-
Based on the single electron effective mass approximation theory and the transfer-matrix method, the spin polarized transport properties of electrons in a diluted-magnetic-semiconductor/semiconductor superlattice are studied. The influence of a light-field and a magnetic-field on spin polarized transport and the tunneling time in the superlattice structure are discussed in more detail. The results show that, due to the sp-d electron interaction between conduction band electrons and doped Mn ions, giant Zeeman splitting occurs. It is shown that a significant spin-dependent transmission and the position and width of the resonant-transmission-band of spin-dependent electron can be manipulated by adjusting the magnetic- and light-field. Considering the light field irradiation, the resonance band of electron is deformed and broadened with the increase of the light field intensity. For the case of a strong magnetic field, the transmission coefficient (TC) in the low-energy region is almost zero when the light field is not added, but with the increase of light intensity, the TC increased significantly in the zone increases significantly, that is, a quasi-bound band appears. These features are due to the energy exchange between electrons and the light field when electrons tunnel through the superlattice structure under light irradiation. In addition, light and magnetic fields can significantly change the spin polarization of electrons. Under a certain magnetic field intensity (B = 2 T), the light field significantly changes the spin polarization of electrons, the main effect is that the width of the spin polarization platform narrows and oscillatory peaks are accompanied on both sides of the platform. This effect is strengthened with the increase of the light field intensity. However, when the magnetic field is stronger (B = 5 T), the opposite is true. These show that the spin polarization can be modulated by the light field. Finally, the tunneling time of spin-up and spin-down electrons is studied by the evolution of Gaussian wave packets in the structure. The results show that the tunneling time depends on a spin of electrons, and it can be seen that the tunneling time of the spin-down electron is shorter than that of the spin-up electron in the superlattice structure. These remarkable properties of spin polarized transport may be beneficial for the devising tunable spin filtering devices based on diluted magnetic semiconductor/semiconductor superlattice structure.
-
Keywords:
- spin polarized transport /
- diluted magnetic semiconductors/semiconductors superlattices /
- tunneling time
[1] Wolf S A, Awschalom D D, Buhrman R A, Daughton J M, Von Molnar S, Roukes M L, Chtchelkanova A Y, Treger D M 2001 Science 294 1488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Egues J C 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 4578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chang K, Peeters F M 2001 Solid State Commun. 120 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Slobodskyy A, Gould C, Slobodskyy T, Becker C R, Schmidt G, Molenkamp L W 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 246601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hijano A, Bergeret F S, Giazotto F, Braggio A 2023 Phys. Rev. Appl. 19 044024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhu Z G, Su G 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 193310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhai F, Guo Y, Gu B L 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 94 5432
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang P F, Zhu R, Guo Y 2015 AIP Advances 5 077115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Furdyna J K 1988 J. Appl. Phys. 64 R29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Papp G, Borza S, Peeters F M 2005 J. Appl. Phys. 97 113901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chishti S S, Ghosh B, Verma A, Salimath A K 2014 J. Nanoelectron. Optoe 9 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Evropeytsev E A, Klimko G V, Komissarova T A, et al. 2014 Semiconductors 48 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ming Y, Gong J, Zhang R Q 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 110 093717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Havu P, Tuomisto N, Väänänen R, Puska M J, Nieminen R M 2005 Phys. Rev. B 71 235301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wójcik P, Adamowski J, Wołoszyn M, Spisak B J 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 165318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Gruber T H, Keim M, Fiederling R, Reuscher G, Ossau W, Schmidt G, Molenkamp L W, Waag A 2001 Appl. Phys. Lett. 78 1101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Schmidt G, Richter G, Grabs P, Gould C, Ferrand D, Molenkamp L W 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 227203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Schmidt G, Gould C, Grabs P, Lunde A M, Richter G, Slobodskyy A, Molenkamp L W 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 226602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Guo Y, Wang H, Gu B L, Kawazoe Y 2000 J. Appl. Phys. 88 6614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Guo Y, Chen X Y, Zhai F, Gu B L, Kawazoe Y 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 80 4591
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Guo Y, Shen F R, Chen X Y 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 012410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 张存喜, 王瑞, 孔令民 2010 59 4980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang C X, Wang R, Kong L M 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 4980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li C L, Ruan R Y, Guo Y 2016 J. Appl. Phys. 119 014306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Dayem A H, Martin R J 1962 Phys. Rev. Lett. 8 246
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Tien P K, Gordon J P 1963 Phys. Rev. 129 647
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Sun Q F, Wang J, Lin T H 2000 Phys. Rev. B 61 12643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bruder C, Schoeller H 1994 Phys. Rev. Lett. 72 1076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Shibata K, Umeno A, Cha K M, Hirakawa K 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 077401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Schoelkopf R J, Kozhevnikov A A, Prober D E 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 2437
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] König B, Zehnder U, Yakovlev D R, Ossau W, Gerhard T, Keim M, Waag A, Landwehr G 1999 Phys. Rev. B 60 2653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Harada N, Kuroda S 1986 Jap. J. Appl.Phys. 25 L871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 曾谨言 2000 量子力学(上卷) (北京: 科学出版社) 第721页
Zeng J Y 2000 Quantum Mechanics (Vol. 1) (Beijing: Science Press) p721
-
图 1 光场
$ V_{1}\mathrm{cos}(\omega t) $ 辐照下自旋相关$ {\rm ZnSe}/{\rm Zn}_{1-x}{\rm Mn}_{x}{\rm Se} $ 超晶格势 (a)$ B = 5 $ T; (b)$ B = 2 $ TFigure 1. Spin-dependent potential profiles of the
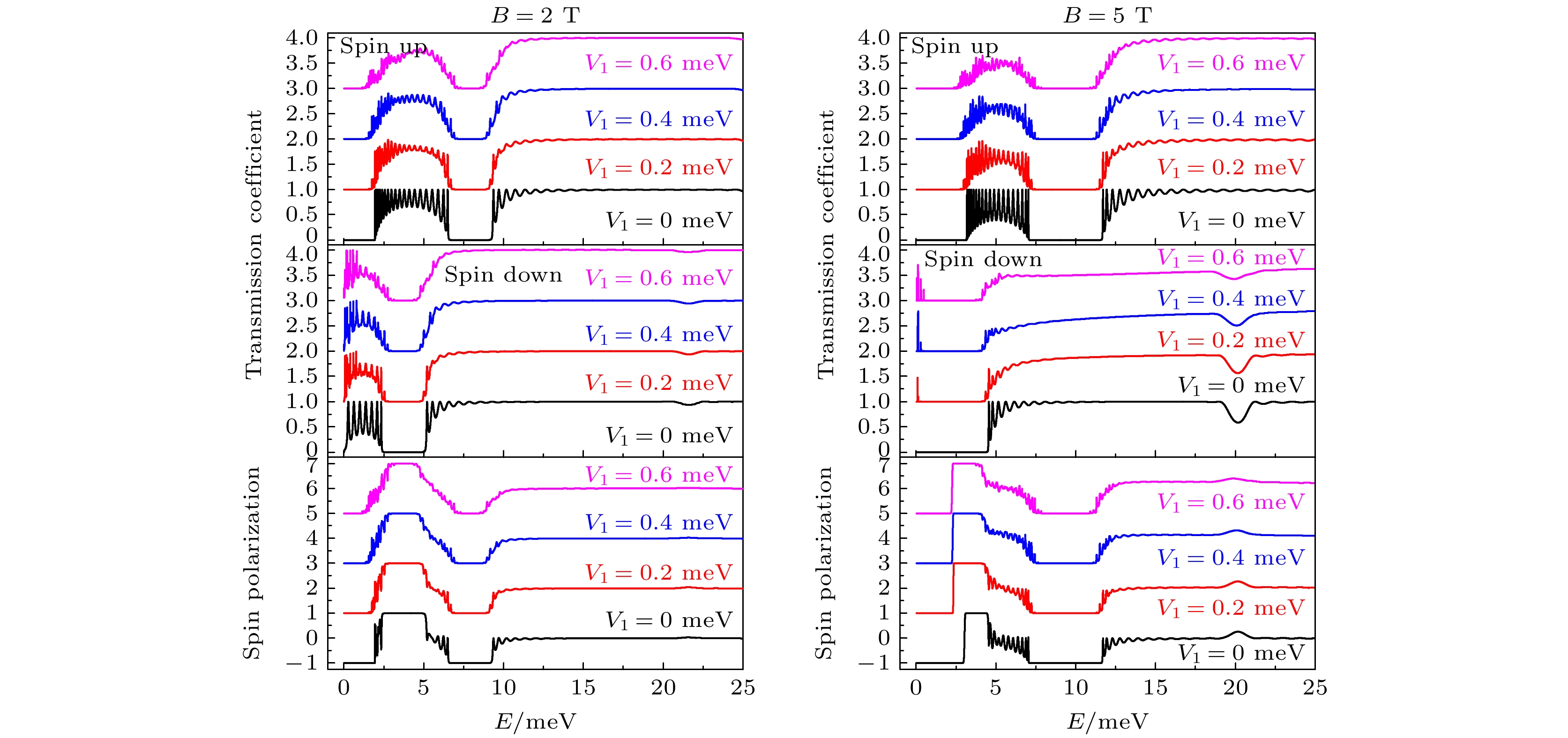
$ {\rm ZnSe}/ $ $ {\rm Zn}_{1-x}{\rm Mn}_{x}{\rm Se} $ superlattice under a light field$ V_{1}\mathrm{cos}(\omega t) $ : (a)$ B = 5 $ T; (b)$ B = 2 $ T.图 2 光场辐照下, 不同磁场强度电子自旋相关透射系数和自旋极化度, 其中光子能量
$ \hbar \omega = 0.2 $ meV, 光场强度$ V_{1} = 0, $ $ 0.2, \;0.4, \;0.6 $ meVFigure 2. Spin-dependent transmission coefficients and spin polarization for different magnetic induction intensity under the light field, where the energy of photon is
$ \hbar \omega = 0.2 $ meV, and amplitude of the light field is$ V_{1} = 0,\; 0.2,\; 0.4,\; 0.6 $ meV.图 3 稀磁半导体/半导体超晶格结构中, 不同时刻不同自旋方向电子概率密度
$ |\psi(z, t)|^{2} $ 随坐标z的变化关系曲线 (a)自旋向上; (b) 自旋向下Figure 3. Spin-dependent electron probability density
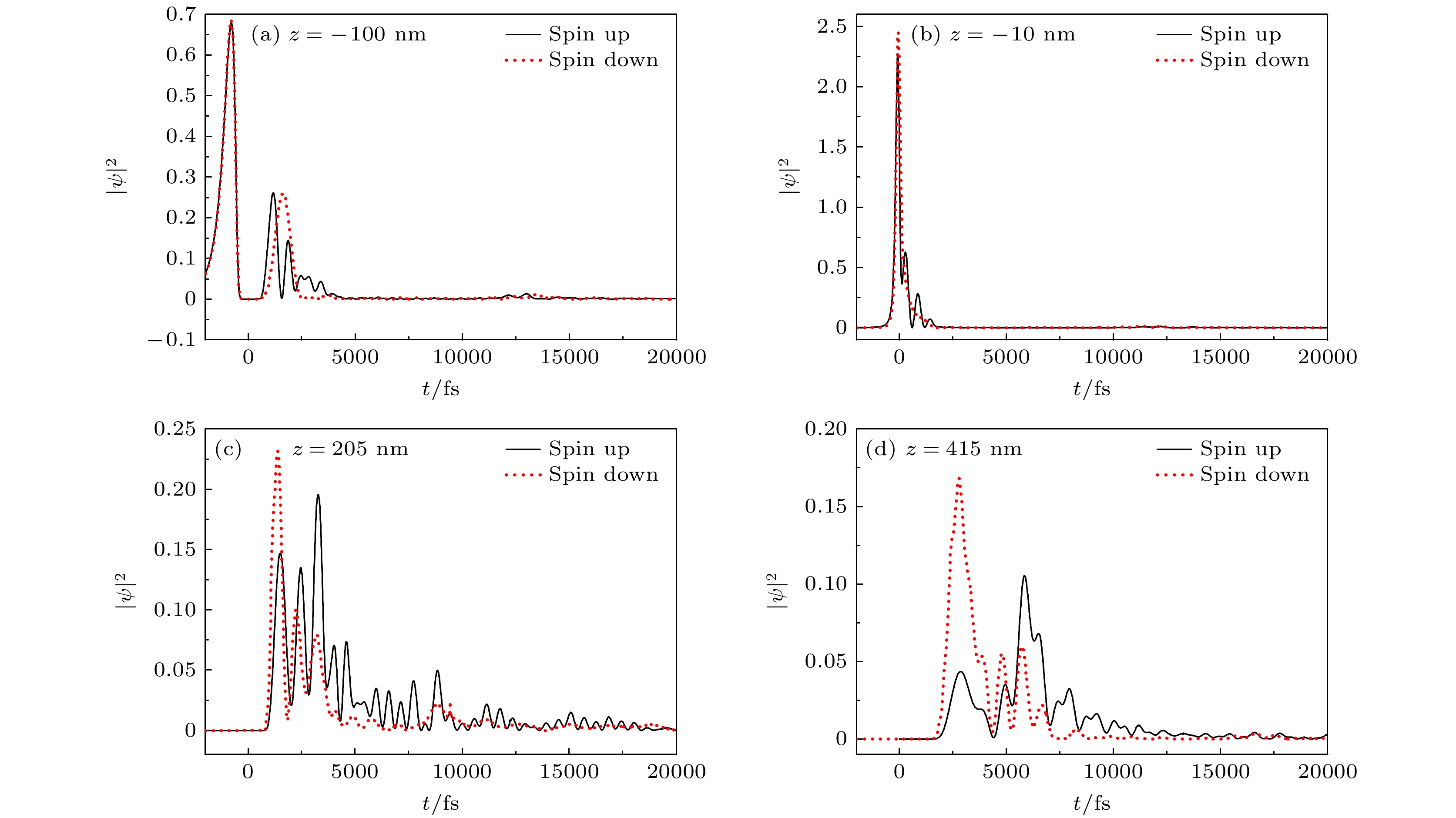
$ |\psi(z, t)|^{2} $ as a function of coordinate z for different times in the superlattices of dilute magnetic semiconductors/semiconductors structure: (a) Spin up; (b) spin down.图 4 稀磁半导体/半导体(DMS/S) 超晶格结构中, 位置
$ z=-100,\; -10, \;205,\; 415 $ nm 处, 不同自旋方向电子概率密度$ |\psi(z, t)|^{2} $ 随时间t的变化关系曲线Figure 4. Spin-dependent electron probability density
$ |\psi(z, t)|^{2} $ as a function of time t for different coordinates$ z=-100, \;-10, $ $ 205, \;415 $ nm in the superlattices of dilute magnetic semiconductors/semiconductors structure. -
[1] Wolf S A, Awschalom D D, Buhrman R A, Daughton J M, Von Molnar S, Roukes M L, Chtchelkanova A Y, Treger D M 2001 Science 294 1488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Egues J C 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 4578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chang K, Peeters F M 2001 Solid State Commun. 120 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Slobodskyy A, Gould C, Slobodskyy T, Becker C R, Schmidt G, Molenkamp L W 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 246601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hijano A, Bergeret F S, Giazotto F, Braggio A 2023 Phys. Rev. Appl. 19 044024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhu Z G, Su G 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 193310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhai F, Guo Y, Gu B L 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 94 5432
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang P F, Zhu R, Guo Y 2015 AIP Advances 5 077115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Furdyna J K 1988 J. Appl. Phys. 64 R29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Papp G, Borza S, Peeters F M 2005 J. Appl. Phys. 97 113901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chishti S S, Ghosh B, Verma A, Salimath A K 2014 J. Nanoelectron. Optoe 9 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Evropeytsev E A, Klimko G V, Komissarova T A, et al. 2014 Semiconductors 48 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ming Y, Gong J, Zhang R Q 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 110 093717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Havu P, Tuomisto N, Väänänen R, Puska M J, Nieminen R M 2005 Phys. Rev. B 71 235301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wójcik P, Adamowski J, Wołoszyn M, Spisak B J 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 165318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Gruber T H, Keim M, Fiederling R, Reuscher G, Ossau W, Schmidt G, Molenkamp L W, Waag A 2001 Appl. Phys. Lett. 78 1101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Schmidt G, Richter G, Grabs P, Gould C, Ferrand D, Molenkamp L W 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 227203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Schmidt G, Gould C, Grabs P, Lunde A M, Richter G, Slobodskyy A, Molenkamp L W 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 226602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Guo Y, Wang H, Gu B L, Kawazoe Y 2000 J. Appl. Phys. 88 6614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Guo Y, Chen X Y, Zhai F, Gu B L, Kawazoe Y 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 80 4591
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Guo Y, Shen F R, Chen X Y 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 012410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 张存喜, 王瑞, 孔令民 2010 59 4980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang C X, Wang R, Kong L M 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 4980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li C L, Ruan R Y, Guo Y 2016 J. Appl. Phys. 119 014306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Dayem A H, Martin R J 1962 Phys. Rev. Lett. 8 246
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Tien P K, Gordon J P 1963 Phys. Rev. 129 647
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Sun Q F, Wang J, Lin T H 2000 Phys. Rev. B 61 12643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Bruder C, Schoeller H 1994 Phys. Rev. Lett. 72 1076
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Shibata K, Umeno A, Cha K M, Hirakawa K 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 077401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Schoelkopf R J, Kozhevnikov A A, Prober D E 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 2437
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] König B, Zehnder U, Yakovlev D R, Ossau W, Gerhard T, Keim M, Waag A, Landwehr G 1999 Phys. Rev. B 60 2653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Harada N, Kuroda S 1986 Jap. J. Appl.Phys. 25 L871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 曾谨言 2000 量子力学(上卷) (北京: 科学出版社) 第721页
Zeng J Y 2000 Quantum Mechanics (Vol. 1) (Beijing: Science Press) p721
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3555
- PDF Downloads: 75
- Cited By: 0
























 DownLoad:
DownLoad: