-
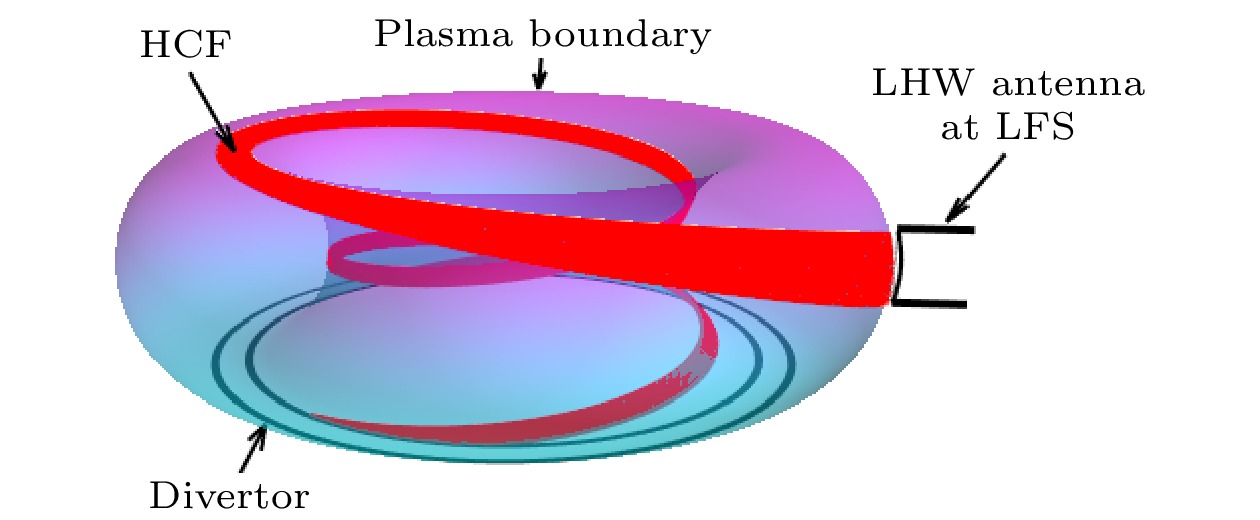
The high-confinement mode (H-mode) significantly enhances the energy and particle confinement in fusion plasma compared with the low-confinement mode (L-mode), and it is the basic operation scenario for ITER and CFETR. Edge localized mode (ELM) often appears in H-mode, helping to expel impurities to maintain a longer stable state. However, the particle burst and energy burst from ELM eruptions can severely damage the first wall of fusion device, so, it is necessary to control the ELM. Experiments on EAST tokamak and HL-2A tokamak have been conducted with ELM mitigation by lower hybrid wave (LHW), confirming the effect of LHW on ELMs, but the physical mechanism of ELM mitigation by LHW is still not fully understood. In this paper, the influences of LHW injection on the linear and nonlinear characteristics of peeling-ballooning mode (P-B mode) are investigated in the edge pedestal region of H-mode plasma in tokamak by using the BOUT++ code. The simulations take into consideration both the conventional main plasma current driven by LHW and the three-dimensional perturbed magnetic field generated by the scrape-off layer helical current filament (HCF) on the P-B mode. The linear results show that the core plasma current driven by LHW moves the linear toroidal mode spectrum towards higher mode numbers and lower growth rates by reducing the normalized pressure gradient and magnetic shear of the equilibrium. Nonlinear simulations indicate that due to the broadening of the linear mode spectrum, the core current driven by LHW can reduce the pedestal energy loss caused by ELM through globally suppressing different toroidal modes of the P-B mode, and the three-dimensional perturbed magnetic field generated by LHW-driven HCF can reduce the energy loss caused by ELMs through promoting the growth of modes other than the main mode and enhancing the coupling between different modes. It is found in the study that the P-B mode promoted by the three-dimensional perturbed magnetic field generated by HCF has a mode number threshold, and when the dominant mode of the P-B mode is far from the mode number threshold driven by the three-dimensional perturbed magnetic field, the energy loss due to ELMs is more significantly reduced. These results contribute to a more in-depth understanding of the physical mechanism in ELM control experiment by LHW.
-
Keywords:
- magnetic confinement fusion plasma /
- edge localized modes /
- lower hybrid wave /
- peeling-ballooning modes
[1] Zohm H 1996 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 38 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Leonard A W 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 090501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Loarte A, Saibene G, Sartori R, et al. 2003 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 45 1549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lang P T, Loarte A, Saibene G, et al. 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 043004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Loarte A, Huijsmans G, Futatani S, et al. 2014 Nucl. Fusion 54 033007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hughes J W, Hubbard A E, Wallace G, et al. 2010 Nucl. Fusion 50 064001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wan B, Li J, Guo H, Liang Y, Xu G, Gong X Z for the EAST Team, International Collaborators 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 104006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Rossel J X, Moret J M, Coda S, Sauter O, Goodman T P, Felici F, Testa D, Martin Y 2012 Nucl. Fusion 52 032004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Felici F, Rossel J X, Duval B P, Coda S, Goodman T P, Martin Y, Moret J M, Sauter O, the TCV Team 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 113018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Baylor L R, Commaux N, Jernigan T C, et al. 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 245001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen S Y, Huang J, Sun T T, Wang Z H, Tang C J 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 112512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Evans T E, Moyer R A, Watkins J G, et al. 2005 J. Nucl. Mater. 337–339 691
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Canik J M, Maingi R, Evans T E, et al. 2010 Nucl. Fusion 50 034012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xiao W W, Diamond P H, Zou X L, et al. 2012 Nucl. Fusion 52 114027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Huang J, Chen S Y, Wang Z H, Tang C J 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 122507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Degeling A W, Martin Y R, Lister J B, Villard L, Dokouka V N, Lukash V E, Khayrutdinov R R 2003 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 45 1637
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wu N, Chen S Y, Song X M, Mou M L, Huang J, Wang Z T, Tang C J, Song X, Xia F, Jiang M, HL-2A Team 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 092507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang H M, Wu J, Li J X, Yao L M, Xu J C, Wu Y Z, Liu Q Y, Guo P C 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 235203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 刘冠男, 李新霞, 刘洪波, 孙爱萍 2023 72 245202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu G N, Li X X, Liu H B, Sun A P 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 245202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhou T T, Xiang N, Gan C Y, Jia G Z, Chen J L 2022 Chin. Phys. B 31 095201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Xu Z, Wu Z W, Zhang L, Huang Y H, Gao W, Cheng Y X, Lin X D, Gao X, Chen Y J, Li L, Jie Y X, Zang Q, Liu H Q, EAST Team 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 075205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liang Y, Gong X Z, Gan K F, et al. 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 235002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xiao G L, Zhong W L, Zou X L, et al. 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 122507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Cui B T, Ji X Q, Sun T F, Liang S Y, Zhang J Z, Wang A, He M Y 2021 Fusion Eng. Des. 173 112963
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li S H, Wang N C, Ding Y H, et al. 2022 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 64 075005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Snyder P B, Wilson H R, Ferron J R, Lao L L, Leonard A W, Osborne T H, Turnbull A D, Mossessian D, Murakami M, Xu X Q 2002 Phys. Plasmas 9 2037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bernard L C, Helton F J, Moore R W 1981 Comput. Phys. Commun. 24 377
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Pankin A Y, Bateman G, Brennan D P, Kritz A H, Kruger S, Snyder P B, Sovinec C, the NIMROD Team 2007 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 49 S63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Pamela S J P, Huijsmans G T A, Eich T, et al. 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 076006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Dudson B D, Umansky M V, Xu X Q, Snyder P B, Wilson H R 2009 Comput. Phys. Commun. 180 1467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Xu X Q, Dudson B, Snyder P B, Umansky M V, Wilson H 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 175005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Xia T Y, Xu X Q 2013 Phys. Plasmas 20 052102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Xia T Y, Xu X Q, Xi P W 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 073009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Mou M L, Huang J, Wu N, Chen S Y, Tang C J 2016 Phys. Lett. A 380 2544
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Dong L K, Chen S Y, Mou M L, Tang C J 2020 Plasma Sci. Technol. 22 115101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Huang J, Chen S Y, Tang C J 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 052513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Xia T Y, Gui B, Huang Y Q, Wu Y B, Xiao X T, EAST Team 2019 Nucl. Fusion 59 076043
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Shi Y J, Xu G S, Wang F D, et al. 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 235001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Rice J E, Podpaly Y A, Reinke M L, et al. 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 093015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Chouli B, Fenzi C, Garbet X, et al. 2014 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 56 095018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Chen W, Wang Z X 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 125001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Fisch N J, Rax J M 1992 Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 612
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Smirnov A P, Harvey R W 2001 The GENRAY Ray Tracing Code CompX Report No. CompX-2000-01
[44] Ehst D A, Karney C F F 1991 Nucl. Fusion 31 1933
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Crotinger J A, LoDestro L, Pearlstein L D, Tarditi A, Casper T A, Hooper E B 1997 CORSICA: A Comprehensive Simulation of Toroidal Magnetic-fusion Devices. Final Report to the LDRD Program (Livermore: Lawrence Livermore National Lab.) Report No: UCRL-ID-126284
[46] Xu X Q, Ma J F, Li G Q 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 120704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Burrell K H 1997 Phys. Plasmas 4 1499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Ding B J, Bonoli P T, Tuccillo A, et al. 2018 Nucl. Fusion 58 095003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Li G Q, Xu X Q, Snyder P B, Turnbull A D, Xia T Y, Ma C H, Xi P W 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 102511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Zhang Y, Huang J, Chen S Y, Tang C J 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 062108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Li J, Guo H Y, Wan B N, et al. 2013 Nat. Phys. 9 817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Dong L K, Chen S Y, Mou M L, Luo Y, Qin C C, Tang C J 2023 Nucl. Fusion 63 086023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Liu Y, Ham C J, Kirk A, Li L, Loarte A, Ryan D A, Sun Y, Suttrop W, Yang X, Zhou L 2016 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 58 114005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[54] Oyama N, Sakamoto Y, Isayama A, et al. 2005 Nucl. Fusion 45 871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[55] Aiba N, Giroud C, Honda M, et al. 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 126001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Luo Y, Chen S Y, Huang J, Xiong Y Y, Tang C J 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 042302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[57] Xi P W, Xu X Q, Wang X G, Xia T Y 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 092503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[58] 李春雨, 郝广周, 刘钺强, 王炼, 刘艺慧子 2022 71 075202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C Y, Hao G Z, Liu Y Q, Wang L, Liu Y H Z 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 075202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
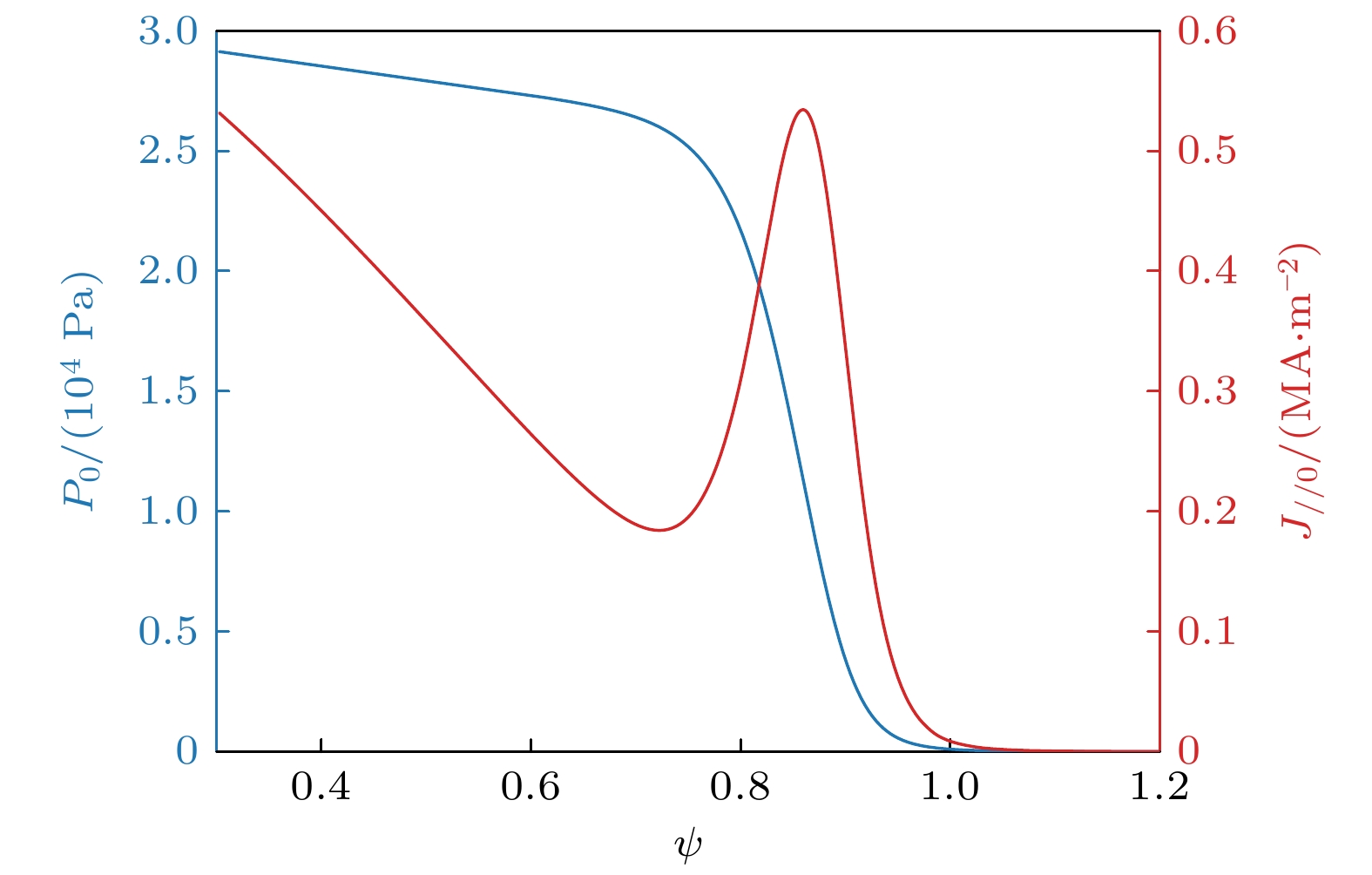
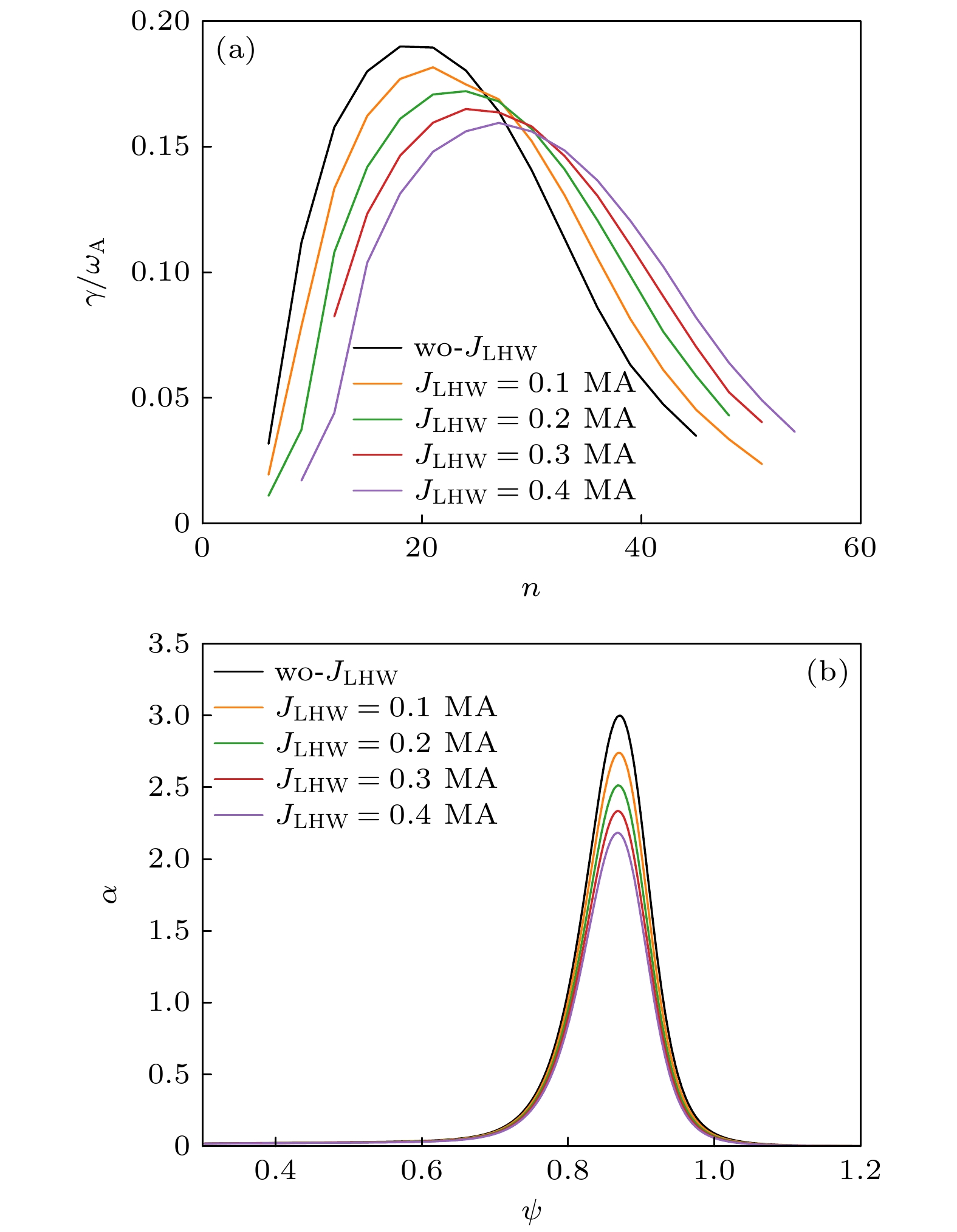
图 5 (a) P-B模归一化线性增长率, 其中$ {\omega }_{{\mathrm{A}}}=1/{\tau }_{{\mathrm{A}}} $为阿尔芬频率; (b)平衡的归一化压强梯度, 其中$ \alpha = $ $\left(2{\mu }_{0}{R}_{0}{q}^{2}{\mathrm{d}}p\right)/\left({B}^{2}{\mathrm{d}}r\right) $
Figure 5. (a) Linear growth rates of the P-B mode; (b) normalized pressure gradient of the equilibrium with different $ {J}_{{\mathrm{L}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{W}}} $. Here, $ \alpha =\left(2{\mu }_{0}{R}_{0}{q}^{2}{\mathrm{d}}p\right)/\left({B}^{2}{\mathrm{d}}r\right) $.
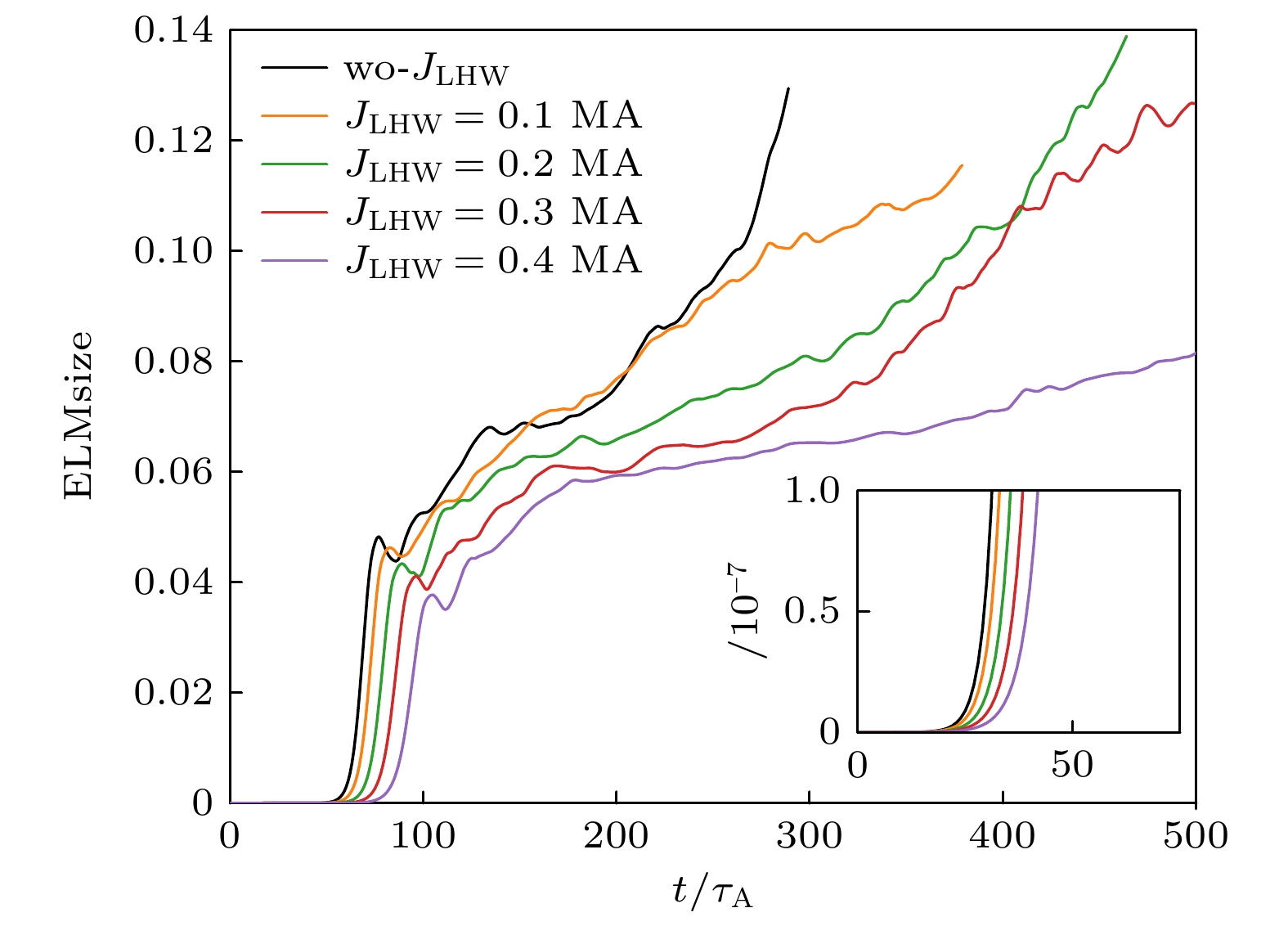
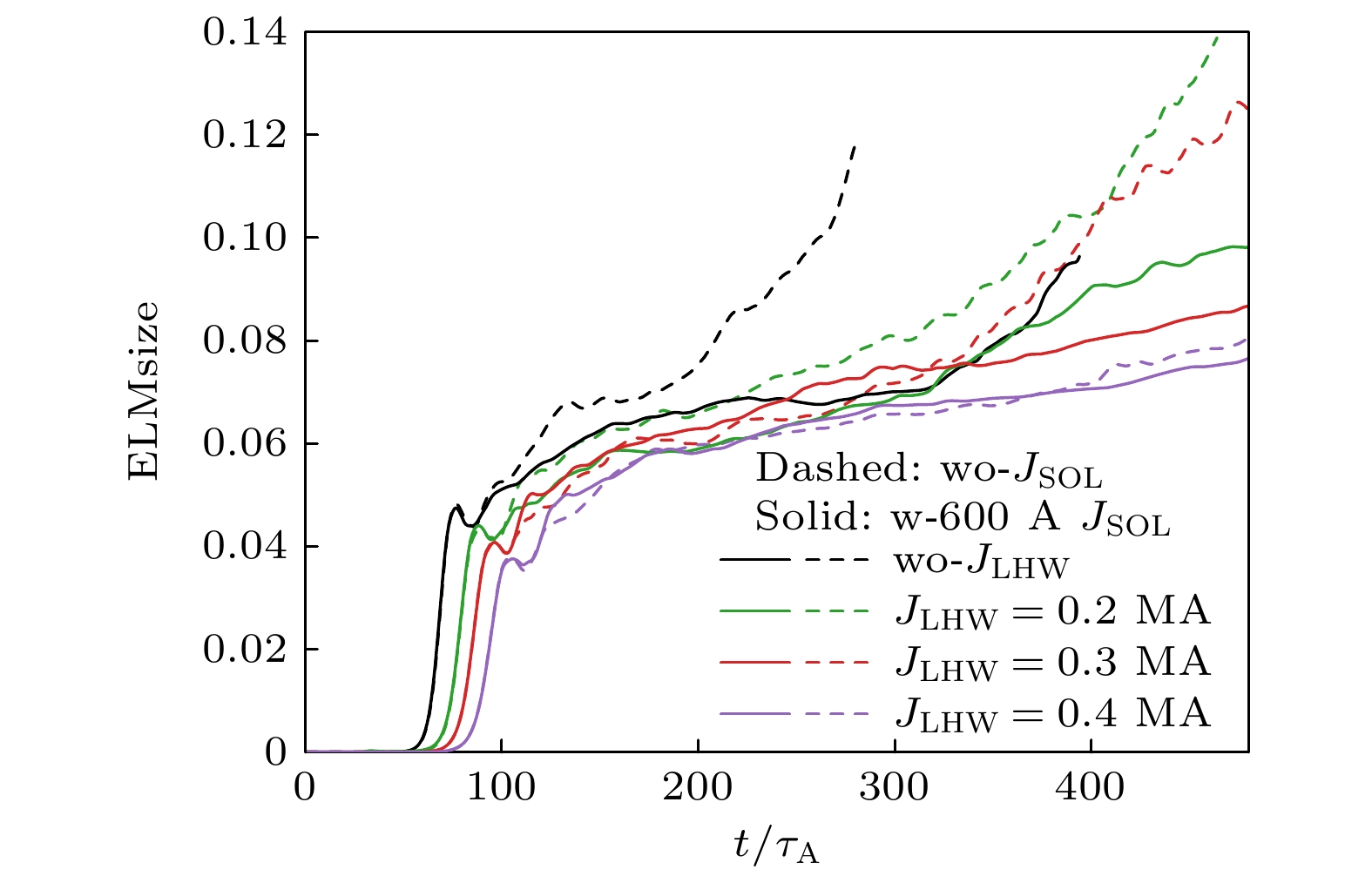
图 6 LHW驱动的不同大小$ {J}_{{\mathrm{L}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{W}}} $对ELMsize时间演化的影响, 插图为0—75$ {\tau }_{{\mathrm{A}}} $时刻的放大
Figure 6. Influence of different $ {J}_{{\mathrm{L}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{W}}} $ driven by LHW on the time evolution of ELMsize, The inset in the lower right corner is an enlargement of the from 0 to 75$ {\tau }_{{\mathrm{A}}} $.
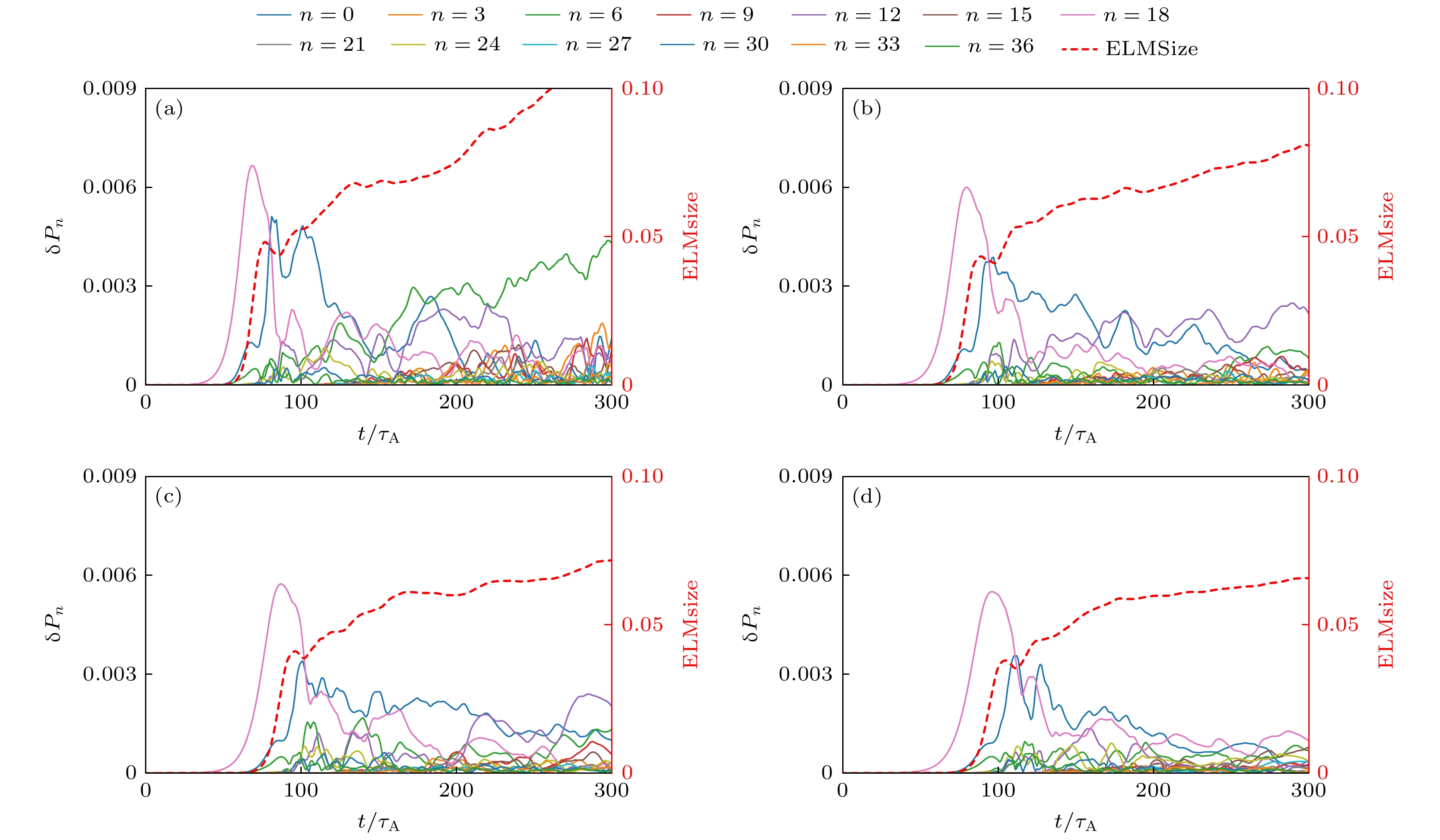
图 9 P-B模非线性模式演化, 分别对应未加入$ {A}_{//{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{F}}} $ (a), 以及300 A HCF (b), 450 A HCF (c), 600 A HCF (d) 产生的$ {A}_{//{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{F}}} $下的模拟, 图中红色虚线为ELMsize
Figure 9. Temporal evolutions of the P-B mode spectrum, for cases without $ {A}_{//{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{F}}} $ (a) and with $ {A}_{//{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{F}}} $ generated by 300 A HCF (b), 450 A HCF (c), 600 A HCF (d). The red dashed line represents ELMsize.
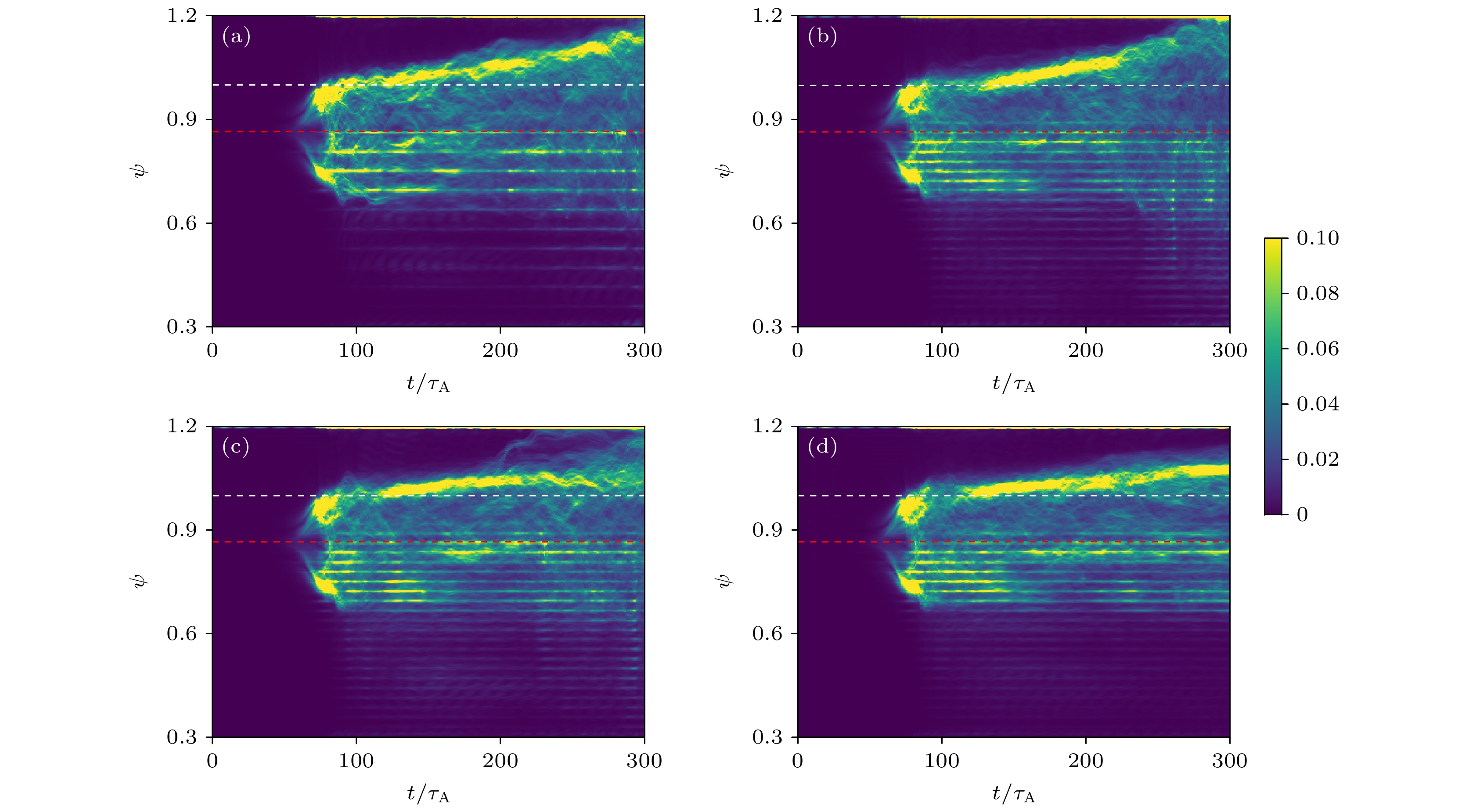
图 10 环向平均的$ E\times B $剪切流随时间的演化, 分别为未加入$ {A}_{//{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{F}}} $(a) 以及加入300 A HCF (b), 450 A HCF (c), 600 A HCF (d). 图中白色虚线为$ \psi =1 $的位置, 红色虚线为平衡压强梯度最大位置$ \psi =0.871 $
Figure 10. Temporal evolutions of the toroidal averaged $ E\times B $ shear flow, for cases without $ {A}_{//{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{F}}} $ (a) and with $ {A}_{//{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{F}}} $ generated by 300 A HCF (b), 450 A HCF (c), 600 A HCF (d). The white and red dashed lines represent locations of $ \psi =1 $ and the maximum pressure gradient location $ \psi =0.871 $, respectively.
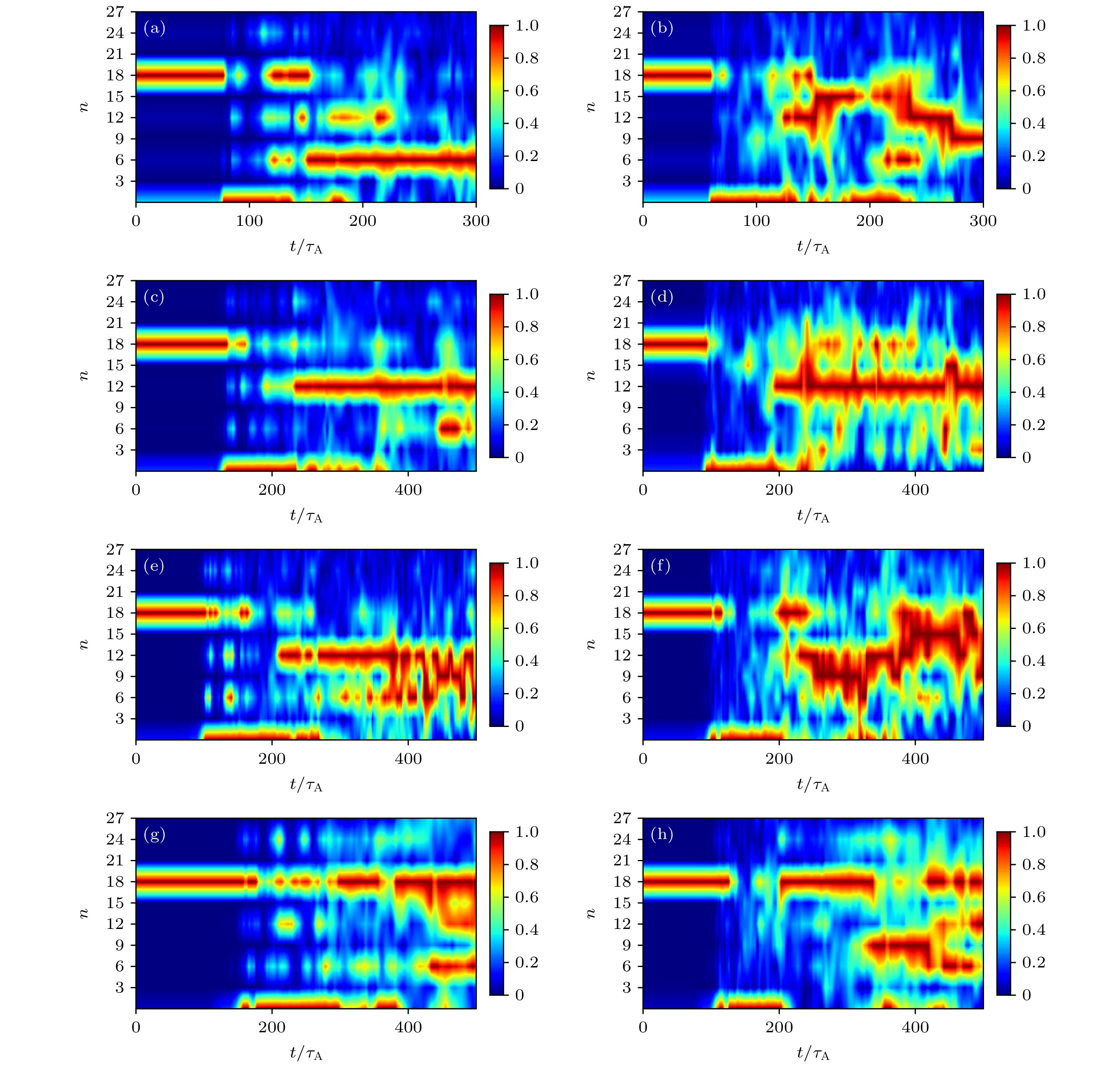
图 12 考虑HCF后的P-B模谱结构随时间的演化, 其中, 从上到下依次为初始平衡(a), (b); JLHW = 0.2 MA (c), (d); JLHW = 0.3 MA (e), (f); JLHW = 0.4 MA (g), (h)下的平衡. 左侧的一列(a), (c), (e), (g)为未加入$ {A}_{//{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{F}}} $的模拟; 右侧(b), (d), (f), (h)为加入600 A HCF产生的$ {A}_{//{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{F}}} $的模拟
Figure 12. Temporal evolutions of the P-B mode spectrum structure considering HCF. From top to bottom, the sequences are the orginal equilibrium (a), (b); equilibrium with JLHW = 0.2 MA (c), (d); JLHW = 0.3 MA (e), (f); JLHW = 0.4 MA (g), (h), respectively. The left column (a), (c), (e), (g) represent cases without $ {A}_{//{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{F}}} $; the right column (b), (d), (f), (h) represent cases with $ {A}_{//{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{F}}} $ from 600 A HCF.
-
[1] Zohm H 1996 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 38 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Leonard A W 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 090501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Loarte A, Saibene G, Sartori R, et al. 2003 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 45 1549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lang P T, Loarte A, Saibene G, et al. 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 043004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Loarte A, Huijsmans G, Futatani S, et al. 2014 Nucl. Fusion 54 033007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hughes J W, Hubbard A E, Wallace G, et al. 2010 Nucl. Fusion 50 064001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wan B, Li J, Guo H, Liang Y, Xu G, Gong X Z for the EAST Team, International Collaborators 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 104006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Rossel J X, Moret J M, Coda S, Sauter O, Goodman T P, Felici F, Testa D, Martin Y 2012 Nucl. Fusion 52 032004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Felici F, Rossel J X, Duval B P, Coda S, Goodman T P, Martin Y, Moret J M, Sauter O, the TCV Team 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 113018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Baylor L R, Commaux N, Jernigan T C, et al. 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 245001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen S Y, Huang J, Sun T T, Wang Z H, Tang C J 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 112512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Evans T E, Moyer R A, Watkins J G, et al. 2005 J. Nucl. Mater. 337–339 691
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Canik J M, Maingi R, Evans T E, et al. 2010 Nucl. Fusion 50 034012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xiao W W, Diamond P H, Zou X L, et al. 2012 Nucl. Fusion 52 114027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Huang J, Chen S Y, Wang Z H, Tang C J 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 122507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Degeling A W, Martin Y R, Lister J B, Villard L, Dokouka V N, Lukash V E, Khayrutdinov R R 2003 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 45 1637
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wu N, Chen S Y, Song X M, Mou M L, Huang J, Wang Z T, Tang C J, Song X, Xia F, Jiang M, HL-2A Team 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 092507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang H M, Wu J, Li J X, Yao L M, Xu J C, Wu Y Z, Liu Q Y, Guo P C 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 235203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 刘冠男, 李新霞, 刘洪波, 孙爱萍 2023 72 245202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu G N, Li X X, Liu H B, Sun A P 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 245202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhou T T, Xiang N, Gan C Y, Jia G Z, Chen J L 2022 Chin. Phys. B 31 095201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Xu Z, Wu Z W, Zhang L, Huang Y H, Gao W, Cheng Y X, Lin X D, Gao X, Chen Y J, Li L, Jie Y X, Zang Q, Liu H Q, EAST Team 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 075205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liang Y, Gong X Z, Gan K F, et al. 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 235002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xiao G L, Zhong W L, Zou X L, et al. 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 122507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Cui B T, Ji X Q, Sun T F, Liang S Y, Zhang J Z, Wang A, He M Y 2021 Fusion Eng. Des. 173 112963
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li S H, Wang N C, Ding Y H, et al. 2022 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 64 075005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Snyder P B, Wilson H R, Ferron J R, Lao L L, Leonard A W, Osborne T H, Turnbull A D, Mossessian D, Murakami M, Xu X Q 2002 Phys. Plasmas 9 2037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bernard L C, Helton F J, Moore R W 1981 Comput. Phys. Commun. 24 377
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Pankin A Y, Bateman G, Brennan D P, Kritz A H, Kruger S, Snyder P B, Sovinec C, the NIMROD Team 2007 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 49 S63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Pamela S J P, Huijsmans G T A, Eich T, et al. 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 076006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Dudson B D, Umansky M V, Xu X Q, Snyder P B, Wilson H R 2009 Comput. Phys. Commun. 180 1467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Xu X Q, Dudson B, Snyder P B, Umansky M V, Wilson H 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 175005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Xia T Y, Xu X Q 2013 Phys. Plasmas 20 052102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Xia T Y, Xu X Q, Xi P W 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 073009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Mou M L, Huang J, Wu N, Chen S Y, Tang C J 2016 Phys. Lett. A 380 2544
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Dong L K, Chen S Y, Mou M L, Tang C J 2020 Plasma Sci. Technol. 22 115101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Huang J, Chen S Y, Tang C J 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 052513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Xia T Y, Gui B, Huang Y Q, Wu Y B, Xiao X T, EAST Team 2019 Nucl. Fusion 59 076043
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Shi Y J, Xu G S, Wang F D, et al. 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 235001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Rice J E, Podpaly Y A, Reinke M L, et al. 2013 Nucl. Fusion 53 093015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Chouli B, Fenzi C, Garbet X, et al. 2014 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 56 095018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Chen W, Wang Z X 2020 Chin. Phys. Lett. 37 125001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Fisch N J, Rax J M 1992 Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 612
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Smirnov A P, Harvey R W 2001 The GENRAY Ray Tracing Code CompX Report No. CompX-2000-01
[44] Ehst D A, Karney C F F 1991 Nucl. Fusion 31 1933
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Crotinger J A, LoDestro L, Pearlstein L D, Tarditi A, Casper T A, Hooper E B 1997 CORSICA: A Comprehensive Simulation of Toroidal Magnetic-fusion Devices. Final Report to the LDRD Program (Livermore: Lawrence Livermore National Lab.) Report No: UCRL-ID-126284
[46] Xu X Q, Ma J F, Li G Q 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 120704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Burrell K H 1997 Phys. Plasmas 4 1499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Ding B J, Bonoli P T, Tuccillo A, et al. 2018 Nucl. Fusion 58 095003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Li G Q, Xu X Q, Snyder P B, Turnbull A D, Xia T Y, Ma C H, Xi P W 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 102511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Zhang Y, Huang J, Chen S Y, Tang C J 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 062108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Li J, Guo H Y, Wan B N, et al. 2013 Nat. Phys. 9 817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Dong L K, Chen S Y, Mou M L, Luo Y, Qin C C, Tang C J 2023 Nucl. Fusion 63 086023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Liu Y, Ham C J, Kirk A, Li L, Loarte A, Ryan D A, Sun Y, Suttrop W, Yang X, Zhou L 2016 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 58 114005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[54] Oyama N, Sakamoto Y, Isayama A, et al. 2005 Nucl. Fusion 45 871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[55] Aiba N, Giroud C, Honda M, et al. 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 126001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Luo Y, Chen S Y, Huang J, Xiong Y Y, Tang C J 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 042302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[57] Xi P W, Xu X Q, Wang X G, Xia T Y 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 092503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[58] 李春雨, 郝广周, 刘钺强, 王炼, 刘艺慧子 2022 71 075202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C Y, Hao G Z, Liu Y Q, Wang L, Liu Y H Z 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 075202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4419
- PDF Downloads: 70
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: