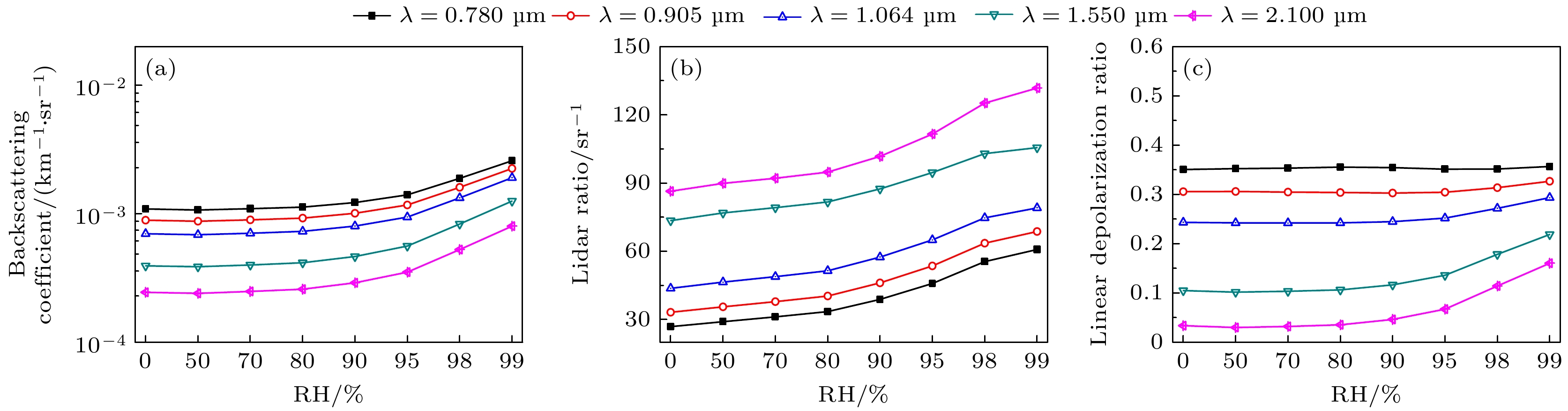
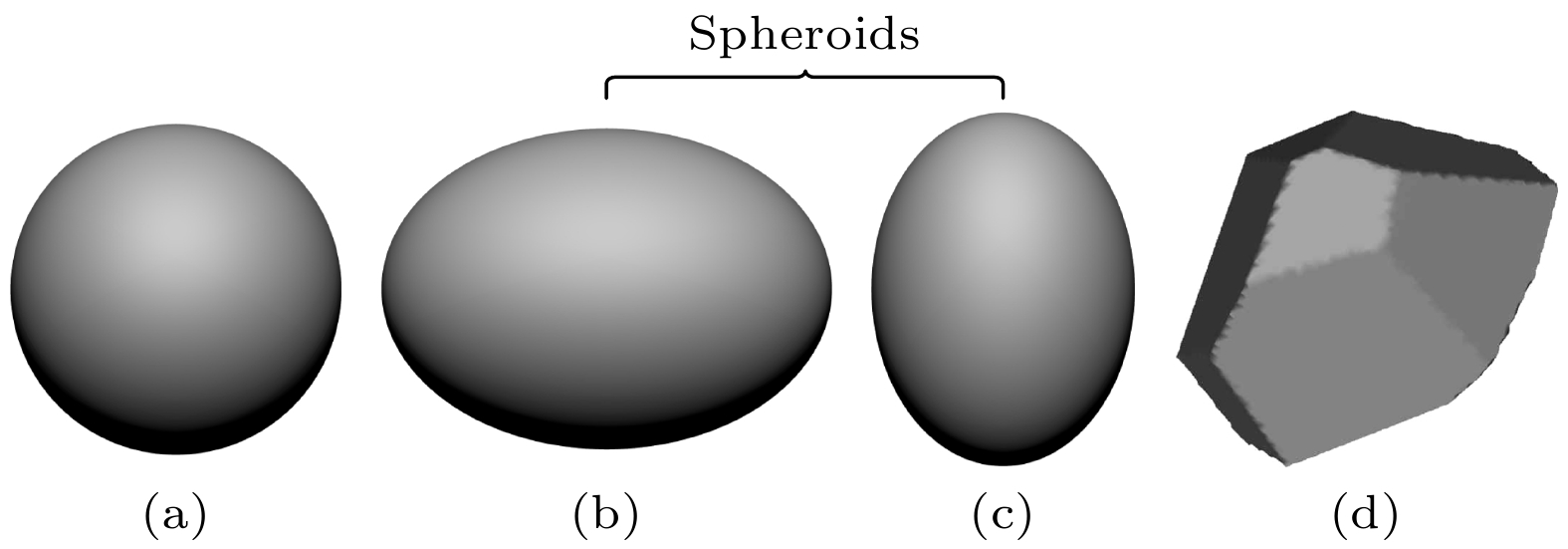
Microphysical quantities (particle shape, composition, size, density, complex refractive index, size distribution model, aspect ratio, hygroscopic parameter, etc.) of the ensemble of complex externally mixed aerosol particles vary greatly in humid environments (sea fog, water mist, haze, etc.). These microphysical quantities directly affect the transmission and scattering characteristics of laser. The optical properties (extinction coefficient, absorption coefficient, backscattering coefficient, phase function, etc.) of the ensemble of complex externally mixed aerosol particles directly determine the propagation properties of laser signals in the atmosphere, as well as the intensity and shape of echo signals. Therefore, studying the optical properties of the ensemble of complex externally mixed aerosol particles in humid environments is of significant importance for engineering applications such as autonomous driving, mapping, and remote sensing detection. Based on the various possibilities of aerosol particles existing in humid environments, the physicochemical properties of aerosol particles, including their shapes (sphere, oblate spheroid, prolate spheroid, and irregular), size distributions, complex refractive indices, densities, aspect ratios, their distribution models, and hygroscopicity parameters, are all taken into consideration in this work. Therefore, a scattering model of the ensemble of complex externally mixed aerosol particles is presented. Based on the presented complex aerosol scattering model, the influences of different mixing ratios (MR), and relative humidity (RH) on the optical properties, such as extinction coefficient, single scattering albedo, scattering phase matrix, asymmetry factor, backscattering coefficient, lidar ratio, and linear depolarization ratio, are numerically analyzed at typical incident laser wavelengths (0.78, 0.905, 1.064, 1.55, and 2.1 μm). In order to verify and demonstrate the rationality of the complex aerosol scattering model presented in this work, this model is compared with the scattering model of maritime pollution aerosol in optical properties of aerosols and clouds (OPAC). The results show that the optical properties of these two different aerosol scattering models vary similarly with wavelengths, although differences exist, but they are relatively small. Therefore, the influences of MR on the optical properties of the ensemble of complex internally mixed aerosol particles are analyzed. The influences of RH on the optical properties of the ensemble of complex internally mixed aerosol particles are also analyzed. The numerical results indicate that the extinction coefficient and phase function P11 exhibit strong sensitivity to both the MR and RH. As RH increases, the extinction coefficient and the forward scattering of P11 also increase. Compared with MR, single scattering albedo and asymmetry factor are more sensitive to RH. Significant differences in the sensitivity to RH and wavelength between linear and circular polarization properties are observed at different scattering angles. The backscattering coefficient is found to be inversely proportional to the lidar ratio, and the backscattering coefficient and the lidar ratio are both sensitive to MR and RH. It is observed that RH has a more pronounced effect on the linear depolarization ratio, while the influence of MR is weaker. The complex scattering model presented in this work further expands the study of aerosol optical properties and provides theoretical support for studying engineering applications involving lasers in different RHs environments. It is worth emphasizing that this work only focuses on external mixing. Therefore, the optical properties of the ensemble of complex internally mixed aerosol particles under different RHs will be discussed in the future. [1] Hess M, Koepke P, Schult I 1998 B. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 79 831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 王莉 2022 硕士学位论文 (武汉: 武汉科技大学)
Wang L 2022 M. S. Thesis (Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology
[3] 赵佳佳, 顾芳, 张加宏, 崔芬萍 2020 光学学报 40 0501001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao J J, Gu F, Gu J H, Cui F P 2020 Acta Opt. Sin. 40 0501001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Koepke P, Gasteiger J, Hess M 2015 Atmos. Chem. Phys. 15 5947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Tao Z M, Wang Z Z, Yang S J, Shan H H, Ma X M, Zhang H, Zhao S G, Liu D, Xie C B, Wang Y J 2016 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 9 1369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lian W T, Dai C M, Chen S P, Zhang Y X, Wu F, Zhang C, Wang C, Wei H L 2024 Remote Sens. 16 770
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Petters M D, Kreidenweis S M 2007 Atmos. Chem. Phys. 7 1961
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zieger P, Fierz-Schmidhauser R, Weingartner E, Baltensperger U 2013 Atmos. Chem. Phys. 13 10609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Gasteiger J, Wiegner M 2018 Geosci. Model Dev. 11 2739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 张学海, 戴聪明, 张鑫, 魏合理, 朱希娟, 马静 2019 红外与激光工程 48 0809002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X H, Dai C M, Zhang X, Wei H L, Zhu X J, Ma J 2019 Infrar. Laser Eng. 48 0809002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 战俊彤, 张肃, 付强, 段锦, 李英超, 姜会林 2020 红外与激光工程 49 20200057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhan J T, Zhang S, Fu Q, Duan J, Li Y C, Jiang H L 2020 Infrar. Laser Eng. 49 20200057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Shen C, Zhang S, Fu Q, Zhan J T, Duan J, Li Y C 2023 Front. Phys. 11 1266027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wu S X, Gao X B, Dou X Q, Xie L 2024 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 312 108808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Gasteiger J, Wiegner M, Groß S, Freudenthaler V, Toledano C, Tesche M, Kandler K 2011 Tellus B: Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 63 725
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 张学海, 魏合理, 戴聪明, 曹亚楠, 李学彬 2015 22 224205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X H, Wei H L, Dai C M, Cao Y N, Li X B 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 22 224205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Dubovik O, Sinyuk A, Lapyonok T, Holben B N, Mishchenko M, Yang P, Eck T F, Volten H, Muñoz O, Veihelmann B, Van der Zande W J, Leon J F, Sorokin M, Slutsker I 2006 J. Geophys. Res. 111 D11208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kandler K, Schütz L, Deutscher C, Ebert M, Hofmann H, Jäckel S, Jaenicke R, Knippertz P, Lieke K, Massling A, Petzold A, Schladitz B, Weinzierl A, Wiedensohler, Zorn S, Weinbruch1 S 2009 Tellus B 61 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li L, Zheng X, Li Z Q, Li Z H, Dubovik O, Chen X F, Wendisch M 2017 Opt. Express 25 A813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 王明军, 吴振森, 李应乐, 张小安, 由金光 2006 红外与激光工程 35 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang M J, Wu Z S, Li Y L, Zhang X, You J G 2006 Infrar. Laser Eng. 35 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang M J, Yu J H, Ke X Z, Wu T 2018 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium Toyama, Japan, August 1−4, 2018 p1141
[21] Meng Z, Yang P, Kattawar G W, Bi L, Liou K N, Laszlo I 2010 J. Aerosol Sci. 41 501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jung C H, Lee J Y, Um J, Lee S S, Yoon Y J, Kim Y P 2019 Appl. Sci. 9 1443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Castellanos P, Colarco P, Espinosa W R, Guzewich S D, Levy R C, Miller R L, Chin M, Kahn R A, Kemppinen O, Moosmüller H, Nowottnick E P 2024 Remote Sens. Environ. 303 113982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Liou K N, Yang P 2016 Light Scattering by Ice Crystals: Fundamentals and Applications (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp100, 101
[25] Akpootu D O, Bello G, Alaiyemola S R, Abdullahi Z, Aruna S, Umar M, Badmus T O, Isah A K, Abdulsalam M K, Aminu Z 2023 DUJOPAS 9 86
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
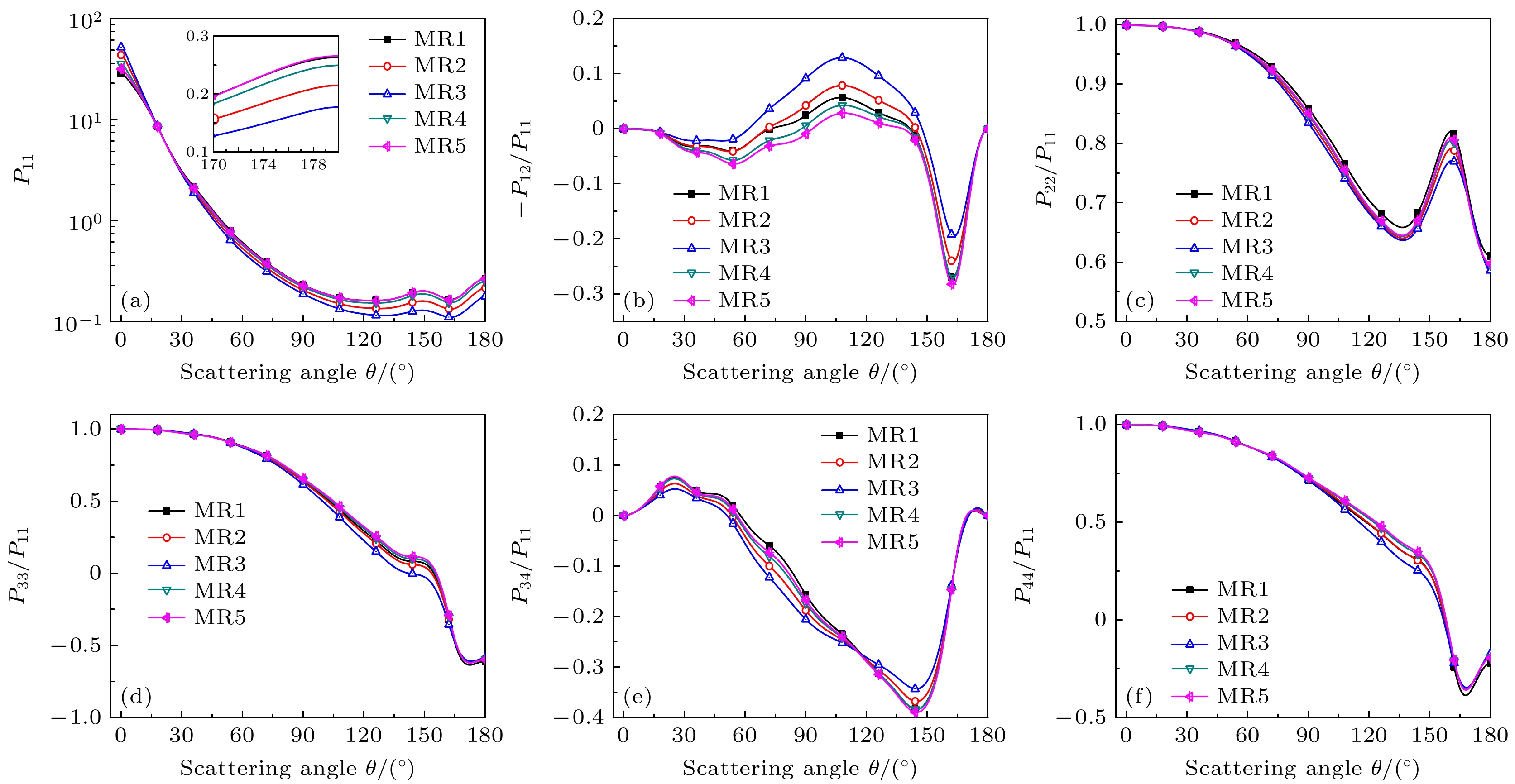
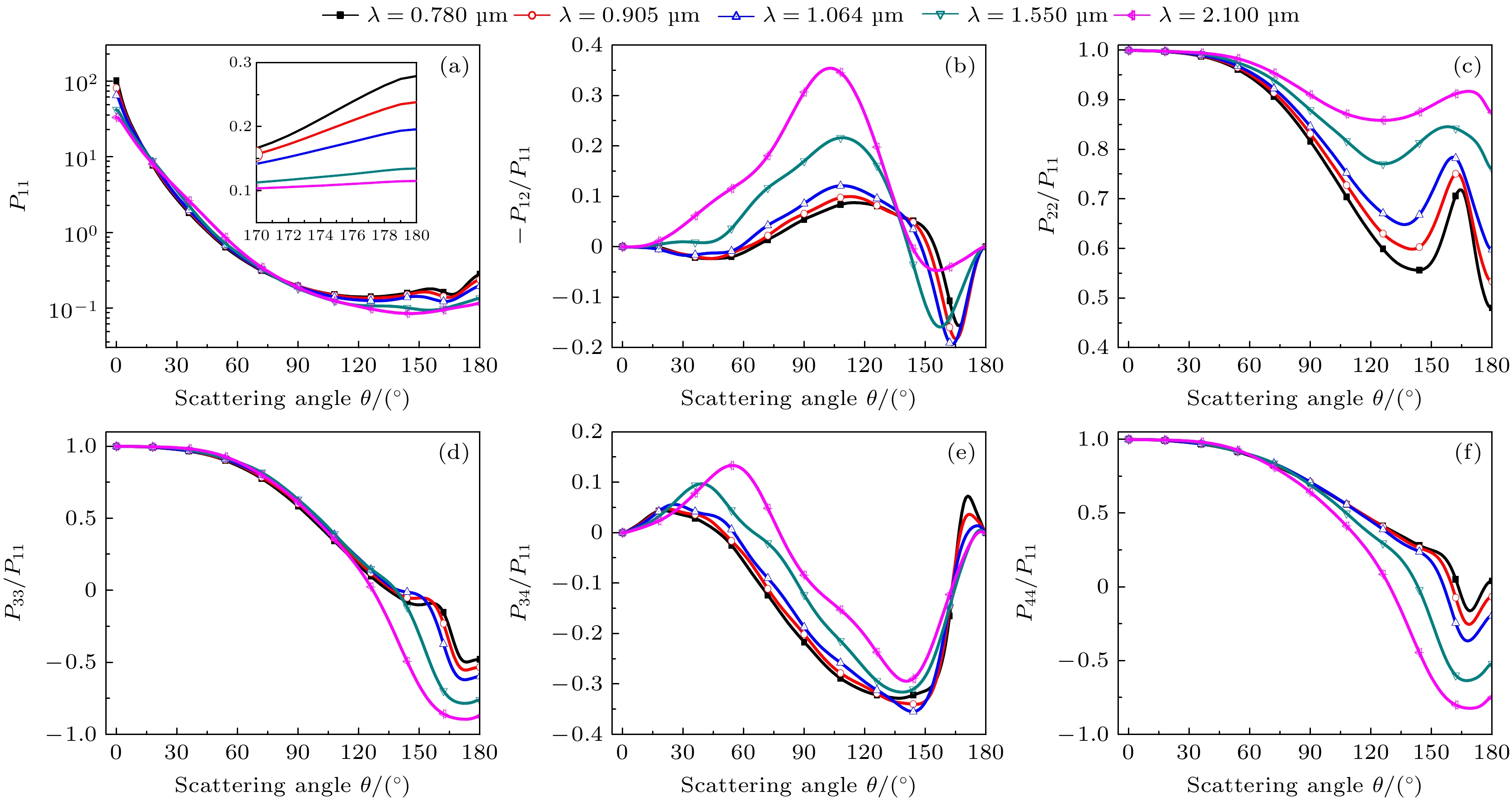
图 5 入射波长为1.064 μm时不同混合比例下散射相矩阵随散射角的变化 (a) $ {P_{11}} $; (b) $ - {P_{12}}/{P_{11}} $; (c) $ {P_{22}}/{P_{11}} $; (d) $ {P_{33}}/{P_{11}} $; (e) $ {P_{34}}/{P_{11}} $; (f) $ {P_{44}}/{P_{11}} $
Figure 5. Scattering phase matrix vs. scattering angle for different MRs at λ = 1.064 μm: (a) $ {P_{11}} $; (b) $ - {P_{12}}/{P_{11}} $; (c) $ {P_{22}}/{P_{11}} $; (d) $ {P_{33}}/{P_{11}} $; (e) $ {P_{34}}/{P_{11}} $; (f) $ {P_{44}}/{P_{11}} $.
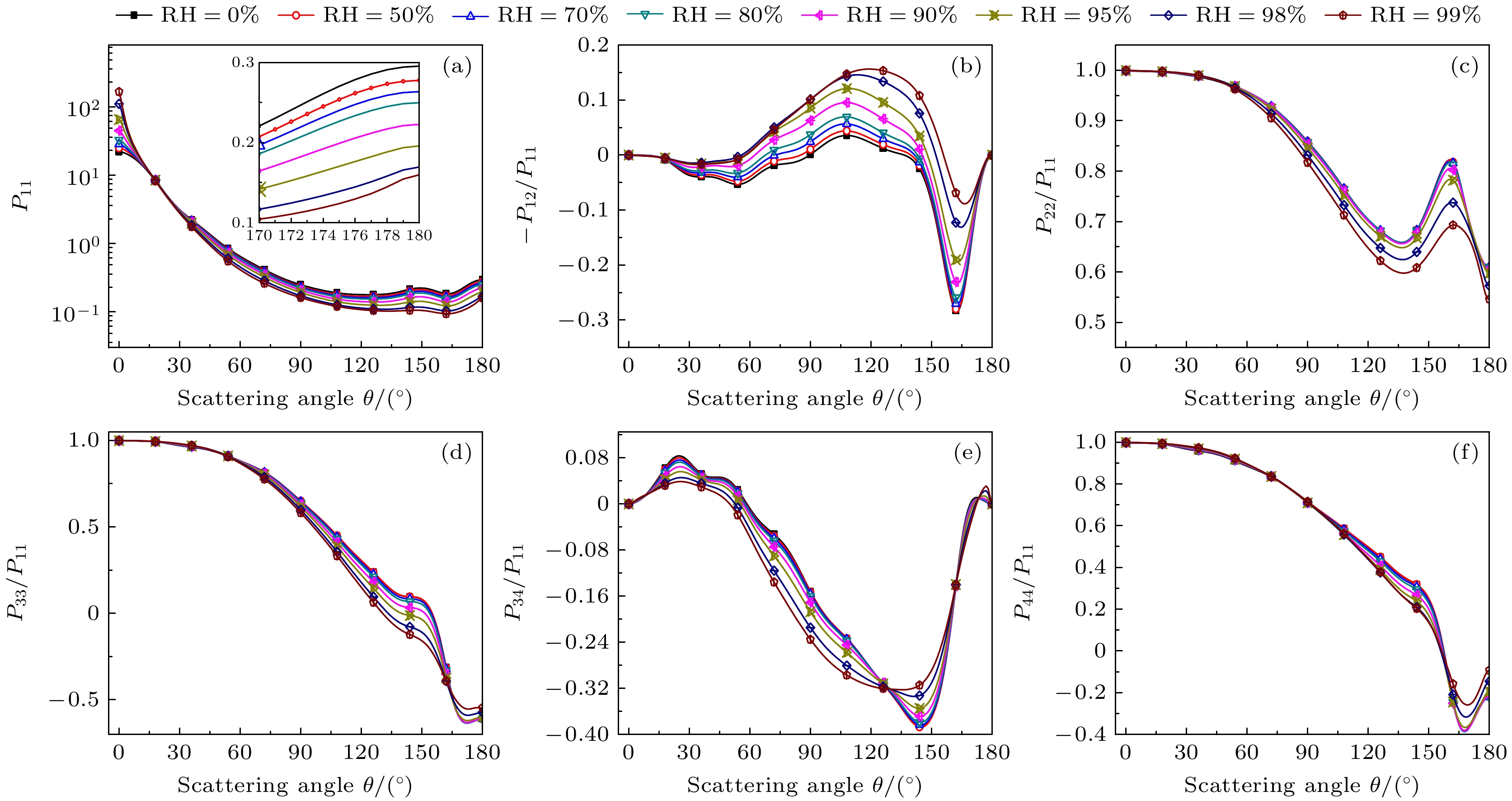
图 8 入射波长为1.064 μm时不同相对湿度条件下散射相矩阵随散射角的变化 (a) $ {P_{11}} $; (b) $ - {P_{12}}/{P_{11}} $; (c) $ {P_{22}}/{P_{11}} $; (d) $ {P_{33}}/{P_{11}} $; (e) $ {P_{34}}/{P_{11}} $; (f) $ {P_{44}}/{P_{11}} $
Figure 8. Scattering phase matrix vs. scattering angle for different RHs at λ = 1.064 μm: (a) $ {P_{11}} $; (b) $ - {P_{12}}/{P_{11}} $; (c) $ {P_{22}}/{P_{11}} $; (d) $ {P_{33}}/{P_{11}} $; (e) $ {P_{34}}/{P_{11}} $; (f) $ {P_{44}}/{P_{11}} $.
图 9 RH为95%时典型激光波长入射下散射相矩阵随散射角的变化 (a) $ {P_{11}} $; (b) $ - {P_{12}}/{P_{11}} $; (c) $ {P_{22}}/{P_{11}} $; (d) $ {P_{33}}/{P_{11}} $; (e) $ {P_{34}}/{P_{11}} $; (f) $ {P_{44}}/{P_{11}} $
Figure 9. Scattering phase matrix vs. scattering angle at typical laser wavelength incident when RH is 95%: (a) $ {P_{11}} $; (b) $ - {P_{12}}/{P_{11}} $; (c) $ {P_{22}}/{P_{11}} $; (d) $ {P_{33}}/{P_{11}} $; (e) $ {P_{34}}/{P_{11}} $; (f) $ {P_{44}}/{P_{11}} $.
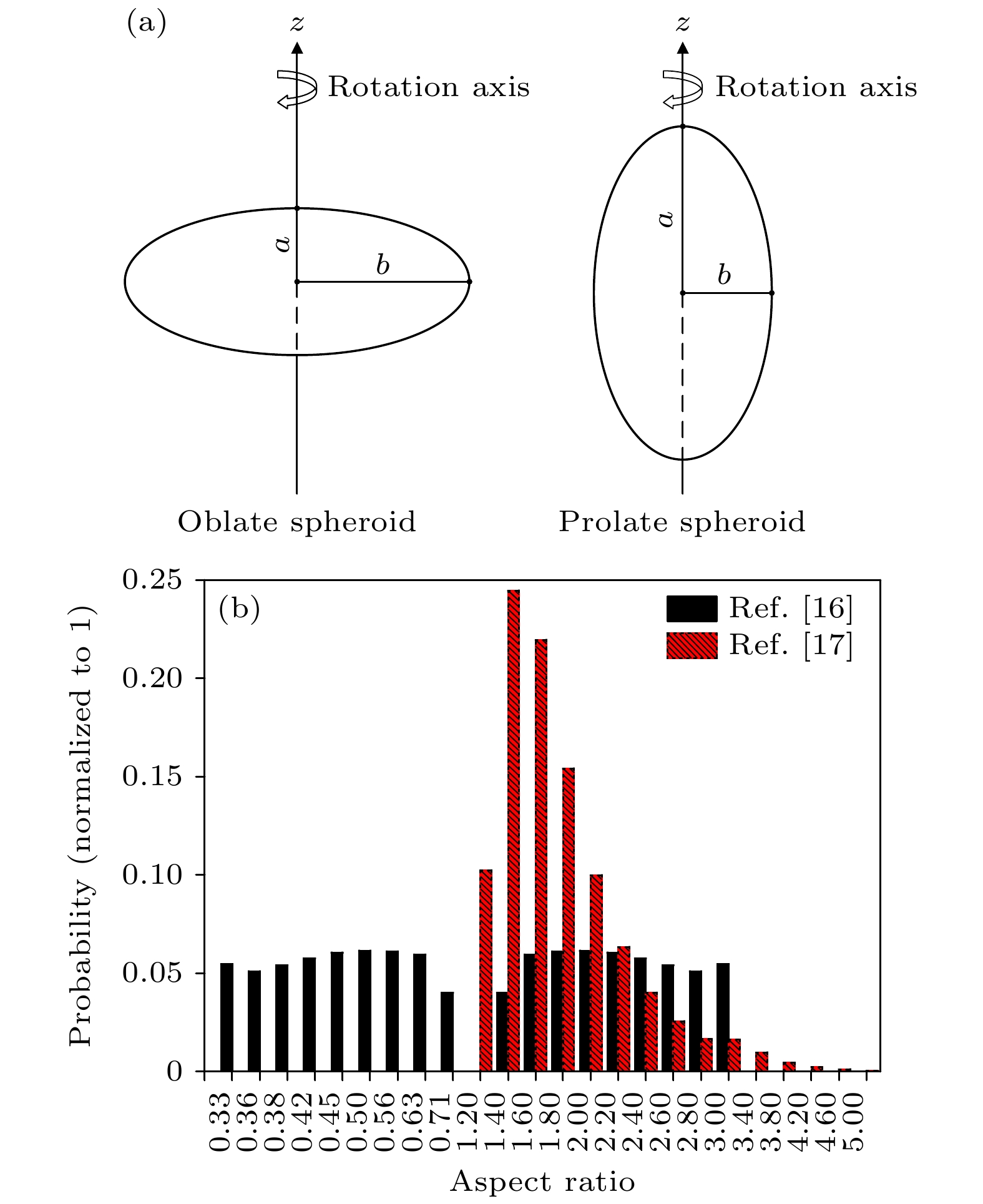
表 1 复杂外混合气溶胶粒子群的光散射模型
Table 1. Scattering model of the ensemble of complex externally mixed aerosol particles.
Aerosol shape Aerosol density Hygroscopicity
parameterAspect ratio Type of refractive
index of aerosolLog-normal distribution σ rmod Sphere 1.8 0.2 1 Water soluble 2.24 0.0212 Spheroids 2.2 0.8 Ref. [16] Sea salt 2.03 0.209 Spheroids 1.7 0.5 Ref. [17] Sulfate 2.03 0.0695 Irregular 2.6 0 1.3 Mineral 2 0.5 -
[1] Hess M, Koepke P, Schult I 1998 B. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 79 831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 王莉 2022 硕士学位论文 (武汉: 武汉科技大学)
Wang L 2022 M. S. Thesis (Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology
[3] 赵佳佳, 顾芳, 张加宏, 崔芬萍 2020 光学学报 40 0501001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao J J, Gu F, Gu J H, Cui F P 2020 Acta Opt. Sin. 40 0501001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Koepke P, Gasteiger J, Hess M 2015 Atmos. Chem. Phys. 15 5947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Tao Z M, Wang Z Z, Yang S J, Shan H H, Ma X M, Zhang H, Zhao S G, Liu D, Xie C B, Wang Y J 2016 Atmos. Meas. Tech. 9 1369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lian W T, Dai C M, Chen S P, Zhang Y X, Wu F, Zhang C, Wang C, Wei H L 2024 Remote Sens. 16 770
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Petters M D, Kreidenweis S M 2007 Atmos. Chem. Phys. 7 1961
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zieger P, Fierz-Schmidhauser R, Weingartner E, Baltensperger U 2013 Atmos. Chem. Phys. 13 10609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Gasteiger J, Wiegner M 2018 Geosci. Model Dev. 11 2739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 张学海, 戴聪明, 张鑫, 魏合理, 朱希娟, 马静 2019 红外与激光工程 48 0809002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X H, Dai C M, Zhang X, Wei H L, Zhu X J, Ma J 2019 Infrar. Laser Eng. 48 0809002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 战俊彤, 张肃, 付强, 段锦, 李英超, 姜会林 2020 红外与激光工程 49 20200057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhan J T, Zhang S, Fu Q, Duan J, Li Y C, Jiang H L 2020 Infrar. Laser Eng. 49 20200057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Shen C, Zhang S, Fu Q, Zhan J T, Duan J, Li Y C 2023 Front. Phys. 11 1266027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wu S X, Gao X B, Dou X Q, Xie L 2024 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 312 108808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Gasteiger J, Wiegner M, Groß S, Freudenthaler V, Toledano C, Tesche M, Kandler K 2011 Tellus B: Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 63 725
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 张学海, 魏合理, 戴聪明, 曹亚楠, 李学彬 2015 22 224205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X H, Wei H L, Dai C M, Cao Y N, Li X B 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 22 224205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Dubovik O, Sinyuk A, Lapyonok T, Holben B N, Mishchenko M, Yang P, Eck T F, Volten H, Muñoz O, Veihelmann B, Van der Zande W J, Leon J F, Sorokin M, Slutsker I 2006 J. Geophys. Res. 111 D11208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kandler K, Schütz L, Deutscher C, Ebert M, Hofmann H, Jäckel S, Jaenicke R, Knippertz P, Lieke K, Massling A, Petzold A, Schladitz B, Weinzierl A, Wiedensohler, Zorn S, Weinbruch1 S 2009 Tellus B 61 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Li L, Zheng X, Li Z Q, Li Z H, Dubovik O, Chen X F, Wendisch M 2017 Opt. Express 25 A813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 王明军, 吴振森, 李应乐, 张小安, 由金光 2006 红外与激光工程 35 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang M J, Wu Z S, Li Y L, Zhang X, You J G 2006 Infrar. Laser Eng. 35 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang M J, Yu J H, Ke X Z, Wu T 2018 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium Toyama, Japan, August 1−4, 2018 p1141
[21] Meng Z, Yang P, Kattawar G W, Bi L, Liou K N, Laszlo I 2010 J. Aerosol Sci. 41 501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jung C H, Lee J Y, Um J, Lee S S, Yoon Y J, Kim Y P 2019 Appl. Sci. 9 1443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Castellanos P, Colarco P, Espinosa W R, Guzewich S D, Levy R C, Miller R L, Chin M, Kahn R A, Kemppinen O, Moosmüller H, Nowottnick E P 2024 Remote Sens. Environ. 303 113982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Liou K N, Yang P 2016 Light Scattering by Ice Crystals: Fundamentals and Applications (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp100, 101
[25] Akpootu D O, Bello G, Alaiyemola S R, Abdullahi Z, Aruna S, Umar M, Badmus T O, Isah A K, Abdulsalam M K, Aminu Z 2023 DUJOPAS 9 86
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 2286
- PDF Downloads: 77
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: