-
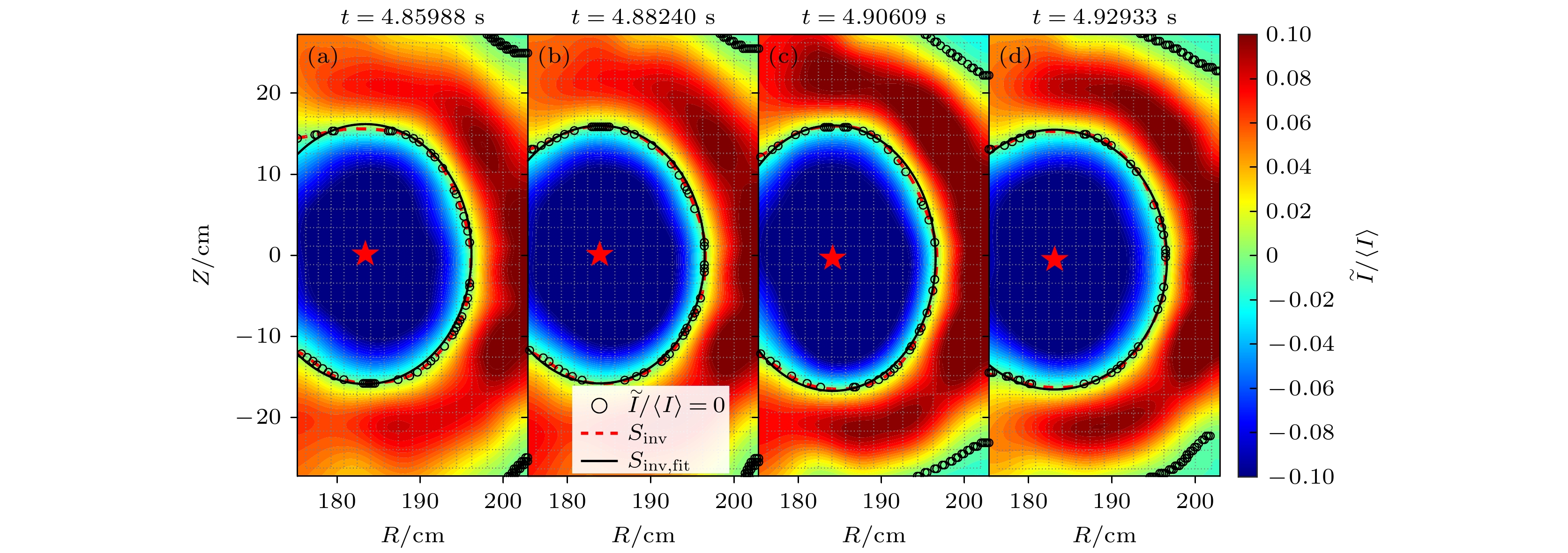
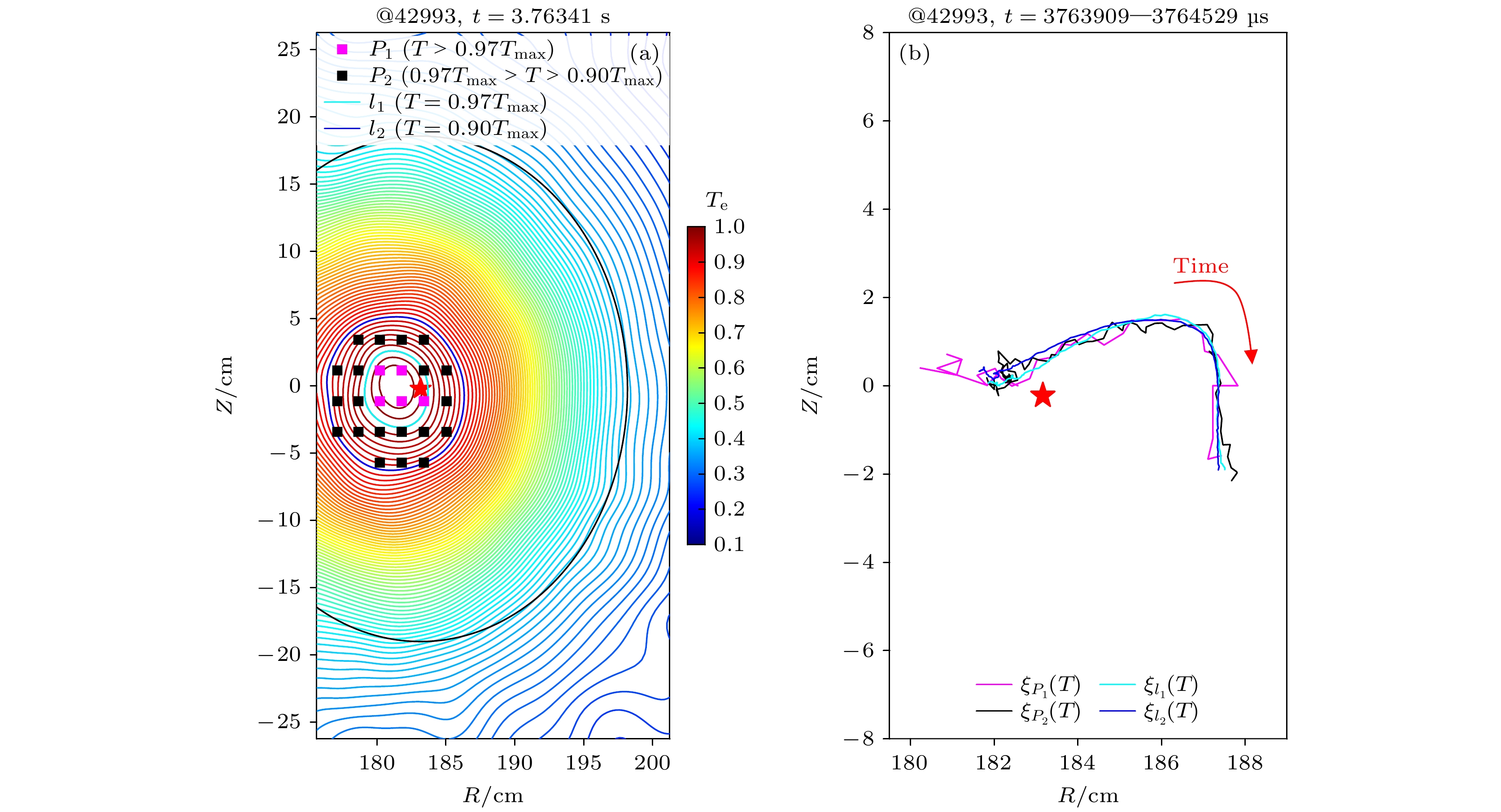
Electron cyclotron emission imaging (ECEI) system can provide the poloidal two-dimensional (2D) relative electron temperature perturbation profile of the core plasma with high spatial and temporal resolution. After absolute calibration of ECEI system, 2D absolute electron temperature profile and its perturbation can be provided. It can provide experimental data support for studying the local heat transport and the evolution of magnetic surface of macro magneto-hydro-dynamics instability. However, due to a large number of measurement channels and the wide measuring area of ECEI diagnostic system, the absolute calibration method in which a blackbody radiation source is used as a standard source, still has technical difficulties. This paper provides an absolute calibration method of ECEI diagnostic system on EAST tokamak, which can cover all the channels of ECEI system. Firstly, the sawtooth inversion surface can be determined by measuring the relative electron temperature change before and after the collapse of the sawtooth. The magnetic surface position and the shape ( ${S_{{\text{inv}}}}$ ) of the ECEI measuring area are fitted based on the position and shape of the inversion surface. Then, the one-to-one mapping relationship between laboratory coordinates of each ECEI channel and magnetic surface is obtained. Secondly, according to the assumption that the electron temperature is the same on each magnetic surface in equilibrium, the electron temperature of each magnetic surface is fitted by the electron cyclotron emission (ECE) system result, while the ECE system is absolutely calibrated. The calibration coefficient k(i, j) of each ECEI channel is obtained by comparing with the signal amplitude and the electron temperature on the magnetic surface. The relative error of absolute electron temperature between ECEI and ECE is no more than 6% at the same location.Based on the absolute electron temperature profile provided by ECEI, the motion of the magnetic axis during sawtooth instability can be tracked. It is found that the radial displacement of the magnetic axis occurs followed by the poloidal displacement during sawtooth collapse. This result indicates that after absolute calibration, the ECEI system can provide more abundant information about experimental research. -
Keywords:
- plasma diagnostics /
- calibration /
- sawtooth /
- electron cyclotron emission imaging
[1] Hutchinson I H 1987 Principles of Plasma Diagnostics (New York: Cambridge University Press) pp139–144
[2] Sajjad S, Gao X, Ling B, Ti A, Du Q 2008 Meas. Sci. Technol. 19 075701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu X, Zhao H L, Liu Y, Li E Z, Han X, Domier C W, Luhmann N C, Ti A, Hu L Q, Zhang X D 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 093508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Qian J P, Lao L L, Holcomb C T, Wan B N, Sun Y W, Moreau D, Li E, Zeng L, Hanada K, Garofalo A M, Gong X Z, Shen B, Xiao B J 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 084001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Nagayama Y, Taylor G, Yamada M, Fredrickson E D, Janos A C, McGuire K M 1996 Nucl. Fusion 36 521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Nagayama Y, Kawahata K, Inagaki S, et al. 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 205001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Nagayama Y, Taylor G, Fredrickson E D, Budny R V, Janos A C, Mansfield D K, McGuire K M, Yamada M 1996 Phys. Plasmas 3 2631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Park H, Mazzucato E, Munsat T, Domier C W, Johnson M, Luhmann N C, Wang J, Xia Z, Classen I G J, Donné A J H, VanDePol M J 2004 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75 3787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Park H K, Luhmann N C, Donné A J H, Classen I G J, Domier C W, Mazzucato E, Munsat T, van de Pol M J, Xia Z 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 195003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Igochine V, Boom J, Classen I, Dumbrajs O, Günter S, Lackner K, Pereverzev G, Zohm H, ASDEX Upgrade Team 2010 Phys. Plasmas 17 122506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nam Y B, Ko J S, Choe G H, Bae Y, Choi M J, Lee W, Yun G S, Jardin S, Park H K 2018 Nucl. Fusion 58 066009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Choi M J, Yun G S, Lee W, Park H K, Park Y S, Sabbagh S A, Gibson K J, Bowman C, Domier C W, Luhmann N C, Bak J G, Lee S G, the KSTAR Team 2014 Nucl. Fusion 54 083010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kim G, Yun G S, Woo M, the KSTAR team 2019 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 61 055001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Han D Q, Xie J L, Hussain A, Gao B X, Qu C M, Liao W, Xu X H, Gao F X, Li H, Lan T, Liu A, Zhuang G, Liu W D 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 10H119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 高炳西 2013 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Gao B X 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China
[16] Kadomtsev B B 1975 Sov. J. Plasma Phys. 1 389
[17] Powell M J D 1977 Math. Program. 12 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Holmström K 2008 J. Global Optim. 41(3) 447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Fitzgibbon A, Pilu M, Fisher R B 1999 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 21 476
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Waltz R E, Miller R L 1999 Phys. Plasmas 6 4265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Luo Z P, Xiao B J, Zhu Y F, Yang F 2010 Plasma Sci. Technol. 12 412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 伟森J 著(王文浩 译) 2021 托卡马克(北京: 清华大学出版社)第75—78页
Wesson J (translated by Wang W H) 2021 Tokamaks (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) pp75–78
[23] Vezinet D, Igochine V, Weiland M, Yu Q, Gude A, Meshcheriakov D, Sertoli M, the Asdex Upgrade Team, the EUROfusion MST1 Team 2016 Nucl. Fusion 56 086001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
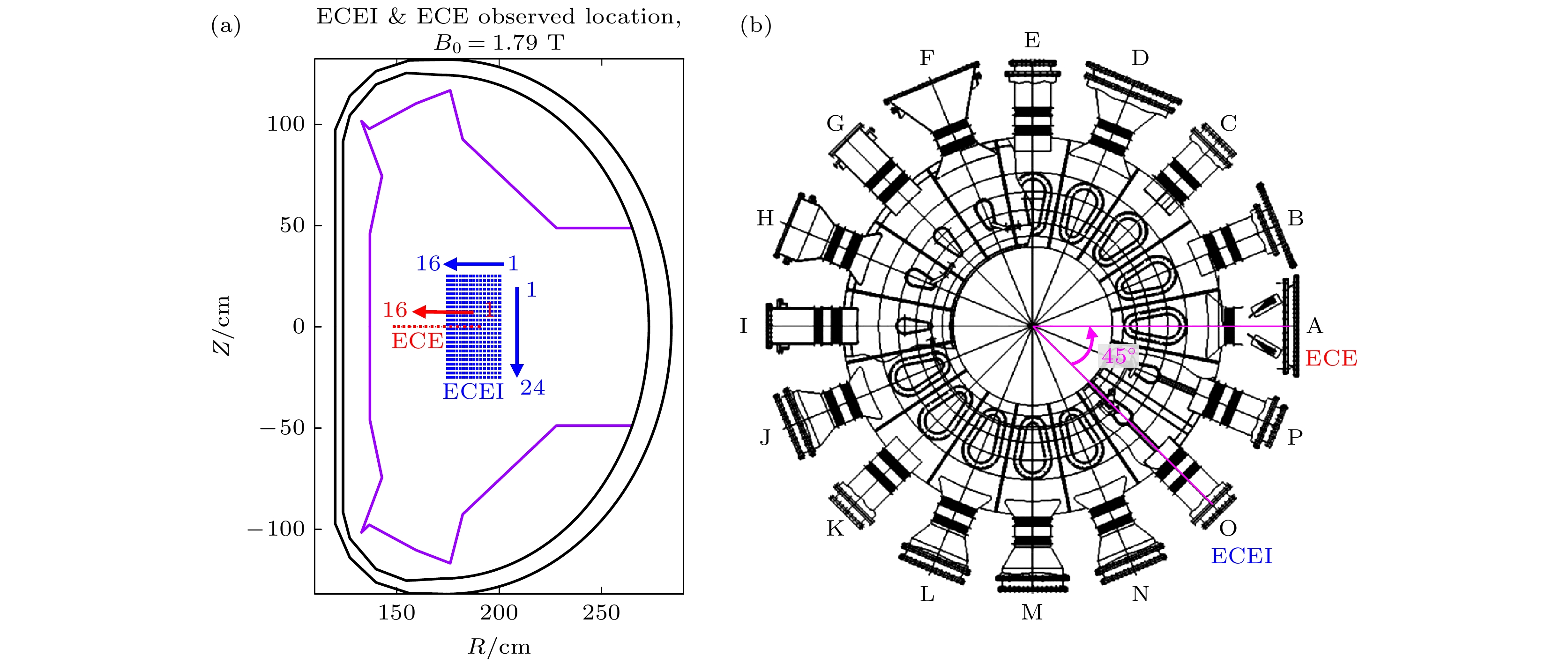
图 1 (a) EAST上ECE和ECEI诊断的测量位置在极向截面上的投影(B0 = 1.79 T); (b) EAST上ECE和ECEI诊断的环向位置, 环向角$\phi $相差45°
Figure 1. (a) Projection of ECE and ECEI diagnostic measurement positions on the poloidal cross section on the EAST (B0 = 1.79 T); (b) toroidal location of ECE and ECEI diagnoses on the EAST, with a 45° difference in toroidal angle $\phi $.
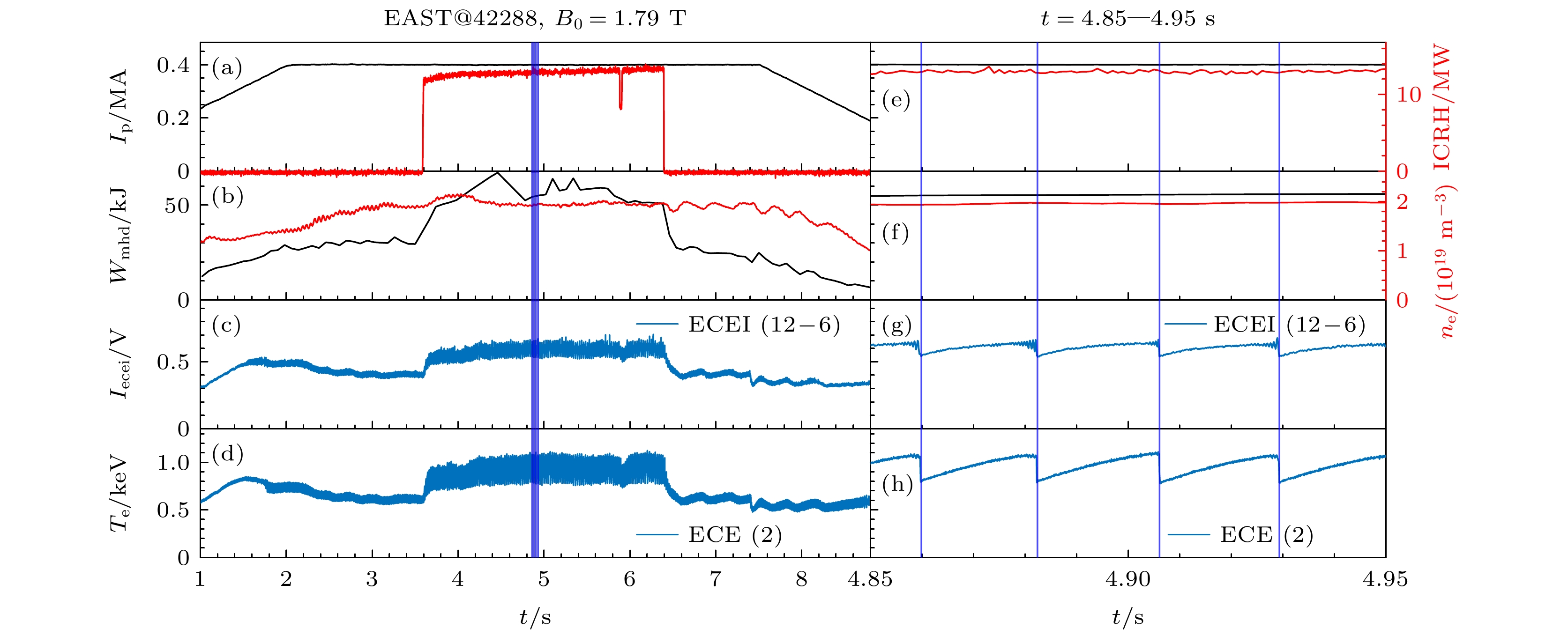
图 2 EAST的42288炮放电数据 (a)黑线为Ip 电流/MA, 红线为ICRH总加热功率; (b)黑线为等离子体储能Wmhd, 红线为等离子体密度${n_{\text{e}}} \times {10^{19}}$; (c) ECEI的第12行、6列通道的幅值Iecei ; (d) ECE的第2个测量通道(R =187 cm)的绝对温度${T_{\text{e}}}$. 图(a)—(d)为1—8.8 s的放电参数随时间变化图, 图(e)—(h)为截取4.85—4.95 s的放电参数随时间变化图, 蓝竖线为选取的判断锯齿反转面时刻
Figure 2. Data of shot 42288 of the EAST: (a) Black line is Ip, plasma current, and the red line is the total power of ICRH; (b) the black line indicates plasma energy storage Wmhd, and the red line indicates plasma density ${n_{\text{e}}} \times {10^{19}}$; (c) the radial value Iecei of the channel in row 12 and column 6 of ECEI; (d) absolute temperature ${T_{\text{e}}}$ of ECE’s second measurement channel (R = 187 cm). The diagram on the panels (a)–(d) show the variation of discharge parameters of 1—8.8 s over time, the diagram on the panels (e)–(h) show the variation of discharge parameters of 4.85—4.95 s over time, and the blue verticals line show the time when the sawtooth inversion surface is given.
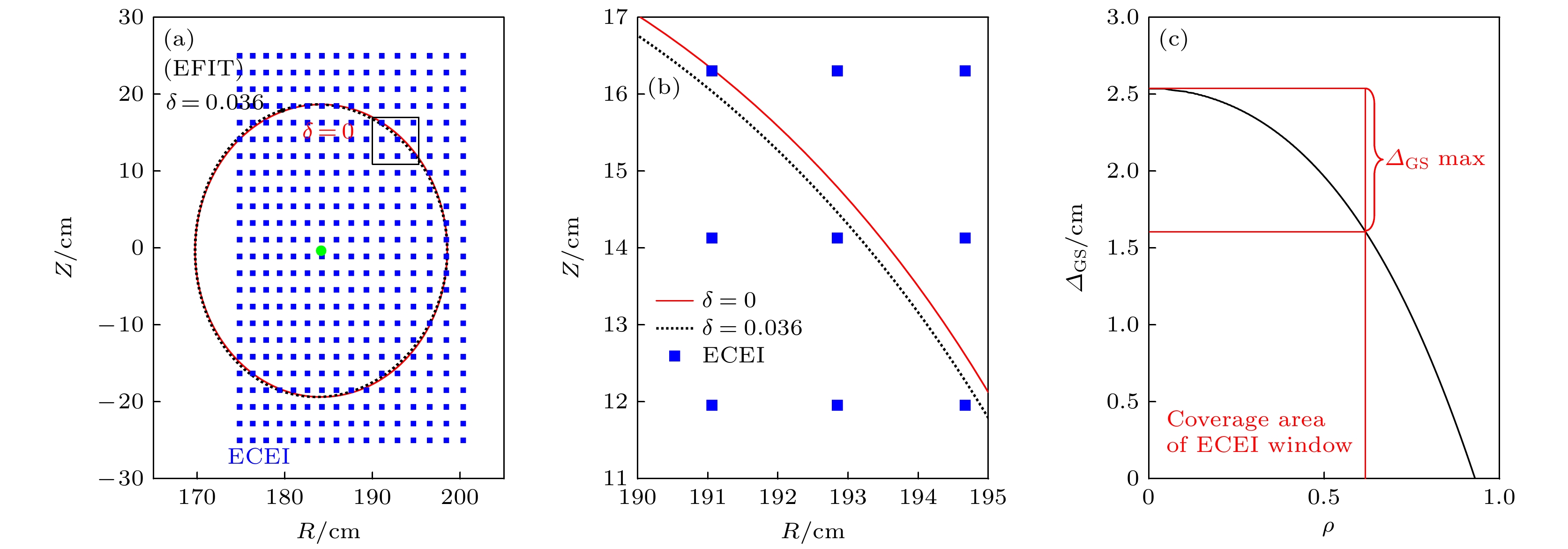
图 5 (a) EAST的42288炮4.90609 s时, 由ECEI锯齿反转面拟合的磁面形状(红线)与EFIT反演的磁面形状(黑虚线)对比; (b) 图(a)的局部放大结果; (c) EFIT反演磁面的沙夫拉诺夫位移随归一化小半径$\rho $的变化, 其中红竖线是ECEI诊断窗口在$\rho $的最大范围
Figure 5. (a) For EAST of 42288 shot 4.90609 s, the shape of the magnetic surface fitted by the ECEI sawtooth inversion surface (red line) is compared with the shape of the EFIT magnetic surface (black dashed line); (b) local magnification of panel (a); (c) change of Shafranov shift of EFIT magnetic surface with normalized small radius $\rho $, where the red vertical line is the maximum range of the ECEI diagnostic window in $\rho $.
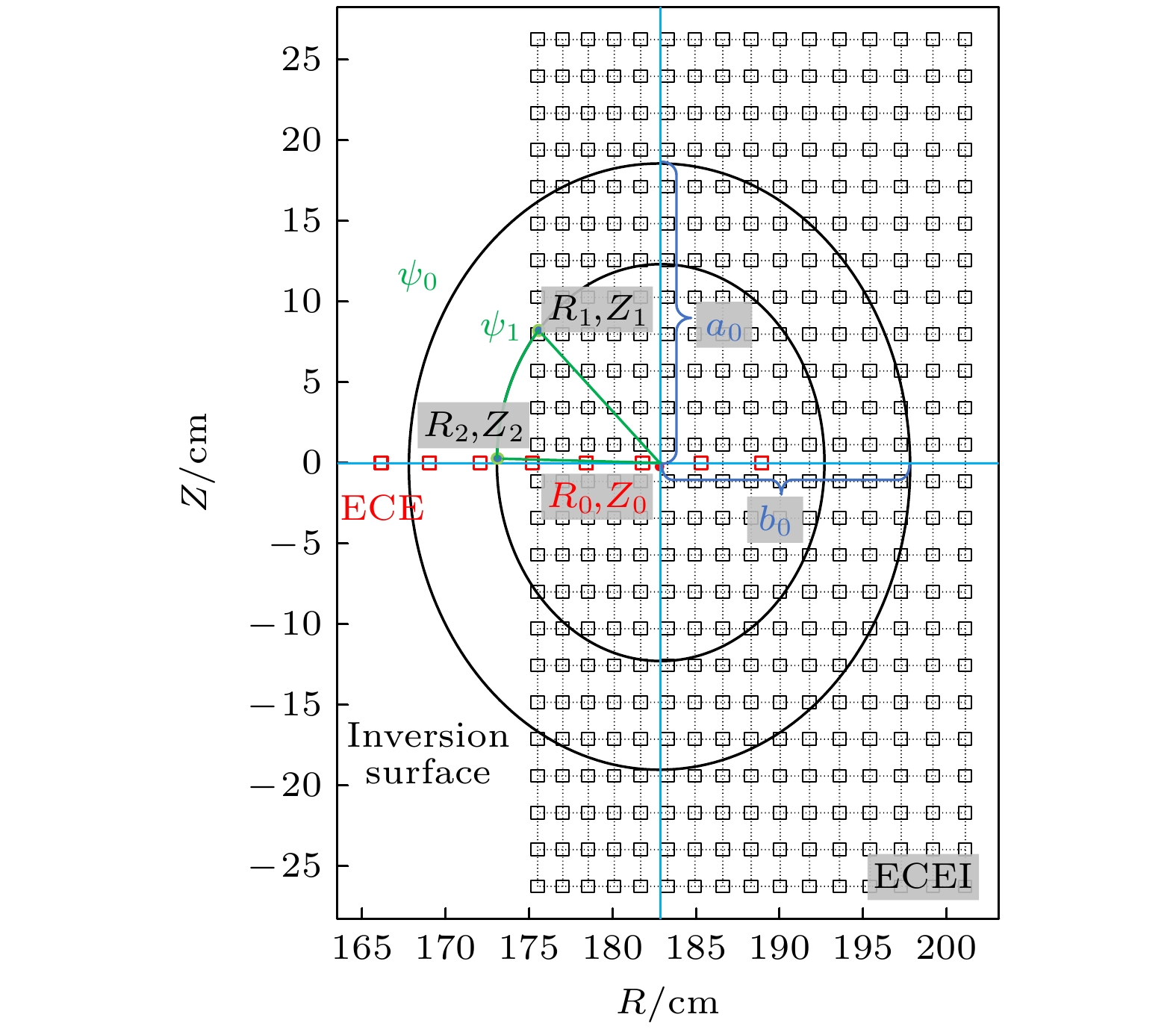
图 6 ECEI实验室坐标与磁面坐标对映的示意图, 将ECE数据插值得到磁面${\psi _1}$位置处(${R_2}, {Z_2}$)的绝对温度, 并使用坐标变换得到同一磁面处的ECEI通道(${R_1}, {Z_1}$), 其中锯齿反转面近似为椭圆, 长轴为${a_0}$, 短轴为${b_0}$, 所处的磁面为${\psi _0}$
Figure 6. Schematic showing the ECEI laboratory coordinates mapping to the magnetic surface coordinates. Interpolate ECE data to obtain the absolute temperature at the magnetic surface ${\psi _1}$ position (${R_2}, {Z_2}$), and then the ECEI channel (${R_1}, {Z_1}$) at the same magnetic surface is obtained by using coordinate transformation. The zigzag inversion surface is approximately an ellipse, the major axis is ${a_0}$, the short axis is ${b_0}$, and the magnetic surface is ${\psi _0}$.
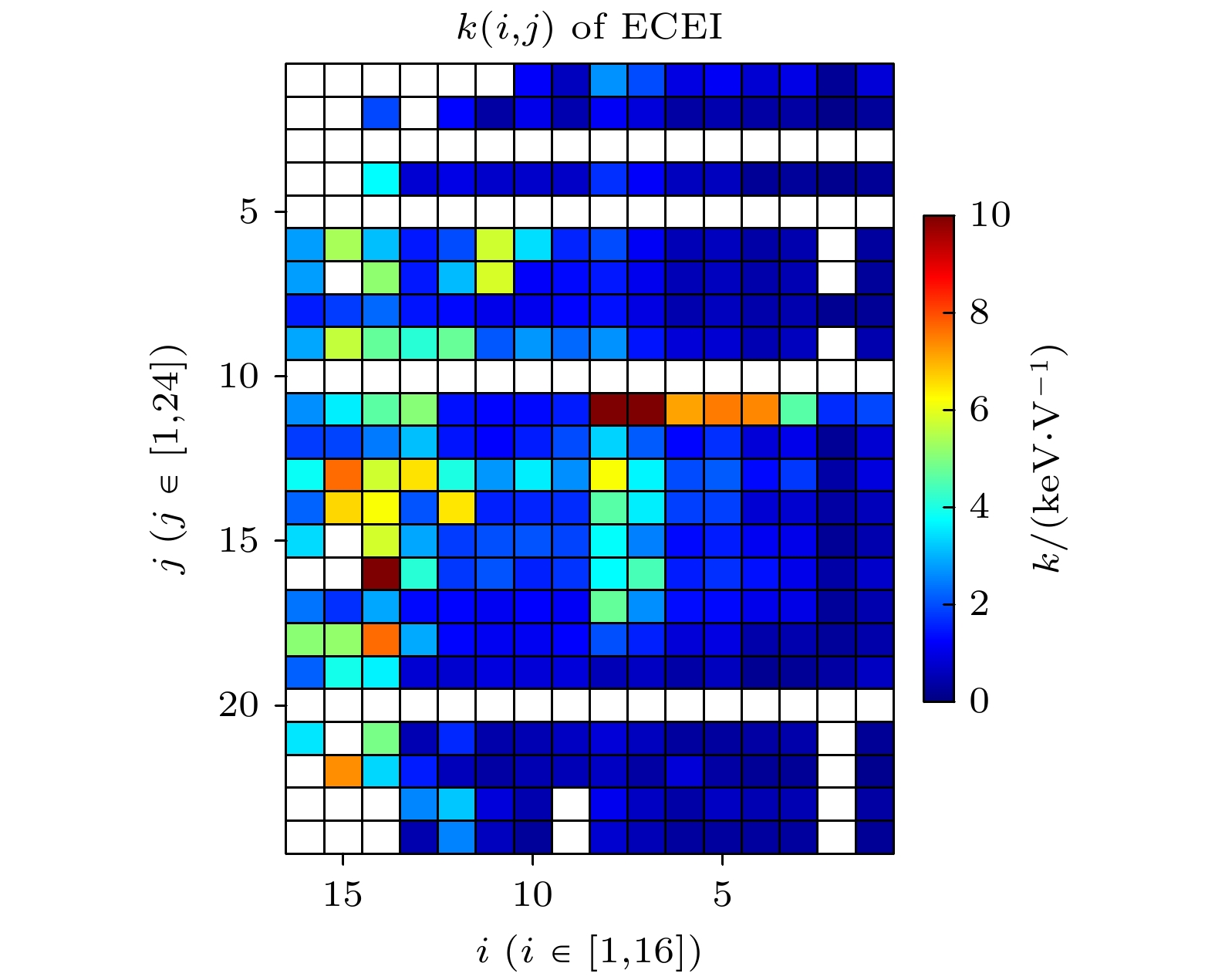
图 7 EAST的ECEI标定系数, 横纵坐标分别表示ECEI的径向与纵向的道号, 不同颜色为标定的系数大小, 白色为坏道位置
Figure 7. ECEI calibration coefficient of EAST, the horizontal and vertical coordinates represent the radial and vertical channel numbers of ECEI respectively, the color bars represent the value of the calibrated coefficient, and white is the position of the bad track.
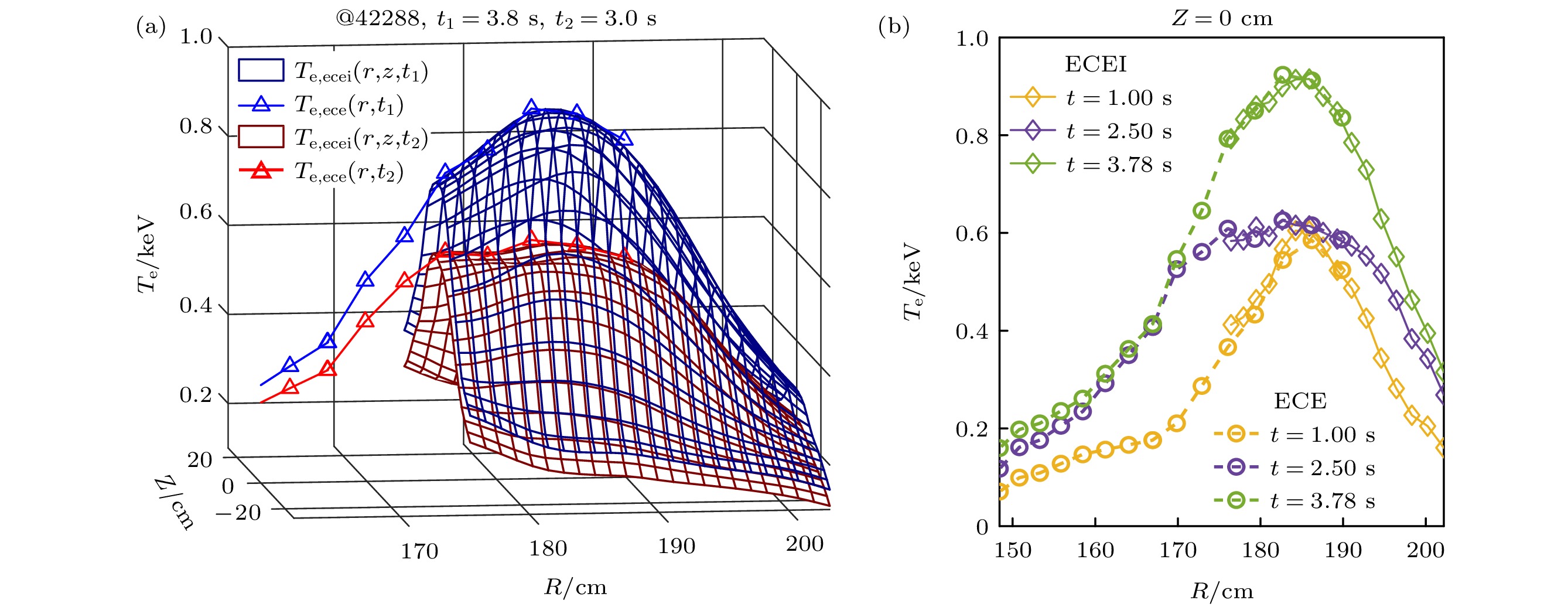
图 8 ECEI标定结果与ECE对比 (a)标定后ECEI所有道与ECE绝对温度的对比; (b)标定后ECEI中心道($j$= 12)与ECE绝对温度的对比
Figure 8. Results of ECEI calibration were compared with those of ECE: (a) Comparison of all ECEI channels and ECE absolute temperatures after calibration; (b) the absolute temperature of ECEI center channel ($j$= 12) compared with ECE after calibration.
-
[1] Hutchinson I H 1987 Principles of Plasma Diagnostics (New York: Cambridge University Press) pp139–144
[2] Sajjad S, Gao X, Ling B, Ti A, Du Q 2008 Meas. Sci. Technol. 19 075701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu X, Zhao H L, Liu Y, Li E Z, Han X, Domier C W, Luhmann N C, Ti A, Hu L Q, Zhang X D 2014 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85 093508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Qian J P, Lao L L, Holcomb C T, Wan B N, Sun Y W, Moreau D, Li E, Zeng L, Hanada K, Garofalo A M, Gong X Z, Shen B, Xiao B J 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 084001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Nagayama Y, Taylor G, Yamada M, Fredrickson E D, Janos A C, McGuire K M 1996 Nucl. Fusion 36 521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Nagayama Y, Kawahata K, Inagaki S, et al. 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 205001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Nagayama Y, Taylor G, Fredrickson E D, Budny R V, Janos A C, Mansfield D K, McGuire K M, Yamada M 1996 Phys. Plasmas 3 2631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Park H, Mazzucato E, Munsat T, Domier C W, Johnson M, Luhmann N C, Wang J, Xia Z, Classen I G J, Donné A J H, VanDePol M J 2004 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75 3787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Park H K, Luhmann N C, Donné A J H, Classen I G J, Domier C W, Mazzucato E, Munsat T, van de Pol M J, Xia Z 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 195003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Igochine V, Boom J, Classen I, Dumbrajs O, Günter S, Lackner K, Pereverzev G, Zohm H, ASDEX Upgrade Team 2010 Phys. Plasmas 17 122506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nam Y B, Ko J S, Choe G H, Bae Y, Choi M J, Lee W, Yun G S, Jardin S, Park H K 2018 Nucl. Fusion 58 066009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Choi M J, Yun G S, Lee W, Park H K, Park Y S, Sabbagh S A, Gibson K J, Bowman C, Domier C W, Luhmann N C, Bak J G, Lee S G, the KSTAR Team 2014 Nucl. Fusion 54 083010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kim G, Yun G S, Woo M, the KSTAR team 2019 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 61 055001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Han D Q, Xie J L, Hussain A, Gao B X, Qu C M, Liao W, Xu X H, Gao F X, Li H, Lan T, Liu A, Zhuang G, Liu W D 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 10H119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 高炳西 2013 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Gao B X 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China
[16] Kadomtsev B B 1975 Sov. J. Plasma Phys. 1 389
[17] Powell M J D 1977 Math. Program. 12 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Holmström K 2008 J. Global Optim. 41(3) 447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Fitzgibbon A, Pilu M, Fisher R B 1999 IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 21 476
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Waltz R E, Miller R L 1999 Phys. Plasmas 6 4265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Luo Z P, Xiao B J, Zhu Y F, Yang F 2010 Plasma Sci. Technol. 12 412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 伟森J 著(王文浩 译) 2021 托卡马克(北京: 清华大学出版社)第75—78页
Wesson J (translated by Wang W H) 2021 Tokamaks (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) pp75–78
[23] Vezinet D, Igochine V, Weiland M, Yu Q, Gude A, Meshcheriakov D, Sertoli M, the Asdex Upgrade Team, the EUROfusion MST1 Team 2016 Nucl. Fusion 56 086001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3076
- PDF Downloads: 94
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: